Structure-Based Discovery of N-Sulfonylpiperidine-3-Carboxamides as Novel Capsid Assembly Modulators for Potent Inhibition of HBV Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Infection of HepG2-NTCP with HBV Particles
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Quantification of Secreted and Intracellular HBV DNA
2.6. HBV cccDNA Isolation and Taq-Man Probe RT-qPCR
2.7. Quantification of Intracellular HBV RNAs and Northern Blotting
2.8. Southern Blotting
2.9. Detection of HBV Antigens
2.10. Immunofluorescence
2.11. Drug Susceptibility Assay
2.12. Analysis of Intracellular HBV Capsid
2.13. Purification of Cp149 and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.14. Virtual Screening and Molecular Modeling
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Virtual Screening and Antiviral Activity Measurement of Potential HBV CAMs
3.2. Anti-HBV Activity Verification and Molecular Interaction Analysis
3.3. C-18 Inhibited Capsid Formation and HBV Replication
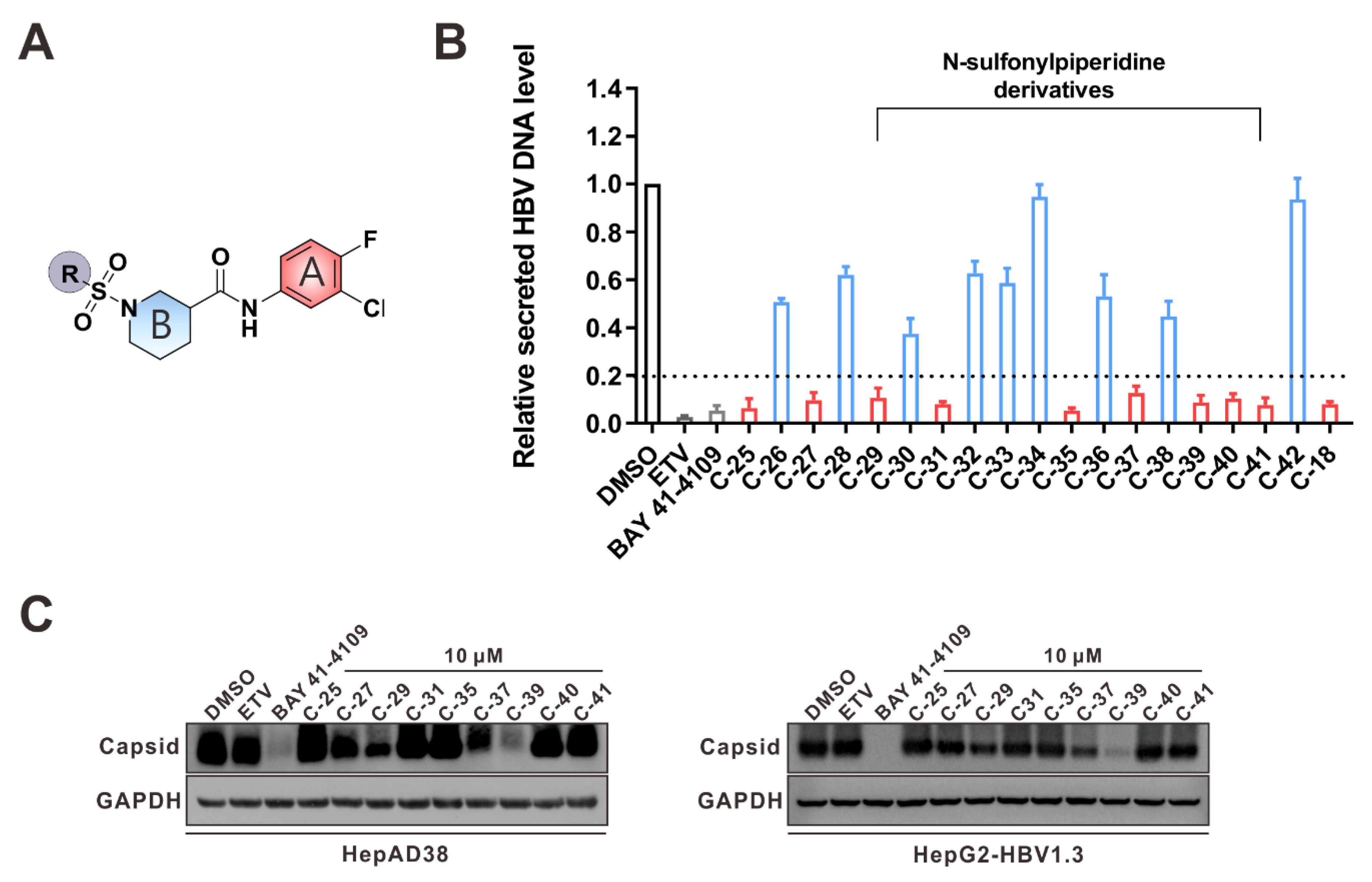
3.4. Structure−Activity Relationship (SAR) Analysis of SPCs
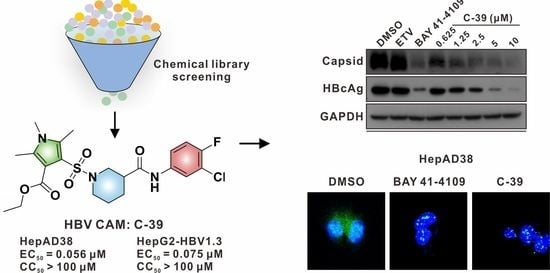
3.5. C-39 Inhibited HBV Replication In Vitro
3.6. C-39 Remained Sensitive to Nucleos(t)ide-Resistant HBV Variant and Showed Additive Antiviral Activity In Vitro with ETV
3.7. C-39 Induced HBc Aggregation and Modulates Capsid Assembly
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razavi-Shearer, D.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Nguyen, M.H.; Chen, D.-S.; Van Damme, P.; Abbas, Z.; Abdulla, M.; Abou Rached, A.; Adda, D.; Aho, I.; et al. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Liu, F.; Tong, X.; Hoffmann, D.; Zuo, J.; Lu, M. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Using Small Molecule Modulators of Nucleocapsid Assembly: Recent Advances and Perspectives. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnick, A.; Venkatakrishnan, B.; Tan, Z.; Lewellyn, E.; Turner, W.; Francis, S. Core protein: A pleiotropic keystone in the HBV lifecycle. Antivir. Res. 2015, 121, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diab, A.; Foca, A.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D.; Andrisani, O. The diverse functions of the hepatitis B core/capsid protein (HBc) in the viral life cycle: Implications for the development of HBc-targeting antivirals. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; White, S.J.; Thompson, R.F.; Bingham, R.; Weiss, E.U.; Maskell, D.P.; Zlotnick, A.; Dykeman, E.; Tuma, R.; Twarock, R.; et al. HBV RNA pre-genome encodes specific motifs that mediate interactions with the viral core protein that promote nucleocapsid assembly. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kock, J.; Rosler, C.; Zhang, J.J.; Blum, H.E.; Nassal, M.; Thoma, C. Generation of covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B viruses via intracellular recycling is regulated in a virus specific manner. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.; Kim, E.S.; Guo, H. Epigenetic regulation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA: Implications for epigenetic therapy against chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2017, 66, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruffaz, M.; Testoni, B.; Luangsay, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Petit, M.A.; Ma, H.; Klumpp, K.; Javanbakht, H.; Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F. Hepatitis B Core (Hbc) Protein Is a Key and Very Early Negative Regulator of the Interferon Response. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, S155–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, S.A.; Crowther, R.A.; Leslie, A.G. The crystal structure of the human hepatitis B virus capsid. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.G.; Jurgens, M.C.; Shepherd, D.A.; Freund, S.M.; Ashcroft, A.E.; Ferguson, N. Thermodynamic origins of protein folding, allostery, and capsid formation in the human hepatitis B virus core protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2782–E2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birnbaum, F.; Nassal, M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: Primary structure requirements in the core protein. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3319–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceres, P.; Zlotnick, A. Weak protein-protein interactions are sufficient to drive assembly of hepatitis B virus capsids. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11525–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berke, J.M.; Dehertogh, P.; Vergauwen, K.; Van Damme, E.; Mostmans, W.; Vandyck, K.; Pauwels, F. Capsid Assembly Modulators Have a Dual Mechanism of Action in Primary Human Hepatocytes Infected with Hepatitis B Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00560-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, U.; Mani, N.; Hu, Z.; Ban, H.; Du, Y.; Hu, J.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.T. Targeting the multifunctional HBV core protein as a potential cure for chronic hepatitis B. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wei, Z.M.; Wu, G.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.H.; Xie, X.W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. In vitro inhibition of HBV replication by a novel compound, GLS4, and its efficacy against adefovir-dipivoxil-resistant HBV mutations. Antivir. Ther. 2012, 17, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stray, S.J.; Bourne, C.R.; Punna, S.; Lewis, W.G.; Finn, M.G.; Zlotnick, A. A heteroaryldihydropyrimidine activates and can misdirect hepatitis B virus capsid assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8138–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlicksup, C.J.; Laughlin, P.; Dunkelbarger, S.; Wang, J.C.; Zlotnick, A. Local Stabilization of Subunit-Subunit Contacts Causes Global Destabilization of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katen, S.P.; Chirapu, S.R.; Finn, M.G.; Zlotnick, A. Trapping of hepatitis B virus capsid assembly intermediates by phenylpropenamide assembly accelerators. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, A.M.; Espiritu, C.; Vogel, R.; Ren, S.; Lau, V.; Kelly, M.; Kuduk, S.D.; Hartman, G.D.; Flores, O.A.; Klumpp, K. Preclinical Characterization of NVR 3-778, a First-in-Class Capsid Assembly Modulator against Hepatitis B Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01734-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Lu, D.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Tong, X.; Zeng, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Discovery of Phthalazinone Derivatives as Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8134–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlali, T.; Berke, J.M.; Vergauwen, K.; Foca, A.; Vandyck, K.; Pauwels, F.