Recent Drug Development in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Woodchuck Animal Model of CHB
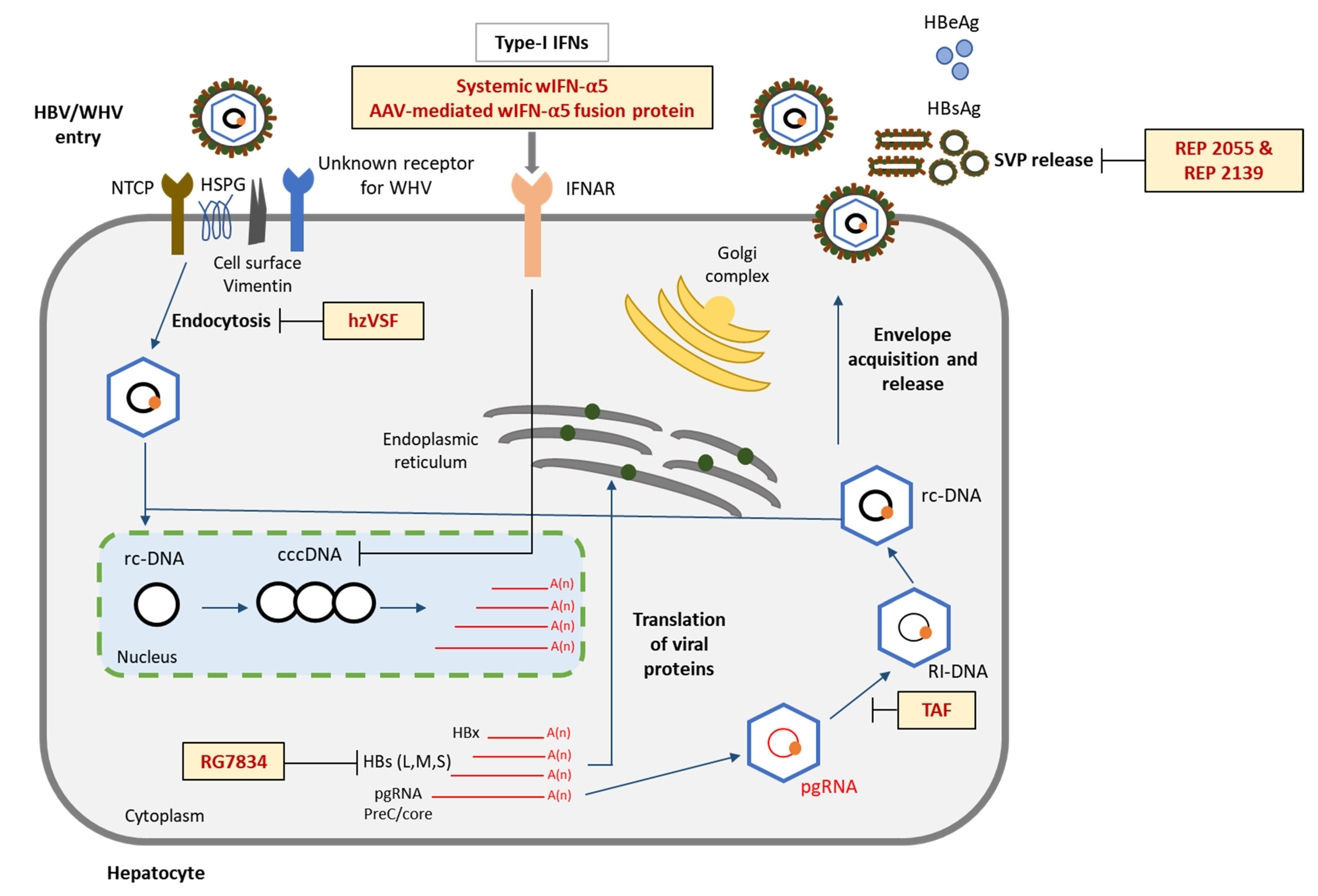
3. Immunopathogenesis of HBV/WHV Infection
4. Nucleos(t)ide Analog Treatment in Woodchucks
5. Immunomodulation in Woodchucks
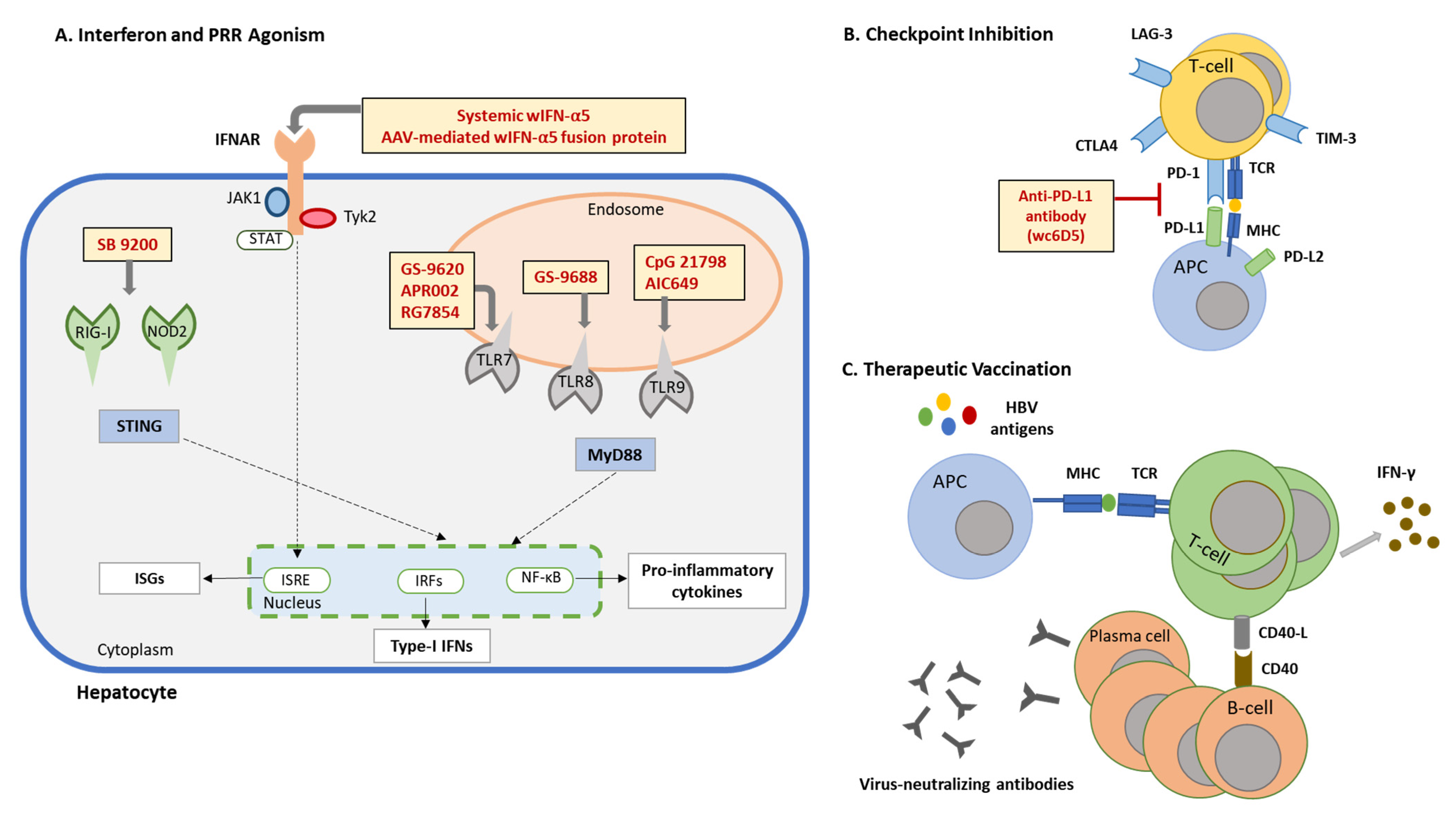
5.1. IFN-α Therapy
5.2. TLR7 Agonists
5.3. TLR8 Agonist
5.4. TLR9 Agonists
5.5. Cytoplasmic PRR Agonists
5.6. Checkpoint Inhibitor
5.7. Therapeutic Vaccination
6. Evaluation of Novel Host and Viral Targets in Woodchucks
6.1. Entry Inhibition
6.2. Surface Inhibition
7. Significance of Preclinical Woodchuck Studies for Clinical Trials in Patients
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.-L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnius, L.; Mason, W.S.; Taylor, J.; Kann, M.; Glebe, D.; Dény, P.; Sureau, C.; Norder, H.; ICTV Report Consortium. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepadnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Seeger, C. Hepadnavirus Genome Replication and Persistence. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Sugiyama, R.; Ishii, K.; Ohki, M.; Nagamori, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ryo, A.; Yun, J.-H.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a host-entry cofactor triggering hepatitis B virus internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection. Virology 2015, 479–480, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.D.; Sarica, N.; Neuveut, C. Early Steps of Hepatitis B Life Cycle: From Capsid Nuclear Import to cccDNA Formation. Viruses 2021, 13, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Luckenbaugh, L.; Perlman, D.; Revill, P.A.; Wieland, S.F.; Menne, S.; Hu, J. Characterization and Application of Precore/Core-Related Antigens in Animal Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2021, 74, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Luckenbaugh, L.; Mendenhall, M.; Walsh, R.; Cabuang, L.; Soppe, S.; Revill, P.A.; Burdette, D.; Feierbach, B.; Delaney, W.; et al. Characterization of Hepatitis B Precore/Core-Related Antigens. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01695-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B: The virus and disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Mason, W.S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B-like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell 1982, 29, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttleman, J.S.; Pourcel, C.; Summers, J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell 1986, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, A.; Xia, Y. Insights into Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration-55 Years after Virus Discovery. Innovation 2020, 1, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis, B. 2022. Available online: https://wwwwhoint/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Global Hepatitis Report, 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565455 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Cox, A.L.; El-Sayed, M.H.; Kao, J.-H.; Lazarus, J.V.; Lemoine, M.; Lok, A.S.; Zoulim, F. Progress towards elimination goals for viral hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoulim, F.; Lebossé, F.; Levrero, M. Current treatments for chronic hepatitis B virus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirode, G.; Choi, H.S.J.; Chen, C.-H.; Su, T.-H.; Seto, W.-K.; Van Hees, S.; Papatheodoridi, M.; Lens, S.; Wong, G.; Brakenhoff, S.M.; et al. Off-Therapy Response After Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Withdrawal in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B: An International, Multicenter, Multiethnic Cohort (RETRACT-B Study). Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 757–771.e754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.B.; Dufeu-Duchesne, T.; Leroy, V.; Bertucci, I.; Bouvier-Alias, M.; Pouget, N.; Brevot-Lutton, O.; Bourliere, M.; Zoulim, F.; Plumas, J.; et al. Pegylated Interferon α-2a Triggers NK-Cell Functionality and Specific T-Cell Responses in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection without HBsAg Seroconversion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, J. Interferon and Hepatitis B: Current and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 733364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Protzer, U.; Siddiqui, A. Revisiting Hepatitis B Virus: Challenges of Curative Therapies. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01032-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, S.; Cote, P.J. The woodchuck as an animal model for pathogenesis and therapy of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellezza, C.A.; Sexton, S.S.; Curtin, L.I.; Concannon, P.W.; Baldwin, B.H.; Graham, L.A.; Hornbuckle, W.E.; Roth, L.; Tennant, B.C. The Laboratory Woodchuck (Marmota monax). In Laboratory Animal Medicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 351–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, T.I. Diverse Virus and Host-Dependent Mechanisms Influence the Systemic and Intrahepatic Immune Responses in the Woodchuck Model of Hepatitis B. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Smolec, J.M.; Snyder, R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4533–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, P.J.; Korba, B.E.; Miller, R.H.; Jacob, J.R.; Baldwin, B.H.; Hornbuckle, W.