The First Whole Genome Sequence and Characterisation of Avian Nephritis Virus Genotype 3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Next Generation Sequencing
2.2. Sequencing, Phylogenetic, and Recombination Analysis
2.3. ANV-3 Sequence Confirmation
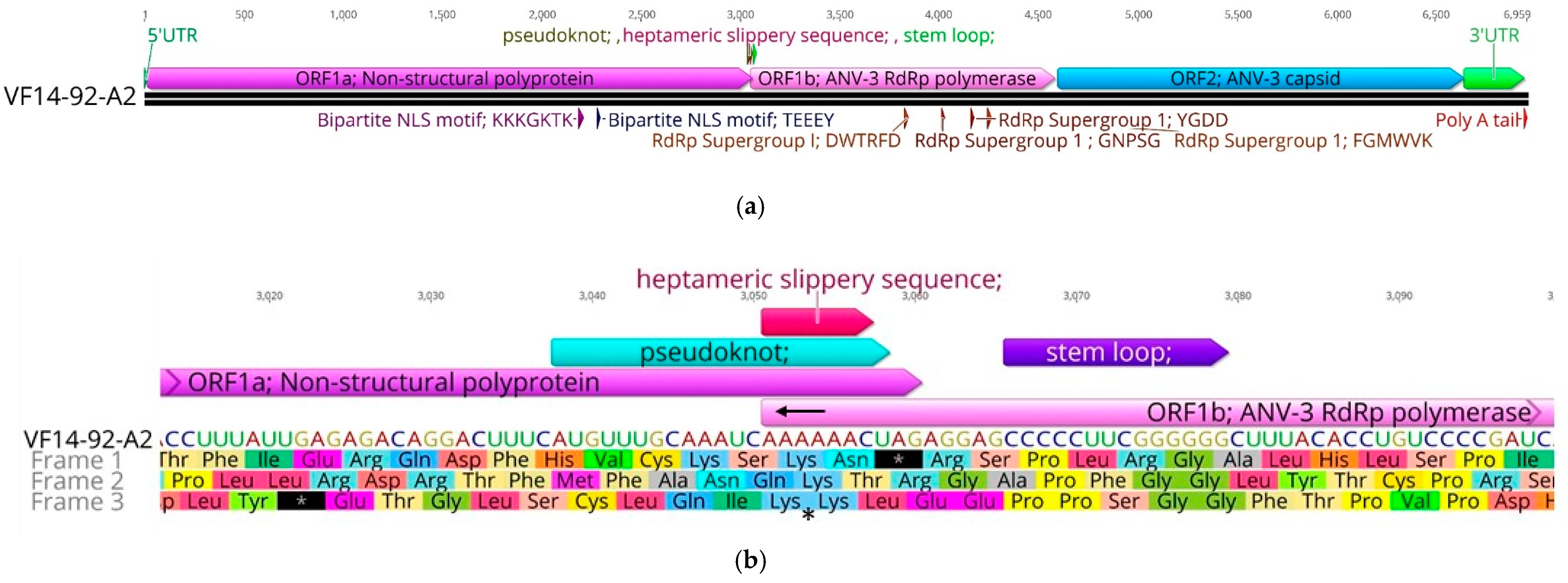
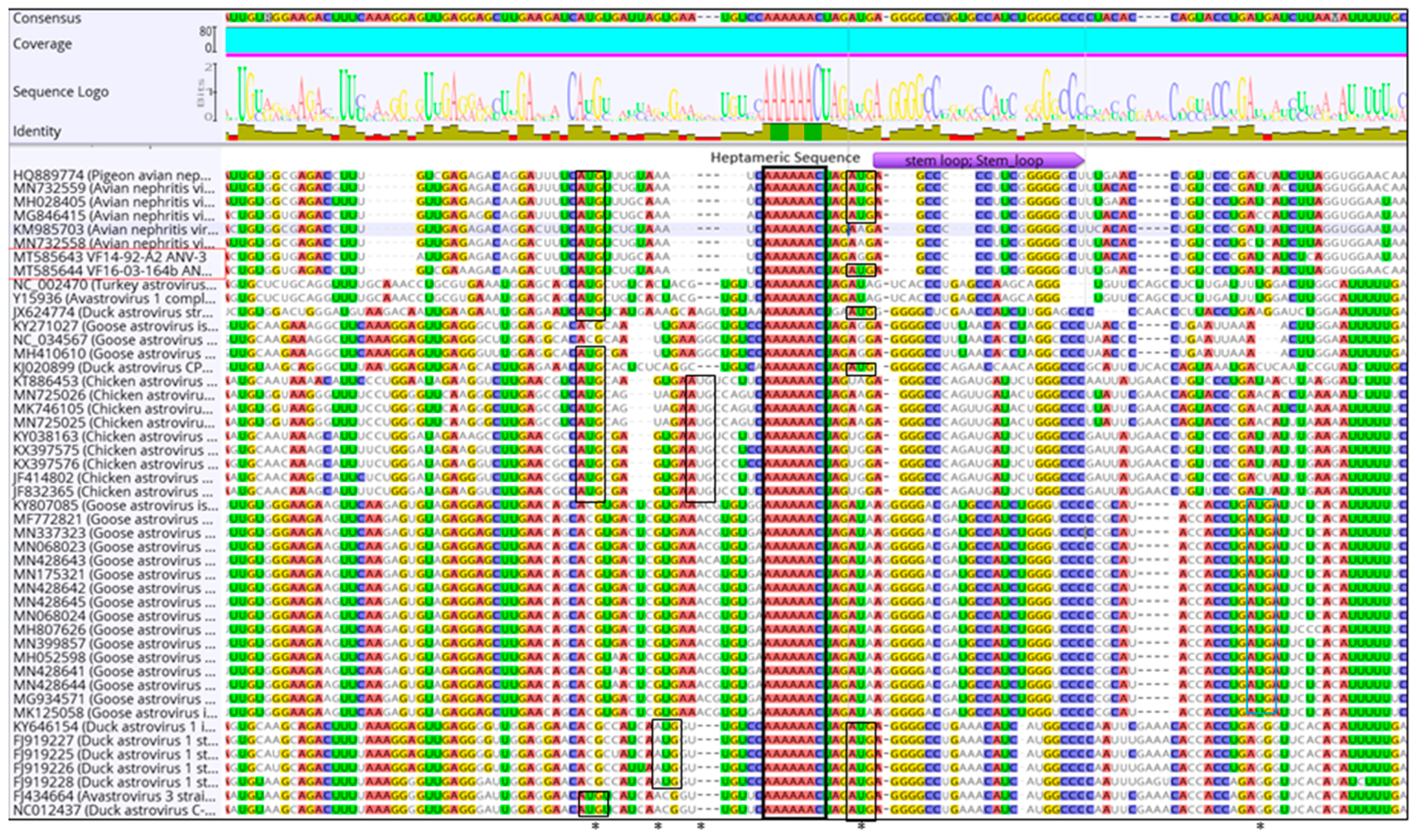
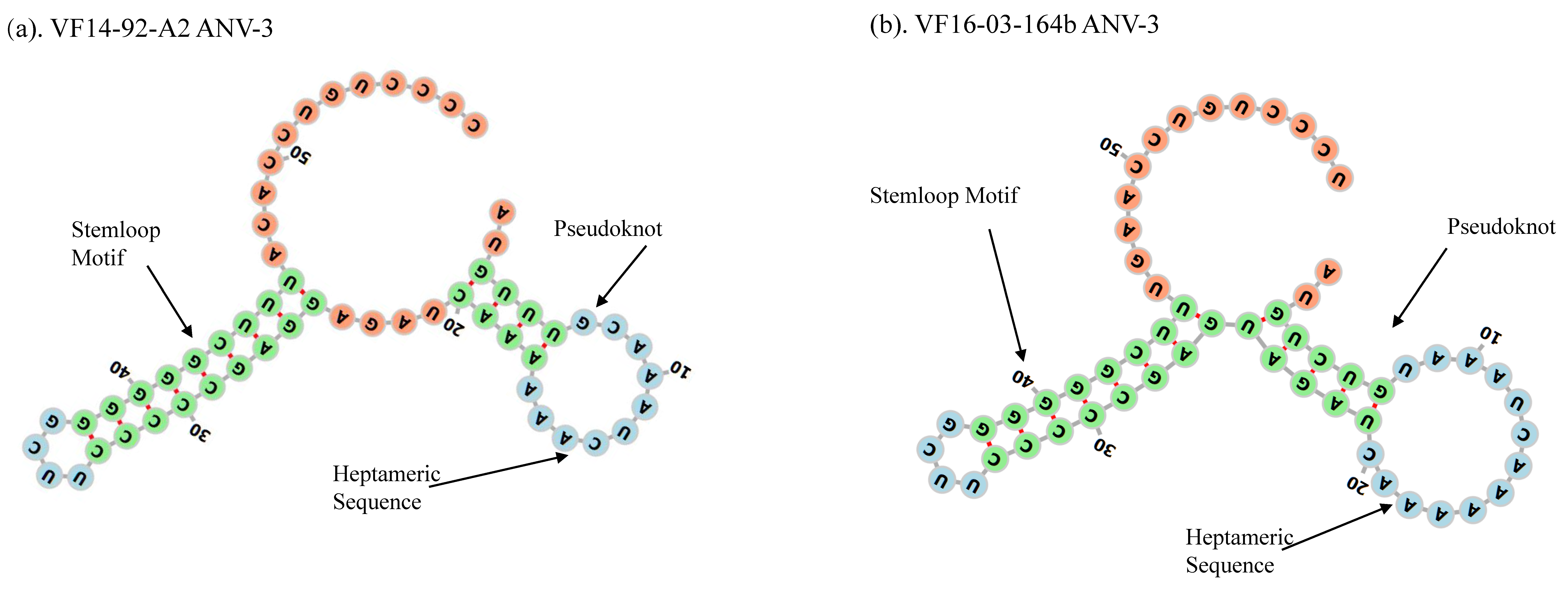
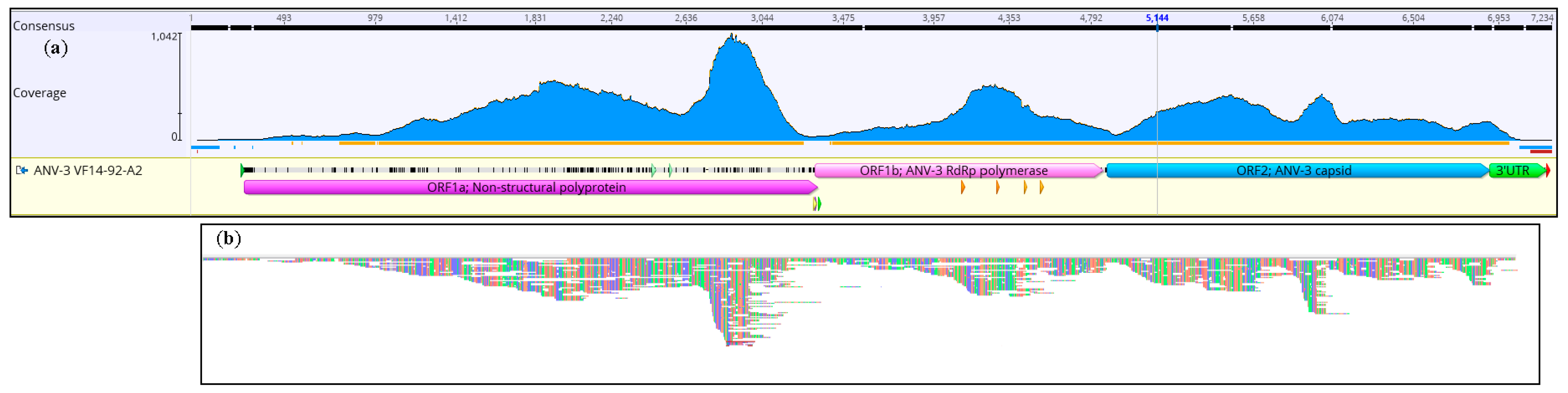
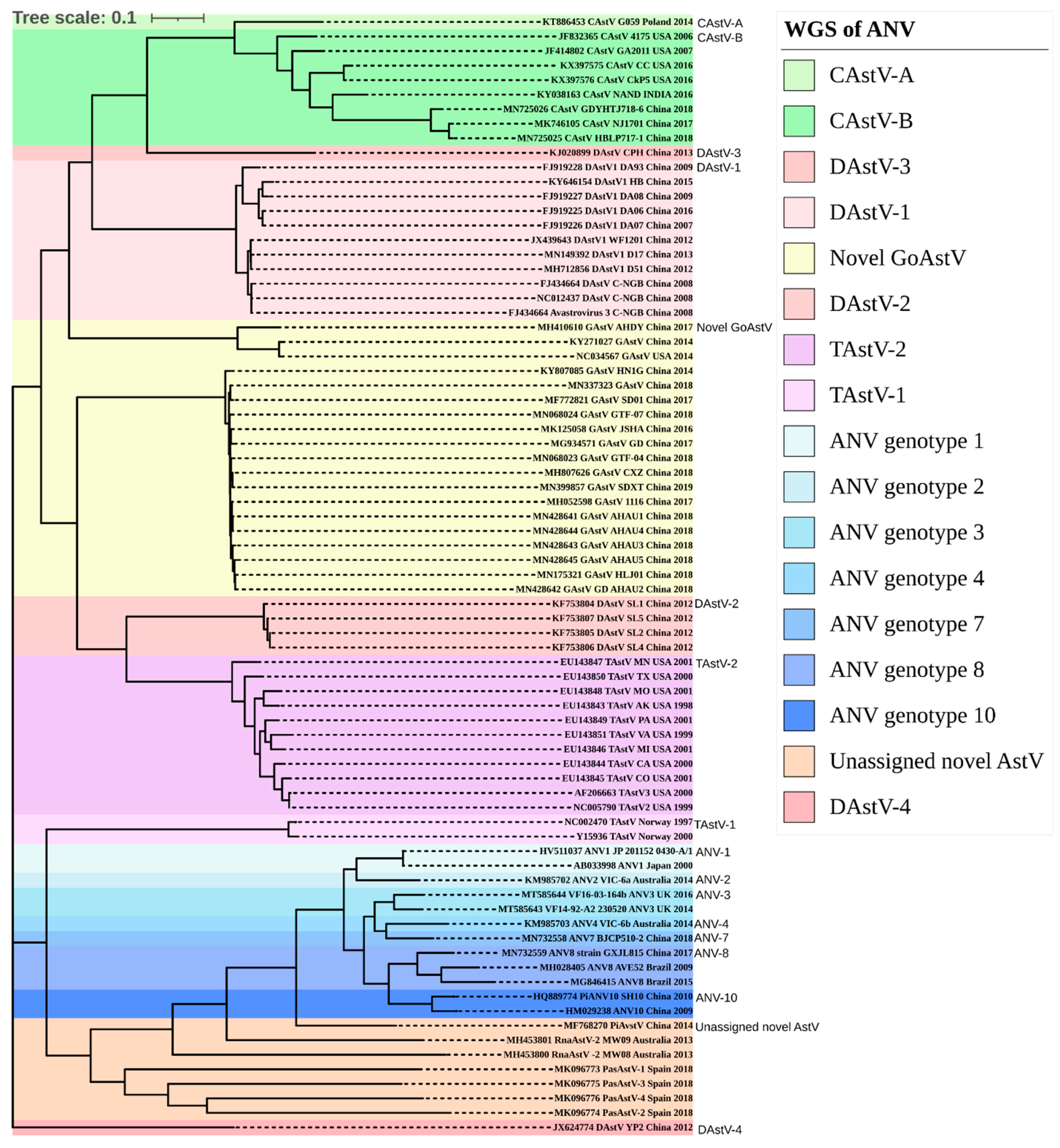
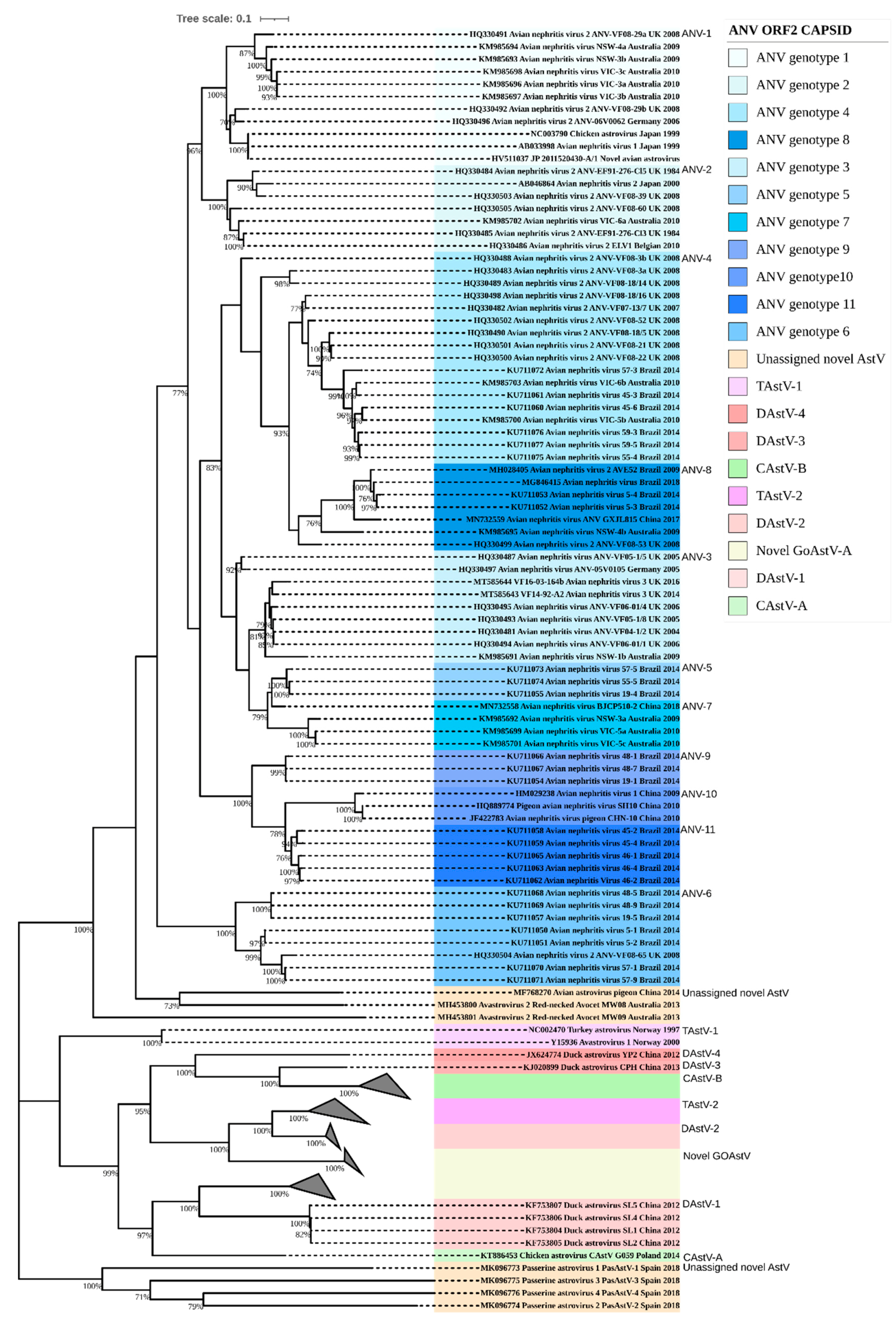
3. Results
3.1. Confirmatory NGS Genome Coverage
3.2. Amino Acid Percentage Homology, Pairwise Distance Percentage Homology, and Recombination
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blomstrom, A.L.; Widen, F.; Hammer, A.S.; Belak, S.; Berg, M. Detection of a novel astrovirus in brain tissue of mink suffering from shaking mink syndrome by use of viral metagenomics. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4392–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Dubovi, E.J.; Simmonds, P.; Medina, J.L.; Henriquez, J.A.; Mishra, N.; Wagner, J.; Tokarz, R.; Cullen, J.M.; Iadarola, M.J.; et al. Serology-enabled discovery of genetically diverse hepaciviruses in a new host. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6171–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Diab, S.; McGraw, S.; Barr, B.; Traslavina, R.; Higgins, R.; Talbot, T.; Blanchard, P.; Rimoldi, G.; Fahsbender, E.; et al. Divergent astrovirus associated with neurologic disease in cattle. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, F.; Schlottau, K.; Scholes, S.; Courtenay, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Höper, D.; Beer, M. A novel astrovirus associated with encephalitis and ganglionitis in domestic sheep. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplin, F.D. Duck Hepatitis. Vet. Rec. 1965, 77, 487–488. [Google Scholar]
- Gough, R.; Collins, M.; Borland, E.; Keymer, L. Astrovirus-like particles associated with hepatitis in ducklings. Vet. Rec. 1984, 114, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Imada, T.; Kawamura, H. Characterization of a picornavirus isolated from broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 1979, 23, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Minetoma, T.; Maeda, M.; Kawamura, H. Susceptibility of Chickens to Avian Nephritis Virus at Various Inoculation Routes and Ages. Avian Dis. 1981, 25, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, T.J.; McNeilly, F.; McFerran, J.B.; McNulty, M.S. A survey of avian sera from Northern Ireland for antibody to avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 1987, 16, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, J.A.; Howes, K.; Reece, R.L.; Kidd, A.W.; Cavanagh, D. Isolation of non-cytopathic viruses