Abstract
Hepatitis E virus (HEV), a pathogen that causes acute viral hepatitis, is a small icosahedral, quasi-enveloped, positive ssRNA virus. Its genome has three open reading frames (ORFs), with ORF1 and ORF3 encoding for nonstructural and regulatory proteins, respectively, while ORF2 is translated into the structural, capsid protein. ORF2 is most widely used for vaccine development in viral hepatitis. Hepatitis E virus-like particles (VLPs) are potential vaccine candidates against HEV infection. VLPs are composed of capsid subunits mimicking the natural configuration of the native virus but lack the genetic material needed for replication. As a result, VLPs are unable to replicate and cause disease, constituting safe vaccine platforms. Currently, the recombinant VLP-based vaccine Hecolin® against HEV is only licensed in China. Herein, systematic information about the expression of various HEV ORF2 sequences and their ability to form VLPs in different systems is provided.
1. Introduction
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is an enterically transmitted pathogen and a major cause of acute hepatitis in many developing countries within Africa and Asia [1]. Approximately one third of the world population live in areas in which HEV is endemic and thus are at risk of infection [2]. Unlike other viruses causing hepatitis, HEV-related disease is a zoonotic infection with pigs, wild boars and certain other species such as deer and rabbits being considered as reservoirs for the virus [3,4]. Although the fatality rate during epidemics is low, i.e., between 0.2–5% [5], the mortality rate in pregnant women is as high as 25%, possibly due to altered hormone status and decreased immunity [6,7,8]. Even though HEV infection is considered self-limiting or asymptomatic in healthy individuals, it can lead to severe disease in patients with preexisting liver conditions, with high morbidity and mortality [9,10]. Chronic infection could develop in immunocompromised patients such as organ transplant recipients [11], individuals administered immunosuppressants [12], patients on chemotherapy for hematological malignancies [13], HIV-infected patients [14] and cases of superinfection with other hepatitis viruses [15]. In 10% of chronically infected patients, HEV leads to rapid progression to liver cirrhosis in less than 3 years [16]. In addition, it has become evident in recent years that HEV infections can be associated with neurological manifestations [17,18], renal aliments [19], hematological disorders [20] and acute pancreatitis [21]. Furthermore, recent data indicate a link between HEV infection and progression to hepatocellular carcinoma in patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) [22,23]. Atsama et al. [22] reported significantly higher prevalence of anti-HEV IgG in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients infected with either HBV or HCV compared with HBV/HCV-infected patients with chronic liver disease but not suffering from HCC [22]. This finding suggests that infection with HEV could worsen liver inflammation and increase the severity of other infections. Another study also reported that HEV superinfection accelerates the progression of chronic HBV infection and increases 1-year mortality [23].
Traditional approaches for the development of an HEV vaccine have been ruled out because the manufacturing of either live attenuated or inactivated vaccine would be impossible due to the complexity and low yield of viral culture. Even though culturing the virus has been difficult in the past, a few strains have been adapted to cell culture, leading to a better understanding of the HEV life cycle [24].
Presently, significant progress has been made in the development of HEV vaccines based on the ORF2 capsid protein as either a subunit or virus-like particle (VLP) [25]. VPLs represent one of the most attractive systems for vaccine development due to their safety, immunogenic properties and ease of production [26]. VLPs are generated from one or more viral capsid proteins that self-assemble into high-molecular-weight structures that resemble the native virions but lack the viral genome [27]. As a result, VLPs are replication- and infection-incompetent, making them a safe alternative to attenuated or inactivated viruses in vaccine development. Since they are structurally similar to the native virus, they can induce stronger B and T cell responses than traditional small subunit vaccines [28]. Additionally, VLPs can be better taken up by professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs) as exogenous and endogenous antigens for processing and presentation by MHC class II and I molecules, respectively. Cross-presentation by MHC class molecules activates CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that elicit specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses resulting in infection control [29]. Furthermore, VLPs can be assembled not only from proteins from a single virus, but also from proteins of distinct viruses or various other pathogens, e.g., bacteria and protozoa [30]. To date, several VLPs have been produced for protection against infectious diseases in prokaryotic or eukaryotic expression systems [31], and in some cases assembled in cell-free conditions [32]. Some of these products have been licensed, including Engerix® (Hepatitis B virus) [33], Cervarix® (human papilloma virus) [34], Recombivax HB® (HBV) [35] and Gardasil® (HPV) [36], while others are still under pre-clinical and clinical evaluation [37,38]. This review summarizes the basic information about HEV genome organization, the expression of ORF2 capsid protein in several expression systems and current progress in developing VLP-based HEV vaccines. In addition, we described in detail all recombinantly expressed HEV sequences discovered in humans and animal species as well as the amino acid sequences required for VLP formation with different levels of success.
2. Hepatitis E Genome Organization
Previously known as non-A non B hepatitis, HEV is currently classified in the Hepeviridae family with the two genera Orthohepeviruses and Pischihepeviruses [39]. The Orthohepevirus A genus includes genotypes 1 and 2 isolated from humans, genotypes 3 and 4 from both humans and animals, the newly proposed genotypes 5 and 6 from wild boars and genotype 7 from dromedary camels [40,41].
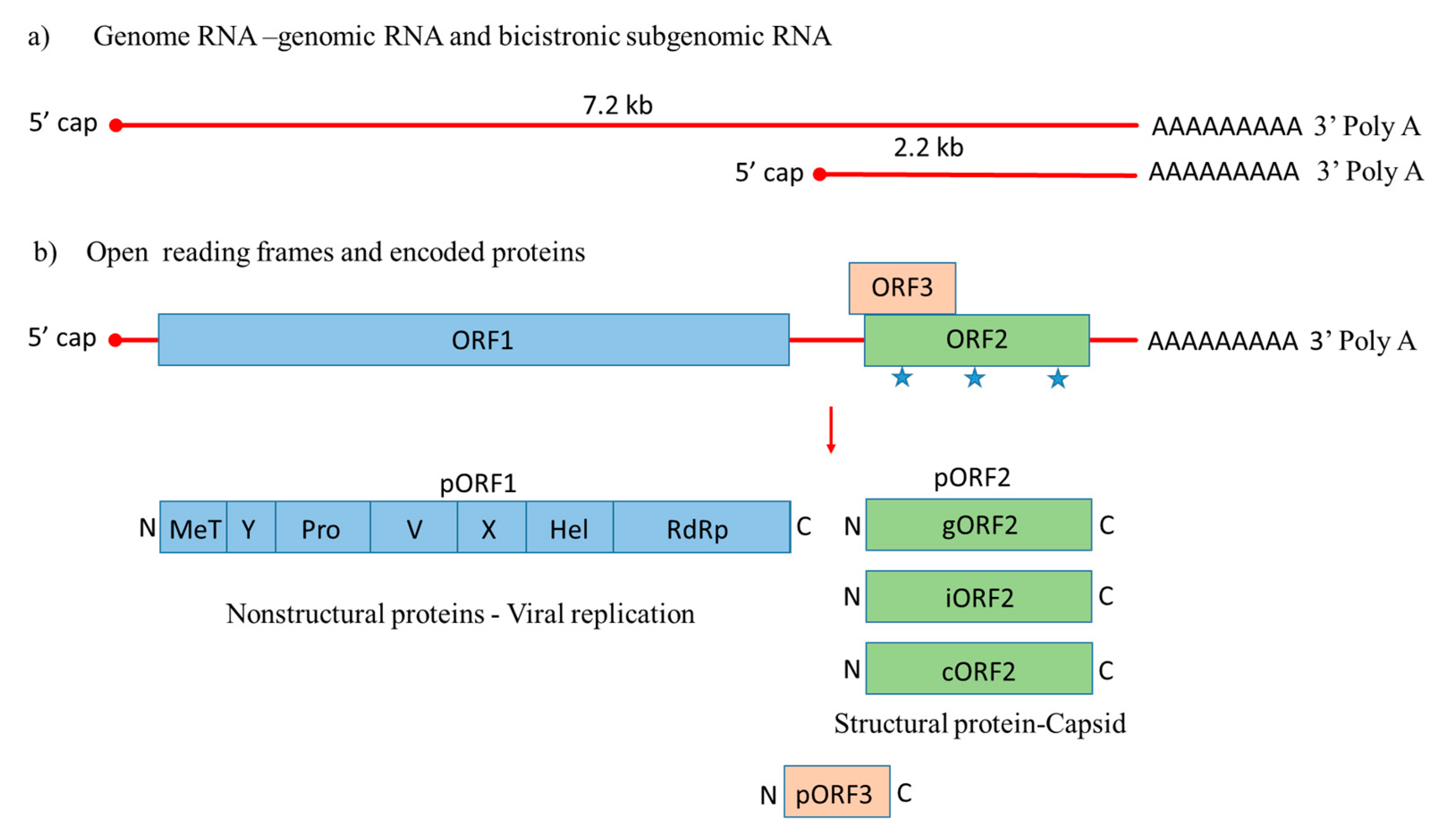
HEV is a quasi-enveloped, icosahedral, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus that was molecularly characterized for the first time in 1990 [42]. Its genome is around 7.2 kb with features of a eukaryotic mRNA, including a 5′ cap and 3′ poly A tail, 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), and three open reading frames, including ORF1, ORF2, and ORF3 [43]. During HEV genome replication two viral RNA species are generated, i.e., the full-length genomic RNA and a subgenomic RNA [44]. The subgenomic RNA allows the expression of ORF2 and ORF3 (Figure 1).