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Tennant, B.C.; Gerin, J.L. Effects of age and viral determinants on chronicity as an outcome of experimental woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology 2000, 31, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, I.W.; Browne, J.K.; Salser, W.A.; Tyler, G.V.; Snyder, R.L.; Smolec, J.M.; Summers, J. Isolation, characterization, and comparison of recombinant DNAs derived from genomes of human hepatitis B virus and woodchuck hepatitis virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.; Roth, L.; Purcell, R.H.; Tennant, B.C.; Gerin, J.L. Hepatocarcinogenicity of the woodchuck hepatitis virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Menne, S. Application of the woodchuck animal model for the treatment of hepatitis B virus-induced liver cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 509–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.F. The Chimpanzee Model for Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Ghildyal, R.; Yuan, Z. Animal Models for the Study of Hepatitis B Virus Pathobiology and Immunity: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 715450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burwitz, B.J.; Wettengel, J.; Mück-Häusl, M.A.; Ringelhan, M.; Ko, C.; Festag, M.M.; Hammond, K.B.; Northrup, M.; Bimber, B.N.; Jacob, T.; et al. Hepatocytic expression of human sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide enables hepatitis B virus infection of macaques. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Rust, L.N.; Wettengel, J.M.; Yusova, S.; Fischer, M.; Carson, J.N.; Johnson, J.; Wei, L.; Thode, T.; Kaadige, M.R.; et al. Long-term hepatitis B virus infection of rhesus macaques requires suppression of host immunity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, S.P.; Chin, D.J.; Ji, Y.; Iniguez, A.L.; Taillon, B.; Swinney, D.C.; Ravindran, P.; Cheng, D.T.; Bitter, H.; Lopatin, U.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2012, 56, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Vikash, V.; Wang, Q.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M.; Yang, D.; Liu, J. Transcriptome Analysis and Comparison of Marmota monax and Marmota himalayana. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alioto, T.S.; Cruz, F.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Triyatni, M.; Gut, M.; Frias, L.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Menne, S.; Kiialainen, A.; Kumpesa, N.; et al. The Genome Sequence of the Eastern Woodchuck (Marmota monax)—A Preclinical Animal Model for Chronic Hepatitis B. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2019, 9, 3943–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puiu, D.; Zimin, A.; Shumate, A.; Ge, Y.; Qiu, J.; Bhaskaran, M.; Salzberg, S.L. The genome of the American groundhog, Marmota monax. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, S.; Butler, S.D.; George, A.L.; Tochkov, I.A.; Zhu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Gerin, J.L.; Cote, P.J.; Tennant, B.C. Antiviral Effects of Lamivudine, Emtricitabine, Adefovir Dipivoxil, and Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Administered Orally Alone and in Combination to Woodchucks with Chronic Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3617–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, E.V.; Lamb, L.; Medina, I.; Taylor, D.; Seifer, M.; Innaimo, S.; Colonno, R.J.; Standring, D.N.; Clark, J.M. Efficacy of the Carbocyclic 2′-Deoxyguanosine Nucleoside BMS-200475 in the Woodchuck Model of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 3209–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonno, R.J.; Genovesi, E.V.; Medina, I.; Lamb, L.; Durham, S.K.; Huang, M.L.; Corey, L.; Littlejohn, M.; Locarnini, S.; Tennant, B.C.; et al. Long-Term Entecavir Treatment Results in Sustained Antiviral Efficacy and Prolonged Life Span in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korba, B.E.; Cote, P.; Hornbuckle, W.; Tennant, B.C.; Gerin, J.L. Treatment of chronic woodchuck hepatitis virus infection in the eastern woodchuck (marmota monax) with nucleoside analogues is predictive of therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in humans. Hepatology 2000, 31, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.F.; Chisari, F.V. Stealth and Cunning: Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Viruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, M.K.; Gehring, A.J. The role of innate immunity in the immunopathology and treatment of HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S60–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Clark, D.N.; Liu, K.; Xu, X.-D.; Guo, J.-T.; Hu, J. Viral DNA-Dependent Induction of Innate Immune Response to Hepatitis B Virus in Immortalized Mouse Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA Sensor RIG-I Dually Functions as an Innate Sensor and Direct Antiviral Factor for Hepatitis B Virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.-Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, J.-G. Innate immune targets of hepatitis B virus infection. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Revill, P.; Yuan, Z. New Insights into how HBV Manipulates the Innate Immune Response to Establish Acute and Persistent Infection. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslov, A.; Boldanova, T.; Wang, X.; Wieland, S.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis B Virus Does Not Interfere With Innate Immune Responses in the Human Liver. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.; Peppa, D.; Khanna, P.; Nebbia, G.; Jones, M.; Brendish, N.; Lascar, R.M.; Brown, D.; Gilson, R.J.; Tedder, R.; et al. Temporal Analysis of Early Immune Responses in Patients With Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-J.; Wong, D.K.; Wahed, A.S.; Lee, W.M.; Feld, J.J.; Terrault, N.; Khalili, M.; Sterling, R.K.; Kowdley, K.V.; Bzowej, N.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus–Specific and Global T-Cell Dysfunction in Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 684–695.e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.R.; Pallett, L.J.; McCoy, L.E.; Suveizdytė, K.; Amin, O.E.; Swadling, L.; Alberts, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Kennedy, P.T.