Natural Immunity against HIV-1: Progression of Understanding after Association Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Natural Immunity to HIV
3. Human Leukocyte Antigens and the Differential Susceptibility to HIV Infection
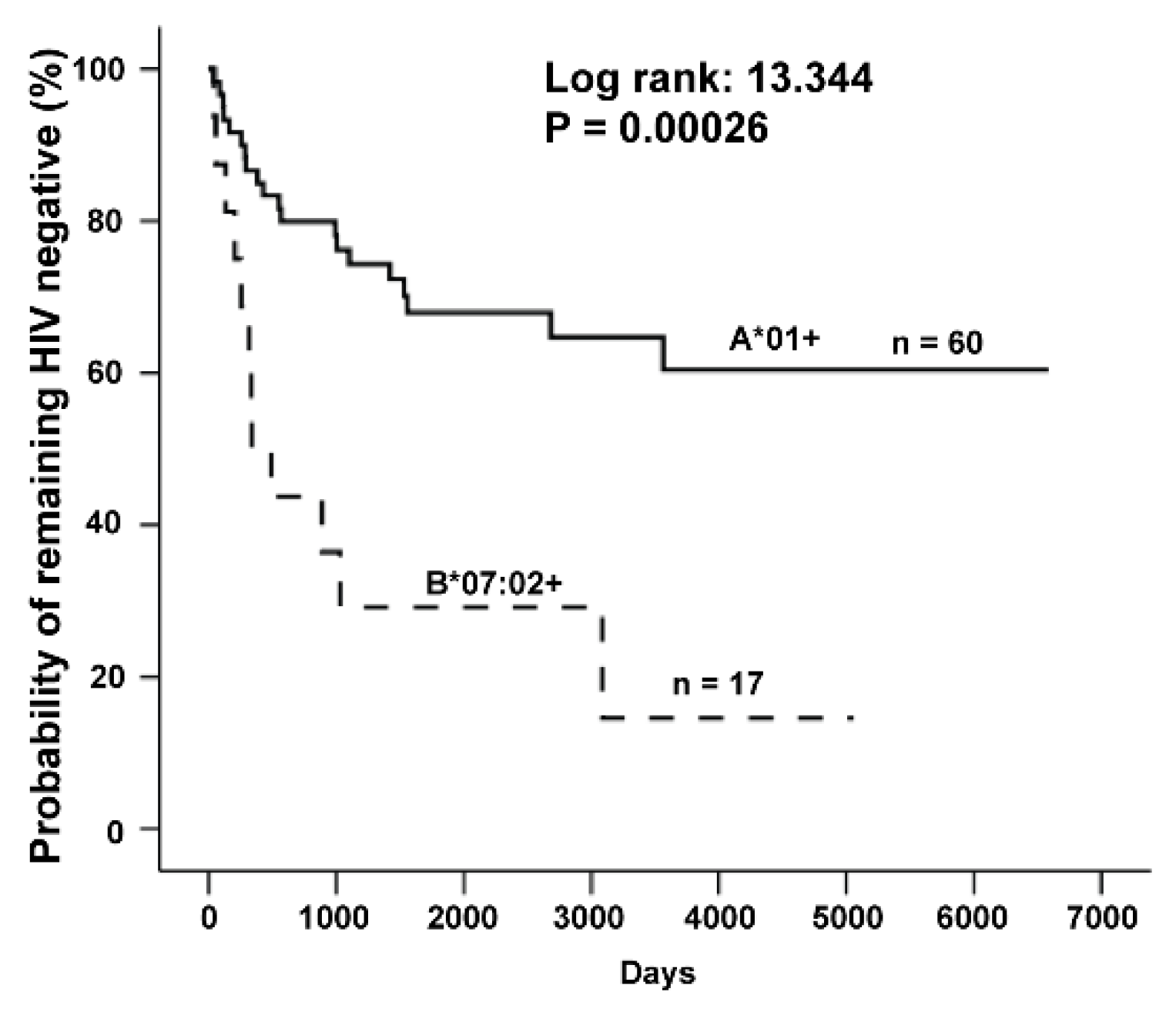
3.1. Identification of HLA Class I Alleles Associated with Resistance/Susceptibility to HIV Infection
3.2. Analysis of CD8 T Cell Epitopes of A*01:01 and B*07:02
3.3. From HLA Epitope Analysis to Novel HIV Vaccine Development and Testing
3.4. The T Cell Responses Generated by Immunization with the PCS Vaccine Correlated with Vaccine Efficacy
4. Role of FREM1 and Its Isoform TILRR in HIV-1 Acquisition
4.1. A Low-Resolution Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Analysis Identified a FREM1 SNP rs1552896
4.2. The Potential Role of FREM1 in HIV Infection
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A Timeline of HIV and AIDS. 2021. Available online: https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/history/hiv-and-aids-timeline (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Gallo, R.C.; Sarin, P.S.; Gelmann, E.P.; Robert-Guroff, M.; Richardson, E.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Mann, D.; Sidhu, G.D.; Stahl, R.E.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; et al. Isolation of human T-cell leukemia virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 1983, 220, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barre-Sinoussi, F.; Chermann, J.C.; Rey, F.; Nugeyre, M.T.; Chamaret, S.; Gruest, J.; Dauguet, C.; Axler-Blin, C.; Vezinet-Brun, F.; Rouzioux, C.; et al. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 1983, 220, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, R. Researchers halt HIV vaccine trial—What’s the next step? AIDS Alert 2008, 23, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, S.P.; Mehrotra, D.V.; Duerr, A.; Fitzgerald, D.W.; Mogg, R.; Li, D.; Gilbert, P.B.; Lama, J.R.; Marmor, M.; Del Rio, C.; et al. Efficacy assessment of a cell-mediated immunity HIV-1 vaccine (the Step Study): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, test-of-concept trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HIV vaccine failure prompts Merck to halt trial. Nature 2007, 449, 390. [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.E.; Bekker, L.G.; Laher, F.; Malahleha, M.; Allen, M.; Moodie, Z.; Grunenberg, N.; Huang, Y.; Grove, D.; Prigmore, B.; et al. Vaccine Efficacy of ALVAC-HIV and Bivalent Subtype C gp120-MF59 in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J&J to Discontinue Phase IIb HIV Vaccine Trial in Sub-Saharan Africa. News. 2021. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/jj-discontinue-hiv-vaccine-trial/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Haynes, B.F. SARS-CoV-2 and HIV-1—A tale of two vaccines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, B.O.; Chang, D.; Vasan, S.; Ake, J.; Modjarrad, K. HIV and SARS-CoV-2: Tracing a Path of Vaccine Research and Development. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2022, 19, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Vasan, S.; Kim, J.H.; Ake, J.A. Current approaches to HIV vaccine development: A narrative review. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2021, 24 (Suppl. S7), e25793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolla-Pazner, S.; Michael, N.L.; Kim, J.H. A tale of four studies: HIV vaccine immunogenicity and efficacy in clinical trials. Lancet HIV 2021, 8, e449–e452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng’uni, T.; Chasara, C.; Ndhlovu, Z.M. Major Scientific Hurdles in HIV Vaccine Development: Historical Perspective and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.V. The immunogenetics of human infectious diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgner, D.; Jamieson, S.E.; Blackwell, J.M. Genetic susceptibility to infectious diseases: Big is beautiful, but will bigger be even better? