Differential Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Binding and Functional Antibodies upon BNT162b2 Vaccine: A 6-Month Follow-Up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Immunoassays
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 Microneutralization Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differential Kinetics of SARS-CoV2 Anti-RBD IgG and Anti-Trimeric S IgG
3.2. Comparative Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies and Spike-Binding IgG
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. Coronavirus Resource Center, Global Map. 2021. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Shah, V.K.; Firmal, P.; Alam, A.; Ganguly, D.; Chattopadhyay, S. Overview of Immune Response during SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Lessons from the Past. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haitao, T.; Vermunt, J.V.; Abeykoon, J.; Ghamrawi, R.; Gunaratne, M.; Jayachandran, M.; Narang, K.; Parashuram, S.; Suvakov, S.; Garovic, V.D. COVID-19 and Sex Differences. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, V.; Gadi, N.; Spihlman, A.P.; Wu, S.C.; Choi, C.H.; Moulton, V.R. Aging, Immunity, and COVID-19: How Age Influences the Host Immune Response to Coronavirus Infections? Front. Physiol. 2021, 11, 571416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Al-Ahmed, S.; Garout, M.; Al-Qaaneh, A.; Sule, A.; Tirupathi, R.; Mutair, A.; Alhumaid, S.; Hasan, A.; Dhawan, M.; et al. Diverse Immunological Factors Influencing Pathogenesis in Patients with COVID-19: A Review on Viral Dissemination, Immunotherapeutic Options to Counter Cytokine Storm and Inflammatory Responses. Pathogens 2021, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tilbeurgh, M.; Lemdani, K.; Beignon, A.-S.; Chapon, C.; Tchitchek, N.; Cheraitia, L.; Lopez, E.M.; Pascal, Q.; Le Grand, R.; Maisonnasse, P.; et al. Predictive Markers of Immunogenicity and Efficacy for Human Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. A correlate of protection for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines is urgently needed. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1147–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, K.A.; Ambrosino, D.M.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Goldblatt, D.; Gilbert, P.B.; Siber, G.R.; Dull, P.; Plotkin, S.A. Evidence for antibody as a protective correlate for COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Phillips, D.J.; White, T.; Sayal, H.; Aley, P.K.; Bibi, S.; Dold, C.; Fuskova, M.; Gilbert, S.C.; Hirsch, I.; et al. Correlates of protection against symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.B.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science 2022, 375, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Standardised neutralising antibody assays are needed for evaluating COVID-19 vaccines. eBioMedicine 2021, 73, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, I.; Mattiuzzo, G.; Page, M.; Minor, P.; Griffiths, E.; Nuebling, M.; Moorthy, V. WHO International Standard for evaluation of the antibody response to COVID-19 vaccines: Call for urgent action by the scientific community. Lancet Microbe 2021, 21, 00266-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Clementi, N.; Spanò, S.M.; Albitar-Nehme, S.; Ranno, S.; Colombini, A.; Criscuolo, E.; Di Resta, C.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Viganó, M.; et al. Harmonization of six quantitative SARS-CoV-2 serological assays using sera of vaccinated subjects. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 522, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkmann, T.; Perkmann-Nagele, N.; Koller, T.; Mucher, P.; Radakovics, A.; Marculescu, R.; Wolzt, M.; Wagner, O.F.; Binder, C.J.; Haslacher, H. Anti-Spike Protein Assays to Determine SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Five Quantitative Assays. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0024721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A. Vaccines: Correlates of vaccine-induced immunity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotkin, S.A. Correlates of protection induced by vaccination. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meschi, S.; Matusali, G.; Colavita, F.; Lapa, D.; Bordi, L.; Puro, V.; Leoni, B.D.; Galli, C.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Castilletti, C. Predicting the protective humoral response to a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2021, 59, 2010–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Mellinghoff, S.C.; Shamsrizi, P.; Addo, M.M.; Dahlke, C. Correlates of Vaccine-Induced Protection against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2021, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; O’Connell, S.E.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; Talana, C.A.; Lai, L.; Albert, J.; Anderson, E.; Bennett, H.; Corbett, K.S.; et al. Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine–induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2021, 373, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.S.A. Vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 variants: The urgent need for a correlate of protection. Lancet 2021, 397, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, P.A.; Page, M.; Bernasconi, V.; Mattiuzzo, G.; Dull, P.; Makar, K.; Plotkin, S.; Knezevic, I. WHO International Standard for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin. Lancet 2021, 397, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusali, G.; Colavita, F.; Lapa, D.; Meschi, S.; Bordi, L.; Piselli, P.; Gagliardini, R.; Corpolongo, A.; Nicastri, E.; Antinori, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Serum Neutralization Assay: A Traditional Tool for a Brand-New Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, M.S.; Arunachalam, P.S.; Hu, M.; Reis, N.; Trisal, M.; Raeber, O.; Chinthrajah, S.; Davis-Gardner, M.E.; Manning, K.; Mudvari, P.; et al. Durability of immune responses to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, L.; Gao, X.-S.; Zheng, B.-Y.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Li, J.-X.; Feng, R.; Bian, Q.; Guo, X.-L.; Wang, N.; et al. A proof of concept for neutralizing antibody-guided vaccine design against SARS-CoV-2. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratesi, F.; Caruso, T.; Testa, D.; Tarpanelli, T.; Gentili, A.; Gioè, D.; Migliorini, P. BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Elicits High Avidity and Neutralizing Antibodies in Healthcare Workers. Vaccines 2021, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfström, E.; Eringfält, A.; Kötz, A.; Wickbom, F.; Tham, J.; Lingman, M.; Nygren, J.M.; Undén, J. Dynamics of IgG-avidity and antibody levels after Covid-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 144, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Henry, B.M.; Pighi, L.; De Nitto, S.; Gianfilippi, G.; Lippi, G. The pronounced decline of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike trimeric IgG and RBD IgG in baseline seronegative individuals six months after BNT162b2 vaccination is consistent with the need for vaccine boosters. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 60, e29–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlcochova, P.; Kemp, S.A.; Dhar, M.S.; Papa, G.; Meng, B.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Datir, R.; Collier, D.A.; Albecka, A.; Singh, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion. Nature 2021, 599, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muik, A.; Lui, B.G.; Wallisch, A.K.; Bacher, M.; Mühl, J.; Reinholz, J.; Ozhelvaci, O.; Beckmann, N.; Güimil Garcia, R.C.; Poran, A.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron by BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine-elicited human sera. Science 2022, eabn7591, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 1, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
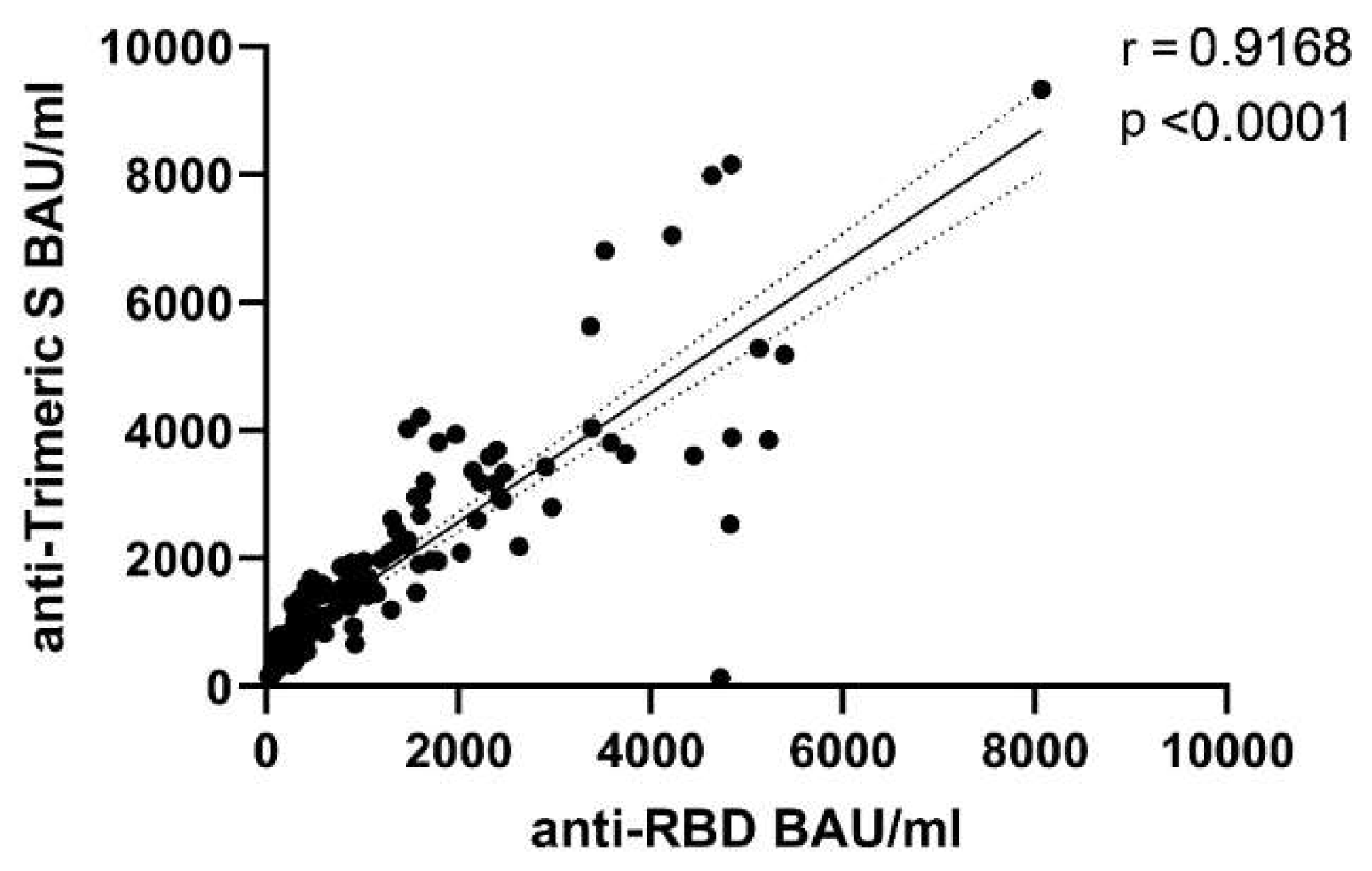
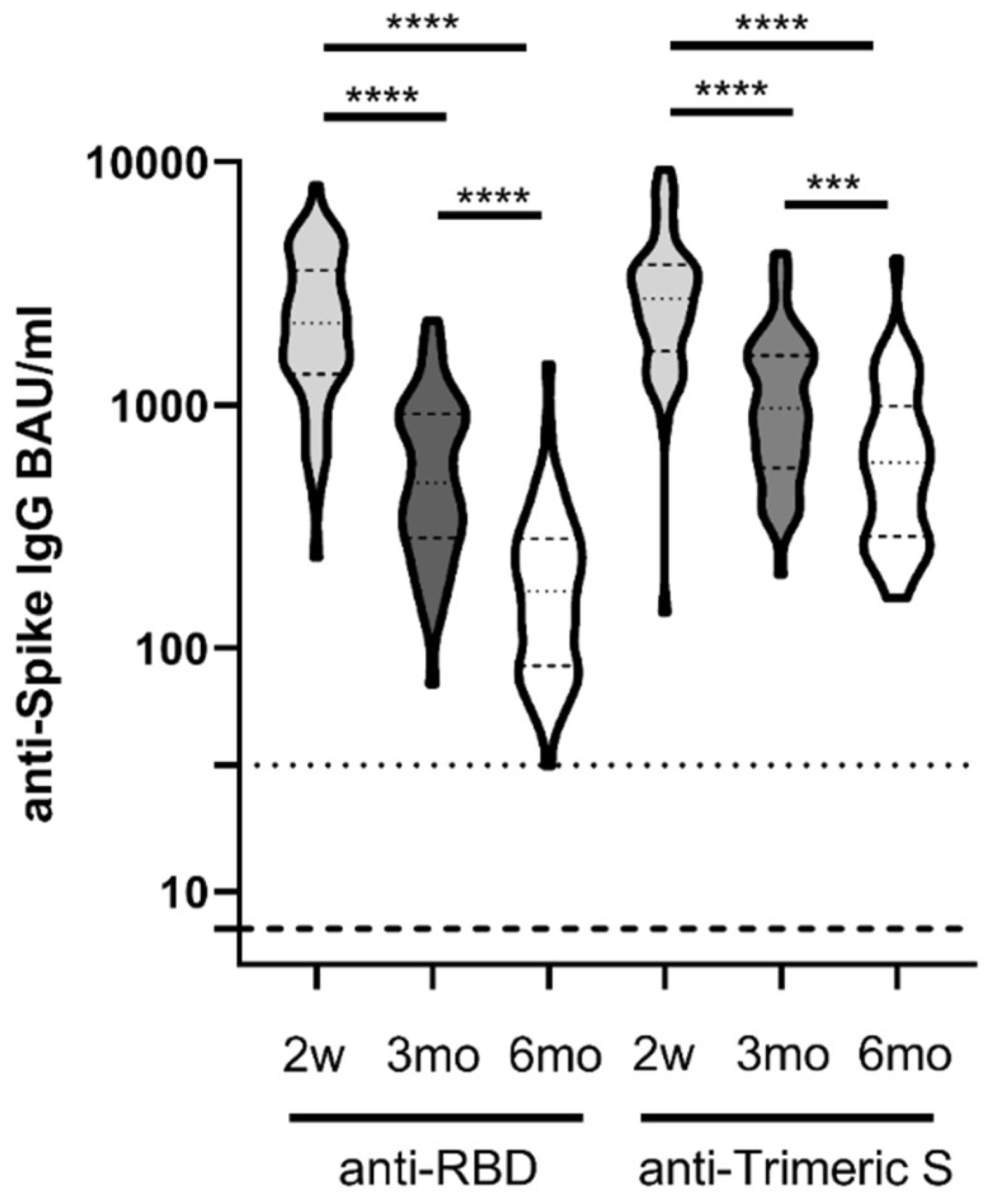
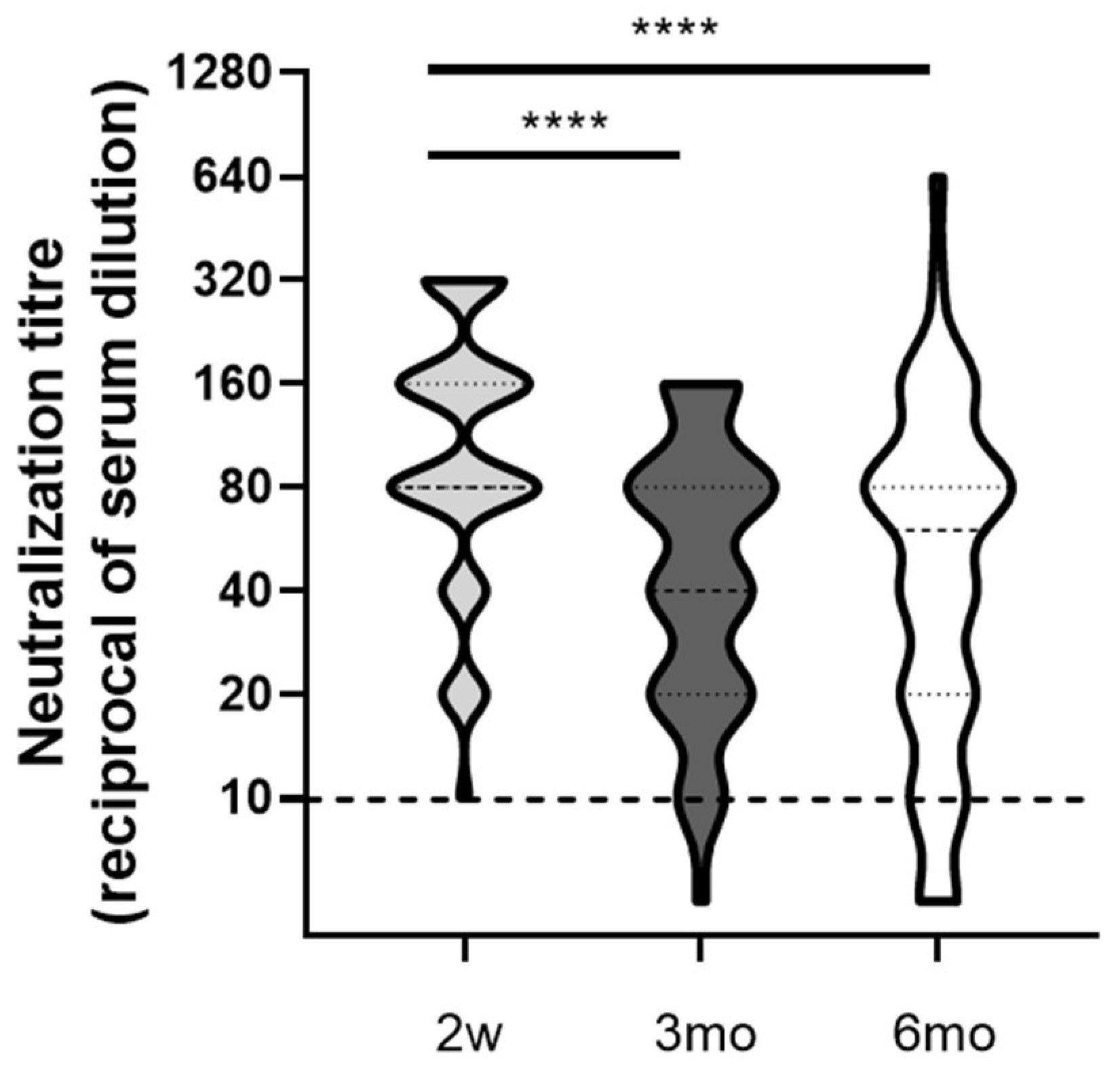

| Antibody Type | 2w | 3mo | 6mo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-RBD IgG | 0.727 | 0.782 | 0.703 |
| Anti-Trimeric S IgG | 0.655 | 0.749 | 0.710 |
| 2w (Specificity-Sensitivity) | 3mo (Specificity-Sensitivity) | 6mo (Specificity-Sensitivity) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-RBD Optimal criterion | 870.8 (100.0–97.8) | 383.1 (88.2–80.0) | 121.5 (77.8–82.4) |
