Neutralizing and Epitope-Specific Antibodies against Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Maternal and Cord Blood Paired Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
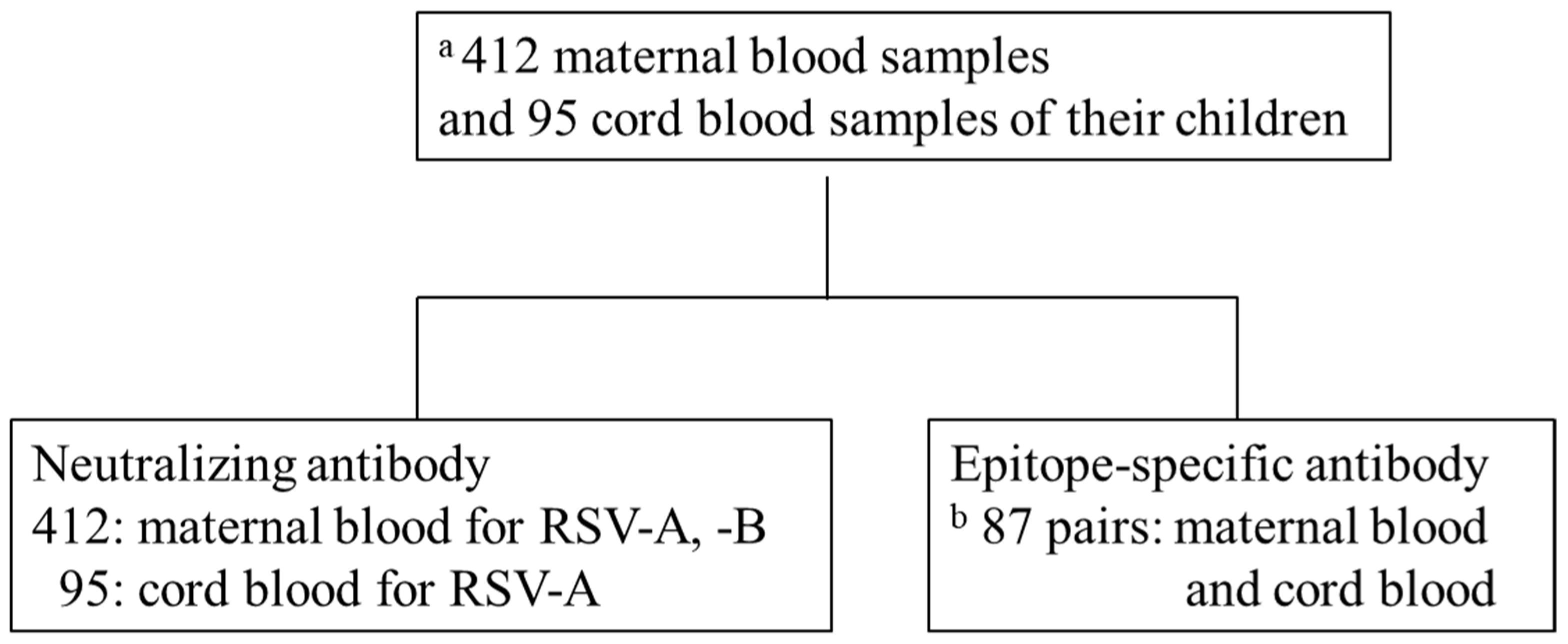
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Viruses and Cells
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Virus Titration
2.5. Neutralization Test
2.6. Determination of ESA Levels against RSV
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Maternal and Infant Background
3.2. NATs against RSV-A and -B in MB
3.3. NATs against RSV-A in MB and CB
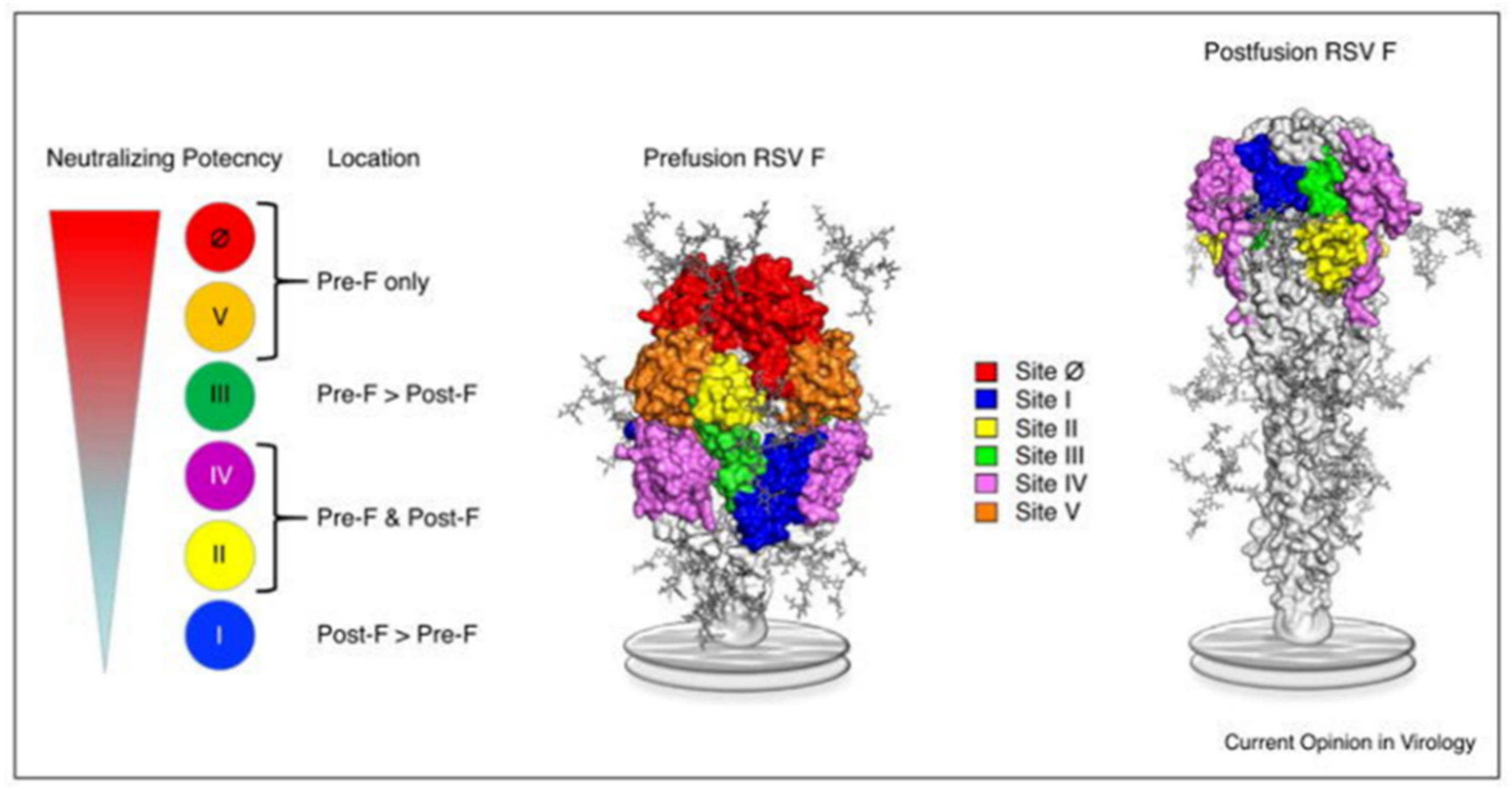
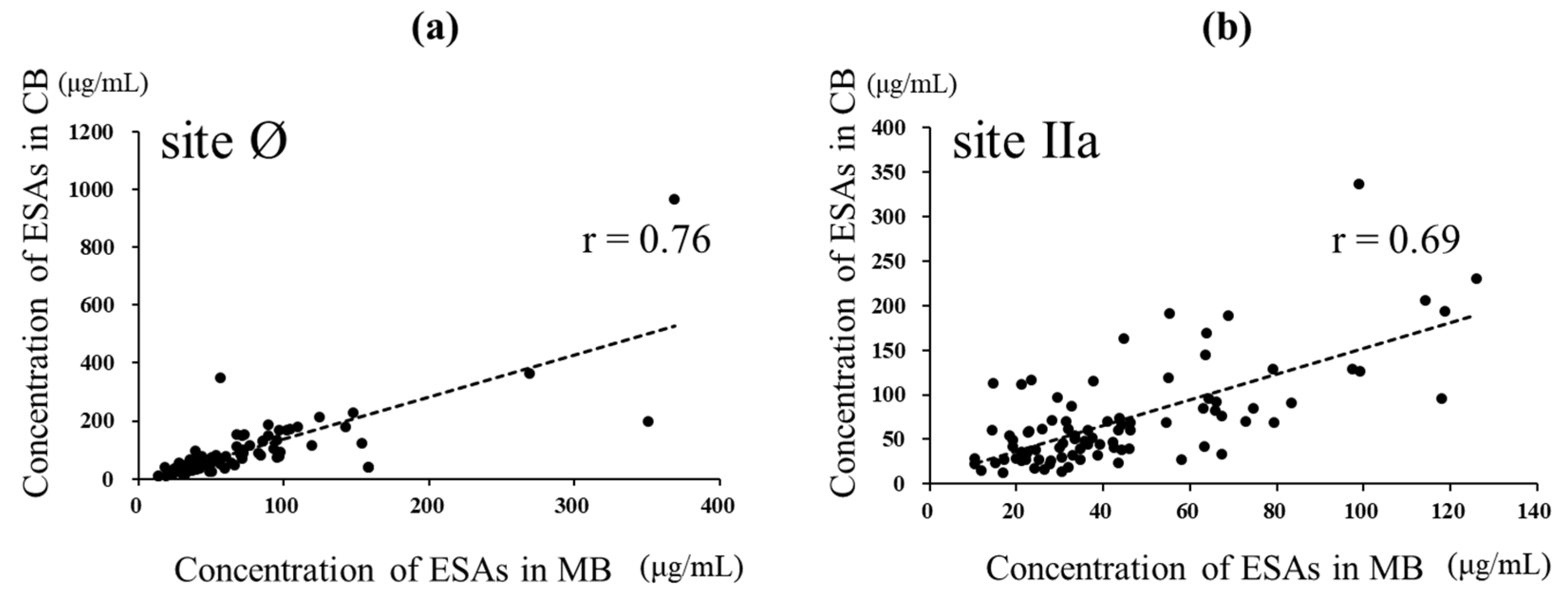
3.4. Amount of Anti-RSV-Specific Antibodies against Various Epitopes in MB and CB
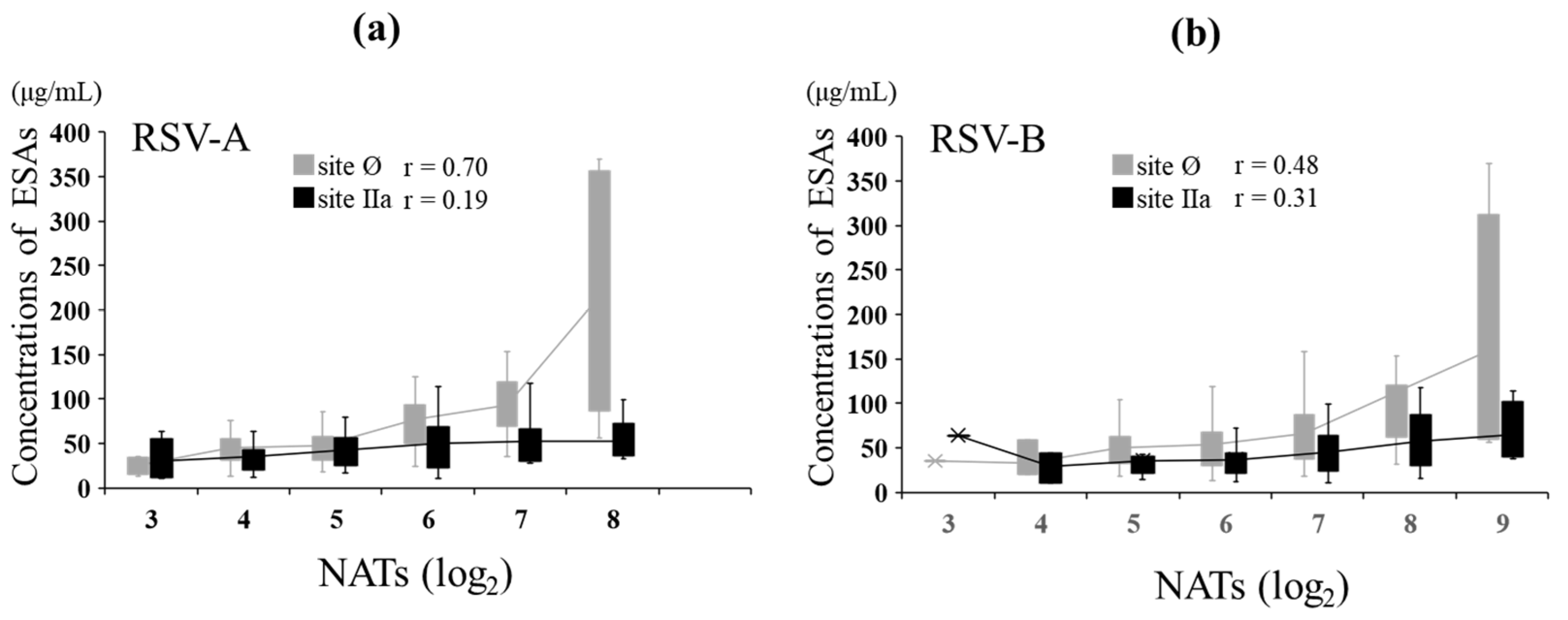
3.5. NATs and ESA Levels against RSV-A and RSV-B in MB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alansari, K.; Toaimah, F.H.; Almatar, D.H.; El Tatawy, L.A.; Davidson, B.L.; Qusad, M.I.M. Monoclonal Antibody Treatment of RSV Bronchiolitis in Young Infants: A Randomized Trial. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20182308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modjarrad, K.; Giersing, B.; Kaslow, D.C.; Smith, P.G.; Moorthy, V.S.; Group, W.R.V.C.E. WHO consultation on Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Development Report from a World Health Organization Meeting held on 23–24 March 2015. Vaccine 2016, 34, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, J.A.; Moore, M.L. Influence of respiratory syncytial virus strain differences on pathogenesis and immunity. Curr Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welliver, R.C.; Hall, C.B. Respiratory Syncytial Virus. In Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Cherry, J.D., Harrison, G.J., Kaplan, S.L., Steinbach, W.J., Hotes, P.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia PA, USA, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 1780–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.S. Vaccine development for respiratory syncytial virus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Diaz, D.; Mousa, J.J. Antibody Epitopes of Pneumovirus Fusion Proteins. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battles, M.B.; McLellan, J.S. Respiratory syncytial virus entry and how to block it. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, J.S.; Chen, M.; Leung, S.; Graepel, K.W.; Du, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Baxa, U.; Yasuda, E.; Beaumont, T.; et al. Structure of RSV fusion glycoprotein trimer bound to a prefusion-specific neutralizing antibody. Science 2013, 340, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.A.; Settembre, E.C.; Shaw, C.A.; Dey, A.K.; Rappuoli, R.; Mandl, C.W.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Carfi, A. Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9619–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zheng, Z.Z.; Chen, M.; Modjarrad, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, L.T.; Cao, J.L.; Sun, Y.P.; McLellan, J.S.; Graham, B.S.; et al. Discovery of a Prefusion Respiratory Syncytial Virus F-Specific Monoclonal Antibody That Provides Greater In Vivo Protection than the Murine Precursor of Palivizumab. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00176-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.P.; Khan, A.A.; Esser, M.T.; Jensen, K.; Takas, T.; Kankam, M.K.; Villafana, T.; Dubovsky, F. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of MEDI8897, the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F-Targeting Monoclonal Antibody with an Extended Half-Life, in Healthy Adults. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01714-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.P.; Yuan, Y.; Takas, T.; Domachowske, J.B.; Madhi, S.A.; Manzoni, P.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Esser, M.T.; Khan, A.A.; Dubovsky, F.; et al. Single-Dose Nirsevimab for Prevention of RSV in Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedra, P.A.; Hause, A.M.; Aideyan, L. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV): Neutralizing Antibody, a Correlate of Immune Protection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1442, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvie, M.M.; Vathenen, A.S.; Radford, M.; Codd, J.; Key, S. Maternal antibody and respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. J. Med. Virol. 