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgner, D.; Levin, M. Genetic susceptibility to infectious diseases. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, R.; Zhou, Y.; Elleder, D.; Diamond, T.L.; Bonamy, G.M.; Irelan, J.T.; Chiang, C.Y.; Tu, B.P.; De Jesus, P.D.; Lilley, C.E.; et al. Global analysis of host-pathogen interactions that regulate early-stage HIV-1 replication. Cell 2008, 135, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, A.; Pirofski, L. Host-pathogen interactions: The attributes of virulence. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall, A.; Pirofski, L.A. Host-pathogen interactions: Redefining the basic concepts of virulence and pathogenicity. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3703–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, J.E.; Cossart, P. Host-pathogen interactions: A diversity of themes, a variety of molecular machines. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiss, J.K.; Koech, D.; Plummer, F.A.; Holmes, K.K.; Lightfoote, M.; Piot, P.; Ronald, A.R.; Ndinya-Achola, J.O.; D’Costa, L.J.; Roberts, P.; et al. AIDS virus infection in Nairobi prostitutes. Spread of the epidemic to East Africa. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piot, P.; Kreiss, J.K.; Ndinya-Achola, J.O.; Ngugi, E.N.; Simonsen, J.N.; Cameron, D.W.; Taelman, H.; Plummer, F.A. Heterosexual transmission of HIV. AIDS 1987, 1, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen, J.N.; Plummer, F.A.; Ngugi, E.N.; Black, C.; Kreiss, J.K.; Gakinya, M.N.; Waiyaki, P.; D’Costa, L.J.; Ndinya-Achola, J.O.; Piot, P.; et al. HIV infection among lower socioeconomic strata prostitutes in Nairobi. AIDS 1990, 4, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, F.A.; D’Costa, L.J.; Nsanze, H.; Dylewski, J.; Karasira, P.; Ronald, A.R. Epidemiology of chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi in Nairobi, Kenya. Lancet 1983, 2, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowke, K.R.; Nagelkerke, N.J.; Kimani, J.; Simonsen, J.N.; Anzala, A.O.; Bwayo, J.J.; MacDonald, K.S.; Ngugi, E.N.; Plummer, F.A. Resistance to HIV-1 infection among persistently seronegative prostitutes in Nairobi, Kenya. Lancet 1996, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowke, K.R.; Kaul, R.; Rosenthal, K.L.; Oyugi, J.; Kimani, J.; Rutherford, W.J.; Nagelkerke, N.J.; Ball, T.B.; Bwayo, J.J.; Simonsen, J.N.; et al. HIV-1-specific cellular immune responses among HIV-1-resistant sex workers. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimonti, J.B.; Kimani, J.; Matu, L.; Wachihi, C.; Kaul, R.; Plummer, F.A.; Fowke, K.R. Characterization of CD8 T-cell responses in HIV-1-exposed seronegative commercial sex workers from Nairobi, Kenya. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2006, 84, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimonti, J.B.; Koesters, S.A.; Kimani, J.; Matu, L.; Wachihi, C.; Plummer, F.A.; Fowke, K.R. CD4+ T cell responses in HIV-exposed seronegative women are qualitatively distinct from those in HIV-infected women. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 20–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.M.; Ball, T.B.; Kimani, J.; Kiama, P.; Thottingal, P.; Embree, J.E.; Fowke, K.R.; Plummer, F.A. Elevated T cell counts and RANTES expression in the genital mucosa of HIV-1-resistant Kenyan commercial sex workers. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.M.; Ball, T.B.; Levinson, P.; Maranan, L.; Jaoko, W.; Wachihi, C.; Pak, B.J.; Podust, V.N.; Broliden, K.; Hirbod, T.; et al. Elevated elafin/trappin-2 in the female genital tract is associated with protection against HIV acquisition. AIDS 2009, 23, 1669–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Dong, T.; Fowke, K.R.; Kimani, J.; Krausa, P.; Newell, H.; Blanchard, T.; Ariyoshi, K.; Oyugi, J.; Ngugi, E.; et al. Cytotoxic T cell responses to multiple conserved HIV epitopes in HIV-resistant prostitutes in Nairobi. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, F.A.; Ball, T.B.; Kimani, J.; Fowke, K.R. Resistance to HIV-1 infection among highly exposed sex workers in Nairobi: What mediates protection and why does it develop? Immunol. Lett. 1999, 66, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devito, C.; Broliden, K.; Kaul, R.; Svensson, L.; Johansen, K.; Kiama, P.; Kimani, J.; Lopalco, L.; Piconi, S.; Bwayo, J.J.; et al. Mucosal and plasma IgA from HIV-1-exposed uninfected individuals inhibit HIV-1 transcytosis across human epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5170–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, R.; Plummer, F.A.; Kimani, J.; Dong, T.; Kiama, P.; Rostron, T.; Njagi, E.; MacDonald, K.S.; Bwayo, J.J.; McMichael, A.J.; et al. HIV-1-specific mucosal CD8+ lymphocyte responses in the cervix of HIV-1-resistant prostitutes in Nairobi. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Pinheiro, S.; Kaul, R.; Hansasuta, P.; Gillespie, G.; Dong, T.; Plummer, F.A.; Bwayo, J.B.; Fidler, S.; Weber, J.; et al. How important is the ‘quality’ of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response in protection against HIV infection? Immunol. Lett. 2001, 79, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, R.; Rutherford, J.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Kimani, J.; Onyango, J.I.; Fowke, K.; MacDonald, K.; Bwayo, J.J.; McMichael, A.J.; Plummer, F.A. HIV-1 Env-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in exposed, uninfected Kenyan sex workers: A prospective analysis. AIDS 2004, 18, 2087–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, T.B.; Ji, H.; Kimani, J.; McLaren, P.; Marlin, C.; Hill, A.V.; Plummer, F.A. Polymorphisms in IRF-1 associated with resistance to HIV-1 infection in highly exposed uninfected Kenyan sex workers. AIDS 2007, 21, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgener, A.; Boutilier, J.; Wachihi, C.; Kimani, J.; Carpenter, M.; Westmacott, G.; Cheng, K.; Ball, T.B.; Plummer, F. Identification of differentially expressed proteins in the cervical mucosa of HIV-1-resistant sex workers. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4446–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.A.; Knight, E.; Bruneau, B.; Semeniuk, C.; Gill, K.; Nagelkerke, N.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Ngugi, E.; Luo, M.; et al. A common human leucocyte antigen-DP genotype is associated with resistance to HIV-1 infection in Kenyan sex workers. AIDS 2008, 22, 2038–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.A.; Luo, M.; Bruneau, B.; Knight, E.; Nagelkerke, N.J.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Ngugi, E.N.; Plummer, F.A. Human leukocyte antigen-DQ alleles and haplotypes and their associations with resistance and susceptibility to HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2008, 22, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacap, P.A.; Huntington, J.D.; Luo, M.; Nagelkerke, N.J.; Bielawny, T.