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Circulating and intrahepatic antiviral B cells are defective in hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bert, N.; Gill, U.S.; Hong, M.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tan, D.Z.M.; Ahmad, R.; Cheng, Y.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Heinecke, A.; Rivino, L.; et al. Effects of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen on Virus-Specific and Global T Cells in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus infection. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bert, N.; Salimzadeh, L.; Gill, U.S.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Facchetti, F.; Tan, A.; Hung, M.; Novikov, N.; Lampertico, P.; Fletcher, S.P.; et al. Comparative characterization of B cells specific for HBV nucleocapsid and envelope proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Menne, S.; Baldwin, B.H.; Tennant, B.C.; Gerin, J.L.; Cote, P.J. Kinetics of viremia and acute liver injury in relation to outcome of neonatal woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, C.S.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Churchill, N.D.; Michalak, T.I. Intrahepatic Expression of Genes Affiliated with Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses Immediately after Invasion and during Acute Infection with Woodchuck Hepadnavirus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8579–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, S.; Roneker, C.A.; Roggendorf, M.; Gerin, J.L.; Cote, P.J.; Tennant, B.C. Deficiencies in the Acute-Phase Cell-Mediated Immune Response to Viral Antigens Are Associated with Development of Chronic Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Infection following Neonatal Inoculation. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Czerwinski, S.; Murreddu, M.G.; Kallakury, B.V.; Ramesh, A.; Gudima, S.O.; Menne, S. Innate and adaptive immunity associated with resolution of acute woodchuck hepatitis virus infection in adult woodchucks. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, N.; Lukash, T.; Rodrigues, L.; Litwin, S.; Kallakury, B.V.; Menne, S.; Gudima, S.O. Infection Patterns Induced in Naive Adult Woodchucks by Virions of Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Collected during either the Acute or Chronic Phase of Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8749–8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudi, I.; Kawashima, K.; Isogawa, M. HBV-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Tolerance in the Liver. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 721975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T Cells Mediate Viral Clearance and Disease Pathogenesis during Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Kong, H.; Tian, L.; Chen, Y. T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: Current knowledge and clinical significance. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Menne, S.; Jacob, J.R.; Tennant, B.C.; Gerin, J.L.; Cote, P.J. Role of type 1 versus type 2 immune responses in liver during the onset of chronic woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology 2003, 37, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, S.; Maschke, J.; Lu, M.; Grosse-Wilde, H.; Roggendorf, M. T-Cell Response to Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus (WHV) Antigens during Acute Self-Limited WHV Infection and Convalescence and after Viral Challenge. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6083–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwolleghem, T.; Adomati, T.; Van Hees, S.; Janssen, H.L.A. Humoral immunity in hepatitis B virus infection: Rehabilitating the B in HBV. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Trippler, M.; Real, C.I.; Werner, M.; Luo, X.; Schefczyk, S.; Kemper, T.; Anastasiou, O.E.; Ladiges, Y.; Treckmann, J.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Particles Activate Toll-Like Receptor 2 Signaling Initially Upon Infection of Primary Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2020, 72, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, F.; et al. Expression profiles and function of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 128, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterbach-Rivière, L.; Bergez, M.; Mönch, S.; Qu, B.; Riess, M.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Liese, J.; Hornung, V.; Urban, S.; König, R. Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes. Viruses 2020, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Li, B.; Murreddu, M.G.; Gudima, S.O.; Menne, S. Involvement of Innate Immune Receptors in the Resolution of Acute Hepatitis B in Woodchucks. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolowicz, K.E.; Suresh, M.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Yon, C.; Kallakury, B.V.; Lee, K.-P.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.-W.; Menne, S. Combination Treatment with the Vimentin-Targeting Antibody hzVSF and Tenofovir Suppresses Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Infection in Woodchucks. Cells 2021, 10, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.Y.; Fung, S.; Seto, W.K.; Chuang, W.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hui, A.J.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Chowdhury, A.; Tsang, T.Y.O.; et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, S.; Wildum, S.; Steiner, G.; Suresh, M.; Korolowicz, K.; Balarezo, M.; Yon, C.; Murreddu, M.; Hong, X.; Kallakury, B.V.; et al. Efficacy of an Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus Expression in Combination With Entecavir and Interferon-α in Woodchucks Chronically Infected With Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöneweis, K.; Motter, N.; Roppert, P.L.; Lu, M.; Wang, B.; Roehl, I.; Glebe, D.; Yang, D.; Morrey, J.D.