Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression and Purification of Wild-Type and Mutant VPg Proteins
2.2. Generation of RNA Probes and mRNA Transcripts
2.3. RNA Binding Assays
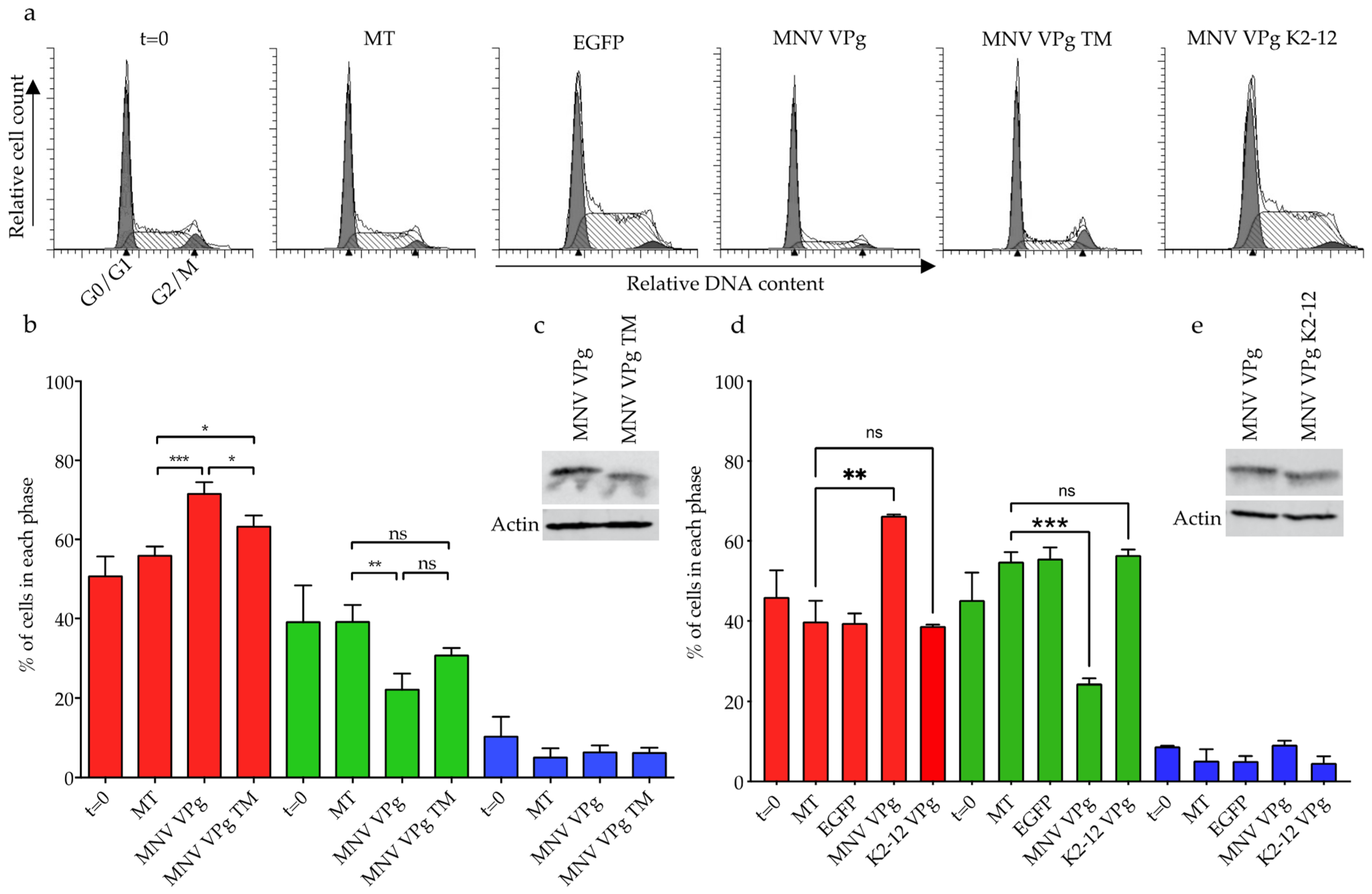
2.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
3. Results
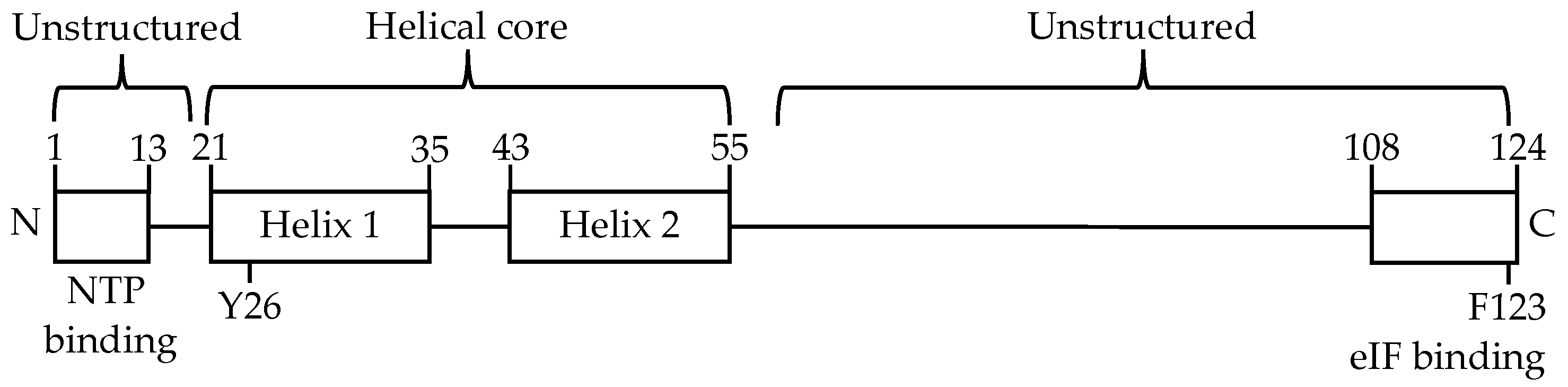
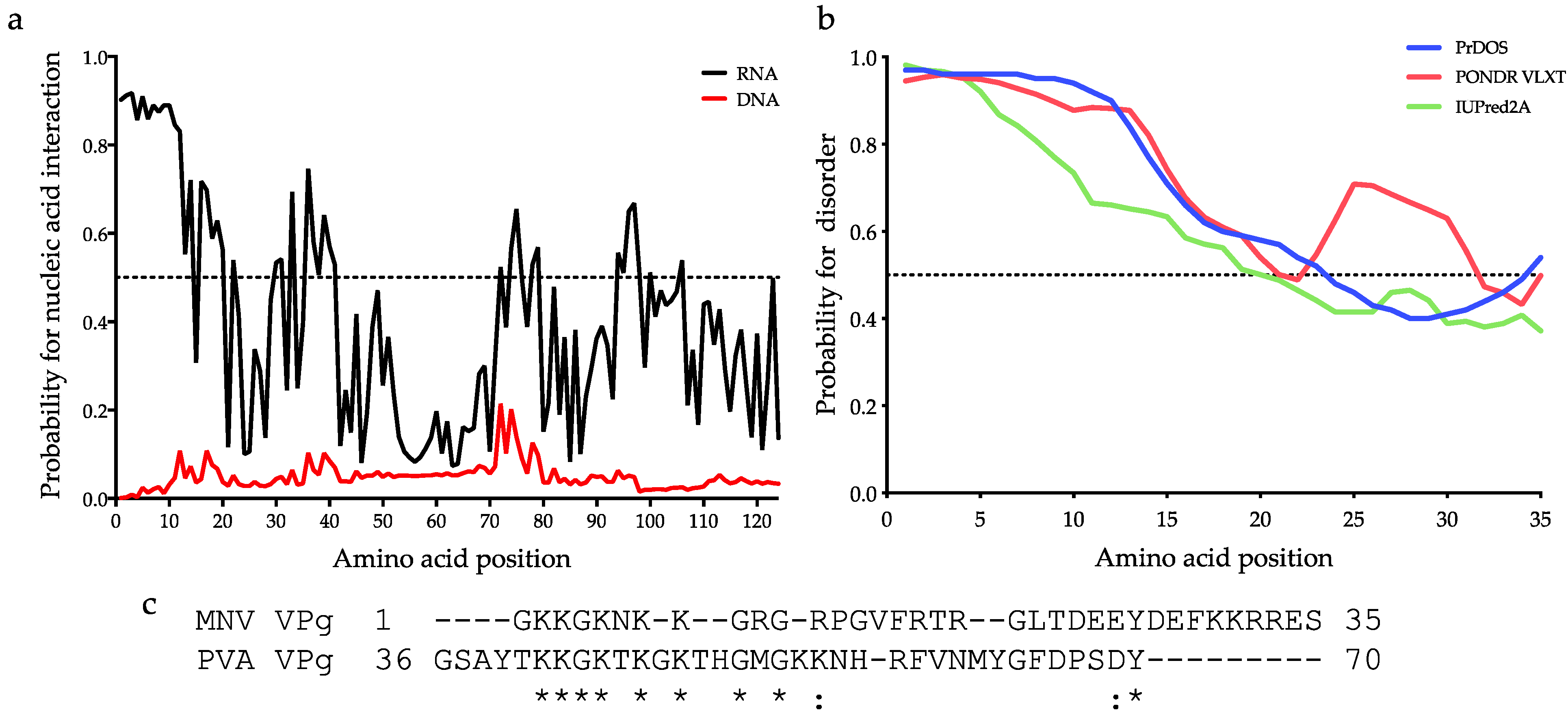
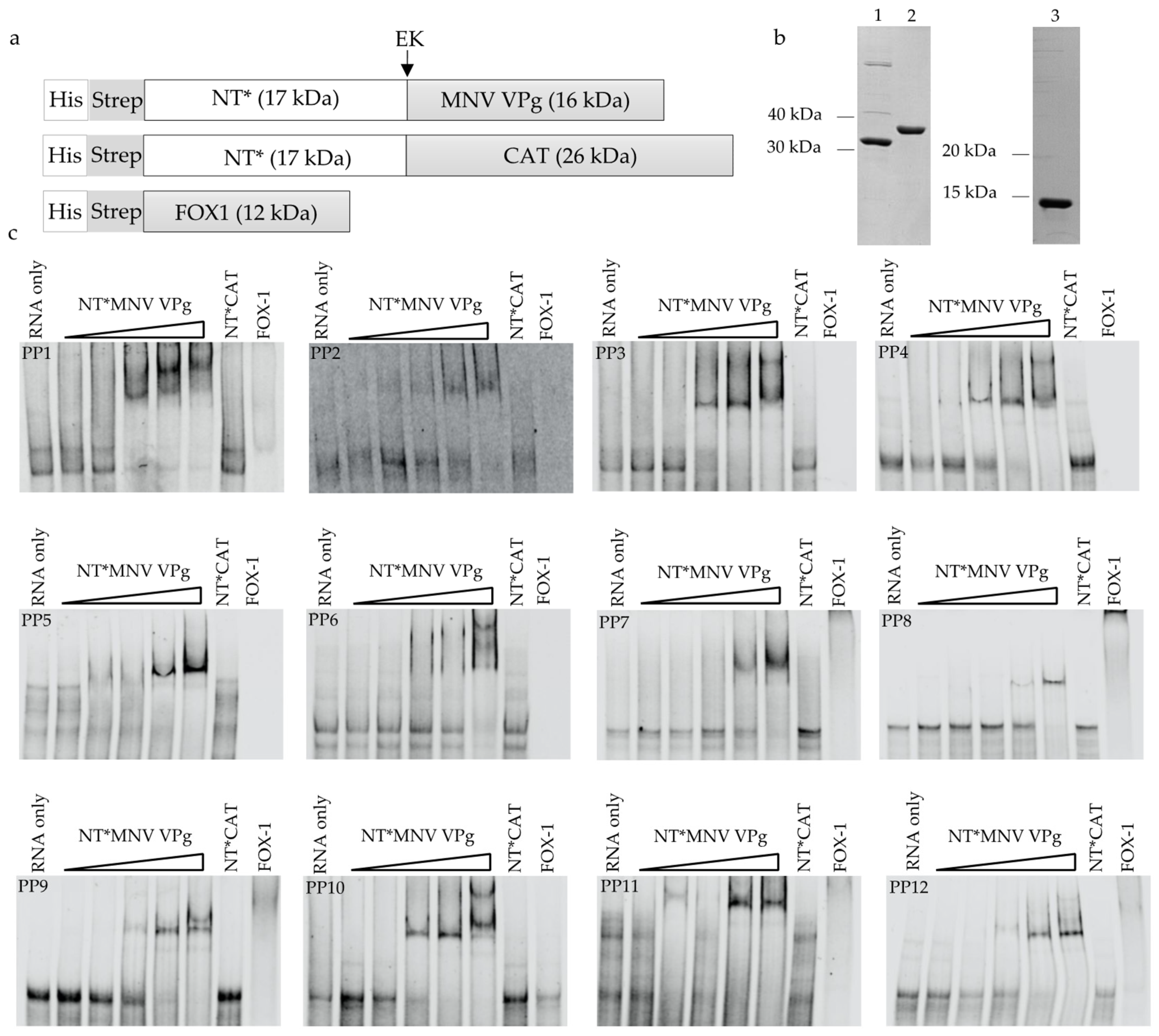
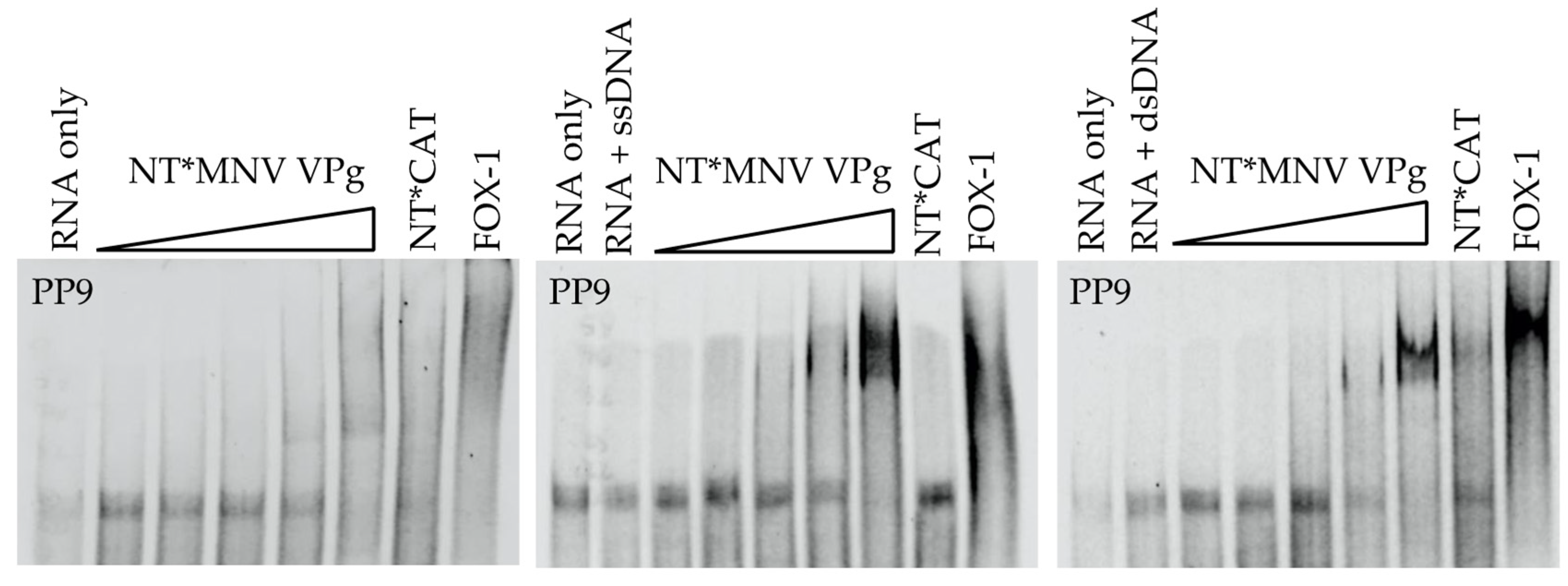
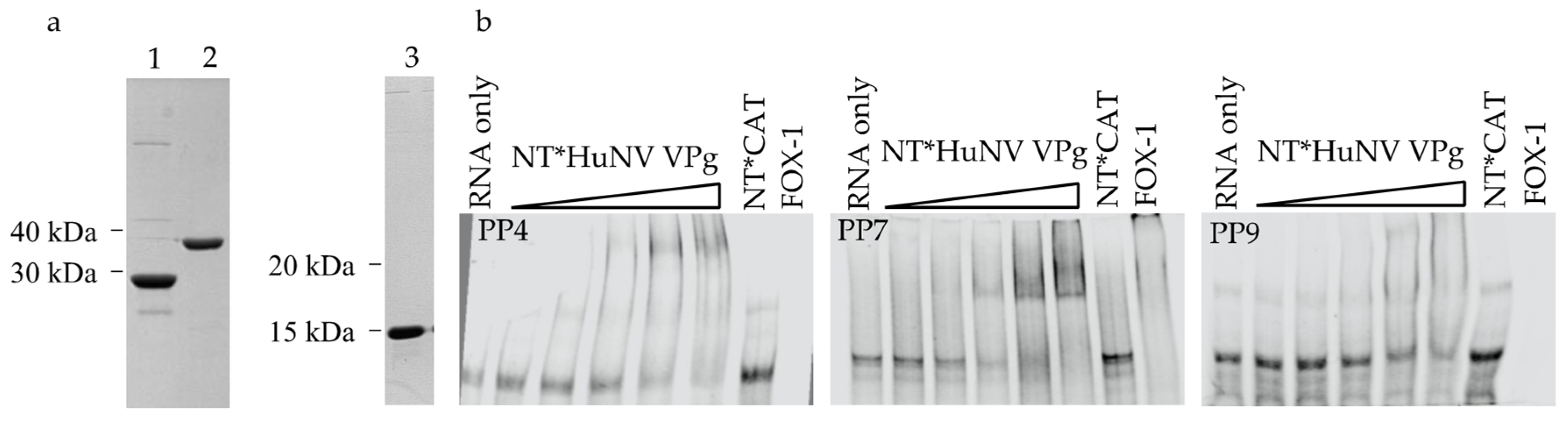
3.1. MNV VPg Is an RNA Binding Protein
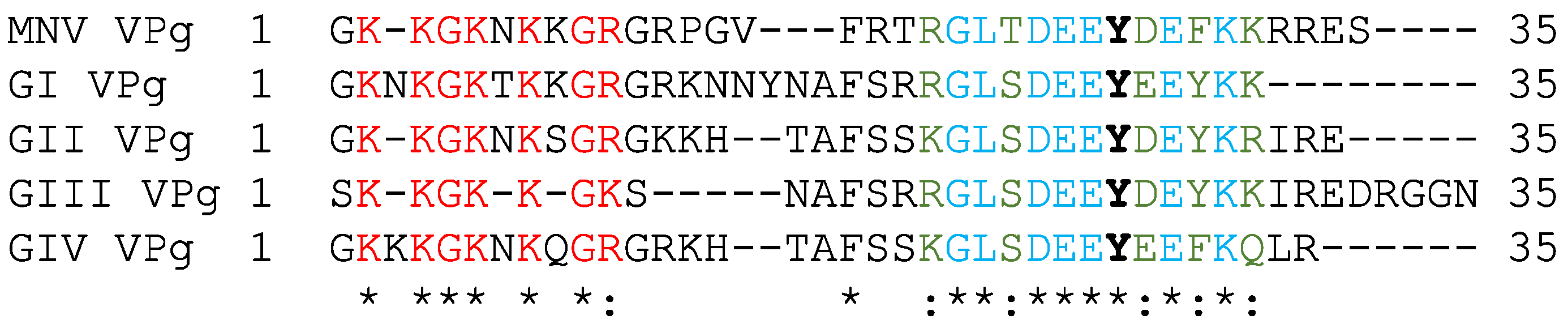
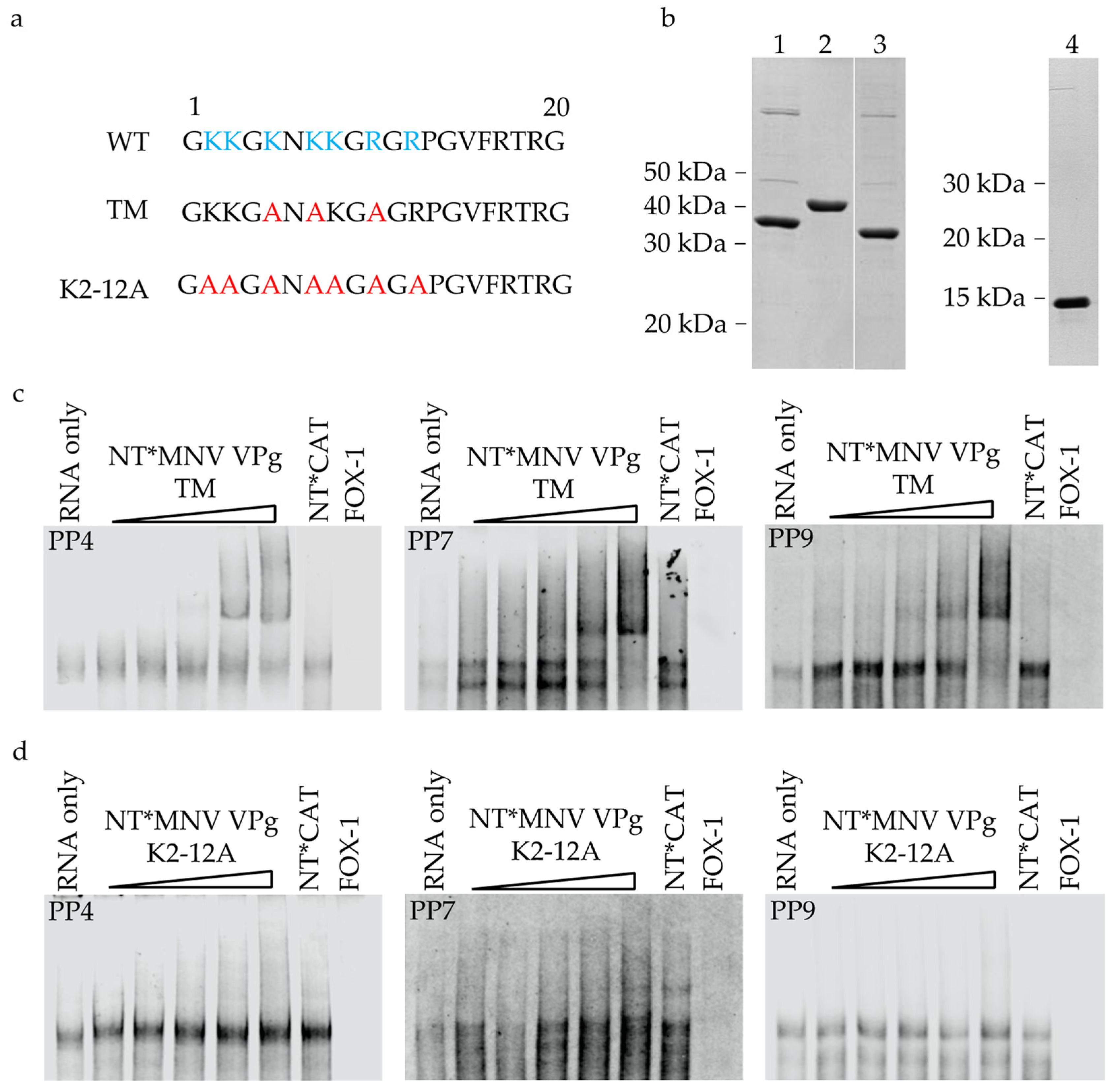
3.2. The Basic Amino Acid Patch Near the N-Terminus of MNV VPg Is Required for Binding to RNA
4. Discussion
4.1. MNV VPg Is an RNA Binding Protein
4.2. Identification of a Motif/Region of MNV VPg Required for Binding to RNA
4.3. Biological Significance of RNA Binding by MNV VPg
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.K.; Watanabe, M.; Zhu, S.; Graves, C.L.; Keyes, L.R.; Grau, K.R.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.B.; Iovine, N.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Vinje, J.; et al. Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of B cells. Science 2014, 346, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dycke, J.; Ny, A.; Conceicao-Neto, N.; Maes, J.; Hosmillo, M.; Cuvry, A.; Goodfellow, I.; Nogueira, T.C.; Verbeken, E.; Matthijnssens, J.; et al. A robust human norovirus replication model in zebrafish larvae. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, M.K.; Ettayebi, K.; Tenge, V.R.; Murakami, K.; Karandikar, U.; Lin, S.C.; Ayyar, B.V.; Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Haga, K.; Neill, F.H.; et al. Human Norovirus Cultivation in Nontransformed Stem Cell-Derived Human Intestinal Enteroid Cultures: Success and Challenges. Viruses 2019, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wobus, C.E.; Karst, S.M.; Thackray, L.B.; Chang, K.O.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Belliot, G.; Krug, A.; Mackenzie, J.M.; Green, K.Y.; Virgin, H.W. Replication of Norovirus in cell culture reveals a tropism for dendritic cells and macrophages. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobus, C.E.; Thackray, L.B.; Virgin, H.W.T. Murine norovirus: A model system to study norovirus biology and pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5104–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Belliot, G.; Chang, K.O.; Prikhodko, V.G.; Thackray, L.B.; Wobus, C.E.; Karst, S.M.; Virgin, H.W.; Green, K.Y. Cleavage map and proteolytic processing of the murine norovirus nonstructural polyprotein in infected cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7816–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFadden, N.; Bailey, D.; Carrara, G.; Benson, A.; Chaudhry, Y.; Shortland, A.; Heeney, J.; Yarovinsky, F.; Simmonds, P.; Macdonald, A.; et al. Norovirus regulation of the innate immune response and apoptosis occurs via the product of the alternative open reading frame 4. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leen, E.N.; Kwok, K.Y.; Birtley, J.R.; Simpson, P.J.; Subba-Reddy, C.V.; Chaudhry, Y.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Green, K.Y.; Prater, S.N.; Tong, M.; et al. Structures of the compact helical core domains of feline calicivirus and murine norovirus VPg proteins. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5318–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belliot, G.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Chang, K.O.; McPhie, P.; Green, K.Y. Nucleotidylylation of the VPg protein of a human norovirus by its proteinase-polymerase precursor protein. Virology 2008, 374, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohayem, J.; Robel, I.; Jager, K.; Scheffler, U.; Rudolph, W. Protein-primed and de novo initiation of RNA synthesis by norovirus 3Dpol. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7060–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olspert, A.; Hosmillo, M.; Chaudhry, Y.; Peil, L.; Truve, E.; Goodfellow, I. Protein-RNA linkage and posttranslational modifications of feline calicivirus and murine norovirus VPg proteins. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daughenbaugh, K.F.; Wobus, C.E.; Hardy, M.E. VPg of murine norovirus binds translation initiation factors in infected cells. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, L.; Bailey, D.; Leen, E.N.; Emmott, E.P.; Chaudhry, Y.; Roberts, L.O.; Curry, S.; Locker, N.; Goodfellow, I.G. Norovirus translation requires an interaction between the C Terminus of the genome-linked viral protein VPg and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21738–21750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leen, E.N.; Sorgeloos, F.; Correia, S.; Chaudhry, Y.; Cannac, F.; Pastore, C.; Xu, Y.; Graham, S.C.; Matthews, S.J.; Goodfellow, I.G.; et al. A Conserved Interaction between a C-Terminal Motif in Norovirus VPg and the HEAT-1 Domain of eIF4G Is Essential for Translation Initiation. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McSweeney, A.; Davies, C.; Ward, V.K. Cell Cycle Arrest is a Conserved Function of Norovirus VPg Proteins. Viruses 2019, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, C.; Ward, V.K. Expression of the NS5 (VPg) Protein of Murine Norovirus Induces a G1/S Phase Arrest. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Brown, C.M.; Westphal, D.; Ward, J.M.; Ward, V.K. Murine norovirus replication induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in asynchronously growing cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6057–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodfellow, I. The genome-linked protein VPg of vertebrate viruses—A multifaceted protein. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Laliberte, J.F. The genome-linked protein VPg of plant viruses-a protein with many partners. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, J.; Sanz, M.A.; Rodriguez, P.L. A role for 3AB protein in poliovirus genome replication. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14430–14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rantalainen, K.I.; Eskelin, K.; Tompa, P.; Makinen, K. Structural flexibility allows the functional diversity of potyvirus genome-linked protein VPg. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gangaramani, D.R.; Eden, E.L.; Shah, M.; Destefano, J.J. The twenty-nine amino acid C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of poliovirus 3AB is critical for nucleic acid chaperone activity. RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medvedev, A.; Viswanathan, P.; May, J.; Korba, B. Regulation of human norovirus VPg nucleotidylylation by ProPol and nucleoside triphosphate binding by its amino terminal sequence in vitro. Virology 2017, 503, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvelin, A.I.; Noerenberg, M.; Davis, I.; Castello, A. The new (dis)order in RNA regulation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balcerak, A.; Trebinska-Stryjewska, A.; Konopinski, R.; Wakula, M.; Grzybowska, E.A. RNA-protein interactions: Disorder, moonlighting and junk contribute to eukaryotic complexity. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corley, M.; Burns, M.C.; Yeo, G.W. How RNA-Binding Proteins Interact with RNA: Molecules and Mechanisms. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kurgan, L. DRNApred, fast sequence-based method that accurately predicts and discriminates DNA- and RNA-binding residues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishida, T.; Kinoshita, K. PrDOS: Prediction of disordered protein regions from amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W460–W464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Romero, P.; Rani, M.; Dunker, A.K.; Obradovic, Z. Predicting Protein Disorder for N-, C-, and Internal Regions. Genome Inform. Ser. Workshop Genome Inform. 1999, 10, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romero, P.; Obradovic, Z.; Dunker, K. Sequence Data Analysis for Long Disordered Regions Prediction in the Calcineurin Family. Genome Inform. Ser. Workshop Genome Inform. 