Abrogation of Constitutive and Induced Type I and Type III Interferons and Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Keratinocytes by Canine Papillomavirus 2 E6 and E7
Abstract
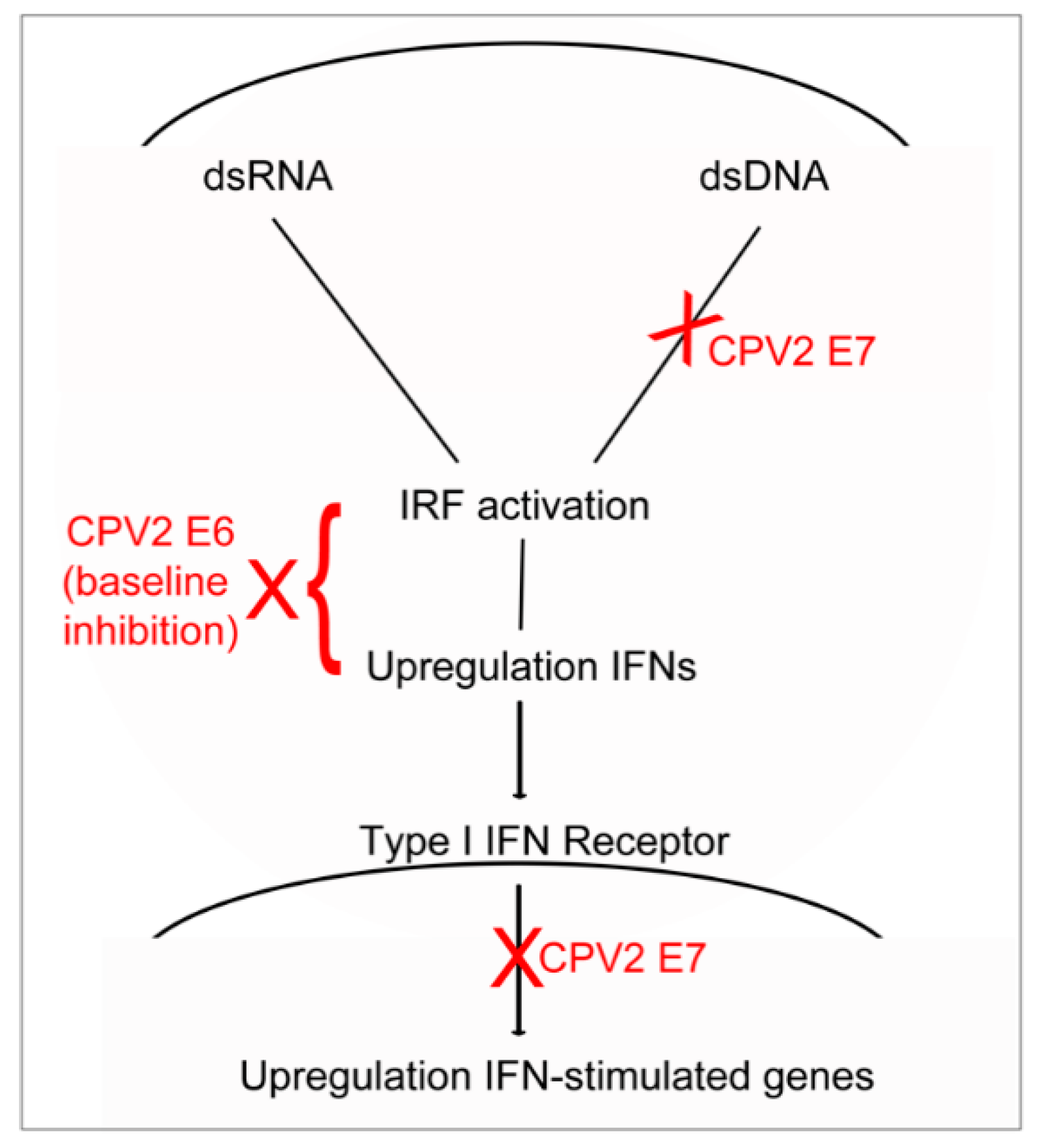
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids and Retrovirus Transduction
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Reverse Transcription Real Time PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
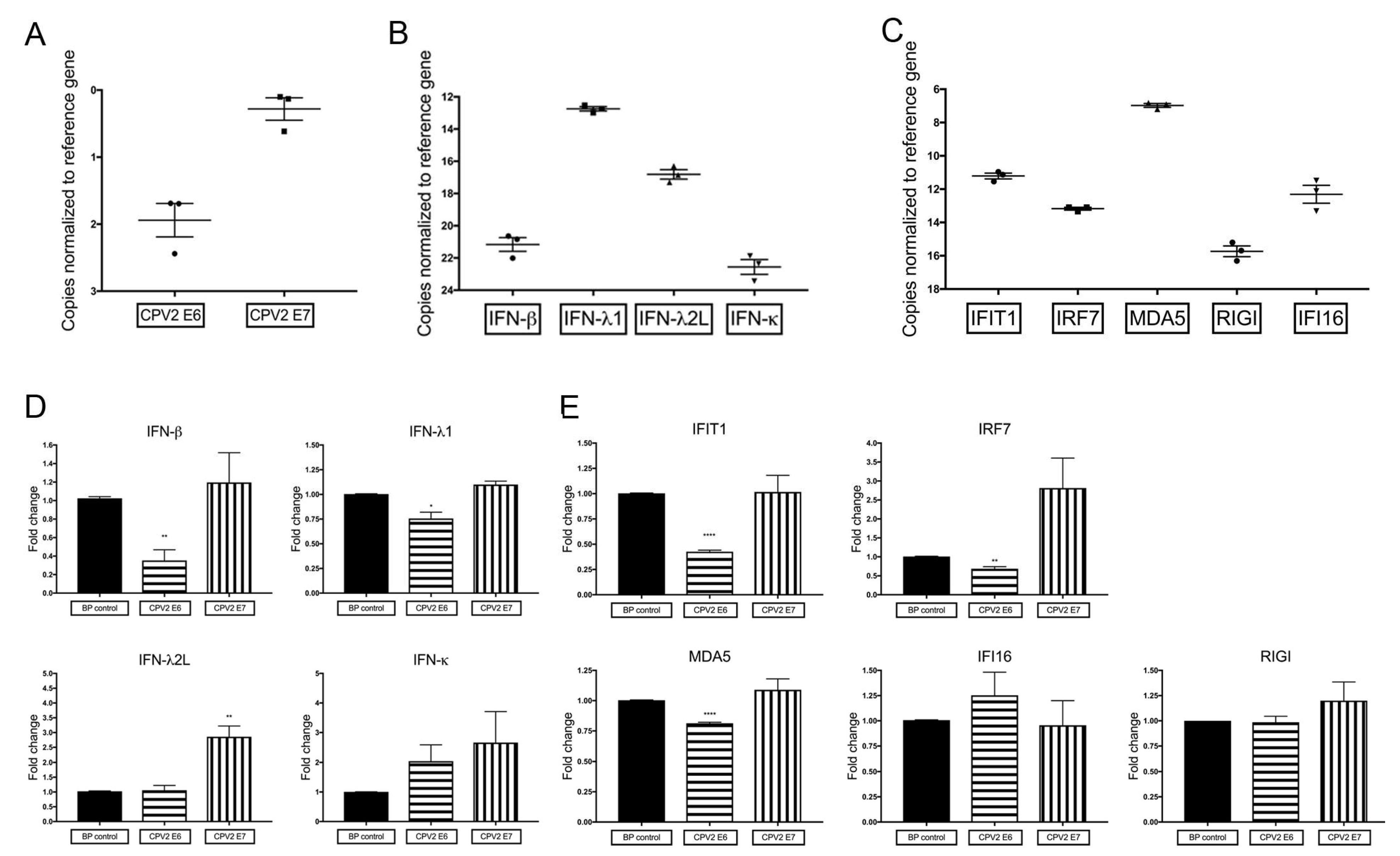
3.1. Constitutive mRNA Expression of a Subset of IFN and IFN-Stimulated Genes Is Reduced by CPV2 E6 in Canine Keratinocytes
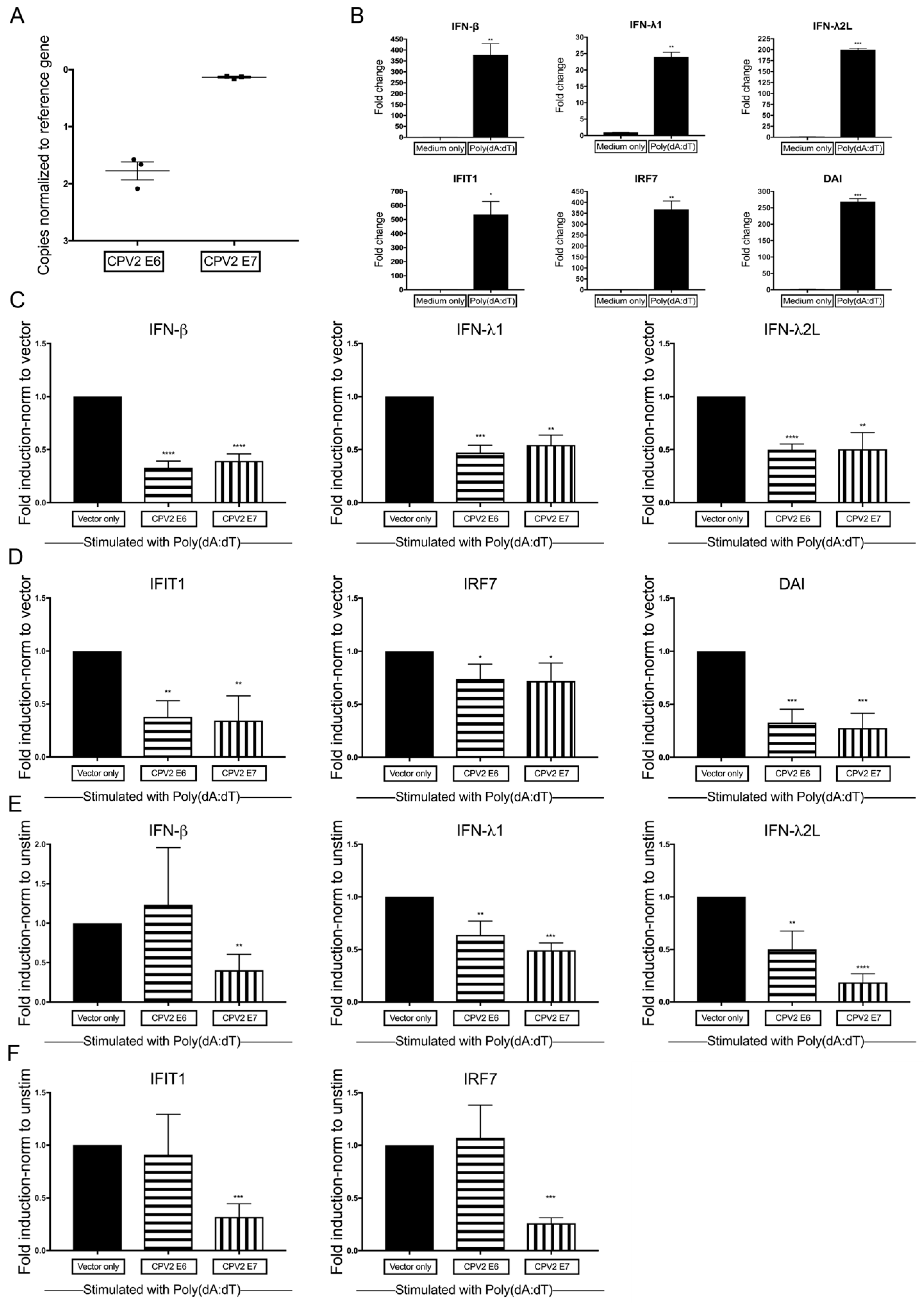
3.2. Diminished Poly(dA:dT)-Induction of IFN and IFN-Stimulated Genes by CPV2 E6 and E7 in Canine Keratinocytes
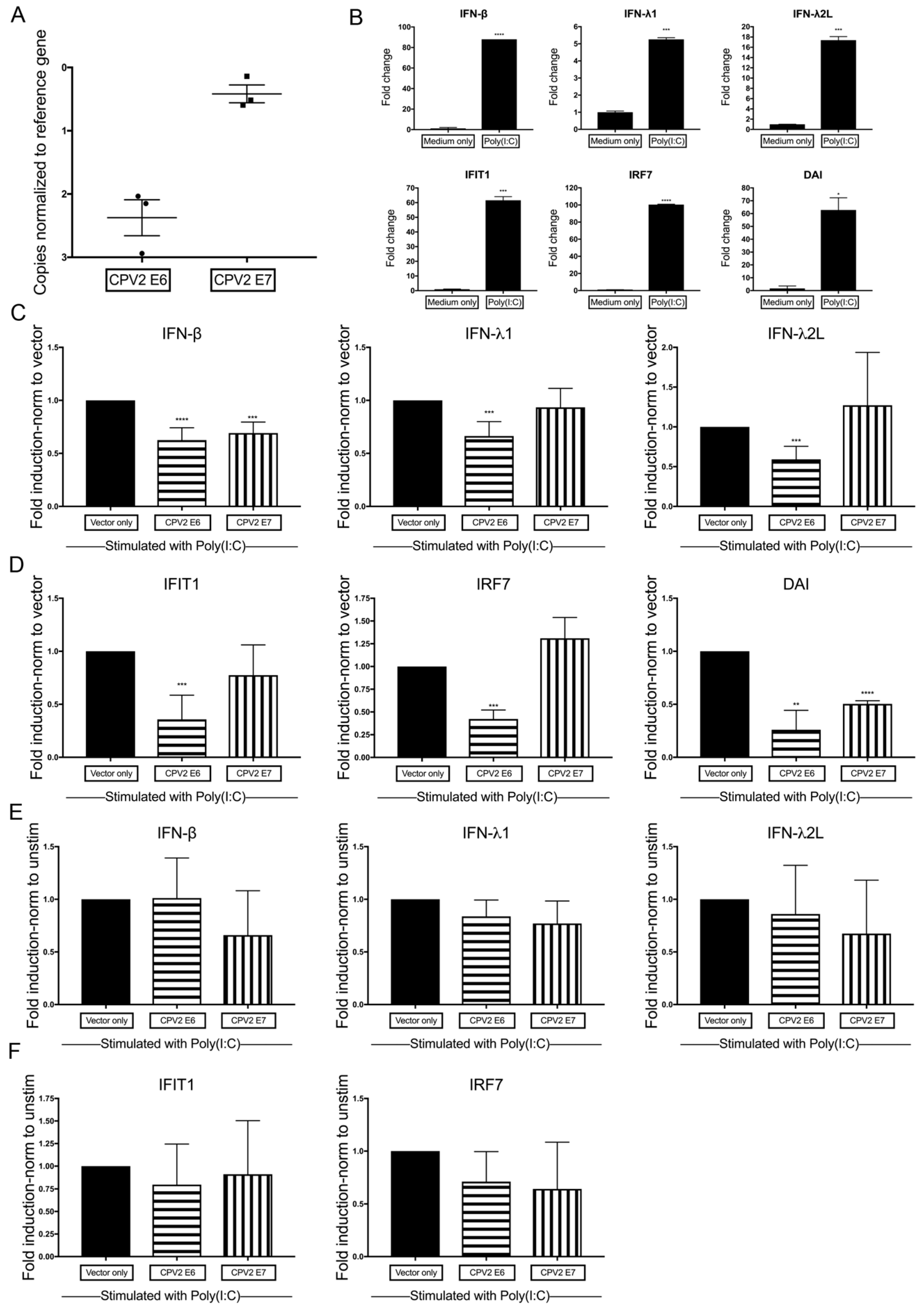
3.3. Diminished Poly(I:C)-Induction of IFN and IFN-Stimulated Genes by CPV2 E6 and E7 in Canine Keratinocytes
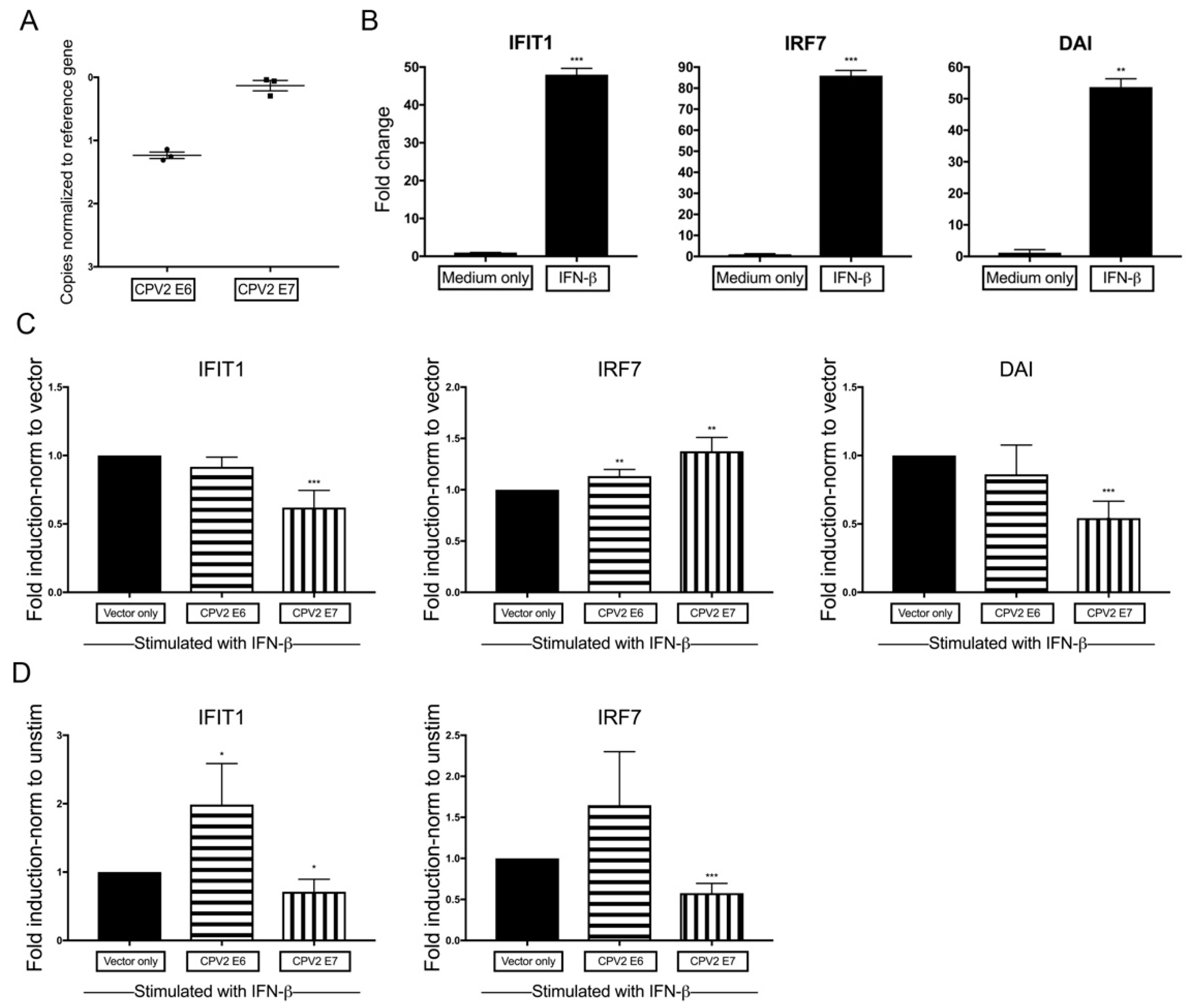
3.4. Diminished IFN-β-Induction of IFN-Stimulated Genes by CPV2 E7 but Not E6 in Canine Keratinocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernard, H.U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.M. Classification of papillomaviruses (PVs) based on 189 PV types and proposal of taxonomic amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, E.M.; Fauquet, C.; Broker, T.R.; Bernard, H.U.; zur Hausen, H. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology 2004, 324, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.A. Oncogenic human papillomaviruses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheit, T. Mucosal and Cutaneous Human Papillomavirus Infections and Cancer Biology. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiding, J.W.; Holland, S.M. Warts and all: Human papillomavirus in primary immunodeficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1030–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, U.; Kreuter, A.; Pfister, H. Human papillomavirus and immunosuppression. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2014, 45, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamura, G.; Corteggio, A.; Pacini, L.; Conte, A.; Pierantoni, G.M.; Tommasino, M.; Accardi, R.; Borzacchiello, G. Transforming properties of Felis catus papillomavirus type 2 E6 and E7 putative oncogenes in vitro and their transcriptional activity in feline squamous cell carcinoma in vivo. Virology 2016, 496, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschmidt, M.H.; Kennedy, J.S.; Kennedy, D.R.; Yuan, H.; Holt, D.E.; Casal, M.L.; Traas, A.M.; Mauldin, E.A.; Moore, P.F.; Henthorn, P.S.; et al. Severe papillomavirus infection progressing to metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in bone marrow-transplanted X-linked SCID dogs. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6621–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsburg, P.J.; Hartnett, B.J.; Henthorn, P.S.; Moore, P.F.; Krakowka, S.; Ochs, H.D. Canine X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 69, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsburg, P.J.; Somberg, R.L.; Hartnett, B.J.; Henthorn, P.S.; Carding, S.R. Canine X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. A model for investigating the requirement for the common gamma chain (gamma c) in human lymphocyte development and function. Immunol. Res. 1998, 17, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ghim, S.; Newsome, J.; Apolinario, T.; Olcese, V.; Martin, M.; Delius, H.; Felsburg, P.; Jenson, B.; Schlegel, R. An epidermotropic canine papillomavirus with malignant potential contains an E5 gene and establishes a unique genus. Virology 2007, 359, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, M.B.; Ank, N.; Melchjorsen, J.; Paludan, S.R. Expression of type III interferon (IFN) in the vaginal mucosa is mediated primarily by dendritic cells and displays stronger dependence on NF-kappaB than type I IFNs. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4579–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, M.A. Epithelial cell responses to infection with human papillomavirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalat, R.; Ewald, S.E.; Mouchess, M.L.; Barton, G.M. Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalali, B.N.; Kollisch, G.; Mages, J.; Muller, T.; Bauer, S.; Wagner, H.; Ring, J.; Lang, R.; Mempel, M.; Ollert, M. Double-stranded RNA induces an antiviral defense status in epidermal keratinocytes through TLR3-, PKR-, and MDA5/RIG-I-mediated differential signaling. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almine, J.F.; O′Hare, C.A.; Dunphy, G.; Haga, I.R.; Naik, R.J.; Atrih, A.; Connolly, D.J.; Taylor, J.; Kelsall, I.R.; Bowie, A.G.; et al. IFI16 and cGAS cooperate in the activation of STING during DNA sensing in human