implicated in the aetiology of nephritis and baby chick nephropathy and serologically related to avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 1990, 19, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, J.; Tanimura, N.; Uramoto, K.; Narita, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kawamura, H. Pathologically and serologically different avian nephritis virus isolates implicated in etiology of baby chick nephropathy. Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandoki, M.; Dobos-Kovacs, M.; Bakonyi, T.; Rusvai, M. Molecular diagnosis of avian nephritis: Preliminary report. Acta Vet. Hung. 2006, 54, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, K.A.; O’Rourke, D.; Noormohammadi, A.H. Detection of avian nephritis virus in Australian chicken flocks. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, S.M.; Gulhane, A.B.; Deshpande, A.A.; Balaguru, P. Isolation and Identification of Avian Nephritis Virus from Commercial Broiler Chickens. J. Anim. Res. 2017, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, J.; Nakamura, K.; Narita, M.; Furuta, K.; Hihara, H.; Kawamura, H. Visceral urate deposits in chicks inoculated with avian nephritis virus. Vet. Rec. 1989, 124, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, M.; Ohta, K.; Kawamura, H.; Shirai, J.; Nakamura, K.; Abe, F. Pathogenesis of renal dysfunction in chicks experimentally induced by avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 1990, 19, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, M.; Kawamura, H.; Nakamura, K.; Shirai, J.; Furuta, K.; Abe, F. An immunohistological study on the nephritis in chicks experimentally produced with avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 1990, 19, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandoki, M.; Bakonyi, T.; Ivanics, E.; Nemes, C.; Dobos-Kovacs, M.; Rusvai, M. Phylogenetic diversity of avian nephritis virus in Hungarian chicken flocks. Avian Pathol. 2006, 35, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Mase, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; Kubo, M.; Morooka, A. Avian nephritis virus (ANV) as a new member of the family Astroviridae and construction of infectious ANV cDNA. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8487–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeley, C.; Cosgrove, B. 28 nm particles in faeces in infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet 1975, 306, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, S.; Greenberg, H. Fields Virology. In Astroviruses; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Takase, K.; Shinohara, K.; Tsuneyoshi, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamada, S. Isolation and characterisation of cytopathic avian enteroviruses from broiler chicks. Avian Pathol. 1989, 18, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, J.; Nakamura, K.; Shinohara, K.; Kawamura, H. Pathogenicity and antigenicity of avian nephritis isolates. Avian Dis. 1991, 35, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcocks, M.M.; Brown, T.D.; Madeley, C.R.; Carter, M.J. The complete sequence of a human astrovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, E.; Fernández-Luna, T.; López, S.; Méndez-Toss, M.; Arias, C.F. Proteolytic processing of a serotype 8 human astrovirus ORF2 polyprotein. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 7996–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, E.; Murillo, A.; Velázquez, R.; Burnham, A.; Arias, C.F. Replication Cycle of Astroviruses: Astrovirus Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Monroe, S.S.; Koonin, E.V.; Stine, S.E.; Glass, R.I. RNA sequence of astrovirus: Distinctive genomic organization and a putative retrovirus-like ribosomal frameshifting signal that directs the viral replicase synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10539–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, S.S.; Jiang, B.; Stine, S.E.; Koopmans, M.; Glass, R.I. Subgenomic RNA sequence of human astrovirus supports classification of Astroviridae as a new family of RNA viruses. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3611–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, N.K. Identification of structural domains involved in astrovirus capsid biology. Viral Immunol. 2005, 18, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, J.J.; Ten Dam, G.B.; van de Laar, J.M.A.M.; Biermann, Y.; Verstegen, I.; Edens, F.; Schrier, C.C. Detection and characterization of a new astrovirus in chicken and turkeys with enteric and locomotion disorders. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.; Trudgett, J.; Smyth, V.J.; Donnelly, B.; McBride, N.; Welsh, M.D. Capsid protein sequence diversity of avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koci, M.D.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Avian astroviruses. Avian Pathol. 2002, 31, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Sarkar, T.; Nandy, A. Bioinformatics studies of Influenza A hemagglutinin sequence data indicate recombination-like events leading to segment exchanges. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Holmes, E.C. Why do RNA viruses recombine? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth, N.; Honce, R.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Astrovirus evolution and emergence. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Spackman, E.; Woolcock, P.R. Molecular characterization and typing of chicken and turkey astroviruses circulating in the United States: Implications for diagnostics. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.E.; Briggs, J.; Guerrero, M.L.; Matson, D.O.; Pickering, L.K.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.; Berke, T.; Mitchell, D.K. Molecular characterization of a novel recombinant strain of human astrovirus associated with gastroenteritis in children. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamings, A.; Hewson, K.A.; O’Rourke, D.; Ignjatovic, J.; Noormohammadi, A.H. High-resolution melt curve analysis to confirm the presence of co-circulating isolates of avian nephritis virus in commercial chicken flocks. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.L.; Beserra, L.A.R.; Soares, R.M.; Gregori, F. Avian nephritis virus (ANV) on Brazilian chickens farms: Circulating genotypes and intra-genotypic diversity. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, I.; Barr, D.; Reece, R.; Forsyth, W.; Ewing, I. Experimental reproduction of the runting-stunting syndrome of broiler chickens. Avian Pathol. 1988, 17, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, F.; Nir, I.; Heller, D. Stunting syndrome in broilers: Effect of stunting syndrome inoculum obtained from stunting syndrome affected broilers, on broilers, leghorns and turkey poults. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, M.S.; Allan, G.M.; Connor, T.J.; McFerran, J.B.; McCracken, R.M. An entero-like virus associated with the runting syndrome in broiler chickens. Avian Pathol. 1984, 13, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, D.; Gough, R.E.; Collins, M.S.; Lanning, D. Isolation of an enterovirus-like agent from the meconium of dead-in-shell chicken embryos. Vet. Rec. 1984, 114, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, J.A.; Connor, T.J.; McNeilly, F.; Moffet, D.A.; Calvert, V.M.; McNulty, M.S. Studies on the pathogenicity of enterovirus-like viruses in chickens. Avian Pathol. 2007, 36, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Strother, K.O.; Mundt, E.; Zsak, L.; Day, J.M.; Spackman, E. Molecular characterization of avian astroviruses. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.I.; El-Gazzar, M.; Sellers, H.S.; Dorea, F.; Williams, S.M.; Kim, T.; Collett, S.; Mundt, E. Investigation into the aetiology of runting and stunting syndrome in chickens. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaney, R.; Trudgett, J.; Trudgett, A.; Meharg, C.; Smyth, V. A metagenomic comparison of endemic viruses from broiler chickens with runting-stunting syndrome and from normal birds. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, L.F.N.; Parra, S.H.S.