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D. Novel Potent Capsid Assembly Modulators Regulate Multiple Steps of the Hepatitis B Virus Life Cycle. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00835-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amblard, F.; Boucle, S.; Bassit, L.; Cox, B.; Sari, O.; Tao, S.; Chen, Z.; Ozturk, T.; Verma, K.; Russell, O.; et al. Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulator Induces Potent Antiviral Responses In Vitro and in Humanized Mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01701–e01719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pei, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Jiang, C.; Tan, X.; Dong, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, G. Discovery of (1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridin-5-yl)sulfonamide Analogues as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators by Conformation Constraint. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6066–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Cai, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tu, Z.; Hu, J.; Tavis, J.E.; Tang, N.; Huang, A.; et al. APOBEC3B edits HBV DNA and inhibits HBV replication during reverse transcription. Antivir. Res. 2018, 149, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, P.; Block, T.M.; Kulp, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, L.; Guo, J.T. Discovery and Mechanistic Study of Benzamide Derivatives That Modulate Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00519-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, U.; Summers, J.; Staeheli, P.; Chisari, F.V. Elimination of duck hepatitis B virus RNA-containing capsids in duck interferon-alpha-treated hepatocytes. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5459–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenney, D.J.; Levine, S.M.; Rose, R.E.; Walsh, A.W.; Weinheimer, S.P.; Discotto, L.; Plym, M.; Pokornowski, K.; Yu, C.F.; Angus, P.; et al. Clinical emergence of entecavir-resistant hepatitis B virus requires additional substitutions in virus already resistant to Lamivudine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3498–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Niu, M.; Chen, R.; Shao, J.; Si, L.; Luo, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Hepatitis B virus mutation pattern rtL180M+A181C+M204V may contribute to entecavir resistance in clinical practice. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Cai, D.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Particles Released from Cultured Cells by Particle Gel Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1540, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhoff, R.J.; Summers, J. Coordinate regulation of replication and virus assembly by the large envelope protein of an avian hepadnavirus. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 4565–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, T.; Cuconati, A.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T. Characterization of the intracellular deproteinized relaxed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus: An intermediate of covalently closed circular DNA formation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12472–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, R.; Zhao, X.; Cai, D.; Liu, Y.