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Ngugi, E.N.; Plummer, F.A. Associations of human leukocyte antigen DRB with resistance or susceptibility to HIV-1 infection in the Pumwani Sex Worker Cohort. AIDS 2008, 22, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, C.M.; McLaren, P.J.; Wachihi, C.; Kimani, J.; Plummer, F.A.; Fowke, K.R. Decreased immune activation in resistance to HIV-1 infection is associated with an elevated frequency of CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Zhang, N.; Routy, J.P.; Tremblay, C.; Thomas, R.; Szabo, J.; Cote, P.; Trottier, B.; LeBlanc, R.; Rouleau, D.; et al. Quantifying Anti-HIV Envelope-Specific Antibodies in Plasma from HIV Infected Individuals. Viruses 2019, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.C.; Sivro, A.; Kimani, J.; Jaoko, W.; Plummer, F.A.; Ball, T.B. Epigenetic control of IRF1 responses in HIV-exposed seronegative versus HIV-susceptible individuals. Blood 2011, 117, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Daniuk, C.A.; Diallo, T.O.; Capina, R.E.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Kimani, M.; Bielawny, T.; Peterson, T.; Mendoza, M.G.; et al. For protection from HIV-1 infection, more might not be better: A systematic analysis of HIV Gag epitopes of two alleles associated with different outcomes of HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1166–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Sainsbury, J.; Tuff, J.; Lacap, P.A.; Yuan, X.Y.; Hirbod, T.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Ramdahin, S.; Bielawny, T.; et al. A genetic polymorphism of FREM1 is associated with resistance against HIV infection in the Pumwani sex worker cohort. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11899–11905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songok, E.M.; Luo, M.; Liang, B.; McLaren, P.; Kaefer, N.; Apidi, W.; Boucher, G.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Sekaly, R.; et al. Microarray analysis of HIV resistant female sex workers reveal a gene expression signature pattern reminiscent of a lowered immune activation state. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songok, E.M.; Osero, B.; McKinnon, L.; Rono, M.K.; Apidi, W.; Matey, E.J.; Meyers, A.F.; Luo, M.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; et al. CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26/DPPIV) is highly expressed in peripheral blood of HIV-1 exposed uninfected female sex workers. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.; Barker, D.J.; Georgiou, X.; Cooper, M.A.; Flicek, P.; Marsh, S.G.E. IPD-IMGT/HLA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D948–D955. [Google Scholar]
- Prugnolle, F.; Manica, A.; Charpentier, M.; Guegan, J.F.; Guernier, V.; Balloux, F. Pathogen-driven selection and worldwide HLA class I diversity. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Mazas, A.; Cerny, V.; Di, D.; Buhler, S.; Podgorna, E.; Chevallier, E.; Brunet, L.; Weber, S.; Kervaire, B.; Testi, M.; et al. The HLA-B landscape of Africa: Signatures of pathogen-driven selection and molecular identification of candidate alleles to malaria protection. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6238–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, M.; Nelson, G.W.; Martin, M.P.; Kissner, T.; Vlahov, D.; Goedert, J.J.; Kaslow, R.; Buchbinder, S.; Hoots, K.; O’Brien, S.J. HLA and HIV-1: Heterozygote advantage and B*35-Cw*04 disadvantage. Science 1999, 283, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Tang, J.; Rivers, C.; Karita, E.; Meizen-Derr, J.; Allen, S.; Kaslow, R.A. HLA-B*5703 independently associated with slower HIV-1 disease progression in Rwandan women. AIDS 1999, 13, 1990–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulpa, D.A.; Collins, K.L. The