Comprehensive Analyses of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in a Public Health Virology Laboratory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Nucleic Acid Extraction and Viral Genome Quantification by Real-Time PCR (q-PCR)
2.2. Specific Amplification of SARS-CoV-2 from Clinical Samples
2.3. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.5. Wipe Test Sampling
2.6. Serology
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Specific qRT PCR Assay Identifies SARS-CoV-2 Positive ICVL Staff and Relatives
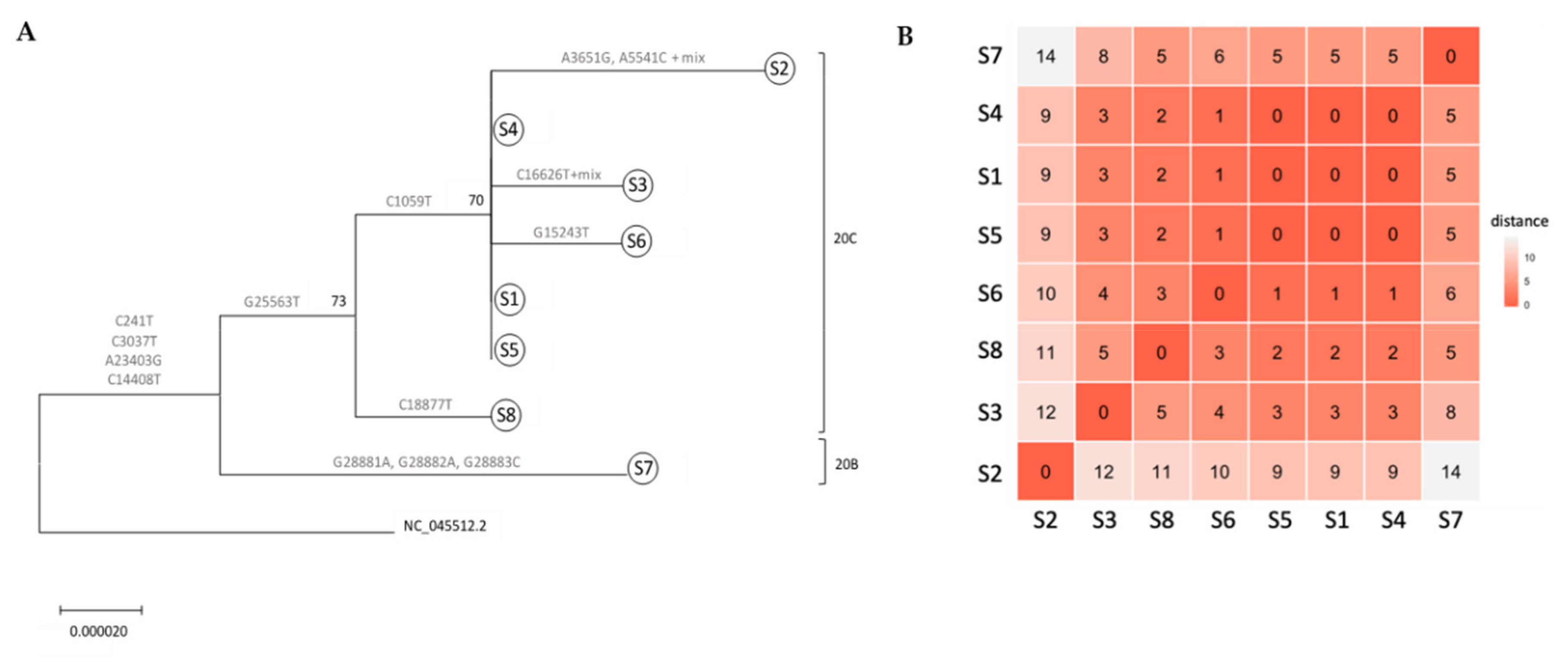
3.2. Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Molecular Epidemiology Elucidates Transmission Events
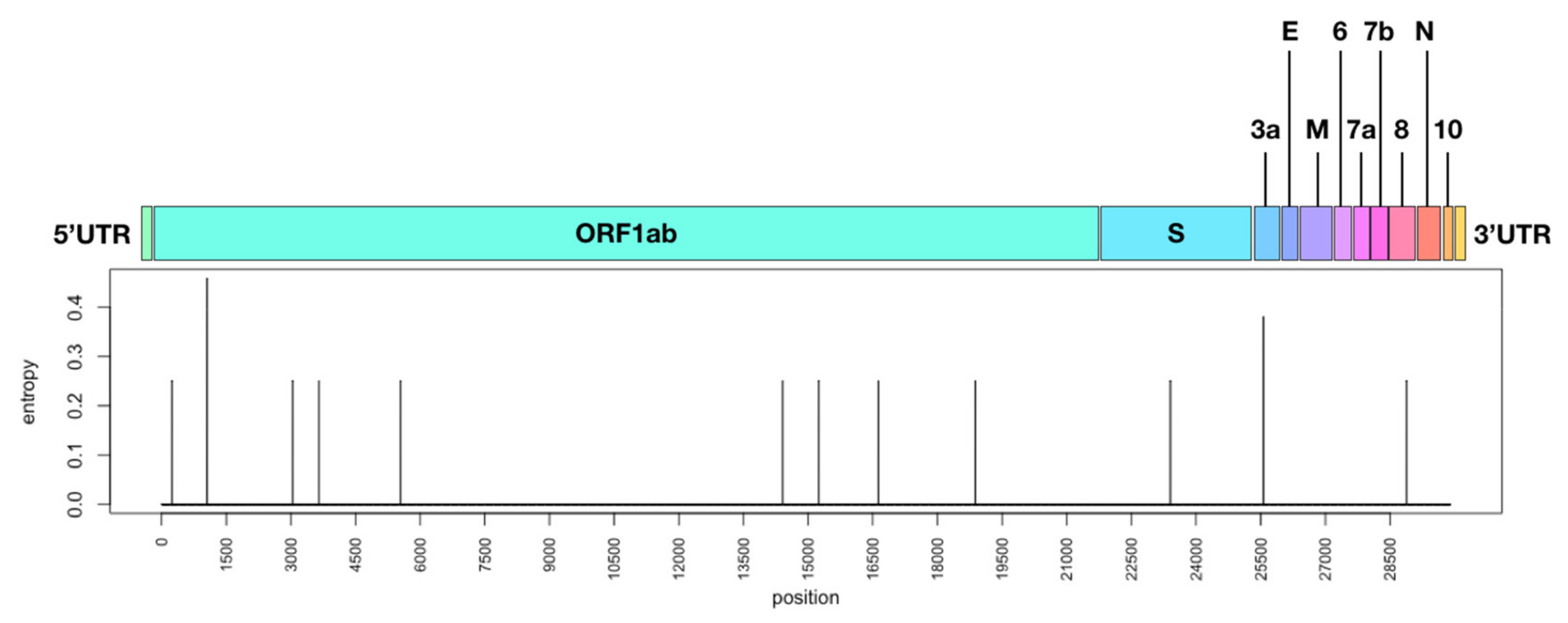
3.3. Mutations along SARS-CoV-2 whole Genome within a Transmission Chain
3.4. Wipe Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 on Laboratory Surfaces
3.5. Serological Analysis of all ICVL Staff Members and Relatives
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H.; Stratton, C.W.; Tang, Y.W. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The mystery and the miracle. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holshue, M.L.; DeBolt, C.; Lindquist, S.; Lofy, K.H.; Wiesman, J.; Bruce, H.; Spitters, C.; Ericson, K.; Wilkerson, S.; Tural, A.; et al. First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajema, K.L.; Oster, A.M.; McGovern, O.L.; Lindstrom, S.; Stenger, M.R.; Anderson, T.C.; Isenhour, C.; Clarke, K.R.; Evans, M.E.; Chu, V.T.; et al. Persons Evaluated for 2019 Novel