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T.; Guo, H. The Interferon-Inducible Protein Tetherin Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Virion Secretion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9200–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X.; Wildum, S.; Garcia-Alcalde, F.; Xu, Z.; Wu, D.; Mao, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Heteroaryldihydropyrimidine (HAP) and Sulfamoylbenzamide (SBA) Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Different Molecular Mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Gyoo Park, S.; Yoo, J.-h.; Jung, G. Calcium ions affect the hepatitis B virus core assembly. Virology 2005, 332, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zlotnick, A.; Lee, A.; Bourne, C.R.; Johnson, J.M.; Domanico, P.L.; Stray, S.J. In vitro screening for molecules that affect virus capsid assembly (and other protein association reactions). Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, A.D.; Pineda, D.L.; Liu, D.; Boschert, K.N.; Gres, A.T.; Wolf, J.J.; Coonrod, E.M.; Tang, J.; Laughlin, T.G.; Yang, Q.; et al. Novel Hepatitis B Virus Capsid-Targeting Antiviral That Aggregates Core Particles and Inhibits Nuclear Entry of Viral Cores. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuduk, S.D.; Stoops, B.; Lam, A.M.; Espiritu, C.; Vogel, R.; Lau, V.; Klumpp, K.; Flores, O.A.; Hartman, G.D. Oxadiazepinone HBV Capsid Assembly Modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 52, 128353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaweera, S.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Kirby, K.A.; Tedbury, P.R.; Xie, J.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Wang, Z. Discovery of New Small Molecule Hits as Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Assembly Modulators: Structure and Pharmacophore-Based Approaches. Viruses 2021, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cherukupalli, S.; Tavis, J.E.; Menendez-Arias, L.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Discovery and optimization of benzenesulfonamides-based hepatitis B virus capsid modulators via contemporary medicinal chemistry strategies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Cha, H.M.; Hwang, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Vishakantegowda, A.G.; Imran, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Yi, Y.S.; Jun, S.; Kim, G.H.; et al. Sulfamoylbenzamide-based Capsid Assembly Modulators for Selective Inhibition of Hepatitis B Viral Replication. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, D.; Hu, H.; Zeng, J.; Yu, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yang, G.; Young, J.A.T.; et al. Direct Inhibition of Hepatitis B e Antigen by Core Protein Allosteric Modulator. Hepatology 2019, 70, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billioud, G.; Pichoud, C.; Puerstinger, G.; Neyts, J.; Zoulim, F. The main hepatitis B virus (HBV) mutants resistant to nucleoside analogs are susceptible in vitro to non-nucleoside inhibitors of HBV replication. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, N.; Cole, A.G.; Phelps, J.R.; Ardzinski, A.; Cobarrubias, K.D.; Cuconati, A.; Dorsey, B.D.; Evangelista, E.; Fan, K.; Guo, F.; et al. Preclinical Profile of AB-423, an Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus Pregenomic RNA Encapsidation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00082-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Q.; Liu, X.