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. Activity of nucleic acid polymers in rodent models of HBV infection. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Le Bert, N. Immunotherapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gut Liver 2018, 12, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslov, A.; Wieland, S.; Menne, S. Modulators of innate immunity as novel therapeutics for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, S.P.; Chin, D.J.; Gruenbaum, L.; Bitter, H.; Rasmussen, E.; Ravindran, P.; Swinney, D.C.; Birzele, F.; Schmucki, R.; Lorenz, S.H.; et al. Intrahepatic Transcriptional Signature Associated with Response to Interferon-α Treatment in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraondo, P.; Di Scala, M.; Korolowicz, K.; Thampi, L.M.; Otano, I.; Suarez, L.; Fioravanti, J.; Aranda, F.; Ardaiz, N.; Yang, J.; et al. Liver-directed gene therapy of chronic hepadnavirus infection using interferon alpha tethered to apolipoprotein A-I. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menne, S.; Tumas, D.B.; Liu, K.H.; Thampi, L.; AlDeghaither, D.; Baldwin, B.H.; Bellezza, C.A.; Cote, P.J.; Zheng, J.; Halcomb, R.; et al. Sustained efficacy and seroconversion with the Toll-like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 in the Woodchuck model of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolowizc, K.E.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Yon, C.; Rodrigo, E.; Corpuz, M.; Plouffe, D.M.; Kallakury, B.V.; Suresh, M.; Wu, T.Y.; et al. Liver-Targeted Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist Combined With Entecavir Promotes a Functional Cure in the Woodchuck Model of Hepatitis B Virus. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1296–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildum, S.; Korolowicz, K.E.; Suresh, M.; Steiner, G.; Dai, L.; Li, B.; Yon, C.; De Vera Mudry, M.C.; Regenass-Lechner, F.; Huang, X.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist RG7854 Mediates Therapeutic Efficacy and Seroconversion in Woodchucks With Chronic Hepatitis B. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 884113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daffis, S.; Balsitis, S.; Chamberlain, J.; Zheng, J.; Santos, R.; Rowe, W.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Pattabiraman, D.; Spurlock, S.; Chu, R.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 8 Agonist GS-9688 Induces Sustained Efficacy in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2020, 73, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pei, R.; Zhang, E.; Kemper, T.; Vollmer, J.; Davis, H.L.; Glebe, D.; Gerlich, W.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. Combination therapy including CpG oligodeoxynucleotides and entecavir induces early viral response and enhanced inhibition of viral replication in a woodchuck model of chronic hepadnaviral infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 125, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolowicz, K.E.; Suresh, M.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Yon, C.; Leng, X.; Kallakury, B.V.; Tucker, R.D.; Menne, S. Treatment with the Immunomodulator AIC649 in Combination with Entecavir Produces Antiviral Efficacy in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. Viruses 2021, 13, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Korolowicz, K.E.; Balarezo, M.; Iyer, R.P.; Padmanabhan, S.; Cleary, D.; Gimi, R.; Sheri, A.; Yon, C.; Kallakury, B.V.; et al. Antiviral Efficacy and Host Immune Response Induction during Sequential Treatment with SB 9200 Followed by Entecavir in Woodchucks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsitis, S.; Gali, V.; Mason, P.J.; Chaniewski, S.; Levine, S.M.; Wichroski, M.J.; Feulner, M.; Song, Y.; Granaldi, K.; Loy, J.K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in the woodchuck model of HBV infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Wu, W.; Kosinska, A.; Zhang, X.; Möller, I.; Seiz, P.; Glebe, D.; Wang, B.; et al. Enhancing Virus-Specific Immunity In Vivo by Combining Therapeutic Vaccination and PD-L1 Blockade in Chronic Hepadnaviral Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Regulation of type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, S.P.; Chin, D.J.; Cheng, D.T.; Ravindran, P.; Bitter, H.; Gruenbaum, L.; Cote, P.J.; Ma, H.; Klumpp, K.; Menne, S. Identification of an intrahepatic transcriptional signature associated with self-limiting infection in the woodchuck model of hepatitis B. Hepatology 2013, 57, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, J.; Gonzalez, I.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Larrea, E.; Ardaiz, N.; González-Aseguinolaza, G.; Prieto, J.; Berraondo, P. Anchoring interferon alpha to apolipoprotein A-I reduces hematological toxicity while enhancing immunostimulatory properties. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, S.K.; Sood, A.; Kumar, M.; Arora, A.; Amrapurkar, D.; Sharma, B.C.; Konar, A.; Chawla, Y.K.; Jain, R.K.; Nanda, V.; et al. Effect of Lowering HBV DNA Levels by Initial Antiviral Therapy Before Adding Immunomodulator on Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, D.A.; Shutova, M.V.; Johnston, N.R.; Smith, O.P.; Fedorin, V.V.; Kukushkin, Y.S.; van der Loo, J.C.M.; Johnstone, E.C. The clinical landscape for AAV gene therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Golenbock, D.; Bowie, A.G. The history of Toll-like receptors—Redefining innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, K.; Shibata, T.; Ohto, U.; Shimizu, T. Emerging roles of the processing of nucleic acids and Toll-like receptors in innate immune responses to nucleic acids. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepehri, Z.; Kiani, Z.; Alavian, S.M.; Arababadi, M.K.; Kennedy, D.H. The link between TLR7 signaling and hepatitis B virus infection. Life Sci. 2016, 158, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatin, U.; Wolfgang, G.; Tumas, D.; Frey, C.R.; Ohmstede, C.; Hesselgesser, J.; Kearney, B.; Moorehead, L.; Subramanian, G.M.; McHutchison, J.G. Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Gs-9620, An Oral Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R.E.; Guerra, B.; Chavez, D.; Giavedoni, L.; Hodara, V.L.; Brasky, K.M.; Fosdick, A.; Frey, C.R.; Zheng, J.; Wolfgang, G.; et al. GS-9620, an Oral Agonist of Toll-Like Receptor-7, Induces Prolonged Suppression of Hepatitis B Virus in Chronically Infected Chimpanzees. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1508–1517.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Brunetto, M.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Ferrari, C.; Massetto, B.; Nguyen, A.-H.; Joshi, A.; Woo, J.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Lim, Y.-S.; Gordon, S.C.; Visvanathan, K.; Sicard, E.; Fedorak, R.N.; Roberts, S.; Massetto, B.; Ye, Z.; Pflanz, S.; et al. The oral toll-like receptor-7 agonist GS-9620 in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, K.; Ahn, S.H.; Elkhashab, M.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; Bulusu, A.; Tian, X.; Cathcart, A.L.; Woo, J.; Subramanian, G.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in patients with chronic hepatitis B who are not currently on antiviral treatment. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luk, A.; Jiang, Q.; Glavini, K.; Triyatni, M.; Zhao, N.; Racek, T.; Zhu, Y.; Grippo, J.F. A Single and Multiple Ascending Dose Study of Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist (RO7020531) in Chinese Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yu, X.; Yu, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L.; Ottaviani, G.; Yun, H.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Ilnicka, M.; et al. Preclinical mechanistic and efficacy evaluation of a novel small molecule TLR7 agonist RO7020531 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S802–S803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yu, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L.; Yun, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, W.; Young, J.; Gao, L. Combination treatment of a TLR7 agonist RO7020531and a capsid assembly modulator RO7049389 achieved sustainable viral loadsuppression and HBsAg loss in an AAV-HBV mouse model. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S17–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschke, F.; Li, C.; Zhu, R.; Han, Q.; Wu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Barale-Thomas, E.; De Jonghe, S.; Lin, T.-I.; De Creus, A. JNJ-64794964 (AL-034/TQ-A3334), a TLR7 agonist, induces sustained anti-HBV activity in AAV/HBV mice via non-cytolytic mechanisms. Antivir. Res. 2021, 196, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Niu, J.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of TQ-A3334, an oral toll-like receptor 7 agonist in healthy individuals. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Espinoza, I.; Guerrero-Plata, A. The Relevance of TLR8 in Viral Infections. Pathogens 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Marcken, M.; Dhaliwal, K.; Danielsen, A.C.; Gautron, A.S.; Dominguez-Villar, M. TLR7 and TLR8 activate distinct pathways in monocytes during RNA virus infection. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaw1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Tan, A.T.; Ussher, J.E.; Sandalova, E.; Tang, X.-Z.; Tan-Garcia, A.; To, N.; Hong, M.; Chia, A.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 8 Agonist and Bacteria Trigger Potent Activation of Innate Immune Cells in Human Liver. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, O.E.; Colbeck, E.J.; Daffis, S.; Khan, S.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Pattabiraman, D.; Chu, R.; Micolochick Steuer, H.; Lehar, S.; Peiser, L.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of TLR8 Agonist GS-9688 (Selgantolimod) in Chronic Hepatitis B: Remodeling of Antiviral and Regulatory Mediators. Hepatology 2020, 74, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayithan, N.; Tang, L.; Tan, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wallin, J.J.; Fletcher, S.P.; Kottilil, S.; Poonia, B. Follicular Helper T (TFH) Cell Targeting by TLR8 Signaling For Improving HBsAg-Specific B Cell Response In Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 735913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Kaisho, T.; Sato, S.; Sanjo, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Hoshino, K.; Wagner, H.; Takeda, K.; et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 2000, 408, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, A.M. Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonists in the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Targeting the TLR9–MyD88 pathway in the regulation of adaptive immune responses. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurk, M.; Vollmer, J. Therapeutic Applications of Synthetic CpG Oligodeoxynucleotides as TLR9 Agonists for Immune Modulation. BioDrugs 2007, 21, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, O.; Mercer, A.; Friebe, A.A.; Knolle, P.A.; Volk, H.-D. Therapeutic immunomodulation using a virus—the potential of inactivated orf virus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 32, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, O.; Siegling, A.; Friebe, A.; Limmer, A.; Schlapp, T.; Knolle, P.A.; Mercer, A.; Schaller, H.; Volk, H.-D. Inactivated parapoxvirus ovis (Orf virus) has antiviral activity against hepatitis B virus and herpes simplex virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, D.; Urban, A.; Knorr, A.; Hirth-Dietrich, C.; Siegling, A.; Volk, H.