Histotype-Dependent Oligodendroglial PrP Pathology in Sporadic CJD: A Frequent Feature of the M2C “Strain”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
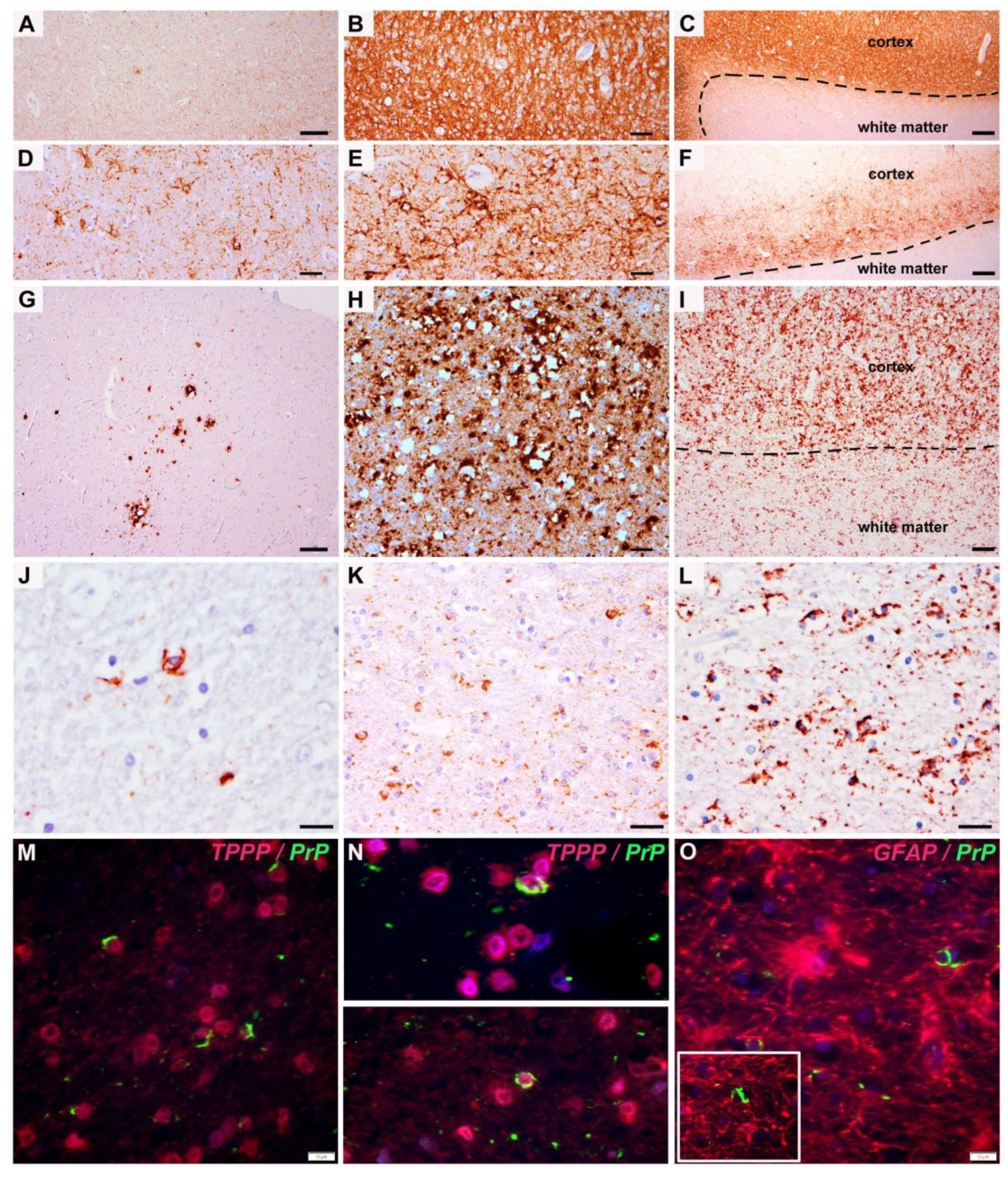
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 1991, 252, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ironside, J.W.; Sutherland, K.; Bell, J.E.; McCardle, L.; Barrie, C.; Estebeiro, K.; Zeidler, M.; Will, R.G. A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Neuropathological and clinical features. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 61, pp. 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, G.G.; Preusser, M.; Strohschneider, M.; Budka, H. Subcellular localization of disease-associated prion protein in the human brain. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bošnjak, M.; Zupan, A.; Fiorini, M.; Popović, K.Š.; Popović, M. A case of MV2K subtype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with florid-like plaques: Similarities and differences to variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neuropathology 2020, 40, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Vega, I.; Díaz-Lucena, D.; Azkune Calle, I.; Geijo, M.; Juste, R.A.; Llorens, F.; Vicente Etxenausia, I.; Santos-Juanes, J.; Zarranz Imirizaldu, J.J.; Ferrer, I. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with glial PrPRes nuclear and perinuclear immunoreactivity. Neuropathology 2018, 38, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehotzky, A.; Lau, P.; Tokési, N.; Muja, N.; Hudson, L.D.; Ovádi, J. Tubulin polymerization-promoting protein (TPPP/p25) is critical for oligodendrocyte differentiation. Glia 2010, 58, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parchi, P.; Giese, A.; Capellari, S.; Brown, P.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Windl, O.; Zerr, I.; Budka, H.; Kopp, N.; Piccardo, P.; et al. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnianski, A.; Meissner, B.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Kallenberg, K.; Bartl, M.; Heinemann, U.; Varges, D.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Zerr, I. Clinical features and diagnosis of the MM2 cortical subtype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Baiardi, S.; Polischi, B.; Mammana, A.; Franceschini, A.; Green, A.; Capellari, S.; Parchi, P. Diagnostic value of surrogate CSF biomarkers for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the era of RT-QuIC. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 3136–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Strammiello, R.; Notari, S.; Giese, A.; Langeveld, J.P.; Ladogana, A.; Zerr, I.; Roncaroli, F.; Cras, P.; Ghetti, B.; et al. Incidence and spectrum of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease variants with mixed phenotype and co-occurrence of PrPSc types: An updated classification. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grau-Rivera, O.; Sánchez-Valle, R.; Bargalló, N.; Lladó, A.; Gaig, C.; Nos, C.; Ferrer, I.; Graus, F.; Gelpi, E. Sporadic MM2-thalamic + cortical Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Utility of diffusion tensor imaging in the detection of cortical involvement In Vivo. Neuropathology 2016, 36, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Saito, Y.; Aiba, I.; Kobayashi, A.; Mimuro, M.; Kitamoto, T.; Yoshida, M. An autopsied case of MV2K+ C-type sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease presenting with widespread cerebral cortical involvement and Kuru plaques. Neuropathology 2017, 37, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, A.; Strammiello, R.; Capellari, S.; Giese, A.; Parchi, P. Regional pattern of microgliosis in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in relation to phenotypic variants and disease progression. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Morrison, B.M.; Li, Y.; Lengacher, S.; Farah, M.H.; Hoffman, P.N.; Liu, Y.; Tsingalia, A.; Jin, L.; Zhang, P.