Metagenomic Insights into the Sewage RNA Virosphere of a Large City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
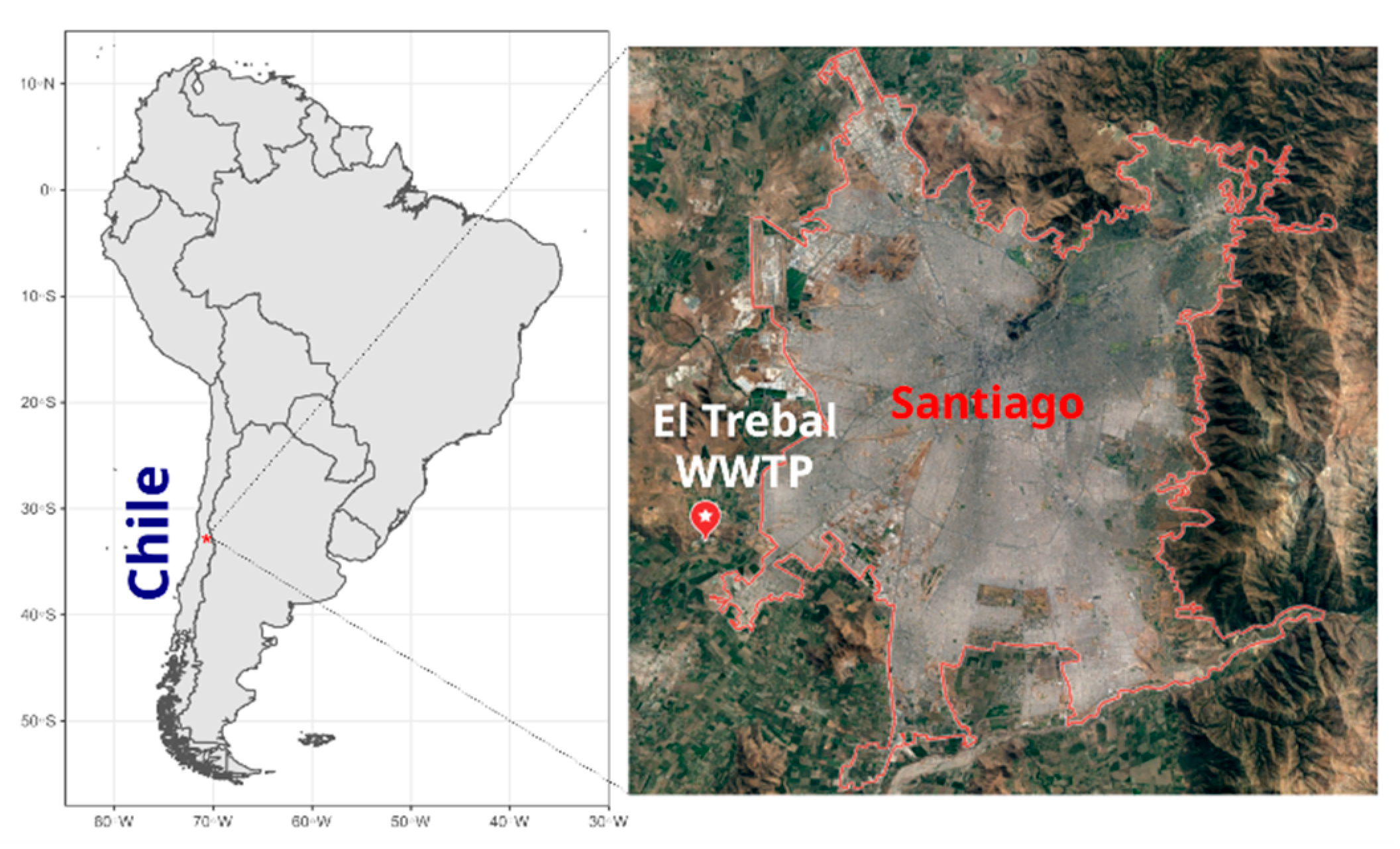
2.1. Study Site and Sample Preparation
2.2. RNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Viral RNA Metagenome Processing
2.4. Taxonomic Assignment of Viral Proteins
2.5. RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Analyses
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis of Picobirnaviruses and Ribosomal Binding Site Prediction
2.7. Human Rotavirus Classification
2.8. Data Availability
3. Results and Discussion
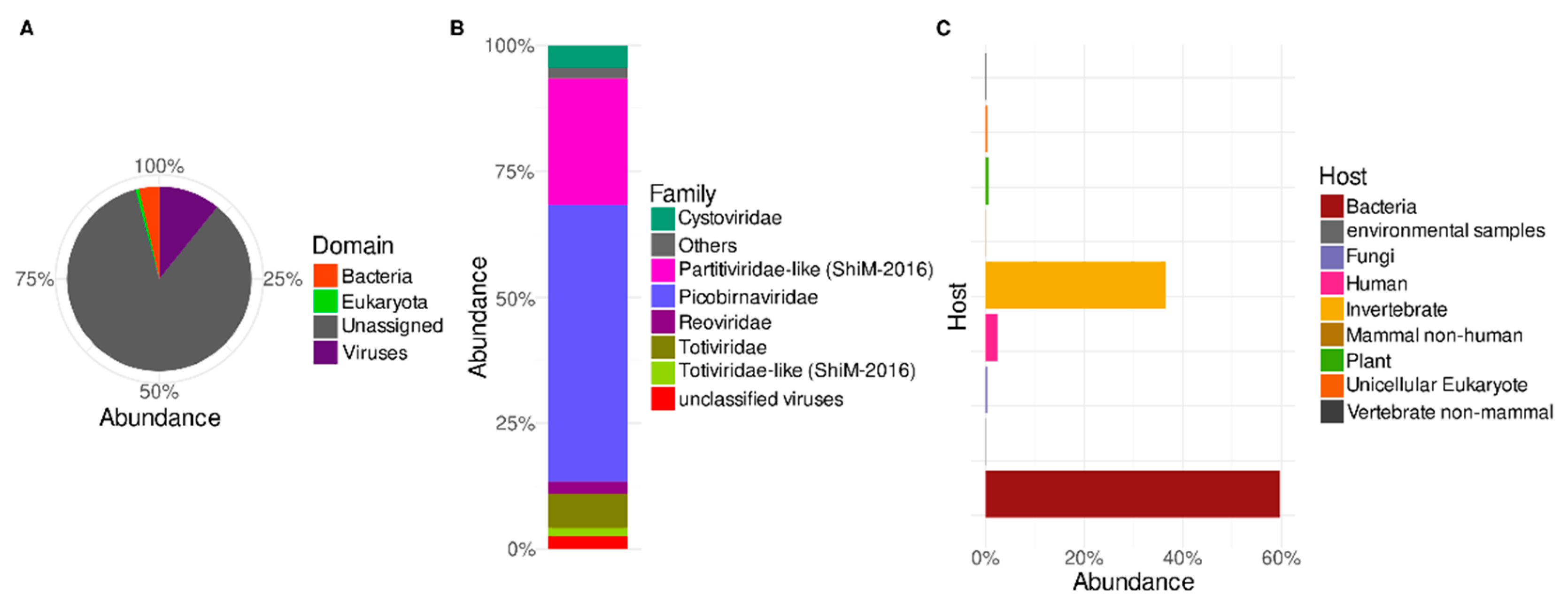
3.1. Predicted Protein-Based Analysis of Trebal RNA Viral Metagenome
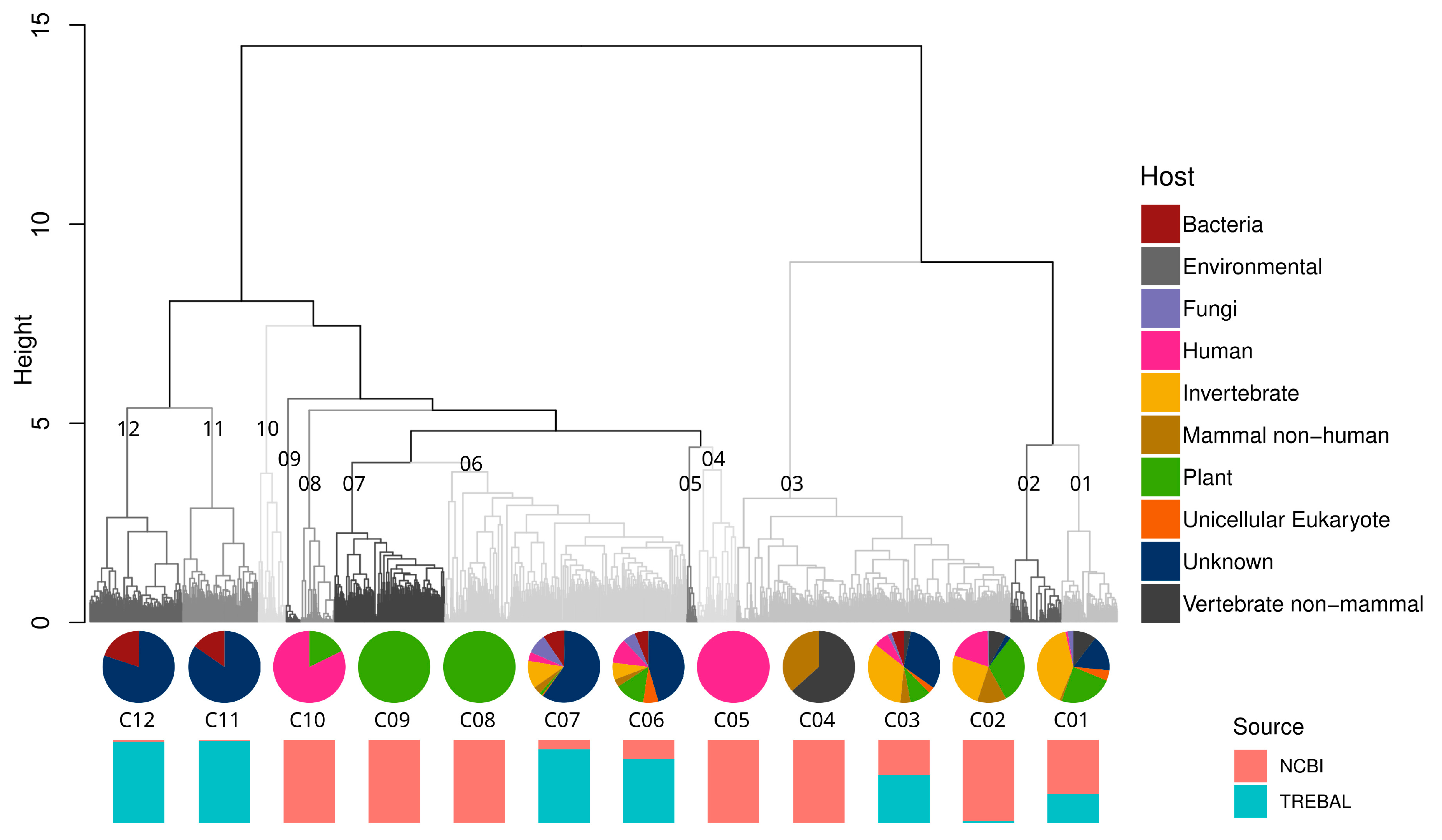
3.2. Putative Hosts of Sewage RNA Viruses
3.3. Tackling the Sewage RNA Viral Dark Matter through RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Analyses
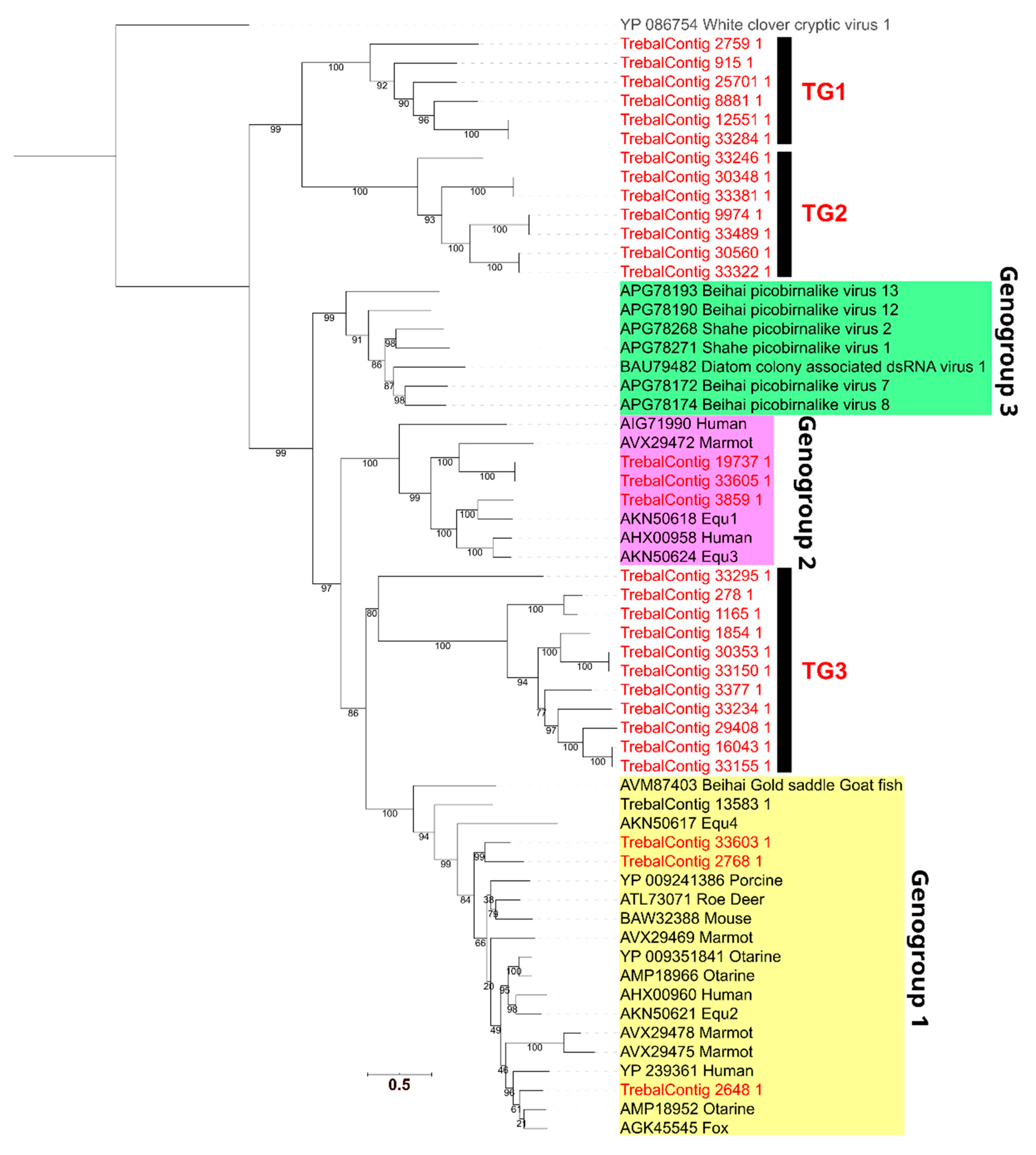
3.4. High Phylogenetic Novelty of Picobirnaviruses in Trebal Sewage
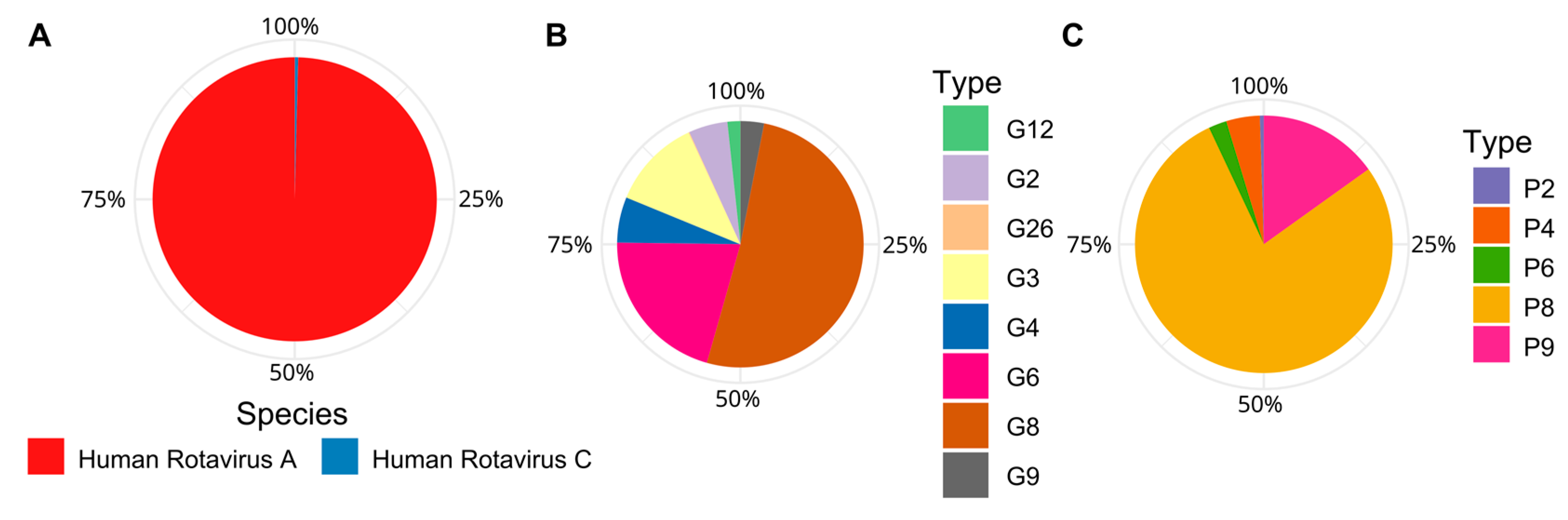
3.5. Dominance of Emergent Rotaviruses Genotypes in Trebal Sewage
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breitbart, M.; Rohwer, F. Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalupo, P.G.; Calgua, B.; Zhao, G.; Hundesa, A.; Wier, A.D.; Katz, J.P.; Grabe, M.; Hendrix, R.W.; Girones, R.; Wang, D.; et al. Raw sewage harbors diverse viral populations. MBio 2011, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.F.F.; Marine, R.; Wang, C.; Simmonds, P.; Kapusinszky, B.; Bodhidatta, L.; Oderinde, B.S.; Wommack, K.E.; Delwart, E. High Variety of Known and New RNA and DNA Viruses of Diverse Origins in Untreated Sewage. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12161–12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Puchol, S.; Rusiñol, M.; Fernández-Cassi, X.; Timoneda, N.; Itarte, M.; Andrés, C.; Antón, A.; Abril, J.F.; Girones, R.; Bofill-Mas, S. Characterisation of the sewage virome: Comparison of NGS tools and occurrence of significant pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cassi, X.; Timoneda, N.; Martínez-Puchol, S.; Rusiñol, M.; Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Figuerola, N.; Bofill-Mas, S.; Abril, J.F.; Girones, R. Metagenomics for the study of viruses in urban sewage as a tool for public health surveillance. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, K.; Cooper, D.M.; McDonald, J.E.; Malham, S.K.; De Rougemont, A.; Jones, D.L. Seasonal and spatial dynamics of enteric viruses in wastewater and in riverine and estuarine receiving waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Farkas, K.; Harrison, C.; Jones, D.L.; Allison, H.E.; McCarthy, A.J. Viromic Analysis of Wastewater Input to a River Catchment Reveals a Diverse Assemblage of RNA Viruses. MSystems 2018, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, M.; Iker, B.C.; Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Relative abundance and treatment reduction of viruses during wastewater treatment processes-Identification of potential viral indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sikora, P.; Rutgersson, C.; Lindh, M.; Brodin, T.; Björlenius, B.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Norder, H. Differential removal of human pathogenic viruses from sewage by conventional and ozone treatments. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, D.; Amarasiri, M.; Hata, A.; Watanabe, T.; Katayama, H. Risk management of viral infectious diseases in wastewater reclamation and reuse: Review. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Latorre, L.; Romero, B.; Bonifaz, E.; Timoneda, N.; Rusiñol, M.; Girones, R.; Rios-Touma, B. Quito’s virome: Metagenomic analysis of viral diversity in urban streams of Ecuador’s capital city. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildenbrand, G.; Bosiek, K.; Dreessen, C.; Froß, P.; Sievers, A.; Hausmann, M.; Bisch, M.; Riedel, J. K-mer Content, Correlation, and Position Analysis of Genome DNA Sequences for the Identification of Function and Evolutionary Features. Genes (Basel) 2017, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greninger, A.L. A decade of RNA virus metagenomics is (not) enough. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumian, T.M.; Leite, J.P.G.; Castello, A.A.; Gaggero, A.; de Caillou, M.S.L.; Miagostovich, M.P. Detection of rotavirus A in sewage samples using multiplex qPCR and an evaluation of the ultracentrifugation and adsorption-elution methods for virus concentration. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 170, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads kenkyuhi hojokin gan rinsho kenkyu jigyo. EMBnet J. 2013, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.M.; Leung, C.M.; Ting, H.F.; Sadakane, K.; Yamashita, H.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT v1.0: A fast and scalable metagenome assembler driven by advanced methodologies and community practices. Methods 2016, 102, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.M.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y.L. IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; Smoot, M.; Shumway, M.; Antonescu, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2014, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Beier, S.; Flade, I.; Górska, A.; El-Hadidi, M.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Tappu, R. MEGAN Community Edition-Interactive Exploration and Analysis of Large-Scale Microbiome Sequencing Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Nishiyama, H.; Yoshikawa, G.; Uehara, H.; Hingamp, P.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. Linking virus genomes with host taxonomy. Viruses 2016, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guajardo-Leiva, S.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Salgado, O.; Pinto, F.; Díez, B. Active Crossfire Between Cyanobacteria and Cyanophages in Phototrophic Mat Communities Within Hot Springs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, S.R. A new generation of homology search tools based on probabilistic inference. Genome Inform. 2009, 32, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zielezinski, A.; Vinga, S.; Almeida, J.; Karlowski, W.M. Alignment-free sequence comparison: Benefits, applications, and tools. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K. Mafft: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, B.; Attoui, H.; Ghosh, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Mundt, E.; Vakharia, V.N. Ictv virus taxonomy profile: Picobirnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Enault, F.; Robin, A.; Ravet, V.; Personnic, S.; Theil, S.; Colombet, J.