Evolutionary Dynamics and Age-Dependent Pathogenesis of Sub-Genotype VI.2.1.1.2.2 PPMV-1 in Pigeons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Virus Isolation and Identification
2.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Genetic and Phylogenetic Analyses
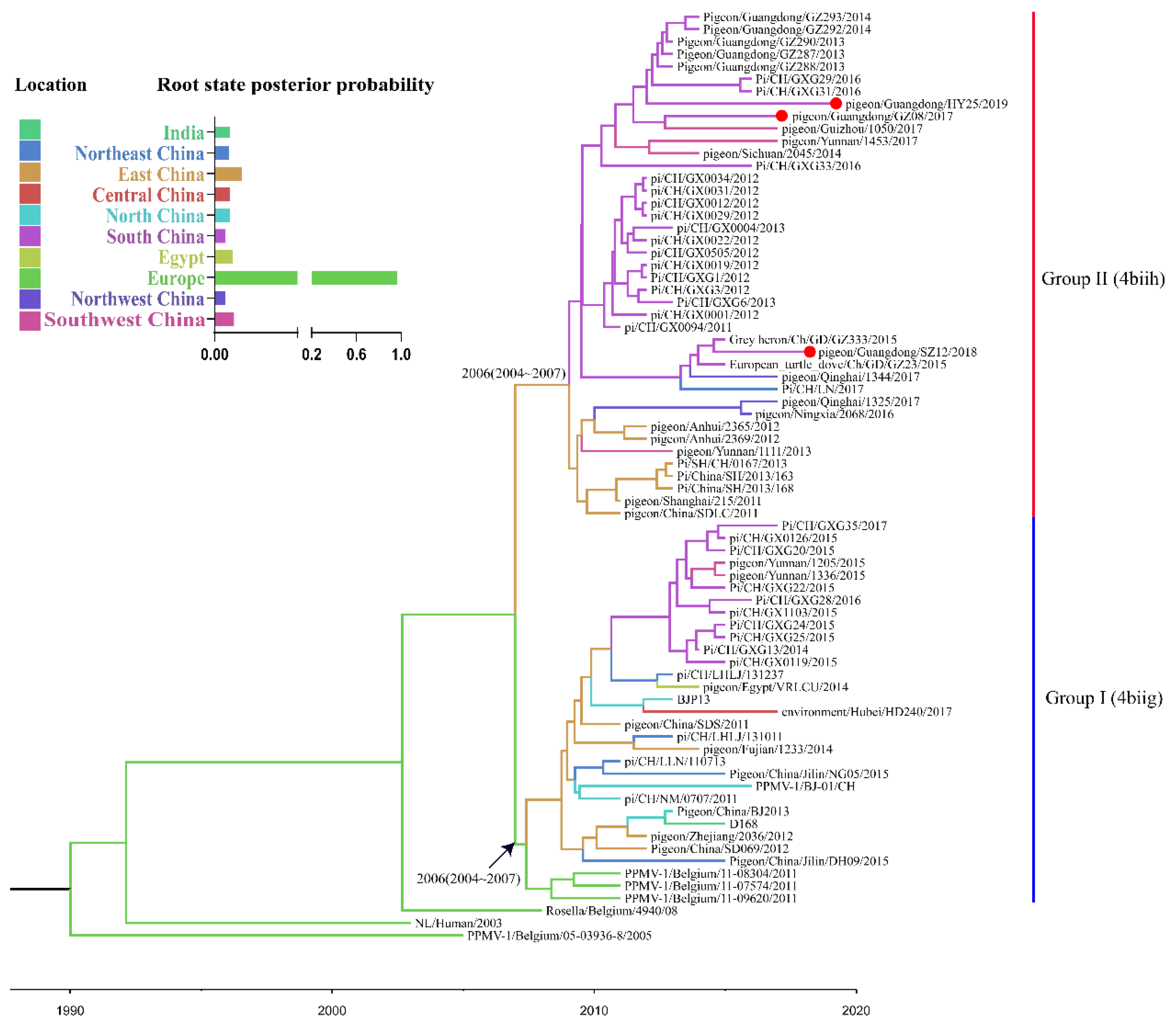
2.5. Bayesian Phylogeographic Analysis
2.6. Pathogenicity and Transmission in Pigeons of Different Ages
2.7. Cross-Reactivity HI Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Virus Isolation and Identification
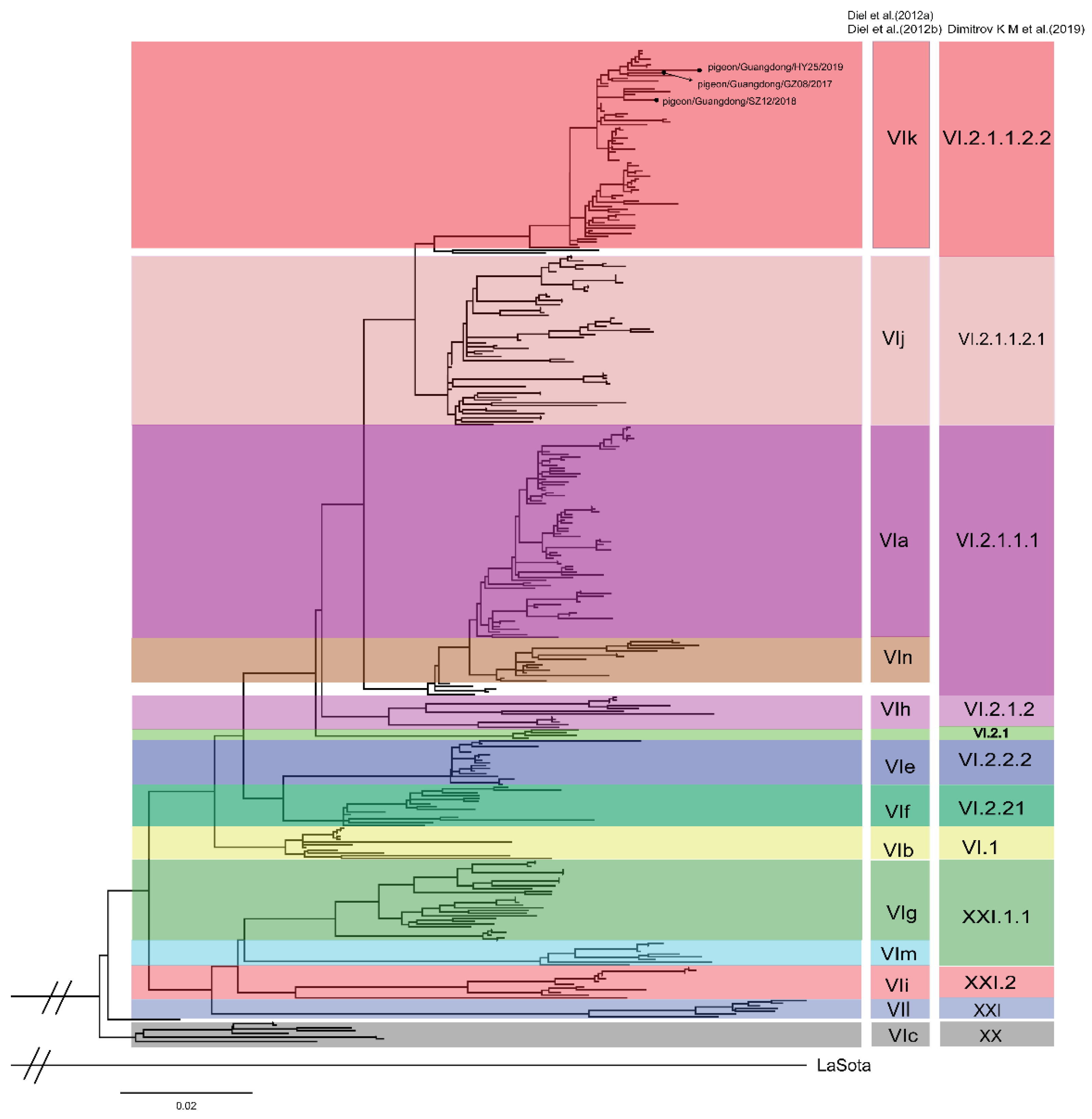
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
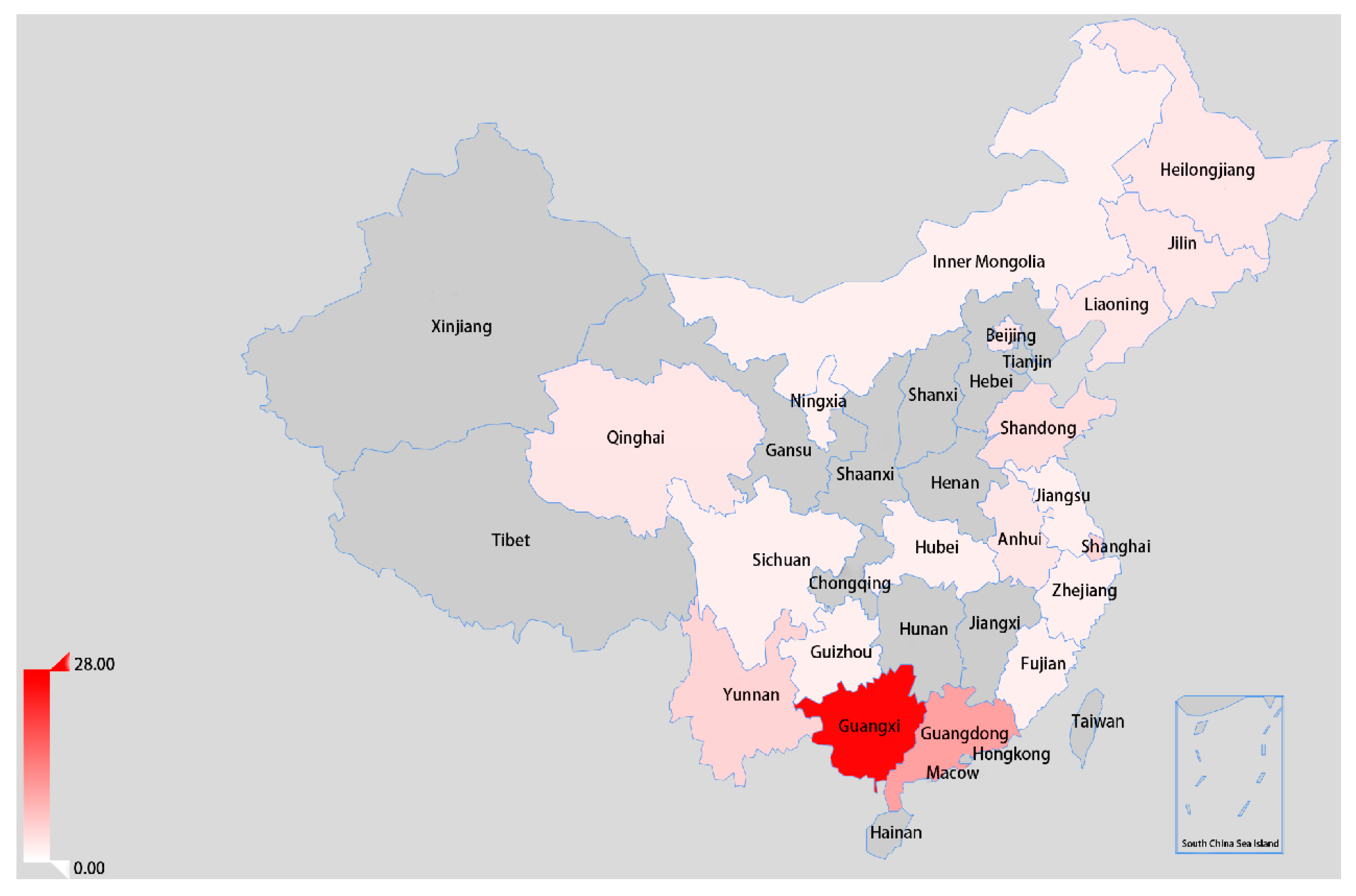
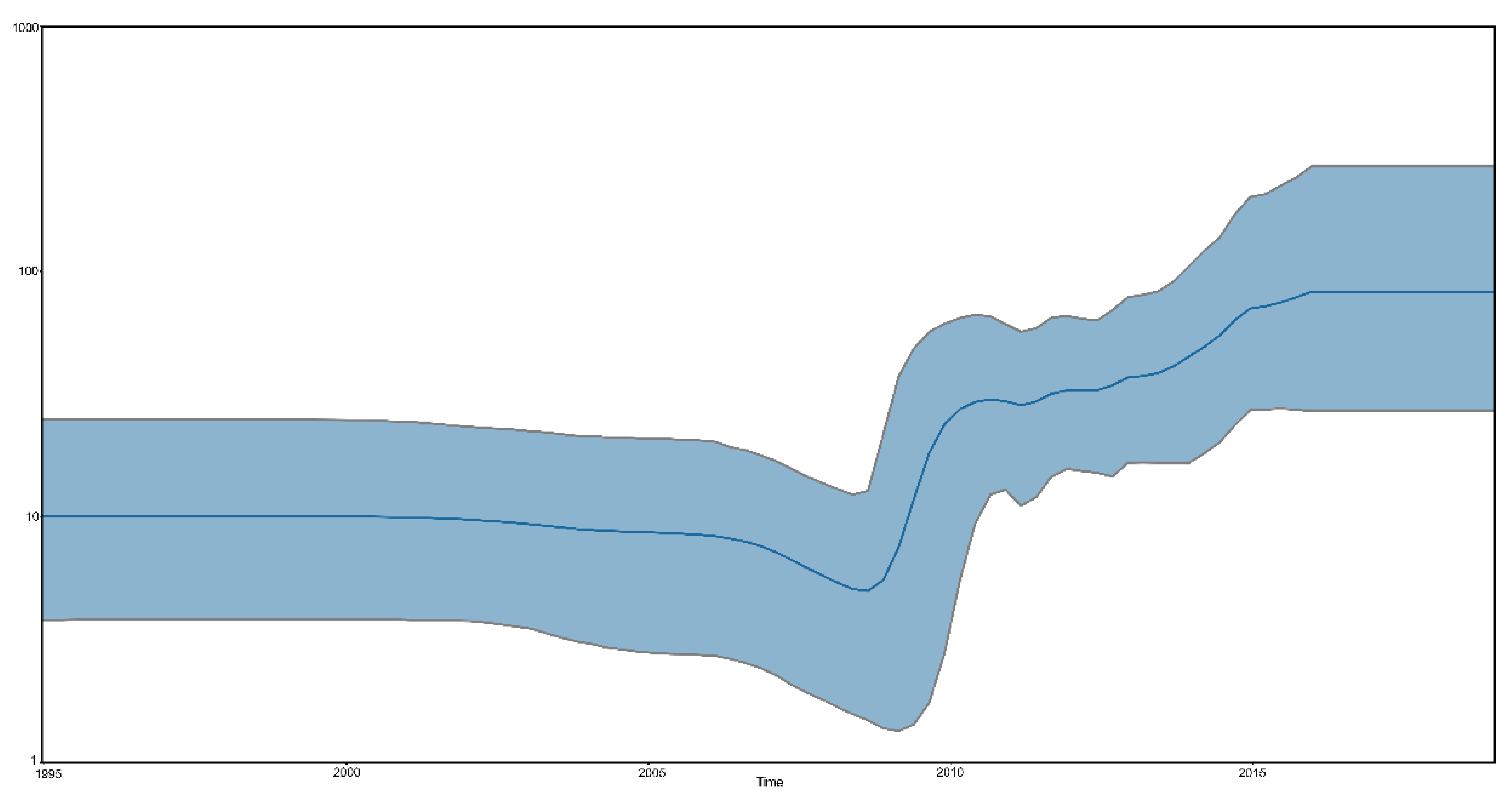
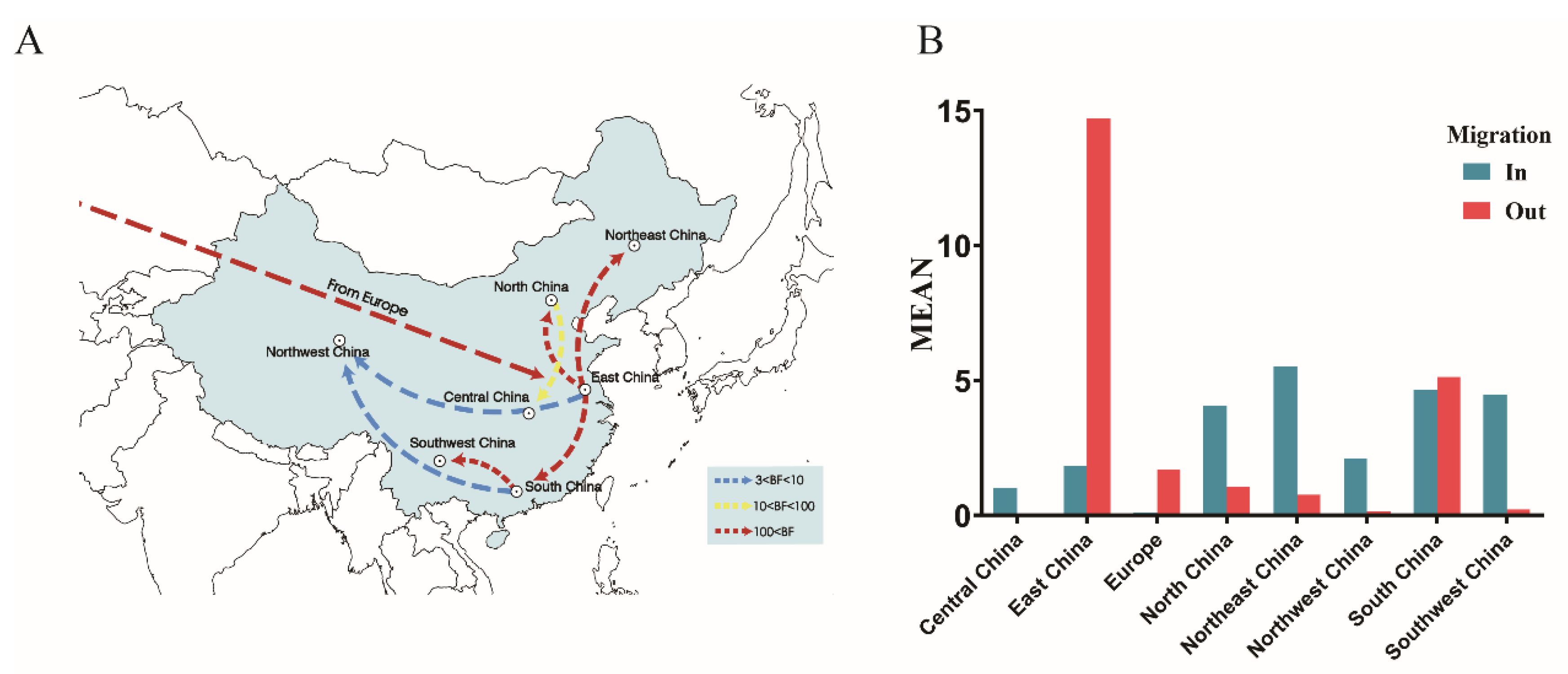
3.3. Spatial Dynamics of the VI.2.1.1.2.2 PPMV-1 Strains
3.4. Pathogenicity of the GZ08 Virus in 3-, 6-, and 12-Week-Old Pigeons
3.5. Transmission of PPMV-1 in 3-, 6-, and 12-Week-Old Pigeons
3.6. Cross-Reactivity HI Test
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, D.J. Newcastle Disease and Other Avian Paramyxoviruses. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2000, 19, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Abolnik, C.; Afonso, C.L.; Albina, E.; Bahl, J.; Berg, M.; Briand, F.X.; Brown, I.H.; Choi, K.S.; Chvala, I.; et al. Updated Unified Phylogenetic Classification System and Revised Nomenclature for Newcastle Disease Virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 74, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Ramey, A.M.; Qiu, X.; Bahl, J.; Afonso, C.L. Temporal, Geographic, and Host Distribution of Avian Paramyxovirus 1 (Newcastle Disease Virus). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldous, E.W.; Fuller, C.M.; Mynn, J.K.; Alexander, D.J. A Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Isolates of the Variant Avian Paramyxovirus Type 1 Virus (PPMV-1) Responsible for the 1978 to Present Panzootic in Pigeons. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.M.; King, D.J.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; da Rosa, A.P.T.; Bueno, R.; Dennett, J.A., Jr.; Afonso, C.L. Biological and Phylogenetic Characterization of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Serotype 1 Circulating in Wild North American Pigeons and Doves. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pchelkina, I.P.; Manin, T.B.; Kolosov, S.N.; Starov, S.K.; Andriyasov, A.V.; Chvala, I.A.; Drygin, V.V.; Yu, Q.; Miller, P.J.; Suarez, D.L. Characteristics of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Serotype-1 Isolates (PPMV-1) from the Russian Federation from 2001 to 2009. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleta, E.F.; Alexander, D.J.; Russell, P.H. The First Isolation of the Avian Pmv-1 Virus Responsible for the Current Panzootic in Pigeons ? Avian Pathol. 1985, 14, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortmans, J.C.; Rottier, P.J.; Koch, G.; Peeters, B.P. Passaging of a Newcastle Disease Virus Pigeon Variant in Chickens Results in Selection of Viruses with Mutations in the Polymerase Complex Enhancing Virus Replication and Virulence. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92 Pt 2, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.J. Newcastle Disease in the European Union 2000 to 2009. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H.L.; Taylor, T.L.; Absalon, A.E.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Cortés-Espinosa, D.V.; Butt, S.L.; Marín-Cruz, J.L.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Volkening, J.D.; Suarez, D.L.; et al. Presence of Newcastle Disease Viruses of Sub-Genotypes Vc and Vin in Backyard Chickens and in Apparently Healthy Wild Birds from Mexico in 2017. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Taylor, T.L.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Butt, S.L.; Stanton, J.B.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Fenton, H.; Poulson, R.; Zhang, J.; Brown, C.C.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Genotype Vi Newcastle Disease Viruses from Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues from Wild Pigeons Reveals Continuous Evolution and Previously Unrecognized Genetic Diversity in the U.S. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Xu, X.H.; Yin, R.F.; Qian, J.; Sun, Y.X.; Wang, C.F.; Ding, C.; Yu, S.Q.; Hu, S.L.; Liu, X.F.; et al. Identification and Pathotypical Analysis of a Novel Vik Sub-Genotype Newcastle Disease Virus Obtained from Pigeon in China. Virus Res. 2017, 238, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, M.; Gao, X.; et al. Phylogenetic and Pathogenic Characterization of a Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 Isolate Reveals Cross-Species Transmission and Potential Outbreak Risks in the Northwest Region of China. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2755–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smietanka, K.; Olszewska, M.; Domanska-Blicharz, K.; Bocian, A.L.; Minta, Z. Experimental Infection of Different Species of Birds with Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 Virus--Evaluation of Clinical Outcomes, Viral Shedding, and Distribution in Tissues. Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Son, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zheng, D.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y. Characterization of Pigeon-Origin Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated in China. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Li, J.; Wong, M.T.; Jiao, P.; Fan, H.; Liu, D.; Liao, M.; Jiang, J.; Shi, M.; Lam, T.T.; et al. Genetic Characterization and Evolutionary Analysis of 4 Newcastle Disease Virus Isolate Full Genomes from Waterbirds in South China During 2003–2007. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Shao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, S. Phylogenetic Analysis and Comparison of Eight Strains of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 (PPMV-1) Isolated in China between 2010 and 2012. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodovski, A.; Cvetkovikj, I.; Krstevski, K.; Naletoski, I.; Savic, V. Characterization and Epidemiology of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type-1 Viruses (PPMV-1) Isolated in Macedonia. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; You, R.; Kang, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhu, W.; Sun, M.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Ren, T. Host Immune Responses of Pigeons Infected with Newcastle Disease Viruses Isolated from Pigeons. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Qu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Sun, H. Genotypic and Pathotypic Characterization of Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from Racing Pigeons in China. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.B.; Liu, X.L.; Xu, Y.; Han, Z.X.; Shao, Y.H.; Kong, X.G.; Liu, S.W. A Comparative Study of Pigeons and Chickens Experimentally Infected with PPMV-1 to Determine Antigenic Relationships between PPMV-1 and NDV Strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, B.; Han, L.; Gao, P.; You, R.