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Carranza, C.; De La Torre, D.I.; Pedroso, A.C.; Ferreira, A.J.P. Detection of enteric viruses in pancreas and spleen of broilers with runting-stunting syndrome (RSS). Pesqui. Veterinária Brasileira 2016, 36, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, V.J. A Review of the Strain Diversity and Pathogenesis of Chicken Astrovirus. Viruses 2017, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, K.; Uchimura, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamada, S. Susceptibility of embryos and chicks, derived from immunized breeding hens, to avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 1994, 23, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodasara, P.; Prajapati, K.S.; Ghodasara, D.J.; Joshi, B.; Thakkar, H.; Banerjee, J.; Pal, J. Isolation and detection of avian nephritis virus by RT-PCR from commercial broiler flocks affected with visceral gout in India. Indian J. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 39, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, L.F.N.; Parra, S.H.S.; De la Torre, D.; Catroxo, M.H.; Buim, M.R.; Chacon, R.V.; Ferreira, C.S.A.; Piantino Ferreira, A.J. Isolation of avian nephritis virus from chickens showing enteric disorders. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3478–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biđin, M.; Biđin, Z.; Majnarić, D.; Tišljar, M.; Lojkić, I. Circulation and phylogenetic relationship of chicken and turkey-origin astroviruses detected in domestic ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus). Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, R.; Howes, K.; Frazier, J.A. Experimental factors affecting mortality following inoculation of chickens with avian nephritis virus (G-4260). Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R. Using the Velvet de novo assembler for short-read sequencing technologies. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010, 31, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geer, L.Y.; Marchler-Bauer, A.; Geer, R.C.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Liu, C.; Shi, W.; Bryant, S.H. The NCBI BioSystems database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D492–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Rupek, P.; Richter, D.C.; Urich, T.; Gilbert, J.A.; Meyer, F.; Wilke, A.; Huson, D.H. Functional analysis of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes using SEED and KEGG. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12 (Suppl. S1), S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Beier, S.; Flade, I.; Gorska, A.; El-Hadidi, M.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Tappu, R. MEGAN Community Edition—Interactive Exploration and Analysis of Large-Scale Microbiome Sequencing Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: Protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33 (Suppl. S2), W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padidam, M.; Sawyer, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 1999, 265, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.; Williamson, C. A modified bootscan algorithm for automated identification of recombinant sequences and recombination breakpoints. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2005, 21, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M. Analyzing the mosaic structure of genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.J.; Armstrong, J.S.; Gibbs, A.J. Sister-scanning: A Monte Carlo procedure for assessing signals in recombinant sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C.; Worobey, M.; Rambaut, A. Phylogenetic evidence for recombination in dengue virus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiller, G.F. Phylogenetic profiles: A graphical method for detecting genetic recombinations in homologous sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Rybicki, E. RDP: Detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.F.; Posada, D.; Feldman, M.W. An exact nonparametric method for inferring mosaic structure in sequence triplets. Genetics 2007, 176, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, V.J.; Jewhurst, H.L.; Wilkinson, D.S.; Adair, B.M.; Gordon, A.W.; Todd, D. Development and evaluation of real-time TaqMan(R) RT-PCR assays for the detection of avian nephritis virus and chicken astrovirus in chickens. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, F. Trim galore. A wrapper tool around Cutadapt and FastQC to consistently apply quality and adapter trimming to FastQ files. Genome Announc. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Afgan, E.; Sloggett, C.; Goonasekera, N.; Makunin, I.; Benson, D.; Crowe, M.; Gladman, S.; Kowsar, Y.; Pheasant, M.; Horst, R.; et al. Genomics Virtual Laboratory: A Practical Bioinformatics Workbench for the Cloud. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, T.R.; Loman, N.J.; Thompson, S.; Smith, A.; Southgate, J.; Poplawski, R.; Bull, M.J.; Richardson, E.; Ismail, M.; Elwood-Thompson, S. CLIMB (the Cloud Infrastructure for Microbial Bioinformatics): An online resource for the medical microbiology community. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Stephen, G.; Bayer, M.; Cock, P.J.; Pritchard, L.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.D.; Marshall, D. Using Tablet for visual exploration of second-generation sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icho, T.; Wickner, R.B. The double-stranded RNA genome of yeast virus L-A encodes its own putative RNA polymerase by fusing two open reading frames. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 6716–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, D.L.; Levin, J.G.; Rein, A.; Oroszlan, S. Translational Suppression in Retroviral Gene Expression: Advances in Virus Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 193–239. [Google Scholar]