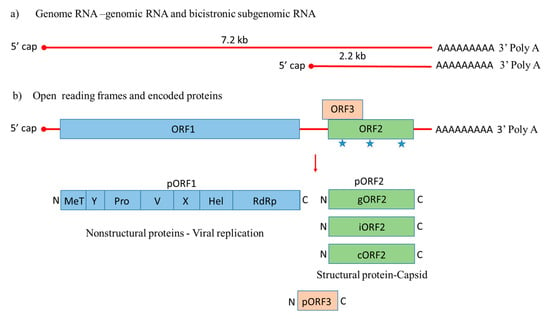
Figure 1.
Genome organization of Hepatitis E virus. (a) Hepatitis E-Virus (HEV) genome generates the full-length genomic RNA and subgenomic RNA with 5′ cap, 3′ Poly A tail, 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR. (b) The genomic RNA has three open reading frames: ORF1, ORF2, and ORF3. ORF1 encodes the nonstructural proteins for viral replication; ORF2 is translated into the capsid protein with three potential glycosylation sites ( ), with a small multifunctional protein encoded by ORF3. Three different capsid proteins have been discovered in vitro during infection, i.e., gORF2-glycosylated, iORF2-infectious and cORF2-cleaved ORF2.
), with a small multifunctional protein encoded by ORF3. Three different capsid proteins have been discovered in vitro during infection, i.e., gORF2-glycosylated, iORF2-infectious and cORF2-cleaved ORF2.
 ), with a small multifunctional protein encoded by ORF3. Three different capsid proteins have been discovered in vitro during infection, i.e., gORF2-glycosylated, iORF2-infectious and cORF2-cleaved ORF2.
), with a small multifunctional protein encoded by ORF3. Three different capsid proteins have been discovered in vitro during infection, i.e., gORF2-glycosylated, iORF2-infectious and cORF2-cleaved ORF2.
ORF1 encodes nonstructural proteins involved in viral replication [45,46]. A small multifunctional 13 kDa protein is expressed from ORF3, which facilitates HEV transport throughout the cell and acts as viroporin for the release of the infectious virus from the host cell [47,48]. ORF2 encodes the 72 kDa capsid protein comprising 660 amino acids that contains a hydrophobic stretch of 14–34 amino acids at the N-terminus, which functions as a signal sequence for its secretion [49]. ORF2 is involved in virion assembly, attachment to the host cell and immunogenicity [50,51,52]. Additionally, the capsid protein has three potential glycosylation sites (Asn 132, 310 and 562) [53].
Native HEV particles are round non-enveloped with spikes covering the surface [54,55]. It is considered that 180 copies of the ORF2 protein form the HEV virion giving it T = 3 icosahedral symmetry [56]. Recently, a few strains have been adapted for replication in cell culture, providing novel insights into the HEV cycle. Even though HEV particles present in the bile and feces are non-enveloped, it was demonstrated that in patient serum and cell cultures, HEV particles are partially associated with lipids and the ORF3 protein [57]. Moreover, recent studies have identified different forms of ORF2 in cultured cells. Large ORF2 protein amounts are released from HEV-infected cells in vitro and found in serum from HEV-infected patients. This secreted protein (ORF2s) was shown to be glycosylated form of the capsid protein that is not associated with the HEV virion. The other intracellular protein (ORF2c), a translation product of the same gene starting with the second AUG codon, is involved in HEV assembly [58]. Montpellier et al. reported iORF2 (infectious), gORF2 (glycosylated) and additional ORF2 truncated protein (ORF2c) are not involved in virion assembly using another genotype and cell culture for replication [59].
Great efforts have been made towards understanding the HEV life cycle in recent years by developing cellular systems and infectious HEV clones [60]. Polarized cell models have been developed to closely mimic in vivo infection with HEV, which are highly permissive to infection, making them a good tool for molecular studies of the HEV cycle. For example, human hepatoma-derived HepaRG and porcine hepatocyte-like PICM-19 cell lines have been shown to support HEV replication, and are useful for studying virus–host interactions and species barrier crossing, especially since HEV infection is a zoonosis in developed countries [61]. Capelli et al. [62,63] showed that different HEV genotypes release more than 90% of the virus from the apical membrane after infecting polarized human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2/C3A cells, suggesting the main route of release for infectious virions [62,63]. In recent years, the key steps of HEV’s natural infectious cycle in vivo have been confirmed by employing polarized human stem-cell-derived, hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs). Infection of these cells with HEV results in the secretion of two different progeny particle types, including quasi-enveloped particles from the basolateral membrane and naked highly infectious virions from the apical membrane [64]. These findings provide novel insights into the HEV infectious cycle. The release of HEV particles basolaterally could spread the infection in the host and lead to extrahepatic manifestations [65].
