The Unknown Unknowns: Recovering Gamma-Delta T Cells for Control of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Abstract
:Reports that say that something hasn’t happened are always interesting to me, because as we know, there are known knowns; there are things we know we know. We also know there are known unknowns; that is to say we know there are some things we do not know. But there are also unknown unknowns—the ones we don’t know we don’t know. And if one looks throughout the history of our country and other free countries, it is the latter category that tends to be the difficult ones. United States Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld; 12 February 2002.
1. Introduction
2. Phenotypic and Functional Subsets of γδ T Cells
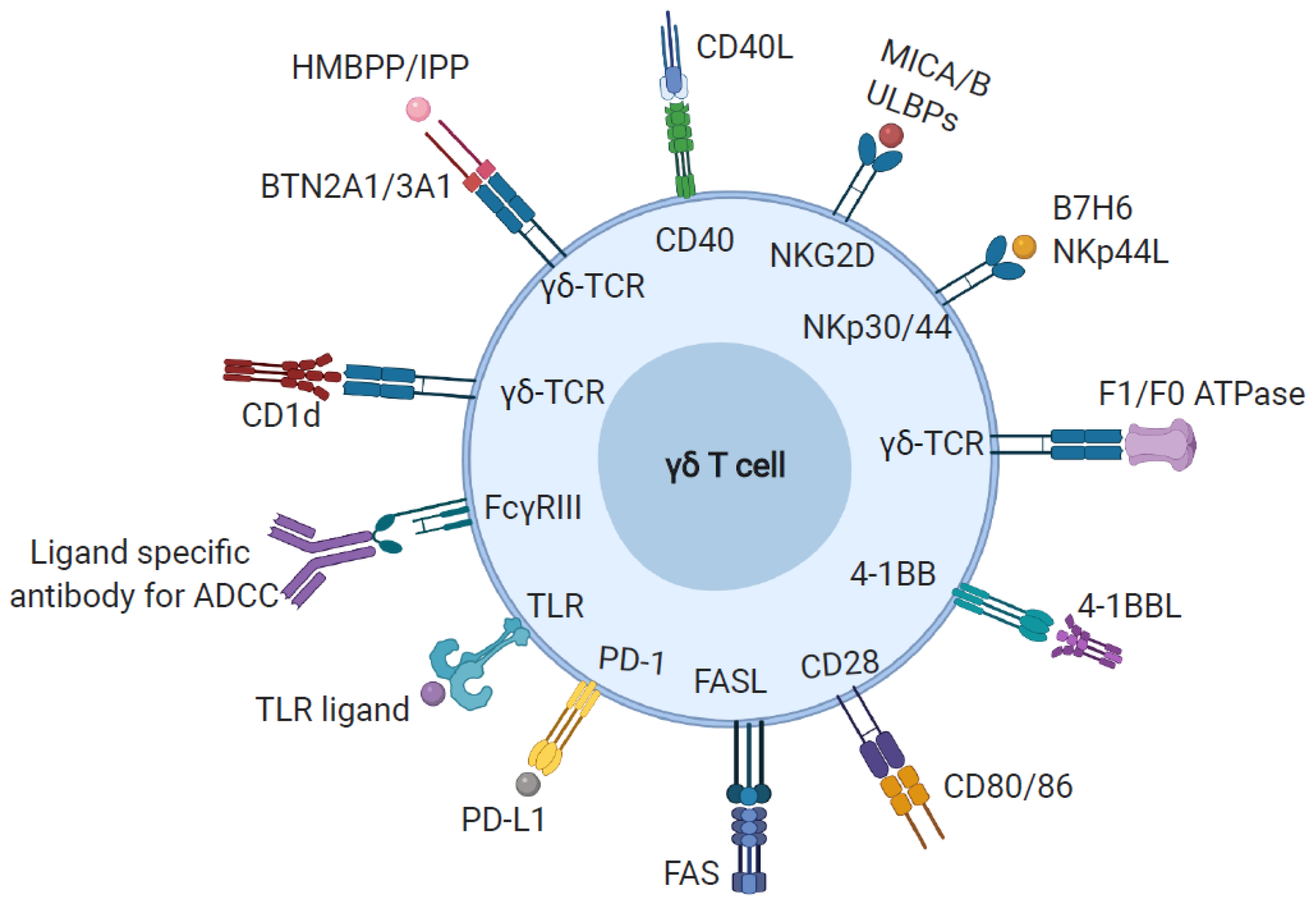
3. Ligand Recognition by γδ T Cells
3.1. Phosphoantigen
3.2. MHC-Like Ligands
3.3. Other Cell Surface and Soluble Proteins
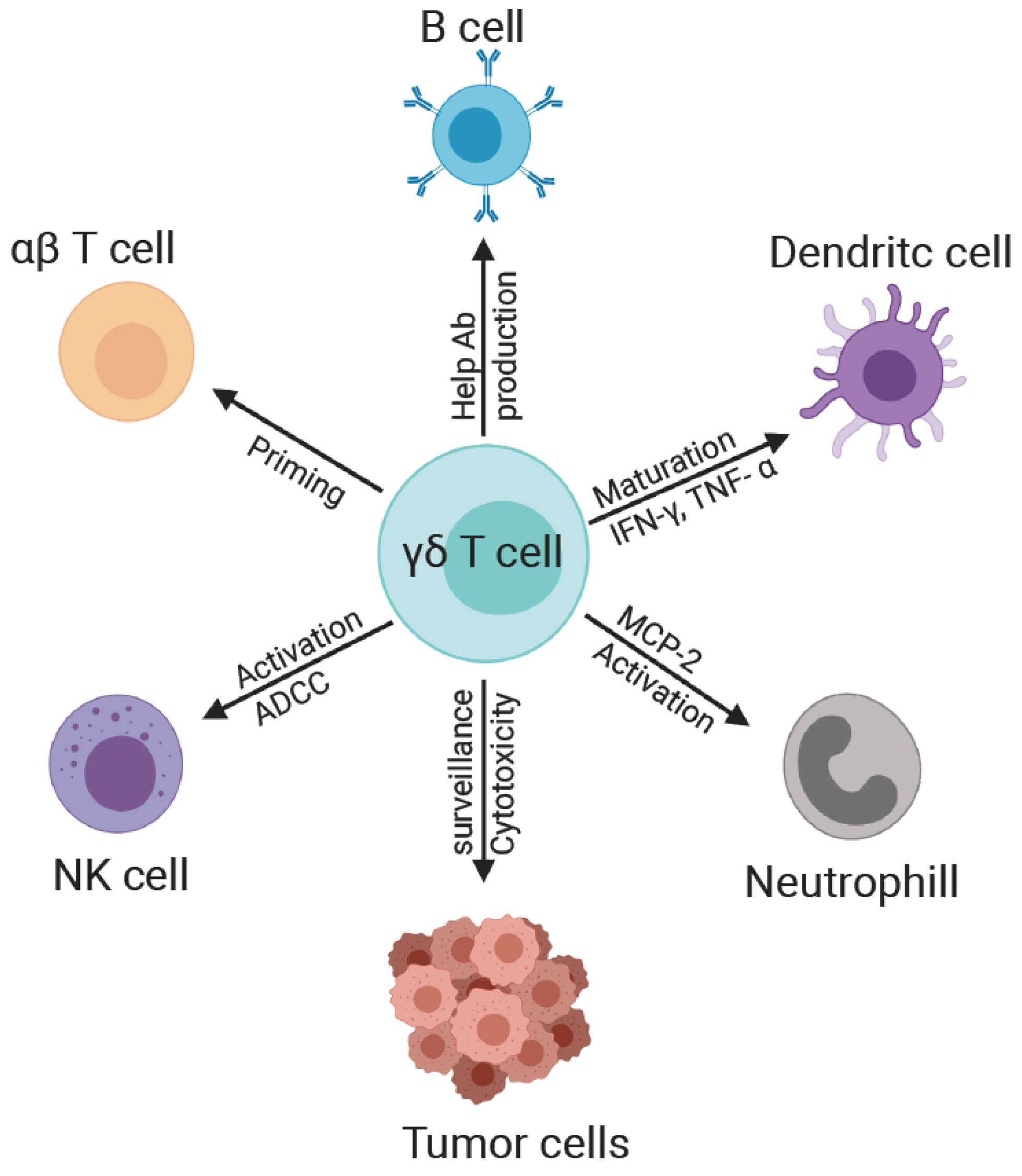
4. γδ T Cell Interaction with Other Immune Cells
4.1. γδ and NK Cells
4.2. γδ and B Cells
4.3. γδ and Monocyte/Macrophages
4.4. γδ and Dendritic Cells
4.5. γδ T and αβ T Cells
5. γδ T Cells in HIV-1 Infection
5.1. Impact of HIV on γδ T Cells
5.2. Impact of γδ T Cell Perturbations on Immune Control of HIV
5.3. γδ T Cell Contribution to HIV Reservoirs
5.4. Impact of Anti-Retroviral Therapy on γδ T Cells in HIV-Infection
5.5. γδ T Cells in HIV Immunotherapy
6. Into the Unknown with γδ T Cells
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, S.; Nawrocka, W.; Adams, E.J. Sensing of Pyrophosphate Metabolites by Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caccamo, N.; Dieli, F.; Wesch, D.; Jomaa, H.; Eberl, M. Sex-specific phenotypical and functional differences in peripheral human Vγ9/Vδ2 T-cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneville, M.; O’Brien, R.L.; Born, W.K. Gammadelta T-cell effector functions: A blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegers, G.M.; Lamb, L.S., Jr. Cytotoxic and regulatory properties of circulating Vdelta1+ gammadelta T-cells: A new player on the cell therapy field? Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenna, T.; Golden-Mason, L.; Norris, S.; Hegarty, J.E.; O’Farrelly, C.; Doherty, D.G. Distinct subpopulations of gamma delta T-cells are present in normal and tumor-bearing human liver. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, M.R.; Elliott, L.; Hussey, S.; Mahmud, N.; Kelly, J.; Doherty, D.G.; Feighery, C.F. Persistent changes in circulating and intestinal gammadelta T-cell subsets, invariant natural killer T-cells and mucosal-associated invariant T-cells in children and adults with coeliac disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allison, T.J.; Winter, C.C.; Fournie, J.J.; Bonneville, M.; Garboczi, D.N. Structure of a human gammadelta T-cell antigen receptor. Nature 2001, 411, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dechanet, J.; Merville, P.; Lim, A.; Retiere, C.; Pitard, V.; Lafarge, X.; Michelson, S.; Meric, C.; Hallet, M.M.; Kourilsky, P.; et al. Implication of gammadelta T-cells in the human immune response to cytomegalovirus. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartkowiak, J.; Kulczyck-Wojdala, D.; Blonski, J.Z.; Robak, T. Molecular diversity of gammadelta T-cells in peripheral blood from patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Neoplasma 2002, 49, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Petrasca, A.; Melo, A.M.; Breen, E.P.; Doherty, D.G. Human Vdelta3(+) gammadelta T-cells induce maturation and IgM secretion by B cells. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 196, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, B.A.; Dunne, M.R.; O’Reilly, V.P.; Dunne, P.J.; Exley, M.A.; O’Shea, D.; Scotet, E.; Hogan, A.E.; Doherty, D.G. Cutting edge: CD1d restriction and Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokine secretion by human Vdelta3 T-cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, C.; Zhu, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y. The feature of distribution and clonality of TCR gamma/delta subfamilies T-cells in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 241246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wesch, D.; Glatzel, A.; Kabelitz, D. Differentiation of resting human peripheral blood gamma delta T-cells toward Th1- or Th2-phenotype. Cell Immunol. 2001, 212, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Wu, D.; Ni, C.; Ye, J.; Chen, W.; Hu, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, W.; et al. γδT17 cells promote the accumulation and expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in human colorectal cancer. Immunity 2014, 40, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zocchi, M.R.; Ferrarini, M.; Rugarli, C. Selective lysis of the autologous tumor by delta TCS1+ gamma/delta+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from human lung carcinomas. Eur. J. Immunol. 1990, 20, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couzi, L.; Pitard, V.; Sicard, X.; Garrigue, I.; Hawchar, O.; Merville, P.; Moreau, J.F.; Déchanet-Merville, J. Antibody-dependent anti-cytomegalovirus activity of human γδ T-cells expressing CD16 (FcγRIIIa). Blood 2012, 119, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fausther-Bovendo, H.; Wauquier, N.; Cherfils-Vicini, J.; Cremer, I.; Debré, P.; Vieillard, V. NKG2C is a major triggering receptor involved in the V[delta]1 T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against HIV-infected CD4 T-cells. Aids 2008, 22, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, B.; Pauza, C.D. Gamma delta T-cells from HIV+ donors can be expanded in vitro by zoledronate/interleukin-2 to become cytotoxic effectors for antibody-dependenT-cellular cytotoxicity. Cytotherapy 2012, 14, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrasca, A.; Doherty, D.G. Human Vδ2(+) γδ T-cells Differentially Induce Maturation, Cytokine Production, and Alloreactive T-cell Stimulation by Dendritic Cells and B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maniar, A.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Gastman, B.R.; Pauza, C.D.; Strome, S.E.; Chapoval, A.I. Human gammadelta T lymphocytes induce robust NK cell-mediated antitumor cytotoxicity through CD137 engagement. Blood 2010, 116, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Ding, Y.P.; Tanaka, Y.; Shen, L.W.; Wei, C.H.; Minato, N.; Zhang, W. gammadelta T-cells and their potential for immunotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehner, T.; Mitchell, E.; Bergmeier, L.; Singh, M.; Spallek, R.; Cranage, M.; Hall, G.; Dennis, M.; Villinger, F.; Wang, Y. The role of gammadelta T-cells in generating antiviral factors and beta-chemokines in protection against mucosal simian immunodeficiency virus infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2245–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, J.F.; Morita, C.T.; Tanaka, Y.; Bloom, B.R.; Brenner, M.B.; Band, H. V gamma 2V delta 2 TCR-dependent recognition of non-peptide antigens and Daudi cells analyzed by TCR gene transfer. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gober, H.J.; Kistowska, M.; Angman, L.; Jeno, P.; Mori, L.; De Libero, G. Human T-cell receptor gammadelta cells recognize endogenous mevalonate metabolites in tumor cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigau, M.; Ostrouska, S.; Fulford, T.S.; Johnson, D.N.; Woods, K.; Ruan, Z.; McWilliam, H.E.G.; Hudson, C.; Tutuka, C.; Wheatley, A.K.; et al. Butyrophilin 2A1 is essential for phosphoantigen reactivity by gammadelta T-cells. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.A.; Reith, W.; Trowsdale, J. Regulation of Immunity by Butyrophilins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agea, E.; Russano, A.; Bistoni, O.; Mannucci, R.; Nicoletti, I.; Corazzi, L.; Postle, A.D.; De Libero, G.; Porcelli, S.A.; Spinozzi, F. Human CD1-restricted T-cell recognition of lipids from pollens. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Born, W.K.; Kemal, M.A.; O’Brien, R.L. Diversity of gammadelta T-cell antigens. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scotet, E.; Martinez, L.O.; Grant, E.; Barbaras, R.; Jeno, P.; Guiraud, M.; Monsarrat, B.; Saulquin, X.; Maillet, S.; Esteve, J.P.; et al. Tumor recognition following Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cell receptor interactions with a surface F1-ATPase-related structure and apolipoprotein A-I. Immunity 2005, 22, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rust, C.J.; Verreck, F.; Vietor, H.; Koning, F. Specific recognition of staphylococcal enterotoxin A by human T-cells bearing receptors with the V gamma 9 region. Nature 1990, 346, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ziegler, H.K.; Safley, S.A.; Niesel, D.W.; Vaidya, S.; Klimpel, G.R. Human T-cell recognition of Listeria monocytogenes: Recognition of listeriolysin O by TcR alpha beta + and TcR gamma delta + T-cells. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 2288–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozbor, D.; Trinchieri, G.; Monos, D.S.; Isobe, M.; Russo, G.; Haney, J.A.; Zmijewski, C.; Croce, C.M. Human TCR-gamma+/delta+, CD8+ T lymphocytes recognize tetanus toxoid in an MHC-restricted fashion. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 169, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Happ, M.P.; Kubo, R.T.; Palmer, E.; Born, W.K.; O’Brien, R.L. Limited receptor repertoire in a mycobacteria-reactive subset of gamma delta T lymphocytes. Nature 1989, 342, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Portales-Perez, D.P.; Baranda, L.; Moncada, B.; Toro, C.; Lopez-Briones, S.; Espitia, C.; Mancilla, R. Co-stimulatory signals increase the reactivity of gammadelta T-cells towards mycobacterial antigens. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 120, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherden, D.A.; Johnson, M.D.; Havran, W.L. Coreceptors and Their Ligands in Epithelial gammadelta T-cell Biology. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokuyama, H.; Hagi, T.; Mattarollo, S.R.; Morley, J.; Wang, Q.; So, H.F.; Moriyasu, F.; Nieda, M.; Nicol, A.J. V gamma 9 V delta 2 T-cell cytotoxicity against tumor cells is enhanced by monoclonal antibody drugs--rituximab and trastuzumab. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, U.J.; Vogt, F.; Grosse-Hovest, L.; Jung, G.; Handgretinger, R.; Lang, P. gammadelta T-cell-Mediated Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity with CD19 Antibodies Assessed by an Impedance-Based Label-Free Real-Time Cytotoxicity Assay. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinski, P.; Mailliard, R.B.; Giermasz, A.; Zeh, H.J.; Basse, P.; Bartlett, D.L.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Lotze, M.T.; Herberman, R.B. Natural killer-dendritic cell cross-talk in cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinski, P.; Giermasz, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Basse, P.; Storkus, W.J.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Mailliard, R.B. Helper role of NK cells during the induction of anticancer responses by dendritic cells. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailliard, R.B.; Son, Y.I.; Redlinger, R.; Coates, P.T.; Giermasz, A.; Morel, P.A.; Storkus, W.J.; Kalinski, P. Dendritic cells mediate NK cell help for Th1 and CTL responses: Two-signal requirement for the induction of NK cell helper function. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladel, C.H.; Blum, C.; Kaufmann, S.H. Control of natural killer cell-mediated innate resistance against the intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes by gamma/delta T lymphocytes. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Wu, K.; Hu, Y.; Sheng, L.; Tie, R.; Wang, B.; Huang, H. gammadelta T-cell and oTher. immune cells crosstalk in cellular immunity. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 960252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermijlen, D.; Ellis, P.; Langford, C.; Klein, A.; Engel, R.; Willimann, K.; Jomaa, H.; Hayday, A.C.; Eberl, M. Distinct cytokine-driven responses of activated blood gammadelta T-cells: Insights into unconventional T-cell pleiotropy. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4304–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansel, K.M.; Ngo, V.N.; Hyman, P.L.; Luther, S.A.; Forster, R.; Sedgwick, J.D.; Browning, J.L.; Lipp, M.; Cyster, J.G. A chemokine-driven positive feedback loop organizes lymphoid follicles. Nature 2000, 406, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Pao, W.; Wong, F.S.; Peng, Q.; Craft, J.; Zheng, B.; Kelsoe, G.; Dianda, L.; Owen, M.J.; Hayday, A.C. Germinal center formation, immunoglobulin class switching, and autoantibody production driven by “non alpha/beta” T-cells. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascan, H.; Aversa, G.G.; Gauchat, J.F.; Van Vlasselaer, P.; Roncarolo, M.G.; Yssel, H.; Kehry, M.; Spits, H.; De Vries, J.E. Membranes of activated CD4+ T-cells expressing T-cell receptor (TcR) alpha beta or TcR gamma delta induce IgE synthesis by human B cells in the presence of interleukin-4. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, M.; Roberts, G.W.; Meuter, S.; Williams, J.D.; Topley, N.; Moser, B. A rapid crosstalk of human gammadelta T-cells and monocytes drives the acute inflammation in bacterial infections. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, F.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Minato, N. Essential requirement of antigen presentation by monocyte lineage cells for the activation of primary human gamma delta T-cells by aminobisphosphonate antigen. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5508–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, E.; Biswas, P.; Vettoretto, K.; Ferrarini, M.; Uguccioni, M.; Piali, L.; Leone, B.E.; Moser, B.; Rugarli, C.; Pardi, R. Macrophages exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis release chemokines able to recruit selected leucocyte subpopulations: Focus on gammadelta cells. Immunology 2003, 108, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Mao, H.; Zheng, J.; Sia, S.F.; Liu, Y.; Chan, P.L.; Lam, K.T.; Peiris, J.S.; Lau, Y.L.; Tu, W. Phosphoantigen-expanded human gammadelta T-cells display potent cytotoxicity against monocyte-derived macrophages infected with human and avian influenza viruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedov, M.R.; Scholzen, A.; Nair, R.V.; Cumnock, K.; Kenkel, J.A.; Oliveira, J.H.M.; Trujillo, D.L.; Saligrama, N.; Zhang, Y.; Rubelt, F.; et al. A Macrophage Colony-Stimulating-Factor-Producing γδ T-cell Subset Prevents Malarial Parasitemic Recurrence. Immunity 2018, 48, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismaili, J.; Olislagers, V.; Poupot, R.; Fournie, J.J.; Goldman, M. Human gamma delta T-cells induce dendritic cell maturation. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 103, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescigno, M.; Martino, M.; Sutherland, C.L.; Gold, M.R.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cell survival and maturation are regulated by different signaling pathways. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, D.S.; Vincent, M.S.; Spada, F.M.; Das, H.; Sugita, M.; Morita, C.T.; Brenner, M.B. CD1-mediated gamma/delta T-cell maturation of dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ladel, C.H.; Blum, C.; Dreher, A.; Reifenberg, K.; Kaufmann, S.H. Protective role of gamma/delta T-cells and alpha/beta T-cells in tuberculosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 2877–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, M.; Willimann, K.; Moser, B. Professional antigen-presentation function by human gammadelta T-cells. Science 2005, 309, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, M.; Willimann, K.; Bioley, G.; Levy, N.; Eberl, M.; Luo, M.; Tampe, R.; Levy, F.; Romero, P.; Moser, B. Cross-presenting human gammadelta T-cells induce robust CD8+ alphabeta T-cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Himoudi, N.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Yan, M.; Vernay, B.; Saraiva, L.; Wu, Y.; Cohen, C.J.; Gustafsson, K.; Anderson, J. Human γδ T lymphocytes are licensed for professional antigen presentation by interaction with opsonized target cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muto, M.; Baghdadi, M.; Maekawa, R.; Wada, H.; Seino, K. Myeloid molecular characteristics of human γδ T-cells support their acquisition of tumor antigen-presenting capacity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Pei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhi, H.; Wong, W.H.; Wei, H.; Ng, I.O.; et al. Exosomes derived from Vδ2-T-cells control Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors and induce T-cell antitumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.V.; Fogli, M.; Hudspeth, K.; da Silva, M.G.; Mavilio, D.; Silva-Santos, B. Differentiation of human peripheral blood Vdelta1+ T-cells expressing the natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp30 for recognition of lymphoid leukemia cells. Blood 2011, 118, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanca, T.; Correia, D.V.; Moita, C.F.; Raquel, H.; Neves-Costa, A.; Ferreira, C.; Ramalho, J.S.; Barata, J.T.; Moita, L.F.; Gomes, A.Q.; et al. The MHC class Ib protein ULBP1 is a nonredundant determinant of leukemia/lymphoma susceptibility to gammadelta T-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2010, 115, 2407–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halary, F.; Pitard, V.; Dlubek, D.; Krzysiek, R.; de la Salle, H.; Merville, P.; Dromer, C.; Emilie, D.; Moreau, J.F.; Dechanet-Merville, J. Shared reactivity of V{delta}2(neg) {gamma}{delta} T-cells against cytomegalovirus-infected cells and tumor intestinal epithelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehl, S.; Schwarz, K.; Enders, A.; Duffner, U.; Pannicke, U.; Kuhr, J.; Mascart, F.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Niemeyer, C.; Fisch, P. A variant of SCID with specific immune responses and predominance of gamma delta T-cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3140–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paoli, P.; Gennari, D.; Martelli, P.; Basaglia, G.; Crovatto, M.; Battistin, S.; Santini, G. A subset of gamma delta lymphocytes is increased during HIV-1 infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 83, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, C.T.; Abate, G.; Sakala, I.G.; Xia, M.; Truscott, S.M.; Eickhoff, C.S.; Linn, R.; Blazevic, A.; Metkar, S.S.; Peng, G.; et al. Granzyme A produced by gamma(9)delta(2) T-cells induces human macrophages to inhibit growth of an intracellular pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Han, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z. Identification of a new tuberculosis antigen recognized by gammadelta T-cell receptor. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Emami, S.N.; Pettersson, J.; Ranford-Cartwright, L.; Faye, I.; Parmryd, I. Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells proliferate in response to phosphoantigens released from erythrocytes infected with asexual and gametocyte stage Plasmodium falciparum. Cell Immunol. 2018, 334, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elloso, M.M.; van der Heyde, H.C.; vande Waa, J.A.; Manning, D.D.; Weidanz, W.P. Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum In Vitro by human gamma delta T-cells. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Qian, L.; Miao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Miao, P.; Wang, P.; Yu, Q.; Nie, H.; Zhang, J.; He, D.; et al. Antigen-presenting effects of effector memory Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, X.; Ding, C.; Qi, C.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Jala, V.R.; Zhang, H.G.; Wang, T.; Zheng, J.; et al. Pivotal role of dermal IL-17-producing gammadelta T-cells in skin inflammation. Immunity 2011, 35, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poles, M.A.; Barsoum, S.; Yu, W.; Yu, J.; Sun, P.; Daly, J.; He, T.; Mehandru, S.; Talal, A.; Markowitz, M.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 induces persistent changes in mucosal and blood gammadelta T-cells despite suppressive therapy. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10456–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Peng, H.; Ma, P.; Ruan, Y.; Su, B.; