Multiple Types of Novel Enteric Bopiviruses (Picornaviridae) with the Possibility of Interspecies Transmission Identified from Cloven-Hoofed Domestic Livestock (Ovine, Caprine and Bovine) in Hungary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background Information of Samples, Animals and Farms
2.2. RT-PCR-Based Screening and Genome Acquisition Reactions
2.3. In Silico Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Cell Culture and Virus Inoculation
3. Results
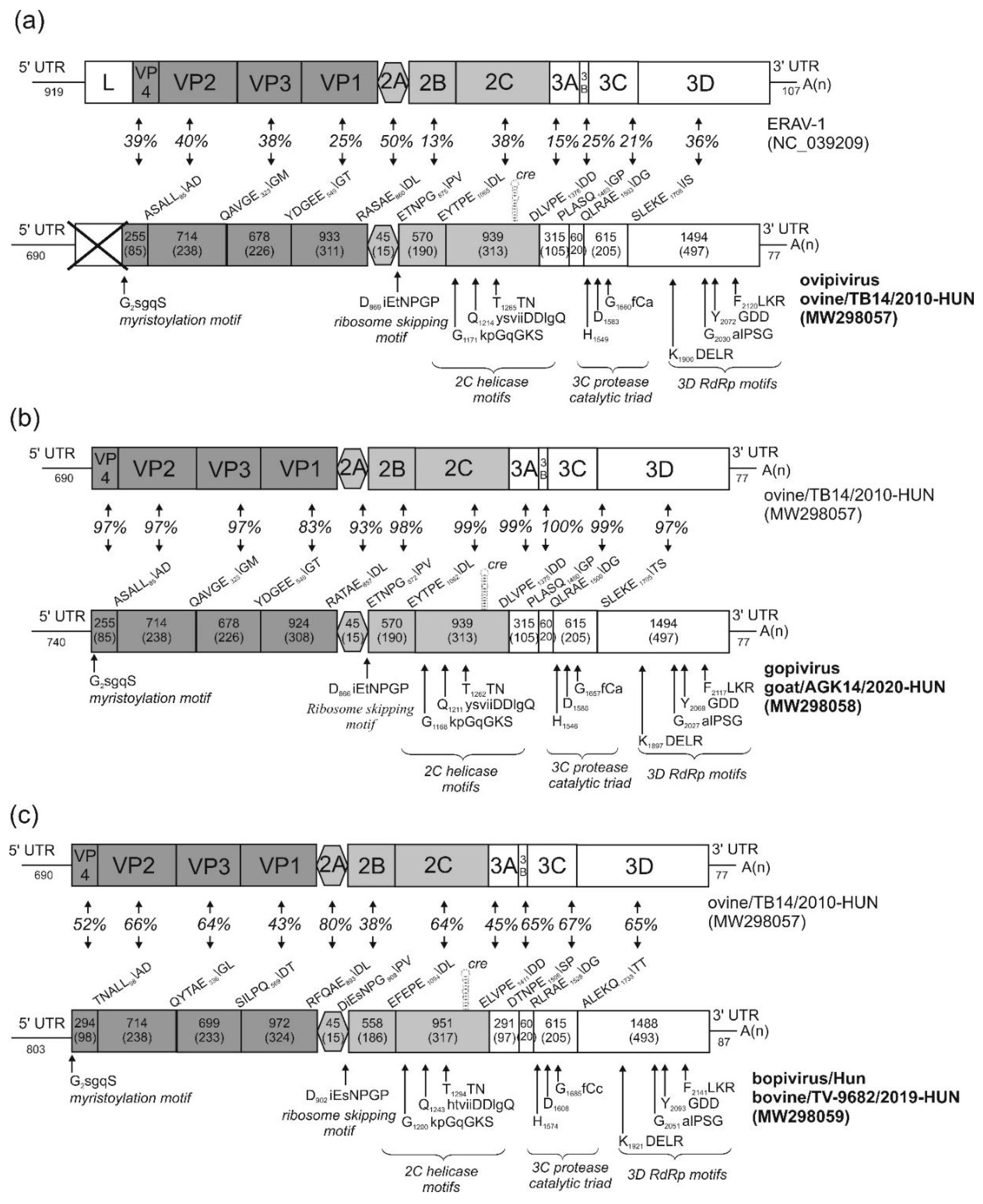
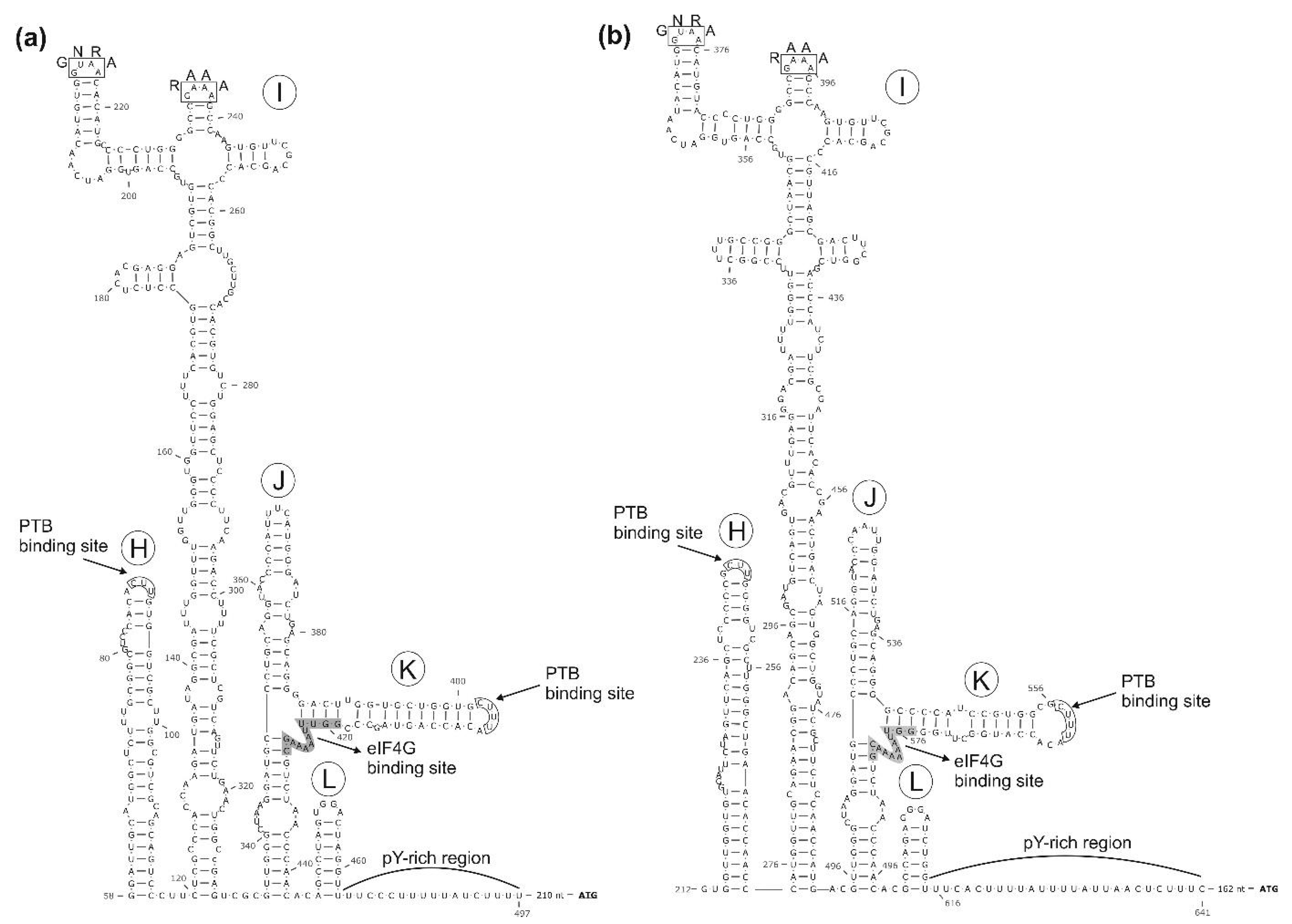
3.1. Genome Characterisation of Ovine Picornavirus (Ovipivirus)
3.2. Genome Characterisation of Caprine Picornavirus (Gopivirus)
3.3. Genome Characterisation of Bovine Picornavirus (Bopivirus/Hun)
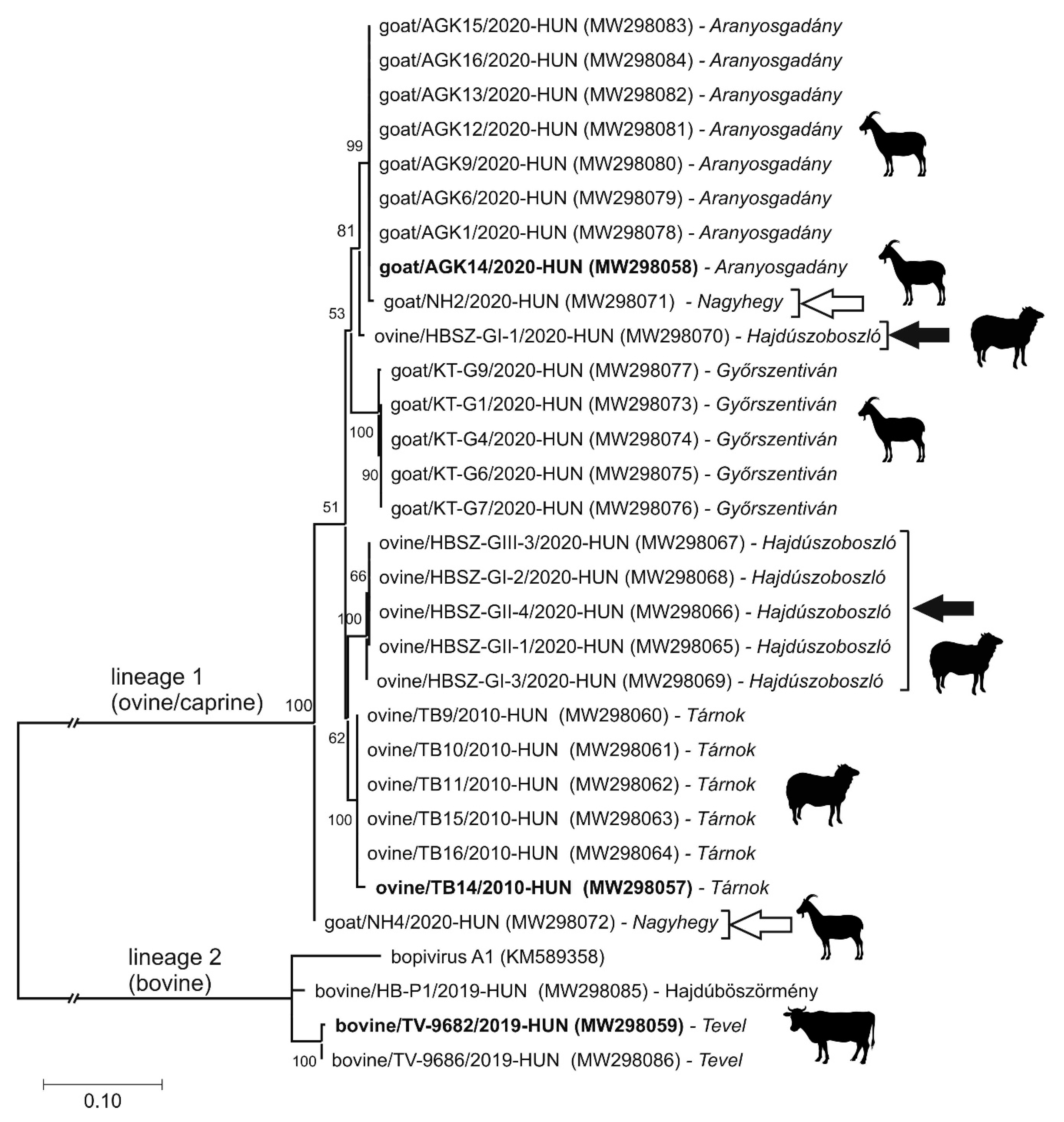
3.4. Epidemiological Investigation of Different Bopiviruses in Hungarian Animal Farms
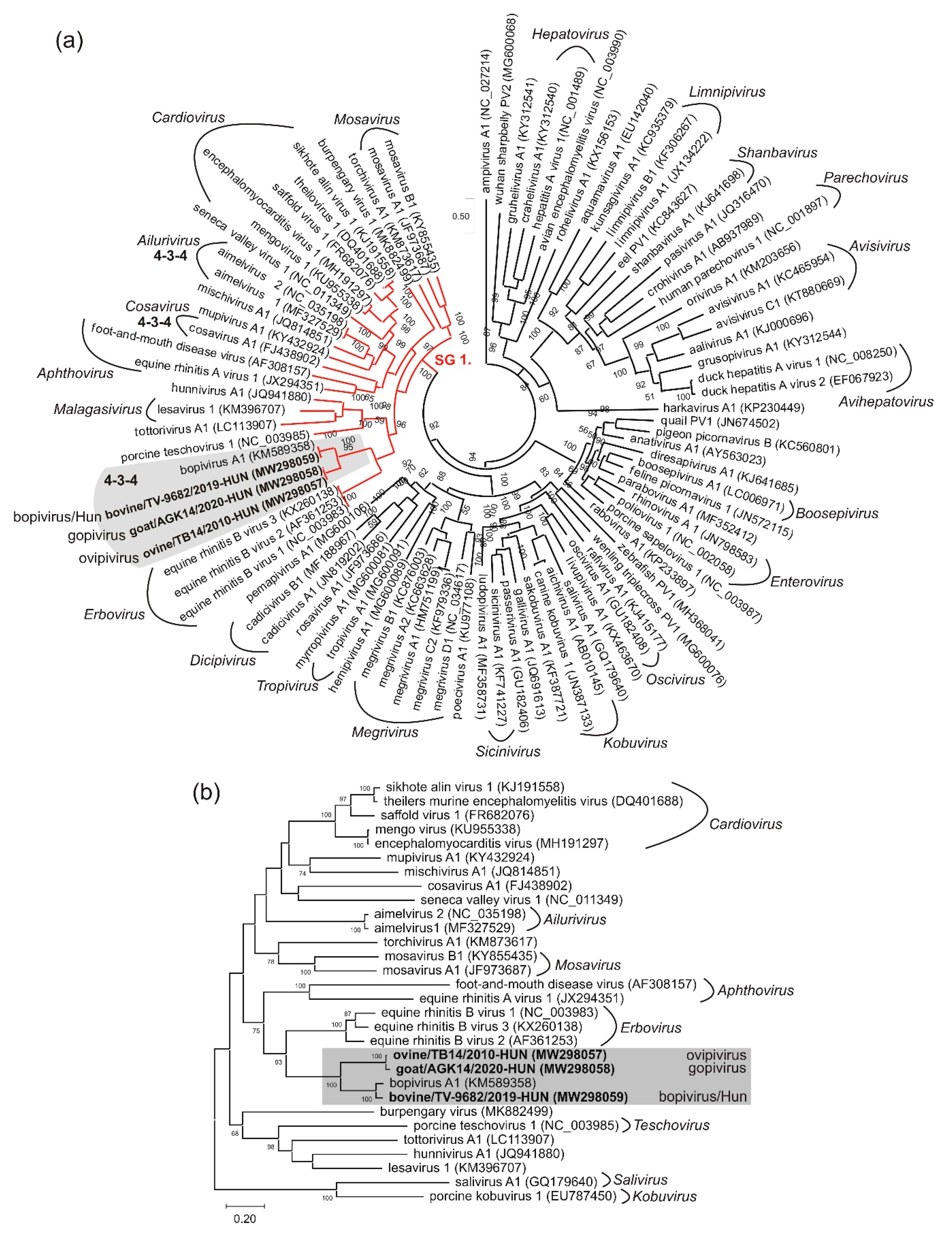
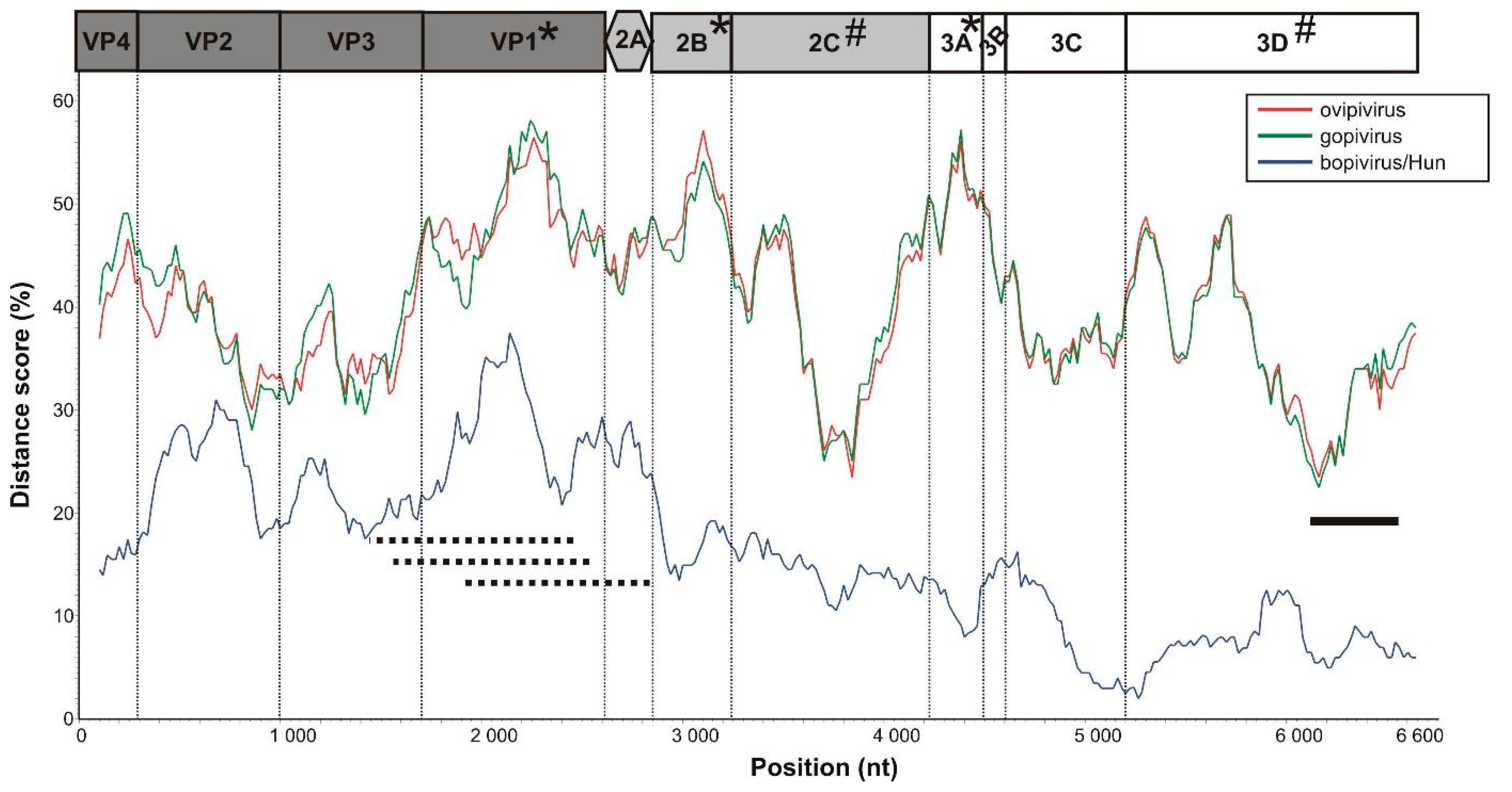
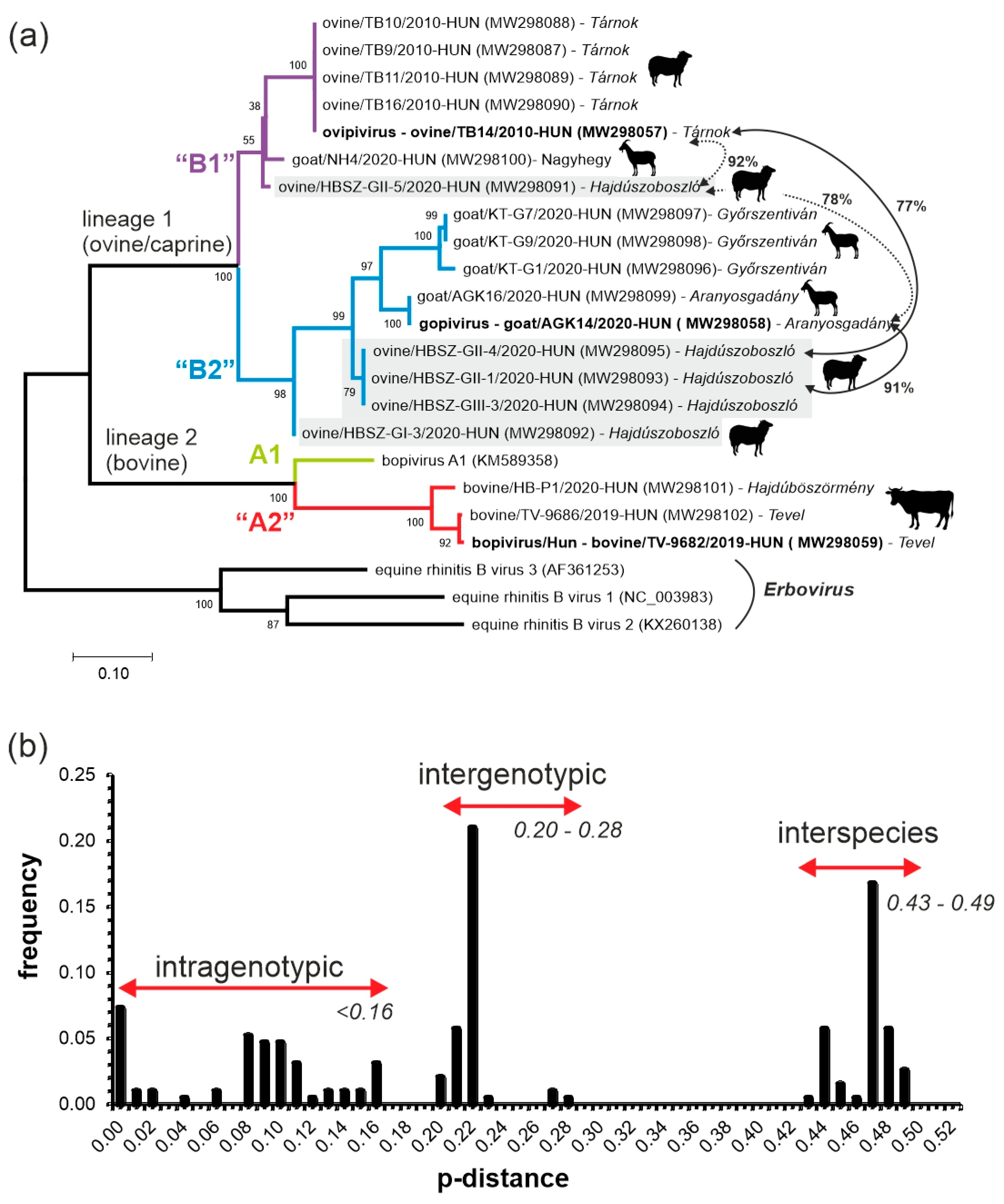
3.5. VP1-Capsid-Based Analyses of Different Bopiviruses
3.6. Results of Virus Cultivation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palmenberg, A.; Neubauer, D.; Skern, T. Genome Organization and Encoded Proteins. In The Picornaviruses; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zell, R. Picornaviridae—The ever-growing virus family. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnani, M.; Kumar, P.; Hellen, C.U.T. Widespread distribution and structural diversity of Type IV IRESs in members of Picornaviridae. Virology 2015, 478, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordey, S.; Gerlach, D.; Junier, T.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Kaiser, L.; Tapparel, C. The cis-acting replication elements define human enterovirus and rhinovirus species. RNA 2008, 14, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Steil, B.P.; Barton, D.J. Cis-active RNA elements (CREs) and picornavirus RNA replication. Virus Res. 2009, 139, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Choi, G.K.Y.; Huang, Y.