Characterization and Genomic Analysis of Novel Vibrio parahaemolyticus Phage vB_VpaP_DE10
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Isolation of Phage
2.3. Phage Concentration and Morphological Observation
2.4. Spot Assay
2.5. Efficiency of Plating (EOP)
2.6. Phage Nucleotide Extraction
2.7. Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.8. Phage One-Step Growth Curve Assay
2.9. Accession Number
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation, Identification, and General Characterization of Phages
3.2. Host Range
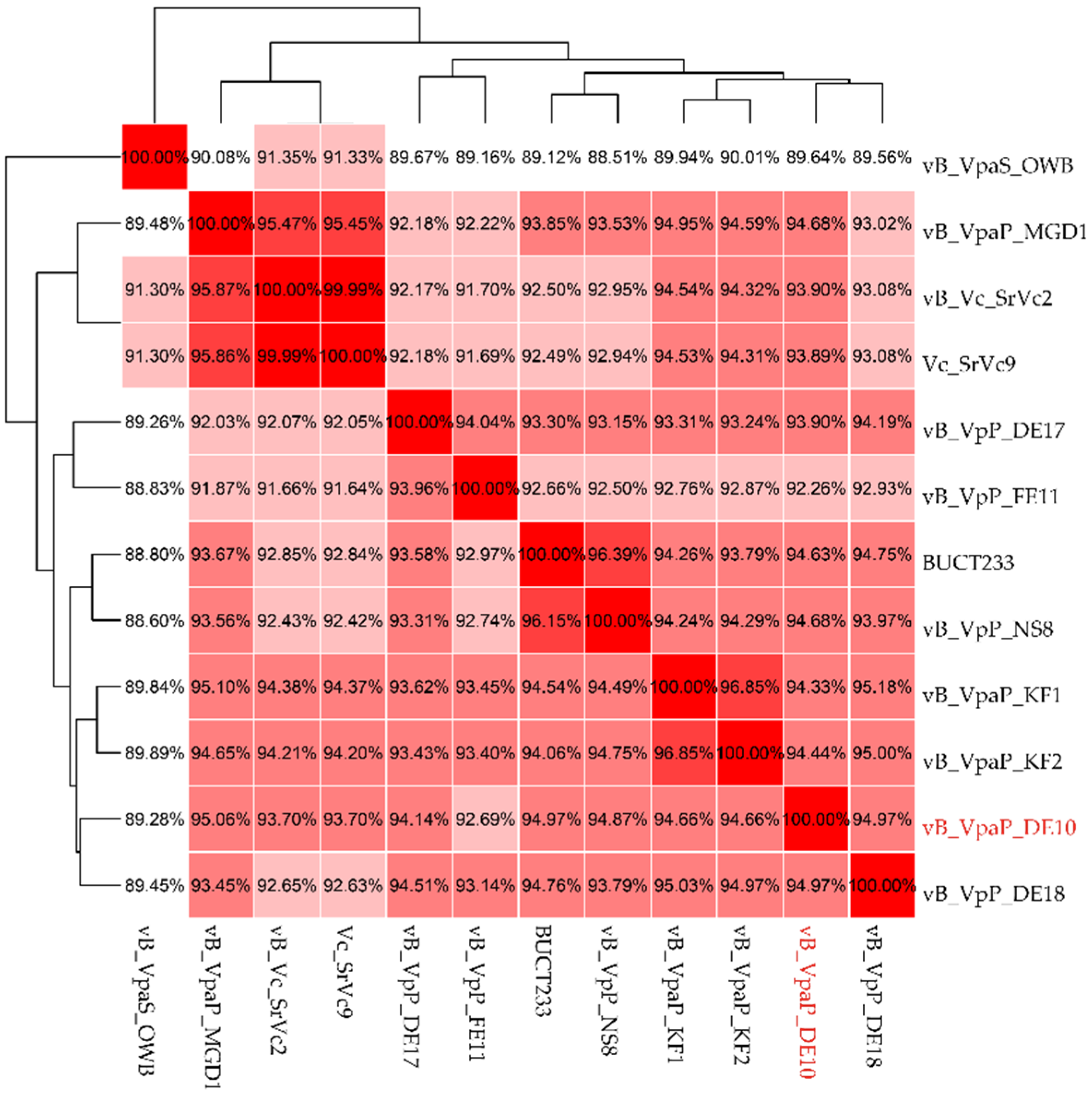
3.3. Genomic Signature of Phage vB_VpaP_DE10
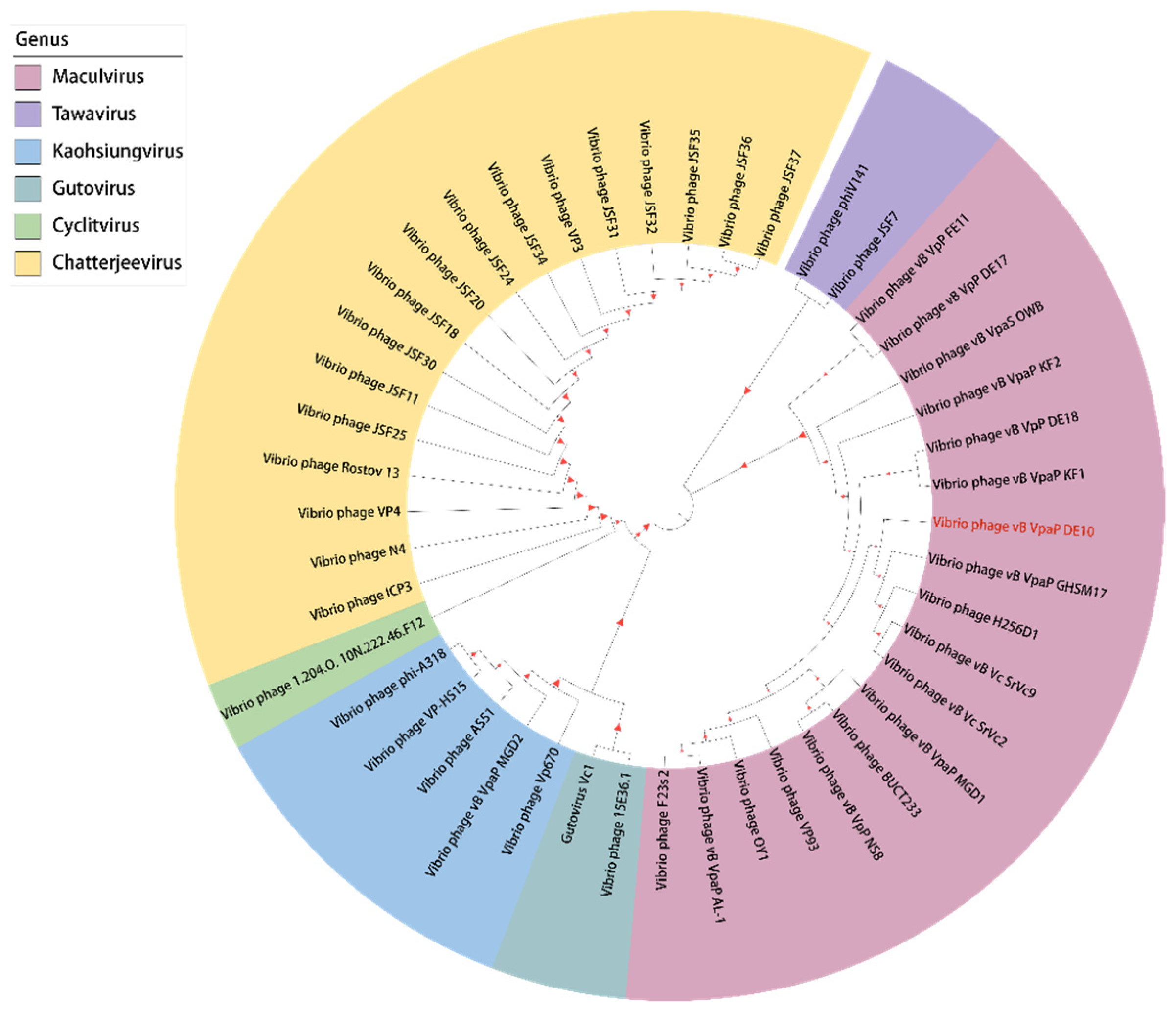
3.4. Phage Taxonomy and Phylogeny Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacian, C.; Verdugo, C.; García, K.; Perez-Larruscain, J.; de Blas, I.; Cachicas, V.; Lopez-Joven, C. Longitudinal Study of Total and Pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus (tdh+ and/or trh+) in Two Natural Extraction Areas of Mytilus chilensis in Southern Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 621737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Hiyoshi, H.; Tandhavanant, S.; Kodama, T. Advances on Vibrio parahaemolyticus research in the postgenomic era. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Yu, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, J. Challenges in Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections caused by the pandemic clone. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamp, N.; Bhat, S.G. Phage Endolysins as Potential Antimicrobials against Multidrug Resistant Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus: Current Status of Research and Challenges Ahead. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Liao, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Yue, M. A Meta-Analysis of Major Foodborne Pathogens in Chinese Food Commodities between 2006 and 2016. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, L.; Chen, Y. Pathogenic Characteristics of and Variation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus Isolated from Acute Diarrhoeal Patients in Southeastern China from 2013 to 2017. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, P.; Chakraborty, H.J.; Behera, B.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.D.; Das, B.K. Computational characterization and molecular dynamics simulation of the thermostable direct hemolysin-related hemolysin (TRH) amplified from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, D.; Li, Y.; Jia, M. Molecular mechanisms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 222, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Jiang, F.; He, M.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Pang, R.; Wu, S.; Wei, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Prevalence, virulence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance of Vibrio parahaemolyticus from different types of food samples in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 317, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Li, Y. Intervention Strategies for Reducing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Seafood: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, R10–R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Han, G.; Li, Z.; Cun, S.; Hao, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Bacteriophage therapy in aquaculture: Current status and future challenges. Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Ye, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, Q.; Tan, Z. Isolation and Characterization of the Novel Phages vB_VpS_BA3 and vB_VpS_CA8 for Lysing Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liang, Y.; Su, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Kong, L.; Zeng, H.; Xue, L.; et al. Genome characterization of the novel lytic Vibrio parahaemolyticus phage vB_VpP_BA6. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2627–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, W.; Sun, X. Characterization of vB_VpaP_MGD2, a newly isolated bacteriophage with biocontrol potential against multidrug-resistant Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Tan, S.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Tan, Z. Characterization and genome analysis of a novel Vibrio parahaemolyticus phage vB_VpP_DE17. Virus Res. 2022, 307, 198580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wu, Q.; et al. Characterization of the Novel Phage vB_VpaP_FE11 and Its Potential Role in Controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilms. Viruses 2022, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, N.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Marmo, P.; Demattè, E.; Amisano, F.; Di Pilato, V.; Fraziano, M.; Lupetti, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Thaller, M.C. Characterization of vB_Kpn_F48, a Newly Discovered Lytic Bacteriophage for Klebsiella pneumoniae of Sequence Type 101. Viruses 2018, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Mi, Z.; Pei, G.; Huang, Y.; An, X.; Fu, K.; Zhou, L.; et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel, virulent Ahjdlikevirus bacteriophage that infects Enterococcus faecium. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3843–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Pop, M. ARDB—Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D443–D447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stothard, P.; Grant, J.R.; Van Domselaar, G. Visualizing and comparing circular genomes using the CGView family of tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.; Bouzari, M.; Ghaemi, E.A. Genomic analyses of a novel bacteriophage (VB_PmiS-Isfahan) within Siphoviridae family infecting Proteus mirabilis. Genomics 2019, 111, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Sullivan, M.B.; Knezevic, P.; van Zyl, L.J.; Sarkar, B.L.; Dutilh, B.E.