Blood Counts, Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory, and Immune Responses in Pigs Infected Experimentally with the African Swine Fever Virus Isolate Pol18_28298_O111
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Properties and Experiment Settings
2.2. Blood and Blood Counts Analyses
2.3. Viremia Detection
2.4. Sera and Biochemistry Analyses
2.5. C-reactive Protein (CRP) Concentration
2.6. Histology
2.7. Antibody Detection and Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
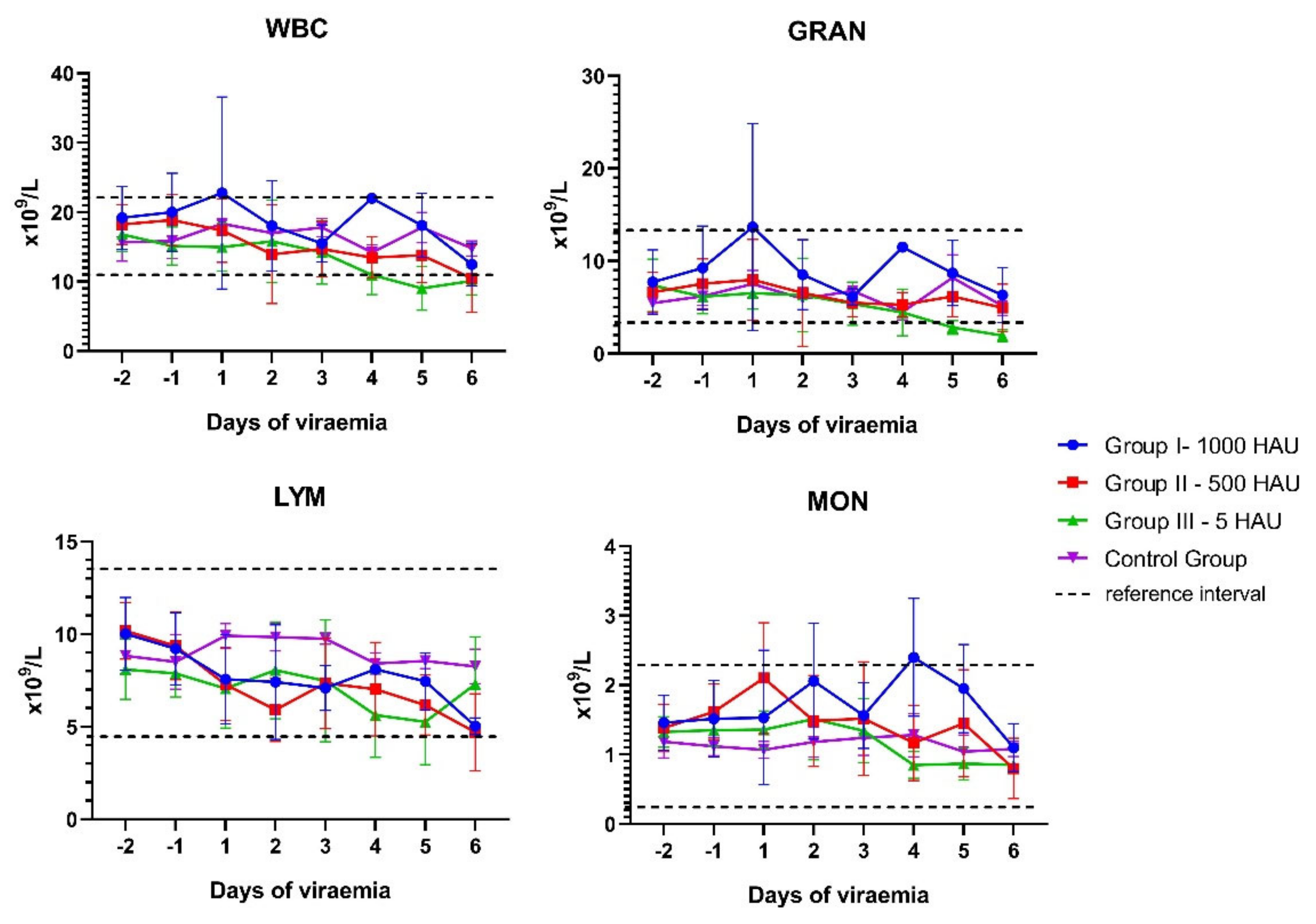
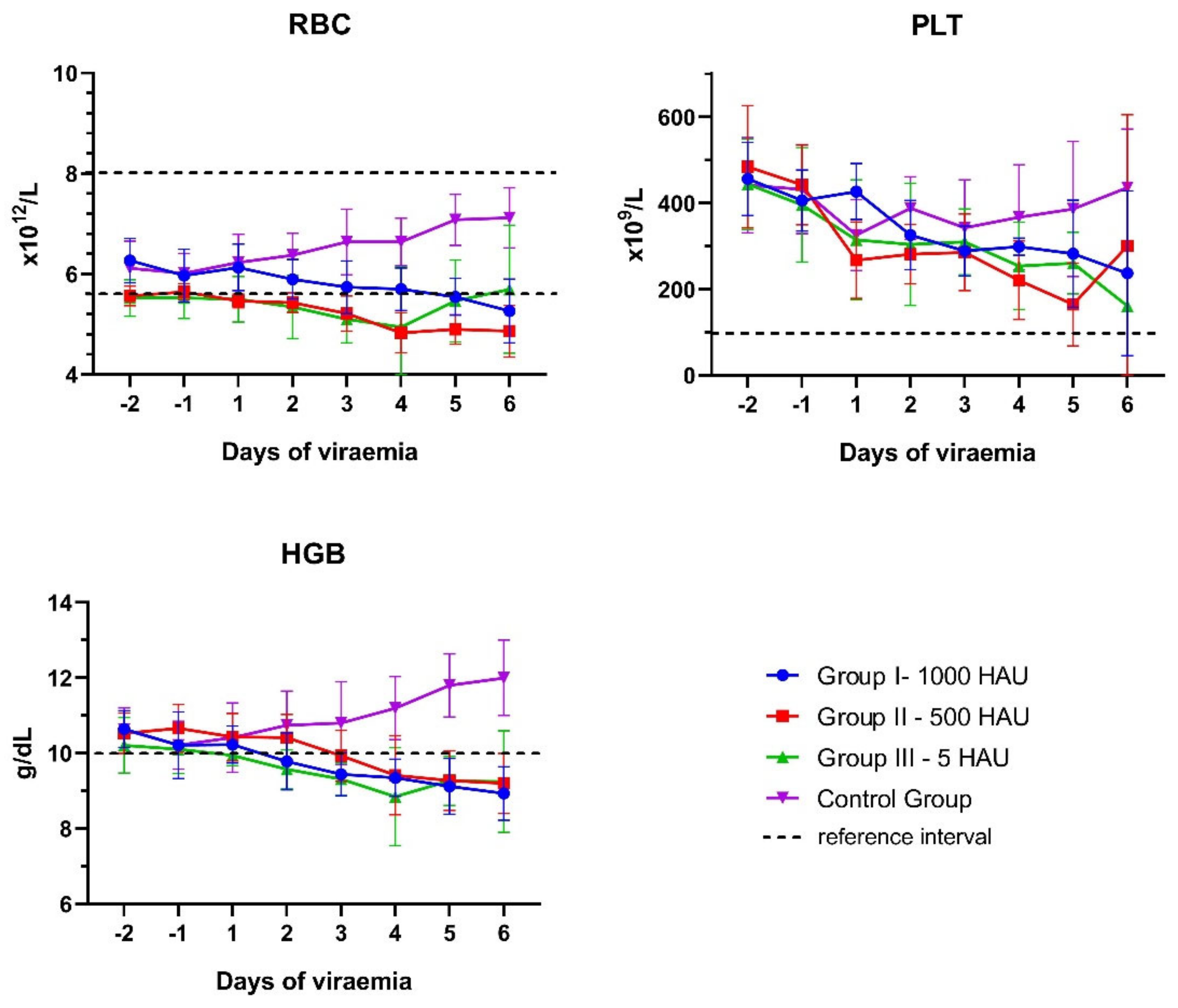
3.1. Blood Counts
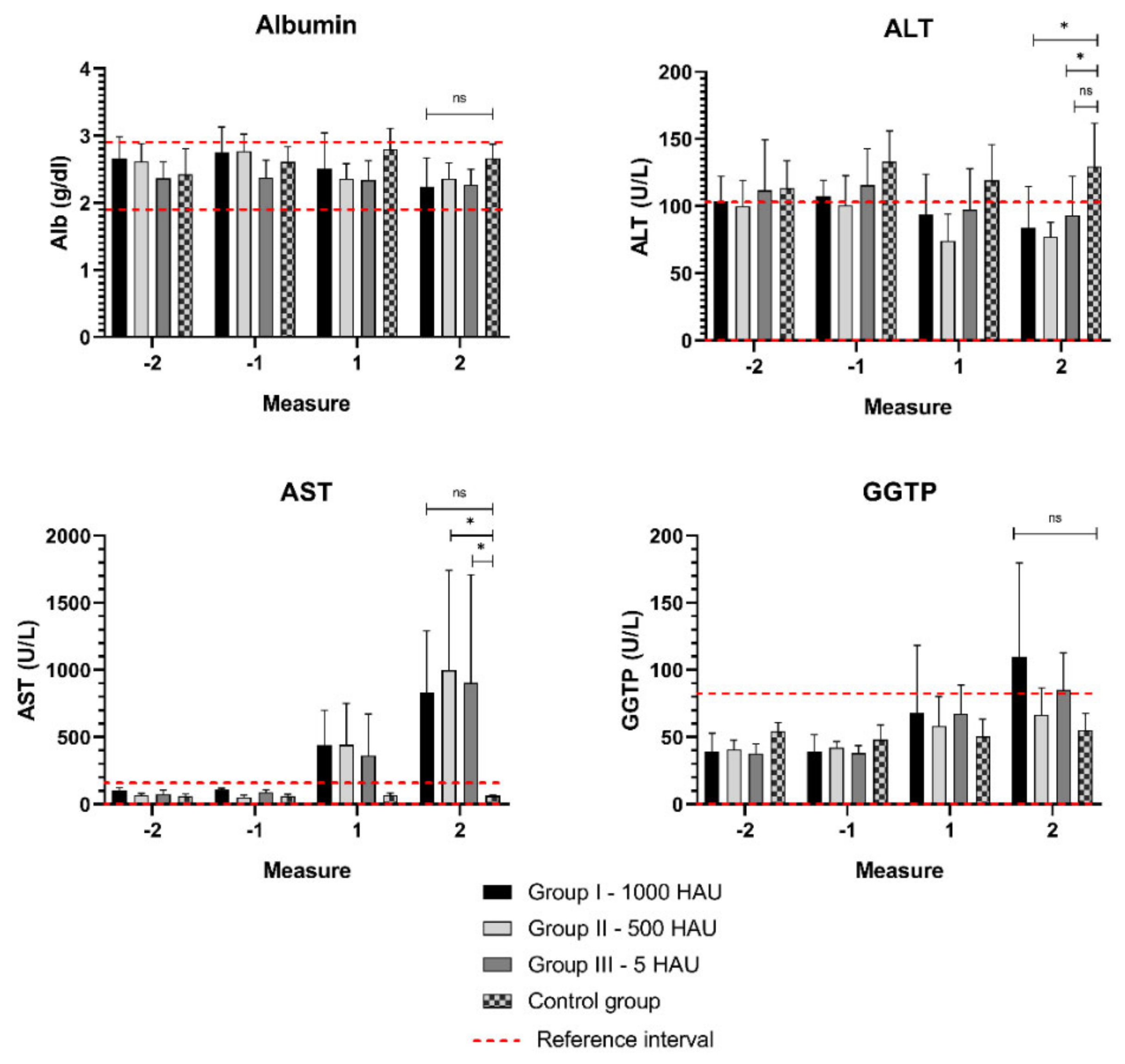
3.2. Biochemical Parameters
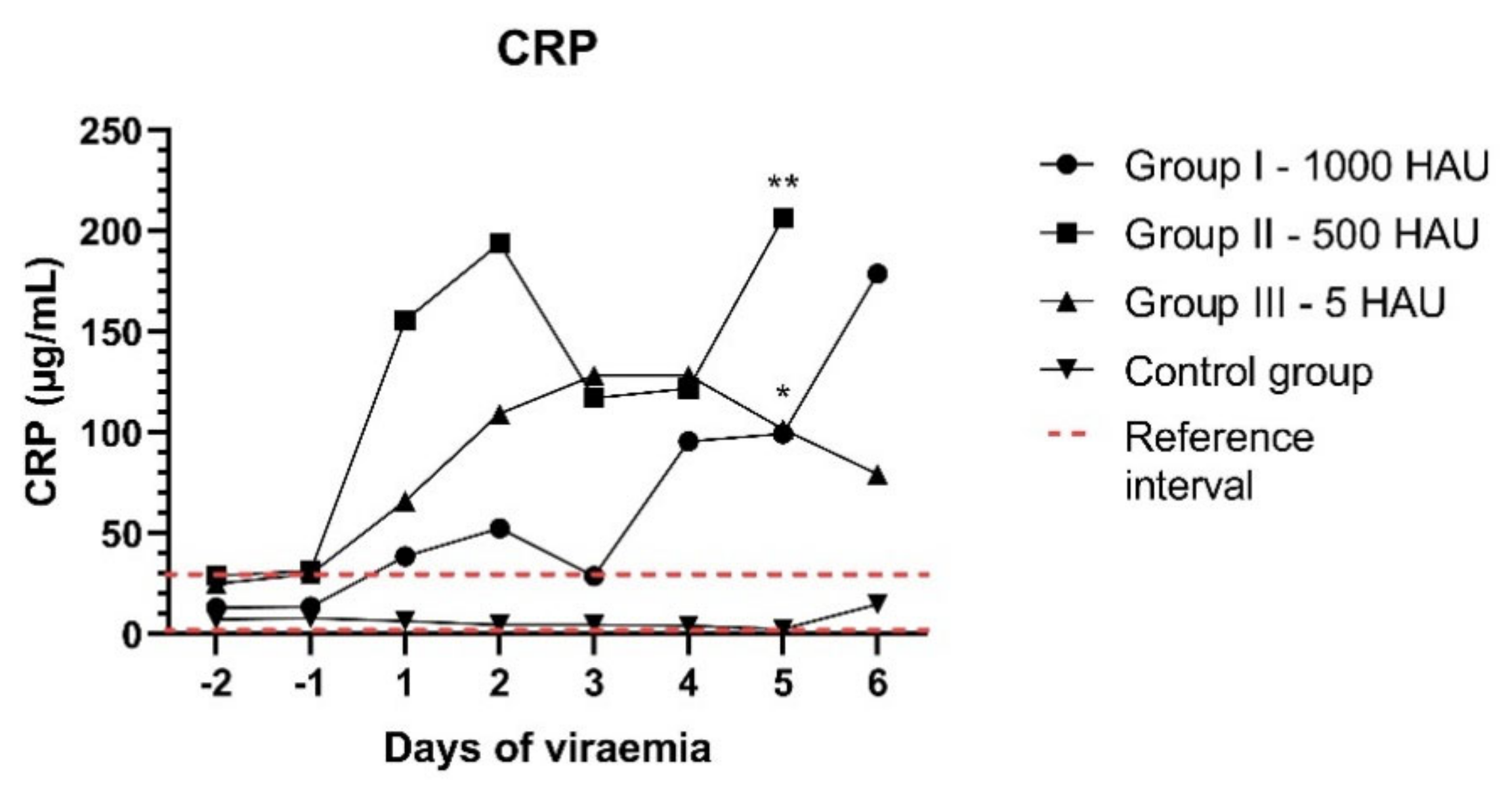
3.3. CRP Concentration and Histology
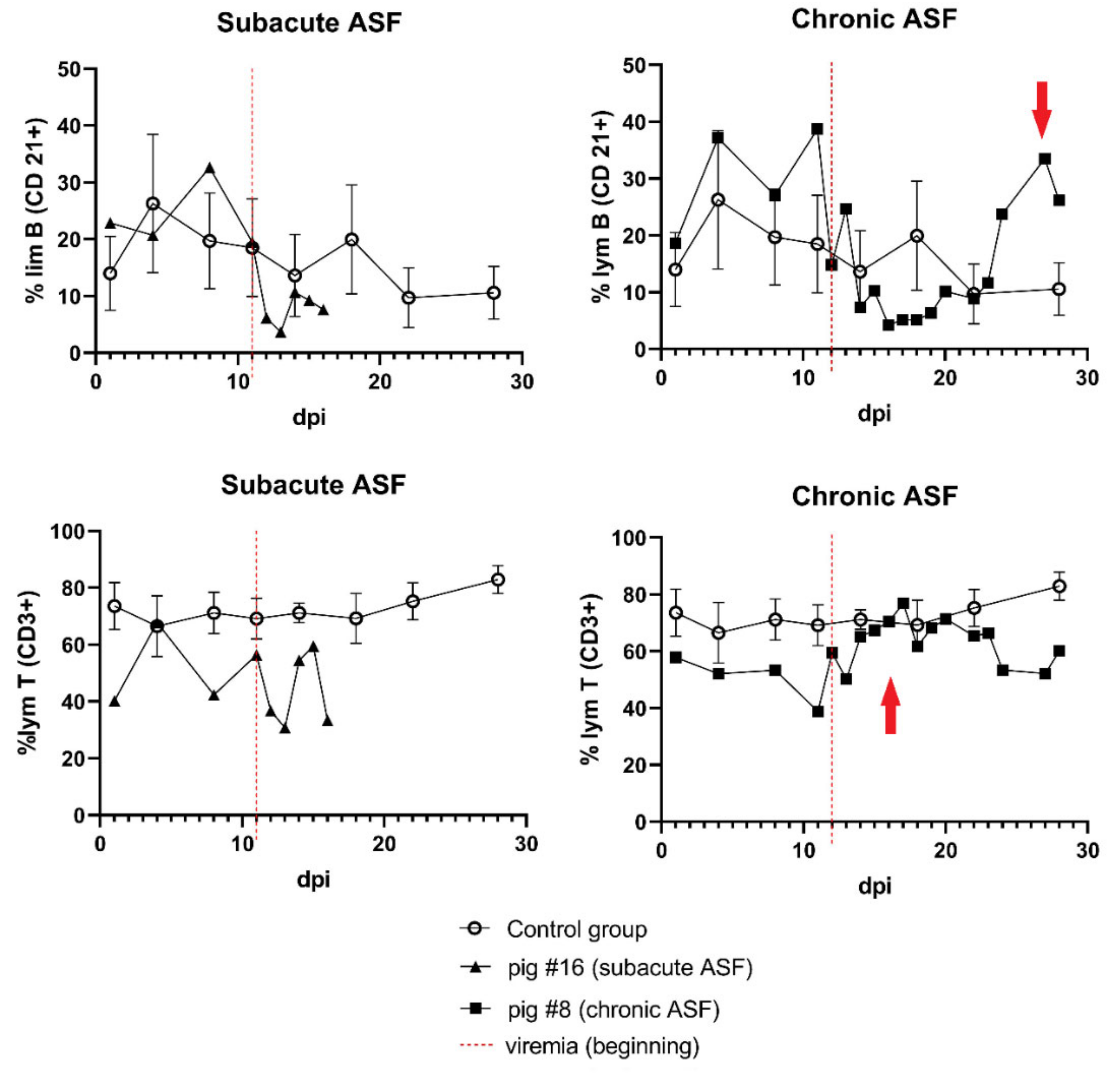
3.4. Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus: A Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borca, M.V.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Vuono, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Holinka, L.G.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Zhu, J.; Gladue, D.P. Development of a Highly Effective African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine by Deletion of the I177L Gene Results in Sterile Immunity against the Current Epidemic Eurasia Strain. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goatley, L.C.; Reis, A.L.; Portugal, R.; Goldswain, H.; Shimmon, G.L.; Hargreaves, Z.; Ho, C.; Montoya, M.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Taylor, G.; et al. A Pool of Eight Virally Vectored African Swine Fever Antigens Protect Pigs Against Fatal Disease. Vaccines 2020, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, D.; He, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Shan, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. A seven-gene-deleted African swine fever virus is safe and effective as a live attenuated vaccine in pigs. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszkiewicz, M.; Walczak, M.; Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Woźniakowski, G. Virucidal effect of chosen disinfectants against African swine fever virus (ASFV) – preliminary studies. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 22, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Stahl, K.; Jori, F.; Vial, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Rev, A.; Biosci, A.; Dixon, L.K.; Stahl, K.; Jori, F.; et al. African Swine Fever Epidemiology and Control. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, C.; Fernández-Pinero, J.; Arias, M. African swine fever (ASF) diagnosis, an essential tool in the epidemiological investigation. Virus Res. 2019, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietschmann, J.; Guinat, C.; Beer, M.; Pronin, V.; Blome, S.; Tauscher, K.; Petrov, A.; Keil, G.; Blome, S.; Tauscher, K.; et al. Course and transmission characteristics of oral low-dose infection of domestic pigs and European wild boar with a Caucasian African swine fever virus isolate. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Żmudzki, J.; Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Juszkiewicz, M.; Woźniakowski, G. Analysis of the Clinical Course of Experimental Infection with Highly Pathogenic African Swine Fever Strain, Isolated from an Outbreak in Poland. Aspects Related to the Disease Suspicion at the Farm Level. Pathogens 2020, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalo, J.; Zani, L.; Hühr, J.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar – Lessons learned from recent animal trials. Virus Res. 2019, 271, 197614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Mur, L.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Carrasco, L. An update on the epidemiology and pathology of African swine fever. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace Montgomery, R. On A Form of Swine Fever Occurring in British East Africa (Kenya Colony). J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 1921, 34, 159–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Bautista, M.J.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Carrasco, L. Pathology of African swine fever: The role of monocyte-macrophage. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinat, C.; Reis, A.L.; Netherton, C.L.; Goatley, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Dixon, L. Dynamics of African swine fever virus shedding and excretion in domestic pigs infected by intramuscular inoculation and contact transmission. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blome, S.; Gabriel, C.; Beer, M. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Montoya, M.; Reis, A.L.; Dixon, L.K. African swine fever: A re-emerging viral disease threatening the global pig industry. Vet. J. 2018, 233, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernáez, B.; Guerra, M.; Salas, M.L.; Andrés, G. African Swine Fever Virus Undergoes Outer Envelope Disruption, Capsid Disassembly and Inner Envelope Fusion before Core Release from Multivesicular Endosomes. PLOS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salguero, F.J.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Núñez, A.; Fernández de Marco, M.; Gómez-Villamandos, J.C. Proinflammatory Cytokines Induce Lymphocyte Apoptosis in Acute African Swine Fever Infection. J. Comp. Pathol. 2005, 132, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.J.; Ramanathan, P.; Bishop, E.A.; O’Donnell, V.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Mechanisms of African swine fever virus pathogenesis and immune evasion inferred from gene expression changes in infected swine macrophages. PLoS One 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerjyan, A.B.; Tatoyan, M.R.; Karalyan, N.Y.; Nersisyan, N.H.; Hakobyan, L.H.; Arzumanyan, H.H.; Karalyan, Z.A. Cardiopathology in acute African Swine Fever. Ann. Parasitol. 2018, 64, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalyan, Z.; Zakaryan, H.; Arakelova, E.; Aivazyan, V.; Tatoyan, M.; Kotsinyan, A.; Izmailyan, R.; Karalova, E. Evidence of hemolysis in pigs infected with highly virulent African swine fever virus. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Correia, S.; Ventura, S.; Parkhouse, R.M. Identification and utility of innate immune system evasion mechanisms of ASFV. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Abrams, C.C.; Bowick, G.; Goatley, L.C.; Kay-Jackson, P.C.; Chapman, D.; Liverani, E.; Nix, R.; Silk, R.; Zhang, F. African swine fever virus proteins involved in evading host defence systems. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 100, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, C.; Soler, A.; Nieto, R.; Cano, C.; Pelayo, V.; Sánchez, M.A.; Pridotkas, G.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Briones, V.; Arias, M. Experimental Infection of Domestic Pigs with African Swine Fever Virus Lithuania 2014 Genotype II Field Isolate. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzuoli, E.; Franzoni, G.; Carta, T.; Zinellu, S.; Amadori, M.; Modesto, P.; Oggiano, A. Modulation of Type I Interferon System by African Swine Fever Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejsak, Z.; Niemczuk, K.; Frant, M.; Mazur, M.; Pomorska-Mól, M.; Ziętek-Barszcz, A.; Bocian, Ł.; Łyjak, M.; Borowska, D.; Woźniakowski, G.; et al. Four years of African swine fever in Poland. New insights into epidemiology and prognosis of future disease spread. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 21, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Woźniakowski, G.; Niemczuk, K. The first complete genomic sequences of African swine fever virus isolated in Poland. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Walczak, M.; Juszkiewicz, M.; Woźniakowski, G. The spillover of African swine fever in Western Poland revealed its estimated origin on the basis of O174L, K145R, MGF 505-5R and IGR I73R/I329L genomic sequences. Viruses 2020, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, T.B.; Bleken, E.; Morberg, H.; Thoresen, S.I.; Framstad, T. Hematologic and biochemical reference intervals for Norwegian crossbreed grower pigs. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 39, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomorska-Mól, M.; Kwit, K.; Markowska-Daniel, I. Major Acute Phase Proteins in Pig Serum from Birth to Slaughter. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Cardiel, I.; Ballester, M.; Solanes, D.; Nofrarías, M.; López-Soria, S.