3. VLP-Based Vaccines for HEV Prevention
Improving the sanitary conditions in endemic areas would significantly curb HEV infection incidence; however, vaccination is also needed for protection. In non-enveloped viruses, the capsid not only protects the viral nucleic acid, but is also involved in cell receptor binding, virus internalization, and genome release into the cytoplasm. Prevention of HEV infection by vaccination relies on the capsid protein as it is highly immunogenic and elicits effective virus-neutralizing antibodies [25,66]. Previous studies suggest that the neutralization epitopes are located in the C-terminal region of the capsid protein [55,67], with residues 458–607 of ORF2 being the shortest neutralization fragment [68]. By contrast, proteins translated from ORF1 are immunogenic but do not confer protection since they are not part of the virion. Furthermore, antibodies raised against the small ORF3 protein are produced during infection; however, they are short-lived and have no neutralizing capability [69]. As a result, research is currently focused on expressing the capsid protein for the development of prophylactic vaccines. To date, three vaccine candidates have been evaluated in clinical trials. Two of them are produced in E. coli as VLPs, including p179 and p239 [70]. The third one, a 56 kDa recombinant protein produced in insect cells, has undergone phase II clinical trials [71]. To date, several different systems have been used to express the HEV capsid protein, including E. coli [72], insect cells [73], mammalian cells [49] and plants [74]. However, E. coli and the baculovirus-insect cell system are considered the most effective systems for producing HEV VLPs [70,73,75].
3.1. Expression of HEV ORF2 in E. Coli
Several HEV ORF2 proteins with different lengths have been expressed and purified in E. coli in order to determine their particle-forming properties (Table 1). The shortest protein, termed E2s (459–606 aa), represents the minimal requirement for the formation of dimers in solution, contains the neutralizing site, and is considered to be necessary for virus–host interaction [76,77]. Another fragment, pE2, comprising amino acids 394–606 of HEV-1 (Chinese strain) ORF2 also forms dimers upon expression in E. coli. It was shown that pE2 is recognized strongly by HEV reactive human sera in its dimeric rather than monomeric form, suggesting that the dimer could mimic the structural features of the virus capsid [72]. Not surprisingly, immunization of macaques with the peptide triggered a strong antibody response and prevented experimental HEV infection of the animals [78]. Moreover, pretreatment with two monoclonal antibodies raised against pE2, diminishes HEV infectivity in rhesus monkeys, providing further support that the pE2 dimer models the 3D features of HEV’s native capsid [79]. Adding 26 amino acids toward the N-terminus of the pE2 peptide results in higher-order assembly structures beyond dimerization. Expressed in E. coli, p239 (HEV 239) forms VLPs with a diameter of 23 nm. These VLPs (HEV 239) are highly immunogenic in both rhesus macaques and mice [75,80]. Even though HEV 239 and pE2 have similar antigenic activities, HEV 239 appears to be 200 times more immunogenic compared with pE2. Unlike pE2, HEV 239 can induce vigorous antigen-specific T-cell response in mice [81]. Generally, the formation of VLPs is considered key for immune recognition and response, and HEV 239 has been further studied as a potential vaccine candidate [82]. Since the latter showed immunogenicity in preclinical experiments, it was approved for use in human trials. HEV 239 VLPs were shown to be safe and immunogenic in humans in a phase II clinical trial of seronegative patients [83]. In addition, more than 110,000 individuals participated in a phase III trial of the vaccine candidate HEV 239 that showed 100% efficacy over the 12 month period after three immunizations [84]. To date, the HEV 239 (Hecolin®) vaccine has been licensed for use only in China [70,85]. Recent research showed that the HEV vaccine could provide long-term protection, i.e., up to 4.5 years, with 86.6% efficacy [86]. In order to be recommended for global use, the HEV239 vaccine must be further investigated for safety and protection in various risk groups. Currently, several studies have shown that the p239-based vaccine is well tolerated in the elderly population (>65 years old) [87] and hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg)-positive adults [88]. In addition, two clinical trials evaluating the HEV239 vaccine are ongoing, including: a phase I safety study in the USA (NCT03827395) and a phase IV trial in Bangladesh (NCT02759991) evaluating its safety and efficacy in pregnant women, who are at higher risk of acute liver failure and elevated neonatal mortality and morbidity [89]. The most recent VLP vaccine, termed p179 (439–617 aa of ORF2 protein), derived from HEV genotype 4, has been developed and assessed in a phase I clinical trial in China [90]. The p179 vaccine candidate was found to be safe and well tolerated among the included participants. The p179 and p239 vaccines showed a difference in immunogenicity due to possible genotype-specific neutralization epitopes, which raises questions about the effectiveness of a vaccine towards different genotypes and the need to develop a vaccine with broader efficacy [91]. Even though p239 is the shortest sequence necessary for assembly in VLPs, it was also shown that a longer sequence of ORF2 112–606 aa (p495) can self-assemble into VLPs after expression in E. coli. The difference between both peptides is that p495 is capable of self-assembly in vitro [92].

Table 1.
Expressed HEV ORF2 protein and VLPs formation in different systems.
3.2. Expression of HEV VLPs in the Baculovirus-Insect Cell System
The baculovirus expression system has been used extensively for the production of recombinant proteins [100,101,102]. This system is an attractive platform for protein expression for several reasons, including a rapid growth rate, easy scalability, and eukaryotic posttranslational modifications of the expressed proteins [103]. The first commercially available vaccine (Cervarix®) expressed in this system was based on HPV type 18 and 16 L1 VLPs, and used to prevent human papillomavirus infections [104,105]. Additionally, many other VLPs have been produced in the baculovirus-insect cell system such as Influenza A [106], Norwalk virus [107], Bluetongue virus [108] and Chikungunya virus VLPs [109].
The baculovirus-insect cell system is the most extensively applied and successful system for the expression of HEV as VLPs to date. Initially, expression of the whole ORF2 protein in the Sf9 cell line yielded several proteins with different molecular weights (72, 63, 56 and 53 kDa), none of which self-assembled into VLPs [73,110]. These proteins were immunoreactive and characterized as by-products of the whole protein undergoing a series of truncations at the N-and/or C-terminus after expression in Sf9 cells. Among these, the 56 kDa protein was the only protein evaluated as a potential vaccine in a phase II clinical trial in Nepal [71]. This protein was shown to be highly immunogenic in cynomolgus monkeys, and after two administrated doses the animals were protected against virulent HEV [111,112]. Despite promising results, this vaccine candidate did not undergo further clinical development, possibly due to limited commercial potential [113]. The first report of the assembly of HEV VLPs in insect cells dated 1997 [73]. After expressing the whole HEV ORF2 sequence, the three major proteins 72, 58 and 50 kDa were found in two different insect cell lines, including Tn5 and Sf9 cells. Despite their immunoreactivity, these proteins were cell-associated and did not form VLPs. However, expression of ORF2 with a truncation of the N-terminal 111 residues in Tn5 cells produced two proteins of 58 and 50 kDa, respectively, with the latter found in the culture medium as VLPs of 23–24 nm (Table 1) [73]. It was concluded that both the N-terminal truncation and the cell line used for expression are important for VLP formation. Additionally, the 50 kDa (C- and N-end truncated ORF2) protein expressed in Sf9 cells could assemble into VLPs [76]. Li et al. with a series of truncations of the capsid protein, determined that the core structure of the ORF2 protein that can form VLPs is in the 126–601 aa range [75]. The HEV capsid protein can self-assemble into either a small VLP composed of 60 copies of a truncated ORF2 (112–608 aa) with T = 1 symmetry [67] or a large VLP made up of 180 capsid subunits (14–608 aa) with T = 3 symmetry [56]. Since large VLPs have different symmetry than the small ones, the additional amino acids (14–112 aa) at the N-terminus seem to play a role in the efficient formation of T = 3 symmetry capsids and the ability to encapsulate RNA [114].
