RSV Reprograms the CDK9•BRD4 Chromatin Remodeling Complex to Couple Innate Inflammation to Airway Remodeling
Abstract
1. Impact and Sequelae of RSV Infections
2. The Airway Epithelial Cell as a Sensor of RSV Replication
3. Activation and Cross-Talk of the NFκB and IRF3 Pathways in Response to RSV
4. The Role of the Airway Epithelium in Innate Responses to RSV
5. NFκB Signaling in Bronchiolar Cells Generate Unique Innate Signals Important in LRTI Pathogenesis
6. Unique RSV-Induced Bronchiolar Cell Factors Mediate LRTI Disease
7. Bronchiolar NFκB Signaling Mediates RSV Disease In Vivo
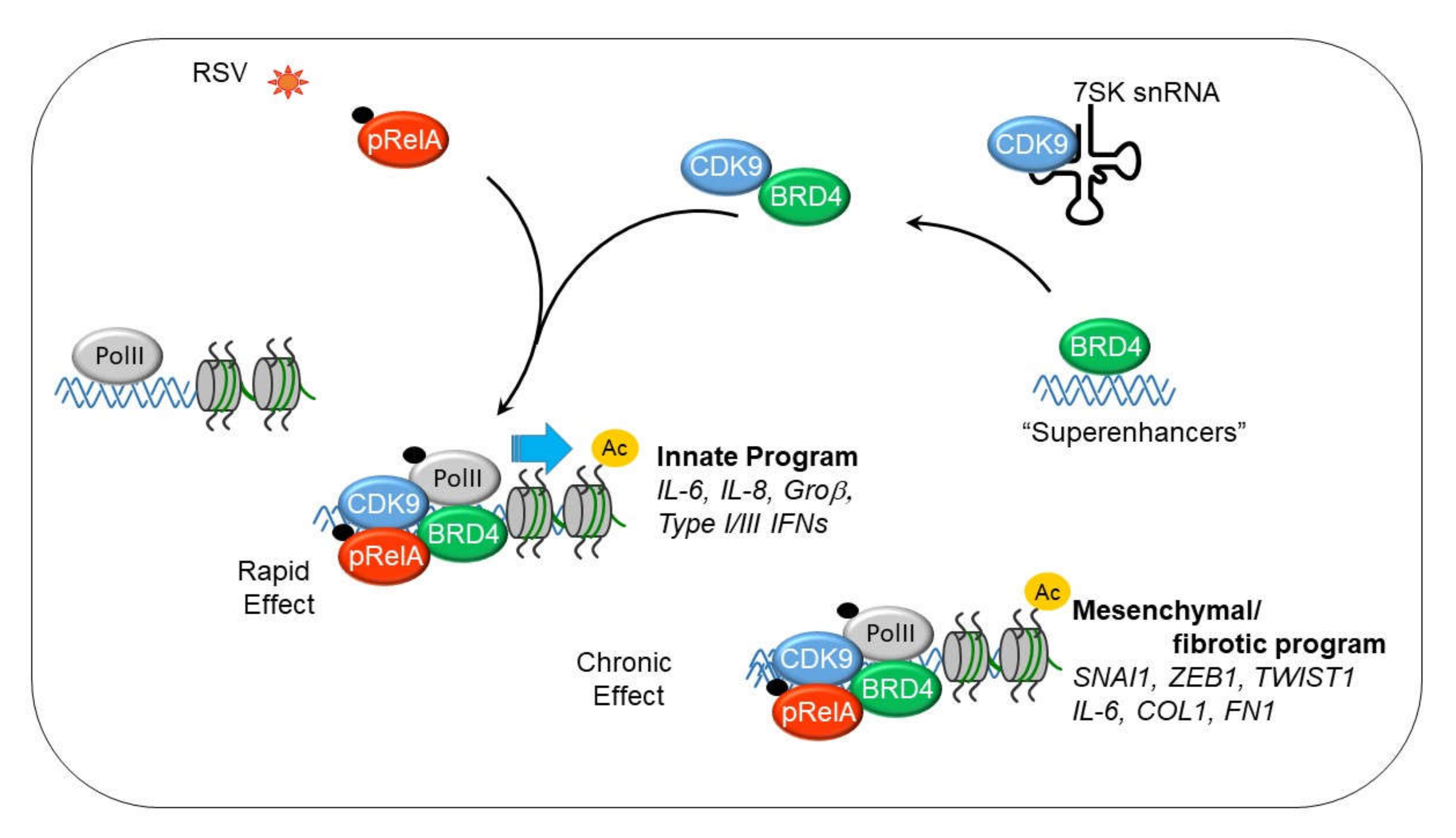
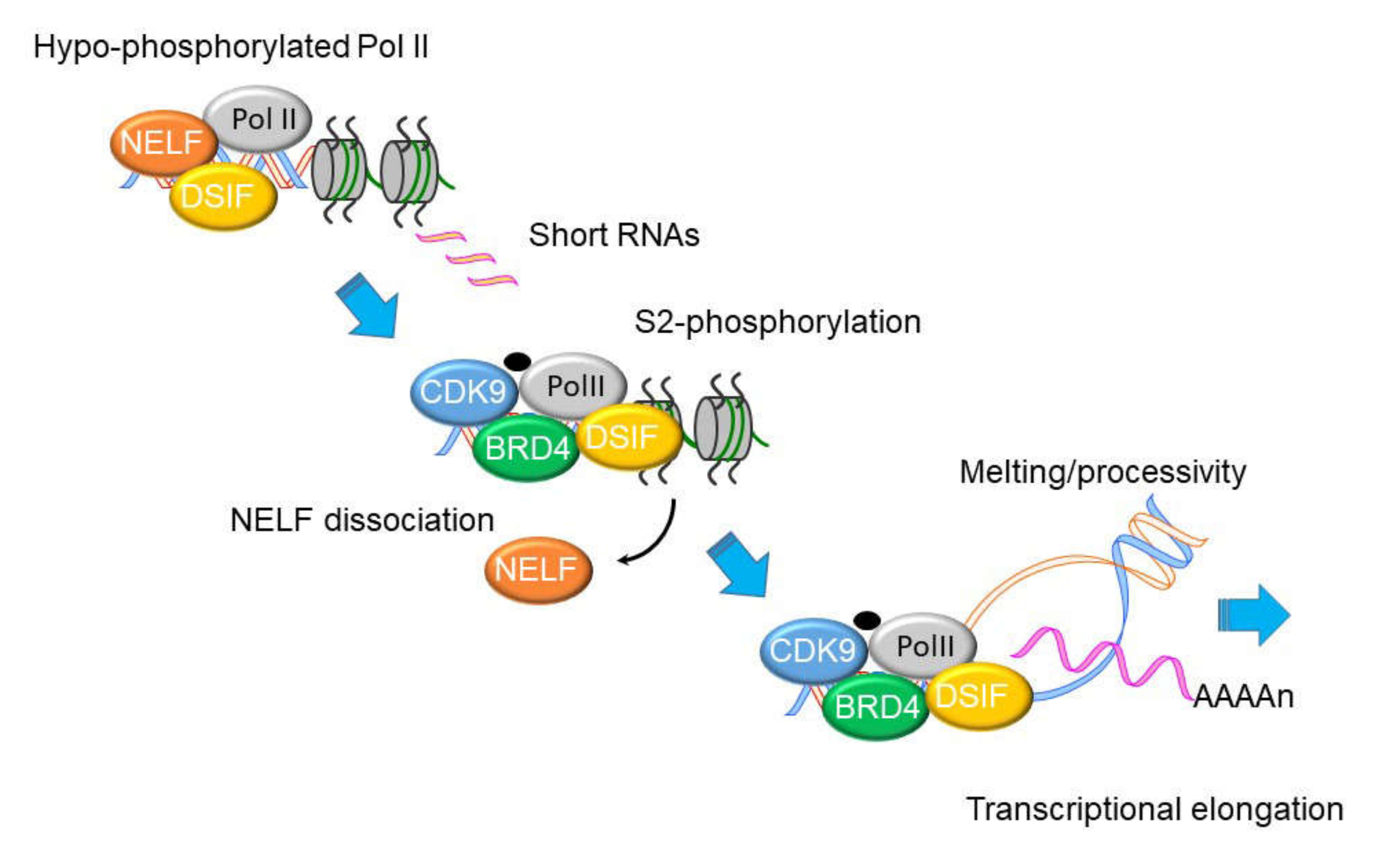
8. NFκB Mediates the IIR by Transcriptional Elongation
9. Mechanism of Transcriptional Elongation in the IIR
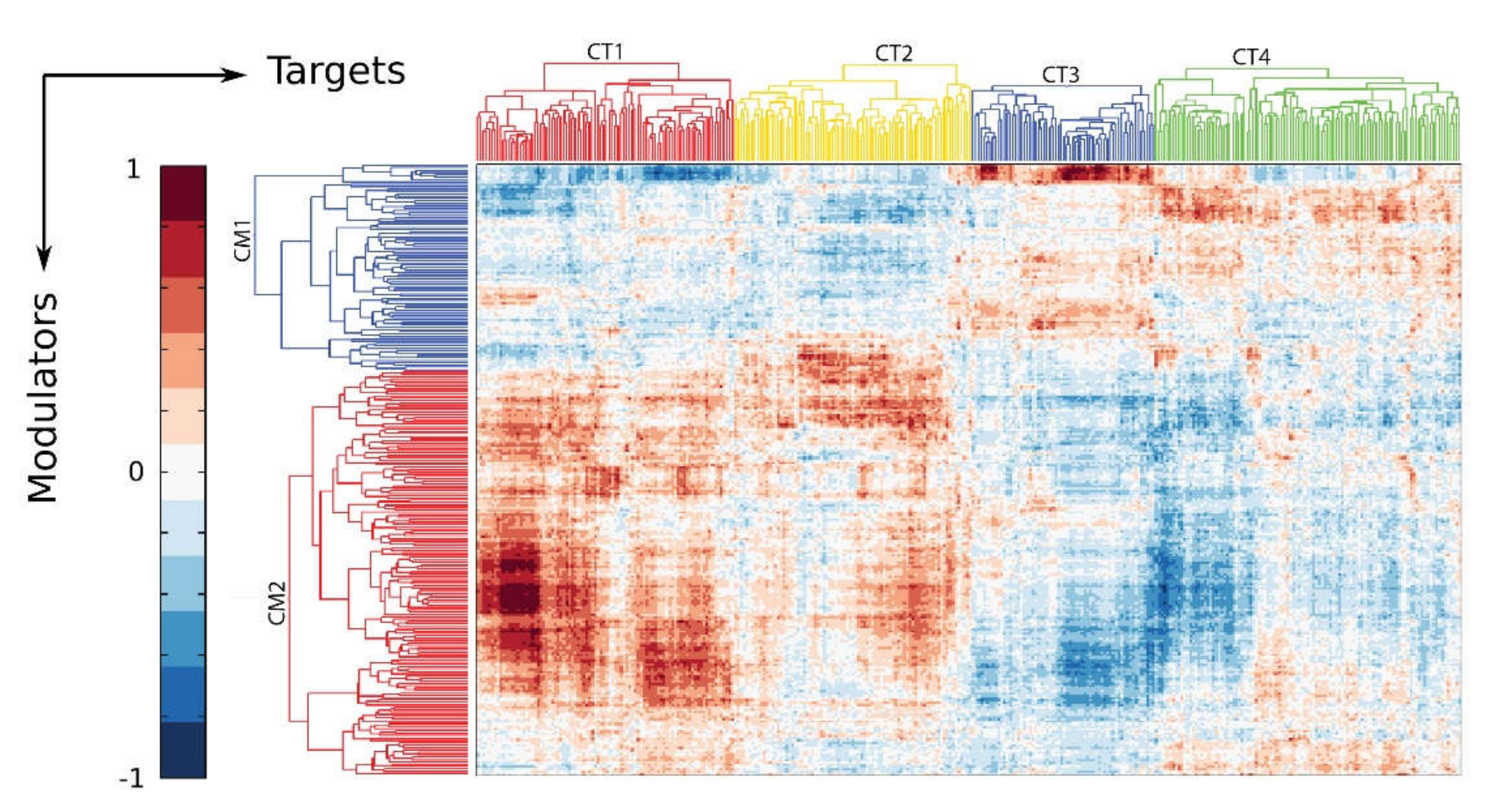
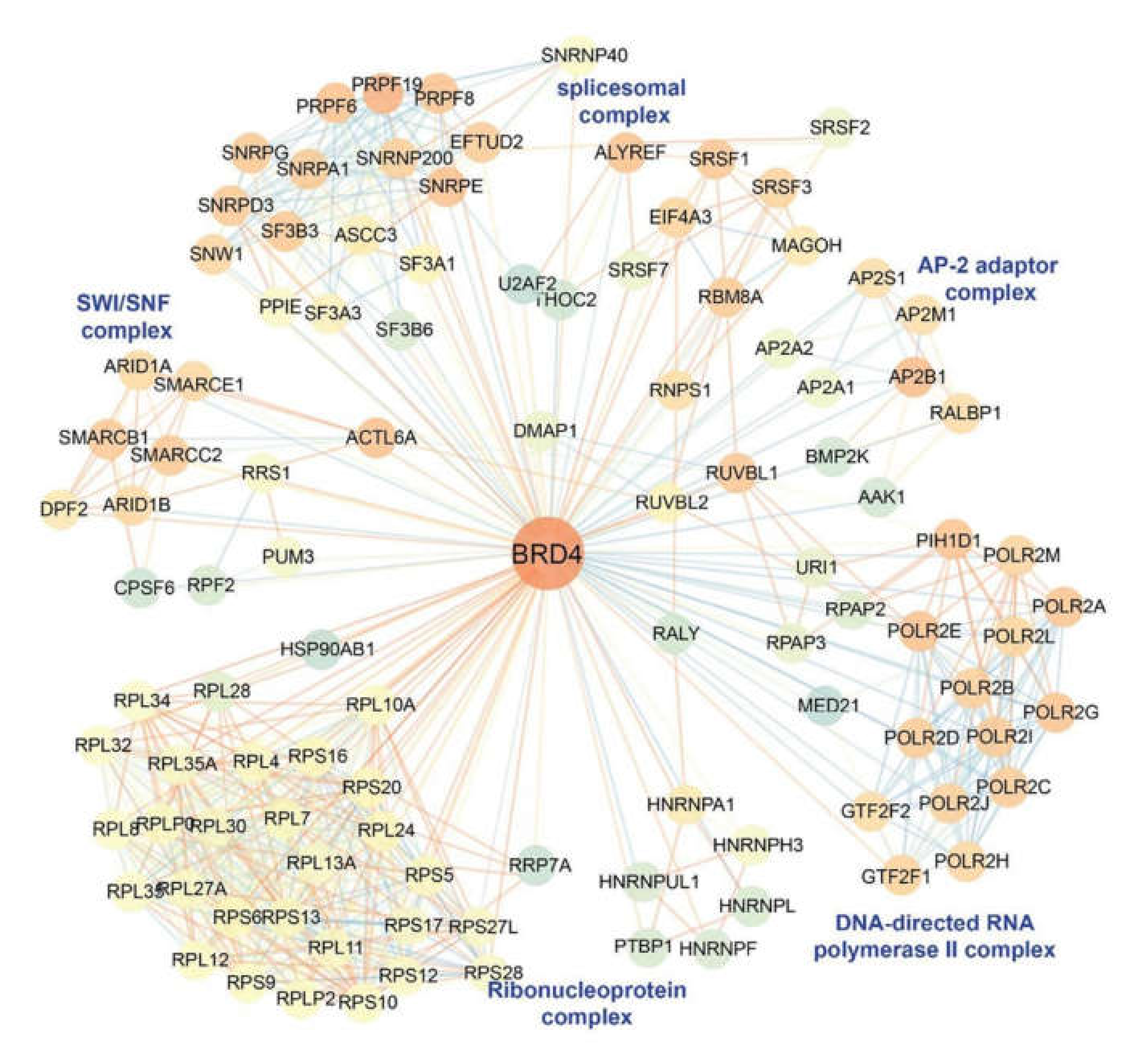
10. The IIR Induces Dynamic Changes in the P-TEFb Interactome and Its Gene Targets
11. BRD4 is a Pleiotrophic Coactivator of the P-TEFb Complex
12. P-TEFb Plays a Role in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
13. Mesenchymal Transitioned Epithelial Cells Release Paracrine Factors that Expand Myofibroblast Population
14. Discussion and Future Directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pneumonia Etiology Research for Child Health Study Group Causes of severe pneumonia requiring hospital admission in children without hiv infection from africa and asia: The perch multi-country case-control study. Lancet 2019, 394, 757–779. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.E.; Gonzales, R.A.; Olson, S.J.; Wright, P.F.; Graham, B.S. The histopathology of fatal untreated human respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welliver, T.P.; Garofalo, R.P.; Hosakote, Y.; Hintz, K.H.; Avendano, L.; Sanchez, K.; Velozo, L.; Jafri, H.; Chavez-Bueno, S.; Ogra, P.L.; et al. Severe human lower respiratory tract illness caused by respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus is characterized by the absence of pulmonary cytotoxic lymphocyte responses. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherne, W.T.; Bird, T.; Court, S.D.B.; Gardner, P.S.; McQuillin, J. Pathological changes in virus infections of the lower respiratory tract in children. J. Clin. Pathol. 1970, 23, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lay, M.K.; Bueno, S.M.; Galvez, N.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M. New insights on the viral and host factors contributing to the airway pathogenesis caused by the respiratory syncytial virus. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.L.; Garofalo, R.P.; Cron, S.G.; Hosakote, Y.M.; Atmar, R.L.; Macias, C.G.; Piedra, P.A. Immunopathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukens, M.V.; van de Pol, A.C.; Coenjaerts, F.E.; Jansen, N.J.; Kamp, V.M.; Kimpen, J.L.; Rossen, J.W.; Ulfman, L.H.; Tacke, C.E.; Viveen, M.C.; et al. A systemic neutrophil response precedes robust cd8(+) t-cell activation during natural respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.D.; Unger, S.A.; Walton, M.; Schwarze, J. The human immune response to respiratory syncytial virus infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwik, A.; Habibi, M.S.; Paras, A.; Zhu, J.; Guvenel, A.; Dhariwal, J.; Almond, M.; Wong, E.H.; Sykes, A.; Maybeno, M.; et al. Rsv-specific airway resident memory cd8+ t cells and differential disease severity after experimental human infection. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jiang, L.; Moser, E.K.; Jewett, L.B.; Wright, J.; Du, J.; Zhou, B.; Davis, S.D.; Krupp, N.L.; Braciale, T.J.; et al. Control of pathogenic effector t-cell activities in situ by pd-l1 expression on respiratory inflammatory dendritic cells during respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.S.; Chiu, C. Controlled human infection with rsv: The opportunities of experimental challenge. Vaccine 2017, 35, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva-Juarez, M.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Evans, S.E. Lung epithelial cells: Therapeutically inducible effectors of antimicrobial defense. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Alenghat, T. Respiratory epithelial cells orchestrate pulmonary innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; Boldogh, I.; Brasier, A.R. Inside-out signaling pathways from nuclear reactive oxygen species control pulmonary innate immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, F. Polyinosinic:Polycytidylic acid induces protein kinase d-dependent disassembly of apical junctions and barrier dysfunction in airway epithelial cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Patrikeev, I.; Ochoa, L.; Vargas, G.; Belanger, K.K.; Litvinov, J.; Boldogh, I.; Ameredes, B.T.; Motamedi, M.; Brasier, A.R. Nf-kappab mediates mesenchymal transition, remodeling, and pulmonary fibrosis in response to chronic inflammation by viral rna patterns. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, A.R. The nf- k b signaling network: Insights from systems approaches. In Cellular Signaling and Innate Immune Responses to RNA Virus Infections; Brasier, A.R., Lemon, S.M., Garcia-Sastre, A., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolusso, R.; Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Vergara, L.A.; Sabree, A.; Iwanaszko, M.; Lipniacki, T.; Brasier, A.; Kimmel, M. Dynamic cross talk model of the epithelial innate immune response to double-stranded rna stimulation: Coordinated dynamics emerging from cell-level noise. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battles, M.B.; McLellan, J.S. Respiratory syncytial virus entry and how to block it. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincheval, V.; Lelek, M.; Gault, E.; Bouillier, C.; Sitterlin, D.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Galloux, M.; Zimmer, C.; Eleouet, J.-F.; Rameix-Welti, M.-A. Functional organization of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in cells infected by respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jamaluddin, M.; Li, K.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A.; Brasier, A.R. Retinoic acid-inducible gene i mediates early antiviral response and toll-like receptor 3 expression in respiratory syncytial virus-infected airway epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Uematsu, S.; Matsui, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Takeda, K.; Fujita, T.; Takeuchi, O.; et al. Cell type-specific involvement of rig-i in antiviral response. Immunity 2005, 23, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Mikamo-Satoh, E.; Hirai, R.; Kawai, T.; Matsushita, K.; Hiiragi, A.; Dermody, T.S.; Fujita, T.; Akira, S. Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-i and melanoma differentiation associated gene 5. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, D.E.; Tian, B.; Jamaluddin, M.; Boldogh, I.; Vergara, L.A.; Choudhary, S.; Brasier, A.R. Rela ser276 phosphorylation is required for activation of a subset of nf-{kappa}b-dependent genes by recruiting cyclin-dependent kinase 9/cyclin t1 complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3623–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaluddin, M.; Wang, S.; Boldogh, I.; Tian, B.; Brasier, A.R. Tnf-alpha-induced nf-kappab/rela ser(276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by an ros-dependent pkac pathway. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamaluddin, M.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Han, Y.; Elliott, T.; Ogra, P.L.; Brasier, A.R. The major component of ikappabalpha proteolysis occurs independently of the proteasome pathway in respiratory syncytial virus-infected pulmonary epithelial cells. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4849–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahopoulos, S.; Boldogh, I.; Brasier, A.R. Nf- k b dependent induction of interleukin-8 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor à: Evidence for an antioxidant sensitive activating pathway distinct from nuclear translocation. Blood 1999, 94, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, M.; Tian, B.; Boldogh, I.; Garofalo, R.P.; Brasier, A.R. Respiratory syncytial virus infection induces a reactive oxygen species-msk1-phospho-ser-276 rela pathway required for cytokine expression. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10605–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type i interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, T.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Ji, P.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y.; Tan, R.X.; Li, E. Respiratory syncytial virus infection upregulates nlrc5 and major histocompatibility complex class i expression through rig-i induction in airway epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7636–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerkies, M.; Korwek, Z.; Prus, W.; Kochanczyk, M.; Jaruszewicz-Blonska, J.; Tudelska, K.; Blonski, S.; Kimmel, M.; Brasier, A.R.; Lipniacki, T. Cell fate in antiviral response arises in the crosstalk of irf, nf-kappab and jak/stat pathways. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, S.; Beg, A.A. Defining emerging roles for nf-kappab in antivirus responses: Revisiting the interferon-beta enhanceosome paradigm. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ivanciuc, T.; Sun, H.; Garofalo, R.P.; Brasier, A.R. Bromodomain containing 4 (brd4) couples nfkb/rela with airway inflammation and the irf-rig-i amplification loop in respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolli, D.; Gupta, M.B.; Sbrana, E.; Velayutham, T.S.; Chao, H.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R. Alveolar macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of hmpv infection while protecting against rsv infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Luxon, B.A.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Jamaluddin, M.; Brasier, A.R. Expression of respiratory syncytial virus-induced chemokine gene networks in lower airway epithelial cells revealed by cdna microarrays. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9044–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jamaluddin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Ivanciuc, T.; Garofalo, R.P.; Brasier, A.R. Systematic analysis of cell-type differences in the epithelial secretome reveals insights into the pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus-induced lower respiratory tract infections. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3345–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosakote, Y.M.; Brasier, A.R.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Kurosky, A. Respiratory syncytial virus infection triggers epithelial hmgb1 release as a damage-associated molecular pattern promoting a monocytic inflammatory response. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9618–9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, R.P.; Haeberle, H. Epithelial regulation of innate immunity to respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravia, J.; You, D.; Shrestha, B.; Jaligama, S.; Siefker, D.; Lee, G.I.; Harding, J.N.; Jones, T.L.; Rovnaghi, C.; Bagga, B.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus disease is mediated by age-variable il-33. PLoS Pathog 2015, 11, e1005217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayavara, K.; Kurosky, A.; Stafford, S.J.; Garg, N.J.; Brasier, A.R.; Garofalo, R.P.; Hosakote, Y.M. Proinflammatory effects of respiratory syncytial virus-induced epithelial hmgb1 on human innate immune cell activation. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2753–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, P.S.; Fonceca, A.M.; Howarth, D.; Correia, J.B.; Slupsky, J.R.; Trinick, R.E.; al Turaiki, W.; Smyth, R.L.; Flanagan, B.F. Respiratory syncytial virus infection of airway epithelial cells, in vivo and in vitro, supports pulmonary antibody responses by inducing expression of the b cell differentiation factor baff. Thorax 2013, 68, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurs, N.; Aljassim, F.; Kjellman, B.; Robinson, P.D.; Sigurbergsson, F.; Bjarnason, R.; Gustafsson, P.M. Asthma and allergy patterns over 18 years after severe rsv bronchiolitis in the first year of life. Thorax 2010, 65, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Headley, M.B.; Loo, Y.M.; Berlin, A.; Gale, M., Jr.; Debley, J.S.; Lukacs, N.W.; Ziegler, S.F. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is induced by respiratory syncytial virus-infected airway epithelial cells and promotes a type 2 response to infection. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallal, L.E.; Schaller, M.A.; Lindell, D.M.; Lira, S.A.; Lukacs, N.W. Ccl20/ccr6 blockade enhances immunity to rsv by impairing recruitment of dc. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangodt, T.C.; van Herck, M.A.; Nullens, S.; Ramet, J.; de Dooy, J.J.; Jorens, P.G.; de Winter, B.Y. The role of th17 and treg responses in the pathogenesis of rsv infection. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ivanciuc, T.; Sun, H.; Wakamiya, M.; Garofalo, R.P.; Brasier, A.R. Central role of the nf-kappab pathway in the scgb1a1-expressing epithelium in mediating respiratory syncytial virus-induced airway inflammation. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wakamiya, M.; Chen, H.; Rytting, E.; Zhou, J.; Brasier, A.R. Selective antagonists of the bronchiolar epithelial nf-kappab-bromodomain-containing protein 4 pathway in viral-induced airway inflammation. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mitra, A.; Dojer, N.; Fu, S.; Rowicka, M.; Brasier, A.R. A probabilistic approach to learn chromatin architecture and accurate inference of the nf-kappab/rela regulatory network using chip-seq. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7240–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Luxon, B.A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A.; Sinha, M.; Brasier, A.R. Identification of nf-kappab-dependent gene networks in respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6800–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Nowak, D.E.; Brasier, A.R. A tnf-induced gene expression program under oscillatory nf-kappab control. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, A.R.; Tian, B.; Jamaluddin, M.; Kalita, M.K.; Garofalo, R.P.; Lu, M. Rela ser276 phosphorylation-coupled lys310 acetylation controls transcriptional elongation of inflammatory cytokines in respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11752–11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Kalita, M.; Edeh, C.B.; Paessler, S.; Casola, A.; Teng, M.N.; Garofalo, R.P.; Brasier, A.R. Cdk9-dependent transcriptional elongation in the innate interferon-stimulated gene response to respiratory syncytial virus infection in airway epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7075–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egloff, S.; van Herreweghe, E.; Kiss, T. Regulation of polymerase ii transcription by 7sk snrna: Two distinct rna elements direct p-tefb and hexim1 binding. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, C.; Forget, D.; Bouchard, A.; Li, Q.; Chua, G.; Poitras, C.; Therien, C.; Bergeron, D.; Bourassa, S.; Greenblatt, J.; et al. Systematic analysis of the protein interaction network for the human transcription machinery reveals the identity of the 7sk capping enzyme. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboric, M.; Nissen, R.M.; Kanazawa, S.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N.; Peterlin, B.M. Nf-kb binds p-tefb to stimulate transcriptional elongation by rna polymerase ii. Mol. Cell 2001, 3, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.H. P-tefb, a cyclin-dependent kinase controlling elongation by rna polymerase ii. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.; Lis, J.T. Control of transcriptional elongation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 483–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelman, K.; Lis, J.T. Promoter-proximal pausing of rna polymerase ii: Emerging roles in metazoans. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlin, B.M.; Price, D.H. Controlling the elongation phase of transcription with p-tefb. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Brasier, A.R. Brd4 mediates nfkb-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis via transcriptional elongation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L1183–L1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Wold, E.A.; Tian, B.; Brasier, A.R.; Zhou, J. Drug discovery targeting bromodomain-containing protein 4. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4533–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Tian, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Brasier, A.R.; Zhou, J. Discovery of potent and selective brd4 inhibitors capable of blocking tlr3-induced acute airway inflammation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Hosoki, K.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhou, J.; Rytting, E.; Kaphalia, L.; Calhoun, W.J.; et al. Mucosal bromodomain-containing protein 4 mediates aeroallergen-induced inflammation and remodeling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 143, 1380–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Liu, Z.; Litvinov, J.; Maroto, R.; Jamaluddin, M.; Rytting, E.; Patrikeev, I.; Ochoa, L.; Vargas, G.; Motamedi, M.; et al. Efficacy of novel highly specific bromodomain-containing protein 4 inhibitors in innate inflammation-driven airway remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ivannikov, M.; Motamedi, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Kaphalia, L.; et al. Pharmacoproteomics reveal novel protective activity of bromodomain containing 4 inhibitors on vascular homeostasis in tlr3-mediated airway remodeling. J. Proteom. 2019, 205, 103415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Kalita, M.; Li, X.; Jamaluddin, M.; Tian, B.; Edeh, C.B.; Wiktorowicz, J.E.; Kudlicki, A.; Brasier, A.R. Systematic determination of human cyclin dependent kinase (cdk)-9 interactome identifies novel functions in rna splicing mediated by the ddx5/17 rna helicases. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2015, 14, 2701–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Brasier, A.R.; Kudlicki, A.S. Inferring genome-wide functional modulatory network: A case study on nf-kappab/rela transcription factor. J. Comput. Biol. 2015, 22, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, B.; Jamaluddin, M.; Mitra, A.; Yang, J.; Rowicka, M.; Brasier, A.R.; Kudlicki, A. Modulation of gene expression regulated by the transcription factor nf-kappab/rela. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11927–11944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, B.N.; Lewis, B.A.; Cherman, N.; Hewitt, M.C.; Albrecht, B.K.; Robey, P.G.; Ozato, K.; Sims, R.J., 3rd; Singer, D.S. Brd4 is an atypical kinase that phosphorylates serine2 of the rna polymerase ii carboxy-terminal domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6927–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, T.; Kanno, Y.; LeRoy, G.; Campos, E.; Sun, H.W.; Brooks, S.R.; Vahedi, G.; Heightman, T.D.; Garcia, B.A.; Reinberg, D.; et al. Brd4 assists elongation of both coding and enhancer rnas by interacting with acetylated histones. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Philpott, M.; Muller, S.; Schulze, J.; Badock, V.; Eberspacher, U.; Moosmayer, D.; Bader, B.; Schmees, N.; Fernandez-Montalvan, A.; et al. Affinity map of bromodomain protein 4 (brd4) interactions with the histone h4 tail and the small molecule inhibitor jq1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9304–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.D.; Lin, C.Y.; Duan, Q.; Griffin, G.; Federation, A.J.; Paranal, R.M.; Bair, S.; Newton, G.; Lichtman, A.H.; Kung, A.L.; et al. Nf-kappab directs dynamic super enhancer formation in inflammation and atherogenesis. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaiah, B.N.; Case-Borden, C.; Gegonne, A.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, Q.; Meerzaman, D.; Dey, A.; Ozato, K.; Singer, D.S. Brd4 is a histone acetyltransferase that evicts nucleosomes from chromatin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzen, F.; Greifenberg, A.K.; Bosken, C.A.; Geyer, M. Brd4 activates p-tefb for rna polymerase ii ctd phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7577–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, K.; Jung, K.-J.; Cho, W.-K.; Klase, Z.; Kashanchi, F.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Brady, J.N. Bromodomain protein brd4 regulates human immunodeficiency virus transcription through phosphorylation of cdk9 at threonine 29. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Huang, B.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qi, J.; Bradner, J.; Nair, S.; Chen, L.F. Brd4 maintains constitutively active nf-kappab in cancer cells by binding to acetylated rela. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.K.; Mochizuki, K.; Zhou, M.; Jeong, H.S.; Brady, J.N.; Ozato, K. The bromodomain protein brd4 is a positive regulatory component of p-tefb and stimulates rna polymerase ii-dependent transcription. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Brasier, A.R.; Zhao, Y. Quantitative assessment of the effects of trypsin digestion methods on affinity purification-mass spectrometry-based protein-protein interaction analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3068–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.E.; Billheimer, D.; Jenkins, I.C.; Lu, Z.J.; Stern, D.A.; Gerald, L.B.; Carr, T.F.; Guerra, S.; Morgan, W.J.; Wright, A.L.; et al. A distinct low lung function trajectory from childhood to the fourth decade of life. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, T.; Pazdrak, K.; Kalita, M.; Konig, R.; Choudhary, S.; Tian, B.; Boldogh, I.; Brasier, A.R. Systems biology approaches to understanding epithelial mesenchymal transition (emt) in mucosal remodeling and signaling in asthma. World Allergy Organ. J. 2014, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Widen, S.G.; Yang, J.; Wood, T.G.; Kudlicki, A.; Zhao, Y.; Brasier, A.R. The nfkappab subunit rela is a master transcriptional regulator of the committed epithelial-mesenchymal transition in airway epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 16528–16545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Li, X.; Kalita, M.; Widen, S.G.; Yang, J.; Bhavnani, S.K.; Dang, B.; Kudlicki, A.; Sinha, M.; Kong, F.; et al. Analysis of the tgfbeta-induced program in primary airway epithelial cells shows essential role of nf-kappab/rela signaling network in type ii epithelial mesenchymal transition. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Liu, H.; Du, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P. Synergistic action of master transcription factors controls epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2514–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Holloway, J.; Wilson, S.; Bucchieri, F.; Puddicombe, S.; Davies, D.E. Epithelial-mesenchymal communication in the pathogenesis of chronic asthma. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2004, 1, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, C.E.P.; Howarth, P.H.; Djukanovic, R.; Wilson, J.; Holgate, S.T.; Roche, W.R. Myofibroblasts and subepithelial fibrosis in bronchial asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1990, 3, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

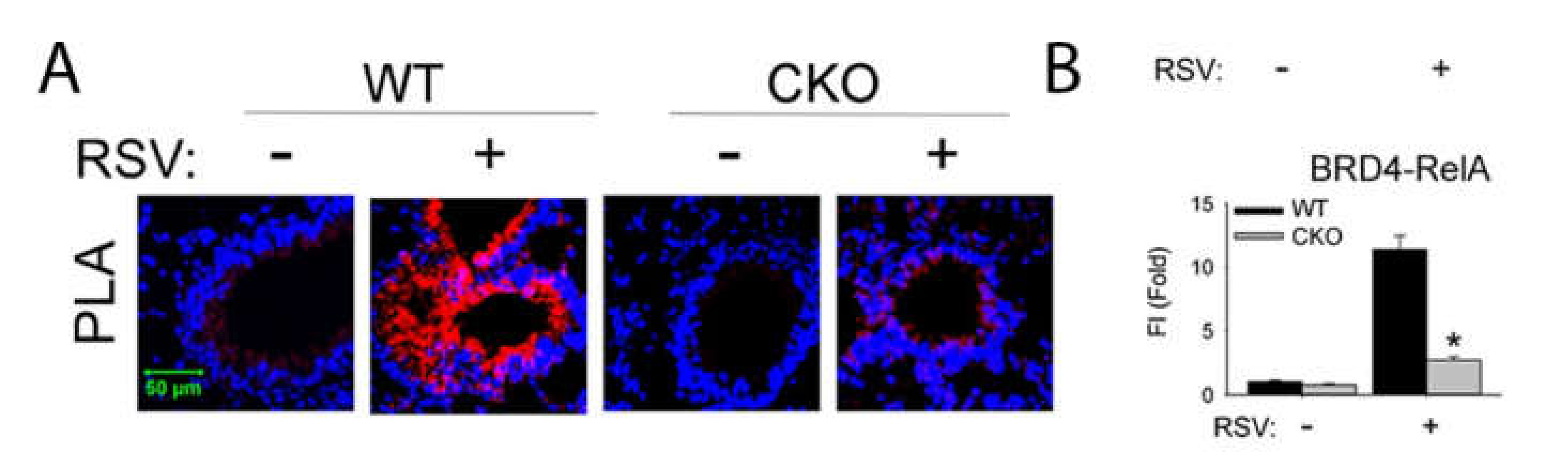
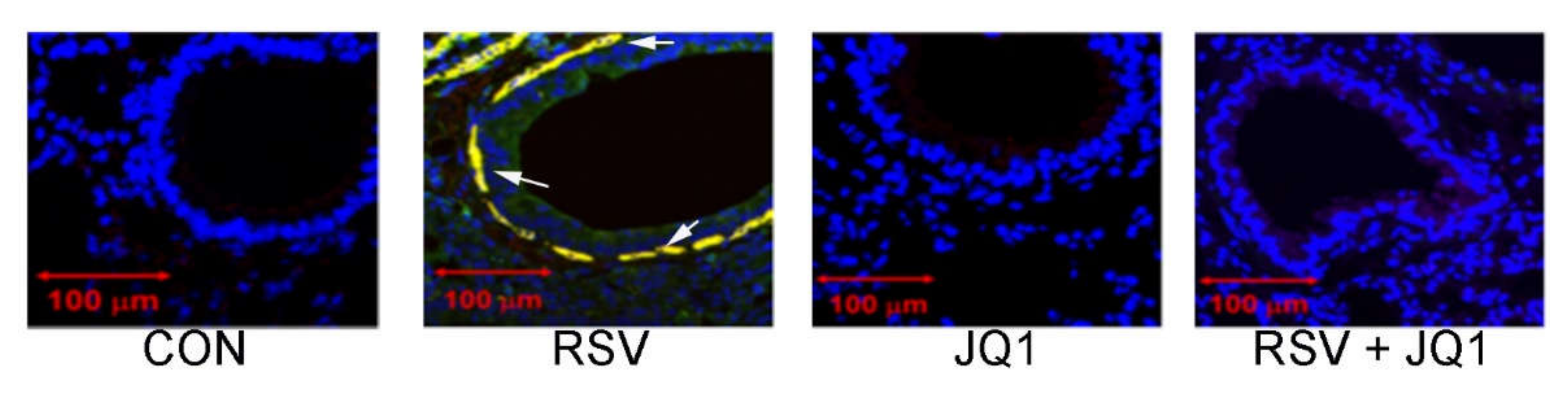

© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brasier, A.R. RSV Reprograms the CDK9•BRD4 Chromatin Remodeling Complex to Couple Innate Inflammation to Airway Remodeling. Viruses 2020, 12, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040472
Brasier AR. RSV Reprograms the CDK9•BRD4 Chromatin Remodeling Complex to Couple Innate Inflammation to Airway Remodeling. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040472
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrasier, Allan R. 2020. "RSV Reprograms the CDK9•BRD4 Chromatin Remodeling Complex to Couple Innate Inflammation to Airway Remodeling" Viruses 12, no. 4: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040472
APA StyleBrasier, A. R. (2020). RSV Reprograms the CDK9•BRD4 Chromatin Remodeling Complex to Couple Innate Inflammation to Airway Remodeling. Viruses, 12(4), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040472



