Vector Competence of German Aedes punctor (Kirby, 1837) for West Nile Virus Lineages 1 and 2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
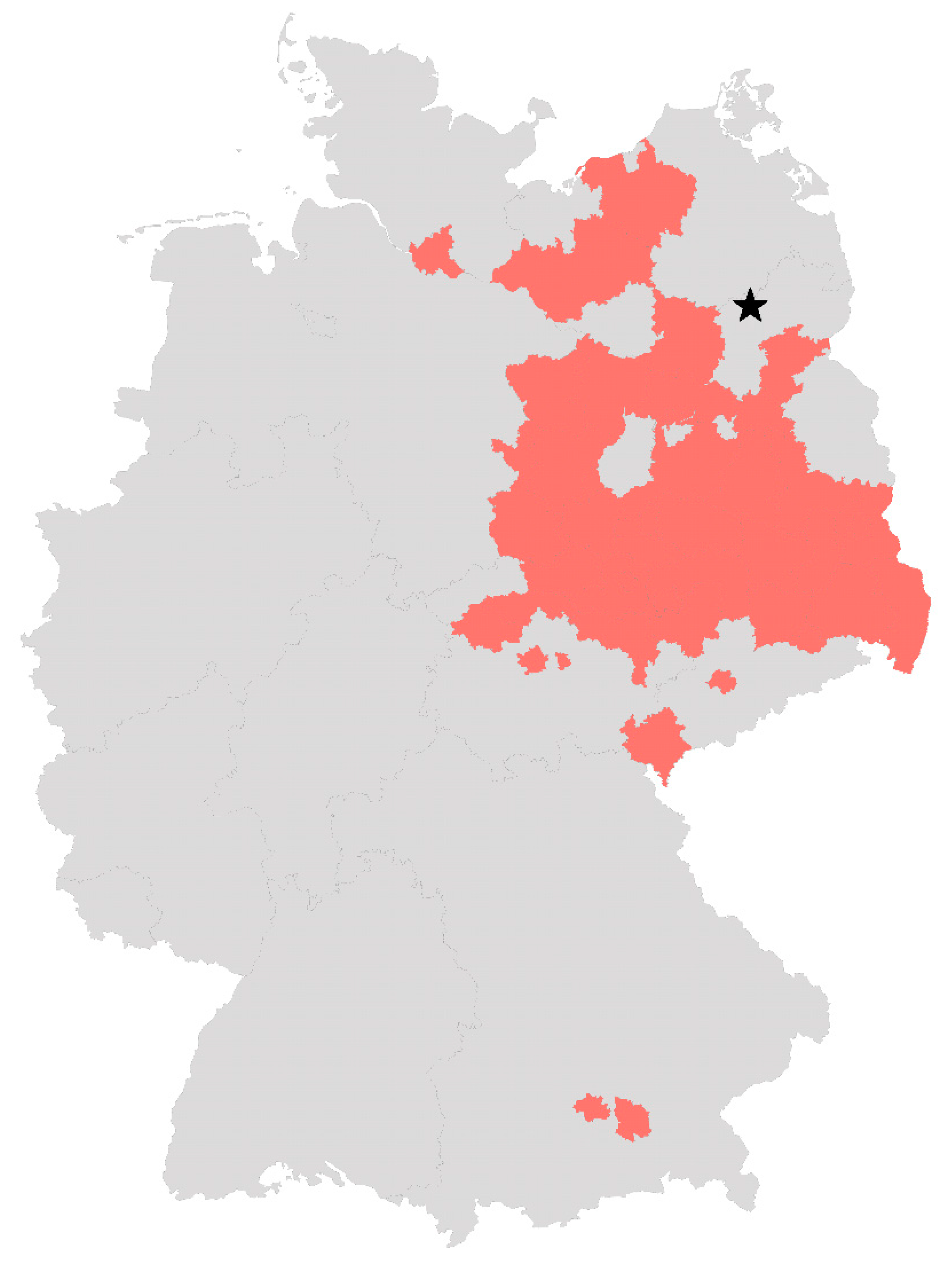
2.1. Mosquito Collection, Identification and Rearing
2.2. Cells and Viruses
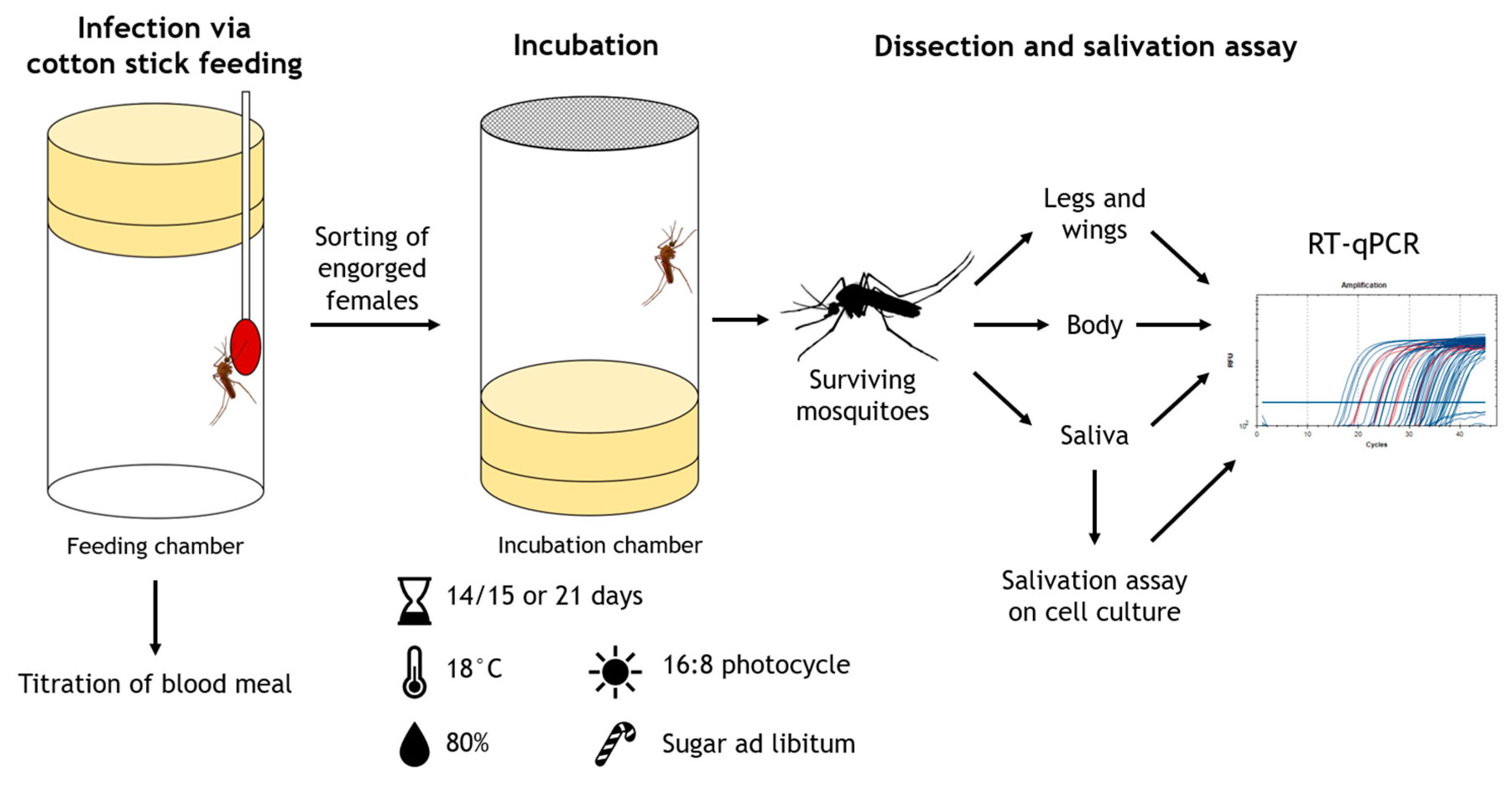
2.3. Vector Competence Study
2.4. Nucleic Acid Extractions and Analysis
2.5. Bloodfeeding, Mosquito Survival and Vector Competence Indices
3. Results
3.1. Mosquito Species Confirmation amd Flavivirus Screening
3.2. Titration and Incubation
3.3. Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hubálek, Z. Mosquito-borne viruses in Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habarugira, G.; Suen, W.W.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Hall, R.A.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H. West Nile virus: An update on pathobiology, epidemiology, diagnostics, control and “One Health” implications. Pathogens 2020, 9, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiakos, G.; Athanasious, L.V.; Touloudi, A.; Papatsiros, V.; Spyrou, V.; Petrovska, L.; Billinis, C. West Nile Virus: Basic Principles, Replication Mechanism, Immune Response and Important Genetic Determinants of Virulence. In Viral Replication; Rosas-Acosta, G., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 43–68. ISBN 978-953-51-1055-2. [Google Scholar]
- Byas, A.D.; Ebel, G.D. Comparative pathology of West Nile virus in humans and non-human animals. Pathogens 2020, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardos, V.; Adamcova, J.; Dedei, S.; Gjini, N.; Rosicky, B.; Simkova, A. Neutralizing antibodies against some neurotropic viruses determined in human sera in Albania. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1959, 3, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murgue, B.; Murri, S.; Triki, H.; Deubel, V.; Zeller, H.G. West Nile in the Mediterranean Basin: 1950-2000. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.F.; Popovici, F.; Cernescu, C.; Campbell, G.L.; Nedelcu, N.I. West Nile encephalitis epidemic in southeastern Romania. Lancet 1998, 352, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancey, C.; Grinev, A.; Volkova, E.; Rios, M. The global ecology and epidemiology of West Nile virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 376230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, T.; Ivanics, E.; Erdélyi, K.; Ursu, K.; Ferenczi, E.; Weissenböck, H.; Nowotny, N. Lineage 1 and 2 strains of encephalitic West Nile virus, central Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, T.; Ferenczi, E.; Erdélyi, K.; Kutasi, O.; Csörgő, T.; Seidel, B.; Weissenböck, H.; Brugger, K.; Bán, E.; Nowotny, N. Explosive spread of a neuroinvasive lineage 2 West Nile virus in central Europe, 2008/2009. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danis, K.; Papa, A.; Theocharopoulos, G.; Dougas, G.; Athanasiou, M.; Detsis, M.; Baka, A.; Lytras, T.; Mellou, K.; Bonovas, S.; et al. Outbreak of West Nile virus infection in Greece, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, I.; Bakonyi, T.; Sebesta, O.; Mendel, J.; Peško, J.; Betášová, L.; Blažejová, H.; Venclíková, K.; Straková, P.; Nowotny, N.; et al. West Nile virus lineage 2 isolated from Culex modestus mosquitoes in the Czech Republic, 2013: Expansion of the European WNV endemic area to the North? Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, U.; Lühken, R.; Keller, M.; Cadar, D.; van der Grinten, E.; Michel, F.; Albrecht, K.; Eiden, M.; Rinder, M.; Lachmann, L.; et al. West Nile virus epizootic in Germany, 2018. Antivir. Res. 2019, 162, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, U.; Santos, P.D.; Groschup, M.H.; Hattendorf, C.; Eiden, M.; Höper, D.; Eisermann, P.; Keller, M.; Michel, F.; Klopfleisch, R.; et al. West Nile virus epidemic in Germany triggered by epizootic emergence, 2019. Viruses 2020, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, U.; Bergmann, F.; Fischer, D.; Müller, K.; Holicki, C.M.; Sadeghi, B.; Sieg, M.; Keller, M.; Schwehn, R.; Reuschel, M.; et al. Spread of West Nile virus and Usutu virus in the German bird population, 2019–2020. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C.; Lachmann, R.; Stark, K.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Eisermann, P.; Lühken, R. Autochthone Infektionen mit dem West-Nil-Virus in Deutschland 2018 und 2019. Epid. Bull. 2020, 25, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, C.; Michalski, D.; Münch, J.; Petros, S.; Bergs, S.; Trawinski, H.; Lübbert, C.; Liebert, U.G. Autochthonous West Nile virus infection outbreak in humans, Leipzig, Germany, August to September 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, H.; Holicki, C.M.; Ziegler, U.; Groschup, M.H.; Tews, B.A.; Werner, D. West Nile virus mosquito vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) in Germany. Viruses 2020, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, H.; Tews, B.A.; Werner, D. First evidence of West Nile virus overwintering in mosquitoes in Germany. Viruses 2021, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, A.W.E.; Kantor, A.M.; Passarelli, A.L.; Clem, R.J. Tissue barriers to arbovirus infection in mosquitoes. Viruses 2015, 7, 3741–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciota, A.T.; Kramer, L.D. Vector-virus interactions and transmission dynamics of West Nile virus. Viruses 2013, 5, 3021–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holicki, C.M.; Ziegler, U.; Răileanu, C.; Kampen, H.; Werner, D.; Schulz, J.; Silaghi, C.; Groschup, M.H.; Vasić, A. West Nile virus lineage 2 vector competence of indigenous Culex and Aedes mosquitoes from Germany at temperate climate conditions. Viruses 2020, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fros, J.J.; Geertsema, C.; Vogels, C.B.; Roosjen, P.P.; Failloux, A.-B.; Vlak, J.M.; Koenraadt, C.J.; Takken, W.; Pijlman, G.P. West Nile virus: High transmission rate in north-western European mosquitoes indicates its epidemic potential and warrants increased surveillance. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, A.M.; Fonseca, D.M.; Ebel, G.D.; Reddy, M.R.; Kramer, L.D. Spatial and temporal variation in vector competence of Culex pipiens and Cx. restuans mosquitoes for West Nile virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogels, C.B.F.; Göertz, G.P.; Pijlman, G.P.; Koenraadt, C.J. Vector competence of European mosquitoes for West Nile virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, H.; Walther, D. Vector potential of mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae) occurring in central Europe. In Mosquito-Borne Diseases; Benelli, G., Mehlhorn, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 41–68. ISBN 978-3-319-94074-8. [Google Scholar]
- Martinet, J.-P.; Ferté, H.; Failloux, A.-B.; Schaffner, F.; Depaquit, J. Mosquitoes of north-western Europe as potential vectors of arboviruses: A review. Viruses 2019, 11, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Krüger, A.; Kuhn, C.; Plenge-Bönig, A.; Thomas, S.M.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Tannich, E. Stechmücken als Überträger exotischer Krankheitserreger in Deutschland. Bundesgesundheitsbl. Gesundheitsforsch. Gesundheitssch. 2014, 57, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, D.; Kowalczyk, S.; Kampen, H. Nine years of mosquito monitoring in Germany, 2011-2019, with an updated inventory of German culicid species. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Petrić, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.B.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes: Identification, Ecology and Control, 3rd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-11623-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, K.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Isawa, H.; Sasaki, T.; Higa, Y.; Kasai, S.; Tsuda, Y.; Sawabe, K.; Kobayashi, M. Entomological surveillance for flaviviruses at migratory bird stopover sites in Hokkaido, Japan, and a new insect flavivirus detected in Aedes galloisi (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejiri, H.; Sato, Y.; Kim, K.S.; Tsuda, Y.; Murata, K.; Saito, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Shimura, Y.; Yukawa, M. Blood meal identification and prevalence of avian malaria parasite in mosquitoes collected at Kushiro wetland, a subarctic zone of Japan. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Service, M.W. Feeding behaviour and host preferences of British mosquitoes. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1971, 60, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeil, C.; Lavillaureix, J.; Beeb, E. Sur la conservation et la transmission du virus West Nile par quelques arthropodes. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1960, 53, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Medlock, J.M.; Snow, K.R.; Leach, S. Potential transmission of West Nile virus in the British Isles: An ecological review of candidate mosquito bridge vectors. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2005, 19, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, O.; Savini, G.; Papa, A.; Figuerola, J.; Groschup, M.H.; Kampen, H.; Medlock, J.; Vaux, A.; Wilson, A.J.; Werner, D.; et al. European surveillance for West Nile virus in mosquito populations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4869–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TierSeuchenInformationsSystem (TSIS): Infektion Mit Dem West-Nil-Virus bei Einem Vogel Oder Pferd [WNV]. Available online: https://tsis.fli.de/ (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Sachse, K.; Ziegler, U.; Chaintoutis, S.C.; Keller, M.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. A novel pan-flavivirus detection and identification assay based on RT-qPCR and microarray. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4248756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Heitmann, A.; Jansen, S.; Lühken, R.; Leggewie, M.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Tannich, E. Forced salivation as a method to analyze vector competence of mosquitoes. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, 57980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Depner, K.; Schirrmeier, H.; Beer, M. A universal heterologous internal control system for duplex real-time RT-PCR assays used in a detection system for pestiviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 136, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiden, M.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Ziegler, U.; Groschup, M.H. Two new real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays with unique target sites for the specific and sensitive detection of lineages 1 and 2 West Nile virus strains. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.D.; Ciota, A.T. Dissecting vectorial capacity for mosquito-borne viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, C.B.F.; Fros, J.J.; Göertz, G.P.; Pijlman, G.P.; Koenraadt, C.J.M. Vector competence of northern European Culex pipiens biotypes and hybrids for West Nile virus is differentially affected by temperature. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaslow, D.C.; Welburn, S. Insect-transmitted pathogens in the insect midgut. In Biology of the Insect Midgut; Lehane, M.J., Billingsley, P.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 432–462. ISBN 978-94-010-7179-6. [Google Scholar]
- Brackney, D.E.; Beane, J.E.; Ebel, G.D. RNAi targeting of West Nile virus in mosquito midguts promotes virus diversification. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjona, A.; Wang, P.; Montgomery, R.R.; Fikrig, E. Innate immune control of West Nile virus infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggewie, M.; Badusche, M.; Rudolf, M.; Jansen, S.; Börstler, J.; Krumkamp, R.; Huber, K.; Krüger, A.