Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of CMV or 2b-Deficient CMV-Infected dcl2dcl4 Reveals the Effects of Viral Infection on Symptom Induction in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growth and Virus Infection
2.2. Transcriptome Sequencing
2.3. Mapping and Quantification Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.4. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis and Venn Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and De Novo Assembly of Transcriptome
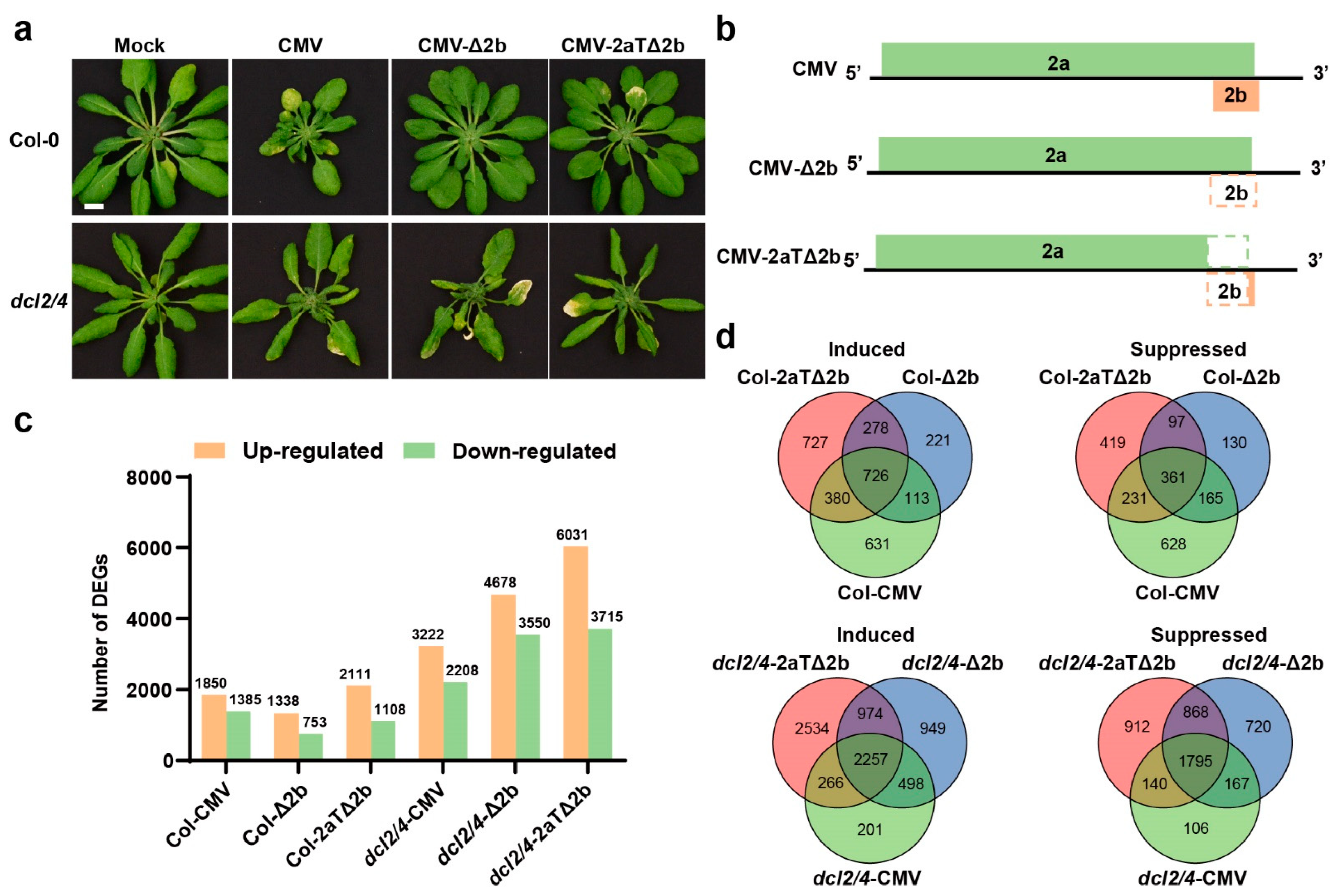
3.2. Comparison of the Differential Transcriptome between CMV-Infected and Mock Plants
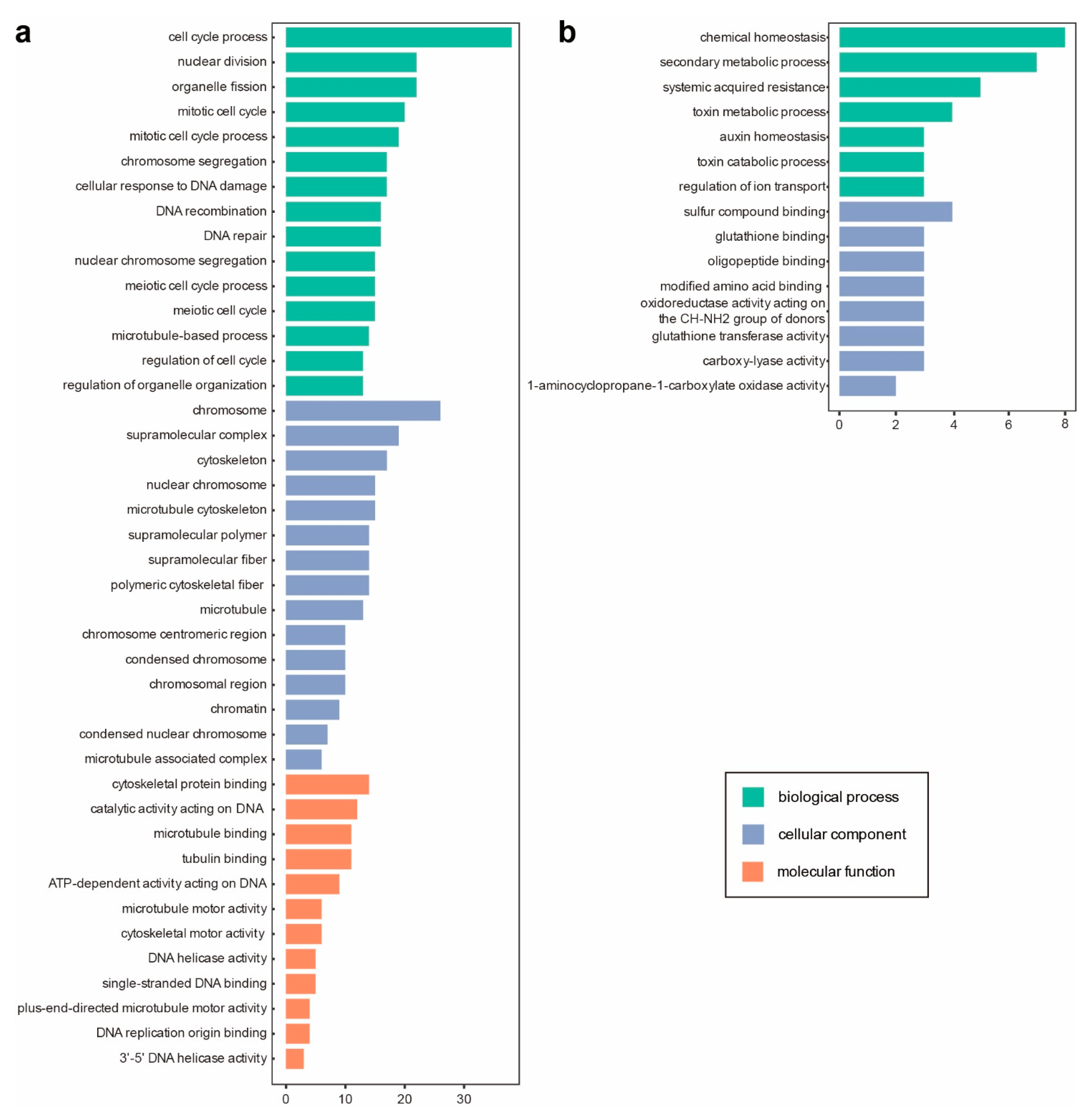
3.3. Asymptomatic Infections of CMV-Δ2b or CMV-2aTΔ2b in Col-0 Are in Relation to Cell Division and Cellular Metabolism
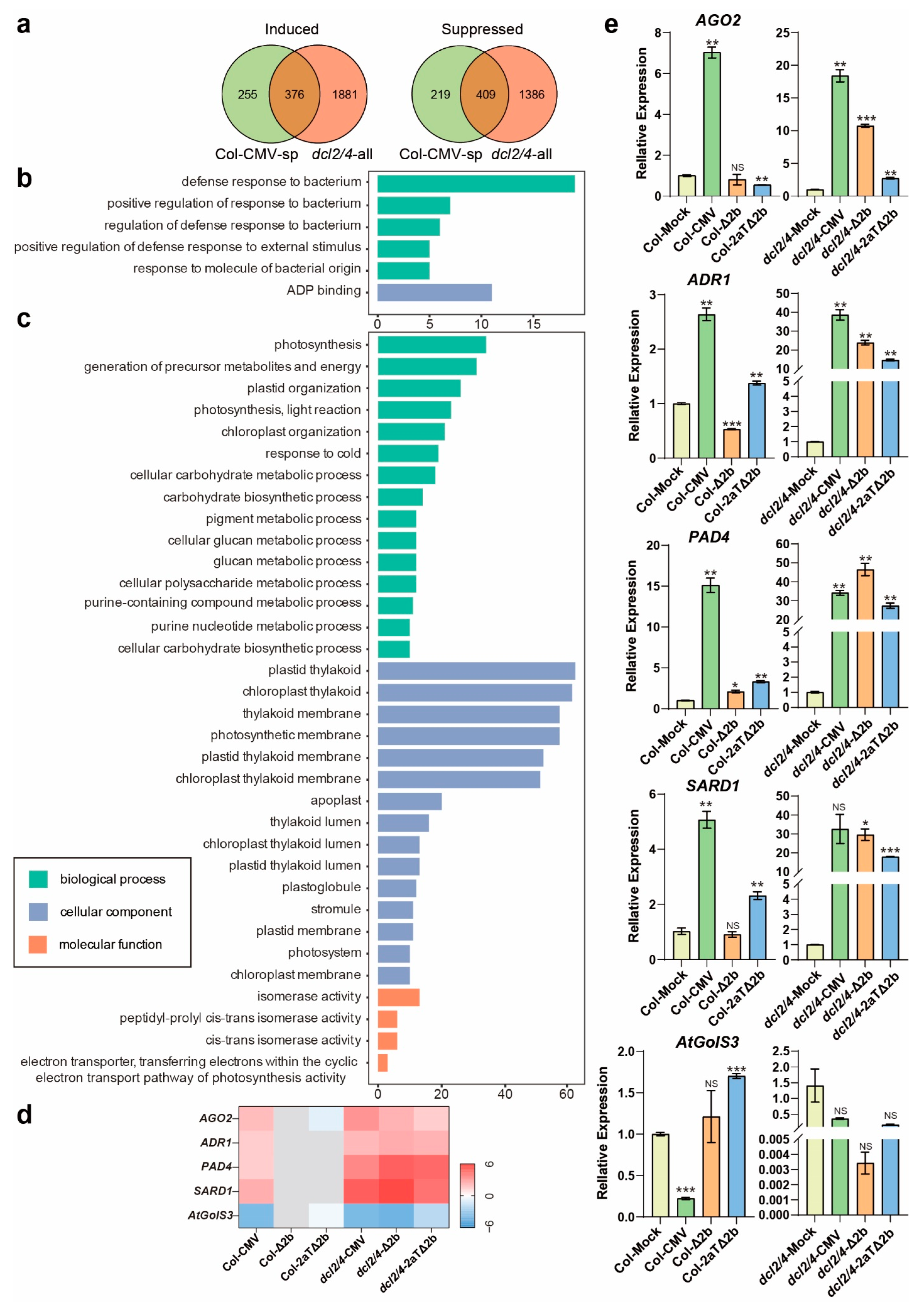
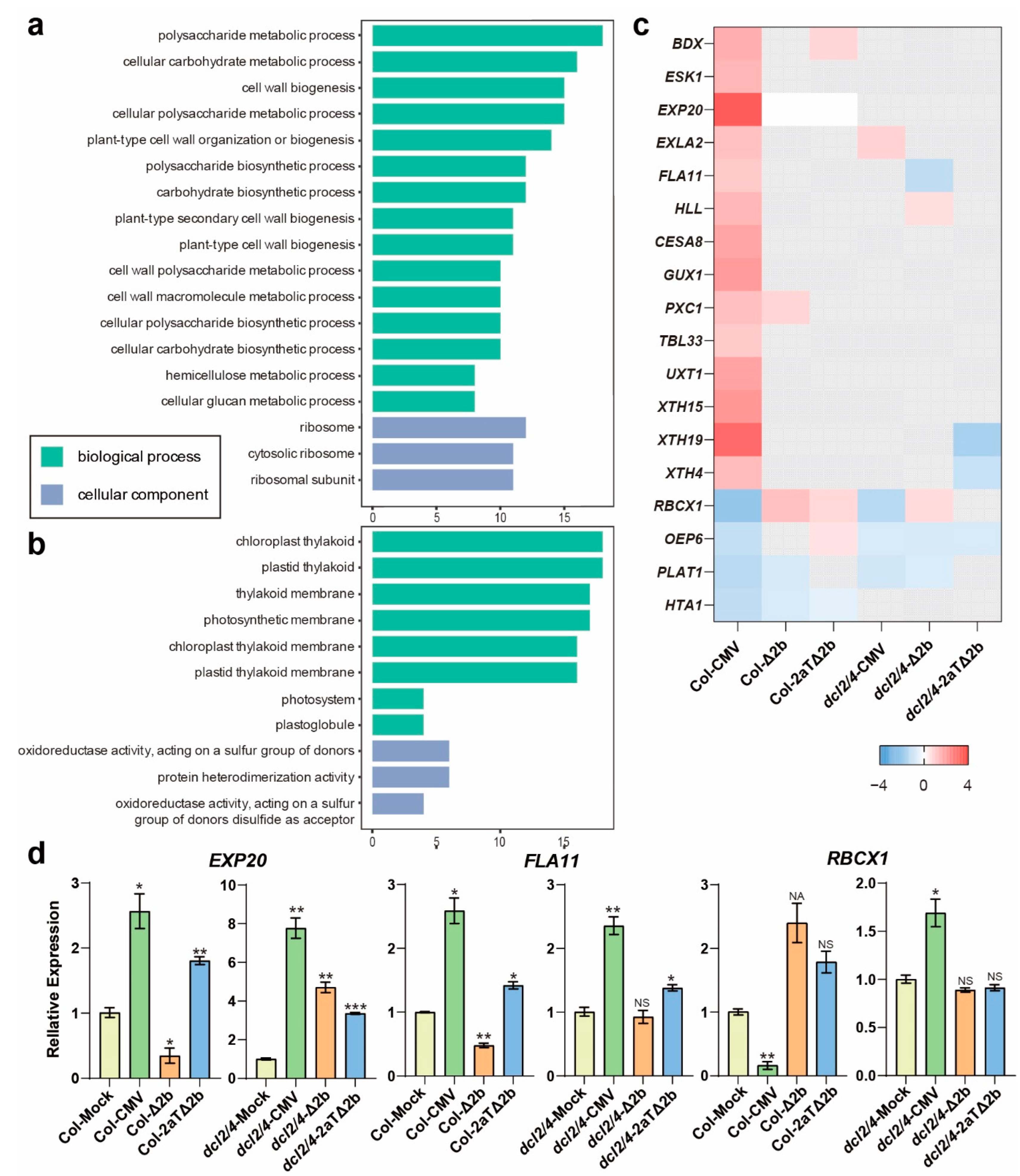
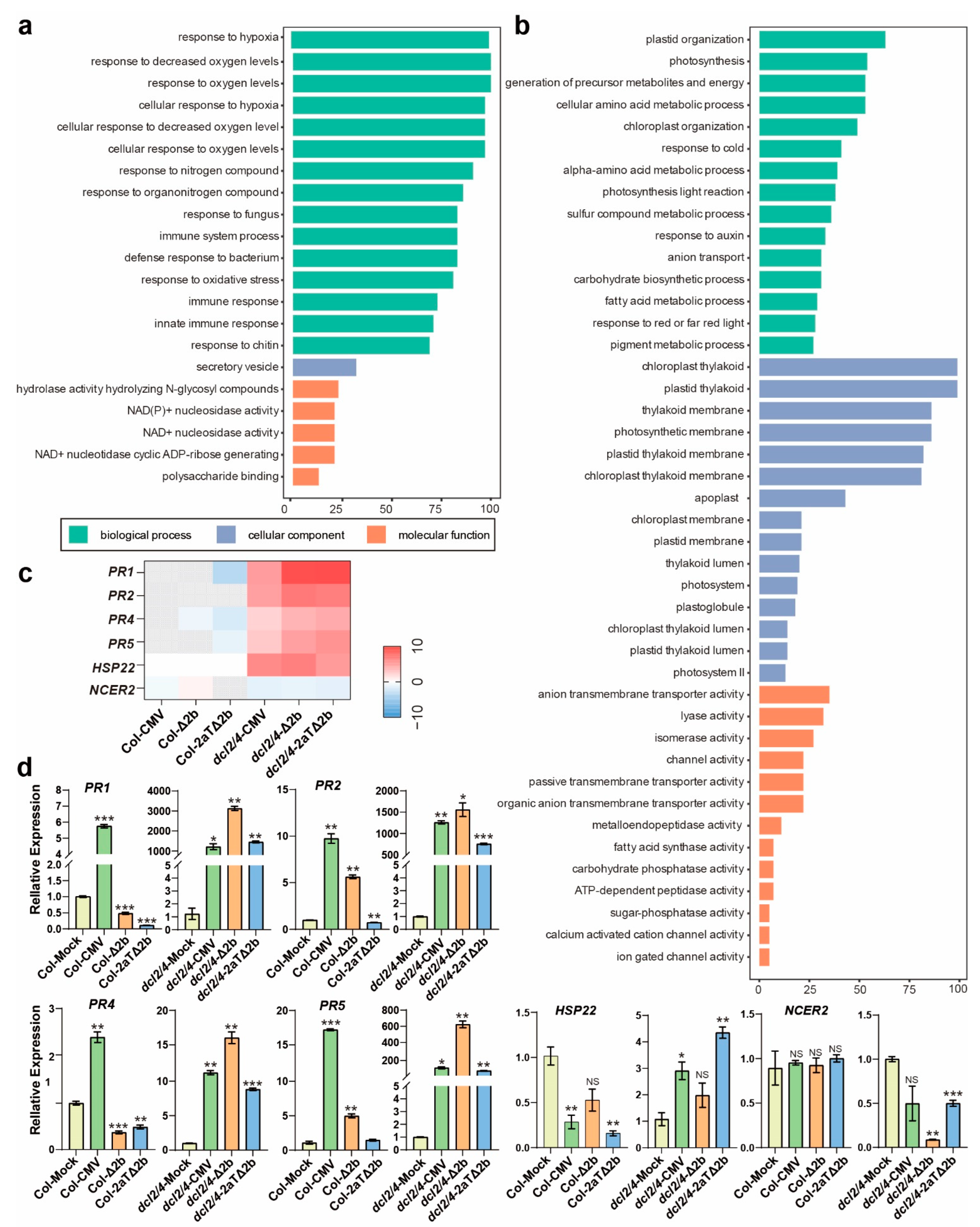
3.4. Disease Symptom of Col-CMV, dcl2/4-CMV, dcl2/4-Δ2b, and dcl2/4-2aTΔ2b Could Be Connected to Resistance Genes and Photosynthesis
3.5. Distinct Pathways Affected in Col-0 Infected by Intact CMV
3.6. Pathways Specifically Modified in Antiviral RNAi-Defecient dcl2/4 Mutant
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savary, S.; Willocquet, L.; Pethybridge, S.J.; Esker, P.; McRoberts, N.; Nelson, A. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholthof, K.B.; Adkins, S.; Czosnek, H.; Palukaitis, P.; Jacquot, E.; Hohn, T.; Hohn, B.; Saunders, K.; Candresse, T.; Ahlquist, P.; et al. Top 10 plant viruses in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 938–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagan, I.; Fraile, A.; Fernandez-Fueyo, E.; Montes, N.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Garcia-Arenal, F. Arabidopsis thaliana as a model for the study of plant-virus co-evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camborde, L.; Planchais, S.; Tournier, V.; Jakubiec, A.; Drugeon, G.; Lacassagne, E.; Pflieger, S.; Chenon, M.; Jupin, I. The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates the accumulation of Turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase during viral infection. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3142–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Pendon, J.A.; Li, F.; Li, W.X.; Ding, S.W. Suppression of antiviral silencing by cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein in Arabidopsis is associated with drastically reduced accumulation of three classes of viral small interfering RNAs. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elena, S.F.; Rodrigo, G. Towards an integrated molecular model of plant-virus interactions. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, D.; Garcia, S.; Voinnet, O. Nonsense-mediated decay serves as a general viral restriction mechanism in plants. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Ruiz, H. Host factors against plant viruses. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1588–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, H.; Takeda, A.; Chapman, E.J.; Sullivan, C.M.; Fahlgren, N.; Brempelis, K.J.; Carrington, J.C. Arabidopsis RNA-dependent RNA polymerases and Dicer-like proteins in antiviral defense and small interfering RNA biogenesis during Turnip Mosaic Virus infection. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhan, B.; Li, W.; Ding, S.W. Lipid flippases promote antiviral silencing and the biogenesis of viral and host siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lellis, A.D.; Kasschau, K.D.; Whitham, S.A.; Carrington, J.C. Loss-of-susceptibility mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana reveal an essential role for eIF(iso)4E during potyvirus infection. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.F.; Zhang, C.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Wu, G.W.; Hou, X.L.; Zhou, X.P.; Wang, A.M. Beclin1 restricts RNA virus infection in plants through suppression and degradation of the viral polymerase. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1268–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, M.; Nishikiori, M.; Tomita, K.; Yoshioka, N.; Kozuka, R.; Naito, S.; Ishikawa, M. The Arabidopsis cucumovirus multiplication 1 and 2 loci encode translation initiation factors 4E and 4G. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6102–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.W. RNA-based antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, S.W. Small RNA-based antimicrobial immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Y. Dissection of RNAi-based antiviral immunity in plants. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 32, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, T.; Rajeswaran, R.; Shivaprasad, P.V.; Beknazariants, D.; Si-Ammour, A.; Park, H.S.; Vazquez, F.; Robertson, D.; Meins, F., Jr.; Hohn, T.; et al. Four plant Dicers mediate viral small RNA biogenesis and DNA virus induced silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 6233–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouche, N.; Lauressergues, D.; Gasciolli, V.; Vaucheret, H. An antagonistic function for Arabidopsis DCL2 in development and a new function for DCL4 in generating viral siRNAs. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3347–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukudome, A.; Fukuhara, T. Plant dicer-like proteins: Double-stranded RNA-cleaving enzymes for small RNA biogenesis. J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Ye, X.; Morris, T.J. Arabidopsis DRB4, AGO1, AGO7, and RDR6 participate in a DCL4-initiated antiviral RNA silencing pathway negatively regulated by DCL1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14732–14737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.B.; Wu, Q.; Ito, T.; Cillo, F.; Li, W.X.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.L.; Ding, S.W. RNAi-mediated viral immunity requires amplification of virus-derived siRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deleris, A.; Gallego-Bartolome, J.; Bao, J.; Kasschau, K.D.; Carrington, J.C.; Voinnet, O. Hierarchical action and inhibition of plant Dicer-like proteins in antiviral defense. Science 2006, 313, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Guo, H.S. Recent advances in understanding plant antiviral RNAi and viral suppressors of RNAi. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 46, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.G.; Fang, Y.Y.; Zhou, B.J.; Zhao, J.H.; Hou, W.N.; Zhu, H.; Ding, S.W.; Guo, H.S. Suppression of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1-mediated slicing, transgene-induced RNA silencing, and DNA methylation by distinct domains of the Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Liu, S.W.; Wang, S.; Duan, C.G.; Guo, H.S. CMV2b-AGO interaction is required for the suppression of RDR-Dependent antiviral silencing in Arabidopsis. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamera, S.; Song, X.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; Fang, R. Cucumber mosaic virus suppressor 2b binds to AGO4-related small RNAs and impairs AGO4 activities. Plant J. 2012, 69, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Yuan, Y.R.; Pei, Y.; Lin, S.S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J.; Chua, N.H. Cucumber mosaic virus-encoded 2b suppressor inhibits Arabidopsis Argonaute1 cleavage activity to counter plant defense. Gene Dev. 2006, 20, 3255–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.-W.; Li, W.-X.; Symons, R. A novel naturally occurring hybrid gene encoded by a plant RNA virus facilitates long distance virus movement. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5762–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Chen, F.F.; Liao, Q.S.; Zhang, H.R.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, J.S. 2b ORFs encoded by subgroup IB strains of cucumber mosaic virus induce differential virulence on Nicotiana species. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soards, A.J.; Murphy, A.M.; Palukaitis, P.; Carr, J.P. Virulence and differential local and systemic spread of Cucumber mosaic virus in tobacco are affected by the CMV 2b protein. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-B.; Jovel, J.; Udomporn, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.-X.; Gasciolli, V.; Vaucheret, H.; Ding, S.-W. The 21-nucleotide, but not 22-nucleotide, viral secondary small interfering rnas direct potent antiviral defense by two cooperative argonautes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xu, G.; Xie, C.; Wu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; et al. Arabidopsis ENOR3 regulates RNAi-mediated antiviral defense. J. Genet. Genom. 2018, 45, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, X.B.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.X.; Gal-On, A.; Ding, S.W. Identification of a new host factor required for antiviral RNAi and amplification of viral siRNAs. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 10–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewsey, M.; Surette, M.; Robertson, F.C.; Ziebell, H.; Choi, S.H.; Ryu, K.H.; Canto, T.; Palukaitis, P.; Payne, T.; Walsh, J.A.; et al. The role of the Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein in viral movement and symptom induction. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, W.N.; Duan, C.G.; Fang, R.X.; Zhou, X.Y.; Guo, H.S. Satellite RNA reduces expression of the 2b suppressor protein resulting in the attenuation of symptoms caused by Cucumber mosaic virus infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Gao, H.; Xu, G.; Wu, D.; Song, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Qi, T.; Xie, D. Arabidopsis ALA1 and ALA2 mediate RNAi-based antiviral immunity. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Ruiz, H.; Carbonell, A.; Hoyer, J.S.; Fahlgren, N.; Gilbert, K.B.; Takeda, A.; Giampetruzzi, A.; Garcia Ruiz, M.T.; McGinn, M.G.; Lowery, N.; et al. Roles and programming of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE proteins during Turnip mosaic virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, J.J.; Lewsey, M.G.; Patel, K.; Westwood, J.; Heimstadt, S.; Carr, J.P.; Baulcombe, D.C. An antiviral defense role of AGO2 in plants. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaubert, M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mello, A.F.; Perry, K.L.; Moffett, P. ARGONAUTE2 mediates RNA-silencing antiviral defenses against Potato virus X in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Singh, J.; Li, D.; Qu, F. Temperature-dependent survival of Turnip crinkle virus-infected arabidopsis plants relies on an RNA silencing-based defense that requires DCL2, AGO2, and HEN1. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6847–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ando, S.; Miyashita, S.; Takahashi, H. Plant defense systems against cucumber mosaic virus: Lessons learned from CMV-Arabidopsis interactions. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ronde, D.; Butterbach, P.; Kormelink, R. Dominant resistance against plant viruses. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandadi, K.K.; Scholthof, K.B. Plant immune responses against viruses: How does a virus cause disease? Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1489–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Zhi, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, E.; Feng, G.; Tang, S.; Guo, W.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Diao, X. Response of Multiple Tissues to Drought Revealed by a Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis in Foxtail Millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 746166. [Google Scholar]
- Kyselakova, H.; Prokopova, J.; Naus, J.; Novak, O.; Navratil, M.; Safarova, D.; Spundova, M.; Ilik, P. Photosynthetic alterations of pea leaves infected systemically by pea enation mosaic virus: A coordinated decrease in efficiencies of CO2 assimilation and photosystem II photochemistry. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Spetz, C.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis in Triticum aestivum infecting wheat dwarf virus reveals the effects of viral infection on phytohormone and photosynthesis metabolism pathways. Phytopathol. Res. 2020, 2, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Yamazaki, R.; Wada, T.; Ohki, S.T. Coat protein mutations in an attenuated Cucumber mosaic virus encoding mutant 2b protein that lacks RNA silencing suppressor activity induces chlorosis with photosynthesis gene repression and chloroplast abnormalities in infected tobacco plants. Virology 2014, 457, 292299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Técsi, L.I.; Maule, A.J.; Smith, A.M.; Leegood, R.C. Complex, localized changes in CO2 