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Lacasta, A.; Accensi, F.; Rodríguez, F.; Segalés, J. Standardization of pathological investigations in the framework of experimental ASFV infections. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Cordon, P.J.; Ceron, J.J.; Nunez, A.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Pedrera, M.; Romero-Trevejo, J.L.J.L.; Garrido, M.R.M.R.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Sánchez-Cordón, P.J.; Cerón, J.J.; et al. Serum concentrations of C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A, and haptoglobin in pigs inoculated with African swine fever or classical swine fever viruses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 68, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikalo, J.; Schoder, M.; Sehl, J.; Breithaupt, A.; Tignon, M.; Cay, A.B.; Gager, A.M.; Fischer, M.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. The African swine fever virus isolate Belgium 2018/1 shows high virulence in European wild boar. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehl, J.; Pikalo, J.; Schäfer, A.; Franzke, K.; Pannhorst, K.; Elnagar, A.; Blohm, U.; Blome, S.; Breithaupt, A. Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”. Pathogens 2020, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalyan, Z.; Zakaryan, H.; Arzumanyan, H.; Sargsyan, K.; Voskanyan, H.; Hakobyan, L.; Abroyan, L.; Avetisyan, A.; Karalova, E. Pathology of porcine peripheral white blood cells during infection with African swine fever virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardley, R.C.; Wilkinson, P.J. The association of African swine fever virus with blood components of infected pigs. Arch. Virol. 1977, 55, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hühr, J.; Schäfer, A.; Schwaiger, T.; Zani, L.; Sehl, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Blome, S.; Blohm, U. Impaired T-cell responses in domestic pigs and wild boar upon infection with a highly virulent African swine fever virus strain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 3016–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panteghini, M. Aspartate aminotransferase isoenzymes. Clin. Biochem. 