- Koonin, E.V. The phylogeny of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of positive-strand RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72 Pt 9, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.G.S.; Krishna, N.K.; Méndez, E.; Monroe, S.S.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses; Ninth Report of the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 953–959. [Google Scholar]
- Jonassen, C.M.; Jonassen, T.T.; Sveen, T.M.; Grinde, B. Complete genomic sequences of astroviruses from sheep and turkey: Comparison with related viruses. Virus Res. 2003, 91, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, E.; Salas-Ocampo, M.P.; Munguia, M.E.; Arias, C.F. Protein products of the open reading frames encoding nonstructural proteins of human astrovirus serotype 8. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11378–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingwall, C.; Laskey, R.A. Nuclear targeting sequences—A consensus? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1991, 16, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.; Dilwortht, S.M.; Laskey, R.A.; Dingwall, C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: Identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell 1991, 64, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcocks, M.M.; Boxall, A.S.; Carter, M.J. Processing and intracellular location of human astrovirusnon-structural proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2607–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadevi, N.; Rodriguez, J.; Roy, P. A leucine zipper-like domain is essential for dimerization and encapsidation of bluetongue virus nucleocapsid protein VP4. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinman, J.D. Mechanisms and implications of programmed translational frameshifting. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, C.M.; Jonassen, T.O.; Grinde, B. A common RNA motif in the 3′ end of the genomes of astroviruses, avian infectious bronchitis virus and an equine rhinovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 Pt 4, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofstad, T.; Jonassen, C.M. Screening of Feral and Wood Pigeons for Viruses Harbouring a Conserved Mobile Viral Element: Characterization of Novel Astroviruses and Picornaviruses. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengs, T.; Jonassen, C.M. Distribution and Evolutionary History of the Mobile Genetic Element s2m in Coronaviruses. Diseases 2016, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.; Trudgett, J.; McNeilly, F.; McBride, N.; Donnelly, B.; Smyth, V.J.; Jewhurst, H.L.; Adair, B.M. Development and application of an RT-PCR test for detecting avian nephritis virus. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imada, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Miura, N.; Kawamura, H. Antibody survey against avian nephritis virus among chickens in Japan. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q. 1980, 20, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Domingo, E.; Holland, J.J. RNA virus mutations and fitness for survival. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Welch, J. Frequency and dynamics of recombination within different species of human enteroviruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temp (°C) | Amplicon Size in Base Pairs (nt) | Position in the ANV-3 VF14-92-A2 Genome (5′-3′) (nt) | Assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1AF | GCGCAAAGTGACTCTAG | 55 | 425 | 341–357 | In-house |
| 1AR | CAAGTGCCAGAGCTTC | 749–764 | |||
| 2AF | GCTTGGATTGACTACCAG | 55 | 323 | 2363–2380 | In-house |
| 2AR | CTGAGCGCTGCTTCT | 2671–2685 | |||
| 3AF | AGGGATTGAACTTCCTG | 54 | 332 | 4527–4543 | In-house |
| 3AR | TATCTGCCTAGTGAGACC | 4841–4858 | |||
| 4AF | CCTGAAGCTGTGTCCTA | 51 | 365 | 4465–4481 | In-house |
| 4AR | GTCCAGAAATCGTACCAAG | 4811–4829 | |||
| 5AF | AGGTCATTTCCACCTACTC | 54 | 777 | 5716–5816 | In-house |
| 5AR | TTCGAGTTGATCCACAC | 6558–6574 | |||
| 6AF | GCCCGGAGAAGGCGACT | 53 | 345 | 6229–6245 | In-house |
| 6AR | TCGAGTTGATCCACACAATCAAACCTC | 6547–6573 | |||
| 5′ F | CCGAATAGATGGGATGGCT | 50 | 321 | 1–19 | In-house |
| 5′ R | GTCATCACAGCCTTTTCCTC | 302–321 | |||
| 3′ F | GTAAACCACTGGYTGGCTGACT | 50 | 271 | 6682–6703 | [73] |
| 3′R | TTTTTTTTTTTTAAAAGTTAGC | 6931–6952 | In-house | ||
| Pre-ORF2 | ACCTTGAATCCCTGTGGGGCA | 57 | 2535 | 4406–4426 | [31] |
| Post-ORF2 | AAAAGTTAGCCAATTCAAAATTAATTC | 6914–6940 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagan Tregaskis, P.; Devaney, R.; Smyth, V.J. The First Whole Genome Sequence and Characterisation of Avian Nephritis Virus Genotype 3. Viruses 2021, 13, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020235
Lagan Tregaskis P, Devaney R, Smyth VJ. The First Whole Genome Sequence and Characterisation of Avian Nephritis Virus Genotype 3. Viruses. 2021; 13(2):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagan Tregaskis, Paula, Ryan Devaney, and Victoria J. Smyth. 2021. "The First Whole Genome Sequence and Characterisation of Avian Nephritis Virus Genotype 3" Viruses 13, no. 2: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020235
APA StyleLagan Tregaskis, P., Devaney, R., & Smyth, V. J. (2021). The First Whole Genome Sequence and Characterisation of Avian Nephritis Virus Genotype 3. Viruses, 13(2), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020235