assimilation and starch content associated with the susceptible interaction between cucumber mosaic virus and a cucurbit host. Plant J. 1994, 5, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szittya, G.; Silhavy, D.; Molnar, A.; Havelda, Z.; Lovas, A.; Lakatos, L.; Banfalvi, Z.; Burgyan, J. Low temperature inhibits RNA silencing-mediated defence by the control of siRNA generation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Chen, F.; Mannas, J.P.; Feldman, T.; Sumner, L.W.; Roossinck, M.J. Virus infection improves drought tolerance. New Phytol. 2008, 180, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Mao, W.H.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Nogués, S.; Yu, J.Q. Effects of cucumber mosaic virus infection on electron transport and antioxidant system in chloroplasts and mitochondria of cucumber and tomato leaves. Physiol. Plant 2009, 135, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreti, E.; Betti, F.; Ladera-Carmona, M.J.; Fontana, F.; Novi, G.; Valeri, M.C.; Perata, P. ARGONAUTE1 and ARGONAUTE4 regulate gene expression and hypoxia tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Licausi, F.; Weits, D.A.; Pant, B.D.; Scheible, W.R.; Geigenberger, P.; van Dongen, J.T. Hypoxia responsive gene expression is mediated by various subsets of transcription factors and miRNAs that are determined by the actual oxygen availability. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moldovan, D.; Spriggs, A.; Yang, J.; Pogson, B.J.; Dennis, E.S.; Wilson, I.W. Hypoxia-responsive microRNAs and trans-acting small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, L.H.; Liu, Z.J.; Zou, X.L.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Qiu, F.Z.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of microRNA responding to long-term waterlogging in crown roots of maize seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 147, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varallyay, E.; Valoczi, A.; Agyi, A.; Burgyan, J.; Havelda, Z. Plant virus-mediated induction of miR168 is associated with repression of ARGONAUTE1 accumulation. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3507–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewsey, M.G.; Murphy, A.M.; Maclean, D.; Dalchau, N.; Westwood, J.H.; Macaulay, K.; Bennett, M.H.; Moulin, M.; Hanke, D.E.; Powell, G.; et al. Disruption of two defensive signaling pathways by a viral RNA silencing suppressor. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ando, S.; Jaskiewicz, M.; Mochizuki, S.; Koseki, S.; Miyashita, S.; Takahashi, H.; Conrath, U. Priming for enhanced ARGONAUTE2 activation accompanies induced resistance to cucumber mosaic virus in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.E. Salicylic acid in the machinery of hypersensitive cell death and disease resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.T.; Gobbato, E.; Kracher, B.; Qiu, J.D.; Bautor, J.; Parker, J.E. A core function of EDS1 with PAD4 is to protect the salicylic acid defense sector in Arabidopsis immunity. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1802–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Locci, F.; Wanke, F.; Zhang, L.; Saile, S.C.; Joe, A.; Karelina, D.; Hua, C.; Frohlich, K.; Wan, W.L.; et al. The EDS1-PAD4-ADR1 node mediates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Nature 2021, 598, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.J.; Chini, A.; Basu, D.; Loake, G.J. Targeted activation tagging of the Arabidopsis NBS-LRR gene, ADR1, conveys resistance to virulent pathogens. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Ding, P.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y.T.; He, J.; Gao, M.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Control of salicylic acid synthesis and systemic acquired resistance by two members of a plant-specific family of transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18220–18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; MacMillan, C.P.; de Vries, L.; Mansfield, S.D.; Hao, P.; Ratcliffe, J.; Bacic, A.; Johnson, K.L. FLA11 and FLA12 glycoproteins fine-tune stem secondary wall properties in response to mechanical stresses. New Phytol 2022, 233, 1750–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, C.; Zhao, L.; Qin, G.; Peng, L.; Zheng, Q.; Nie, W.; Song, C.; Shi, H.; et al. SWO1 modulates cell wall integrity under salt stress by interacting with importin α in Arabidopsis. Stress Biol. 2021, 1, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otulak-Koziel, K.; Koziel, E.; Lockhart, B.E.L. Plant cell wall dynamics in compatible and incompatible potato response to infection caused by Potato Virus Y (PVYNTN). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zribi, I.; Ghorbel, M.; Brini, F. Pathogenesis Related Proteins (PRs): From Cellular Mechanisms to Plant Defense. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2021, 22, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamouch, N.; Li, C.; Seo, P.J.; Park, C.M.; Davis, E.L. Expression of Arabidopsis pathogenesis-related genes during nematode infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, O.K.; Shchennikova, A.V.; Kochieva, E.Z.; Filyushin, M.A. Pathogenesis-Related Genes of PR1, PR2, PR4, and PR5 Families Are Involved in the Response to Fusarium Infection in Garlic (Allium sativum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Ganai, B.A.; Kamili, A.N.; Bhat, A.A.; Mir, Z.A.; Bhat, J.A.; Tyagi, A.; Islam, S.T.; Mushtaq, M.; Yadav, P.; et al. Pathogenesis-related proteins and peptides as promising tools for engineering plants with multiple stress tolerance. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 212–213, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, A.; Gömann, J.; König, S.; Herrfurth, C.; Liu, Y.T.; Meldau, D.; Feussner, I. Disruption of Arabidopsis neutral ceramidases 1 and 2 results in specific sphingolipid imbalances triggering different phytohormone-dependent plant cell death programmes. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Nemoto, K.; Shimizu, M.; Abe, A.; Asai, S.; Ishihama, N.; Matsuoka, S.; Daimon, T.; Ojika, M.; Kawakita, K.; et al. Recognition of pathogen-derived sphingolipids in Arabidopsis. Science 2022, 376, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Shen, L.; Jin, L.; Wang, M.; Chang, F.; Guo, Z. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of CMV or 2b-Deficient CMV-Infected dcl2dcl4 Reveals the Effects of Viral Infection on Symptom Induction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Viruses 2022, 14, 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071582
Xu Q, Shen L, Jin L, Wang M, Chang F, Guo Z. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of CMV or 2b-Deficient CMV-Infected dcl2dcl4 Reveals the Effects of Viral Infection on Symptom Induction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Viruses. 2022; 14(7):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071582
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qian, Li Shen, Liying Jin, Meng Wang, Fenghan Chang, and Zhongxin Guo. 2022. "Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of CMV or 2b-Deficient CMV-Infected dcl2dcl4 Reveals the Effects of Viral Infection on Symptom Induction in Arabidopsis thaliana" Viruses 14, no. 7: 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071582
APA StyleXu, Q., Shen, L., Jin, L., Wang, M., Chang, F., & Guo, Z. (2022). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of CMV or 2b-Deficient CMV-Infected dcl2dcl4 Reveals the Effects of Viral Infection on Symptom Induction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Viruses, 14(7), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071582