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Tse, H.; Yeung, M.L.; Chan, K.-H.; Jin, D.-Y.; et al. Natural Occurrence and Characterization of Two Internal Ribosome Entry Site Elements in a Novel Virus, Canine Picodicistrovirus, in the Picornavirus-Like Superfamily. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Kilpatrick, D.R.; Flemister, M.R.; Brown, B.A.; Pallansch, M.A. Typing of human enteroviruses by partial sequencing of VP1. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberste, M.S.; Maher, K.; Pallansch, M.A. Genomic evidence that simian virus 2 and six other simian picornaviruses represent a new genus in Picornaviridae. Virology 2003, 314, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesande, H.; Edman, K.; Rondahl, E.; Falkeborn, T.; Serrander, L.; Lindberg, A.M. Saffold virus infection in elderly people with acute gastroenteritis in Sweden. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.D.; Studdert, M.J. Formerly unclassified, acid-stable equine picornaviruses are a third equine rhinitis B virus serotype in the genus Erbovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3023–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofstad, T.; Jonassen, C.M. Screening of feral and wood pigeons for viruses harbouring a conserved mobile viral element: Characterization of novel astroviruses and picornaviruses. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, Á.; Pankovics, P.; Reuter, G. Avian picornaviruses: Molecular evolution, genome diversity and unusual genome features of a rapidly expanding group of viruses in birds. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.S.; Cao, S.; Holtz, L.R.; Antonio, M.; Stine, O.C.; Wang, D. Discovery of rosavirus 2, a novel variant of a rodent-associated picornavirus, in children from The Gambia. Virology 2014, 454–455, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zell, R.; Delwart, E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Hovi, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2421–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin-Murphy, M.; Almond, J.W. Picornaviruses; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Austin, TX, USA, 1996; ISBN 0963117211. [Google Scholar]
- Kopliku, L.; Relmy, A.; Romey, A.; Gorna, K.; Zientara, S.; Bakkali-Kassimi, L.; Blaise-Boisseau, S. Establishment of persistent foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) infection in MDBK cells. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2503–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kang, M.I.; Son, K.Y.; Bak, G.Y.; Park, J.G.; Hosmillo, M.; Seo, J.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Alfajaro, M.M.; Soliman, M.; et al. Pathogenesis of Korean Sapelovirus A in piglets and chicks. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Yue, H.; Ruan, W.; Qin, S.; Tang, C. Transcriptomic analysis reveals that enterovirus F strain SWUN-AB001 infection activates JNK/SAPK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in MDBK cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosts. Available online: https://www.picornaviridae.com/hosts.htm (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Reuter, G.; Boros, Á.; Pankovics, P.; Egyed, L. Kobuvirus in domestic sheep, Hungary. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, Á.; Pankovics, P.; Knowles, N.J.; Reuter, G. Natural interspecies recombinant bovine/porcine enterovirus in sheep. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocci, M.; Bakkali-Kassimi, L. The encephalomyocarditis virus. Virulence 2012, 3, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oem, J.K.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, K.K.; An, D.J. Novel Kobuvirus species identified from black goat with diarrhea. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguedour, R.; Ripani, A. Review of the foot and mouth disease situation in North Africa and the risk of introducing the disease into Europe. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2016, 35, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Lin, Q.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Cai, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Discovery of a virus of the species Enterovirus F in goats. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forth, L.F.; Scholes, S.F.E.; Pesavento, P.A.; Jackson, K.; Mackintosh, A.; Carson, A.; Howie, F.; Schlottau, K.; Wernike, K.; Pohlmann, A.; et al. Novel picornavirus in lambs with severe encephalomyelitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boros, Á.; Pankovics, P.; Simmonds, P.; Reuter, G. Novel positive-sense, single-stranded RNA (+ssRNA) virus with di-cistronic genome from intestinal content of freshwater carp (cyprinus carpio). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, L.F. Improved rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) for mapping both the 5′ and 3′ terminal sequences of paramyxovirus genomes. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 130, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blastx: Search Protein Databases Using a Translated Nucleotide Query. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastx&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&BLAST_SPEC=&LINK_LOC=blasttab (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Nucleotide BLAST: Search Nucleotide Databases Using a Nucleotide Query. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?LINK_LOC=blasthome&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&PROGRAM=blastn (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- MUSCLE < Multiple Sequence Alignment < EMBL-EBI. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/ (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.R.; Harpending, H. Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutz, G.; Auer, H.; Nowotny, N.; Grosse, B.; Skern, T.; Kuechler, E. Equine rhinovirus serotypes 1 and 2: Relationship to each other and to aphthoviruses and cardioviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darty, K.; Denise, A.; Ponty, Y. VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-Length Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Genomes from Subtype C-Infected Seroconverters in India, with Evidence of Intersubtype Recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, G.M.; Hoffman, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C. Sequence and structural elements that contribute to efficient encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolupaeva, V.G.; Pestova, T.V.; Hellen, C.U.T.; Shatsky, I.N. Translation eukaryotic initiation factor 4G recognizes a specific structural element within the internal ribosome entry site of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18599–18604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Miragall, O.; Martínez-Salas, E. Structural organization of a viral IRES depends on the integrity of the GNRA motif. RNA 2003, 9, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, D.; Drugeon, G.; Haenni, A.L.; Girard, M.; Van der Werf, S. Role of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid protein VP4 as determined by site-directed mutagenesis of its N-terminal sequence. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 2661–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, M.L.L.; Luke, G.; Mehrotra, A.; Li, X.; Hughes, L.E.; Gani, D.; Ryan, M.D. Analysis of the aphthovirus 2A/2B polyprotein “cleavage” mechanism indicates not a proteolytic reaction, but a novel translational effect: A putative ribosomal “skip”. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Koonin, E.V.; Wolf, Y.I. A new superfamily of putative NTP-binding domains encoded by genomes of small DNA and RNA viruses. FEBS Lett. 1990, 262, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Donchenko, A.P.; Blinov, V.M.; Koonin, E.V. Cysteine proteases of positive strand RNA viruses and chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. A distinct protein superfamily with a common structural fold. FEBS Lett. 1989, 243, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argos, P.; Kamer, G.; Nicklin, M.J.H.; Wimmer, E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picomaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 7251–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, G.; Boros, Á.; Pankovics, P. Kobuviruses—A comprehensive review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2011, 21, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerovitch, K.; Sonenberg, N. Internal initiation of picornavirus rna translation. Semin. Virol. 1993, 4, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, Á.; Pankovics, P.; Adonyi, Á.; Fenyvesi, H.; Day, J.M.; Phan, T.G.; Delwart, E.; Reuter, G. A diarrheic chicken simultaneously co-infected with multiple picornaviruses: Complete genome analysis of avian picornaviruses representing up to six genera. Virology 2016, 489, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.P., Jr.; Gary, H.E., Jr.; Pallansch, M.A. Duration of poliovirus excretion and its implications for acute flaccid paralysis surveillance: A review of the literature. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175 (Suppl. S1), S176–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, P.H.; Arruda, B.L.; Schwartz, K.J.; Vannucci, F.; Resende, T.; Rovira, A.; Sundberg, P.; Nietfeld, J.; Hause, B.M. Detection of a novel sapelovirus in central nervous tissue of pigs with polioencephalomyelitis in the USA. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, V.; Ar Gouilh, M.; Cheval, J.; Muth, E.; Pariente, K.; Burguiere, A.; Caro, V.; Manuguerra, J.