-W.; et al. Oligodendroglia metabolically support axons and contribute to neurodegeneration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 487, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Gould, E.; Xu, J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.H. Oligodendrocytes regulate presynaptic properties and neurotransmission through BDNF signaling in the mouse brainstem. eLife 2019, 8, e42156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, J.W.; Oohashi, T.; Pizzorusso, T. The roles of perineuronal nets and the perinodal extracellular matrix in neuronal function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheva, K.D.; Wolman, D.; Mensh, B.D.; Pax, E.; Buchanan, J.; Smith, S.J.; Bock, D.D. A large fraction of neocortical myelin ensheathes axons of local inhibitory neurons. eLife 2016, 5, e15784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermacher, C.; Angulo, M.C.; Benamer, N. Glutamate versus GABA in neuron–oligodendroglia communication. Glia 2019, 67, 2092–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turko, P.; Groberman, K.; Browa, F.; Cobb, S.; Vida, I. Differential Dependence of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Neurons on Glia for the Establishment of Synaptic Transmission. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Casas, R.; Rivera, R. Parvalbumin-immunoreactive cortical neurons in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 34, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guentchev, M.; Groschup, M.H.; Kordek, R.; Liberski, P.P.; Budka, H. Severe, early and selective loss of a subpopulation of GABAergic inhibitory neurons in experimental transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belichenko, P.V.; Miklossy, J.; Belser, B.; Budka, H.; Celio, M.R. Early destruction of the extracellular matrix around parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 1999, 6, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guentchev, M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Trabattoni, G.R.; Budka, H. Distribution of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in brain correlates with hippocampal and temporal cortical pathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenning, G.K.; Stefanova, N.; Jellinger, K.A.; Poewe, W.; Schlossmacher, M.G. Multiple system atrophy: A primary oligodendrogliopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; de Boni, L.; Saverioni, D.; Cohen, M.L.; Ferrer, I.; Gambetti, P.; Gelpi, E.; Giaccone, G.; Hauw, J.J.; Höftberger, R.; et al. Consensus classification of human prion disease histotypes allows reliable identification of molecular subtypes: An inter-rater study among surveillance centres in Europe and USA. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Head, M.W.; Bunn, T.; Laszlo, L.; Will, R.G.; Ironside, J.W. Clinicopathological phenotype of codon 129 valine homozygote sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2000, 26, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hachimi, K.H.; Chaunu, M.P.; Brown, P.; Foncin, J.F. Modifications of oligodendroglial cells in spongiform encephalopathies. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 154, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres Benito, P.; Dominguez Gonzalez, M.; Ferrer, I. Altered gene transcription linked to astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in frontal cortex in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Prion 2018, 12, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrés-Benito, P.; Carmona, M.; Douet, J.Y.; Cassard, H.; Andreoletti, O.; Ferrer, I. Differential astrocyte and oligodendrocyte vulnerability in murine Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Prion 2021, 15, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalone, C.; Caramelli, M.; Crescio, M.I.; Spencer, Y.I.; Simmons, M.M. BSE immunohistochemical patterns in the brainstem: A comparison between UK and Italian cases. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 111, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, M.M.; Spiropoulos, J.; Webb, P.R.; Spencer, Y.I.; Czub, S.; Mueller, R.; Davis, A.; Arnold, M.E.; Marsh, S.; Hawkins, S.A.; et al. Experimental classical bovine spongiform encephalopathy: Definition and progression of neural PrP immunolabeling in relation to diagnosis and disease controls. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiropoulos, J.; Casalone, C.; Caramelli, M.; Simmons, M.M. Immunohistochemistry for PrPSc in natural scrapie reveals patterns which are associated with the PrP genotype. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konold, T.; Bone, G.E.; Clifford, D.; Chaplin, M.J.; Cawthraw, S.; Stack, M.J.; Simmons, M.M. Experimental H-type and L-type bovine spongiform encephalopathy in cattle: Observation of two clinical syndromes and diagnostic challenges. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Case no. | Sex | Age at Death (years) | Disease Duration (months) | Histotype | Oligodendroglial PrPd White Matter | Main PrPd Pattern Frontal | Main PrPd Pattern Occipital | Intensity PrPd Deposits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | f | 72 | 3 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive |
| 2 | m | 71 | 3 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic deep laminar | diffuse synaptic | mild frontal, extensive occipital |
| 3 | m | 72 | 3 | MM/MV1 | isolated frontal (severe cortical degeneration) | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive |
| 4 | m | 73 | 5 | MM/MV1 | no | Diffuse synaptic deep laminar | diffuse synaptic deep laminar | moderate |
| 5 | f | 63 | 1.5 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive |
| 6 | m | 62 | 6 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic laminar | diffuse synaptic laminar | mild |
| 7 | f | 57 | 3 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive |
| 8 | m | 75 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | mild |
| 9 | m | 72 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate frontal, extensive occipital |
| 10 | m | 72 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 11 | f | 74 | 6 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive |
| 12 | f | 67 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 13 | m | 63 | 1 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 14 | f | 67 | 3 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 15 | m | 59 | 3.5 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate frontal, extensive occipital |
| 16 | m | 56 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 17 | f | 65 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive |
| 18 | f | 54 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate, extensive occipital |
| 19 | m | 77 | 2 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | extensive frontal, mild occipital |
| 20 | f | 65 | 1.5 | MM/MV1 | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 1 | f | 66 | 5 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal | moderate |
| 2 | m | 62 | 3 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal | moderate |
| 3 | m | 62 | 4 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal | extensive |
| 4 | f | 69 | 6 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal + plaque-like | extensive |
| 5 | f | 74 | 3 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal + plaque-like | deep perineuronal + plaque-like | moderate |
| 6 | m | 81 | 2 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal + plaque-like | deep perineuronal | mild |
| 7 | m | 74 | 3 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal + plaque-like | deep perineuronal + plaque-like | extensive frontal, mild occipital |
| 8 | m | 78 | 4 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal | extensive frontal, moderate occipital |
| 9 | f | 75 | 5 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal | moderate frontal, mild occipital |
| 10 | f | 80 | 3 | VV2 | no | deep perineuronal | deep perineuronal | moderate |
| 1 | m | 74 | 7 | MM/MV1+2C | yes, isol | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | diffuse synaptic + patchy | moderate-extensive |
| 2 | m | 65 | 17 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | extensive synaptic frontal, mild synaptic occipital |
| 3 | f | 77 | 2 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | moderate |
| 4 | m | 59 | 3 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | mild synaptic frontal, moderate synaptic occipital |
| 5 | m | 81 | 2 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | mild synaptic |
| 6 | m | 55 | 9 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic + patchy | diffuse synaptic | moderate frontal, extensive synaptic occipital |
| 7 | f | 68 | 1 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | extensive synaptic |
| 8 | f | 51 | 5 | MM/MV1+2C | yes, few frontal | patchy perivacuolar | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | extensive patchy frontal, extensive synaptic occipital |
