Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Endemic and Emerging Coronaviruses in Humans, Domestic Animals, and Wildlife
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Coronaviruses in Livestock and Companion Animals
3.1.1. Bovine Coronaviruses (BCoVs) in Ruminants
3.1.2. Swine Coronaviruses
3.1.3. Coronaviruses in Camel
3.1.4. Coronavirus Diversity in Birds
3.1.5. Coronavirus in Companion Animals (Dogs and Cats)
3.1.6. Other Coronaviruses
3.2. Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Coronaviruses in Wild Animals
3.2.1. Coronaviruses Diversity in Bats
3.2.2. Coronaviruses Diversity in Pangolin
3.2.3. Coronaviruses in Wild Felids
3.2.4. Coronaviruses in Miscellaneous Wild Animals
3.2.5. Coronaviruses in Ferret and Mink
3.2.6. Coronavirus in Rodents
3.2.7. Coronavirus in Non-Human Primates
3.2.8. Coronavirus in Marine Mammals
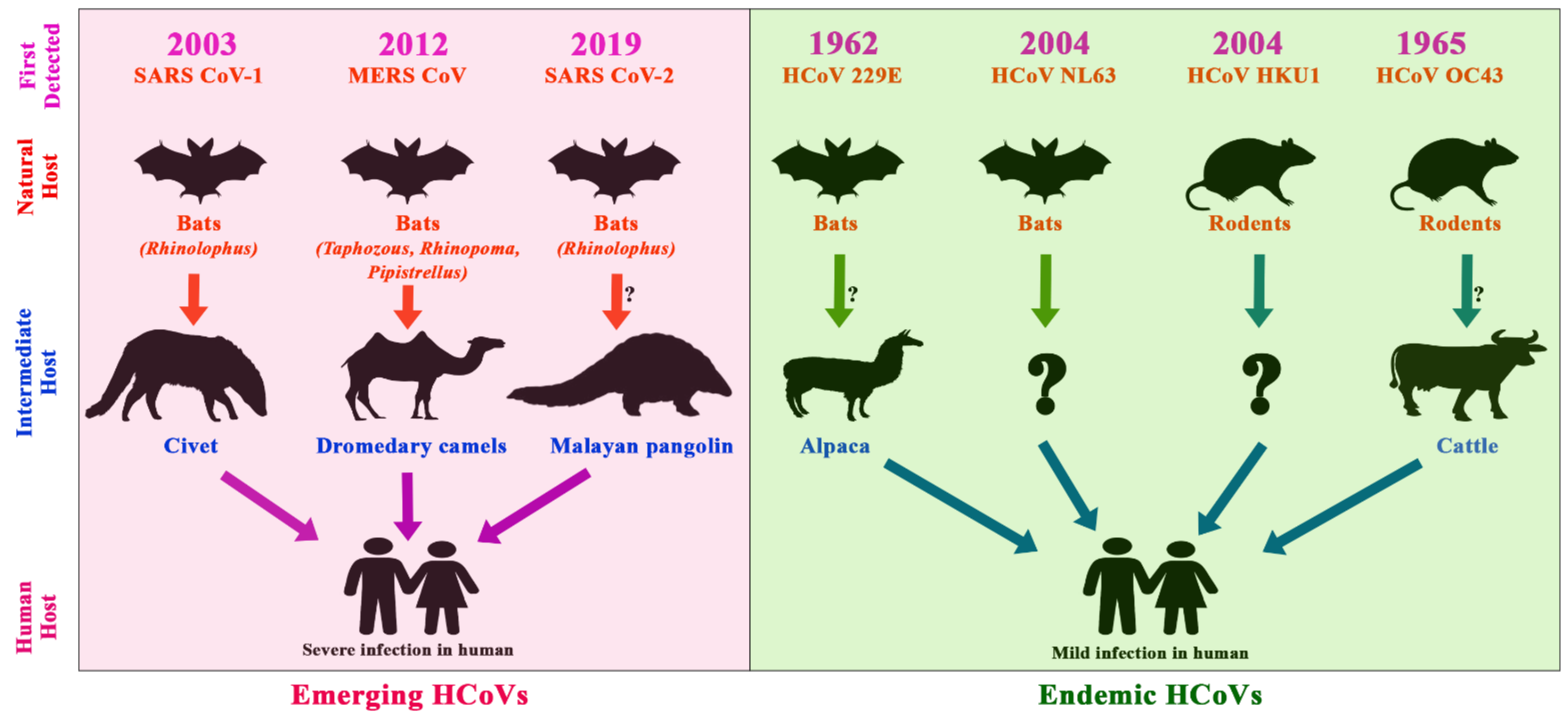
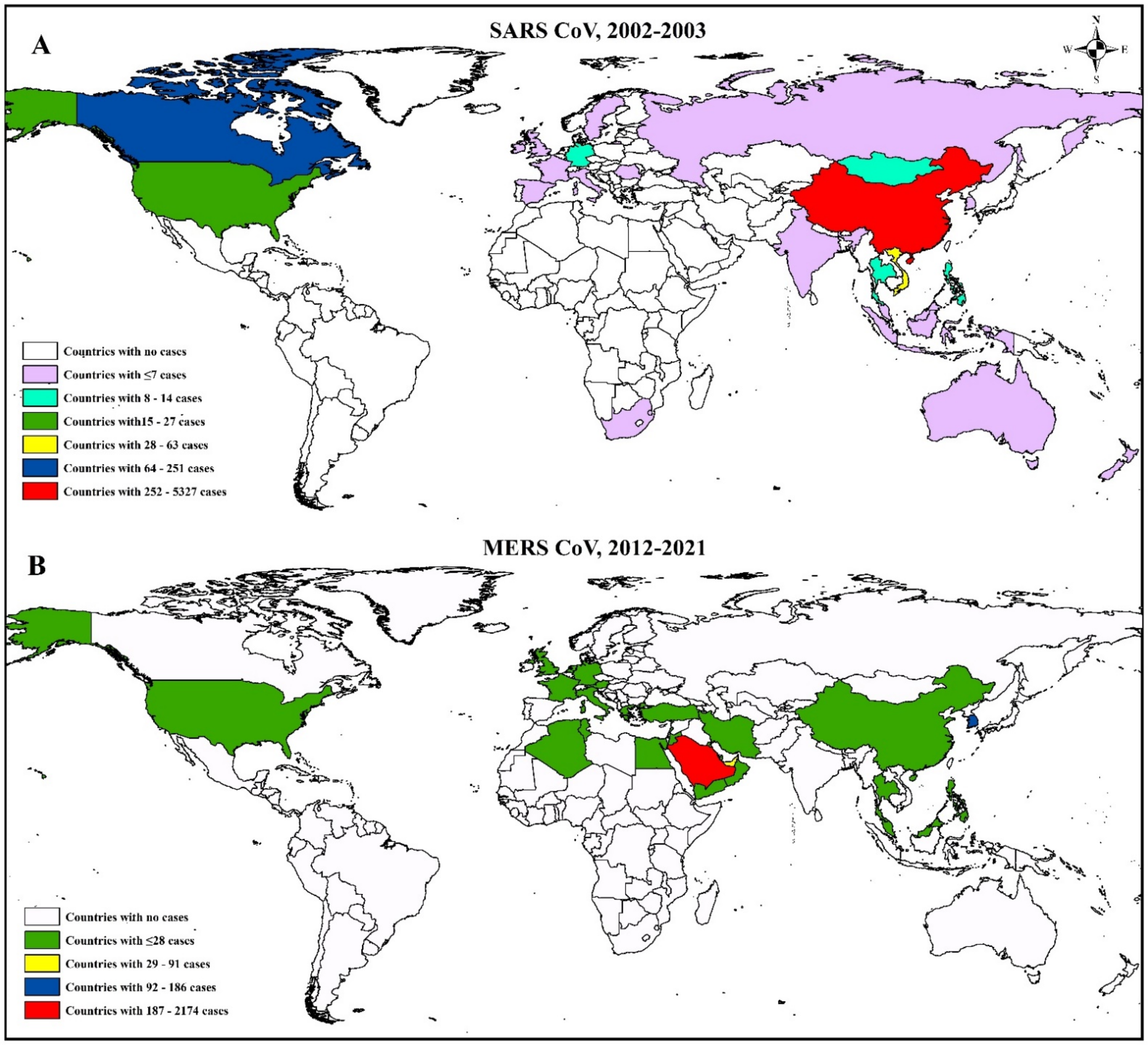
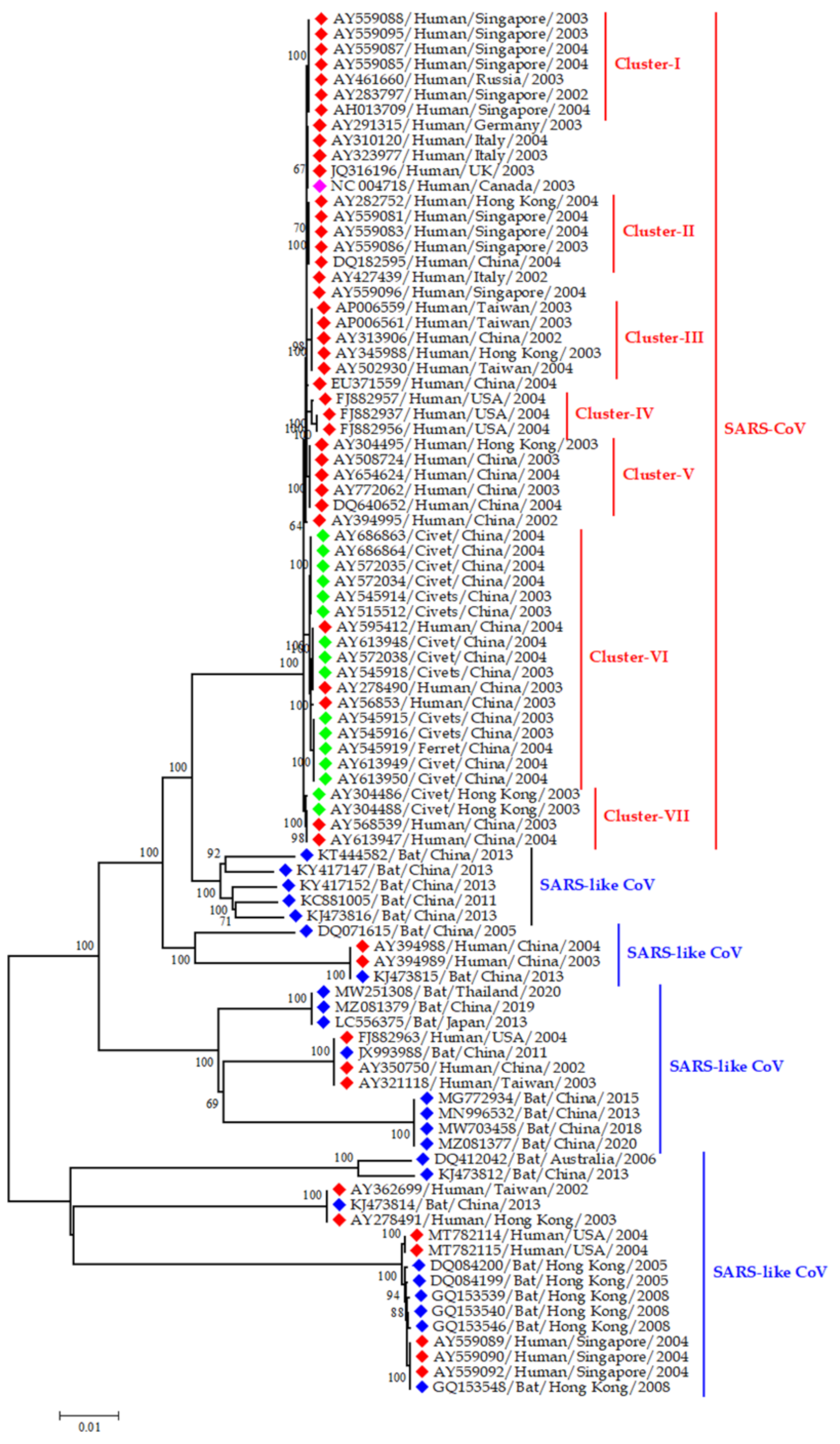
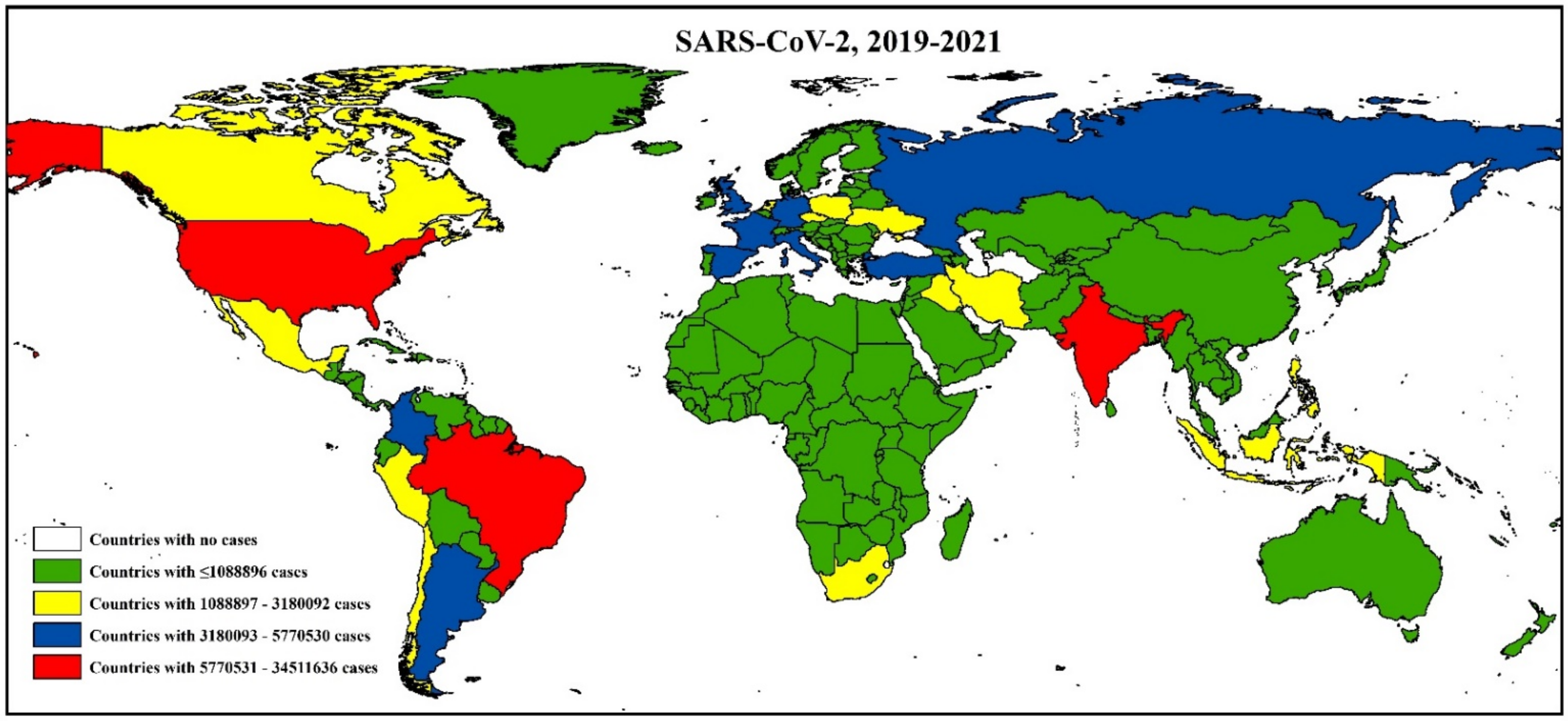
3.3. Epidemiology and Evolutionary Dynamics of Emerging Coronaviruses in Humans
4. Discussion
4.1. Emerging and Endemic CoVs Infection in Livestock and Companion Animals
4.2. Emerging CoVs in Wildlife
4.3. Emerging and Endemic CoVs Infection in Humans
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, A.; Sayeed, M.A.; Rahman, M.K.; Ferdous, J.; Shano, S.; Choudhury, S.D.; Hassan, M.M. Spatiotemporal patterns and trends of community transmission of the pandemic COVID-19 in South Asia: Bangladesh as a case study. Biosaf. Health 2020, 3, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Virtual Press Conference on COVID-19—11 March 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/transcripts/who-audio-emergencies-coronavirus-press-conference-full-and-final-11mar2020.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Arora, P.; Jafferany, M.; Lotti, T.; Sadoughifar, R.; Goldust, M. Learning from history: Coronavirus outbreaks in the past. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. In Coronaviruses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.; Wang, M. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malik, Y.A. Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2. Malays. J. Pathol. 2020, 42, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Micro. 2020, 5, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. Receptor recognition mechanisms of coronaviruses: A decade of structural studies. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1954–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. Receptor recognition and cross-species infections of SARS coronavirus. Antiviral. Res. 2013, 100, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. Recombination, reservoirs, and the modular spike: Mechanisms of coronavirus cross-species transmission. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3134–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Micro. 2006, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hulswit, R.J.; Kenney, S.P.; Widjaja, I.; Jung, K.; Alhamo, M.A.; van Dieren, B.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Saif, L.J.; Bosch, B.-J. Broad receptor engagement of an emerging global coronavirus may potentiate its diverse cross-species transmissibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5135–E5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Leibowitz, J.L. Coronavirus pathogenesis. Adv. Virus Res. 2011, 81, 85–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crossley, B.M.; Mock, R.E.; Callison, S.A.; Hietala, S.K. Identification and characterization of a novel alpaca respiratory coronavirus most closely related to the human coronavirus 229E. Viruses 2012, 4, 3689–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Peng, G.; Qi, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Du, L. Receptor usage and cell entry of porcine epidemic diarrhea coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6121–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.-W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.-S.; Fung, S.-Y.; Chan, C.-P.; Jin, D.-Y. Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Holmes, E.C. A genomic perspective on the origin and emergence of SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2020, 181, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshukairi, A.N.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Nehdi, A.; Baharoon, S.A.; Layqah, L.; Bokhari, A.; Al Johani, S.M.; Samman, N.; Boudjelal, M. High prevalence of MERS-CoV infection in camel workers in Saudi Arabia. MBio 2018, 9, e01985-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; Bi, Y.-H.; Wang, Q.-H.; Chen, X.-W.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Yao, Y.-G. Zoonotic origins of human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19/SARS-CoV-2): Why is this work important? Zool. Res. 2020, 41, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallapaty, S. Coronaviruses closely related to the pandemic virus discovered in Japan and Cambodia. Nature 2020, 588, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacharapluesadee, S.; Tan, C.W.; Maneeorn, P.; Duengkae, P.; Zhu, F.; Joyjinda, Y.; Kaewpom, T.; Chia, W.N.; Ampoot, W.; Lim, B.L. Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 related coronaviruses circulating in bats and pangolins in Southeast Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Liu, R.; He, X.; Shuai, L.; Sun, Z. Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS–coronavirus 2. Science 2020, 368, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfmann, P.J.; Hatta, M.; Chiba, S.; Maemura, T.; Fan, S.; Takeda, M.; Kinoshita, N.; Hattori, S.