The Detection and Association of Canine Papillomavirus with Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions in Dogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Ethical Approval
2.2. DNA Extraction from FFPE Tissue
2.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for the Detection of CPVs
2.4. Sequence Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemistry Staining of Viral Antigens
3. Results
3.1. Case Information and Histological Findings
3.2. Molecular Viral Investigation
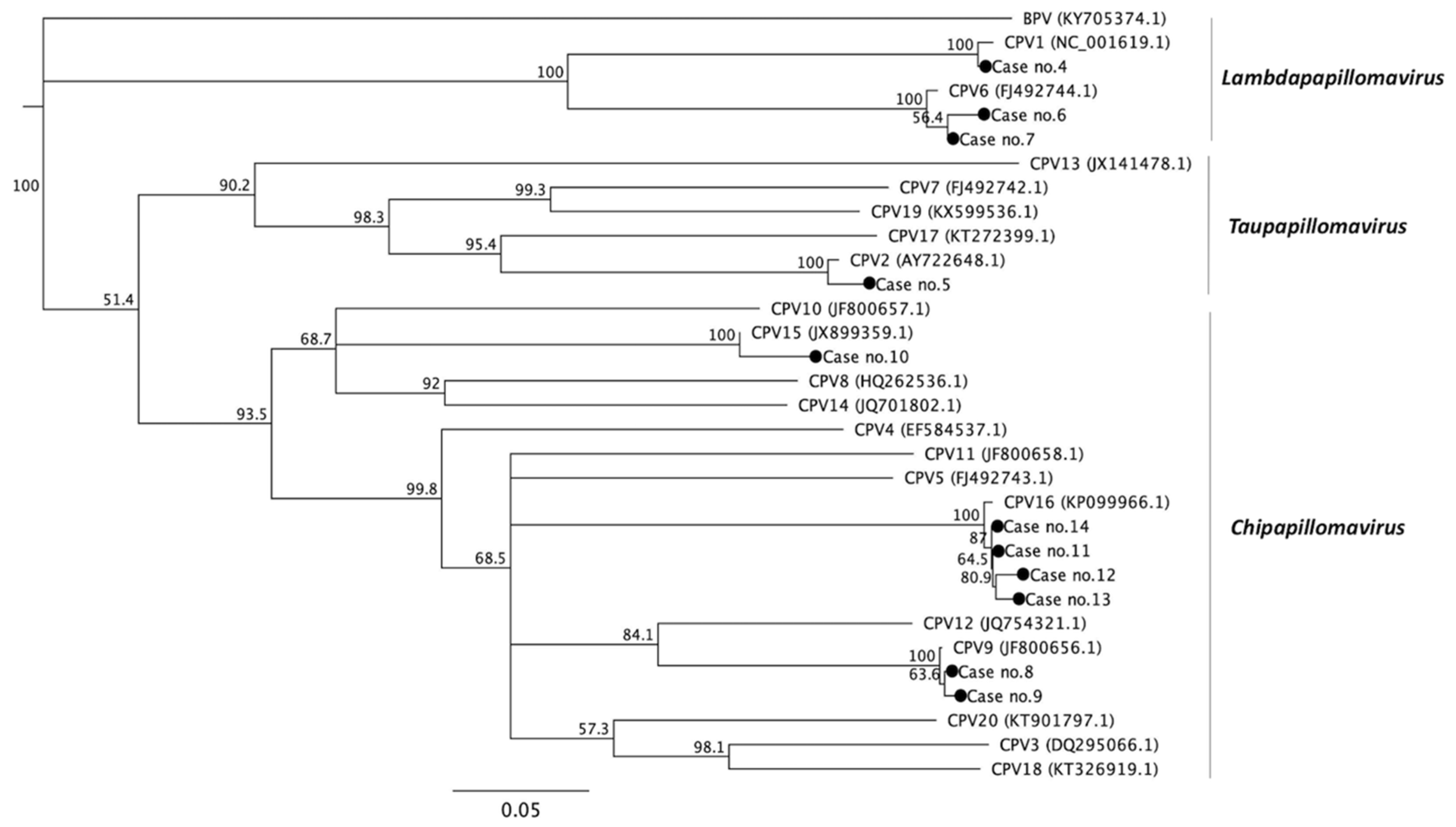
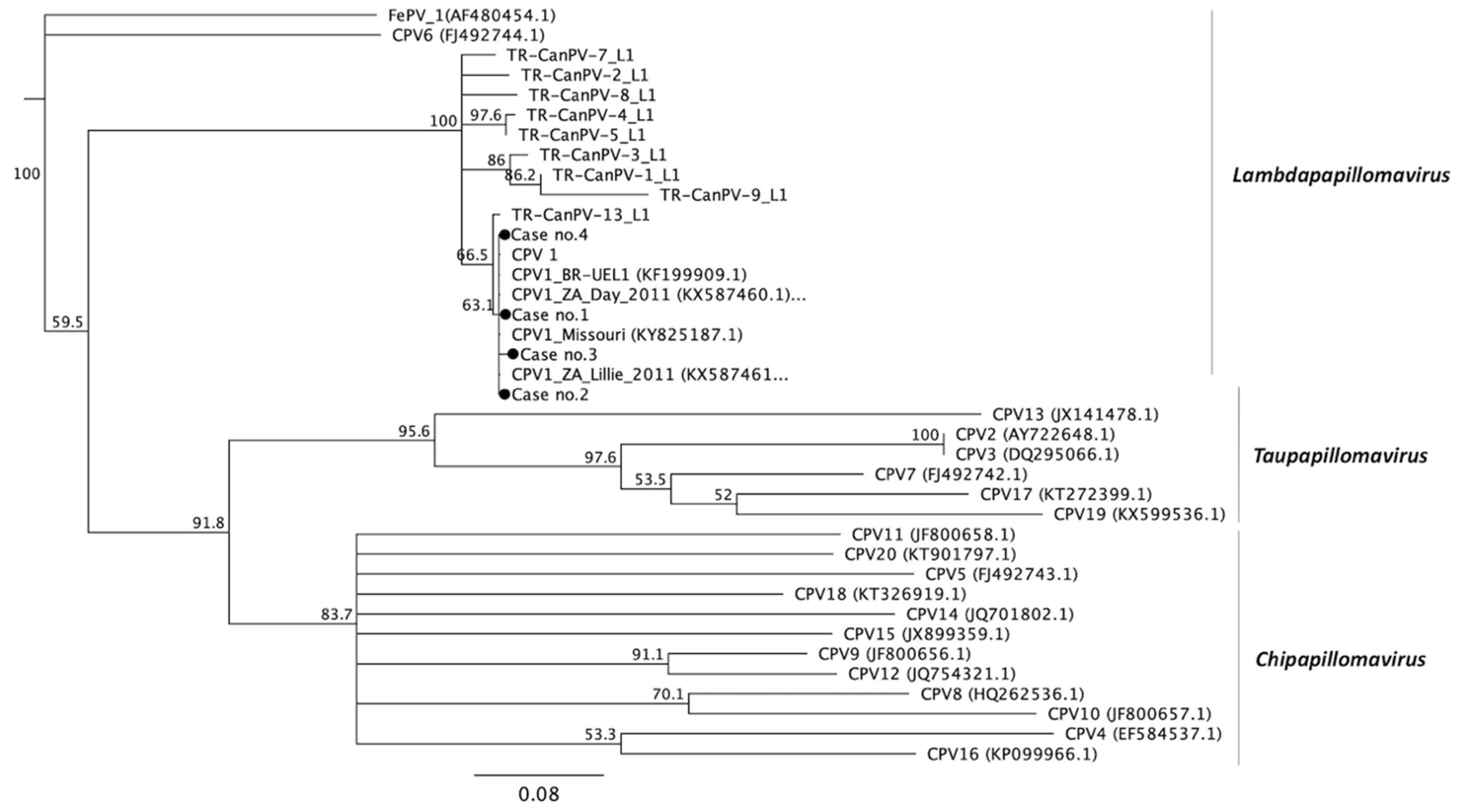
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
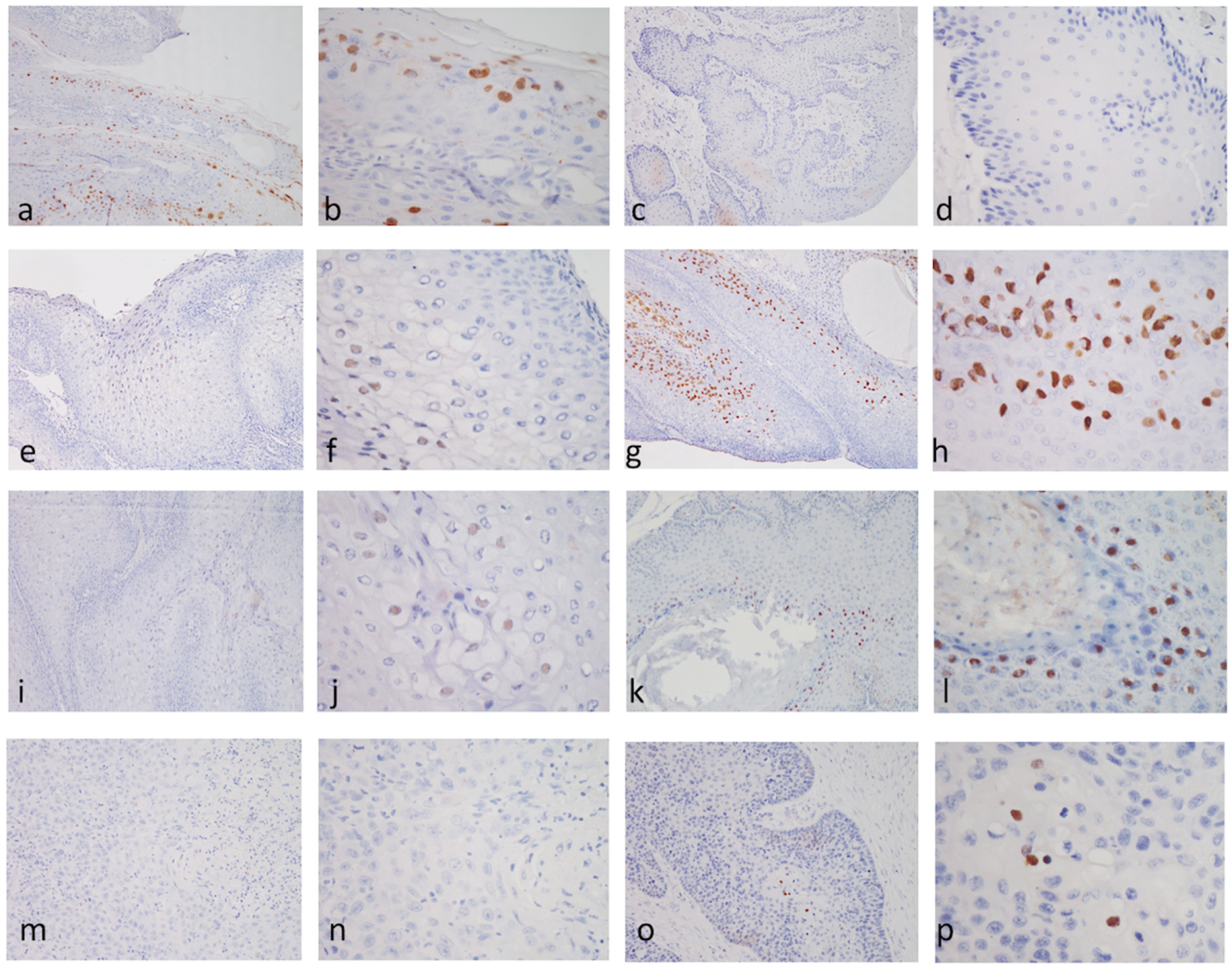
3.4. Immunohistochemical Staining (IHC) for the Antigens of Papillomavirus
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gil da Costa, R.M.; Peleteiro, M.C.; Pires, M.A.; DiMaio, D. An Update on Canine, Feline and Bovine Papillomaviruses. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J. The papillomavirus life cycle. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 32, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rector, A.; Van Ranst, M. Animal papillomaviruses. Virology 2013, 445, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, G.; Ellsmore, V.A.; O’Brien, P.M.; Reid, S.W.; Love, S.; Campo, M.S.; Nasir, L. Association of bovine papillomavirus with the equine sarcoid. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcântara, B.K.d.; Alfieri, A.A.; Headley, S.A.; B.Rodrigues, W.; Otonel, R.A.A.; Lunardi, M.; Alfieri, A.F. Caracterização molecular de DNA de Delta papillomavirus bovino (BPV1, 2 e 13) em sarcoides equinos. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2015, 35, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Araldi, R.P.; Assaf, S.M.R.; Carvalho, R.F.; Carvalho, M.; Souza, J.M.; Magnelli, R.F.; Modolo, D.G.; Roperto, F.P.; Stocco, R.C.; Becak, W. Papillomaviruses: A systematic review. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maver, P.J.; Poljak, M. Progress in prophylactic human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in 2016: A literature review. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5416–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Dillner, J. The Launch of an International Animal Papillomavirus Reference Center. Viruses 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillison, M.L.; Koch, W.M.; Capone, R.B.; Spafford, M.; Westra, W.H.; Wu, L.; Zahurak, M.L.; Daniel, R.W.; Viglione, M.; Symer, D.E.; et al. Evidence for a Causal Association Between Human Papillomavirus and a Subset of Head and Neck Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.E.; Tobler, K.; Markau, T.; Alhaidari, Z.; Bornand, V.; Stockli, R.; Trussel, M.; Ackermann, M.; Favrot, C. Sequence and classification of FdPV2, a papillomavirus isolated from feline Bowenoid in situ carcinomas. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravens, P.A.; Vogelnest, L.J.; Tong, L.J.; Demos, L.E.; Bennett, M.D. Papillomavirus-associated multicentric squamous cell carcinoma in situ in a cat: An unusually extensive and progressive case with subsequent metastasis. Vet. Derm. 2013, 24, 642–645, e161-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part B: Biological agents. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnenmacher, M.; Salmon, J.; Jacob, Y.; Orth, G.; Breitburd, F. Cottontail rabbit papillomavirus E8 protein is essential for wart formation and provides new insights into viral pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4890–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.V. Keratinocyte Differentiation-Dependent Human Papillomavirus Gene Regulation. Viruses 2017, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J.; Quint, W.; Banks, L.; Bravo, I.G.; Stoler, M.; Broker, T.R.; Stanley, M.A. The biology and life-cycle of human papillomaviruses. Vaccine 2012, 30, F55–F70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J.; Egawa, N.; Griffin, H.; Kranjec, C.; Murakami, I. Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease association. Rev. Med. Virol. 2015, 25, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, I.; Trave, G. Structural Insights in Multifunctional Papillomavirus Oncoproteins. Viruses 2018, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrich, J.A.; Warren, C.J.; Pyeon, D. Evasion of host immune defenses by human papillomavirus. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.E.; Diallo, A.; Zewe, C.; Ferrer, L. Novel canine papillomavirus type 18 found in pigmented plaques. Papillomavirus Res. 2016, 2, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, J.S.; Thomson, N.A.; Luff, J.A. Papillomaviruses in dogs and cats. Vete. J. 2017, 225, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisza, M.J.; Yuan, H.; Schlegel, R.; Buck, C.B. Genomic Sequence of Canine Papillomavirus 19. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, C.E.; Ackermann, M.; Favrot, C.; Tobler, K. Entire Genomic Sequence of Novel Canine Papillomavirus Type 13. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10226–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, P.K.; Klaunberg, B.A.; Moore, R.A.; Santos, E.B.; Parry, N.R.; Gough, G.W.; Stanley, M.A. Naturally Occurring, Nonregressing Canine Oral Papillomavirus Infection: Host Immunity, Virus Characterization, and Experimental Infection. Virology 1999, 265, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.E.; Weese, J.S.; Stull, J.W. Canine oral papillomavirus outbreak at a dog daycare facility. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2017, 58, 747–749. [Google Scholar]
