Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Genotypes Associated with the Immunopathological Profile of People Living with HIV-1: Immunological Aspects of Primary EBV Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Confirmatory Methods
2.3. Quantification of T Lymphocytes and Measurement of Cytokines
2.4. Quantification of HIV-1 and EBV Viral Loads
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characterization
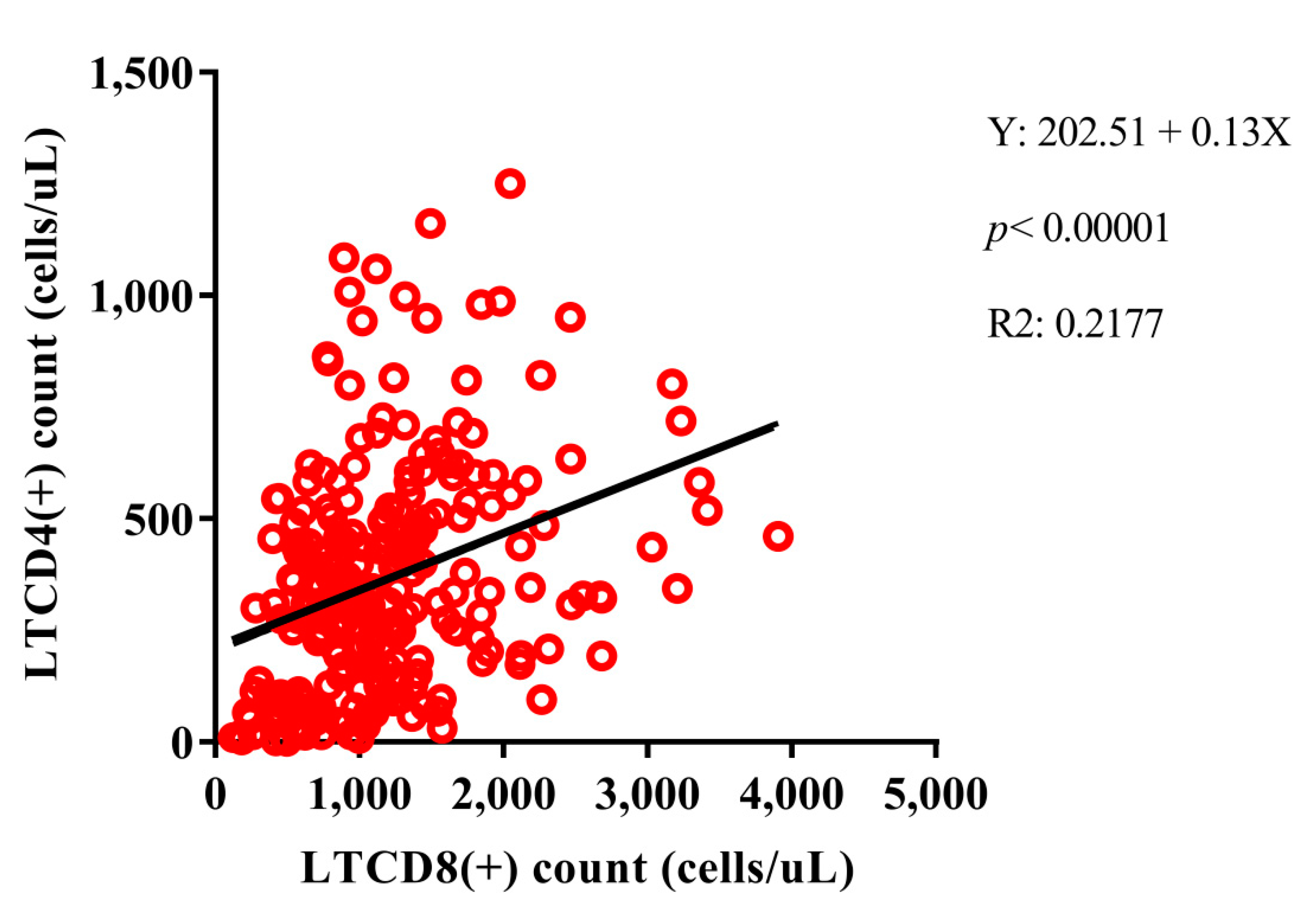
3.2. Evaluation of the EBV Viral Load in Different Blood Extracts and Its Correlation with HIV-1 Viral Load
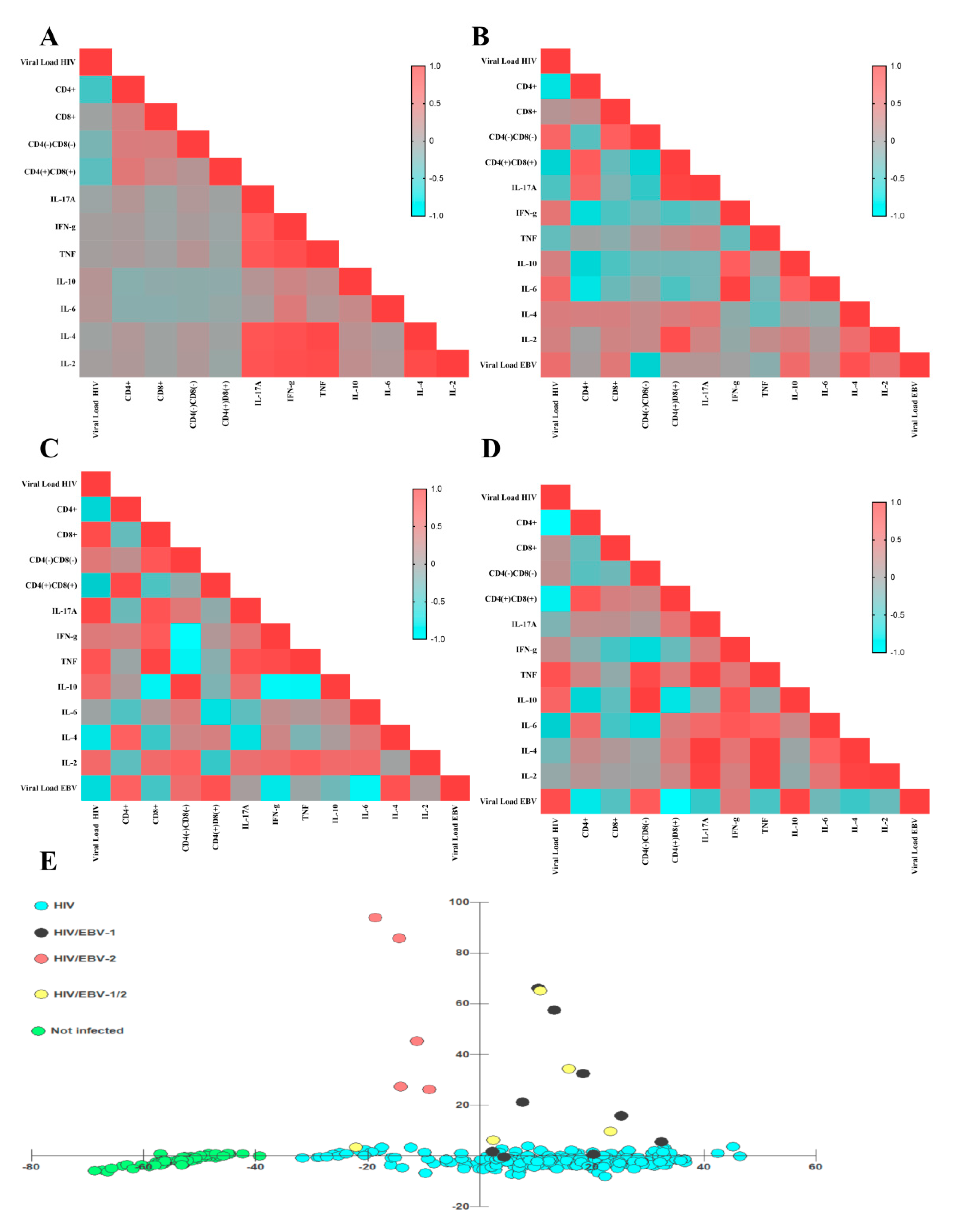
3.3. Different Immunological Profiles Were Associated with the EBV Genotypes
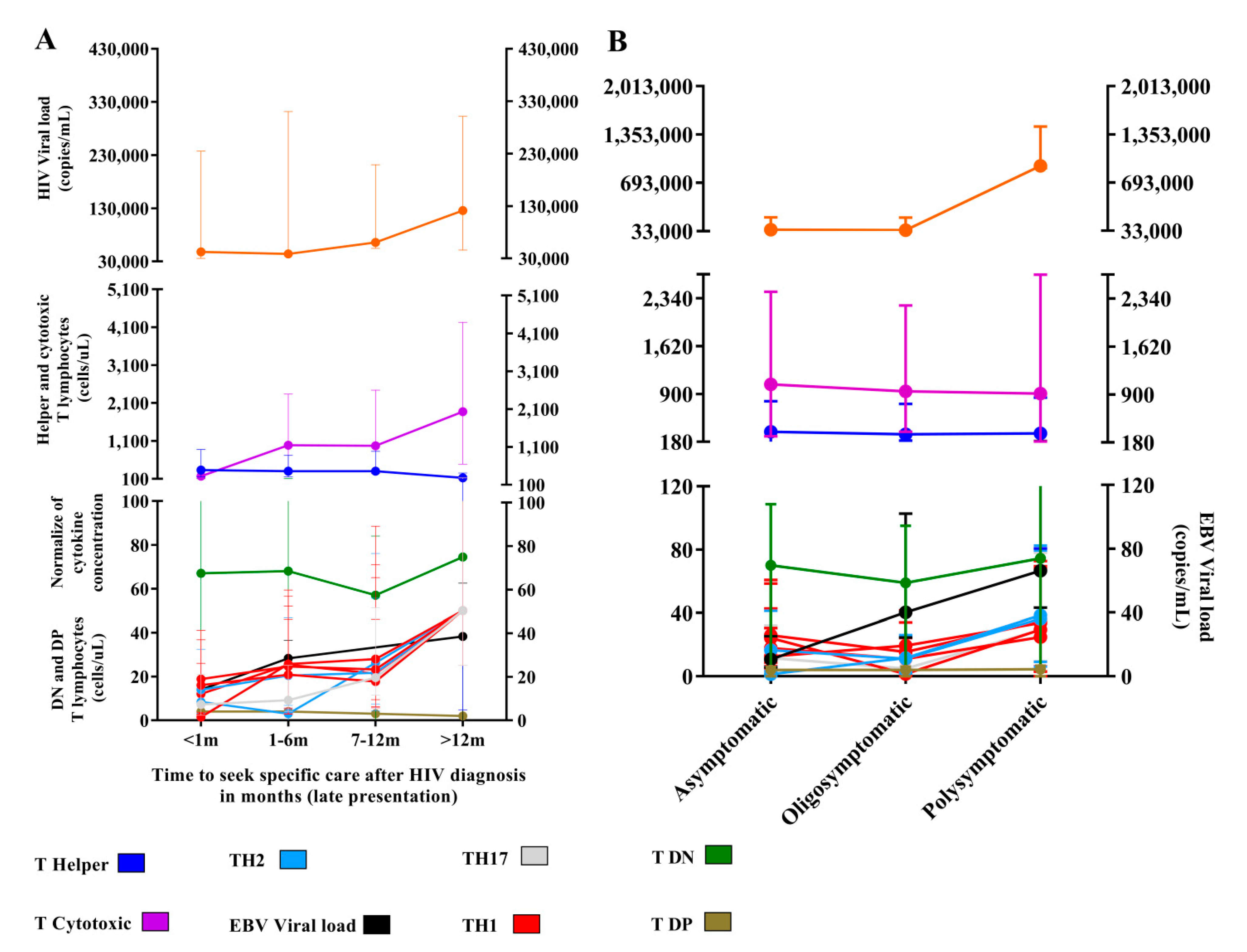
3.4. Late Attendance and Symptomatology Affect the Profile of Immunological and Virological Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacoste, V.; Judde, J.G.; Bestetti, G.; Cadranel, J.; Antoine, M.; Valensi, F.; Delabesse, E.; MacIntyre, E.; Gessain, A. Virological and molecular characterisation of a new B lymphoid cell line, established from an AIDS patient with primary effusion lymphoma, harbouring both KSHV/HHV8 and EBV viroses. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 38, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Silverberg, M.J.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Chi, M.; Abrams, D.I.; Haque, R.; Zha, H.D.; McGuire, M.; Xu, L.; Said, J. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Expression of B-cell Oncogenic Markers in HIV-Related Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4702–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Pei, Y.; Lamplugh, Z.L.; Robertson, E.S. Molecular Biology of EBV in Relationship to HIV/AIDS-Associated Oncogenesis. Cancer Treat Res. 2019, 177, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friis, A.M.C.; Åkerlund, B.; Gyllensten, K.; Aleman, A.; Ernberg, I. Host–Epstein–Barr virus relationship affected by immunostimulation in HIV-infected patients representing distinct progressor profile groups. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Riedel, D.J.; Tang, L.S.; Rositch, A.F. The Role of Viral Co-Infection in HIV-Associated Non-AIDS-Related Cancers. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, D.M.; Valderrama, S.; Gualtero, S.; Hernández, C.; López, M.; Herrera, M.V.; Solano, J.; Fiorentino, S.; Quijano, S. Loss of T-Cell Multifunctionality and TCR-Vβ Repertoire Against Epstein-Barr Virus Is Associated With Worse Prognosis and Clinical Parameters in HIV+ Patients. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balfour, J.H.H.; Verghese, P. Primary Epstein–Barr Virus Infection: Impact of Age at Acquisition, Coinfection, and Viral Load. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyker, J.A.; Casper, C.; Tapia, K.; Richardson, B.; Bunts, L.; Huang, M.-L.; Maleche-Obimbo, E.; Nduati, R.; John-Stewart, G. Clinical and Virologic Manifestations of Primary Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Infection in Kenyan Infants Born to HIV-Infected Women. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrara, M.R.; Cattelan, A.; Zanchetta, M.; Sasset, L.; Freguja, R.; Gianesin, K.; Cecchetto, M.G.; Carmona, F.; De Rossi, A. Epstein-Barr Virus load and immune activation in Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1-infected patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, L.A.S.; De Azevedo, K.M.L.; Silva, L.E.; Oliveira, L.H.S. Epstein-Barr virus in oral mucosa from human immunodeficiency virus positive patients. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2014, 60, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traore, L.; Nikiema, O.; Ouattara, A.K.; Compaore, T.R.; Soubeiga, S.T.; Diarra, B.; Obiri-Yeboah, D.; Sorgho, P.A.; Djigma, F.W.; Bisseye, C.; et al. EBV and HHV-6 Circulating Subtypes in People Living with HIV in Burkina Faso, Impact on CD4 T cell count and HIV Viral Load. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, e2017049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueira-Silva, C.M.; Pereira, F.E. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in healthy children and adolescents in Vitória, State of Espírito Santo, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2004, 37, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerpe, N.F.; Vistarop, A.; Moyano, A.; De Matteo, E.; Preciado, M.; Chabay, P. Distinctive EBV infection characteristics in children from a developing country. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, M.A.; Altcheh, J.; Moroni, S.; Moscatelli, G.; Chabay, P.A.; Preciado, M.V. EBNA1 sequences in Argentinean pediatric acute and latent Epstein-Barr virus infection reflect circulation of novel South American variants. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, J.; Young, L.; Martin, B.; Chatman, T.; Kieff, E.; Rickinson, A.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, M.; Ayres Júnior, M.; Ayres, D.L.; Santos, A.S. BioEstat 5.0: Aplicações Estatísticas nas Áreas de Ciências Biológicas e Médicas; Sociedade Civil Mamirauá: Belém, Brazil, 2008; CNPq; 364p. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Yan, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Ni, A. Anti-Epstein–Barr virus antibodies in Beijing during 2013–2017: What we have found in the different patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beader, N.; Kolarić, B.; Slačanac, D.; Tabain, I.; Vilibić-Čavlek, T. Seroepidemiological Study of Epstein-Barr Virus in Different Population Groups in Croatia. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2018, 20, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Okonko, I.O.; Makinde, T.S.; Okonko, B.J.; Ogbu, O. Immunological and epidemiological evaluation of EBV infections among HIV-1 infected individuals in Abakaliki, Nigeria supports the potential use of neutrophils as a marker of EBV in HIV disease progression and as useful markers of immune activation. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2020, 41, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ramos, A.; Patel, M.; Kadakia, K.; Haque, T. Performance of the Architect EBV Antibody Panel for Determination of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Stage in Immunocompetent Adolescents and Young Adults with Clinical Suspicion of Infectious Mononucleosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakry, J.; Ambinder, R. The Biology and Clinical Utility of EBV Monitoring in Blood. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 391, 475–499. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, S.J.C.; Pronk, I.; Middeldorp, J.M. Toward Standardization of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Load Monitoring: Unfractionated Whole Blood as Preferred Clinical Specimen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.