emerging role of HLA-C in HIV-1 infection. Immunology 2011, 134, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, A.; Matthews, P.C.; Listgarten, J.; Carlson, J.M.; Kadie, C.; Ndung’u, T.; Brander, C.; Coovadia, H.; Walker, B.D.; Heckerman, D.; et al. Additive contribution of HLA class I alleles in the immune control of HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9879–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, P.C.; Adland, E.; Listgarten, J.; Leslie, A.; Mkhwanazi, N.; Carlson, J.M.; Harndahl, M.; Stryhn, A.; Payne, R.P.; Ogwu, A.; et al. HLA-A*7401-mediated control of HIV viremia is independent of its linkage disequilibrium with HLA-B*5703. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5675–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migueles, S.A.; Sabbaghian, M.S.; Shupert, W.L.; Bettinotti, M.P.; Marincola, F.M.; Martino, L.; Hallahan, C.W.; Selig, S.M.; Schwartz, D.; Sullivan, J.; et al. HLA B*5701 is highly associated with restriction of virus replication in a subgroup of HIV-infected long term nonprogressors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2709–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, P.; Marinic, K.; Sorrentino, A.; Lopez, R.; Iliovich, E.; Habegger de Sorrentino, A. Association of HLA-DQ and HLA-DR alleles with susceptibility or resistance to HIV-1 infection among the population of Chaco Province, Argentina. Medicina 2002, 62, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Peixinho, Z.F.; Mendes, N.F. HLA antigens and resistance to HIV. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1994, 8, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, F.; Jia, X.; McLaren, P.J.; Telenti, A.; de Bakker, P.I.; Walker, B.D.; Ripke, S.; Brumme, C.J.; Pulit, S.L.; Carrington, M.; et al. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 2010, 330, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Polycarpou, A.; Ntais, C.; Korber, B.T.; Elrich, H.A.; Winchester, R.; Krogstad, P.; Wolinsky, S.; Rostron, T.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Ammann, A.J.; et al. Association between maternal and infant class I and II HLA alleles and of their concordance with the risk of perinatal HIV type 1 transmission. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2002, 18, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohowsky-Kochan, C.; Skurnick, J.; Molinaro, D.; Louria, D. HLA antigens associated with susceptibility/resistance to HIV-1 infection. Hum. Immunol. 1998, 59, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, R.; Peters, H.O.; Mendoza, L.; Bielawny, T.; Ngugi, E.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. Influence of HLA class I haplotypes on HIV-1 seroconversion and disease progression in Pumwani sex worker cohort. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, C.M.; Ludlam, C.A.; Beatson, D.; Peutherer, J.F.; Cuthbert, R.J.; Simmonds, P.; Morrison, H.; Jones, M. HLA haplotype A1 B8 DR3 as a risk factor for HIV-related disease. Lancet 1988, 1, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtenberg, E.; Korber, B.; Sollars, C.; Kepler, T.B.; Hraber, P.T.; Hayes, E.; Funkhouser, R.; Fugate, M.; Theiler, J.; Hsu, Y.S.; et al. Advantage of rare HLA supertype in HIV disease progression. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, R.; Dong, T.; Plummer, F.A.; Kimani, J.; Rostron, T.; Kiama, P.; Njagi, E.; Irungu, E.; Farah, B.; Oyugi, J.; et al. CD8(+) lymphocytes respond to different HIV epitopes in seronegative and infected subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.A.