| Anti-Trimeric S Optimal criterion | 1591.2 (100.0–84.8) | 949.0 (100.0–74.3) | 415.0 (83.3–85.3) |
| Anti-RBD criterion ≥99% of specificity | 870.8 (100.0–97.8) | 610.7 (100.0–60.0) | 272.3 (100.0–38.2) |
| Anti-Trimeric S criterion ≥99% of specificity | 1591.2 (100.0–84.8) | 949.0 (100.0–74.3) | 1280.3 (100.0–23.5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matusali, G.; Sberna, G.; Meschi, S.; Gramigna, G.; Colavita, F.; Lapa, D.; Francalancia, M.; Bettini, A.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Puro, V.; et al. Differential Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Binding and Functional Antibodies upon BNT162b2 Vaccine: A 6-Month Follow-Up. Viruses 2022, 14, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020312
Matusali G, Sberna G, Meschi S, Gramigna G, Colavita F, Lapa D, Francalancia M, Bettini A, Capobianchi MR, Puro V, et al. Differential Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Binding and Functional Antibodies upon BNT162b2 Vaccine: A 6-Month Follow-Up. Viruses. 2022; 14(2):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020312
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatusali, Giulia, Giuseppe Sberna, Silvia Meschi, Giulia Gramigna, Francesca Colavita, Daniele Lapa, Massimo Francalancia, Aurora Bettini, Maria R. Capobianchi, Vincenzo Puro, and et al. 2022. "Differential Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Binding and Functional Antibodies upon BNT162b2 Vaccine: A 6-Month Follow-Up" Viruses 14, no. 2: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020312
APA StyleMatusali, G., Sberna, G., Meschi, S., Gramigna, G., Colavita, F., Lapa, D., Francalancia, M., Bettini, A., Capobianchi, M. R., Puro, V., Castilletti, C., Vaia, F., & Bordi, L. (2022). Differential Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Binding and Functional Antibodies upon BNT162b2 Vaccine: A 6-Month Follow-Up. Viruses, 14(2), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020312