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Debroas, D. Assessing the diversity and specificity of two freshwater viral communities through metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e86980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, S.; Arioli, S.; Neri, E.; Della Scala, G.; Gargari, G.; Mora, D. Viromes as genetic reservoir for the microbial communities in aquatic environments: A focus on antimicrobial-resistance genes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enault, F.; Briet, A.; Bouteille, L.; Roux, S.; Sullivan, M.B.; Petit, M.A. Phages rarely encode antibiotic resistance genes: A cautionary tale for virome analyses. ISME J. 2017, 11, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.A.; Rohwer, F. Viral metagenomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, E.M.; Griffin, D.W.; Breitbart, M. Eukaryotic viruses in wastewater samples from the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.; Masachessi, G.; Mladenova, Z. Animal Picobirnavirus. Virusdisease 2014, 25, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.R.; Janowski, A.B.; Zhao, G.; Barouch, D.; Wang, D. Hyperexpansion of RNA Bacteriophage Diversity. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniesa, M.; Imamovic, L.; Jofre, J. Bacteriophages and genetic mobilization in sewage and faecally polluted environments. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, S.R.; Wang, D. Extensive conservation of prokaryotic ribosomal binding sites in known and novel picobirnaviruses. Virology 2018, 516, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boros, Á.; Polgár, B.; Pankovics, P.; Fenyvesi, H.; Engelmann, P.; Phan, T.G.; Delwart, E.; Reuter, G. Multiple divergent picobirnaviruses with functional prokaryotic Shine-Dalgarno ribosome binding sites present in cloacal sample of a diarrheic chicken. Virology 2018, 525, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slekovec, C.; Plantin, J.; Cholley, P.; Thouverez, M.; Talon, D.