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Łobocka, M.; Tong, Y.; Brister, J.R.; et al. Taxonomy of prokaryotic viruses: 2018–2019 update from the ICTV Bacterial and Archaeal Viruses Subcommittee. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Li, D.; Sun, Z.; Lin, W.; Hong, B.; Qin, W.; Xu, L.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, F.; et al. First Characterization of a Hafnia Phage Reveals Extraordinarily Large Burst Size and Unusual Plaque Polymorphism. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 754331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; Koonin, E.V.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Lavigne, R.; Brister, J.R.; Varsani, A.; et al. Minimum Information about an Uncultivated Virus Genome (MIUViG). Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gómez, J.P.; López-Cuevas, O.; Campo, N.C.; González-López, I.; Martínez-Rodríguez, C.I.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Chaidez, C. Genomic and biological characterization of the novel phages vB_VpaP_AL-1 and vB_VpaS_AL-2 infecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus associated with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Virus Res. 2022, 312, 198719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastías, R.; Higuera, G.; Sierralta, W.; Espejo, R.T. A new group of cosmopolitan bacteriophages induce a carrier state in the pandemic strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Env. Microbiol 2010, 12, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, H.; Gu, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X. Identification of a novel bacterial receptor that binds tail tubular proteins and mediates phage infection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Lim, J.A.; Kwak, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Chang, H.J. Comparative genomic analysis of novel bacteriophages infecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from western and southern coastal areas of Korea. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Park, J. Characterization and Food Application of the Novel Lytic Phage BECP10: Specifically Recognizes the O-polysaccharide of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Viruses 2021, 13, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denes, T.; den Bakker, H.C.; Tokman, J.I.; Guldimann, C.; Wiedmann, M. Selection and Characterization of Phage-Resistant Mutant Strains of Listeria monocytogenes Reveal Host Genes Linked to Phage Adsorption. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4295–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Melo, A.C.C.; Da Mata Gomes, A.; Melo, F.L.; Ardisson-Araújo, D.M.P.; de Vargas, A.P.C.; Ely, V.L.; Kitajima, E.W.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Wolff, J.L.C. Characterization of a bacteriophage with broad host range against strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from domestic animals. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.N.W.; Yen, M.; Seed, K.D.; Lazinski, D.W.; Camilli, A. A Tail Fiber Protein and a Receptor-Binding Protein Mediate ICP2 Bacteriophage Interactions with Vibrio cholerae OmpU. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e0014121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, F.L.; Vlot, M.; de Jonge, P.A.; Dreesens, L.L.; Beaumont, H.J.E.; Lavigne, R.; Dutilh, B.E.; Brouns, S.J.J. Targeting mechanisms of tailed bacteriophages. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
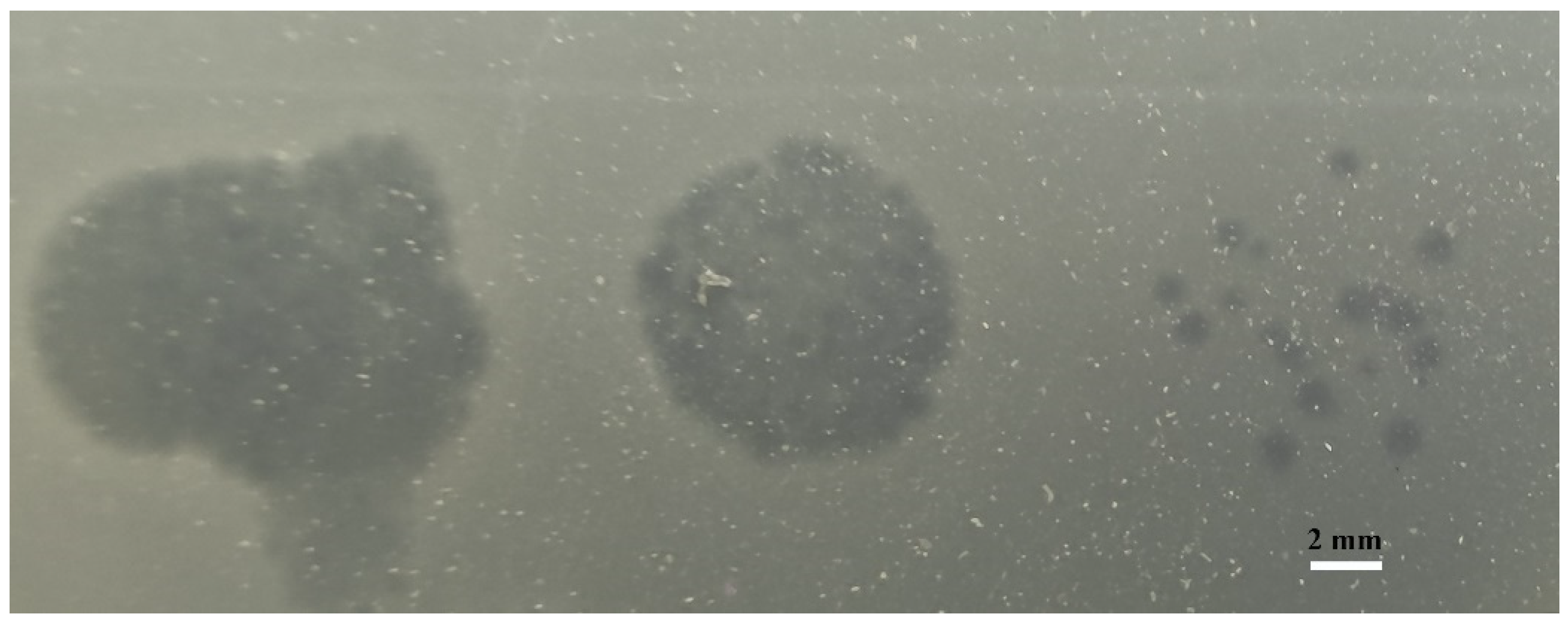
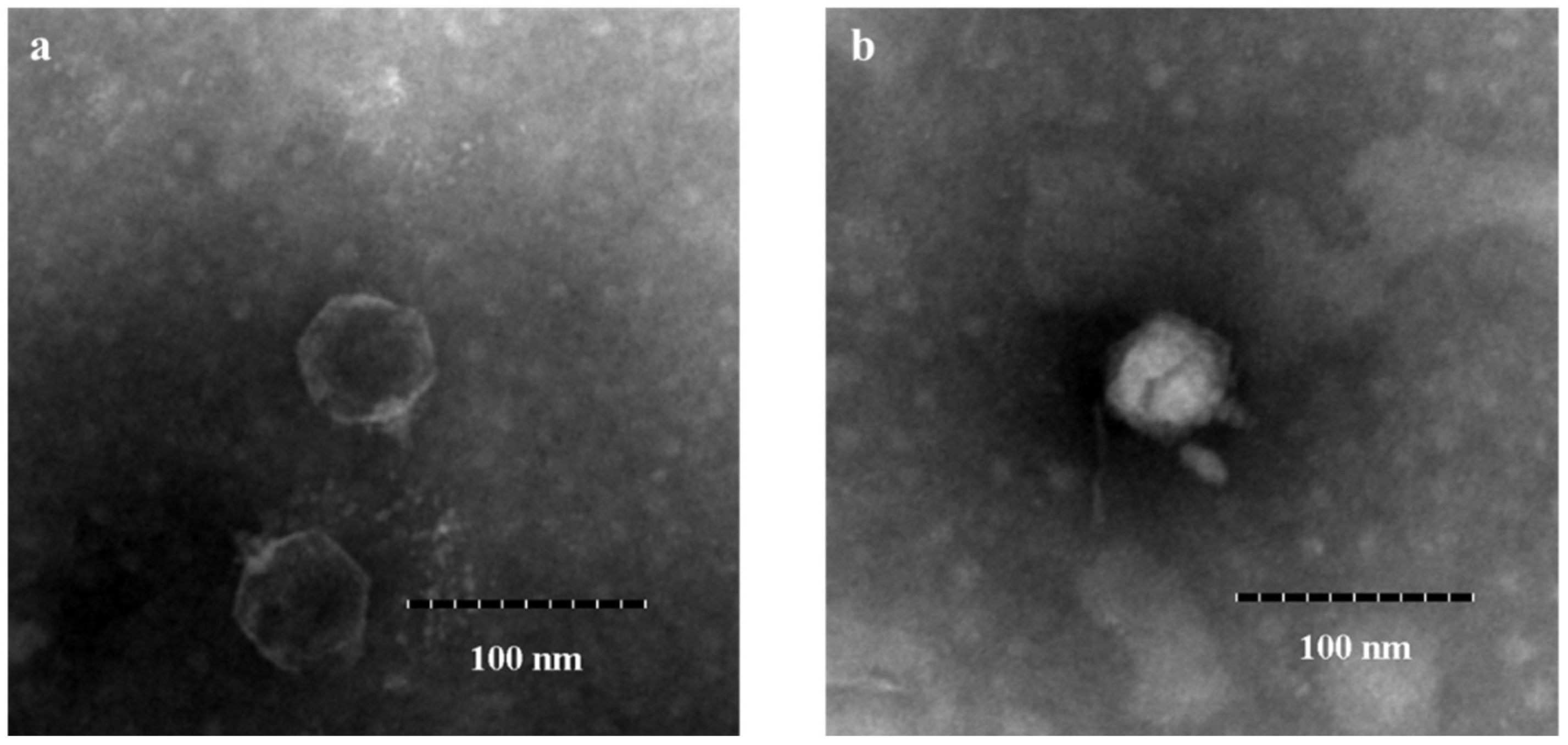
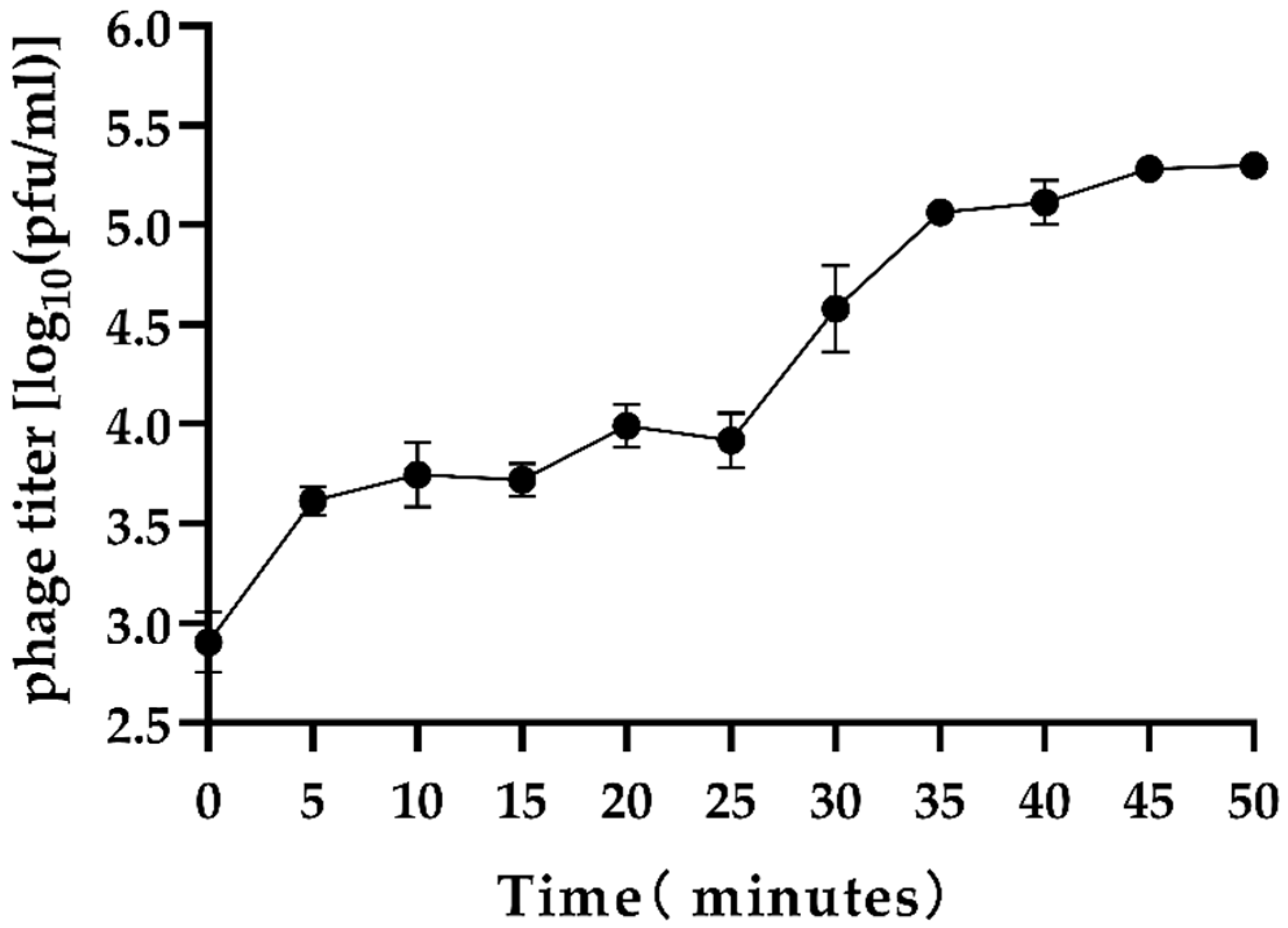


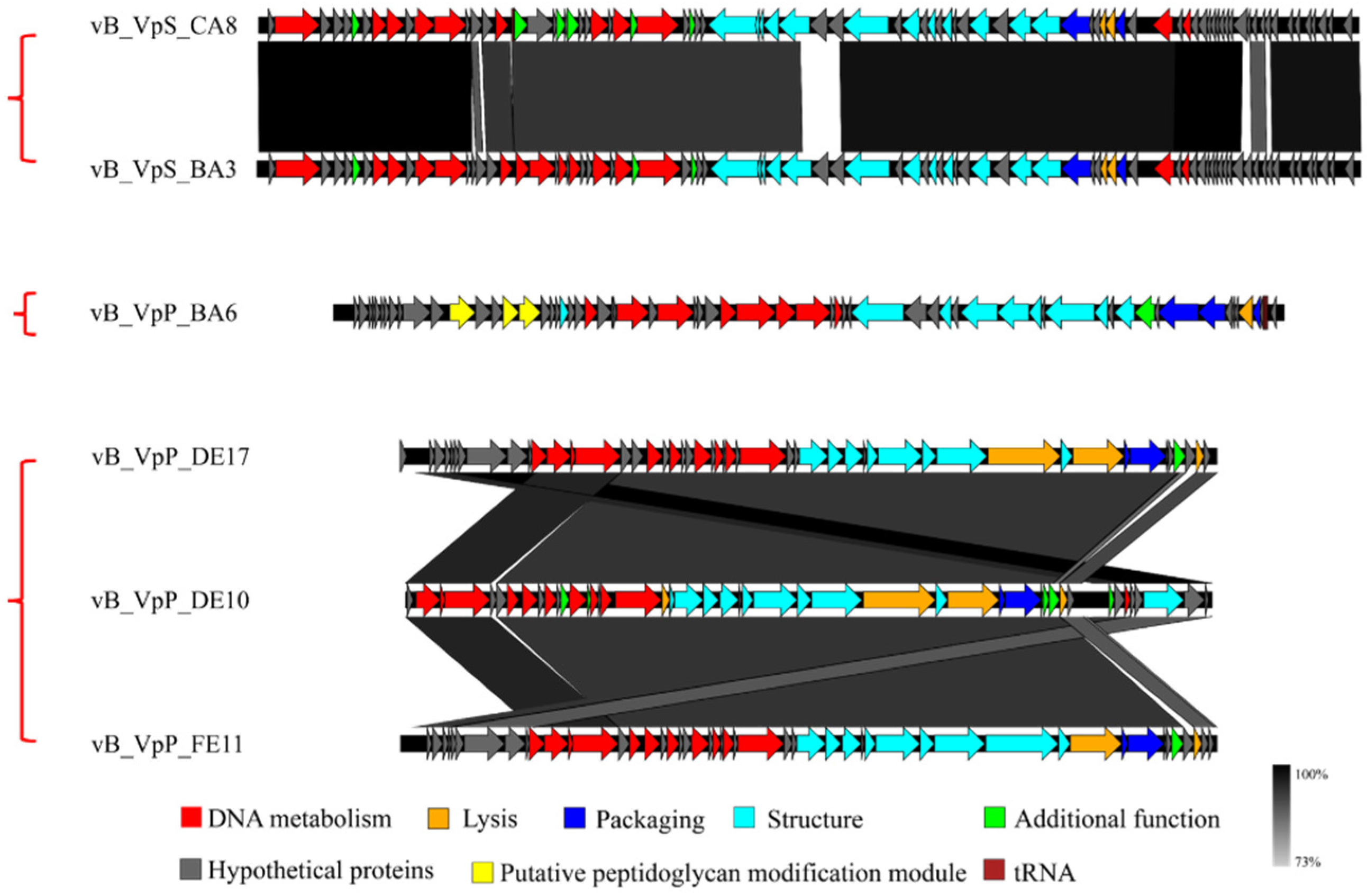

| No. | V. parahaemolyticus Strains | Serotype | Antibiotic Resistance | Spot Test | EOP Value | EOP Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | O1-1 | O1 | CN-K-CIP-S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 2 | O1-3 | O1 | K-CIP-S-AMP-C | + | 0.32 | Medium |