-D.; Mercer, A.A.; Limmer, A.; Schumak, B.; Knolle, P.A.; et al. Inactivated Orf Virus Shows Antifibrotic Activity and Inhibits Human Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Replication in Preclinical Models. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, D.; Weber, O.; Ruebsamen-Schaeff, H.; Tennant, B.C.; Menne, S. AIC649 Induces a Bi-Phasic Treatment Response in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, M.E.; Davidson-Wright, J.; Chilton, M.; Jones, M.; Pandey, R.K.; Sheri, A.; Padmanabhan, S.; Iyer, R.P.; Foster, G.R. Pan-genotypic anti-HCV activity of SB 9200 assessed in the “capture-fusion” replication assay. Hepatology 2013, 58, 92A–207A. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, R.P.; Sheri, R.; Pandey, R.K.; Padmanabhan, S.; Korba, B.E.; Bose, S. Activation of intracellular viral sensors by the anti-hepatitis Agent SB 9200—Implications for broad-spectrum antiviral activity. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Antiviral Research 2014, Raleigh, NC, USA, 12–16 May 2014; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, R.P.; Padmanabhan, S.; Zhang, G.; Morrey, J.D.; Korba, B.E. Nucleotide analogs as novel anti-hepatitis B virus agents. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, J.E.; Padmanabhan, S.; Zhang, G.; Kirk, C.J.; Govardhan, C.P.; Korba, B.E.; O’Loughlin, K.; Green, C.E.; Mirsalis, J.; Morrey, J.D.; et al. Orally bioavailable anti-HBV dinucleotide acyloxyalkyl prodrugs. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, J.E.; Pandey, R.K.; Padmanabhan, S.; O’Loughlin, K.G.; Marquis, J.; Green, C.E.; Mirsalis, J.C.; Iyer, R.P. Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Stability Studies of the Prodrug Analog of an Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Dinucleoside Phosphorothioate. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, R.P.; Roland, A.; Jin, Y.; Mounir, S.; Korba, B.; Julander, J.G.; Morrey, J.D. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of ORI-9020, a Novel Phosphorothioate Dinucleotide, in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2318–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Korolowicz, K.E.; Iyer, R.P.; Czerwinski, S.; Suresh, M.; Yang, J.; Padmanabhan, S.; Sheri, A.; Pandey, R.K.; Skell, J.; Marquis, J.K.; et al. Antiviral Efficacy and Host Innate Immunity Associated with SB 9200 Treatment in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, K.; Chen, W.; Liao, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, R. Switching to PegIFNα-2b leads to HBsAg loss in patients with low HBsAg levels and HBV DNA suppressed by NAs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Shu, W.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Gao, B.; Xiong, S. Nuclear Sensor Interferon-Inducible Protein 16 Inhibits the Function of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA by Integrating Innate Immune Activation and Epigenetic Suppression. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Han, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.; Wei, L.; Jiang, J.-D.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.-T.; et al. STING Agonists Induce an Innate Antiviral Immune Response against Hepatitis B Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Islam, H.; Kirschning, C.; Lu, H.; Hoffmann, D.; Dittmer, U.; Lu, M. Hepatitis B virus particles activate B cells through the TLR2–MyD88–mTOR axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.B.; Hüppner, A.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Michalak, T.I. Differential Expression of Woodchuck Toll-Like Receptors 1–10 in Distinct Forms of Infection and Stages of Hepatitis in Experimental Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, M.-M.; Li, F.-H.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.-Z.; Lu, Y.-P.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Zheng, X.; et al. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of woodchuck retinoic acid-inducible gene I. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2016, 36, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Korolowicz, K.E.; Murreddu, M.G.; Gudima, S.O.; Menne, S. Agonistic Activation of Cytosolic DNA Sensing Receptors in Woodchuck Hepatocyte Cultures and Liver for Inducing Antiviral Effects. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, P.; Barili, V.; Rossi, M.; Montali, I.; Vecchi, A.; Acerbi, G.; Laccabue, D.; Zecca, A.; Penna, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of T Cell Dysfunction in Chronic HBV Infection and Related Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Tian, Y.; Kosinska, A.D.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Dittmer, U.; Roggendorf, M.; et al. The Expression of PD-1 Ligands and Their Involvement in Regulation of T Cell Functions in Acute and Chronic Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Massari, M.; Loggi, E.; Biasini, E.; Sacchelli, L.; Cavallo, M.C.; Silini, E.M.; Andreone, P.; Missale, G.; et al. Antiviral Intrahepatic T-Cell Responses Can Be Restored by Blocking Programmed Death-1 Pathway in Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 682–693.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Bauer, T.; Protzer, U. Therapeutic vaccination for chronic hepatitis B. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggendorf, M.; Yang, D.; Lu, M. The woodchuck: A model for therapeutic vaccination against hepadnaviral infection. Pathol. Biol. 2010, 58, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Zhang, E.; Johrden, L.; Liu, J.; Seiz, P.L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Kemper, T.; Fiedler, M.; Glebe, D.; et al. Combination of DNA Prime—Adenovirus Boost Immunization with Entecavir Elicits Sustained Control of Chronic Hepatitis B in the Woodchuck Model. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Schreiter, T.