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.; Liao, M.; Kang, Y.; Ren, T. Spillover of Newcastle Disease Viruses from Poultry to Wild Birds in Guangdong Province, Southern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, R.; Li, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Feng, M.; Jiao, P.; Ren, T. Phylogenetic Relationships and Pathogenicity Variation of Two Newcastle Disease Viruses Isolated from Domestic Ducks in Southern China. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Meng, C.; Zhan, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Ren, T.; Yuan, W.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.; Tan, L.; et al. Phylogenetic, Antigenic and Biological Characterization of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 Circulating in China. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onorati, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Sousa, A.M.M.; Nakagawa, N.; Li, M.; Dell’Anno, M.T.; Gulden, F.O.; Pochareddy, S.; Tebbenkamp, A.T.N.; et al. Zika Virus Disrupts Phospho-TBK1 Localization and Mitosis in Human Neuroepithelial Stem Cells and Radial Glia. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2576–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-Tree: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Carvalho, L.M.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the Temporal Structure of Heterochronous Sequences Using Tempest (Formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian Phylogenetic and Phylodynamic Data Integration Using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. Modelfinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baele, G.; Lemey, P.; Bedford, T.; Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.A.; Alekseyenko, A.V. Improving the Accuracy of Demographic and Molecular Clock Model Comparison While Accommodating Phylogenetic Uncertainty. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemey, P.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A. Bayesian Phylogeography Finds Its Roots. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009, 5, e1000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielejec, F.; Baele, G.; Vrancken, B.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P. Spread3: Interactive Visualization of Spatiotemporal History and Trait Evolutionary Processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2167–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ge, S.; Lv, Y.; Zuo, Y.; et al. Genomic Characterizations of Six Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 Viruses Isolated from Live Bird Markets in China During 2011 to 2013. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archetti, I.; Horsfall, F.L., Jr. Persistent Antigenic Variation of Influenza a Viruses after Incomplete Neutralization in Ovo with Heterologous Immune Serum. J. Exp. Med. 1950, 92, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diel, D.G.; Susta, L.; Garcia, S.C.; Killian, M.L.; Brown, C.C.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. Complete Genome and Clinicopathological Characterization of a Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus Isolate from South America. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Deng, Q.; Li, H.; Pan, C.; Zhai, G.; Yuan, Y.; Cheng, E.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, M.; Huang, T.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Two Novel Sub-Sublineages of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 in China. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2971–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GenBank Overview. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/GenBank/ (accessed on 31 December 2019).