| 9 | f | 79 | 5 | MM/MV1+2C | yes, few frontal | patchy perivacuolar | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | extensive patchy frontal, extensive synaptic occipital |
| 10 | m | 74 | 2 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | moderate synaptic |
| 11 | m | 70 | 2 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | extensive synaptic frontal, moderate synaptic occipital |
| 12 | m | 62 | 5 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | extensive |
| 13 | m | 62 | 2 | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic | diffuse synaptic | moderate |
| 14 | f | 55 | 2 | MM/MV1+2C | yes, few occipital | diffuse synaptic + patchy | diffuse synaptic + patchy | moderate frontal, extensive patchy occipital |
| 15 | f | 96 | n.a. | MM/MV1+2C | no | diffuse synaptic + focal patchy | diffuse synaptic + patchy | moderate-extensive |
| 1 | m | 66 | 3 | MV2K+C | no | mild | mild | mild |
| 2 | m | 62 | 7 | MV2K+C | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 3 | f | 62 | 13 | MV2K+C | no | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | moderate |
| 4 | m | 78 | 8 | MV2K+C | yes, few occipital | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 5 | f | 77 | 12 | MV2K+C | yes, few occipital | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 6 | m | 70 | 18 | MV2K+C | yes, isolated | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | moderate |
| 7 * | m | 63 | 31 | MV2K+C | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 8 | m | 57 | 2 | MV2K+C | no | deep perineuronal | patchy perivacuolar + synaptic | moderate frontal, extensive occipital |
| 9 | f | 73 | 9 | MV2K+C | yes, few | moderate deep laminar + extensive patchy perivacuolar | moderate deep laminar + extensive patchy perivacuolar | moderate-extensive |
| 10 | m | 57 | 57 | MV2K+C | yes, isolated | moderate deep laminar + focal patchy perivacuolar | moderate deep laminar + extensive patchy perivacuolar | moderate frontal, extensive occipital |
| 1 | f | 79 | 5 | MM2C + 1 | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 2 | f | 52 | 58 | MM2C | yes, extensive | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 3 | f | 80 | 2 | MM2C | yes, few | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | moderate frontal, extensive occipital |
| 4 | m | 78 | 22 | MMC | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
| 5 | f | 60 | 11 | MM2C + 1 | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar + synaptic | extensive |
| 6 | f | 76 | 12 | MM2C | yes, few | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | moderate |
| 7 | f | 77 | 3 | MM2C | no | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | moderate-extensive |
| 8 | f | 64 | 12 | MM2C | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | moderate frontal, extensive occipital |
| 9 | f | 60 | 2 | MM2C + 1 | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar + synaptic | extensive frontal, moderate occipital |
| 10 | f | 51 | 11 | MM2C | yes | patchy perivacuolar | patchy perivacuolar | extensive |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gelpi, E.; Klotz, S.; Vidal-Robau, N.; Ricken, G.; Regelsberger, G.; Ströbel, T.; Kalev, O.; Leoni, M.; Budka, H.; Kovacs, G.G. Histotype-Dependent Oligodendroglial PrP Pathology in Sporadic CJD: A Frequent Feature of the M2C “Strain”. Viruses 2021, 13, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091796
Gelpi E, Klotz S, Vidal-Robau N, Ricken G, Regelsberger G, Ströbel T, Kalev O, Leoni M, Budka H, Kovacs GG. Histotype-Dependent Oligodendroglial PrP Pathology in Sporadic CJD: A Frequent Feature of the M2C “Strain”. Viruses. 2021; 13(9):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091796
Chicago/Turabian StyleGelpi, Ellen, Sigrid Klotz, Nuria Vidal-Robau, Gerda Ricken, Günther Regelsberger, Thomas Ströbel, Ognian Kalev, Marlene Leoni, Herbert Budka, and Gabor G. Kovacs. 2021. "Histotype-Dependent Oligodendroglial PrP Pathology in Sporadic CJD: A Frequent Feature of the M2C “Strain”" Viruses 13, no. 9: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091796
APA StyleGelpi, E., Klotz, S., Vidal-Robau, N., Ricken, G., Regelsberger, G., Ströbel, T., Kalev, O., Leoni, M., Budka, H., & Kovacs, G. G. (2021). Histotype-Dependent Oligodendroglial PrP Pathology in Sporadic CJD: A Frequent Feature of the M2C “Strain”. Viruses, 13(9), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091796