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Roggendorf, M.; Schlaak, J.; Lu, M. Inhibition of woodchuck hepatitis virus gene expression in primary hepatocytes by siRNA enhances the cellular gene expression. Virology 2009, 384, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Pei, R.; Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. RNAi Induces Innate Immunity through Multiple Cellular Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Bartenschlager, R.; Kubitz, R.; Zoulim, F. Strategies to Inhibit Entry of HBV and HDV Into Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Mbarek, M.B.; Warlich, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Alexandrov, A.; Urban, S.; Petersen, J.; Lütgehetmann, M.; et al. The entry inhibitor Myrcludex-B efficiently blocks intrahepatic virus spreading in humanized mice previously infected with hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: First results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.K.; Choe, P.G.; Park, S.; Kim, T.S.; Seong, M.W.; Kim, N.J.; Oh, M.D.; Park, W.B.; Kim, Y.W. Compassionate use of hzVSF-v13 in two patients with severe COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2371–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.W.; Park, S. An Antibody or Peptide Specifically Binding to Peptide Derived from Vimentin. Korea Patent 10201600726972016, 10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Sekiba, K.; Funato, K.; Koike, K. Humanized virus-suppressing factor inhibits hepatitis B virus infection by targeting viral cell entry. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlich, W. Functional cure of chronic hepatitis B—Predictable? eBioMedicine 2021, 70, 103499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Discovery of RG7834: The First-in-Class Selective and Orally Available Small Molecule Hepatitis B Virus Expression Inhibitor with Novel Mechanism of Action. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10619–10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, H.; Wildum, S.; Luangsay, S.; Walther, J.; Lopez, A.; Tropberger, P.; Ottaviani, G.; Lu, W.; Parrott, N.J.; Zhang, J.D.; et al. A novel orally available small molecule that inhibits hepatitis B virus expression. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.; Sun, L.; Noe, D.; Lam, P.Y.S.; Zhou, T.; Block, T.M.; Du, Y. Hepatoselective Dihydroquinolizinone Bis-acids for HBsAg mRNA Degradation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A. REP 2139: Antiviral Mechanisms and Applications in Achieving Functional Control of HBV and HDV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahtab, M.; Bazinet, M.; Vaillant, A. Safety and Efficacy of Nucleic Acid Polymers in Monotherapy and Combined with Immunotherapy in Treatment-Naive Bangladeshi Patients with HBeAg+ Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pântea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Albrecht, J.; Schmid, P.; Le Gal, F.; Gordien, E.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): A non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordeen, F.; Scougall, C.A.; Grosse, A.; Qiao, Q.; Ajilian, B.B.; Reaiche-Miller, G.; Finnie, J.; Werner, M.; Broering, R.; Schlaak, J.F.; et al. Therapeutic Antiviral Effect of the Nucleic Acid Polymer REP 2055 against Persistent Duck Hepatitis B Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, L.; Vaillant, A.; Stelma, F.; Kootstra, N.; Bazinet, M.; Al-Mahtab, M.; Reesink, H. O114: Serum HBV-RNA levels decline significantly in chronic hepatitis B patients dosed with the nucleic-acid polymer REP2139-CA. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, C.; Vecchi, A.; Rossi, M.; Laccabue, D.; Giuberti, T.; Alfieri, A.; Lampertico, P.; Grossi, G.; Facchetti, F.; Brunetto, M.R.; et al. TLR7 Agonist Increases Responses of Hepatitis B Virus–Specific T Cells and Natural Killer Cells in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Treated With Nucleos(T)Ide Analogues. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1764–1777.e1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.; Lutz, J.D.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; Grant, E.P.; Joshi, A.; Mackman, R.L.; Ling, J.; Tan, S.K.; Ayithan, N.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Selgantolimod, an Oral Toll-Like Receptor 8 Agonist: A Phase Ia Study in Healthy Subjects. Antivir. Ther. 2020, 25, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Visvanathan, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Nguyen, A.H.; Wallin, J.J.; Chen, D.Y.; McDonald, C.; Arora, P.; Tan, S.K.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of the Oral TLR8 Agonist Selgantolimod in Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harry, L.; Janssen, Y.-S.L.; Hyung, J.L.; Tseng, C.-H.; Coffin, C.; Elkashab, M.; Anh, S.H.; Nguyen, A.-H.; Chen, D.; Wallin, J. Safety and efficacy of oral TLR8 agonist, selgantolimod, in viremic adult patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S757. [Google Scholar]
- Gane, E.; Dunbar, P.R.; Brooks, A.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, S.; Lau, A.; Yang, J.; Gaggar, A.; Subramanian, M.; Kottilil, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of 24 weeks treatment with oral TLR8 agonist, selgantolimod, in virally-suppressed adult patients with chronic hepatitis B: A phase 2 study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, I.; Jambrecina, A.; Berg, T.; Van Bömmel, F.; Kropeit, D.; Vank, C.; Bigge, A.; Nedoschinsky, K.; Stobernack, H.-P.; Rangaraju, M.; et al. FRI-199-First in Human, single ascending dose clinical trial of AIC649 in patients with chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e478–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-J.; Jeng, R.-J.; Elkhashab, M.; Coffin, C.; Kim, W.; Greenbloom, S.; Ramji, A.; Lim, Y.-S.; et al. GS-12-Ascending dose cohort study of inarigivir—A novel RIG I agonist in chronic HBV patients: Final results of the ACHIEVE trial. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e47–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring Bank Halts Development of Inarigivir for Hepatitis B. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/spring-bank-stops-inarigivir-hbv/ (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Gill, U.S.; Pallett, L.J.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Maini, M.K. Liver sampling: A vital window into HBV pathogenesis on the path to functional cure. Gut 2018, 67, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antiviral | Abbreviation/Brand Name | Dose | Group Size (Animal Number) | Treatment/ Follow-Up Duration (Weeks) | Antiviral Effect (Serum) | Treatment Outcome | Additional Results | Adverse Effects | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHV DNA (Log Red.) | WHsAg (Log Red.) | WHeAg (ODU Red.) | |||||||||
