HHV-6 Infection and Chemokine RANTES Signaling Pathway Disturbance in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Groups
2.2. Nucleic Acid Isolation, Complementary DNA (cDNA) Synthesis and Quality Determination
2.3. Detection of HHV-6 Genomic Sequences and Gene Expression Using Nested PCR (nPCR)
2.4. HHV-6 Load Determination Using Quantitative PCR
2.5. Determination of RANTES (CCL5) Level in Peripheral Blood Plasma by ELISA
2.6. Determination of IFNγ, IL-6, TNFα and RANTES (CCL5) Levels in Peripheral Blood Plasma by Suspension Multiplex Immuno Assay (SMIA)
2.7. Immunofluorescence Labelling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Thyroid Tissues
3. Results
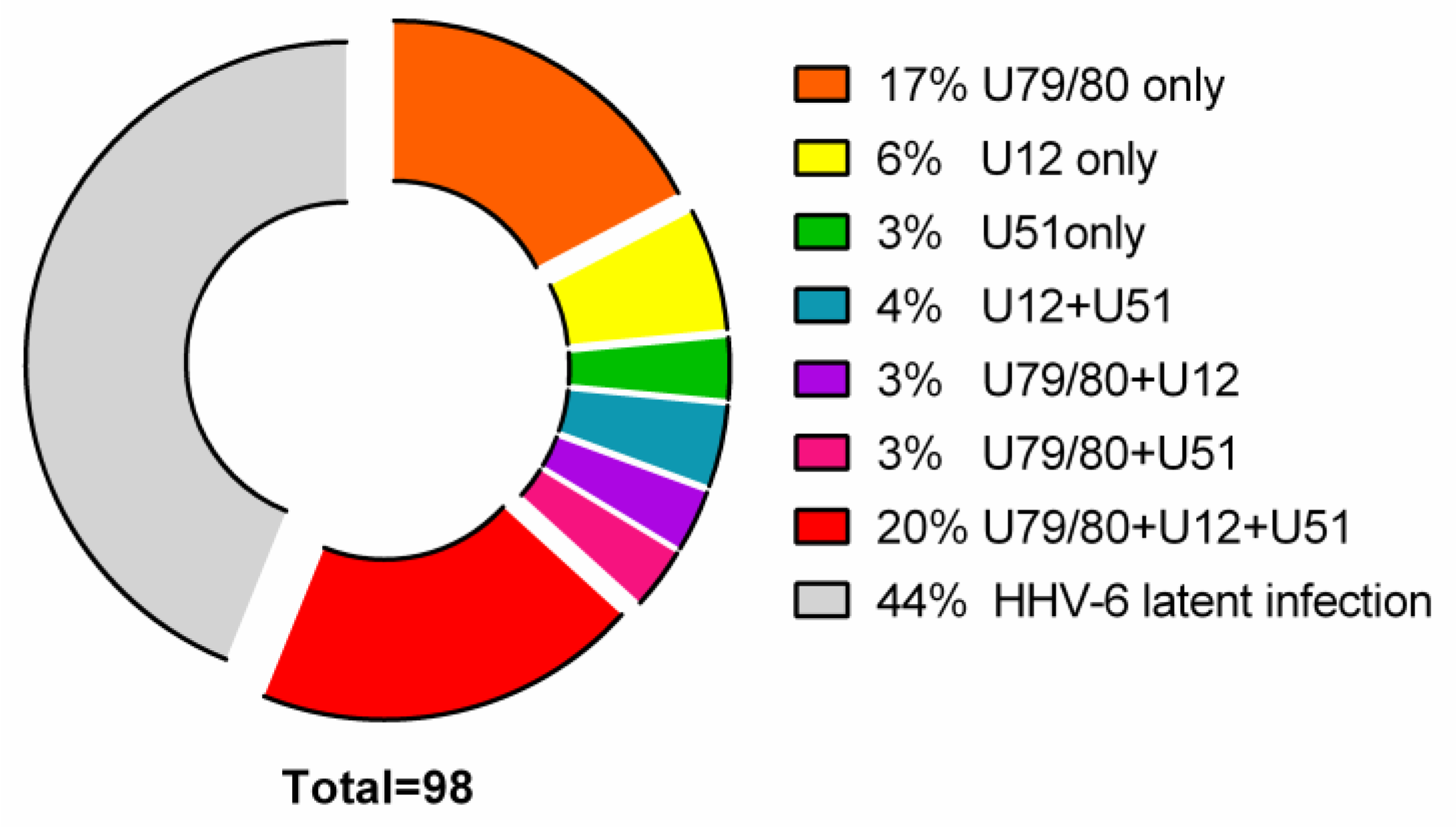
3.1. Detection of HHV-6 Virus Genomic Sequence and Its mRNAs in AIT Patients and Control Group Autopsy Specimens
- 17/98 (17%) AIT patients’ thyroid tissue samples and 8/16 (50%) PBMC samples were positive for HHV-6 U79/80 mRNA.