1981, 7, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glezen, W.P.; Paredes, A.; Allison, J.E.; Taber, L.H.; Frank, A.L. Risk of respiratory syncytial virus infection for infants from low-income families in relationship to age, sex, ethnic group, and maternal antibody level. J. Pediatr. 1981, 98, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhi, S.A.; Polack, F.P.; Piedra, P.A.; Munoz, F.M.; Trenholme, A.A.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Swamy, G.K.; Agrawal, S.; Ahmed, K.; August, A.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination during Pregnancy and Effects in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.Y.; Steinhoff, M.C.; Magaret, A.; Zaman, K.; Roy, E.; Langdon, G.; Formica, M.A.; Walsh, E.E.; Englund, J.A. Respiratory syncytial virus transplacental antibody transfer and kinetics in mother-infant pairs in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwuta, J.O.; Chen, M.; Modjarrad, K.; Joyce, M.G.; Kanekiyo, M.; Kumar, A.; Yassine, H.M.; Moin, S.M.; Killikelly, A.M.; Chuang, G.Y.; et al. Prefusion F-specific antibodies determine the magnitude of RSV neutralizing activity in human sera. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 309ra162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, I.; Wicht, O.; Luytjes, W.; Leenhouts, K.; Rottier, P.J.M.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Haijema, B.J.; de Haan, C.A.M. Characterization of Epitope-Specific Anti-Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Anti-RSV) Antibody Responses after Natural Infection and after Vaccination with Formalin-Inactivated RSV. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5965–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Nitta, H.; Murata, K.; Toda, E.; Tsukamoto, N.; Hasegawa, M.; Yamagata, Z.; Kayama, F.; Kishi, R.; Ohya, Y.; et al. Rationale and study design of the Japan environment and children’s study (JECS). BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michikawa, T.; Nitta, H.; Nakayama, S.F.; Yamazaki, S.; Isobe, T.; Tamura, K.; Suda, E.; Ono, M.; Yonemoto, J.; Iwai-Shimada, M.; et al. Baseline Profile of Participants in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS). J. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jounai, N.; Yoshioka, M.; Tozuka, M.; Inoue, K.; Oka, T.; Miyaji, K.; Ishida, K.; Kawai, N.; Ikematsu, H.; Kawakami, C.; et al. Age-Specific Profiles of Antibody Responses against Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englund, J.; Glezen, W.P.; Piedra, P.A. Maternal immunization against viral disease. Vaccine 1998, 16, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englund, J.A.; Mbawuike, I.N.; Hammill, H.; Holleman, M.C.; Baxter, B.D.; Glezen, W.P. Maternal immunization with influenza or tetanus toxoid vaccine for passive antibody protection in young infants. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacimustafaoglu, M.; Celebi, S.; Aynaci, E.; Sinirtas, M.; Koksal, N.; Kucukerdogan, A.; Ercan, I.; Goral, G.; Ildirim, I. The progression of maternal RSV antibodies in the offspring. Arch. Dis. Child 2004, 89, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simister, N.E. Placental transport of immunoglobulin G. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3365–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, P.F.; Farr, R.S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: Evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature 1966, 210, 1070–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H. Comparison of maternal and fetal serum IgG levels at birth. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi 1988, 40, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto, K.; Nieminen, T.; Mejias, A.; Capella Gonzalez, C.; Ye, F.; Mertz, S.; Peeples, M.; Ramilo, O.; Saxen, H. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)-Specific Antibodies in Pregnant Women and Subsequent Risk of RSV Hospitalization in Young Infants. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedra, P.A.; Jewell, A.M.; Cron, S.G.; Atmar, R.L.; Glezen, W.P. Correlates of immunity to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) associated-hospitalization: Establishment of minimum protective threshold levels of serum neutralizing antibodies. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3479–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The IMpact-RSV Study Group. Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. Pediatrics 1998, 102, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Battles, M.B.; Lin, C.C.; Bianchi, S.; Corti, D.; McLellan, J.S. Alternative conformations of a major antigenic site on RSV F. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensballe, L.G.; Ravn, H.; Kristensen, K.; Meakins, T.; Aaby, P.; Simoes, E.A. Seasonal variation of maternally derived respiratory syncytial virus antibodies and association with infant hospitalizations for respiratory syncytial virus. J. Pediatr. 2009, 154, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobugawa, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Hibino, A.; Hassan, M.R.; Yagami, R.; Kondo, H.; Odagiri, T.; Saito, R. Occurrence of human respiratory syncytial virus in summer in Japan. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Hosoya, M. Neutralizing epitopes of RSV and palivizumab resistance in Japan. Fukushima J. Med. Sci. 2017, 63, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | 412 pairs | 95 pairs | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal | |||
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 31 (27–34) | 30 (27–33) | 0.575 |
| Gestational age (weeks (w) +days (d)), median (IQR) | 39 w + 3 d (38 w + 2 d − 40 w + 2 d) | 39 w + 4 d (38 w + 5 d − 40 w + 4 d) | 0.137 |
| Delivery type: cesarean section, n (%) | 84 (20.4) | 18 (19.0) | 0.796 |
| Children living together, n (%) | 227 (55.2) | 50 (52.6) | 0.803 |
| Neonates | |||
| Birth weight (g), median (IQR) | 2991 (2733–3253) | 2992 (2720–3248) | 0.594 |
| Male, n (%) | 208 (50.5) | 53 (55.8) | 0.602 |
| Premature birth, n (%) | 22 (5.3) | 4 (4.2) | 0.801 |
| Umbilical artery blood pH, median (IQR) | 7.33 (7.29–7.36) | 7.32 (7.28–7.35) | 0.443 |
| Sample (n) | RSV-A (412) | RSV-B (412) | p * Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAT, median (IQR) | 1:32 (1:32–1:64) | 1:64 (1:64–1:128) | - |
| GMT (95% CI) | 5.45 (5.33–5.56) | 6.48 (6.36–6.60) | <0.001 0.85 |
| Sample (n) | Maternal Blood (95) | Cord Blood (95) | p * Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAT, median (IQR) | 1:32 (1:32–1:64) | 1:64 (1:32–1:128) | - |
| GMT (95% CI) | 5.49 (5.25–5.73) | 5.91 (5.69–6.12) | 0.0103 0.36 |