3.2.1. Formation of VLPs from Animal HEV Sequences in the Baculovirus-Insect Cell System
With the discovery of new HEV strains in many animals such as rats [96], camels [98], wild boars [99], and ferrets [115], HEV has the potential to cause a serious veterinary problem, hence the need for research into animal-specific strains of HEV. Li et al. expressed the rat sequence of HEV with the same genome organization as genotype 1–4 in two different cell types [96,116]. The only sequence that could form VLPs in the Tn5 cell line was the 110–660 aa peptide, corresponding to the 112–660 sequence of genotype 1, which produced two proteins, p58 and p53 [96]. Electron microscopy assessment of purified p53 revealed two types of VLPs, with diameters of 24 and 35 nm, respectively (Table 1). The morphology of the particles was similar to that of other HEV VLPs purified previously, and they were apparently empty [96]. The same group also expressed the HEV ORF2 sequence, which was firstly discovered in ferrets in the Netherlands [115]. Alignment showed that amino acids 19–113 in the ferret ORF2 sequence correspond to amino acids 14–112 in genotypes 1–4. Even though VLPs were still generated after the deletion of amino acid 13 or 111 from the N-terminus in genotypes 1–4, deletion of the corresponding sequence in the ferret ORF2 sequence abolished the assembly of VLPs [97]. Only the sequence with truncations at both termini (112N/47C) could [97]. With the discovery of a novel HEV in camels (DcHEV), two of these sequences have been expressed to assess their antigenicity and pathogenicity. The authors determined that expressed 13N truncated proteins could form large VLPs and package RNA after the deletion of an additional 50 amino acids at the C-terminus. The expression of 111N truncated proteins resulted in small VLPs only in one of the sequences. These two proteins had differences in only two amino acids, with one (a methionine residue at position 358) being uncommon compared to other ORF2 sequences, demonstrating that even small changes to the primary sequence can affect VLP formation [98]. Two other sequences isolated from wild boars pertaining to genotypes 5 and 6 have also been expressed. The expression of the 111N ORF2 truncation yielded two proteins, including the 58 and 53 kDa peptides, of which the latter could self-assemble in VLPs with a diameter of 24 nm, similar to that of other HEV VLPs produced in this system [99]. On the other hand, the 13N truncation of both ORF2 sequences yielded proteins with different molecular weights, i.e., 71, 64, 53 and 40 kDa. Only the 64 kDa protein could form VLPs with a diameter of 35 nm resembling the native viral particle. None of the human and animal ORF2 sequences could form VLPs after expression of the whole ORF2 protein; for VLP formation, N-terminal and/or C-terminal truncations were needed for assembly in insect cells. More research is needed to comprehensively determine what sequences are necessary for VLP formation.
3.2.2. HEV VLPs as a Platform for Foreign Epitopes
Since HEV is an enterically transmitted virus and spreads through drinking of contaminated water, it is a good candidate for developing an oral vaccine. The benefits of oral over parenteral immunization include cost reduction, better adherence and easy delivery. Therefore, rHEV VLPs produced in insect cells were tested to determine whether they could be used for oral immunization in mice and cynomolgus monkeys. The results showed that rHEV VLPs are highly immunogenic and trigger the immune response without adjuvant application in both animal models [117,118]. Additionally, HEV VLPs can be used as a platform to present foreign epitopes. Niikura et al. showed that expressing the HEV capsid with a B cell epitope tag at the C-end of the protein does not disrupt VLP formation. Additionally, the chimeric VLPs induced an antibody response to both the tagged and HEV-VLPs [119]. The insertion of an epitope, such as the p18 peptide derived from the V3 loop of HIV-1 gp120, at the antibody-binding site in the P domain still allowed the formation of VLPs, which do not react to anti-HEV antibodies, suggesting that chimeric HEV VLPs could escape pre-existing immunity and constitute a platform for the presentation of foreign epitopes [119]. Furthermore, Shima et al. showed that HEV VLPs might be a vehicle for a multivalent mucosal vaccine by co-expressing capsid proteins with different tags and/or neutralizing epitopes from the Japanese encephalitis virus, allowing the formation of chimeric HEV VLPs that display divalent or trivalent foreign epitopes on its surface [120]. These examples show the extensive opportunities of HEV VLPs for the display of heterologous antigens.
3.3. Expression of ORF2 as VLPs in Plants
Since the first plant-derived recombinant protein, human serum albumin, was produced in transgenic tobacco in 1990 [121], plants have been used to successfully express a variety of other therapeutic proteins, blood components, cytokines, hormones, growth factors, vaccines and antibodies [122]. This resulted in federal approval (US Department of Agriculture Center for Veterinary Biologics) in 2006 of the first plant-made vaccine against Newcastle disease in poultry developed by Dow AgroSciences LLC (Indianapolis, India). Plants offer several advantages compared with other recombinant protein expression systems. These include the presence of eukaryotic post-translational modification machinery, simple and low-cost scale-up for manufacturing, and the inability to transmit human pathogens through the manufacturing medium [123,124]. Another advantage of using plants for the production of biopharmaceuticals is that products expressed in edible plant organs could be administered directly as oral vaccines in the form of unprocessed plant materials [125].
The first study expressing truncated ORF2 in plants was performed in transgenic tomatoes, which could enable the production of an oral vaccine against HEV with easy administration and low-cost production (Table 1). The pE2 region corresponding to residues 394–604 aa was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and ELISA showed that the transgenic plants produced the truncated ORF2 protein, which had normal immunoactivity [74]. Unfortunately, in transgenic tomatoes the truncated ORF2 protein does not accumulate to a high level (48–61 ng/g FW). In an attempt to improve pE2 yield, its sequence was transformed into the plastid genome. Transplastomic plants have been shown to express certain proteins at high levels due to the presence of multiple copies of the plastid genome [126]. Transplastomic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum cv. SR1) plants were obtained by inserting a vector for chloroplast-targeting containing the pE2 peptide (394–607 aa) into the plastid genome using biolistic particle bombardment of leaf pieces. The transformed plants expressed pE2 at higher levels (13.27 μg/g FW) compared with transgenic tomatoes, and the pE2 peptide was antigenic in mice [93]. Maloney et al. engineered a transgenic potato line expressing ORF2 in order to develop an oral vaccine [94]. Two different lengths of the capsid protein, including pHEV101 (111N) and pHEV110 (111N/52C truncation), were used, that had previously been shown to form VLPs in insect cells [73]. Western blot analysis showed that expressing both genes in transgenic potatoes results in proteins with a size of 54 kDa (the correct size of pHEV101 but not for pHEV110) and some lower MW degradation products. It was proposed that since the two truncations produce the same size protein, the 52 C-terminal amino acids in pHEV110 must be removed by the plant itself. Oral immunization of mice with potatoes expressing the capsid protein was unsuccessful in producing detectible antibody response, mostly because the expressed proteins do not assemble into VLPs [94]. Additionally, transient expression of truncated ORF2 (110–610 aa) sequence from swine HEV-3 with the highly efficient vector pEAQ-HT was performed in Nicotiana benthamiana plants for the first time [127,128]. The truncated protein was purified in high amounts of up to 100 mg/kg FWT, and could be used as a diagnostic antigen [95]. Attempts were also made to produce HEV VLPs and chimeric M2-HEV VLPs using varying lengths of ORF2 [129]. The immunogenicity and VLP assembly properties of the transiently expressed ORF2 in plants remain to be determined.