-i.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in domestic cats. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertzbach, L.D.; Vladimirova, D.; Dietert, K.; Abdelgawad, A.; Gruber, A.D.; Osterrieder, N.; Trimpert, J. SARS-CoV-2 infection of Chinese hamsters (Cricetulus griseus) reproduces COVID-19 pneumonia in a well-established small animal model. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; Feldmann, F.; Williamson, B.N.; Van Doremalen, N.; Pérez-Pérez, L.; Schulz, J.; Meade-White, K.; Okumura, A.; Callison, J.; Brumbaugh, B. Respiratory disease in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 585, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, M.; Fenollar, F.; Mediannikov, O.; Davoust, B.; Devaux, C.; Raoult, D. Current Status of Putative Animal Sources of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Humans: Wildlife, Domestic Animals and Pets. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamer, S.A.; Ghai, R.R.; Zecca, I.B.; Auckland, L.D.; Roundy, C.M.; Davila, E.; Busselman, R.E.; Tang, W.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Killian, M.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 variant of concern detected in a pet dog and cat after exposure to a person with COVID-19, USA. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 00, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, J. Dutch Minister Confirms Dog, Three Cats Have Caught Novel Coronavirus. Am. Report. 2020. Available online: https://www.reporter.am/dutch-minister-confirms-dog-three-cats-have-caught-novel-coronavirus/ (accessed on 8 February 2021).
- Saha, O.; Islam, I.; Shatadru, R.N.; Rakhi, N.N.; Hossain, M.S.; Rahaman, M.M. Temporal landscape of mutational frequencies in SARS-CoV-2 genomes of Bangladesh: Possible implications from the ongoing outbreak in Bangladesh. Virus Genes 2021, 57, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, M.W.; Hall, D.; Handel, A. Molecular evolution and emergence of avian gammacoronaviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaro, N.; Lorusso, A. Novel human coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A lesson from animal coronaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, M.J.; Kapil, S. Bovine coronavirus associated syndromes. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsuaki, S.; Goto, K.; Nakamura, K.; Yamada, M.; Ueo, H.; Komori, T.; Shirakawa, H.; Uchinuno, Y. Fatal winter dysentery with severe anemia in an adult cow. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2007, 69, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Herbst, W.; Kousoulas, K.; Storz, J. Biological and genetic characterization of a hemagglutinating coronavirus isolated from a diarrhoeic child. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 44, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasoksuz, M.; Alekseev, K.; Vlasova, A.; Zhang, X.; Spiro, D.; Halpin, R.; Wang, S.; Ghedin, E.; Saif, L.J. Biologic, antigenic, and full-length genomic characterization of a bovine-like coronavirus isolated from a giraffe. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4981–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniiappa, L.; Mitov, B.; KhE, K. Demonstration of coronavirus infection in buffaloes. Vet. Med. Nauk. 1985, 22, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, H.M. Bovine-like coronaviruses in domestic and wild ruminants. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2018, 19, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, M.; Kanno, T.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kokado, H. Antibody response to equine coronavirus in horses inoculated with a bovine coronavirus vaccine. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1889–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederwerder, M.; Hesse, R. Swine enteric coronavirus disease: A review of 4 years with porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus in the United States and Canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Hu, H.; Saif, L.J. Porcine deltacoronavirus infection: Etiology, cell culture for virus isolation and propagation, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.-L.; Shi, W.-F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Xie, Q.-M.; Mani, S.; et al. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Lan, T.; Wu, R.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Retrospective detection and phylogenetic analysis of swine acute diarrhoea syndrome coronavirus in pigs in southern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Yu, J.-Q.; Huang, Y.-W. Swine enteric alphacoronavirus (swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus): An update three years after its discovery. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Wen, Z.; Cao, Y. A new bat-HKU2–like coronavirus in swine, China, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, J.S.; Lam, T.T.; Ahmed, M.M.; Li, L.; Shen, Y.; Abo-Aba, S.E.; Qureshi, M.I.; Abu-Zeid, M.; Zhang, Y.; Khiyami, M.A.; et al. Co-circulation of three camel coronavirus species and recombination of MERS-CoVs in Saudi Arabia. Science 2016, 351, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Wernery, U.; Wong, E.Y.; Tsang, A.K.; Johnson, B.; Yip, C.C.; Lau, C.C.; Sivakumar, S.; Cai, J.P.; et al. Novel betacoronavirus in dromedaries of the Middle East, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijawi, B.; Abdallat, M.; Sayaydeh, A.; Alqasrawi, S.; Haddadin, A.; Jaarour, N.; Alsheikh, S.; Alsanouri, T. Novel coronavirus infections in Jordan, April 2012: Epidemiological findings from a retrospective investigation. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2013, 19 (Suppl. 1), S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J. Patient with new strain of coronavirus is treated in intensive care at London hospital. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2012, 345, e6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.K.W.; Poon, L.L.M.; Gomaa, M.; Shehata, M.; Perera, R.A.P.M.; Abu Zeid, D.; El Rifay, A.; Siu, L.; Guan, Y.; Webby, R.; et al. MERS Coronaviruses in Dromedary Camels, Egypt. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, B.M.; Barr, B.C.; Magdesian, K.G.; Ing, M.; Mora, D.; Jensen, D.; Loretti, A.P.; McConnell, T.; Mock, R. Identification of a novel coronavirus possibly associated with acute respiratory syndrome in alpacas (Vicugna pacos) in California, 2007. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killerby, M.E.; Biggs, H.M.; Midgley, C.M.; Gerber, S.I.; Watson, J.T. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagmans, B.L.; Van Den Brand, J.M.; Raj, V.S.; Volz, A.; Wohlsein, P.; Smits, S.L.; Schipper, D.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Okba, N.; Fux, R. An orthopoxvirus-based vaccine reduces virus excretion after MERS-CoV infection in dromedary camels. Science 2016, 351, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wille, M.; Holmes, E.C. Wild birds as reservoirs for diverse and abundant gamma-and deltacoronaviruses. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluwaimi, A.M.; Alshubaith, I.H.; Al-Ali, A.M.; Abohelaika, S. The Coronaviruses of Animals and Birds: Their Zoonosis, Vaccines, and Models for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Mase, M.; Murakami, S.; Horimoto, T.; Chen, H.W. Emerging lethal infectious bronchitis coronavirus variants with multiorgan tropism. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.D.; Iqbal, M.; Nair, V. Recent advances in viral vectors in veterinary vaccinology. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamings, A.; Nelson, T.M.; Vibin, J.; Wille, M.; Klaassen, M.; Alexandersen, S. Detection and characterisation of coronaviruses in migratory and non-migratory Australian wild birds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepojoki, S.; Lindh, E.; Vapalahti, O.; Huovilainen, A. Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in wild birds, Finland. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2017, 7, 1408360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.; Cook, J.K. Spotlight on avian coronaviruses. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronaviruses in poultry and other birds. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domańska-Blicharz, K.; Kuczkowski, M.; Sajewicz-Krukowska, J. Whole genome characterisation of quail deltacoronavirus detected in Poland. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Oem, J.K. Surveillance of avian coronaviruses in wild bird populations of Korea. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, H.; Ghalyanchi Langeroudi, A.; Karimi, V.; Ghafouri, S.A.; Hashemzadeh, M.; Hosseini, H.; Fallah Mehrabadi, M.H.; Sadat Mousavi, F.; Najafi, H. Molecular Detection of Gamma Coronaviruses in Bird Parks of Iran. Arch. Razi Inst. 2019, 74, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paim, F.C.; Bowman, A.S. Epidemiology of Deltacoronaviruses (δ-CoV) and Gammacoronaviruses (γ-CoV) in Wild Birds in the United States. Viruses 2019, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, M.; Kroyer, A.N.K.; Ojkic, D.; Whitney, H.G.; Robertson, G.J.; Lang, A.S. Discovery and Characterization of Novel RNA Viruses in Aquatic North American Wild Birds. Viruses 2019, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, E.C.; Reid, T.J. Animals and SARS-CoV-2: Species susceptibility and viral transmission in experimental and natural conditions, and the potential implications for community transmission. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 1850–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalés, J.; Puig, M.; Rodon, J.; Avila-Nieto, C.; Carrillo, J.; Cantero, G.; Terrón, M.T.; Cruz, S.; Parera, M.; Noguera-Julián, M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in a cat owned by a COVID-19− affected patient in Spain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24790–24793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Mari, V.; Campolo, M.; Lorusso, A.; Camero, M.; Elia, G.; Martella, V.; Cordioli, P.; Enjuanes, L.; Buonavoglia, C. Recombinant canine coronaviruses related to transmissible gastroenteritis virus of swine are circulating in dogs. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, A.D.; Millet, J.K.; Tse, L.P.V.; Chillag, Z.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Licitra, B.N.; Dubovi, E.J.; Town, C.D.; Whittaker, G.R. Characterization of a recombinant canine coronavirus with a distinct receptor-binding (S1) domain. Virology 2012, 430, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, A.; Desario, C.; Mari, V.; Campolo, M.; Lorusso, E.; Elia, G.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, C.; Decaro, N. Molecular characterization of a canine respiratory coronavirus strain detected in Italy. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, M.; Horzinek, M.; Schultz, R.; Squires, R. WSAVA Guidelines for the vaccination of dogs and cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 57, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, L.; Van der Lubben, M.; Te Lintelo, E.G.; Bekker, C.P.; Geerts, T.; Schuijff, L.S.; Grinwis, G.C.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J. Pathogenic characteristics of persistent feline enteric coronavirus infection in cats. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Su, B.-L.; Hsieh, L.-E.; Chueh, L.-L. An outbreak of feline infectious peritonitis in a Taiwanese shelter: Epidemiologic and molecular evidence for horizontal transmission of a novel type II feline coronavirus. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, S.; Hartmann, K. Diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis: A review of the current literature. Viruses 2019, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licitra, B.N.; Millet, J.K.; Regan, A.D.; Hamilton, B.S.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Mutation in spike protein cleavage site and pathogenesis of feline coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrewegh, A.A.; Smeenk, I.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J.; De Groot, R.J. Feline coronavirus type II strains 79-1683 and 79-1146 originate from a double recombination between feline coronavirus type I and canine coronavirus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4508–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; McCauley, J. GISAID: Global initiative on sharing all influenza data–from vision to reality. Euro Surveill 2017, 22, 30494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailleau, C.; Dumarest, M.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Delaplace, M.; Caro, V.; Kwasiborski, A.; Hourdel, V.; Chevaillier, P.; Barbarino, A.; Comtet, L. First detection and genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 in an infected cat in France. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guy, J.S.; Snijder, E.J.; Denniston, D.A.; Timoney, P.J.; Balasuriya, U.B. Genomic characterization of equine coronavirus. Virology 2007, 369, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Oue, Y.; Murakami, S.; Kanno, T.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Kondo, T. Complete genome analysis of equine coronavirus isolated in Japan. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2903–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, C.L.; Higgins, J.K.; Higgins, J.C.; McIntosh, S.; Scott, E.; Giannitti, F.; Mete, A.; Pusterla, N. Disease associated with equine coronavirus infection and high case fatality rate. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Vin, R.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Mittel, L.D.; Divers, T.J. Enteric coronavirus infection in adult horses. Vet. J. (Lond. Engl. 1997) 2018, 231, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. DBatVir: The database of bat-associated viruses. Database 2014, 2014, bau021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C. Ecology, evolution and classification of bat coronaviruses in the aftermath of SARS. Antiviral. Res. 2014, 101, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; Smith, C.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, H.; Crameri, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bats Are Natural Reservoirs of SARS-Like Coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Li, K.S.M.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Wong, B.H.L.; Wong, S.S.Y.; Leung, S.-Y.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14040–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.-Y.; Li, J.-L.; Yang, X.-L.; Chmura, A.A.; Zhu, G.; Epstein, J.H.; Mazet, J.K.; Hu, B.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2013, 503, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, A.G.; Benton, D.J.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S.R.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Gamblin, S.J. SARS-CoV-2 and bat RaTG13 spike glycoprotein structures inform on virus evolution and furin-cleavage effects. Nat. Struct. Moli. Biol. 2020, 27, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Hu, T.; Li, J.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Holmes, E.C. A novel bat coronavirus closely related to SARS-CoV-2 contains natural insertions at the S1/S2 cleavage site of the spike protein. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 2196–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Shan, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Digging metagenomic data of pangolins revealed SARS-CoV-2 related viruses and other significant viruses. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, T.T.; Jia, N.; Zhang, Y.W.; Shum, M.H.; Jiang, J.F.; Zhu, H.C.; Tong, Y.G.; Shi, Y.X.; Ni, X.B.; Liao, Y.S.; et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature 2020, 583, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Hughes, T.; Lee, M.-H.; Field, H.; Rovie-Ryan, J.J.; Sitam, F.T.; Sipangkui, S.; Nathan, S.K.S.S.; Ramirez, D.; Kumar, S.V.; et al. No Evidence of Coronaviruses or Other Potentially Zoonotic Viruses in Sunda pangolins (Manis javanica) Entering the Wildlife Trade via Malaysia. EcoHealth 2020, 17, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeney, J.; Evermann, J.; McKeirnan, A.; Marker-Kraus, L.; Roelke, M.E.; Bush, M.; Wildt, D.E.; Meltzer, D.; Colly, L.; Lukas, J. Prevalence and implications of feline coronavirus infections of captive and free-ranging cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus). J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evermann, J.; Heeney, J.; Roelke, M.; McKeirnan, A.; O’Brien, S.J. Biological and pathological consequences of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection in the cheetah. Arch. Virol. 