| NAT (log2) | Site Ø | Site IIa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSV-A (μg/mL) Mean ± SD | RSV-B (μg/mL) Mean ± SD | p * | RSV-A (μg/mL) Mean ± SD | RSV-B (μg/mL) Mean ± SD | p * | |
| 3 | 25.47 ± 10.29 | 35.44 | - | 30.03 ± 23.67 | 64.19 | - |
| 4 | 44.71 ± 20.02 | 33.30 ± 22.40 | 0.292 | 34.96 ± 25.34 | 29.22 ± 17.17 | 0.924 |
| 5 | 47.42 ± 24.52 | 49.67 ± 24.42 | 0.689 | 43.21 ± 23.85 | 35.89 ± 26.48 | 0.166 |
| 6 | 77.58 ± 35.19 | 53.84 ± 37.30 | 0.007 | 49.77 ± 28.63 | 37.20 ± 18.58 | 0.177 |
| 7 | 93.59 ± 36.86 | 65.67 ± 34.03 | 0.030 | 52.31 ± 31.21 | 45.36 ± 26.61 | 0.664 |
| 8 | 214.22 ± 133.73 | 113.02 ± 90.40 | 0.083 | 53.19 ± 24.78 | 57.15 ± 32.61 | 0.741 |
| 9 | - | 159.08 ± 145.11 | - | - | 65.42 ± 34.34 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashiyama, F.; Hashimoto, K.; Norito, S.; Okabe, H.; Sato, A.; Kume, Y.; Maeda, R.; Sato, M.; Sato, M.; Kyozuka, H.; et al. Neutralizing and Epitope-Specific Antibodies against Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Maternal and Cord Blood Paired Samples. Viruses 2022, 14, 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122702
Mashiyama F, Hashimoto K, Norito S, Okabe H, Sato A, Kume Y, Maeda R, Sato M, Sato M, Kyozuka H, et al. Neutralizing and Epitope-Specific Antibodies against Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Maternal and Cord Blood Paired Samples. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122702
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashiyama, Fumi, Koichi Hashimoto, Sakurako Norito, Hisao Okabe, Akiko Sato, Yohei Kume, Ryo Maeda, Maki Sato, Masatoki Sato, Hyo Kyozuka, and et al. 2022. "Neutralizing and Epitope-Specific Antibodies against Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Maternal and Cord Blood Paired Samples" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122702
APA StyleMashiyama, F., Hashimoto, K., Norito, S., Okabe, H., Sato, A., Kume, Y., Maeda, R., Sato, M., Sato, M., Kyozuka, H., Fujimori, K., Nishigori, H., Shinoki, K., Yasumura, S., Sakuma, H., & Hosoya, M. (2022). Neutralizing and Epitope-Specific Antibodies against Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Maternal and Cord Blood Paired Samples. Viruses, 14(12), 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122702