-J.; Fischer, L.; Jabs, W.J.; Holbe, M.; Pethig, K.; Bucsky, P. Longitudinal analysis of Epstein-Barr viral load in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of transplanted patients by real-time polymerase chain reaction12. Transplantation 2002, 74, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Kimura, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Nishikawa, K.; Ihira, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Morishima, T. Detection of Herpesvirus DNA in the Serum of Immunocompetent Children. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohaus, S.; Santangelo, R.; Giachelia, M.; Vannata, B.; Massini, G.; Cuccaro, A.; Martini, M.; Cesarini, V.; Cenci, T.; D’Alo, F.; et al. The Viral Load of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) DNA in Peripheral Blood Predicts for Biological and Clinical Characteristics in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, M.C.; Cupelli, E.; Santangelo, R.; Maiolo, E.; Alma, E.; Giachelia, M.; Martini, M.; Bellesi, S.; D’Alò, F.; Voso, M.T.; et al. Whole blood EBV-DNA predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Dawson, C.W.; Takada, K.; Curnow, J.; Moody, C.A.; Sixbey, J.W.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A regulates viral and cellular gene expression by modulation of the NF-kappaB transcription factor pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15730–15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.M.; Stewart, S.E.; Wei, W.; Woodman, C.B.J.; O’Neil, J.D.; Dawson, C.W.; Young, L.S. The EBV-encoded latent membrane proteins, LMP2A and LMP2B, limit the actions of interferon by targeting interferon receptors for degradation. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3903–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, A.M.; Huye, L.E.; Ning, S.; Webster-Cyriaque, J.; Pagano, J.S. Interferon Regulatory Factor 7 Is Negatively Regulated by the Epstein-Barr Virus Immediate-Early Gene, BZLF-1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10040–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, I.-C.; Miaw, S.-C. Regulation of IL-4 Expression in Immunity and Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 941, 31–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kis, L.L.; Gerasimčik, N.; Salamon, D.; Persson, E.K.; Nagy, N.; Klein, G.; Severinson, E.; Klein, E. STAT6 signaling pathway activated by the cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 induces expression of the Epstein-Barr virus–encoded protein LMP-1 in absence of EBNA-2: Implications for the type II EBV latent gene expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2011, 117, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malizia, A.P.; Egan, J.J.; Doran, P.P. IL-4 increases CD21-dependent infection of pulmonary alveolar epithelial type II cells by EBV. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Medeiros, R.M.; Valverde-Villegas, J.M.; Junqueira, D.M.; Gräf, T.; Lindenau, J.D.-R.; De Mello, M.G.; Vianna, P.; Almeida, S.E.M.; Chies, J.A.B. Rapid and Slow Progressors Show Increased IL-6 and IL-10 Levels in the Pre-AIDS Stage of HIV Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.L.; Kouyos, R.D.; Balmer, B.; Grube, C.; Weber, R.; Günthard, H.F. Frequency and Spectrum of Unexpected Clinical Manifestations of Primary HIV-1 Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitjean, G.; Chevalier, M.; Tibaoui, F.; Didier, C.; Manea, M.E.; Liovat, A.