-C.; Eloit, M. A Member of a New Picornaviridae Genus Is Shed in Pig Feces. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10036–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.C.Y.; Lo, K.L.; Que, T.L.; Lee, R.A.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P. Epidemiology of human parechovirus, Aichi virus and salivirus in fecal samples from hospitalized children with gastroenteritis in Hong Kong. Virol. J. 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Chen, C.; Bailey, K.; Wang, L. Bovine kobuvirus—A comprehensive review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
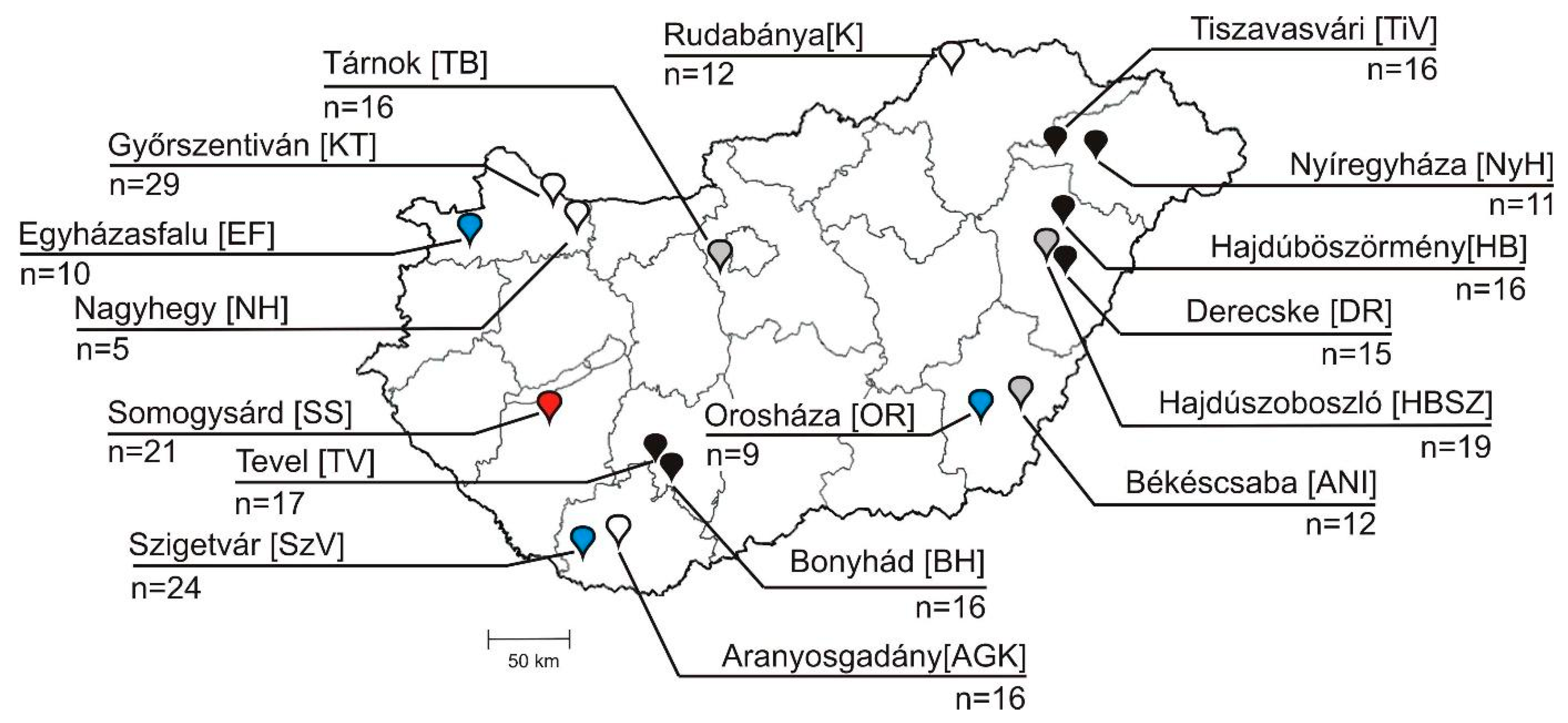
| Host Species | Farm Location | Farm ID | Collection Date | No. of Positive Faecal Samples/Total by Age Groups | No. of Positive Faecal Samples/Total (%) by Farms | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) <2 mo | (II) 2–12 mo | (III) >12 mo | |||||
| Ovine | Hajdúszoboszló | HBSZ | 05/03/2020 | 4/8 | 3/5 | 0/6 | 7/19 (36.8%) |
| Tárnok | TB | 02/04/2010 | 10/16 | 0 | 0 | 10/16 (62.5%) | |
| Békéscsaba | ANI | 06/09/2009 | 0 | 0 | 0/12 | 0/12 | |
| Ʃ = | 14/21 (66.7%) | 3/5 (60.0%) | 0/18 | 17/47 (36.2%) | |||
| Caprine | Aranyosgadány | AGK | 23/04/2020 | 0 | 6/8 | 2/8 | 8/16 (50.0%) |
| Győrszentiván | KT | 11/05/2020 | 0/9 | 5/10 | 0/10 | 5/29 (17.2%) | |
| Nagyhegy | NH | 11/05/2020 | 0 | 0 | 2/5 | 2/5 (40.0%) | |
| Rudabánya | K | 25/06/2008 | 0 | 1/12 | 0 | 1/12 (8.3%) | |
| Ʃ = | 0/9 | 12/30 (40.0%) | 4/23 (17.4%) | 16/62 (25.8%) | |||
| Bovine | Hajdúböszörmény | HB | 05/03/2020 | 1/6 | 0/13 | 1/2 | 2/21 (9.5%) |
| Nyíregyháza | NyH | 06/03/2020 | 0/7 | 0 | 0/4 | 0/11 | |
| Derecske | DR | 05/03/2020 | 0 | 0/4 | 0/11 | 0/15 | |
| Tiszavasvári | TiV | 05/03/2020 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 0/1 | 0/16 | |
| Bonyhád | BH | 04/11/2019 | 0/14 | 0/2 | 0 | 0/16 | |
| Tevel | TV | 04/11/2019 | 0/13 | 2/3 | 0 | 2/17 (11.8%) | |
