Methods to Measure Antibody Neutralization of Live Human Coronavirus OC43
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Human Specimens
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Determining the Titer of OC43
2.6. Expression and Purification of Spike Proteins
2.7. Tetramerization of Antigens
2.8. Tetramer Enrichment
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Neutralization Screen
2.11. B Cell Receptor Sequencing and Cloning
2.12. Monoclonal Antibody Production
2.13. Biolayer Interferometry
2.14. CPE-Based OC43 Neutralization Assay
2.15. ELISA-Based OC43 Microneutralization Assay
2.16. Luminex OC43-Binding IgG Assay
2.17. Statistics
3. Results
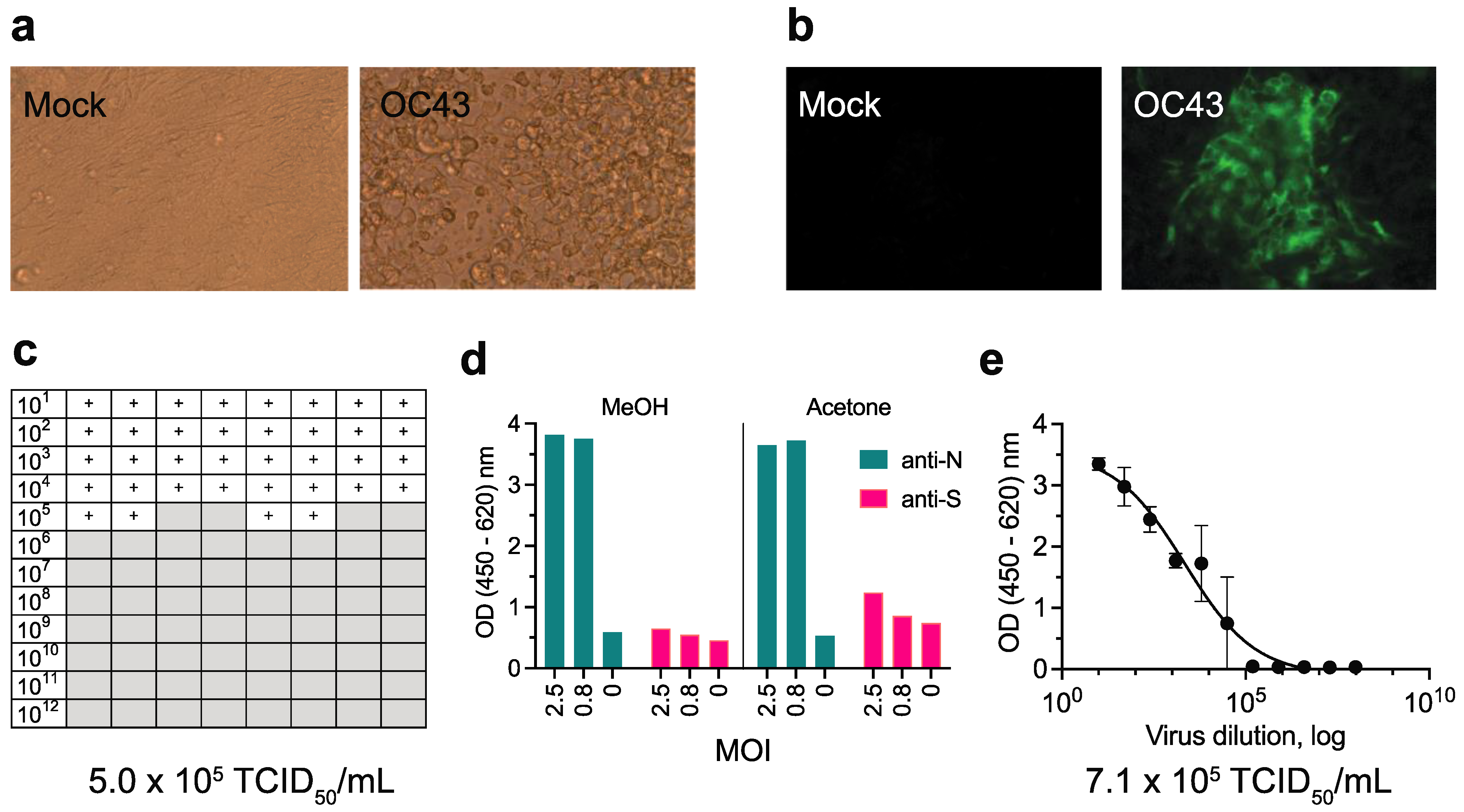
3.1. Comparison of Methods to Determine the Titer of OC43
3.2. Identification of a B Cell Producing an OC43 Neutralizing Antibody
3.3. Comparison of Methods to Determine the Neutralizing Titer of an OC43 Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody
3.4. Measurement of Neutralizing Antibodies in Human Serum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corman, V.M.; Muth, D.; Niemeyer, D.; Drosten, C. Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2018, 100, 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ogimi, C.; Greninger, A.L.; Waghmare, A.A.; Kuypers, J.M.; Shean, R.C.; Xie, H.; Leisenring, W.M.; Stevens-Ayers, T.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Englund, J.A.; et al. Prolonged Shedding of Human Coronavirus in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients: Risk Factors and Viral Genome Evolution. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogimi, C.; Waghmare, A.A.; Kuypers, J.M.; Xie, H.; Yeung, C.C.; Leisenring, W.M.; Seo, S.; Choi, S.M.; Jerome, K.R.; Englund, J.A.; et al. Clinical Significance of Human Coronavirus in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples From Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients and Patients With Hematologic Malignancies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinana, J.L.; Xhaard, A.; Tridello, G.; Passweg, J.; Kozijn, A.; Polverelli, N.; Heras, I.; Perez, A.; Sanz, J.; Berghuis, D.; et al. Seasonal Human Coronavirus Respiratory Tract Infection in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; Dees, J.H.; Becker, W.B.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Chanock, R.M. Recovery in tracheal organ cultures of novel viruses from patients with respiratory disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1967, 57, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruckova, M.; McIntosh, K.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Chanock, R.M. The adaptation of two human coronavirus strains (OC38 and OC43) to growth in cell monolayers. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1970, 135, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; Becker, W.B.; Chanock, R.M. Growth in suckling-mouse brain of “IBV-like” viruses from patients with upper respiratory tract disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1967, 58, 2268–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Moes, E.; Thoelen, I.; Wollants, E.; Lemey, P.; Vandamme, A.M.; Van Ranst, M. Complete genomic sequence of human coronavirus OC43: Molecular clock analysis suggests a relatively recent zoonotic coronavirus transmission event. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Lemey, P.; Maes, P.; Van Reeth, K.; Nauwynck, H.; Pensaert, M.; Van Ranst, M. Evolutionary history of the closely related group 2 coronaviruses: Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus, bovine coronavirus, and human coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7270–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Tsang, A.K.; Fan, R.Y.; Luk, H.K.; Cai, J.P.; Chan, K.H.; Zheng, B.J.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of a novel coronavirus, China Rattus coronavirus HKU24, from Norway rats supports the murine origin of Betacoronavirus 1 and has implications for the ancestor of Betacoronavirus lineage A. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3076–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorse, G.J.; Patel, G.B.; Vitale, J.N.; O’Connor, T.Z. Prevalence of antibodies to four human coronaviruses is lower in nasal secretions than in serum. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.L.; Graham, B.S. Viral and host factors in human respiratory syncytial virus pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2040–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, C.D.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y.; Billings, M.; Eick-Cost, A.; Couzens, L.; Sanchez, J.L.; Hawksworth, A.W.; Seguin, P.; Myers, C.A.; et al. Neutralizing and Neuraminidase Antibodies Correlate With Protection Against Influenza During a Late Season A/H3N2 Outbreak Among Unvaccinated Military Recruits. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krammer, F. The human antibody response to influenza A virus infection and vaccination. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, D.S.; Wheatley, A.K.; Ramuta, M.D.; Reynaldi, A.; Cromer, D.; Subbarao, K.; O’Connor, D.H.; Kent, S.J.; Davenport, M.P. Measuring immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection: Comparing assays and animal models. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.M.; Tortorici, M.A.; Park, Y.J.; Walls, A.C.; Homad, L.; Acton, O.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Wang, C.; Xiong, X.; de van der Schueren, W.; et al. Structural basis for broad coronavirus neutralization. Nat. Struct Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Sauer, M.M.; Czudnochowski, N.; Low, J.S.; Tortorici, M.A.; Housley, M.P.; Noack, J.; Walls, A.C.; Bowen, J.E.; Guarino, B.; et al. Broad betacoronavirus neutralization by a stem helix-specific human antibody. Science 2021, 373, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, R.E.; Ameny, S.; Arkatkar, T.; Seese, A.; Wall, A.; Khan, I.; Carter, J.J.; Scherer, E.M.; Rawlings, D.J.; Galloway, D.A.; et al. Generation of a cost-effective cell line for support of high-throughput isolation of primary human B cells and monoclonal neutralizing antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2020, 488, 112901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, C.C.; Doll, M.K.; Morrison, K.T.; McLaughlin, W.L.; O’Connor, T.; Sholukh, A.M.; Bossard, E.L.; Phasouk, K.; Ford, E.S.; Diem, K.; et al. High Community SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Seroprevalence in a Ski Resort Community, Blaine County, Idaho, US. Preliminary Results. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, K.; McAuliffe, J.; Vogel, L.; Fahle, G.; Fischer, S.; Tatti, K.; Packard, M.; Shieh, W.J.; Zaki, S.; Murphy, B. Prior infection and passive transfer of neutralizing antibody prevent replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the respiratory tract of mice. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3572–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hierholzer, J.; Killington, R. Virus isolation and quantitation. In Virology Methods Manual, 1st ed.; Mahy, B., Kangro, H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; p. 374. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Cottrell, C.A.; Wang, N.; Pallesen, J.; Yassine, H.M.; Turner, H.L.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S.; Ward, A.B. Pre-fusion structure of a human coronavirus spike protein. Nature 2016, 531, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Chuang, G.Y.; Xu, K.; Zhou, T.; Acharya, P.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Ou, L.; Zhang, B.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, B.; Gilardi, V.; et al. Structure-based design of a quadrivalent fusion glycoprotein vaccine for human parainfluenza virus types 1–4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12265–12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Singh, S.; Weidle, C.; Rodarte, J.; Bakthavatsalam, R.; Perkins, J.