4. Discussion
It is estimated that 20.1 million infections, 70,000 deaths and 3000 stillbirths result from HEV genotype 1 and 2 infections in Africa and Asia [130]. Moreover, the possible zoonotic spread of genotypes 3 and 4 through direct contact with or consumption of contaminated food products additionally raises health concerns over the zoonotic risk of Hepatitis E infection [131,132]. Although HEV is a self-limiting disease in immunocompromised patients, such as transplant patients and HIV-infected individuals, it leads to chronic infection [133]. Acute and chronic HEV infections, compounded with the zoonotic spread of the virus, impose even a greater burden on healthcare systems globally. More than ever, an effective vaccine against HEV is needed.
Since the discovery of HEV, knowledge about the virus, its replication cycle, virion structure and usage for vaccine development or diagnostics has been limited by its inability to grow efficiently in tissue culture. The most current data about HEV biology are based on RNA replicons and transient transfection in cell cultures. Hepatitis E infection, similar to many other infectious diseases, is preventable by vaccination. The difficult HEV propagation has also hindered the cost-effective and extensive production of VLPs as vaccine candidates. The ORF2 is the most widely used protein for HEV vaccine development because it encodes a single capsid protein involved in genome encapsidation, attachment to host cells, and immune response induction [50,51,52].
Due to the lack of propagation systems for the virus, most efforts in developing HEV VLP vaccines have focused on recombinant ORF2 capsid protein production in several expression systems. To date, it has been demonstrated that the protein most effectively self-assembles into VLPs in the baculovirus-insect cell system [73]. However, the disparate results upon the expression of different genotype sequences in two different insect cell lines compounded with varying lengths of the capsid protein forming VLPs indicates that more research is needed to determine the factors affecting assembly. Interestingly, with the development of an HEV strain that can replicate in cell culture, we are closer to understanding the role of ORF2 in HEV infection and pathogenesis. Recent studies have shown that, during infection, multiple forms of the ORF2 protein are produced, explaining previously reported results [58,59]. That most of the produced and secreted ORF2 is not associated with the virion could potentially explain the lack of VLPs upon expression of the whole protein in insect cells. The presence of the capsid protein in the serum of infected patients reveals a new role for ORF2 in HEV infection [58]. It was reported that the sequence of ORF2 involved in the virion formation starts from the second internal codon 14 aa from the starting codon [58]. This could potentially explain why only the truncated ORF2 could form VLPs upon expression in insect cell lines. Another group expressing ORF2 from genotype 4 reported three different ORF2 sequences, of which only one is involved in virion formation [59]. Whether these differences are based on the different cell lines used or distinct genotypes deserves further investigation. In addition, HEV replication and infection in humans and animals is not completely defined.
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Overall, HEV infection remains a global challenge, with Africa and Asia greatly affected. In addition, the virus can spread to humans from animals. An increasing number of HEV sequences have been detected in various animal species, some of which have been confirmed as natural reservoirs for HEV and sources of zoonotic infection. This raises concerns about the potential risk of cross-species infection and zoonotic transmission. Even though HEV infection is mostly asymptomatic, immunocompromised individuals have a considerable risk of developing chronic infection. Therefore, there is an urgent need for HEV vaccines for global use, especially in outbreak regions and high-risk groups. Currently, studies developing HEV VLP vaccines have mostly focused on producing recombinant ORF2 capsid protein in various expression systems. To date, the protein is known to most effectively self-assemble into VLPs in the baculovirus-insect cell system and E. coli. However, the sole VLP-based vaccine Hecolin® for HEV prevention is only licensed in China, showing 100% efficacy. Additional studies are under way to assess the safety and efficacy of HEV239 in high-risk groups for potential global distribution, as recommended by the WHO, However, this vaccine is derived from a single genotype; with newly identified HEV isolates from animal species that infect humans, it remains unknown whether it could provide immunity against other genotypes. Therefore, further investigation is needed to address its potential pitfalls and/or to design efficient chimeric VLPs with broad-cross protection.
Author Contributions
The manuscript has been written and revised by M.M. and J.C.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank G.P Lomonossoff for critical review of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kamar, N.; Bendall, R.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Xia, N.-S.; Ijaz, S.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E. Lancet 2012, 379, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holla, R.P.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, Z.; Jameel, S. Molecular virology of hepatitis E virus. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.-J. From barnyard to food table: The omnipresence of hepatitis E virus and risk for zoonotic infection and food safety. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Subhadra, S.; Singh, B.; Panda, B. Hepatitis E virus: The current scenario. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e228–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Thakral, D.; Rehman, S. Hepatitis E virus. Rev. Med Virol. 2007, 17, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Teli, M.R.; Skidmore, S.; Sofi, M.A.; Khuroo, M.I. Incidence and severity of viral hepatitis in pregnancy. Am. J. Med. 1981, 70, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.; Kamili, S. Aetiology, clinical course and outcome of sporadic acute viral hepatitis in pregnancy. J. Viral Hepat. 2003, 10, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, N.; Das, B.C.; Husain, S.A.; Baweja, U.K.; Chattopadhya, D.; Gupta, R.K.; Sardana, S.; Kar, P. Hepatitis E virus infection and fulminant hepatic failure during pregnancy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, M.; Bazille, C.; Selves, J.; Salamé, E.; Altieri, M. Hepatitis E virus infection mimicking acute graft rejection in a liver transplant recipient. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, e68–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, P.; Steinmann, E.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. The impact of hepatitis E in the liver transplant setting. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, O.; Kamar, N. Hepatitis E Infections in Transplants. Emerg. Transpl. Infect. Clin. Chall. Implic. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.; Peron, J.-M.; von Wulffen, M.; von Felden, J.; Höner zu Siederdissen, C.; Fournier, S.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Iking-Konert, C.; Bettinger, D.; Thimme, R. Chronic hepatitis e in rheumatology and internal medicine patients: A retrospective multicenter european cohort study. Viruses 2019, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavitian, S.; Peron, J.-M.; Huguet, F.; Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Beyne-Rauzy, O.; Oberic, L.; Faguer, S.; Alric, L.; Roussel, M. Ribavirin for chronic hepatitis prevention among patients with hematologic malignancies. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Juarez, A.; Lopez-Lopez, P.; Frias, M.; Rivero, A. Hepatitis E infection in HIV-infected patients. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Sarin, S.K. Hepatitis E virus as an etiology of acute exacerbation of previously unrecognized asymptomatic patients with hepatitis B virus-related chronic liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérolami, R.; Moal, V.; Colson, P. Chronic hepatitis E with cirrhosis in a kidney-transplant recipient. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 859–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, B.N.; Gulliver, J.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E virus and neurological disorders. Pract. Neurol. 2017, 17, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abravanel, F.; Pique, J.; Couturier, E.; Nicot, F.; Dimeglio, C.; Lhomme, S.; Chiabrando, J.; Saune, K.; Péron, J.-M.; Kamar, N. Acute hepatitis E in French patients and neurological manifestations. J. Infect. 2018, 77, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Weclawiak, H.; Guilbeau-Frugier, C.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Cointault, O.; Ribes, D.; Esposito, L.; Cardeau-Desangles, I.; Guitard, J.; Sallusto, F. Hepatitis E virus and the kidney in solid-organ transplant patients. Transplantation 2012, 93, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaf, R.K.; O‘Brien, K.L.; Leaf, D.E.; Drews, R.E. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a young man with acute hepatitis E infection. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E77–E79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewicz, J.; Flisiak, R.; Kalinowska, A.; Wierzbicka, I.; Prokopowicz, D. Acute hepatitis E complicated by acute pancreatitis: A case report and literature review. Pancreas 2005, 30, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsama, M.A.; Atangana, P.J.A.; Noah, D.N.; Moundipa, P.F.; Pineau, P.; Njouom, R. Hepatitis E virus infection as a promoting factor for hepatocellular carcinoma in Cameroon: Preliminary observations. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Chang, C.T.; Su, T.-H.; Yang, W.-T.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Yang, H.-C.; Liu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-J. HEV superinfection accelerates disease progression in patients with chronic HBV infection and increases mortality in those with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.; Faulk, K.; Mather, K.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.; Emerson, S. Adaptation of a genotype 3 hepatitis E virus to efficient growth in cell culture depended on an inserted human gene segment acquired by recombination. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, D.; Glamann, J.; Emerson, S.; Purcell, R. Identification by phage display and characterization of two neutralizing chimpanzee monoclonal antibodies to the hepatitis E virus capsid protein. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5548–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldão, A.; Mellado, M.C.M.; Castilho, L.R.; Carrondo, M.J.; Alves, P.M. Virus-like particles in vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1149–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noad, R.; Roy, P. Virus-like particles as immunogens. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgacic, E.V.; Anderson, D.A. Virus-like particles: Passport to immune recognition. Methods 2006, 40, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.G.; Erickson, J.J.; Hastings, A.K.; Becker, J.C.; Johnson, M.; Craven, R.E.; Tollefson, S.J.; Boyd, K.L.; Williams, J.V. Human metapneumovirus virus-like particles induce protective B and T cell responses in a mouse model. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6368–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rts, S.; Agnandji, S.T.; Lell, B.; Fernandes, J.F.; Abossolo, B.P.; Methogo, B.; Kabwende, A.L.; Adegnika, A.A.; Mordmueller, B.; Issifou, S. A phase 3 trial of RTS, S/AS01 malaria vaccine in African infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2284–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Scotti, N.; Rybicki, E.P. Virus-like particles produced in plants as potential vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.; Edwards, D.C.; Brand, C.; Heath, T. Formation of virosomes from influenza subunits and liposomes. Lancet 1975, 306, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, G.M.; Noble, S. Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine (Engerix-B®). Drugs 2003, 63, 1021–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monie, A.; Hung, C.-F.; Roden, R.; Wu, T.C. Cervarix™: A vaccine for the prevention of HPV 16, 18-associated cervical cancer. Biol. Targets Ther. 2008, 2, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Venters, C.; Graham, W.; Cassidy, W. Recombivax-HB: Perspectives past, present and future. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Sings, H.; Bryan, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Mach, H.; Kosinski, M.; Washabaugh, M.; Sitrin, R.; Barr, E. GARDASIL®: Prophylactic human papillomavirus vaccine development–from bench top to bed-side. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 81, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevar, C.J.; Ross, T.M. Elicitation of protective immune responses using a bivalent H5N1 VLP vaccine. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treanor, J.J.; Atmar, R.L.; Frey, S.E.; Gormley, R.; Chen, W.H.; Ferreira, J.; Goodwin, R.; Borkowski, A.; Clemens, R.; Mendelman, P.M. A novel intramuscular bivalent norovirus virus-like particle vaccine candidate—Reactogenicity, safety, and immunogenicity in a phase 1 trial in healthy adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.-J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.; Purdy, M.A.; Members of the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses Hepeviridae Study Group. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai, S.; Kawakami, M.; Sonoda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Shigemoto, K.; Ashida, K. Molecular characterization of a novel hepatitis E virus (HEV) strain obtained from a wild boar in Japan that is highly divergent from the previously recognized HEV strains. Virus Res. 2014, 180, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.; Lau, S.; Teng, J.; Tsang, A.; Joseph, M.; Wong, E.; Tang, Y.; Sivakumar, S.; Xie, J.; Bai, R. New hepatitis E virus genotype in camels, the Middle East. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, G.R.; Purdy, M.A.; Kim, J.P.; Ka-Cheung, L.; Young, L.M. Isolation of a cDNA from the virus responsible for enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science 1990, 247, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.W.; Smith, M.M.; Guerra, M.E.; Huang, C.-C.; Bradley, D.W.; Fry, K.E.; Reyes, G.R. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): Molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 1991, 185, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Holla, R.P.; Jameel, S. Molecular virology of hepatitis E virus. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Meng, X.-J. Molecular biology and replication of hepatitis E virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2012, 1, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, H.; Fan, S.; Patel, D.; Bossis, I.; Zhang, Y.-J. The hepatitis E virus open reading frame 3 product interacts with microtubules and interferes with their dynamics. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6375–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, S.; Zafrullah, M.; Ozdener, M.H.; Panda, S.K. Expression in animal cells and characterization of the hepatitis E virus structural proteins. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Miao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, T.; Xie, M.; Tang, M.; Zhang, J.; Ng, M.-H.; Xia, N. Putative receptor-binding sites of hepatitis E virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Chandra, V.; Rahman, S.A.; Sehgal, D.; Jameel, S. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are required for cellular binding of the hepatitis E virus ORF2 capsid protein and for viral infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12714–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wang, J.C.; Li, T.-C.; Yasutomi, Y.; Lara, J.; Khudyakov, Y.; Schofield, D.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H.; Takeda, N. Spatial configuration of hepatitis E virus antigenic domain. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torresi, J.; Li, F.; Locarnini, S.A.; Anderson, D.A. Only the non-glycosylated fraction of hepatitis E virus capsid (open reading frame 2) protein is stable in mammalian cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Kato, K.; Li, T.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T.; Hammar, L.; Cheng, R.H. Recombinant hepatitis E capsid protein self-assembles into a dual-domain T= 1 particle presenting native virus epitopes. Virology 1999, 265, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guu, T.S.; Liu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Mata, D.A.; Li, K.; Yin, C.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.J. Structure of the hepatitis E virus-like particle suggests mechanisms for virus assembly and receptor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12992–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Li, T.-C.; Mayazaki, N.; Simon, M.N.; Wall, J.S.; Moore, M.; Wang, C.-Y.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T.; Miyamura, T. Structure of hepatitis E virion-sized particle reveals an RNA-dependent viral assembly pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33175–33183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Harrison, T.J.; Huang, W.; Zhao, C.; Kong, W.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y. Hepatitis E virus produced from cell culture has a lipid envelope. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Z. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of ORF2 in hepatitis E virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.-C.; Saliou, J.-M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F. Hepatitis E virus lifecycle and identification of 3 forms of the ORF2 capsid protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.M.; Decker, C.C.; Dao Thi, V.L. Cell culture models for hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogee, S.; Talbot, N.; Caperna, T.; Bouquet, J.M.; Barnaud, E.; Pavio, N. New models of hepatitis E virus replication in human and porcine hepatocyte cell lines. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, N.; Marion, O.; Dubois, M.; Allart, S.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Chapuy-Regaud, S. Vectorial release of hepatitis E virus in polarized human hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelli, N.; Dubois, M.; Pucelle, M.; Da Silva, I.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Izopet, J. Optimized hepatitis E virus (HEV) culture and its application to measurements of HEV infectivity. Viruses 2020, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, V.L.D.; Wu, X.; Belote, R.L.; Andreo, U.; Takacs, C.N.; Fernandez, J.P.