Coronavirus - United States, January 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/covidview/index.html (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Available online: www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, disease and diplomacy: GISAID’s innovative contribution to global health. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B.; Fischer, W.M.; Gnanakaran, S.; Yoon, H.; Theiler, J.; Abfalterer, W.; Hengartner, N.; Giorgi, E.E.; Bhattacharya, T.; Foley, B.; et al. Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell 2020, 182, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradburne, A.F.; Bynoe, M.L.; Tyrrell, D.A. Effects of a “new” human respiratory virus in volunteers. Br. Med. J. 1967, 3, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, H.E.; Reed, S.E.; Tyrrell, D.A. Isolation of rhinoviruses and coronaviruses from 38 colds in adults. J. Med. Virol. 1980, 5, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.; Alter, H.; Hindiyeh, M.; Mendelson, E.; Shemer Avni, Y.; Mandelboim, M. Human Coronavirus Infections in Israel: Epidemiology, Clinical Symptoms and Summer Seasonality of HCoV-HKU1. Viruses 2018, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Laboratory Biorisk Management for Laboratories Handling Human Specimens Suspected or Confirmed to Contain Novel Coronavirus: Interim Recommendations. Available online: www.who.int/csr/disease/coronavirus_infections/Biosafety_InterimRecommendations_NovelCoronavirus_19Feb13.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2013).