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Kwong, P.D.; McGuire, A.T.; Pancera, M.; et al. Protective antibodies against human parainfluenza virus type 3 infection. mABs 2021, 13, 1912884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, A.T.; Gray, M.D.; Dosenovic, P.; Gitlin, A.D.; Freund, N.T.; Petersen, J.; Correnti, C.; Johnsen, W.; Kegel, R.; Stuart, A.B.; et al. Specifically modified Env immunogens activate B-cell precursors of broadly neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in transgenic mice. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholukh, A.M.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Ford, E.S.; Miner, M.D.; Hou, Y.J.; Tse, L.V.; Kaiser, H.; Zhu, H.; Lu, J.; Madarampalli, B.; et al. Evaluation of Cell-Based and Surrogate SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e00527-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.J.; Martinez, R.J.; Titcombe, P.J.; Barsness, L.O.; Thomas, S.R.; Zhang, N.; Katzman, S.D.; Jenkins, M.K.; Mueller, D.L. Deletion and anergy of polyclonal B cells specific for ubiquitous membrane-bound self-antigen. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steach, H.R.; DeBuysscher, B.L.; Schwartz, A.; Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Baker, M.L.; Tooley, M.R.; Pease, N.A.; Taylor, J.J. Cross-Reactivity with Self-Antigen Tunes the Functional Potential of Naive B Cells Specific for Foreign Antigens. J. Immunol. 2019, 204, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, T.; DeBuysscher, B.L.; Weidle, C.; Schwartz, A.; Wall, A.; Gray, M.D.; Feng, J.; Steach, H.R.; Fitzpatrick, K.S.; Gewe, M.M.; et al. Detection and activation of HIV broadly neutralizing antibody precursor B cells using anti-idiotypes. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Taylor, J.J. Techniques to Study Antigen-Specific B Cell Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlburt, N.K.; Homad, L.J.; Sinha, I.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; Wan, Y.-H.; Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Sholukh, A.M.; Zhou, P.; Burton, D.R.; et al. Structural definition of a pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing epitope on the spike S2 subunit. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, P.A.; Page, M.; Bernasconi, V.; Mattiuzzo, G.; Dull, P.; Makar, K.; Plotkin, S.; Knezevic, I. WHO International Standard for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin. Lancet 2021, 397, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biacchesi, S.; Skiadopoulos, M.H.; Yang, L.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L.; Buchholz, U.J. Rapid human metapneumovirus microneutralization assay based on green fluorescent protein expression. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 128, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chang, J.S.; Nason, M.; Rangel, D.; Gall, J.G.; Graham, B.S.; Ledgerwood, J.E. A flow cytometry-based assay to assess RSV-specific neutralizing antibody is reproducible, efficient and accurate. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 362, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Sholukh, A.M.; Gray, M.; Bossard, E.L.; Ford, E.S.; Corbett, K.S.; Corey, L.; Taylor, J.J. Methods to Measure Antibody Neutralization of Live Human Coronavirus OC43. Viruses 2021, 13, 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102075
Boonyaratanakornkit J, Sholukh AM, Gray M, Bossard EL, Ford ES, Corbett KS, Corey L, Taylor JJ. Methods to Measure Antibody Neutralization of Live Human Coronavirus OC43. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102075
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoonyaratanakornkit, Jim, Anton M. Sholukh, Matthew Gray, Emily L. Bossard, Emily S. Ford, Kizzmekia S. Corbett, Lawrence Corey, and Justin J. Taylor. 2021. "Methods to Measure Antibody Neutralization of Live Human Coronavirus OC43" Viruses 13, no. 10: 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102075
APA StyleBoonyaratanakornkit, J., Sholukh, A. M., Gray, M., Bossard, E. L., Ford, E. S., Corbett, K. S., Corey, L., & Taylor, J. J. (2021). Methods to Measure Antibody Neutralization of Live Human Coronavirus OC43. Viruses, 13(10), 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102075