- Yhee, J.Y.; Kwon, B.J.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, C.H.; Im, K.S.; Lee, S.S.; Lyoo, Y.S.; Chang, B.J.; Sur, J.H. Characterization of canine oral papillomavirus by histopathological and genetic analysis in Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 11, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regalado Ibarra, A.M.; Legendre, L.; Munday, J.S. Malignant Transformation of a Canine Papillomavirus Type 1-Induced Persistent Oral Papilloma in a 3-Year-Old Dog. J. Vet. Dent. 2018, 35, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaiwong, T.; Sledge, D.G.; Wise, A.G.; Olstad, K.; Maes, R.K.; Kiupel, M. Malignant transformation of canine oral papillomavirus (CPV1)-associated papillomas in dogs: An emerging concern? Papillomavirus Res. (Amst. Neth.) 2018, 6, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, J.S.; Dunowska, M.; Laurie, R.E.; Hills, S. Genomic characterisation of canine papillomavirus type 17, a possible rare cause of canine oral squamous cell carcinoma. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luff, J.; Rowland, P.; Mader, M.; Orr, C.; Yuan, H. Two Canine Papillomaviruses Associated With Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Two Related Basenji Dogs. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ghim, S.; Newsome, J.; Apolinario, T.; Olcese, V.; Martin, M.; Delius, H.; Felsburg, P.; Jenson, B.; Schlegel, R. An epidermotropic canine papillomavirus with malignant potential contains an E5 gene and establishes a unique genus. Virology 2007, 359, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, K.; Favrot, C.; Nespeca, G.; Ackermann, M. Detection of the prototype of a potential novel genus in the family Papillomaviridae in association with canine epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, C.E.; Tobler, K.; Ackermann, M.; Panakova, L.; Thoday, K.L.; Favrot, C. Three novel canine papillomaviruses support taxonomic clade formation. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschmidt, M.H.; Kennedy, J.S.; Kennedy, D.R.; Yuan, H.; Holt, D.E.; Casal, M.L.; Traas, A.M.; Mauldin, E.A.; Moore, P.F.; Henthorn, P.S.; et al. Severe papillomavirus infection progressing to metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in bone marrow-transplanted X-linked SCID dogs. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6621–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, C.E.; Zollinger, S.; Tobler, K.; Ackermann, M.; Favrot, C. Clinically healthy skin of dogs is a potential reservoir for canine papillomaviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, K.; Fritsche, J.; Mueller, N.; Koerschge, B.; Dierig, B.; Strebelow, G.; Teifke, J.P. Detection of Canine Oral Papillomavirus DNA in Conjunctival Epithelial Hyperplastic Lesions of Three Dogs. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinform 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckwith-Cohen, B.; Teixeira, L.B.; Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Dubielzig, R.R. Squamous Papillomas of the Conjunctiva in Dogs: A Condition Not Associated with Papillomavirus Infection. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roperto, S.; Borzacchiello, G.; Esposito, I.; Riccardi, M.; Urraro, C.; Luca, R.; Corteggio, A.; Tate, R.; Cermola, M.; Paciello, O.; et al. Productive infection of bovine papillomavirus type 2 in the placenta of pregnant cows affected with urinary bladder tumors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, D.-G.; Sim, C.-H.; Lee, T.-J.; Kong, J.-Y.; Hong, I.-H. Sebaceous cell differentiation in a canine oral papilloma. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.E.; Jennings, S.H.; Diallo, A.; Lyons, J. Canine papillomavirus types 1 and 2 in classical papillomas: High abundance, different morphological associations and frequent co-infections. Vet. J. 2019, 250, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, R.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Hoffman, E.M.; Stacy, B.A.; Jensen, E.D.; Nollens, H.H.; Wellehan, J.F.X. Characterization of a novel papillomavirus species (ZcPV1) from two California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 155, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, V.; Mascaux, C.; Weyn, C.; Bernis, A.; Celio, N.; Lefevre, P.; Kaufman, L.; Garbar, C. Evaluation of combined general primer-mediated PCR sequencing and type-specific PCR strategies for determination of human papillomavirus genotypes in cervical cell specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftner, A.; Klug, S.J.; Garbe, C.; Blum, A.; Stancu, A.; Wilczynski, S.P.; Iftner, T. The Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Genotypes in Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers of Nonimmunosuppressed Individuals Identifies High-Risk Genital Types as Possible Risk Factors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Fairley, R.A.; Mills, H.; Kiupel, M.; Vaatstra, B.L. Oral Papillomas Associated With Felis catus Papillomavirus Type 1 in 2 Domestic Cats. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita-Kawanishi, N.; Sawanobori, R.; Matsumiya, K.; Uema, A.; Chambers, J.K.; Uchida, K.; Shimakura, H.; Tsuzuki, M.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chang, H.-W.; et al. Detection of felis catus papillomavirus type 3 and 4 DNA from squamous cell carcinoma cases of cats in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Dittmer, K.E.; Thomson, N.A.; Hills, S.F.; Laurie, R.E. Genomic characterisation of Felis catus papillomavirus type 5 with proposed classification within a new papillomavirus genus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinau, M.; Patel, S.S.; Unger, E.R. Efficient DNA Extraction for HPV Genotyping in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 13, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, I.; Brachelente, C.; Guelfi, G.; Reginato, A.; Sforna, M.; Bongiovanni, L.; Mechelli, L. A Retrospective Investigation on Canine Papillomavirus 1 (CPV1) in Oral Oncogenesis Reveals Dogs Are Not a Suitable Animal Model for High-Risk HPV-Induced Oral Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, J.S.; French, A.; Harvey, C.J. Molecular and immunohistochemical studies do not support a role for papillomaviruses in canine oral squamous cell carcinoma development. Veterinary J. (Lond. Engl. 1997) 2015, 204, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.E.; Tobler, K.; Favrot, C.; Muller, M.; Nothling, J.O.; Ackermann, M. Detection of antibodies against epidermodysplasia verruciformis-associated canine papillomavirus 3 in sera of dogs from Europe and Africa by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altan, E.; Seguin, M.A.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Phan, T.G.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E. Nasal virome of dogs with respiratory infection signs include novel taupapillomaviruses. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luff, J.; Mader, M.; Rowland, P.; Britton, M.; Fass, J.; Yuan, H. Viral genome integration of canine papillomavirus 16. Papillomavirus Res. (Amst. Neth.) 2019, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| CP4/5 | Forward: 5′-ATGGTACARTGGGCATWTGA-3′ Reverse: 5′-GAGGYTGCAACCAAAAMTGRCT-3′ |
| COPV L1+/− | Forward: 5′-CTTGTTTGGGGCTTAAGAGG-3′ Reverse: 5′-TGCAGTGTGTACCTGTCCTG-3′ |
| GAPDH | Forward: 5′-AGGCTGAGAACGGGAAACTT-3′ Reverse: 5′-TTTGGCTAGAGGAGCCAAGC-3′ |
| Case No. | Breed | Age | Location | Histopathological Diagnosis | Type of PVs | Gene Identity | IHC | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mixed | 5y | Gingiva | Viral papilloma | CPV 1 | 100% | + | MN617831 |