- 6/98 (6%) AIT patients’ thyroid tissue samples were positive for HHV-6 U12 mRNA, while none of the PBMC samples were HHV-6 U12 mRNA-positive and 3/98 (3%) thyroid tissue samples of AIT patients and 4/16 (25%) PBMC samples were positive for HHV-6 U51 mRNA.
- U79/80 + U12 mRNA was found in 3/98 (3%) AIT patients’ thyroid tissue samples, while none of the PBMC samples were HHV-6 U79/80 + U12 mRNA-positive; U79/80 + U51 mRNAs were present in 3/98 (3%) AIT patients’ thyroid tissue samples and in none of the PBMC samples.
- U79/80 + U12 + U51 mRNAs were present in 19/98 (20%) AIT patients’ thyroid tissue samples and in none of the PBMC samples.
- U12 + U51 mRNAs were found only in 4/98 (4%) AIT patients’ thyroid tissue samples.
- The presence of HHV-6 U79/80 mRNA was only detected in 1/17 autopsy samples (data from previous study [5]), and no HHV-6 U12 or U51 mRNAs were found in this study.
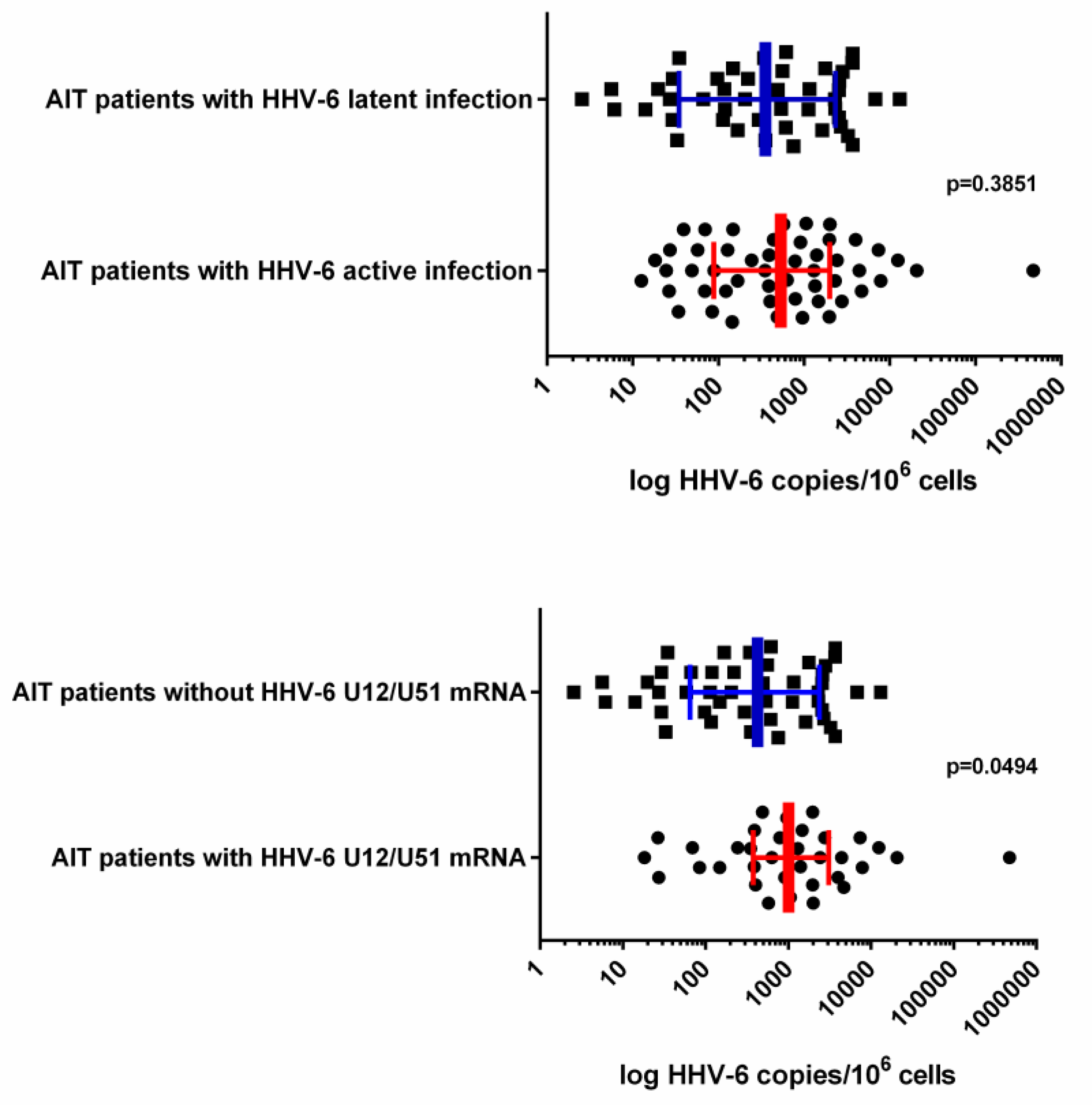
3.2. HHV-6 Load in Thyroid Tissue Samples
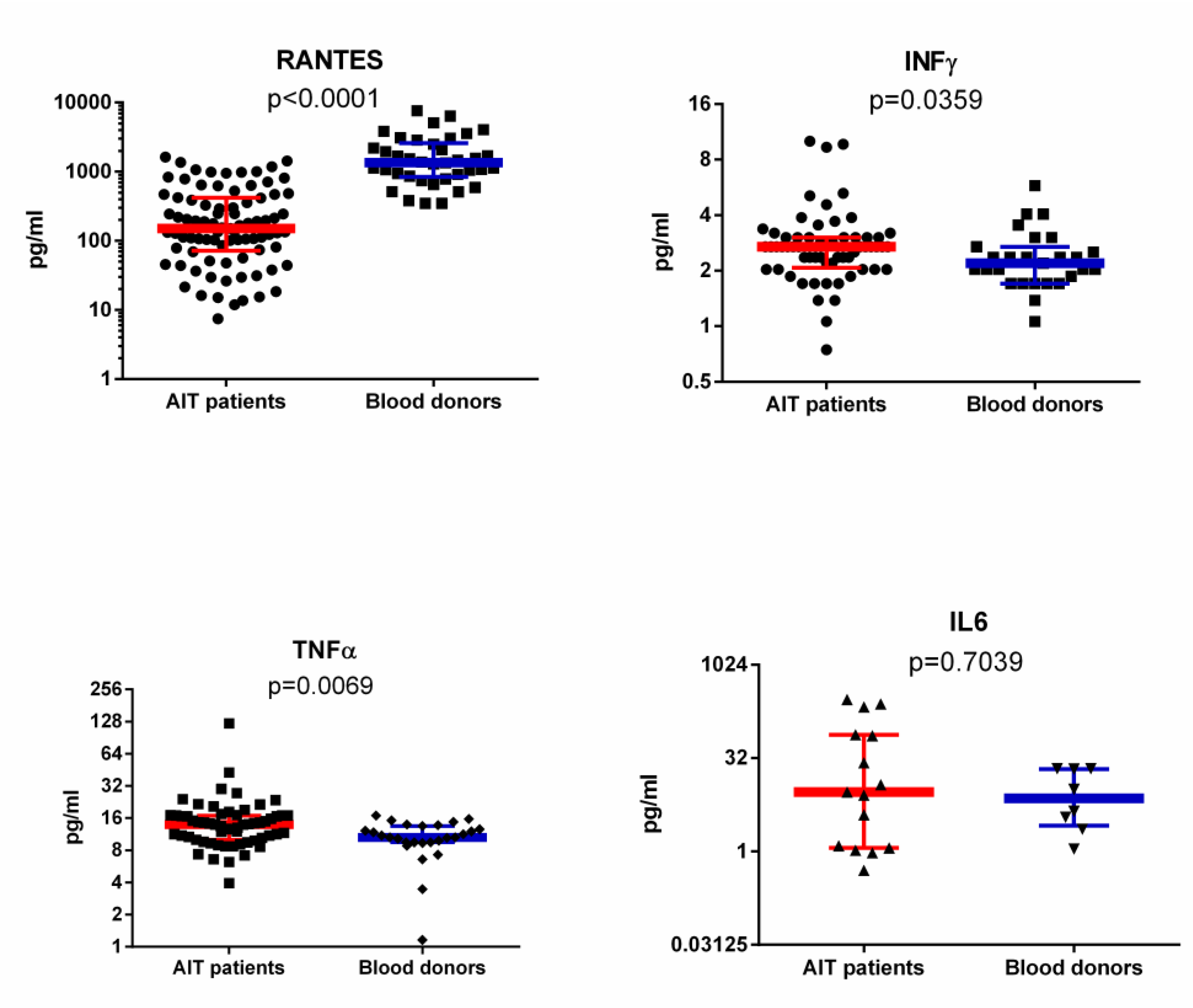
3.3. RANTES Level in Plasma of AIT Patient and Blood Donor Groups Detected with ELISA and SMIA
3.4. IFNγ, IL-6 and TNFα Levels in Plasma of AIT Patient and Blood Donor Groups
3.5. Detection of HHV-6 Antigen and RANTES by Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lerner, A.; Jeremias, P.; Matthias, T. The world incidence and prevalence of autoimmune diseases is increasing. Int. J. Celiac Dis. 2015, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennell, L.M.; Galligan, C.L.; Fish, E.N. Sex affects immunity. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 38, J282–J291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hudnall, S.D. Anatomical mapping of human herpesvirus reservoirs of infection. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, E.; Zatelli, M.C.; Rizzo, R.; Benedetti, S.; Martorelli, D.; Trasforini, G.; Cassai, E.; degli Uberti, E.C.; di Luca, D.; Dolcetti, R. Virologic and immunologic evidence supporting an association between HHV-6 and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultanova, A.; Cistjakovs, M.; Gravelsina, S.; Chapenko, S.; Roga, S.; Cunskis, E.; Nora-Krukle, Z.; Groma, V.; Ventina, I.; Murovska, M. Association of active human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) infection with autoimmune thyroid gland diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 50.e1–50.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasirwan, C.; Furusawa, Y.; Tang, H.; Maeki, T.; Mori, Y. Human herpesvirus-6A gQ1 and gQ2 are critical for human CD46 usage. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagasaki, H.; Kato, M.; Shimizu, N.; Shichino, H.; Chin, M.; Mugishima, H. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia and autoimmune neutropenia in a child with erythroblastopenia of childhood (TEC) caused by human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6). Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, P.; Chiavaroli, R.; Calabrese, P.; Tundo, P.; Grima, P. Severe hepatitis with autoimmune features following a HHV-6: A case report. Cases J. 2008, 1, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapenko, S.; Millers, A.; Nora, Z.; Logina, I.; Kukaine, R.; Murovska, M. Correlation between HHV-6 reactivation and multiple sclerosis disease activity. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nora-Krukle, Z.; Chapenko, S.; Logina, I.; Millers, A.; Platkajis, A.; Murovska, M. Human herpesvirus 6 and 7 reactivation and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Med. Kaunas Lith. 2011, 47, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Simon, M.V.; Zang, Y.C.Q.; Hong, J.; Rivera, V.M.; Zhang, J.Z. Cross-reactivity with myelin basic protein and human herpesvirus-6 in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontiers|Modulation of Cellular Signaling by Herpesvirus-Encoded G Protein-Coupled Receptors|Pharmacology. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2015.00040/full (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Pontejo, S.M.; Murphy, P.M.; Pease, J.E. Chemokine Subversion by Human Herpesviruses. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isegawa, Y.; Ping, Z.; Nakano, K.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamanishi, K. Human herpesvirus 6 open reading frame U12 encodes a functional beta-chemokine receptor. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6104–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menotti, L.; Mirandola, P.; Locati, M.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. Trafficking to the plasma membrane of the seven-transmembrane protein encoded by human herpesvirus 6 U51 gene involves a cell-specific function present in T lymphocytes. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Kondo, T.; Shimada, K.; Amo, K.; Miyagawa, H.; Yamanishi, K. Strong interaction between human herpesvirus 6 and peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages during acute infection. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 67, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Bradel-Tretheway, B.; Sumagin, S.; Bidlack, J.M.; Dewhurst, S. The human herpesvirus 6 G protein-coupled receptor homolog U51 positively regulates virus replication and enhances cell-cell fusion in vitro. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11914–11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, R.S.B.; Mattick, C.; Nicholson, L.; Devaraj, P.; Alcami, A.; Gompels, U.A. RANTES binding and down-regulation by a novel human herpesvirus-6 β chemokine receptor. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appay, V.; Rowland-Jones, S.L. RANTES: A versatile and controversial chemokine. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, A.M.; Fransen, K.; Debaisieux, L.; Marissens, D.; Sprecher, S.; Vaira, D.; Vandenbroucke, A.T.; Verhofstede, C. Standardisation of primers and an algorithm for HIV-1 diagnostic PCR evaluated in patients harbouring strains of diverse geographical origin. The Belgian AIDS Reference Laboratories. J. Virol. Methods 1995, 51, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchiero, P.; Carrigan, D.R.; Asano, Y.; Benedetti, L.; Crowley, R.W.; Komaroff, A.L.; Gallo, R.C.; Lusso, P. Detection of human herpesvirus 6 in plasma of children with primary infection and immunosuppressed patients by polymerase chain reaction. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Shimamoto, T.; Isegawa, Y.; Kondo, K.; Yamanishi, K. Structure of transcripts and proteins encoded by U79-80 of human herpesvirus 6 and its subcellular localization in infected cells. Virology 2000, 271, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.; Liakos, V.; Michou, V.; Kapranos, N.; Kaltsas, G.; Tsilivakos, V.; Tsatsoulis, A. Detection of herpes virus DNA in post-operative thyroid tissue specimens of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 116, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billstrom, M.A.; Johnson, G.L.; Avdi, N.J.; Worthen, G.S. Intracellular signaling by the chemokine receptor US28 during human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5535–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, V.; Subramanian, A.; Agrawal, D.; Bhoi, S.K.; Pallavi, P.; Mukhopadhayay, A.K. RANTES levels in peripheral blood, CSF and contused brain tissue as a marker for outcome in traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.-M.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.-F.; Chen, G.-M.; Li, J.; Cen, H.; Feng, C.-C.; Ye, D.-Q. Increased serum RANTES in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichna, M.; Żurawek, M.; Budny, B.; Komarowska, H.; Niechciał, E.; Fichna, P.; Ruchała, M. Elevated serum RANTES chemokine levels in autoimmune Addison disease. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2018, 128, 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Pavkova Goldbergova, M.; Lipkova, J.; Pavek, N.; Gatterova, J.; Vasku, A.; Soucek, M.; Nemec, P. RANTES, MCP-1 chemokines and factors describing rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 52, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahane, M.