| 3 | O2-5 | O2 | S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 4 | O2-7 | O2 | CIP-S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 5 | O3-8 | O2 | K-CIP-S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 6 | O3-10 | O3 | AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 7 | O3-11 | O3 | CN-S-AMP-C | - | 2.80 | High |
| 8 | O4-12 | O4 | CIP-S-AMP | + | 1 | High |
| 9 | O4-13 | O4 | S-AMP | + | 0.99 | High |
| 10 | O4-14 | O4 | AMP | + | 0.40 | Medium |
| 11 | O5-15 | O5 | CN-K-CIP-S-AMP | + | NT | Inefficient |
| 12 | O6-18 | O6 | K-CIP-S-AMP | + | 0 | Inefficient |
| 13 | O6-20 | O6 | CIP-S-AMP | + | 0.68 | High |
| 14 | O8-21 | O8 | S-AMP | + | 0 | Inefficient |
| 15 | O8-126 | O8 | AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 16 | O9-24 | O9 | CN-CIP-S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 17 | O10-25 | O10 | S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 18 | O10-26 | O10 | CN-CIP-S-AMP-C | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 19 | O10-28 | O10 | AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 20 | O11-29 | O11 | CN-K-CIP-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 21 | O11-30 | O11 | S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 22 | O11-31 | O11 | CIP-S-AMP | + | 8.91 | High |
| 23 | O12-32 | O12 | S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 24 | O12-33 | O12 | CIP-S-AMP | + | 0.065 | Low |
| 25 | O12-34 | O12 | SXT-CIP-AMP-TE-K | - | NT | Inefficient |
| 26 | O12-35 | O12 | CN-CIP-S-AMP | - | NT | Inefficient |
| Label | Length (nt|aa) | Product | Organism | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF2 | 1281|426 | DNA helicase | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 100% |
| ORF3 | 234|77 | putative DNA helicase | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 100% |
| ORF4 | 2427|808 | DNA-directed DNA polymerase | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 99% |