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Goldmann, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of hepatitis B virus capsid assembly inhibitors leading to a heteroaryldihydropyrimidine based clinical candidate (GLS4). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compounds | HepAD38 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 (μM) | CC50 (μM) | SI | |
| C-7 | 1.83 ± 0.44 | >100 | >54.7 |
| C-9 | 1.14 ± 0.23 | 26.6 ± 2.0 | 23.4 |
| C-16 | 1.29 ± 0.35 | 72.4 ± 1.9 | 56.3 |
| C-18 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 14.8 ± 0.7 | 131.2 |
| C-19 | 0.39 ± 0.13 | 75.3 ± 5.2 | 194.1 |
| ETV | 0.003 ± 0.001 | ND | ND |
| BAY 41-4109 | 0.067 ± 0.01 | 30 ± 1.9 | 447 |
| Compound | Structure | EC50 (μM) or Residual HBV DNA Level (%) | CC50 (μM) | SI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-25 |  | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | 33.2 ± 1.9 a | 114.6 a |
| C-26 |  | 48.78 * | ND | ND |
| C-27 |  | 1.12 ± 0.05 a | 81.5 ± 5.8 a | 72.8 a |
| C-28 |  | 60.65 * | ND | ND |
| C-29 | 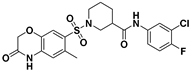 | 1.29 ± 0.01 a | 18.2 ± 2.2 a | 14.1 a |
| C-30 | 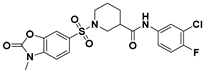 | 33.59 * | ND | ND |
| C-31 |  | 0.26 ± 0.03 a | 25.0 ± 3.3 a | 96.0 a |
| C-32 |  | 72.76 * | ND | ND |
| C-33 |  | 68.77 * | ND | ND |
| C-34 |  | 121.46 * | ND | ND |
| C-35 |  | 0.41 ± 0.01 a | 9.8 ± 1.0 a | 23.9 a |
| C-36 |  | 54.09 * | ND | ND |
| C-37 |  | 0.35 ± 0.05 a | 11.0 ± 0.7 a | 31.3 a |
| C-38 |  | 40.31 * | ND | ND |
| C-39 |  | 0.056 ± 0.013 a | >100 a | >1786 a |
| 0.075 ± 0.016 b | >100 b | >1333 b | ||
| C-40 |  | 0.39 ± 0.01 a | 12.6 ± 0.7 a | 32.3 a |
| C-41 | 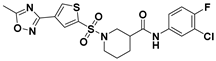 | 0.062 ± 0.013 a | 95.6 ± 15.7 a | 1542 a |
| C-42 |  | 137.39 * | ND | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yin, J.; Hu, J.; Cai, X.; Hu, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, K.; Tang, N.; Huang, L. Structure-Based Discovery of N-Sulfonylpiperidine-3-Carboxamides as Novel Capsid Assembly Modulators for Potent Inhibition of HBV Replication. Viruses 2022, 14, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020348
Yang Y, Yan Y, Yin J, Hu J, Cai X, Hu J, Xia J, Wang K, Tang N, Huang L. Structure-Based Discovery of N-Sulfonylpiperidine-3-Carboxamides as Novel Capsid Assembly Modulators for Potent Inhibition of HBV Replication. Viruses. 2022; 14(2):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020348
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Yu Yan, Jiaxin Yin, Jie Hu, Xuefei Cai, Jieli Hu, Jie Xia, Kai Wang, Ni Tang, and Luyi Huang. 2022. "Structure-Based Discovery of N-Sulfonylpiperidine-3-Carboxamides as Novel Capsid Assembly Modulators for Potent Inhibition of HBV Replication" Viruses 14, no. 2: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020348
APA StyleYang, Y., Yan, Y., Yin, J., Hu, J., Cai, X., Hu, J., Xia, J., Wang, K., Tang, N., & Huang, L. (2022). Structure-Based Discovery of N-Sulfonylpiperidine-3-Carboxamides as Novel Capsid Assembly Modulators for Potent Inhibition of HBV Replication. Viruses, 14(2), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020348