1990, 23, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewid, M.; Sherif, H.; Allihimy, A.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Aldrewesh, D.A.; Alkuraydis, S.A.; Abazid, R. AST/ALT ratio predicts the functional severity of chronic heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Yalta, K.; Turgut, O.O.; Yilmaz, M.B.; Ozyol, A.; Kendirlioglu, O.; Karadas, F.; Tandogan, I. Clinical importance of elevated CK-MB and troponin I levels in congestive heart failure. Adv. Ther. 2006, 23, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S. A More Accurate Method To Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine: A New Prediction Equation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilaguet, J.M.; Pérez-Martín, E.; Nofrarías, M.; Gallardo, C.; Accensi, F.; Lacasta, A.; Mora, M.; Ballester, M.; Galindo-Cardiel, I.; López-Soria, S.; et al. DNA Vaccination Partially Protects against African Swine Fever Virus Lethal Challenge in the Absence of Antibodies. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, J.M.; Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. Antibody-mediated neutralization of African swine fever virus: Myths and facts. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oura, C.A.L.; Denyer, M.S.; Takamatsu, H.; Parkhouse, R.M.E. In vivo depletion of CD8+ T lymphocytes abrogates protective immunity to African swine fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, H.-H.; Denyer, M.S.; Lacasta, A.; Stirling, C.M.A.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Netherton, C.L.; Oura, C.A.L.; Martins, C.; Rodríguez, F. Cellular immunity in ASFV responses. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Organ | Histopathological Changes | Score * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Subacute | Chronic | ||