1997, 8, 110–124. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, P.; Obradovic, Z.; Li, X.; Garner, E.C.; Brown, C.J.; Dunker, A.K. Sequence complexity of disordered protein. Proteins 2001, 42, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdos, G.; Dosztanyi, Z. Analyzing Protein Disorder with IUPred2A. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meszaros, B.; Erdos, G.; Dosztanyi, Z. IUPred2A: Context-dependent prediction of protein disorder as a function of redox state and protein binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W329–W337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronqvist, N.; Sarr, M.; Lindqvist, A.; Nordling, K.; Otikovs, M.; Venturi, L.; Pioselli, B.; Purhonen, P.; Landreh, M.; Biverstal, H.; et al. Efficient protein production inspired by how spiders make silk. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarr, M.; Kronqvist, N.; Chen, G.; Aleksis, R.; Purhonen, P.; Hebert, H.; Jaudzems, K.; Rising, A.; Johansson, J. A spidroin-derived solubility tag enables controlled aggregation of a designed amyloid protein. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendak, K.; Loughlin, F.E.; Cheung, V.; O’Connell, M.R.; Crossley, M.; Mackay, J.P. A rapid method for assessing the RNA-binding potential of a protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E. Characterisation of the NS1-2 and NS4 Proteins of Murine Norovirus. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hebrard, E.; Bessin, Y.; Michon, T.; Longhi, S.; Uversky, V.N.; Delalande, F.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Romero, P.; Walter, J.; Declerck, N.; et al. Intrinsic disorder in Viral Proteins Genome-Linked: Experimental and predictive analyses. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuroyanagi, H. Fox-1 family of RNA-binding proteins. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3895–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auweter, S.D.; Fasan, R.; Reymond, L.; Underwood, J.G.; Black, D.L.; Pitsch, S.; Allain, F.H. Molecular basis of RNA recognition by the human alternative splicing factor Fox-1. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, T.P.; Brierley, I.; Brown, T.D. Identification of a protein linked to the genomic and subgenomic mRNAs of feline calicivirus and its role in translation. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78 Pt 5, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, N.R.; Zuker, M. UNAFold: Software for nucleic acid folding and hybridization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 453, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelin, K.; Hafren, A.; Rantalainen, K.I.; Makinen, K. Potyviral VPg enhances viral RNA Translation and inhibits reporter mRNA translation in planta. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9210–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankowsky, E.; Harris, M.E. Specificity and nonspecificity in RNA-protein interactions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, J.; Warwicker, J. Simulation of non-specific protein-mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 6694–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Green, M.R. A pathway of sequential arginine-serine-rich domain-splicing signal interactions during mammalian spliceosome assembly. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, J.; Gaur, R.K.; Singh, R.; Green, M.R. Interaction of U2AF65 RS region with pre-mRNA branch point and promotion of base pairing with U2 snRNA [corrected]. Science 1996, 273, 1706–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoell, J.I.; Larsson, E.; Runge, S.; Nusbaum, J.D.; Duggimpudi, S.; Farazi, T.A.; Hafner, M.; Borkhardt, A.; Sander, C.; Tuschl, T. RNA targets of wild-type and mutant FET family proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1428–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.; Karakasiliotis, I.; Vashist, S.; Chung, L.M.; Rees, J.; McFadden, N.; Benson, A.; Yarovinsky, F.; Simmonds, P.; Goodfellow, I. Functional analysis of RNA structures present at the 3′ extremity of the murine norovirus genome: The variable polypyrimidine tract plays a role in viral virulence. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmonds, P.; Karakasiliotis, I.; Bailey, D.; Chaudhry, Y.; Evans, D.J.; Goodfellow, I.G. Bioinformatic and functional analysis of RNA secondary structure elements among different genera of human and animal caliciviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 2530–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, W.; Cuconati, A.; Paul, A.V.; Cao, X.; Wimmer, E. Molecular dissection of the multifunctional poliovirus RNA-binding protein 3AB. RNA 1995, 1, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.S.; Xiang, W.; Alexander, L.; Lane, W.S.; Paul, A.V.; Wimmer, E. Interaction of poliovirus polypeptide 3CDpro with the 5′ and 3′ termini of the poliovirus genome. Identification of viral and cellular cofactors needed for efficient binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27004–27014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Harris, K.S.; Alexander, L.; Wimmer, E. Interaction between the 5′-terminal cloverleaf and 3AB/3CDpro of poliovirus is essential for RNA replication. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, K.R.; Alhatlani, B.Y.; Cho, S.; Lee, J.H.; Hosmillo, M.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Kim, K.H.; Yang, J.M. Identification of amino acids within norovirus polymerase involved in RNA binding and viral replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.R.; Choi, Y.; Min, B.S.; Jeong, H.; Cheon, D.; Kim, J.; Jee, Y.; Shin, S.; Yang, J.M. Murine norovirus-1 3Dpol exhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity and nucleotidylylates on Tyr of the VPg. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, M.W.; Castello, A.; Schwarzl, T.; Preiss, T. A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, A.; Fischer, B.; Eichelbaum, K.; Horos, R.; Beckmann, B.M.; Strein, C.; Davey, N.E.; Humphreys, D.T.; Preiss, T.; Steinmetz, L.M.; et al. Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell 2012, 149, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; Calabro, V.; Frankel, A.D. An RNA-binding chameleon. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackinton, J.G.; Keene, J.D. Post-transcriptional RNA regulons affecting cell cycle and proliferation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Forward Primer Sequence (5′–3′) a | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′–3′) b | |
|---|---|---|
| 5′pos | GAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGTGAAA- TGAGGATGGCAACG | GGATCCGATATCAGGGGTCATGTAATTAAT- TTCGTC |
| 3′pos | GAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGACACA- TCCCCTCTACCGA | GGATCCGATATCTTTTTTTTTTAAAATGCAT- CTAACT |
| 5′neg | GAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGTTTTTTT- TTTAAAATGCATCTAACTACCAC | GGATCCGATATCGACACATCCCCTCTACCG- ATCTC |
| 3′neg | GAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGAGGGG- TCATGTAATTAATTTCGTC | GGATCCGATATCGTGAAATGAGGATGGCA- ACG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McSweeney, A.M.; Young, V.L.; Ward, V.K. Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch. Viruses 2021, 13, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071282
McSweeney AM, Young VL, Ward VK. Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch. Viruses. 2021; 13(7):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071282
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcSweeney, Alice M., Vivienne L. Young, and Vernon K. Ward. 2021. "Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch" Viruses 13, no. 7: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071282
APA StyleMcSweeney, A. M., Young, V. L., & Ward, V. K. (2021). Norovirus VPg Binds RNA through a Conserved N-Terminal K/R Basic Patch. Viruses, 13(7), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071282