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Tannich, E.; et al. Culex pipiens and Culex torrentium populations from central Europe are susceptible to West Nile virus infection. One Health 2016, 2, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolay, B.; Diallo, M.; Faye, O.; Boye, C.S.; Sall, A.A. Vector competence of Culex neavei (Diptera: Culicidae) for Usutu virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langevin, S.A.; Bunning, M.; Davis, B.; Komar, N. Experimental infection of chickens as candidate sentinels for West Nile virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holicki, C.M.; Michel, F.; Vasić, A.; Fast, C.; Eiden, M.; Răileanu, C.; Kampen, H.; Werner, D.; Groschup, M.H.; Ziegler, U. Pathogenicity of West Nile virus lineage 1 to German poultry. Vaccines 2020, 8, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhnke, E.; Vasic, A.; Raileanu, C.; Holicki, C.M.; Tews, B.A.; Silaghi, C. Comparison of vector competence of Aedes vexans Green River and Culex pipiens biotype pipiens for West Nile virus lineages 1 and 2. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Nie, K.; Du, S.; Qiu, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, P.; Cheng, G. Flavivirus NS1 protein in infected host sera enhances viral acquisition by mosquitoes. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fros, J.J.; Miesen, P.; Vogels, C.B.; Gaibani, P.; Sambri, V.; Martina, B.E.; Koenraadt, C.J.; van Rij, R.P.; Vlak, J.M.; Takken, W.; et al. Comparative Usutu and West Nile virus transmission potential by local Culex pipiens mosquitoes in north-western Europe. One Health 2015, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, S. Climate change impacts on West Nile virus transmission in a global context. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20130561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutscher Wetterdienst. Deutschlandwetter im Mai 2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/presse/pressemitteilungen/DE/2021/20210531_deutschlandwetter_mai2021_news.html#:~:text=Mit%2010%2C7%20Grad%20Celsius,sogar%20%2D2%2C4%20Grad (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Barker, C.M.; Reisen, W.K. Epidemiology of vector-borne diseases. In Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 3rd ed.; Mullen, G.R., Durden, L.A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK; San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 33–49. ISBN 9780128140437. [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd, L.A.; Gaĭdamovich, S.I.; Obukhova, V.R.; Vigovskiĭ, A.I.; Emdina, I.A. Izuchenie biologicheskikh svoĭstv virusa Olyka, vydelennogo ot komarov (Culicidae) na Zapade Ukrainy. Vopr. Virusol. 1973, 18, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brummer-korvenkontio, M.; Saikku, P.; Kor-honen, P.; Ulmanen, I.; Reunala, T.; Karvonen, J. Arboviruses in Finland. IV. Isolation and characterization of Inkoo virus, a Finnish representative of the California group. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1973, 22, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traavik, T.; Mehl, R.; Wiger, R. Mosquito-borne arboviruses in Norway: Further isolations and detection of antibodies to California encephalitis viruses in human, sheep and wildlife sera. J. Hyg. 1985, 94, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, H.; Werner, D. Die wiederkehrende Notwendigkeit von Stechmücken-Surveillance und -Forschung. Bundesgesundheitsbl. Gesundheitsforsch. Gesundheitssch. 