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Bielawny, T.; Mendoza, L.; Thavaneswaran, S.; Narayansingh, M.J.; Kariri, T.; Liang, B.; Ball, T.B.; et al. HLA class I associations with rates of HIV-1 seroconversion and disease progression in the Pumwani Sex Worker Cohort. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, W.J.; Kimani, J.; Bielawny, T.; Wachihi, C.; Ball, T.B.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. Associations of human leukocyte antigen-G with resistance and susceptibility to HIV-1 infection in the Pumwani sex worker cohort. Aids 2013, 27, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachinsky, M.M.; Guillen, D.E.; Patel, S.R.; Singleton, J.; Chen, C.; Soltis, D.A.; Tussey, L.G. Mapping and binding analysis of peptides derived from the tumor-associated antigen survivin for eight HLA alleles. Cancer Immun. 2005, 5, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wulf, M.; Hoehn, P.; Trinder, P. Identification of human MHC class I binding peptides using the iTOPIA-epitope discovery system. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 524, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Keele, B.F.; Giorgi, E.E.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Decker, J.M.; Pham, K.T.; Salazar, M.G.; Sun, C.; Grayson, T.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; et al. Identification and characterization of transmitted and early founder virus envelopes in primary HIV-1 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bar, K.J.; Wang, S.; Decker, J.M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, C.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Salazar, M.G.; Learn, G.H.; Morgan, C.J.; et al. High Multiplicity Infection by HIV-1 in Men Who Have Sex with Men. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Capina, R.; Daniuk, C.; Tuff, J.; Peters, H.; Kimani, M.; Wachihi, C.; Kimani, J.; Ball, T.B.; Plummer, F.A. Immunogenicity of sequences around HIV-1 protease cleavage sites: Potential targets and population coverage analysis for a HIV vaccine targeting protease cleavage sites. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, N.M.; Lever, A.M. HIV Gag polyprotein: Processing and early viral particle assembly. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, B.; Anders, M.; Akiyama, H.; Welsch, S.; Glass, B.; Nikovics, K.; Clavel, F.; Tervo, H.M.; Keppler, O.T.; Krausslich, H.G. HIV-1 Gag processing intermediates trans-dominantly interfere with HIV-1 infectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29692–29703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, S.C.; Clemente, J.C.; Jeung, J.A.; Dunn, B.M.; Kaplan, A.H. Ordered processing of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 GagPol precursor is influenced by the context of the embedded viral protease. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10601–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, S.C.; Everitt, L.E.; Choudhury, S.; Dunn, B.M.; Kaplan, A.H. Initial cleavage of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 GagPol precursor by its activated protease occurs by an intramolecular mechanism. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8477–8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, S.C.; Henderson, G.J.; Schiffer, C.A.; Swanstrom, R. Replacement of the P1 amino acid of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag processing sites can inhibit or enhance the rate of cleavage by the viral protease. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10226–10233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, S.C.; Lindquist, J.N.; Kaplan, A.H.; Swanstrom, R. Processing sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Gag-Pro-Pol precursor are cleaved by the viral protease at different rates. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, S.C.; Moody, M.D.; Wehbie, R.S.; Kaplan, A.H.; Nantermet, P.V.; Klein, C.A.; Swanstrom, R. The p2 domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag regulates sequential proteolytic processing and is required to produce fully infectious virions. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 8017–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Omange, R.W.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. A novel HIV vaccine targeting the protease cleavage sites. AIDS Res. Ther. 2017, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S.; Marovich, M.A.; Dieffenbach, C.W.; Hunter, E.; Buchbinder, S.P. Immunology. Immune activation with HIV vaccines. Science 2014, 344, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.; Liang, B.; Luo, M. Assessment of the population coverage of an HIV-1 vaccine targeting sequences surrounding the viral protease cleavage sites in Gag, Pol, or all 12 protease cleavage sites. Vaccine 2021, 39, 2676–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Omange, R.W.; Liang, B.; Toledo, N.; Hai, Y.; Liu, L.R.; Schalk, D.; Crecente-Campo, J.; Dacoba, T.G.; Lambe, A.B.; et al. Vaccine targeting SIVmac251 protease cleavage sites protects macaques against vaginal infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6429–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Omange, R.W.; Hai, Y.; Luo, M. Current advances in HIV vaccine preclinical studies using Macaque models. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3388–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauvin, A.J.; Peters, C.; Brennan, F. Advantages and Limitations of Commonly Used Nonhuman Primate Species in Research and Development of Biopharmaceuticals. In The Nonhuman Primate in Nonclinical Drug Development and Safety Assessment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 379–395. [Google Scholar]
- Rohl, M.; Tjernlund, A.; Lajoie, J.; Edfeldt, G.; Bradley, F.; Bergstrom, S.; Kaldhusdal, V.; Ahlberg, A.; Manberg, A.; Omollo, K.; et al. HIV-Exposed Seronegative Sex Workers Express Low T-Cell Activation and an Intact Ectocervical Tissue Microenvironment. Vaccines 2021, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amundadottir, L.T.; Sulem, P.; Gudmundsson, J.; Helgason, A.; Baker, A.; Agnarsson, B.A.; Sigurdsson, A.; Benediktsdottir, K.R.; Cazier, J.B.; Sainz, J.; et al. A common variant associated with prostate cancer in European and African populations. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Hansoul, S.; Nicolae, D.L.; Cho, J.H.; Duerr, R.H.; Rioux, J.D.; Brant, S.R.; Silverberg, M.S.; Taylor, K.D.; Barmada, M.M.; et al. Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, A.; Gerry, N.P.; McQueen, M.B.; Heid, I.M.; Pfeufer, A.; Illig, T.; Wichmann, H.E.; Meitinger, T.; Hunter, D.; Hu, F.B.; et al. A common genetic variant is associated with adult and childhood obesity. Science 2006, 312, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazami, A.M.; Shaheen, R.; Alzahrani, F.; Snape, K.; Saggar, A.; Brinkmann, B.; Bavi, P.; Al-Gazali, L.I.; Alkuraya, F.S. FREM1 mutations cause bifid nose, renal agenesis, and anorectal malformations syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, I.; Du, X.; Taylor, M.S.; Justice, M.J.; Beutler, B.; Jackson, I.J. The extracellular matrix gene Frem1 is essential for the normal adhesion of the embryonic epidermis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13560–13565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyozumi, D.; Sugimoto, N.; Nakano, I.; Sekiguchi, K. Frem3, a member of the 12 CSPG repeats-containing extracellular matrix protein family, is a basement membrane protein with tissue distribution patterns distinct from those of Fras1, Frem2, and QBRICK/Frem1. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, P.; Chiotaki, R.; Dalezios, Y.; Chalepakis, G. Overlapping and divergent localization of Frem1 and Fras1 and its functional implications during mouse embryonic development. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, P.; Pavlakis, E.; Dalezios, Y.; Chalepakis, G. Basement membrane localization of Frem3 is independent of the Fras1/Frem1/Frem2 protein complex within the sublamina densa. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavotinek, A.M.; Baranzini, S.E.; Schanze, D.; Labelle-Dumais, C.; Short, K.M.; Chao, R.; Yahyavi, M.; Bijlsma, E.K.; Chu, C.; Musone, S.; et al. Manitoba-oculo-tricho-anal (MOTA) syndrome is caused by mutations in FREM1. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shephard, F.; Kim, H.B.; Palmer, I.R.; McHarg, S.; Fowler, G.J.; O’Neill, L.A.; Kiss-Toth, E.; Qwarnstrom, E.E. TILRR, a novel IL-1RI co-receptor, potentiates MyD88 recruitment to control Ras-dependent amplification of NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7222–7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashem, M.A.; Li, H.; Liu, L.R.; Liang, B.; Omange, R.W.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. The Potential Role of FREM1 and Its Isoform TILRR in HIV-1 Acquisition through Mediating Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashem, M.A.; Li, H.; Toledo, N.P.; Omange, R.W.; Liang, B.; Liu, L.R.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Yuan, X.Y.; Kindrachuk, J.; et al. Toll-like Interleukin 1 Receptor Regulator Is an Important Modulator of Inflammation Responsive Genes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashem, M.A.; Ren, X.; Li, H.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Lin, F.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. TILRR Promotes Migration of Immune Cells Through Induction of Soluble Inflammatory Mediators. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashem, M.A.; Yuan, X.Y.; Li, L.; Kimani, J.; Plummer, F.; Luo, M. TILRR (Toll-like Interleukin-1 Receptor Regulator), an Important Modulator of Inflammatory Responsive Genes, is Circulating in the Blood. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 4927–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashem, M.A.; Lischynski, J.; Stojak, B.; Li, L.; Yuan, X.Y.; Liang, B.; Kimani, J.; Plummer, F.A.; Luo, M. High level of plasma TILRR protein is associated with faster HIV seroconversion. EBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Y.; Liu, L.R.; Krawchenko, A.; Sainsbury, J.; Zhao, L.; Plummer, F.; Yang, X.; Luo, M. Development of monoclonal antibodies to interrogate functional domains and isoforms of FREM1 protein. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2014, 33, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M. Natural Immunity against HIV-1: Progression of Understanding after Association Studies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061243
Luo M. Natural Immunity against HIV-1: Progression of Understanding after Association Studies. Viruses. 2022; 14(6):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Ma. 2022. "Natural Immunity against HIV-1: Progression of Understanding after Association Studies" Viruses 14, no. 6: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061243
APA StyleLuo, M. (2022). Natural Immunity against HIV-1: Progression of Understanding after Association Studies. Viruses, 14(6), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061243