-S.; Campa, P.; Müller-Trutwin, M.; Girard, P.-M.; Meyer, L.; et al. Level of double negative T cells, which produce TGF-β and IL-10, predicts CD8 T-cell activation in primary HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2012, 26, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.-L.; Wei, X.-S.; Zhang, M.; Niu, Y.-R.; Zhou, Q. The Significance of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type II in CD8+ Regulatory T Cells and CD8+ Effector T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milush, J.M.; Mir, K.D.; Sundaravaradan, V.; Gordon, S.N.; Engram, J.; Cano, C.A.; Reeves, J.D.; Anton, E.; O’Neill, E.; Butler, E.; et al. Lack of clinical AIDS in SIV-infected sooty mangabeys with significant CD4+ T cell loss is associated with double-negative T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, C.B.; Daud, I.I.; Ogolla, S.O.; Ritchie, J.A.; Smith, N.A.; Sumba, P.; Dent, A.E.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr Virus Type 2 Infects T Cells in Healthy Kenyan Children. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, V.; Scherpbier, H.; Beld, M.; Piriou, E.; Van Breda, A.; Lange, J.; van Leth, F.; Jurriaans, S.; Alders, S.; Dillen, P.W.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Infects B and Non-B Lymphocytes in HIV-1–Infected Children and Adolescents. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.B.; Lang, J.; Sweet, L.A.; Smith, N.A.; Freed, B.M.; Pan, Z.; Haverkos, B.; Pelanda, R.; Rochford, R. Epstein-Barr Virus Type 2 Infects T Cells and Induces B Cell Lymphomagenesis in Humanized Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00813-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.-P.; Chang, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Huang, X.-J. Association of Epstein–Barr virus reactivation with the recovery of CD4/CD8 double-negative T lymphocytes after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lucchesi, W.; Brady, G.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Kracht, M.; Russ, R.; Farrell, P.J. Differential Gene Regulation by Epstein-Barr Virus Type 1 and Type 2 EBNA2. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7456–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, S.; Schwartz, D.H. Potentiation of EBV-Induced B Cell Transformation by CXCR4-Tropic, But Not CCR5-Tropic, HIV gp120: Implications for HIV-Associated Lymphomagenesis. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2011, 27, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Fujisawa, R.; Izawa, D.; Hieshima, K.; Takada, K.; Yoshie, O. Human B Cells Immortalized with Epstein-Barr Virus Upregulate CCR6 and CCR10 and Downregulate CXCR4 and CXCR5. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlin-Henriksson, B.; Mowafi, F.; Klein, G.; Nilsson, A. Epstein-Barr virus infection negatively impacts the CXCR4-dependent migration of tonsillar B cells. Immunology 2006, 117, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Maskri, O.; Chaminade, F.; René, B.; Benkaroun, J.; Godet, J.; Mély, Y.; Mauffret, O.; Fossé, P. Structural Insights into the HIV-1 Minus-strand Strong-stop DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3468–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrara, M.R.; Freguja, R.; Gianesin, K.; Zanchetta, M.; De Rossi, A. Epstein-Barr virus-driven lymphomagenesis in the context of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGoff, J.; Amiel, C.; Calisonni, O.; Fromentin, D.; Rajoely, B.; Abuaf, N.; Tartour, E.; Rozenbaum, W.; Bélec, L.; Nicolas, J.