keratinocytes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Aoki, R.; Shimada, S. Innate and intrinsic antiviral immunity in skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 75, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFleur, D.W.; Nardelli, B.; Tsareva, T.; Mather, D.; Feng, P.; Semenuk, M.; Taylor, K.; Buergin, M.; Chinchilla, D.; Roshke, V.; et al. Interferon-kappa, a novel type I interferon expressed in human keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39765–39771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Nice, T.J.; Diamond, M.S. Interferon-lambda: Immune Functions at Barrier Surfaces and Beyond. Immunity 2015, 43, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.; Gray, E.E.; Brunette, R.L.; Stetson, D.B. DNA tumor virus oncogenes antagonize the cGAS-STING DNA-sensing pathway. Science 2015, 350, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, S.E.; Massimi, P.; Banks, L. Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 impairs the activation of the interferon regulatory factor-1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2000, 5, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiser, J.; Hurst, J.; Voges, M.; Krauss, P.; Munch, P.; Iftner, T.; Stubenrauch, F. High-risk human papillomaviruses repress constitutive kappa interferon transcription via E6 to prevent pathogen recognition receptor and antiviral-gene expression. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11372–11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, L.V.; Karpova, A.Y.; Vidal, M.; Howley, P.M. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 oncoprotein binds to interferon regulatory factor-3 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. Genes. Dev. 1998, 12, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordano, P.; Gillan, V.; Bratlie, S.; Bouvard, V.; Banks, L.; Tommasino, M.; Campo, M.S. The E6E7 oncoproteins of cutaneous human papillomavirus type 38 interfere with the interferon pathway. Virology 2008, 377, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, D.; Prabhu, A.; Schlegel, R.; Yuan, H. The canine papillomavirus and gamma HPV E7 proteins use an alternative domain to bind and destabilize the retinoblastoma protein. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luff, J.A.; Yuan, H.; Kennedy, D.; Schlegel, R.; Felsburg, P.; Moore, P.F. Keratinocyte antiviral response to Poly(dA:dT) stimulation and papillomavirus infection in a canine model of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luff, J.A.; Yuan, H.; Suter, M.M.; Muller, E.J.; Schlegel, R.; Moore, P.F. Canine keratinocytes upregulate type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines in response to poly(dA:dT) but not to canine papillomavirus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 153, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.A.; Sheppard, P.O.; O′Hara, P.J. The role of genomic data in the discovery, annotation and evolutionary interpretation of the interferon-lambda family. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Xu, L.; Ren, L.; Qu, H.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Luo, T. Functional characterization of canine interferon-lambda. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Tummers, B.; Meyers, C.; Biryukov, J.L.; Alam, S.; Backendorf, C.; Jha, V.; Offringa, R.; van Ommen, G.J.; Melief, C.J.; et al. Human papillomavirus (HPV) upregulates the cellular deubiquitinase UCHL1 to suppress the keratinocyte’s innate immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Chathuranga, K.; Lee, J.S. Intracellular sensing of viral genomes and viral evasion. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westrich, J.A.; Warren, C.J.; Pyeon, D. Evasion of host immune defenses by human papillomavirus. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses causing cancer: Evasion from host-cell control in early events in carcinogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldak, M.; Tolzmann, L.; Wnorowski, A.; Podgorska, M.J.; Silling, S.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J.; Muller, C.S.; Vogt, T.; Smola, H.; et al. Differential regulation of human papillomavirus type 8 by interferon regulatory factors 3 and 7. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Hwang, E.S.; Namkoong, S.E.; Um, S.J. Inactivation of interferon regulatory factor-1 tumor suppressor protein by HPV E7 oncoprotein. Implication for the E7-mediated immune evasion mechanism in cervical carcinogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6764–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, S.J.; Rhyu, J.W.; Kim, E.J.; Jeon, K.C.; Hwang, E.S.; Park, J.S. Abrogation of IRF-1 response by high-risk HPV E7 protein in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2002, 179, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Donnelly, C.R.; Gong, W.; Heath, B.R.; Hao, Y.; Donnelly, L.A.; Moghbeli, T.; Tan, Y.S.; Lin, X.; Bellile, E.; et al. HPV16 drives cancer immune escape via NLRX1-mediated degradation of STING. J. Clin. Investig. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Cigno, I.; Calati, F.; Borgogna, C.; Zevini, A.; Albertini, S.; Martuscelli, L.; De Andrea, M.; Hiscott, J.; Landolfo, S.; Gariglio, M. Human Papillomavirus E7 Oncoprotein Subverts Host Innate Immunity via SUV39H1-Mediated Epigenetic Silencing of Immune Sensor Genes. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonsson, A.; Payne, E.; Hengst, K.; McMillan, N.A. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein binds human interferon regulatory factor-9 via a novel PEST domain required for transformation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006, 26, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Labrecque, S.; Gauzzi, M.C.; Cuddihy, A.R.; Wong, A.H.; Pellegrini, S.; Matlashewski, G.J.; Koromilas, A.E. The human papilloma virus (HPV)-18 E6 oncoprotein physically associates with Tyk2 and impairs Jak-STAT activation by interferon-alpha. Oncogene 1999, 18, 5727–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.; Pagano, J.S.; Barber, G.N. IRF7: Activation, regulation, modification and function. Genes. Immun. 2011, 12, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence Forward and Reverse (5′–3′) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| RPL13A (reference gene) | TGGGCCGGAAGGTTGTAGTCGT | 99 |
| TTGCGGAGGAAGGCCAGGTAATTCA | ||
| IFN-λ1 | TCCCTACTTCCAAACCCACC | 95 |
| GTTCTTCCAGGAGAGCGACT | ||
| IFN-λ2L | CGCCTCTTCCCTAGAAACCGGGACC | 96 |