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, N.; Miyahara, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Katsumata, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Iwatani, Y. Association of the polymorphisms of chemokine genes (IL8, RANTES, MIG, IP10, MCP1 and IL16) with the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GarcÍa-López, M.Á.; Sancho, D.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Marazuela, M. Thyrocytes from autoimmune thyroid disorders produce the chemokines IP-10 and mig and attract CXCR3+ lymphocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5008–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfaing-Koka, A.; Devergne, O.; Gorgone, G.; Portier, A.; Schall, T.J.; Galanaud, P.; Emilie, D. Regulation of the production of the RANTES chemokine by endothelial cells. Synergistic induction by IFN-gamma plus TNF-alpha and inhibition by IL-4 and IL-13. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, A.J.; Shenk, T. Human cytomegalovirus inhibits transcription of the CC chemokine MCP-1 gene. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelson, S.; Dal Monte, P.; Zipeto, D.; Bodaghi, B.; Laurent, L.; Oberlin, E.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Virelizier, J.L.; Landini, M.P. Modulation of RANTES production by human cytomegalovirus infection of fibroblasts. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6495–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, M.B.; Worthen, G.S. Viral regulation of RANTES expression during human cytomegalovirus infection of endothelial cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultanova, A.; Cistjakovs, M.; Sokolovska, L.; Todorova, K.; Cunskis, E.; Murovska, M. HHV-6 Infection and Chemokine RANTES Signaling Pathway Disturbance in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Viruses 2020, 12, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060689
Sultanova A, Cistjakovs M, Sokolovska L, Todorova K, Cunskis E, Murovska M. HHV-6 Infection and Chemokine RANTES Signaling Pathway Disturbance in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Viruses. 2020; 12(6):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060689
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultanova, Alina, Maksims Cistjakovs, Liba Sokolovska, Katerina Todorova, Egils Cunskis, and Modra Murovska. 2020. "HHV-6 Infection and Chemokine RANTES Signaling Pathway Disturbance in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis" Viruses 12, no. 6: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060689
APA StyleSultanova, A., Cistjakovs, M., Sokolovska, L., Todorova, K., Cunskis, E., & Murovska, M. (2020). HHV-6 Infection and Chemokine RANTES Signaling Pathway Disturbance in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Viruses, 12(6), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060689