-C. Early Impairment of CD8+ T Cells Immune Response Against Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Antigens Associated with High Level of Circulating Mononuclear EBV DNA Load in HIV Infection. J. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 24, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, D.; Myburgh, R.; Caduff, N.; Spohn, M.; Kok, Y.L.; Keller, C.W.; Murer, A.; Chatterjee, B.; Rühl, J.; Engelmann, C.; et al. EBV renders B cells susceptible to HIV-1 in humanized mice. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e202000640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiyegunhi, O.; Ndlovu, B.; Ogunshola, F.; Ismail, N.; Walker, B.D.; Ndung’U, T.; Ndhlovu, Z.M. Frequencies of Circulating Th1-Biased T Follicular Helper Cells in Acute HIV-1 Infection Correlate with the Development of HIV-Specific Antibody Responses and Lower Set Point Viral Load. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00659-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, C.M.; Snelgrove, R.J. Type 2 immunity: Expanding our view. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Peng, X.; Yang, Z.; Tao, R.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Chemokine and Cytokine Cascade Caused by Skewing of the Th1-Th2 Balance Is Associated with High Intracranial Pressure in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 2053958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.-T.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Guan, W.; Wang, R.-R.; He, L.-P.; Zhang, J.-B.; Kuang, Y.-Q. HIV infection confers distinct mechanisms in severe drug eruption: Endogenous virus activation with aberrant Th2/Th1 and CD8 + T cells function. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.K.; Vajpayee, M.; Mojumdar, K.; Singh, R.; Singh, A. Study of CD4+CD8+ Double positive T-lymphocyte phenotype and function in Indian patients infected with HIV-1. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, M.A.; Picking, R.A.; Kuruc, J.D.; McGee, K.; Gay, C.; Eron, J.J.; Hicks, C.B.; Tomaras, G.D.; Ferrari, G. CD4+CD8+ T Cells Represent a Significant Portion of the Anti-HIV T Cell Response to Acute HIV Infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4289–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celis, F.P.; Feria, M.G.; Taborda, N.A.; Rugeles, M.T. A Low Frequency of IL-17-Producing CD8+ T-Cells Is Associated With Persistent Immune Activation in People Living With HIV Despite HAART-Induced Viral Suppression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, C.; Forti, E.; Radin, E.; Cibin, R.; Cossarizza, A. Cytofluorometric Identification of Two Populations of Double Positive (CD4+,CD8+) T Lymphocytes in Human Peripheral Blood. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 191, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Mancera, M.S.; Bolaños, N.I.; Salamanca, M.; Orjuela, G.A.; Rodriguez, A.N.; Gonzalez, J.M. Percentages of CD4+CD8+ double-positive T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of adults from a blood bank in Bogotá, Colombia. Turk. J. Hematol. 