- CDC. Interim Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines for Handling and Processing Specimens Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/lab-biosafety-guidelines.html. (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Lotfi, M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Rezaei, N. COVID-19: Transmission, prevention, and potential therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2020, 508, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.L.; Wang, Y.; Molina, M.J. Identifying airborne transmission as the dominant route for the spread of COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 117, 14857–14863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Hsueh, S.C.; Yen, M.Y.; Ko, W.C.; Hsueh, P.R. Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, C.; Schunk, M.; Sothmann, P.; Bretzel, G.; Froeschl, G.; Wallrauch, C.; Zimmer, T.; Thiel, V.; Janke, C.; Guggemos, W.; et al. Transmission of 2019-nCoV Infection from an Asymptomatic Contact in Germany. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARTIC NETWORK, SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://artic.network/ncov-2019 (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Kaller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, V.; Danecek, P.; Scally, A.; Xue, Y.; Tyler-Smith, C.; Durbin, R. BCFtools/RoH: A hidden Markov model approach for detecting autozygosity from next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charif, D.; Lobry, J.R. SeqinR 1.0-2: A Contributed Package to the R Project for Statistical Computing Devoted to Biological Sequences Retrieval and Analysis. In Structural Approaches to Sequence Evolution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Atchley, W.R.; Terhalle, W.; Dress, A. Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 48, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, K.R.; Boone, S.A.; Gerba, C.P. Occurrence of bacteria and viruses on elementary classroom surfaces and the potential role of classroom hygiene in the spread of infectious diseases. J. Sch. Nurs. 2010, 26, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J.; et al. A serological assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMOH. Home Isolation Regulations due to COVID-19. Available online: https://www.health.gov.il/LegislationLibrary/Kor01.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- IMOH. The novel Coronavirus- Guidance for Isolated Individuals and Household Members. Available online: https://govextra.gov.il/ministry-of-health/corona/corona-virus-en/ (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- CDC. Symptoms of Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Fcoronavirus%2F2019-ncov%2Fabout%2Fsymptoms.html (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Azman, A.S.; Reich, N.G.; Lessler, J. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.; Lau, Y.C.; Wong, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Tan, X.; et al. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, S.A.; Gerba, C.P. Significance of fomites in the spread of respiratory and enteric viral disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampf, G.; Todt, D.; Pfaender, S.; Steinmann, E. Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 104, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Infection prevention and control during health care when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/10665-331495 (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- PHE. COVID-19: Safe handling and processing for samples in laboratories. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/wuhan-novel-coronavirus-guidance-for-clinical-diagnostic-laboratories/wuhan-novel-coronavirus-handling-and-processing-of-laboratory-specimens (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Oran, D.P.; Topol, E.J. Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.; Hatfield, K.M.; Arons, M.; James, A.; Taylor, J.; Spicer, K.; Bardossy, A.C.; Oakley, L.P.; Tanwar, S.; Chisty, Z.; et al. Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Residents of a Long-Term Care Skilled Nursing Facility—King County, Washington, March 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, T.; Li, J.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of novel coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample No. | Facility | Sampled Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Specimen reception area | All work surfaces and equipment in the room including knobs, chairs, doors, etc. |
| 2 | Specimen reception area | Biosafety cabinets’ (BSC) outside and inside surface |
| 3 | Specimen sampling room #1 | All work surfaces and equipment in the room including knobs, chairs, doors, etc. |