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Prallet, S.; Decker, C.C.; Fu, R.M. Stem cell-derived polarized hepatocytes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kamar, N.; Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis E virus. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Dai, X.; Chang, J.C.; Lopareva, E.; Pillot, J.; Fields, H.A.; Khudyakov, Y.E. Identification and characterization of the neutralization epitope (s) of the hepatitis E virus. Virology 2001, 288, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Mori, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Cheng, R.H.; Yoshimura, M.; Unno, H.; Shima, R.; Moriishi, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Li, T.C. Biological and immunological characteristics of hepatitis E virus-like particles based on the crystal structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12986–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. An ELISA for putative neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis E virus detects antibodies to genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4. Vaccine 2004, 22, 2578–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhuang, H.; Kolivas, S.; Locarnini, S.A.; Anderson, D.A. Persistent and transient antibody responses to hepatitis E virus detected by western immunoblot using open reading frame 2 and 3 and glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2060–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-W.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.-S. The development of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine HEV 239. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.P.; Scott, R.M.; Joshi, D.M.; Mammen, M.P., Jr.; Thapa, G.B.; Thapa, N.; Myint, K.S.A.; Fourneau, M.; Kuschner, R.A.; Shrestha, S.K. Safety and efficacy of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Ng, M.H.; Xia, N.; Lau, S.; Che, X.; Chau, T.; Lai, S.; Im, S.W. Conformational antigenic determinants generated by interactions between a bacterially expressed recombinant peptide of the hepatitis E virus structural protein. J. Med. Virol. 2001, 64, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-C.; Yamakawa, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tatsumi, M.; Razak, M.; Uchida, T.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T. Expression and self-assembly of empty virus-like particles of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7207–7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, S.-Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Luo, W.-X.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.-S. Expression of ORF2 partial gene of hepatitis E virus in tomatoes and immunoactivity of expression products. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 2211–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.M.; Ou, S.H.; Huang, G.Y.; He, Z.Q.; Sheng, X.G.; Xian, Y.L.; Pang, S.Q.; Ng, M.H. A bacterially expressed particulate hepatitis E vaccine: Antigenicity, immunogenicity and protectivity on primates. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2893–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.-C.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Engvall, H.; Hammar, L.; Xing, L.; Cheng, R.H. Essential elements of the capsid protein for self-assembly into empty virus-like particles of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12999–13006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tang, X.; Seetharaman, J.; Yang, C.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, H.; Shih, J.W.K.; Hew, C.-L.; Sivaraman, J. Dimerization of hepatitis E virus capsid protein E2s domain is essential for virus–host interaction. PLoS Pathog 2009, 5, e1000537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.W.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhuang, H.; Che, X.Y.; Zhu, W.F.; Xu, G.M.; Li, K.; Xia, N.S.; Ng, M.H. A bacterially expressed peptide prevents experimental infection of primates by the hepatitis E virus. Vaccine 2001, 19, 3726–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Sheng, X.G.; Li, S.W.; He, Z.Q.; Huang, G.Y.; Zhuang, H.; Ng, M.H.; Xia, N.S. Analysis of hepatitis E virus neutralization sites using monoclonal antibodies directed against a virus capsid protein. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, M.; Pan, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, K.; Weng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xin, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, S. Robust manufacturing and comprehensive characterization of recombinant hepatitis E virus-like particles in Hecolin®. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4039–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wu, X.-L.; Ou, S.-H.; Lin, C.-X.; Cheng, T.; Li, S.-W.; Ng, M.H.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N.-S. Difference of T cell and B cell activation in two homologous proteins with similar antigenicity but great distinct immunogenicity. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3261–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, M.P.; Fausch, S.C.; Da Silva, D.M.; Kast, W.M. Human dendritic cells are activated by chimeric human papillomavirus type-16 virus-like particles and induce epitope-specific human T cell responses in vitro. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5917–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.-B.; Li, R.-C.; Li, Y.-M.; Zheng, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-P.; Luo, D.; Pan, B.-B.; Nong, Y.; Ge, S.-X. Randomized-controlled phase II clinical trial of a bacterially expressed recombinant hepatitis E vaccine. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1869–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.-C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Huang, S.-J.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.-L.; Jiang, H.-M.; Cai, J.-P. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine in healthy adults: A large-scale, randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B. Hepatitis E vaccine debuts: Success of Chinese biotech partnership raises hopes for prevention of overlooked diseases. Nature 2012, 491, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Huang, S.-J.; Wu, T.; Hu, Y.-M.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.-M.; Wang, Y.-J.; Yan, Q. Long-term efficacy of a hepatitis E vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-Y.; Chen, Z.-P.; Wang, S.-Y.; Pan, H.-R.; Wang, Z.-F.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Shen, L.-Z.; Zheng, X.-P.; Yan, C.-F.; Lu, M. Safety and immunogenicity of hepatitis E vaccine in elderly people older than 65 years. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4581–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Huang, S.-J.; Zhu, F.-C.; Zhang, X.-F.; Ai, X.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Yang, C.-L.; Jiang, H.-M.; Liu, X.-H. Immunogenicity and safety of hepatitis E vaccine in healthy hepatitis B surface antigen positive adults. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 2474–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, K.; Dudman, S.; Stene-Johansen, K.; Qadri, F.; Yunus, M.; Sandbu, S.; Gurley, E.S.; Overbo, J.; Julin, C.H.; Dembinski, J.L. HEV study protocol: Design of a cluster-randomised, blinded trial to assess the safety, immunogenicity and effectiveness of the hepatitis E vaccine HEV 239 (Hecolin) in women of childbearing age in rural Bangladesh. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-F.; Tao, H.; Hu, Y.-M.; Shi, C.-B.; Wu, X.; Liang, Q.; Chi, C.-P.; Li, L.; Liang, Z.-L.; Meng, J.-H. A phase 1 randomized open-label clinical study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of a novel recombinant hepatitis E vaccine. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5073–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Behloul, N.; Dai, X.; Dong, C.; Liang, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, C.; Meng, J. Immunogenicity difference between two hepatitis E vaccines derived from genotype 1 and 4. Antivir. Res. 2016, 128, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Li, T.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H. Characterization of capsid protein (p495) of hepatitis E virus expressed in Escherichia coli and assembling into particles in vitro. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-X.; Lee, M.Y.-T.; Ng, J.M.-H.; Chye, M.-L.; Yip, W.-K.; Zee, S.-Y.; Lam, E. A truncated hepatitis E virus ORF2 protein expressed in tobacco plastids is immunogenic in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2006, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maloney, B.J.; Takeda, N.; Suzaki, Y.; Ami, Y.; Li, T.C.; Miyamura, T.; Arntzen, C.J.; Mason, H.S. Challenges in creating a vaccine to prevent hepatitis E. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazalovska, M.; Varadinov, N.; Koynarski, T.; Minkov, I.; Teoharov, P.; Lomonossoff, G.P.; Zahmanova, G. Detection of serum antibodies to hepatitis E virus based on HEV genotype 3 ORF2 capsid protein expressed in nicotiana benthamiana. Ann. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, T.-C.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Yasuda, S.P.; Arikawa, J.; Koma, T.; Kataoka, M.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Hoa, N.T.; Yamashiro, T. Characterization of self-assembled virus-like particles of rat hepatitis E virus generated by recombinant baculoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2830–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Kataoka, M.