2020, 37, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, R.; Dillon, S.; Rogers, L.; Palmer, B.; MaWhinney, S.; Blyveis, N.; Schlichtemeier, R.; D’Souza, M.; Ingoldby, L.; Harwood, J.E.F.; et al. Phenotypic and Functional Characterization of HIV-1-Specific CD4+CD8+ Double-Positive T Cells in Early and Chronic HIV-1 Infection. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2009, 50, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Kang, S.-H.; Lee, W.-K. Identification of two types of naturally-occurring intertypic recombinants of Epstein-Barr virus. Mol. Cells 2006, 21, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyle, M.J.; Sculley, T.B.; Penny, R.; Sewell, W.A.; Tschuchnigg, M.; Berger, M.F.; Cooper, D.A. The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus Subtypes in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 1993, 10, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzellos, S.; Farrell, P.J. Epstein-Barr Virus Sequence Variation—Biology and Disease. Pathogens 2012, 1, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.A.; Baresel, P.C.; Jackson, C.L.; Ogolla, S.; Toko, E.N.; Heit, S.; Piriou, E.; Sumba, O.P.; Middeldorp, J.; Colborn, K.L.; et al. Differences in the Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 IgA Antibody Response Are Associated With Increased Risk for Coinfection With a Second Strain of Epstein-Barr Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Yajima, M.; Ikuta, K. Epstein-Barr virus strain variation and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, E.N.; Mellors, J.W. Natural history of HIV-1 infection. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 14, 809–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndhlovu, Z.M.; Kamya, P.; Mewalal, N.; Kløverpris, H.; Nkosi, T.; Pretorius, K.; Laher, F.; Ogunshola, F.; Chopera, D.; Shekhar, K.; et al. Magnitude and Kinetics of CD8+ T Cell Activation during Hyperacute HIV Infection Impact Viral Set Point. Immunity 2015, 43, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appay, V.; Nixon, D.F.; Donahoe, S.M.; Gillespie, G.M.; Dong, T.; King, A.; Ogg, G.S.; Spiegel, H.M.; Conlon, C.; Spina, C.A.; et al. HIV-Specific CD8+ T Cells Produce Antiviral Cytokines but Are Impaired in Cytolytic Function. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streeck, H.; Nixon, D. T Cell Immunity in Acute HIV-1 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202 (Suppl. 2), S302–S308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressing, M.E.; Horst, D.; Griffin, B.D.; Tellam, J.; Zuo, J.; Khanna, R.; Rowe, M.; Wiertz, E.J. Epstein-Barr virus evasion of CD8+ and CD4+ T cell immunity via concerted actions of multiple gene products. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunders, J.J.; Munier, M.L.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Ip, S.; Grey, P.; Smith, D.; Ramacciotti, T.; Quan, D.; Finlayson, R.; Kaldor, J.; et al. Early proliferation of CCR5+ CD38+++ antigen-specific CD4+ Th1 effector cells during primary HIV-1 infection. Blood 2005, 106, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Kinloch-De-Loes, S.; Granath, A.; Sönnerborg, A.; Goh, L.-E.; Andersson, J. Early immune activation in gut-associated and peripheral lymphoid tissue during acute HIV infection. AIDS 2007, 21, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikonda, G.; Von Herrath, M.G. Immunosuppressive Mechanisms during Viral Infectious Diseases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 677, 431–447. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Pang, N.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; Mamuti, W.; Wen, H.; Ding, J. Th17 cells are associated with the Th1/Th2-cell balance during Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Huang, N.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Viral IL-10 promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle progression via JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2020, 67, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, R.D.S.M.; Benzaken, A.S.; Saraceni, V.; Sabidó, M. HIV/AIDS epidemic in the State of Amazonas: Characteristics and trends from 2001 to 2012. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2015, 48, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Verghese, P.S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr. Primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 102, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vouloumanou, E.K.; Rafailidis, P.I.; Falagas, M.E. Current diagnosis and management of infectious mononucleosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2012, 19, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, S.; Nakamura, H. Chronic Active Epstein–Barr Virus Infection: Is It Immunodeficiency, Malignancy, or Both? Cancers 2020, 12, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupia, T.; Milia, M.G.; Atzori, C.; Gianella, S.; Audagnotto, S.; Imperiale, D.; Mighetto, L.; Pirriatore, V.; Gregori, G.; Lipani, F.; et al. Presence of Epstein–Barr virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid is associated with greater HIV RNA and inflammation. AIDS 2020, 34, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massini, G.; Siemer, D.; Hohaus, S. EBV in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 1, e2009013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.L.; Martinez, O.M. Latent Membrane Protein 1 of EBV Activates Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase to Induce Production of IL-10. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 8225–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, E.; Grabowski, M.K.; Gray, R.H.; Ndyanabo, A.; Ssekasanvu, J.; Kigozi, G.; Makumbi, F.; Serwadda, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Laeyendecker, O. Short Communication: The Interaction of HIV Set Point Viral Load and Subtype on Disease Progression. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2019, 35, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durantel, D.; Kusters, I.; Louis, J.; Manel, N.; Ottenhoff, T.H.; Picot, V.; Saaadatian-Elahi, M. Mechanisms behind TB, HBV, and HIV chronic infections. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Characteristics | PLHIV no Primary EBV | HIV/Primary EBV 19 (7.09) | No HIV/Primary EBV | Statistic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV/EBV-1 | HIV/EBV-2 | HIV/EBV-1/2 | ||||
| Sample number | 249 | 9 (47.37) | 5 (26.32) | 5 (26.32) | 65 | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Feminine | 49 (19.7) | 5 (56.0) | 1 (20.00) | 1 (20.0) | 17 (26.2) | 06.22 (0.23) # |
| Masculine | 200 (80.3) | 4 (44.0) | 4 (80.00) | 4 (80.0) | 48 (73.8) | |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 18–38 | 186 (74.70) | 8 (88.89) | 3 (60.00) | 5 (100.00) | 43 (66.15) | 07.31 (0.82) * |