1988, 102, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rensburg, I.; Silkstone, M. Concomitant feline infectious peritonitis and toxoplasmosis in a cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus). J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1984, 55, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, N.; Swift, P.; Moeller, R.B.; Worth, S.J.; Foley, J. Feline infectious peritonitis in a mountain lion (Puma concolor), California, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwase, M.; Shimada, K.; Mumba, C.; Yabe, J.; Squarre, D.; Madarame, H. Positive immunolabelling for feline infectious peritonitis in an African lion (Panthera leo) with bilateral panuveitis. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, N.; MacIntyre, N.; McOrist, S. An extended outbreak of infectious peritonitis in a closed colony of European wildcats (Felis silvestris). J. Comp. Pathol. 1993, 108, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, B.; Duchamp, C.; Möstl, K.; Diehl, P.-A.; Betschart, B. Comparative survey of canine parvovirus, canine distemper virus and canine enteric coronavirus infection in free-ranging wolves of central Italy and south-eastern France. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, F.; Dowgier, G.; Valentino, M.P.; Galiero, G.; Tinelli, A.; Nicola, D.; Fusco, G. Identification of pantropic canine coronavirus in a wolf (Canis lupus italicus) in Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, G.M.; Santos, N.; Grøndahl-Rosado, R.; Fonseca, F.P.; Tavares, L.; Neto, I.; Cartaxeiro, C.; Duarte, A. Unveiling patterns of viral pathogen infection in free-ranging carnivores of northern Portugal using a complementary methodological approach. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 69, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, B.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Cheung, C.; Luo, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Y. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- East, M.L.; Moestl, K.; Benetka, V.; Pitra, C.; Höner, O.P.; Wachter, B.; Hofer, H. Coronavirus infection of spotted hyenas in the Serengeti ecosystem. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goller, K.V.; Fickel, J.; Hofer, H.; Beier, S.; East, M.L. Coronavirus genotype diversity and prevalence of infection in wild carnivores in the Serengeti National Park, Tanzania. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-R.; Bae, Y.-C.; Lee, O.-S.; Oem, J.-K. Detection and characterization of bovine-like coronaviruses from four species of zoo ruminants. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebra, C.K.; Mattson, D.E.; Baker, R.J.; Sonn, R.J.; Dearing, P.L. Potential pathogens in feces from unweaned llamas and alpacas with diarrhea. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasey, D.; Reynolds, D.; Bridger, J.; Debney, T.; Scott, A. Identification of coronaviruses in exotic species of Bovidae. Vet. Rec. 1984, 115, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, M.; Cotti, C.; Lelli, D.; Sozzi, E.; Trogu, T.; Lavazza, A.; Garuti, G.; Castrucci, M.R.; Vaccari, G.; De Marco, M.A. Eco-virological preliminary study of potentially emerging pathogens in hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) recovered at a wildlife treatment and rehabilitation center in Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lin, X.-D.; Liao, Y.; Guan, X.-Q.; Guo, W.-P.; Xing, J.-G.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Discovery of a highly divergent coronavirus in the Asian house shrew from China illuminates the origin of the alphacoronaviruses. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00764-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaro, N.; Cirone, F.; Mari, V.; Nava, D.; Tinelli, A.; Elia, G.; Di Sarno, A.; Martella, V.; Colaianni, M.L.; Aprea, G. Characterisation of bubaline coronavirus strains associated with gastroenteritis in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) calves. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE. COVID-19 (SARS-COV-2), Hong Kong (SAR-PRC). Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?page_refer=MapFullEventReport&reportid=33832 (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Mishra, A.; Kumar, N.; Bhatia, S.; Aasdev, A.; Kanniappan, S.; Thayasekhar, A.; Gopinadhan, A.; Silambarasan, R.; Sreekumar, C.; Dubey, C.K. Natural infection of SARS-CoV-2 delta variant in Asiatic lions (Panthera leo persica) in India. bioRxiv 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.H.; Kiupel, M.; West, K.H.; Raymond, J.T.; Grant, C.K.; Glickman, L.T. Coronavirus-associated epizootic catarrhal enteritis in ferrets. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Kiupel, M.; Maes, R.K. Ferret coronavirus-associated diseases. Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2010, 13, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, A.G.; Kiupel, M.; Maes, R.K. Molecular characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with epizootic catarrhal enteritis (ECE) in ferrets. Virology 2006, 349, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Tochitani, T.; Kouchi, M.; Matsumoto, I.; Yamada, T.; Funabashi, H. Glomerulonephritis in a ferret with feline coronavirus infection. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2015, 27, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, S.E.; Beaufrère, H.H.; Brisson, B.A.; Fraser, R.S.; Smith, D.A. Pancreatitis and systemic coronavirus infection in a ferret (Mustela putorius furo). Comp. Med. 2018, 68, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.; AE, L. A new mink enteritis: An initial report. Vet. Med. Small Anim. Clin. 1975, 70, 291–292. [Google Scholar]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Halpin, R.; Wang, S.; Ghedin, E.; Spiro, D.J.; Saif, L.J. Molecular characterization of a new species in the genus Alphacoronavirus associated with mink epizootic catarrhal gastroenteritis. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; Boklund, A.; Gortázar, C.; Pasquali, P.; Roberts, H.; Nielsen, S.S.; Stahl, K.; Stegeman, A.; Baldinelli, F.; Broglia, A.; et al. Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 infection in mustelids. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munnink, B.B.O.; Sikkema, R.S.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Molenaar, R.J.; Munger, E.; Molenkamp, R.; Van Der Spek, A.; Tolsma, P.; Rietveld, A.; Brouwer, M. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science 2021, 371, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiló-Gisbert, J.; Padilla-Blanco, M.; Lizana, V.; Maiques, E.; Muñoz-Baquero, M.; Chillida-Martínez, E.; Cardells, J.; Rubio-Guerri, C. First Description of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Two Feral American Mink (Neovison vison) Caught in the Wild. Animals 2021, 11, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enserink, M. Coronavirus rips through Dutch mink farms, triggering culls. Science 2020, 368, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aart, A.E.; Velkers, F.C.; Fischer, E.A.; Broens, E.M.; Egberink, H.; Zhao, S.; Engelsma, M.; Hakze-van der Honing, R.W.; Harders, F.; de Rooij, M.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in cats and dogs in infected mink farms. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, D.H.; Barthold, S.W. Pathology of Laboratory Rodents and Rabbits; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunath, S.; Kulkarni, P.G.; Nagavelu, K.; Samuel, R.J.; Srinivasan, S.; Ramasamy, N.; Hegde, N.R.; Gudde, R.S. Sero-prevalence of rodent pathogens in India. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131706. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, D.; Pei, Y.; Christie, N.; Cooper, M. Primary structure of the sialodacryoadenitis virus genome: Sequence of the structural-protein region and its application for differential diagnosis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.J.; Manzer, R.; Miura, T.A.; Groshong, S.D.; Ito, Y.; Travanty, E.A.; Leete, J.; Holmes, K.V.; Mason, R.J. Rat respiratory coronavirus infection: Replication in airway and alveolar epithelial cells and the innate immune response. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.-Y.; Yang, W.-H.; Zhou, J.-H.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Detection of alpha-and betacoronaviruses in rodents from Yunnan, China. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Tsang, A.K.; Fan, R.Y.; Luk, H.K.; Cai, J.-P.; Chan, K.-H.; Zheng, B.-J.; Wang, M. Discovery of a novel coronavirus, China Rattus coronavirus HKU24, from Norway rats supports the murine origin of Betacoronavirus 1 and has implications for the ancestor of Betacoronavirus lineage A. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3076–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaax, G.; Jaax, N.; Petrali, J.; Corcoran, K.; Vogel, A. Coronavirus-like virions associated with a wasting syndrome in guinea pigs. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1990, 40, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patrono, L.V.; Samuni, L.; Corman, V.M.; Nourifar, L.; Röthemeier, C.; Wittig, R.M.; Drosten, C.; Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Leendertz, F.H. Human coronavirus OC43 outbreak in wild chimpanzees, Cote d Ivoire, 2016. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütze, H. Coronaviruses in aquatic organisms. Aquacul. Viro. 2016, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossart, G.; Duignan, P. Emerging viruses in marine mammals. CAB Rev. 2018, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollens, H.H.; Wellehan, J.F.; Archer, L.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Gulland, F.M. Detection of a respiratory coronavirus from tissues archived during a pneumonia epizootic in free-ranging Pacific harbor seals Phoca vitulina richardsii. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 90, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihindukulasuriya, K.A.; Wu, G.; Leger, J.S.; Nordhausen, R.W.; Wang, D. Identification of a novel coronavirus from a beluga whale by using a panviral microarray. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5084–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Tsang, A.K.; Hui, S.-W.; Fan, R.Y.; Martelli, P.; Yuen, K.-Y. Discovery of a novel bottlenose dolphin coronavirus reveals a distinct species of marine mammal coronavirus in Gammacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.F.F.; Wheeler, E.; Greig, D.; Waltzek, T.B.; Gulland, F.; Breitbart, M. Metagenomic identification of a novel anellovirus in Pacific harbor seal (Phoca vitulina richardsii) lung samples and its detection in samples from multiple years. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordecai, G.J.; Hewson, I. Coronaviruses in the Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaji, M.; Farahani, A.; Ranjbar, R.; Heiat, M.; Dehkordi, F.S. Emerging coronaviruses: First SARS, second MERS and third SARS-CoV-2: Epidemiological updates of COVID-19. Infez Med. 2020, 28, 6–17. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, R. Etymologia: Coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Hoek, L.; Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Vermeulen-Oost, W.; Berkhout, R.J.; Wolthers, K.C.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; Kaandorp, J.; Spaargaren, J.; Berkhout, B. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Chu, C.-M.; Chan, K.-H.