2015, 58, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, D.M.; Grass, P.N.; Judd, B.D.; Ligate, L.V.; Peter, K.K. Bunyavirus isolations from mosquitoes in the western Canadian Arctic. J. Hyg. 1977, 79, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z.; Rudolf, I.; Nowotny, N. Arboviruses pathogenic for domestic and wild animals. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 89, 201–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingström, O.; Wesula Lwande, O.; Näslund, J.; Spyckerelle, I.; Engdahl, C.; von Schoenberg, P.; Ahlm, C.; Evander, M.; Bucht, G. Detection of Sindbis and Inkoo virus RNA in genetically typed mosquito larvae sampled in northern Sweden. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Virus | Incubation Period | IR n/n (%) | DR n/n (%) | TR n/n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WNV lineage 1 | 14 days 21 days | 2/58 (3.45) 0/12 (0.00) | 1/2 (50.00) 0/0 (0.00) | 0/0 (0.00) 0/0 (0.00) |
| WNV lineage 2 | 14/15 days 21 days | 4/74 (5.41) 1/11 (9.09) | 1/4 (25.00) 0/0 (0.00) | 0/0 (0.00) 0/0 (0.00) |
| Virus | Sample | Incubation Period (Days) | Bodies | Legs and Wings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cq-Value | Corresponds to TCID50/mL 1 | Cq-Value | Corresponds to TCID50/mL 1 | |||
| WNV lineage 1 | #1 #2 | 14 14 | 32.80 32.00 | 8.38 × 103 2.61 × 103 | ND 33.57 | ND 1.08 × 103 |
| WNV lineage 2 | #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 | 14 14 15 15 21 | 17.71 34.91 21.98 37.95 37.94 | 1.29 × 108 1.21 × 103 2.66 × 107 7.71 × 102 5.52 × 102 | 33.11 ND ND ND ND | 4.09 × 103 ND ND ND ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Körsten, C.; AL-Hosary, A.A.; Schäfer, M.; Tews, B.A.; Werner, D.; Kampen, H.; Vasic, A.; Silaghi, C. Vector Competence of German Aedes punctor (Kirby, 1837) for West Nile Virus Lineages 1 and 2. Viruses 2022, 14, 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122787
Körsten C, AL-Hosary AA, Schäfer M, Tews BA, Werner D, Kampen H, Vasic A, Silaghi C. Vector Competence of German Aedes punctor (Kirby, 1837) for West Nile Virus Lineages 1 and 2. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122787
Chicago/Turabian StyleKörsten, Christin, Amira A. AL-Hosary, Mandy Schäfer, Birke A. Tews, Doreen Werner, Helge Kampen, Ana Vasic, and Cornelia Silaghi. 2022. "Vector Competence of German Aedes punctor (Kirby, 1837) for West Nile Virus Lineages 1 and 2" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122787
APA StyleKörsten, C., AL-Hosary, A. A., Schäfer, M., Tews, B. A., Werner, D., Kampen, H., Vasic, A., & Silaghi, C. (2022). Vector Competence of German Aedes punctor (Kirby, 1837) for West Nile Virus Lineages 1 and 2. Viruses, 14(12), 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122787