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D. Tracking Down Antibiotic-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates in a Wastewater Network. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, P.C.; Mcgehee, S.M. Wading Bird Use of Wastewater Treatment Wetlands in Central Florida, USA. Colon. Waterbirds 1994, 17, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.J.; Cristinacce, A. Use of sewage treatment works as foraging sites by insectivorous bats. Anim. Conserv. 2006, 9, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial Contamination of Drinking Water and Human Health from Community Water Systems. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, J.P.S.; Sena, K.; Hodgers, L.; Palmer, A.; Toze, S. Comparative enteric viruses and coliphage removal during wastewater treatment processes in a sub-tropical environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Gong, P. A structure-function diversity survey of the rna-dependent rna polymerases from the positive-strand rna viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Velthuis, A.J.W. Common and unique features of viral RNA-dependent polymerases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 4403–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.K.W.; Leung, C.Y.H.; Perera, H.K.K.; Ng, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Joyner, P.H.; Grioni, A.; Ades, G.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S.M.; et al. A Novel Group of Avian Astroviruses in Wild Aquatic Birds. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13772–13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, G.; Bonadonna, L.; Lucentini, L.; Kenmoe, S.; Suffredini, E. Coronavirus in water environments: Occurrence, persistence and concentration methods—A scoping review. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Nie, K.; Ma, X.; Liang, G. Discovery and genetic analysis of novel coronaviruses in least horseshoe bats in southwestern China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berto, A.; Anh, P.H.; Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Simmonds, P.; Van Cuong, N.; Tue, N.T.; Van Dung, N.; Woolhouse, M.E.; Smith, I.; Marsh, G.A.; et al. Detection of potentially novel paramyxovirus and coronavirus viral RNA in bats and rats in the Mekong Delta region of southern Viet Nam. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Gildow, F.E. Luteovirus-Aphid Interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2003, 41, 539–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujarski, J.; Gallitelli, D.; García-Arenal, F.; Pallás, V.; Palukaitis, P.; Krishna Reddy, M.; Wang, A. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Bromoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1206–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroneman, A.; Vega, E.; Vennema, H.; Vinjé, J.; White, P.A.; Hansman, G.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Katayama, K.; Koopmans, M. Proposal for a unified norovirus nomenclature and genotyping. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, M.; Van Beek, J.; Koopmans, M.P.G. Human norovirus transmission and evolution in a changing world. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Y.S.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, K.; Dhama, K.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Ganesh, B.; Kobayashi, N.; Banyai, K. Epidemiology, phylogeny, and evolution of emerging enteric picobirnaviruses of animal origin and their relationship to human strains. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Teng, J.L.L.; Bai, R.; Tang, Y.; Wong, A.Y.P.; Li, K.S.M.; Lam, C.S.F.; Fan, R.Y.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Yuen, K. Novel Picobirnaviruses in Respiratory and Alimentary Tracts of Cattle and Monkeys with Large Intra- and Inter-Host Diversity. Viruses 2019, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yinda, C.K.; Ghogomu, S.M.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Beller, L.; Deboutte, W.; Vanhulle, E.; Maes, P.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J. Cameroonian fruit bats harbor divergent viruses, including rotavirus H, bastroviruses, and picobirnaviruses using an alternative genetic code. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, Y.; O’Ryan, M.; Liparoti, G.; Huerta, N.; Mamani, N.; Ramani, S.; Lagomarcino, A.J.; Del Canto, F.; Quense, J. Predominance of Rotavirus G8P(8) in a City in Chile, a Country Without Rotavirus Vaccination. J. Pediatr. 