| Lung | Oedema | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Congestion/haemorrhage | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Inflammatory infiltrates | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Liver | Blood vessels/congestion | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Hepatitis | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Kidney | Congestion/haemorrhage (medulla) | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Congestion/haemorrhage (cortex) | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Necrosis | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Renal inflammation | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Heart | Congestion/haemorrhage | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Spleen | Ratio white pulp/red pulp | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Necrosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Lymphocytolysis | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Vascular damage | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Tonsil (palatine) | Crypt necrosis | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Lymphocytolysis | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Congestion/haemorrhage | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Lymph node (submandibular) | Lymphocytolysis | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Congestion/haemorrhage | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Group | Pig | 1. Day of Detected Viremia (dpi) | Time of Life with Detected Viremia (days) | 1. Day of Antibody Detection (dpi) | Average (± SD) Timespan between Detection of Viremia and Antibodies (days) | Maximum Detected Antibody Titre(log10/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I 1000 HAU | #1 | 16 | 5 | n/d | 4(± 0.5) | n/d |
| #2 | 4 | 3 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #3 | 8 | 3 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #4 | 4 | 2 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #5 | n/d | n/d | n/a | n/a | ||
| #6 | 9 | 6 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #7 | 10 | 6 | 13 | 4.11 | ||
| #8 | 12 | chronic * | 16 | 5.31 | ||
| Group II 500 HAU | #9 | 12 | 4 | 15 | 3(± 0.7) | 3.51 |
| #10 | 11 | 6 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #11 | 13 | 6 | 17 | 3.51 | ||