| ORF7 | 597|198 | putative nucleotidyl transferase | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_KF1 | 98% |
| ORF10 | 630|209 | DNA binding protein | Vibrio phage BUCT233 | 98% |
| ORF13 | 951|316 | exonuclease | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 99% |
| ORF15 | 441|146 | endonuclease | Vibrio phage BUCT233 | 100% |
| ORF17 | 585|194 | putative deoxynucleoside monophosphate kinase | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_KF1 | 80% |
| ORF18 | 2451|816 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase | Vibrio phage BUCT233 | 99% |
| ORF19 | 420|139 | GNAT family N-acetyltransferase | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 100% |
| ORF20 | 246|81 | virion protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 100% |
| ORF21 | 1533|510 | putative head–tail connector protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE17 | 99% |
| ORF22 | 816|271 | putative scaffolding protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_MGD1 | 99% |
| ORF23 | 999|332 | major capsid protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_MGD1 | 99% |
| ORF25 | 561|186 | putative tail tubular protein A | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_MGD1 | 100% |
| ORF26 | 2343|780 | putative tail tubular protein B | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_MGD1 | 99% |
| ORF27 | 741|246 | internal virion protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_FE11 | 86% |
| ORF28 | 2679|892 | internal virion protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_KF1 | 95% |
| ORF29 | 3855|1284 | peptidoglycan lytic exotransglycosylase | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 99% |
| ORF30 | 612|203 | putative tail fiber protein | Vibrio phage VP93 | 99% |
| ORF31 | 2733|910 | putative glycosyl hydrolase | Vibrio phage vB_VpaP_KF1 | 99% |
| ORF32 | 300|99 | terminase small subunit | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 98% |