| 4 | Specimen sampling room #1 | BSC outside and inside surface |
| 5 | Specimen sampling room #2 | All work surfaces and equipment in the room including knobs, chairs, doors, etc. |
| 6 | Specimen sampling room #2 | BSC outside and inside surface |
| Cases Characteristics | Sequencing Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | SARS-CoV-2 Ct | IgG/IgA Values | Age | Date of Detection | Estimated Date of Infection* | Transmission Chain | # Mapped Reads | % Coverage | Avg. Depth |
| S1 | 14.3 | 3.36/3.34 | 55 | 15.3.20 | unknown | ICVL | 3,806,897 | 100.00 | 6095 |
| S2 | 33.07 | 4.87/13.86 | 65 | 15.3.20 | unknown | NA | 5,096,580 | 98.00 | 5357 |
| S3 | 18.77 | 4.52/5.9 | 46 | 15.3.20 | 10.3.20 | NA | 3,495,706 | 99.65 | 5501 |
| S4 | 26 | 4.77/6.77 | 39 | 23.3.20 | 14.3.20 | ICVL | 1,739,690 | 99.24 | 4713 |
| S5 | 28.58 | 4.71/1.83 | 61 | 29.3.20 | 14.3.20 | ICVL | 1,419,044 | 99.96 | 4958 |
| S6 | 22 | 4.75/1.76 | 41 | 23.3.20 | 14.3.20 | ICVL | 3,380,868 | 99.90 | 6014 |
| S7 | 24 | 6.69/2.1 | 41 | 29.3.20 | 14.3.20 | NA | 8,580,675 | 99.99 | 40,466 |
| S8 | 22 | 7.17/10.23 | 52 | 18.3.20 | 10.3.20 | NA | 9,498,576 | 100 | 45,041 |
| Gene | Clade | Nuc # | REF | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | AA # | REF | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | R/S | AA Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5’UTR | 241 | c | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| NSP2 | 20C | 1059 | c | t | t | t | t | t | t | c | c | 85 | T | I | I | I | I | I | I | T | T | R | hydroxilated (T), aliphatic (I) |
| NSP3 | 3037 | c | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | 107 | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | S | aromatic (F) | |
| 3651 | a | a | g | a | a | a | a | a | a | 311 | Q | Q | R | Q | Q | Q | Q | Q | Q | R | aminic (Q), basic (R) | ||
| 5541 | a | a | c | a | a | a | a | a | a | 941 | Q | Q | P | Q | Q | Q | Q | Q | Q | R | aminic (Q), proline (P) | ||
| NSP12 | 20B | 14408 | c | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | t | 314 | P | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | R | proline (P), aliphatic (L) |
| 15243 | g | g | g | g | g | g | t | g | g | 601 | C | C | C | C | C | C | F | C | C | R | cysteine (C), aromatic (F) | ||
| NSP13 | 16626 | c | c | c | t | c | c | c | c | c | 131 | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | S | aliphatic (L) | |
| NSP14 | 18887 | c | c | c | c | c | c | c | c | t | 280 | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | S | aliphatic (L) | |
| SPIKE | 20B | 23403 | a | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | 614 | D | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | R | acidic (D), aliphatic (G) |
| ORF3a | 20C | 25563 | g | t | t | t | t | t | t | g | t | 58 | Q | H | H | H | H | H | H | Q | H | R | basic (H), aminic (Q) |
| NUCAP | 20B | 28881 | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | a | g | 203 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | K | R | R | basic (R/K) |
| 20B | 28882 | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | a | g | 204 | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | K | R | R | basic (R/K) | |
| 20B | 28883 | g | g | g | g | g | g | g | c | g | 204 | G | G | G | G | G | G | G | R | G | R | aliphatic (G), basic (R) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuckerman, N.S.; Pando, R.; Bucris, E.; Drori, Y.; Lustig, Y.; Erster, O.; Mor, O.; Mendelson, E.; Mandelboim, M. Comprehensive Analyses of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in a Public Health Virology Laboratory. Viruses 2020, 12, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080854
Zuckerman NS, Pando R, Bucris E, Drori Y, Lustig Y, Erster O, Mor O, Mendelson E, Mandelboim M. Comprehensive Analyses of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in a Public Health Virology Laboratory. Viruses. 2020; 12(8):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080854
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuckerman, Neta S., Rakefet Pando, Efrat Bucris, Yaron Drori, Yaniv Lustig, Oran Erster, Orna Mor, Ella Mendelson, and Michal Mandelboim. 2020. "Comprehensive Analyses of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in a Public Health Virology Laboratory" Viruses 12, no. 8: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080854
APA StyleZuckerman, N. S., Pando, R., Bucris, E., Drori, Y., Lustig, Y., Erster, O., Mor, O., Mendelson, E., & Mandelboim, M. (2020). Comprehensive Analyses of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in a Public Health Virology Laboratory. Viruses, 12(8), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080854