| #12 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 3.51 | ||
| #13 | 6 | 4 | 9 | 3.51 | ||
| #14 | 16 | chronic * | 18 | 5.01 | ||
| Group III 5 HAU | #15 | 9 | 3 | n/d | 4(± 1.2) | n/d |
| #16 | 11 | 7 | 13 | 3.81 | ||
| #17 | 11 | 2 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #18 | 14 | 5 | 18 | 3.20 | ||
| #19 | 11 | 3 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #20 | 4 | 4 | n/d | n/d | ||
| #21 | 13 | 8 | 18 | 4.41 | ||
| #22 | 13 | 3 | n/d | n/d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walczak, M.; Wasiak, M.; Dudek, K.; Kycko, A.; Szacawa, E.; Olech, M.; Woźniakowski, G.; Szczotka-Bochniarz, A. Blood Counts, Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory, and Immune Responses in Pigs Infected Experimentally with the African Swine Fever Virus Isolate Pol18_28298_O111. Viruses 2021, 13, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030521
Walczak M, Wasiak M, Dudek K, Kycko A, Szacawa E, Olech M, Woźniakowski G, Szczotka-Bochniarz A. Blood Counts, Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory, and Immune Responses in Pigs Infected Experimentally with the African Swine Fever Virus Isolate Pol18_28298_O111. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030521
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalczak, Marek, Magdalena Wasiak, Katarzyna Dudek, Anna Kycko, Ewelina Szacawa, Małgorzata Olech, Grzegorz Woźniakowski, and Anna Szczotka-Bochniarz. 2021. "Blood Counts, Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory, and Immune Responses in Pigs Infected Experimentally with the African Swine Fever Virus Isolate Pol18_28298_O111" Viruses 13, no. 3: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030521
APA StyleWalczak, M., Wasiak, M., Dudek, K., Kycko, A., Szacawa, E., Olech, M., Woźniakowski, G., & Szczotka-Bochniarz, A. (2021). Blood Counts, Biochemical Parameters, Inflammatory, and Immune Responses in Pigs Infected Experimentally with the African Swine Fever Virus Isolate Pol18_28298_O111. Viruses, 13(3), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030521