| CTCCAGGACCTTCAGTGTCAAGGCC | ||
| IRF7 | GCAAGGTCTACTGGGAGGTG | 97 |
| GTGCTGAAGTCGAAGATGGGG | ||
| CPV2 E6 | ATATTTATGAAACCGTTAGCC | 99 |
| CGCAGCTGTCACAAGTGTTCC | ||
| CPV2 E7 | ACAGAGAGAACCTGGGCGATA | 100 |
| ATAATGCCAAGCCCGTCTAA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinlan, S.; May, S.; Weeks, R.; Yuan, H.; Luff, J.A. Abrogation of Constitutive and Induced Type I and Type III Interferons and Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Keratinocytes by Canine Papillomavirus 2 E6 and E7. Viruses 2020, 12, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060677
Quinlan S, May S, Weeks R, Yuan H, Luff JA. Abrogation of Constitutive and Induced Type I and Type III Interferons and Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Keratinocytes by Canine Papillomavirus 2 E6 and E7. Viruses. 2020; 12(6):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060677
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinlan, Sarah, Susan May, Ryan Weeks, Hang Yuan, and Jennifer A. Luff. 2020. "Abrogation of Constitutive and Induced Type I and Type III Interferons and Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Keratinocytes by Canine Papillomavirus 2 E6 and E7" Viruses 12, no. 6: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060677
APA StyleQuinlan, S., May, S., Weeks, R., Yuan, H., & Luff, J. A. (2020). Abrogation of Constitutive and Induced Type I and Type III Interferons and Interferon-Stimulated Genes in Keratinocytes by Canine Papillomavirus 2 E6 and E7. Viruses, 12(6), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060677