| 39–59 | 59 (23.69) | 1 (11.11) | 2 (40.00) | 0 | 20 (30.77) | |
| 60–80 | 4 (01.61) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (03.08) | |
| Delay in seeking assistance (months) | ||||||
| <1 m | 122 (49.00) | 2 (22.0) | 4 (80.0) | 1 (20.0) | - | 27.47 (0.001) * |
| 1–6 m | 95 (38.00) | 7 (78.0) | 1 (20.0) | 2 (40.0) | - | |
| 7–12 m | 32 (13.00) | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| >12 m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (40.0) | - | |
| Symptomatology | ||||||
| Fever | 177 (71.08) | 7 (77.77) | 5 (100.00) | 5 (100.00) | - | 6.54 (0.69) * |
| Headache | 110 (44.18) | 7 (77.77) | 4 (80.00) | 2 (40.00) | - | |
| Myalgia and joint pain | 90 (36.14) | 5 (55.55) | 1 (20.00) | 0 | - | |
| Sore throat | 197 (79.12) | 7 (77.77) | 5 (100.00) | 3 (60.0) | - | |
| Groups | ||||||
| Asymptomatic | 132 (53.01) | 2 (22.22) | 3 (60.00) | 1 (20.00) | - | 6.09 (0.41) * |
| Oligosymptomatic | 67 (26.91) | 3 (33.33) | 1 (20.00) | 3 (60.00) | - | |
| Polysymptomatic | 50 (20.08) | 4 (44.44) | 1 (20.00) | 1 (20.00) | - | |
| Infection history | ||||||
| No | 142 (57.07) | 3 (42.86) | 3 (60.00) | 2 (40.00) | 62 (95.00) | 16.70 (0.67) * |
| Fungi | 1 (00.26) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (01.67) | |
| Bacterial (STD) | 86 (34.45) | 4 (57.14) | 2 (40.00) | 3 (60.00) | 0 | |
| HPV | 10 (4.11) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (01.67) | |
| Herpes | 9 (3.60) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (01.67) | |
| Hepatitis | 1 (00.51) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, L.M.S.; França, E.d.S.; Costa, I.B.; Lima, I.T.; Freire, A.B.C.; Ramos, F.L.d.P.; Monteiro, T.A.F.; Macedo, O.; Sousa, R.C.M.; Freitas, F.B.; et al. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Genotypes Associated with the Immunopathological Profile of People Living with HIV-1: Immunological Aspects of Primary EBV Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020168
Pereira LMS, França EdS, Costa IB, Lima IT, Freire ABC, Ramos FLdP, Monteiro TAF, Macedo O, Sousa RCM, Freitas FB, et al. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Genotypes Associated with the Immunopathological Profile of People Living with HIV-1: Immunological Aspects of Primary EBV Infection. Viruses. 2022; 14(2):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020168
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Leonn Mendes Soares, Eliane dos Santos França, Iran Barros Costa, Igor Tenório Lima, Amaury Bentes Cunha Freire, Francisco Lúzio de Paula Ramos, Talita Antonia Furtado Monteiro, Olinda Macedo, Rita Catarina Medeiros Sousa, Felipe Bonfim Freitas, and et al. 2022. "Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Genotypes Associated with the Immunopathological Profile of People Living with HIV-1: Immunological Aspects of Primary EBV Infection" Viruses 14, no. 2: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020168
APA StylePereira, L. M. S., França, E. d. S., Costa, I. B., Lima, I. T., Freire, A. B. C., Ramos, F. L. d. P., Monteiro, T. A. F., Macedo, O., Sousa, R. C. M., Freitas, F. B., Brasil Costa, I., & Vallinoto, A. C. R. (2022). Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Genotypes Associated with the Immunopathological Profile of People Living with HIV-1: Immunological Aspects of Primary EBV Infection. Viruses, 14(2), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020168