2019, 204, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacharoenmuang, R.; Komoto, S.; Guntapong, R.; Ide, T.; Sinchai, P.; Upachai, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tharmaphornpilas, P.; Sangkitporn, S.; Taniguchi, K. Full Genome Characterization of Novel DS-1-Like G8P(8) Rotavirus Strains that Have Emerged in Thailand: Reassortment of Bovine and Human Rotavirus Gene Segments in Emerging DS-1-Like Intergenogroup Reassortant Strains. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Oda, M.; Somura, Y.; Shinkai, T. Molecular Characteristics of Novel Mono-Reassortant G9P(8) Rotavirus A Strains Possessing the NSP4 Gene of the E2 Genotype Detected in Tokyo, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Delogu, R.; Camilloni, B.; Lorini, C.; Ruggeri, F.M.; Fiore, L. Detection of unusual G6 rotavirus strains in Italian children with diarrhoea during the 2011 surveillance season. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, Z.; Nawaz, S.; Ganesh, B.; Iturriza-Gomara, M. Increased detection of G3P(9) and G6P(9) rotavirus strains in hospitalized children with acute diarrhea in Bulgaria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 29, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guajardo-Leiva, S.; Chnaiderman, J.; Gaggero, A.; Díez, B. Metagenomic Insights into the Sewage RNA Virosphere of a Large City. Viruses 2020, 12, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091050
Guajardo-Leiva S, Chnaiderman J, Gaggero A, Díez B. Metagenomic Insights into the Sewage RNA Virosphere of a Large City. Viruses. 2020; 12(9):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091050
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuajardo-Leiva, Sergio, Jonás Chnaiderman, Aldo Gaggero, and Beatriz Díez. 2020. "Metagenomic Insights into the Sewage RNA Virosphere of a Large City" Viruses 12, no. 9: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091050
APA StyleGuajardo-Leiva, S., Chnaiderman, J., Gaggero, A., & Díez, B. (2020). Metagenomic Insights into the Sewage RNA Virosphere of a Large City. Viruses, 12(9), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091050