| 2 | Mixed | 5y | Lip | Viral papilloma | CPV 1 | 100% | + | MN617832 |
| 3 | Corgi | NE | Oral | Papilloma | CPV 1 | 99.5% | + | MN617833 |
| 4 | Poodle | 6y | Digital Lip | Papilloma Acanthosis | CPV 1 | 99.5% | - | MN617834 MN586852 |
| 5 | Golden retriever | 8y | Elbow | Viral papilloma | CPV 2 | 98.5% | + | MN606026 |
| 6 | Pomeranian | 6y | Digital | Inverted papilloma | CPV 6 | 97.4% | + | MN606027 |
| 7 | Schnauzer | 7y | Paw | Viral papilloma | CPV 6 | 99.2% | + | MN606028 |
| 8 | Unknown | 9y | Digital | Viral papilloma | CPV 9 | 99.7% | + | MN606029 |
| 9 | Schnauzer | 11y | Inguinal Flank | Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) Cutaneous horn Papilloma | CPV 9 | 99.5% | + | MN606030 |
| 10 | Poodle | 7y | Digital | Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma | CPV 15 | 97.9% | + | MN606031 |
| 11 | Mixed | 6y | Inguinal | Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) | CPV 16 | 99.5% | + | MN606032 |
| 12 | Maltese | 8y | Gingiva | Dysplasia of squamous epithelium | CPV 16 | 98.7% | - | MN606033 |
| 13 | Golden retriever | 14y | Sublingual | Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) | CPV 16 | 98.7% | - | MN606034 |
| 14 | Mixed | 6y | Inguinal | Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) | CPV 16 | 99.5% | - | MN606035 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-T.; Haga, T.; Yamashita, N.; Lee, C.-F.; Tsuzuki, M.; Chang, H.-W. The Detection and Association of Canine Papillomavirus with Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions in Dogs. Viruses 2020, 12, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020170
Chang C-Y, Chen W-T, Haga T, Yamashita N, Lee C-F, Tsuzuki M, Chang H-W. The Detection and Association of Canine Papillomavirus with Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions in Dogs. Viruses. 2020; 12(2):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020170
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Chia-Yu, Wei-Tao Chen, Takeshi Haga, Nanako Yamashita, Chi-Fen Lee, Masano Tsuzuki, and Hui-Wen Chang. 2020. "The Detection and Association of Canine Papillomavirus with Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions in Dogs" Viruses 12, no. 2: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020170
APA StyleChang, C.-Y., Chen, W.-T., Haga, T., Yamashita, N., Lee, C.-F., Tsuzuki, M., & Chang, H.-W. (2020). The Detection and Association of Canine Papillomavirus with Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions in Dogs. Viruses, 12(2), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12020170