| Ʃ = | 1/46 (2.2%) | 2/31 (6.5%) | 1/18 (5.6%) | 4/96 (4.2%) | |||
| Swine | Egyházasfalu | EF | 17/08/2016 | 0 | 0/10 | 0 | 0/10 |
| Orosháza | OR | 15/09/2016 | 0/9 | 0 | 0 | 0/9 | |
| Szigetvár | SzV | 18/10/2018 | 0/24 | 0 | 0 | 0/24 | |
| Ʃ = | 0/33 | 0/10 | 0 | 0/43 | |||
| Rabbit | Somogysárd | SS | 03/11/2010 | 0/13 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/21 |
| Ʃ = | 0/13 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/21 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
László, Z.; Pankovics, P.; Reuter, G.; Cságola, A.; Bálint, Á.; Albert, M.; Boros, Á. Multiple Types of Novel Enteric Bopiviruses (Picornaviridae) with the Possibility of Interspecies Transmission Identified from Cloven-Hoofed Domestic Livestock (Ovine, Caprine and Bovine) in Hungary. Viruses 2021, 13, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010066
László Z, Pankovics P, Reuter G, Cságola A, Bálint Á, Albert M, Boros Á. Multiple Types of Novel Enteric Bopiviruses (Picornaviridae) with the Possibility of Interspecies Transmission Identified from Cloven-Hoofed Domestic Livestock (Ovine, Caprine and Bovine) in Hungary. Viruses. 2021; 13(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLászló, Zoltán, Péter Pankovics, Gábor Reuter, Attila Cságola, Ádám Bálint, Mihály Albert, and Ákos Boros. 2021. "Multiple Types of Novel Enteric Bopiviruses (Picornaviridae) with the Possibility of Interspecies Transmission Identified from Cloven-Hoofed Domestic Livestock (Ovine, Caprine and Bovine) in Hungary" Viruses 13, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010066
APA StyleLászló, Z., Pankovics, P., Reuter, G., Cságola, A., Bálint, Á., Albert, M., & Boros, Á. (2021). Multiple Types of Novel Enteric Bopiviruses (Picornaviridae) with the Possibility of Interspecies Transmission Identified from Cloven-Hoofed Domestic Livestock (Ovine, Caprine and Bovine) in Hungary. Viruses, 13(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010066