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Kishida, N.; Shirakura, M.; Imai, M.; Asanuma, H.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Characterization of self-assembled virus-like particles of ferret hepatitis E virus generated by recombinant baculoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Kataoka, M.; Liu, Z.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T.; Li, T.-C. Characterization of self-assembled virus-like particles of dromedary camel hepatitis e virus generated by recombinant baculoviruses. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-C.; Kataoka, M.; Takahashi, K.; Yoshizaki, S.; Kato, T.; Ishii, K.; Takeda, N.; Mishiro, S.; Wakita, T. Generation of hepatitis E virus-like particles of two new genotypes G5 and G6 and comparison of antigenic properties with those of known genotypes. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kost, T.A.; Condreay, J.P. Recombinant baculoviruses as expression vectors for insect and mammalian cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, I.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Richmond, T.J. Baculovirus expression system for heterologous multiprotein complexes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oers, M.M.; Vlak, J.M. Baculovirus expression system. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, T.; Roldão, A.; Peixoto, C.; Carrondo, M.J.; Alves, P.M. Large-scale production and purification of VLP-based vaccines. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 107, S42–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.M.; Franco, E.L.; Wheeler, C.; Ferris, D.G.; Jenkins, D.; Schuind, A.; Zahaf, T.; Innis, B.; Naud, P.; De Carvalho, N.S. Efficacy of a bivalent L1 virus-like particle vaccine in prevention of infection with human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 in young women: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 364, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.M.; Franco, E.L.; Wheeler, C.M.; Moscicki, A.-B.; Romanowski, B.; Roteli-Martins, C.M.; Jenkins, D.; Schuind, A.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Dubin, G. Sustained efficacy up to 4.5 years of a bivalent L1 virus-like particle vaccine against human papillomavirus types 16 and 18: Follow-up from a randomised control trial. Lancet 2006, 367, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Macías, C.; Ferat-Osorio, E.; Tenorio-Calvo, A.; Isibasi, A.; Talavera, J.; Arteaga-Ruiz, O.; Arriaga-Pizano, L.; Hickman, S.P.; Allende, M.; Lenhard, K. Safety and immunogenicity of a virus-like particle pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 vaccine in a blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of adults in Mexico. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7826–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacket, C.O.; Sztein, M.B.; Losonsky, G.A.; Wasserman, S.S.; Estes, M.K. Humoral, mucosal, and cellular immune responses to oral Norwalk virus-like particles in volunteers. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 108, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Diego, A.C.P.; Athmaram, T.N.; Stewart, M.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, B.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Noad, R.; Roy, P. Characterization of protection afforded by a bivalent virus-like particle vaccine against bluetongue virus serotypes 1 and 4 in sheep. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26666. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, S.W.; Gardner, J.; Geertsema, C.; Le, T.T.; Goh, L.; Vlak, J.M.; Suhrbier, A.; Pijlman, G.P. Effective chikungunya virus-like particle vaccine produced in insect cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Burgess, W.H.; Emerson, S.U.; Leibowitz, R.S.; Sosnovtseva, S.A.; Tsarev, S.; Purcell, R.H. Structural characterization of recombinant hepatitis E virus ORF2 proteins in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 1998, 12, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarev, S.A.; Tsareva, T.S.; Emerson, S.U.; Yarbough, P.O.; Legters, L.J.; Moskal, T.; Purcell, R.H. Infectivity titration of a prototype strain of hepatitis E virus in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Med. Virol. 1994, 43, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarev, S.A.; Tsareva, T.S.; Emerson, S.U.; Govindarajan, S.; Shapiro, M.; Gerin, J.L.; Purcell, R.H. Recombinant vaccine against hepatitis E: Dose response and protection against heterologous challenge. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1834–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B. Hepatitis E vaccine debuts. Nature 2012, 491, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.; Singh, P.; Ochoa, W.; Manayani, D.J.; Manchester, M.; Schneemann, A.; Reddy, V.S. Characterization of polymorphism displayed by the coat protein mutants of tomato bushy stunt virus. Virology 2006, 349, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Raj, V.S.; Smits, S.L.; Pas, S.D.; Provacia, L.; Moorman-Roest, H.; Osterhaus, A.; Haagmans, B.L. Novel hepatitis E virus in ferrets, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1369–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johne, R.; Heckel, G.; Plenge-Bonig, A.; Kindler, E.; Maresch, C.; Reetz, J.; Schielke, A.; Ulrich, R.G. Novel hepatitis E virus genotype in Norway rats, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-C.; Takeda, N.; Miyamura, T. Oral administration of hepatitis E virus-like particles induces a systemic and mucosal immune response in mice. Vaccine 2001, 19, 3476–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-C.; Suzaki, Y.; Ami, Y.; Dhole, T.N.; Miyamura, T.; Takeda, N. Protection of cynomolgus monkeys against HEV infection by oral administration of recombinant hepatitis E virus-like particles. Vaccine 2004, 22, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niikura, M.; Takamura, S.; Kim, G.; Kawai, S.; Saijo, M.; Morikawa, S.; Kurane, I.; Li, T.-C.; Takeda, N.; Yasutomi, Y. Chimeric recombinant hepatitis E virus-like particles as an oral vaccine vehicle presenting foreign epitopes. Virology 2002, 293, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, R.; Li, T.C.; Sendai, Y.; Kataoka, C.; Mori, Y.; Abe, T.; Takeda, N.; Okamoto, T.; Matsuura, Y. Production of hepatitis E virus-like particles presenting multiple foreign epitopes by co-infection of recombinant baculoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijmons, P.C.; Dekker, B.M.; Schrammeijer, B.; Verwoerd, T.C.; Van Den Elzen, P.J.; Hoekema, A. Production of correctly processed human serum albumin in transgenic plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 1990, 8, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twyman, R.M.; Schillberg, S.; Fischer, R. Transgenic plants in the biopharmaceutical market. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2005, 10, 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, E.P. Plant-produced vaccines: Promise and reality. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, M.K. Plants as bioreactors: Recent developments and emerging opportunities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 811–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, F.; Rigano, M.M.; Barbante, A.; Basso, B.; Walmsley, A.M.; Castiglione, S. Vaccine antigen production in transgenic plants: Strategies, gene constructs and perspectives. Vaccine 2003, 21, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, J.M.; Garcia, B.; Graves, J.; Hajdukiewicz, P.T.; Hunter, P.; Nehra, N.; Paradkar, V.; Schlittler, M.; Carroll, J.A.; Spatola, L. High-yield production of a human therapeutic protein in tobacco chloroplasts. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainsbury, F.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Extremely high-level and rapid transient protein production in plants without the use of viral replication. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainsbury, F.; Thuenemann, E.C.; Lomonossoff, G.P. pEAQ: Versatile expression vectors for easy and quick transient expression of heterologous proteins in plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2009, 7, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahmanova, G.G.; Mazalovska, M.; Takova, K.H.; Toneva, V.T.; Minkov, I.N.; Mardanova, E.S.; Ravin, N.V.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Rapid high-yield transient expression of swine hepatitis E ORF2 capsid proteins in nicotiana benthamiana plants and production of chimeric hepatitis E virus-like particles bearing the M2e influenza epitope. Plants 2020, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.B.; Stevens, G.A.; Theaker, J.; Wittenborn, J.S.; Wiersma, S.T. The global burden of hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 2 in 2005. Hepatology 2012, 55, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-J. Zoonotic and foodborne transmission of hepatitis E virus. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yazaki, Y.; Mizuo, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Sasaki, N.; Gotanda, Y.; Okamoto, H. Sporadic acute or fulminant hepatitis E in Hokkaido, Japan, may be food-borne, as suggested by the presence of hepatitis E virus in pig liver as food. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Mansuy, J.M.; Cointault, O.; Selves, J.; Abravanel, F.; Danjoux, M.; Otal, P.; Esposito, L.; Durand, D.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E virus-related cirrhosis in kidney-and kidney–pancreas-transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).