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Huang, Y.; Wong, B.H.; Poon, R.W.; Cai, J.J.; Luk, W.-K. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.; Ebach, F.; Corman, V.; Krumkamp, R.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; Eis-Hübinger, A.; Kruppa, T.; Simon, A.; May, J.; Evans, J. Similar virus spectra and seasonality in paediatric patients with acute respiratory disease, Ghana and Germany. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konca, C.; Korukluoglu, G.; Tekin, M.; Almis, H.; Bucak, I.H.; Uygun, H.; Altas, A.B.; Bayrakdar, F. The first infant death associated with human coronavirus NL63 infection. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloniemi, M.; Lappalainen, S.; Vesikari, T. Commonly circulating human coronaviruses do not have a significant role in the etiology of gastrointestinal infections in hospitalized children. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 62, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfopoulou, S.; Brown, J.R.; Davies, E.G.; Anderson, G.; Virasami, A.; Qasim, W.; Chong, W.K.; Hubank, M.; Plagnol, V.; Desforges, M. Human coronavirus OC43 associated with fatal encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, P.; Mi, D.; Ren, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, R.; Chen, T.; Hu, J. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, Z.; Ren, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; He, G.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. MERS-related betacoronavirus in Vespertilio superans bats, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Ferdous, J.; Islam, S.; Sayeed, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Shirin, T. Transmission dynamics and susceptibilty patterns of SARS-CoV-2 in domestic, farmed and wild animals: Sustainable One health surveillance for conservation and public health to prevent future epidemics and pandemics. Authorea Prepr. 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, T.; Song, H.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y. Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses. Cell 2021, 184, 4380–4391.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Naming SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/ (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Oishee, M.J.; Ali, T.; Jahan, N.; Khandker, S.S.; Hoq, M.A.; Khondoker, M.U.; Sil, B.K.; Lugova, H.; Krishnapillai, A.; Abubakar, A.R.; et al. COVID-19 pandemic: Review of contemporary and forthcoming detection tools. Infect Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1049–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Qin, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.-H.; Peng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, S.J.; Huang, Y.-W. Broad cross-species infection of cultured cells by bat HKU2-related swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus and identification of its replication in murine dendritic cells in vivo highlight its potential for diverse interspecies transmission. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdts, V.; Zakhartchouk, A. Vaccines for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and other swine coronaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, W.K.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Rasche, A.; Greenwood, A.D.; Osterrieder, K.; Drexler, J.F. Potential zoonotic sources of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.-D.; Tu, C.-C.; Zhang, G.-W.; Wang, S.-Y.; Zheng, K.; Lei, L.-C.; Chen, Q.-X.; Gao, Y.-W.; Zhou, H.-Q.; Xiang, H. Cross-host evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in palm civet and human. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Yoon, S.W.; Noh, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, D.G.; Kim, H.K. Detection of bovine coronavirus in nasal swab of non-captive wild water deer, Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunemitsu, H.; El-Kanawati, Z.R.; Smith, D.R.; Reed, H.H.; Saif, L.J. Isolation of coronaviruses antigenically indistinguishable from bovine coronavirus from wild ruminants with diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, K.P.; Vlasova, A.N.; Jung, K.; Hasoksuz, M.; Zhang, X.; Halpin, R.; Wang, S.; Ghedin, E.; Spiro, D.; Saif, L.J. Bovine-like coronaviruses isolated from four species of captive wild ruminants are homologous to bovine coronaviruses, based on complete genomic sequences. J. Viro. 2008, 82, 12422–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Tscharke, B.; Bertsch, P.M.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; Choi, P.; Clarke, L.; Dwyer, J.; Edson, J.; Nguyen, T.M.H. SARS-CoV-2 RNA monitoring in wastewater as a potential early warning system for COVID-19 transmission in the community: A temporal case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodder, W.; de Roda Husman, A.M. SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater: Potential health risk, but also data source. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundy, P.M.; Gerba, C.P.; Pepper, I.L. Survival of coronaviruses in water and wastewater. Food Environ. Virol. 2009, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Berhane, S.; Taylor, M.; Adriano, A.; Davenport, C.; Dittrich, S.; Emperador, D.; Takwoingi, Y.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 3, Cd013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.R.; Machalaba, C.; Karesh, W.B.; Crook, P.Z.; Gilardi, K.; Nziza, J.; Uhart, M.M.; Robles, E.A.; Saylors, K.; Joly, D.O. Implementing One Health approaches to confront emerging and re-emerging zoonotic disease threats: Lessons from PREDICT. One Health Outlook 2020, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalava, K. First respiratory transmitted food borne outbreak? Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 226, 113490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilan, M.; Suresh, I.; Nesakumar, N. SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2: A Diagnostic Challenge. Measurement 2021, 168, 108335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Sayeed, M.A.; Rahman, M.K.; Zamil, S.; Abedin, J.; Saha, O.; Hassan, M.M. Assessment of basic reproduction number (R0), spatial and temporal epidemiological determinants, and genetic characterization of SARS-CoV-2 in Bangladesh. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Sayeed, M.A.; Rahman, M.K.; Ferdous, J.; Islam, S.; Hassan, M.M. Geospatial dynamics of COVID-19 clusters and hotspots in Bangladesh. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 00, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Qiu, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y. Lower mortality of COVID-19 by early recognition and intervention: Experience from Jiangsu Province. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, T. New variant of SARS-CoV-2 in UK causes surge of COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e20–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Sayeed, M.A.; Kalam, M.A.; Ferdous, J.; Rahman, M.K.; Abedin, J.; Islam, S.; Shano, S.; Saha, O.; Shirin, T.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Diverse Environmental Samples Globally. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, O.; Sultan, A.A.; Ding, H.; Triggle, C.R. A Review of the Progress and Challenges of Developing a Vaccine for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Hernández, D.; Hupert, N.; Nixon, D.F.J.T.i.I. The Immunologists’ Guide to Pandemic Preparedness. Trends. Immunol. 2020, 42, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
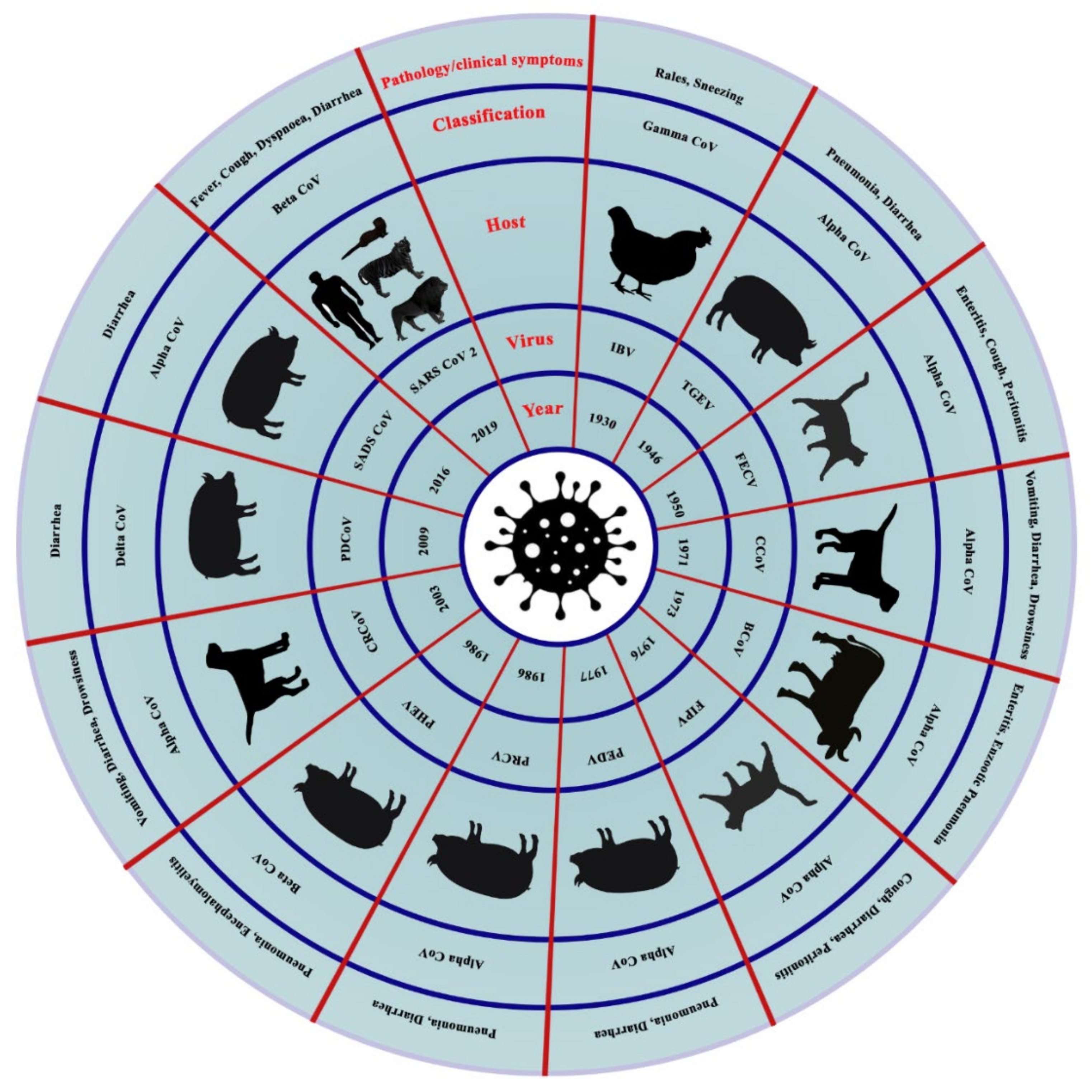
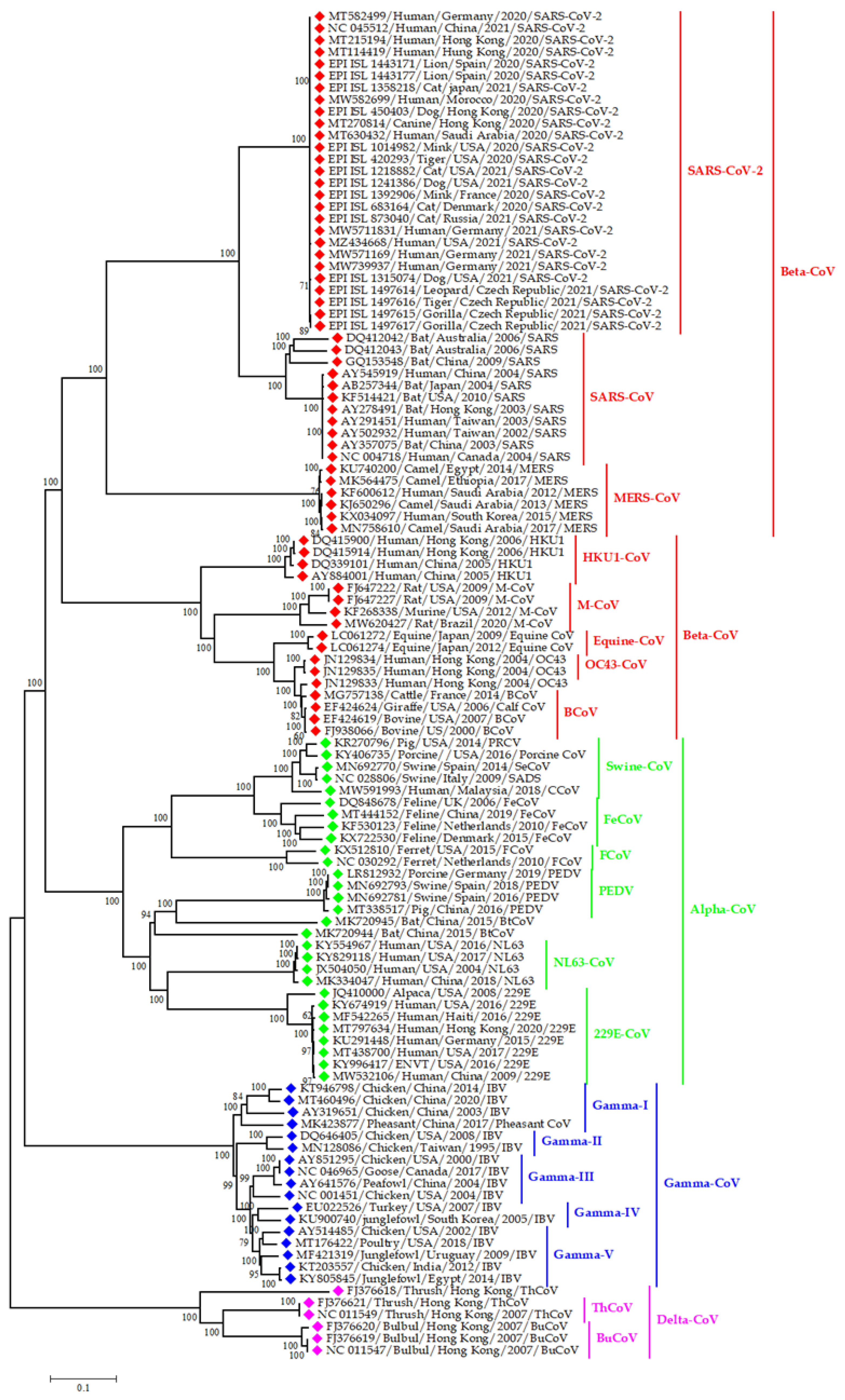
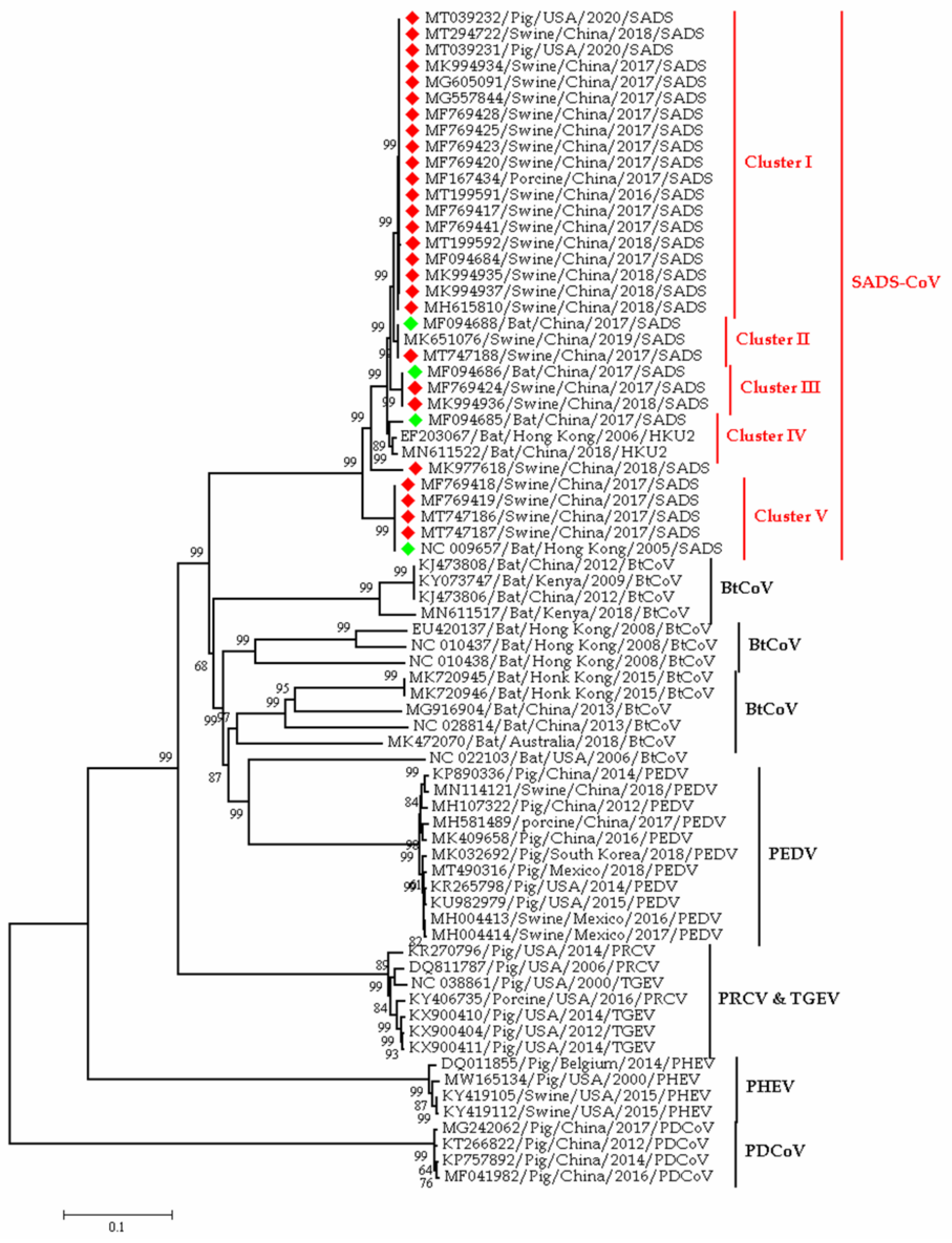
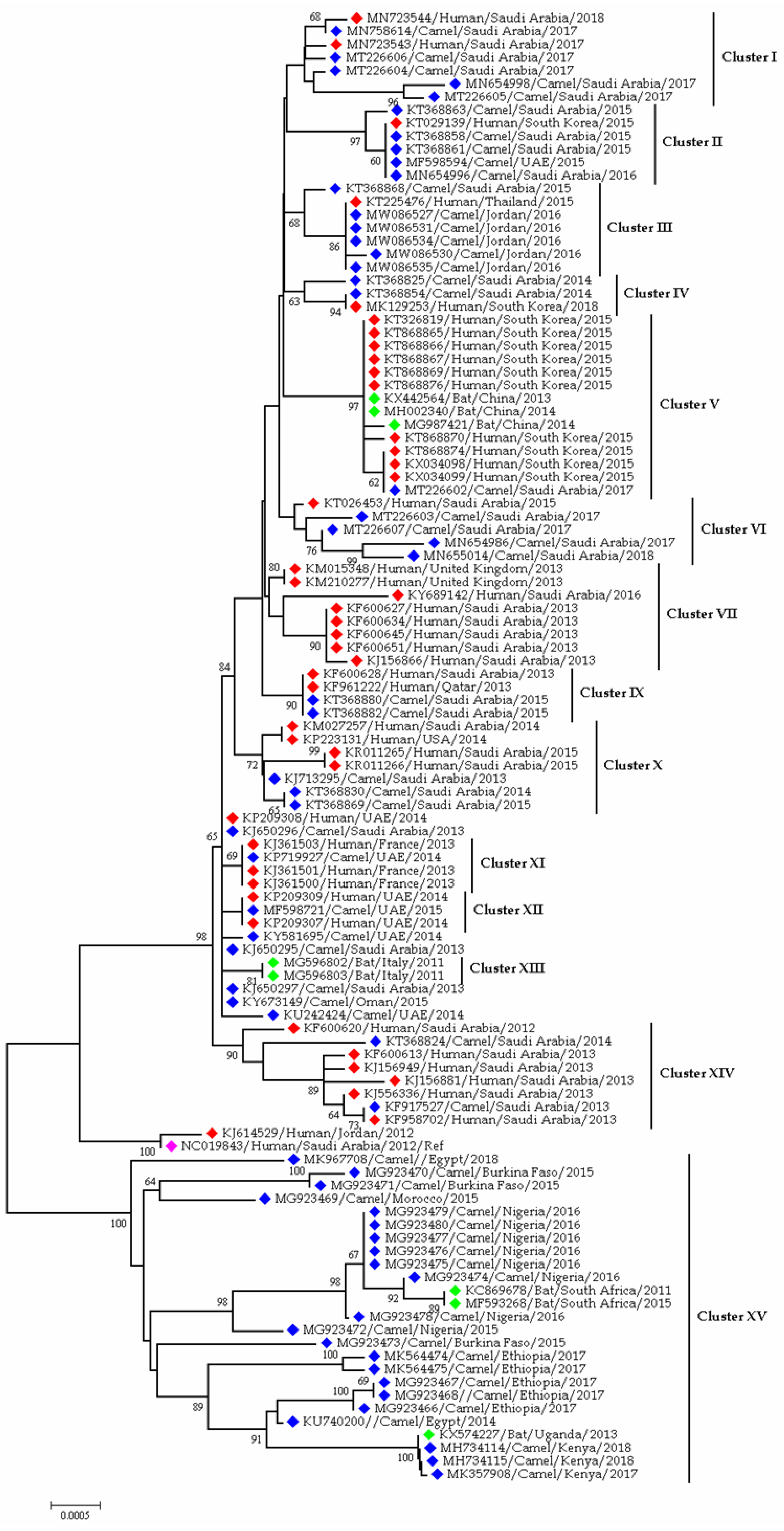
| Term | Keywords |
|---|---|
| Descriptive term | Prevalence OR Incidence OR Frequency OR Occurrence OR Infection OR Detection OR Identification OR Isolation OR Characterization OR Investigation OR Survey OR Rate |
| Outcome term | Coronavirus OR α-CoV OR β-CoV OR γ-CoV OR δ-CoV OR MERS OR SARS-CoV OR COVID-19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR HKU2 OR CCOV OR CRCoV OR FECV OR FIPV OR BCoV OR HCOC43 OR HC229E OR HCNL63 OR HKU1 OR TGEV OR PEDV OR PRCV OR SADS-CoV OR PHEV OR PDCoV OR IBV |
| Population term | Human OR Animal OR Mammals OR Birds OR Avian OR Poultry OR Turkey OR Chicken OR Goose OR Pheasant OR Domestic animals OR Bovine OR Cattle OR Calf OR Equine OR Horse OR Pig OR Camel OR Canine OR Feline OR Dog OR Cat OR Wild animals OR Tiger OR Lion OR Mink OR Rodents OR Bat OR Pangolin OR Monkey OR Mice OR Rat OR Ferret OR Guinea pig OR Masked Civet |
| Host | Disease | Virus Type | System Affected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Bovine CoV | βCoV | Respiratory, Digestive |
| Buffalo | Bubaline CoVs | βCoV | Respiratory, Digestive |
| Pig | TGEV | αCoV | Respiratory, Digestive |
| Pig | PRCV | αCoV | Respiratory |
| Pig | SADS | αCoV | Digestive |
| Pig | PEDV | αCoV | Digestive |
| Pig | PHEV | βCoV | Respiratory, Digestive, Nervous |
| Pig | PDCoV | δCoV | Digestive |
| Camel | MERS | βCoV | Respiratory |
| Camel | β1-HKU23-CoVs | βCoV | Respiratory |
| Camel | Camelid α-CoV | αCoV | Respiratory |
| Alpaca | Alpaca CoV | αCoV | Respiratory |
| Horse | Equine CoV | βCoV | Digestive |
| Turkey | TCoV | ϒCoV | Digestive |
| Chicken | IBV | ϒCoV | Respiratory, Urinary, Reproductive |
| Bulbul | BuCoV HKU11 | δ-CoV | |
| Thrush | ThCoV HKU12 | δ-CoV | |
| Munia | MunCoV HKU13 | δ-CoV | |
| White-eye | HKU16 | δ-CoV | |
| Sparrow | HKU17 | δ-CoV | |
| Magpie robin | HKU18 | δ-CoV | |
| Night heron | HKU19 | δ-CoV | |
| Wigeon | HKU20 | δ-CoV | |
| Common moorhen | HKU21 | δ-CoV | |
| Quail | Quail CoV | δ-CoV | |
| Dog | CCoV | αCoV | Respiratory |
| Dog | CRCoV | βCoV | Respiratory |
| Dog | SARS CoV-2 | βCoV | Respiratory |
| Cat | SARS CoV-2 | βCoV | Respiratory |
| Cat | FIPV | αCoV | Monocyte |
| Cat | FECV | αCoV | Digestive |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, A.; Ferdous, J.; Islam, S.; Sayeed, M.A.; Dutta Choudhury, S.; Saha, O.; Hassan, M.M.; Shirin, T. Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Endemic and Emerging Coronaviruses in Humans, Domestic Animals, and Wildlife. Viruses 2021, 13, 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101908
Islam A, Ferdous J, Islam S, Sayeed MA, Dutta Choudhury S, Saha O, Hassan MM, Shirin T. Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Endemic and Emerging Coronaviruses in Humans, Domestic Animals, and Wildlife. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101908
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Ariful, Jinnat Ferdous, Shariful Islam, Md. Abu Sayeed, Shusmita Dutta Choudhury, Otun Saha, Mohammad Mahmudul Hassan, and Tahmina Shirin. 2021. "Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Endemic and Emerging Coronaviruses in Humans, Domestic Animals, and Wildlife" Viruses 13, no. 10: 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101908
APA StyleIslam, A., Ferdous, J., Islam, S., Sayeed, M. A., Dutta Choudhury, S., Saha, O., Hassan, M. M., & Shirin, T. (2021). Evolutionary Dynamics and Epidemiology of Endemic and Emerging Coronaviruses in Humans, Domestic Animals, and Wildlife. Viruses, 13(10), 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13101908