| ORF33 | 1920|639 | terminase large subunit | Vibrio phage vB_Vc_SrVc2 | 100% |
| ORF37 | 414|137 | peptidase M15A | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 100% |
| ORF44 | 2136|711 | putative structural protein | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 98% |
| ORF45 | 1092|363 | putative peptidase | Vibrio phage vB_VpP_DE18 | 100% |
| Accession Number | Virus Name | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| MT501516.1 | vB_VpaP_MGD1 | 96.41 |
| NC_048035.1 | vB_VpaP_KF1 | 95.97 |
| MZ592921.1 | vB_VpP_NS8 | 95.87 |
| MZ020222.1 | BUCT233 | 95.64 |
| MW331544.1 | vB_Vc_SrVc2 | 95.55 |
| LR794124.1 | vB_Vc_SrVc9 | 95.55 |
| NC_048036.1 | vB_VpaP_KF2 | 95.21 |
| MZ182247.1 | vB_VpP_DE18 | 95.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Huang, S.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Yang, M. Characterization and Genomic Analysis of Novel Vibrio parahaemolyticus Phage vB_VpaP_DE10. Viruses 2022, 14, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081609
Ye Y, Chen H, Huang Q, Huang S, He J, Zhang J, Wu Q, Li X, Hu W, Yang M. Characterization and Genomic Analysis of Novel Vibrio parahaemolyticus Phage vB_VpaP_DE10. Viruses. 2022; 14(8):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081609
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yuanming, Hanfang Chen, Qiaolan Huang, Shixuan Huang, Jiaxin He, Jumei Zhang, Qingping Wu, Xueling Li, Wenfeng Hu, and Meiyan Yang. 2022. "Characterization and Genomic Analysis of Novel Vibrio parahaemolyticus Phage vB_VpaP_DE10" Viruses 14, no. 8: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081609
APA StyleYe, Y., Chen, H., Huang, Q., Huang, S., He, J., Zhang, J., Wu, Q., Li, X., Hu, W., & Yang, M. (2022). Characterization and Genomic Analysis of Novel Vibrio parahaemolyticus Phage vB_VpaP_DE10. Viruses, 14(8), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081609