- Chong, Y.L.; Lam, T.T.; Kim, O.; Lu, H.; Dunn, P.; Poss, M. Successful Establishment and Global Dispersal of Genotype Vi Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype 1 after Cross Species Transmission. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 17, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.T.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Afonso, C.L.; Ramey, A.M.; Bahl, J. Global Phylodynamic Analysis of Avian Paramyxovirus-1 Provides Evidence of Inter-Host Transmission and Intercontinental Spatial Diffusion. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.; Kim, L.M.; Ip, H.S.; Afonso, C.L. Evolutionary Dynamics of Newcastle Disease Virus. Virology 2009, 391, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, A.M.; Reeves, A.B.; Ogawa, H.; Ip, H.S.; Imai, K.; Bui, V.N.; Yamaguchi, E.; Silko, N.Y.; Afonso, C.L. Genetic Diversity and Mutation of Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype 1 (Newcastle Disease Virus) in Wild Birds and Evidence for Intercontinental Spread. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Lee, D.H.; Williams-Coplin, D.; Olivier, T.L.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. Newcastle Disease Viruses Causing Recent Outbreaks Worldwide Show Unexpectedly High Genetic Similarity to Historical Virulent Isolates from the 1940s. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelb, J., Jr.; Fries, P.A.; Peterson, F.S. Pathogenicity and Cross-Protection of Pigeon Paramyxovirus-1 and Newcastle Disease Virus in Young Chickens. Avian Dis. 1987, 31, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Ferreira, H.L.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Taylor, T.L.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Crossley, B.M.; Killian, M.L.; Bergeson, N.H.; Torchetti, M.K.; Afonso, C.L.; et al. Pathogenicity and Transmission of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus from the 2018-2019 California Outbreak and Related Viruses in Young and Adult Chickens. Virology 2019, 531, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Xiang, B.; Yuan, R.; Zhao, X.; Feng, M.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ning, Z.; Ren, T. Phylogenetic and Pathotypic Characterization of Newcastle Disease Viruses Circulating in South China and Transmission in Different Birds. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Qiu, X.; Yu, S.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Tan, L.; Song, C.; et al. Evolution of Newcastle Disease Virus Quasispecies Diversity and Enhanced Virulence after Passage through Chicken Air Sacs. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, J.; Hu, S.; Song, Q.; Ding, P.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. High Levels of Virus Replication and an Intense Inflammatory Response Contribute to the Severe Pathology in Lymphoid Tissues Caused by Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype Viid. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoli, M.; Yeap, S.K.; Tan, S.W.; Moeini, H.; Ideris, A.; Bejo, M.H.; Alitheen, N.B.; Kaiser, P.; Omar, A.R. Alteration in Lymphocyte Responses, Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in Chickens Infected with Genotype Vii and Viii Velogenic Newcastle Disease Virus. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 37, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecco, R.; Brown, C.; Susta, L.; Cagle, C.; Cornax, I.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. In Vivo Transcriptional Cytokine Responses and Association with Clinical and Pathological Outcomes in Chickens Infected with Different Newcastle Disease Virus Isolates Using Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Samples. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 141, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xiang, B.; Li, Y.; Xie, P.; Gao, S.; Kang, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; et al. Generation and Evaluation of a Genetically Attenuated Newcastle Disease Virus Rgm-Viim as a Genotype-Matched Vaccine. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.; King, D.J.; Afonso, C.L.; Suarez, D.L. Antigenic Differences among Newcastle Disease Virus Strains of Different Genotypes Used in Vaccine Formulation Affect Viral Shedding after a Virulent Challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7238–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. A Vaccine Candidate of Attenuated Genotype Vii Newcastle Disease Virus Generated by Reverse Genetics. Vaccine 2009, 27, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.M.; Cheng, J.L.; Yu, X.H.; Qin, Z.M.; Tian, F.L.; Zhang, G.Z. Generation by Reverse Genetics of an Effective Attenuated Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Based on a Prevalent Highly Virulent Chinese Strain. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lu, B.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Liang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. Complete Genome Sequencing, Molecular Epidemiological, and Pathogenicity Analysis of Pigeon Paramyxoviruses Type 1 Isolated in Guangxi, China During 2012–2018. Viruses 2020, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model of Rate Variation | Coalescent Tree Prior | Log Marginal Likelihood (PS) | Log Marginal Likelihood (SS) | TMRCA (Year) | Substitution Rate (Subs/Site/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strict clock | Bayesian skyline | −5796.79 | −5796.03 | 1989 (1984–1993) | 1.317 × 10−3 (1.079 × 10−3–1.557 × 10−3) |
| Strict clock | Constant Size | 5803.62 | 5802.99 | 1987 (1983–1992) | 1.279 × 10−3 (1.047 × 10−3–1.516 × 10−3) |
| Strict clock | Exponential Growth | −5800.19 | −5800.65 | 1989 (1984–1993) | 1.309 × 10−3 (1.071 × 10−3–1.553 × 10−3) |
| Uncorrelated lognormal relaxed clock | Bayesian skyline | −5800.38 | −5799.56 | 1989 (1982–1996) | 1.352 × 10−3 (1.062 × 10−3–1.667 × 10−3) |
| Uncorrelated lognormal relaxed clock | Constant Size | −5809.58 | −5808.59 | 1985 (1975–1993) | 1.239 × 10−3 (9.598 × 10−4–1.515 × 10−3) |
| Uncorrelated lognormal relaxed clock | Exponential Growth | −5807.17 | −5805.57 | 1991 (1984–1999) | 1.355 × 10−3 (1.045 × 10−3–1.657 × 10−3) |
| From | To | Mean Migration Rate | BF a | Indicator b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South China | Northwest China | 0.580 | 3.460 | 0.355 |
| East China | Northwest China | 1.005 | 7.714 | 0.551 |
| North China | Central China | 0.828 | 33.919 | 0.844 |
| East China | North China | 3.900 | 320.421 | 0.981 |
| East China | South China | 4.441 | 324.242 | 0.981 |
| Europe | East China | 1.654 | 336.261 | 0.982 |
| East China | Northeast China | 5.140 | 920.264 | 0.993 |
| South China | Southwest China | 4.224 | 14,123.503 | 1.000 |
| Days Post-Inoculation (Number Positive/Total) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 17 | 21 | |||||||||
| OP | CL | OP | CL | OP | CL | OP | CL | OP | CL | OP | CL | OP | CL | OP | CL | ||
| 3 weeks | Infection a | 6/12 | 10/12 | 4/9 | 7/9 | 3/6 | 5/6 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 2/3 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Contact b | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 1/2 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 1/2 | 2/2 | 1/1 | 1/1 | - | - | |
| 6 weeks | Infection | 3/12 | 10/12 | 6/9 | 9/9 | 3/8 | 7/8 | 2/4 | 4/4 | 2/4 | 4/4 | 1/2 | 1/2 | - | - | - | - |
| Contact | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0/1 | 0/1 | |
| 12 weeks | Infection | 9/12 | 11/12 | 8/9 | 8/9 | 4/9 | 8/9 | 1/6 | 4/6 | 1/4 | 4/4 | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0/2 | 1/2 | 0/2 | 0/2 |
| Contact | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 2/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 | 2/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Ding, C.; Liao, M.; Xu, C.; Xiang, B.; Ren, T. Evolutionary Dynamics and Age-Dependent Pathogenesis of Sub-Genotype VI.2.1.1.2.2 PPMV-1 in Pigeons. Viruses 2020, 12, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040433
Xie P, Chen L, Zhang Y, Lin Q, Ding C, Liao M, Xu C, Xiang B, Ren T. Evolutionary Dynamics and Age-Dependent Pathogenesis of Sub-Genotype VI.2.1.1.2.2 PPMV-1 in Pigeons. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040433
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Peng, Libin Chen, Yifan Zhang, Qiuyan Lin, Chan Ding, Ming Liao, Chenggang Xu, Bin Xiang, and Tao Ren. 2020. "Evolutionary Dynamics and Age-Dependent Pathogenesis of Sub-Genotype VI.2.1.1.2.2 PPMV-1 in Pigeons" Viruses 12, no. 4: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040433
APA StyleXie, P., Chen, L., Zhang, Y., Lin, Q., Ding, C., Liao, M., Xu, C., Xiang, B., & Ren, T. (2020). Evolutionary Dynamics and Age-Dependent Pathogenesis of Sub-Genotype VI.2.1.1.2.2 PPMV-1 in Pigeons. Viruses, 12(4), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040433