| NA | TAF/Vemlidy | 5 mg/kg (po, QD) | 4 | 12/4 | 6.38 | 3.24 | 1.86 | Transient (viral relapse) | Transient red. in:
| None | [72] |
| Viral entry inhibitor | Anti-vimentin monoclonal antibody hzVSF | hzVSF (4 mg/kg, iv, BIW) + TAF (5 mg/kg, po, QD) | 4 | 12/4 | 7.27 | 3.47 | 1.87 | SVR/Functional cure (seroconversion to anti-WHs and anti-WHe antibodies) in a subset of animals | Sustained red. in:
| None | [72] |
| Gene expression inhibitor | RG7834 | RG7834 (10 mg/kg, po, BID) + ETV (0.1 mg/kg, po, QD) + wIFN-α5 (0.1 mg/kg, sc, TIW followed by BIW) | 5 | 14/10 | 7.46 | 5.0 | - | Transient (viral relapse) | Transient red. in:
| IFN-related adverse effects | [74] |
| Antigen release inhibitor | REP 2055/REP 2139-Ca | REP 2055/REP 2139-Ca (10–15 mg/kg, sc, TIW) | 2–6 | 3–5/0–1 | 0 | ~0.5 | - | - | - | None | [75] |
| Immunomodulator | Abbreviation/Brand Name | Dose | Group Size (Animal Number) | Treatment/ Follow-Up Duration (Weeks) | Antiviral Effect (Serum) | Treatment Outcome | Additional Results | Adverse Effects | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHV DNA (Log Red.) | WHsAg (Log Red.) | WHeAg (ODU Red.) | |||||||||
| Interferon-alpha | wIFN-α5 (systemic) | 20 µg/animal (sc, TIW for 7 weeks) then 100 µg/animal (sc, TIW for 8 weeks) | 12 | 15/8 | 3.62 | 2.42 | - | Transient (variable viral relapse) | Transient red. in:
| None | [78] |
| wIFN-α5 (AAV-mediated; fused to apolipoprotein A-I) | 5 × 1012 vg (iv, once) + ETV (0.5 mg/kg, po, QD) | 5 | 4/12 | 4.5 | 0.6 | - | Transient (delayed viral relapse compared to control) | None | [79] | ||
| TLR7 agonist | GS-9620/Vesatolimod | 2.5–5.0 mg/kg (po, QOD, QOD in QOW, or QW) | 12 | 4–8/31 | Up to 6.2 | Undetectable/Loss | - | SVR/Functional cure (seroconversion to anti-WHs antibodies) in a subset of animals | Sustained red. in:
| Thrombocytopenia (reversible) | [80] |
| APR002 | 5–30 mg/kg (po, QW) + ETV (0.1 mg/kg, po, QD) | 4 | 20/16 | 6.64–7.33 | 2.40–3.28 | 2.50–2.77 | SVR/Functional cure (seroconversion to anti-WHs and anti-WHe antibodies) in a subset of animals | Sustained red. in:
| Hypothermia (reversible) | [81] | |
| RG7854 | 30–120 mg/kg (po, QOD) | 5–6 | 14–24/11 | 2.43–5.14 | 2.60–2.87 | 1.40–1.53 | SVR/Functional cure (seroconversion to anti-WHs and anti-WHe antibodies) in a subset of animals | Transient inc. in:
| Neutropenia/Thrombocytopenia (reversible) | [82] | |
| 120 mg/kg (po, QOD) + ETV (0.1 mg/kg, po, QD) | 6 | 14/18 | 7.93 | 4.68 | 2.37 | Sustained red. in:
| |||||
| TLR8 agonist | GS-9688/Selgantolimod | 1–3 mg/kg (po, QW) | 10 | 8/24 | Up to >5.0 | Undetectable/Loss | - | SVR/Functional cure (seroconversion to anti-WHs antibodies) in a subset of animals | Sustained red. in:
| Thrombocytopenia in one animal (reversible) | [83] |
| TLR9 agonist | CpG 21798 | 4 mg/kg (sc, QW) + ETV (0.5 mg/kg, po, QD) | 4 | 16/12 | Undetectable | Undetectable/Loss | - | Transient (delayed viral relapse compared to control) | Transient inc. in:
| None | [84] |
| AIC649 | 109 particles/animal (iv then im, BIW) + ETV (0.2 mg/kg, po, QD) | 5 | 21/- | 7.57 | 4.05 | 2.46 | SVR after ETV withdrawal (seroconversion to anti-WHs and anti-WHe antibodies) in a subset of animals | Sustained red. in:
| None | [85] | |
| RIG-I/NOD2 agonist | SB 9200/Inarigivir | 30 mg/kg (po, QD) followed by ETV (0.5 mg/kg, po, QD) | 5 | 16/8 | 6.4 | 3.3 | - | Transient (delayed viral relapse compared to reversed treatment sequence of ETV followed by SB 9200) | Transient red. in:
| None | [86] |
| Checkpoint inhibitor | Anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody wc6D5 | 15 mg/kg (iv, every 3rd or 4th day over 10 days) + ETV (0.1 mg/kg, po, QD) | 11 | 12/10 | Reduced/Undetectable | Undetectable/Loss | Reduced/Undetectable | SVR in a subset of animals | - | None | [87] |
| Therapeutic vaccine | DNA-based vaccine encoding WHcAg and WHsAg + Anti-PD-L1 polyclonal antibody | Plasmid DNA (500 µL, im, QW) + Anti-PD-L1 (25 mg/kg, iv, QOD) + ETV (0.2 and 1.5 mg/animal, sc, QD and QW) | 3 | 28/14 | Undetectable | Reduced/Undetectable | - | SVR/Functional cure (seroconversion to anti-WHs antibodies) in a subset of animals | Sustained red. in:
| None | [88] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suresh, M.; Menne, S. Recent Drug Development in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. Viruses 2022, 14, 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081711
Suresh M, Menne S. Recent Drug Development in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. Viruses. 2022; 14(8):1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081711
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuresh, Manasa, and Stephan Menne. 2022. "Recent Drug Development in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B" Viruses 14, no. 8: 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081711
APA StyleSuresh, M., & Menne, S. (2022). Recent Drug Development in the Woodchuck Model of Chronic Hepatitis B. Viruses, 14(8), 1711. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081711






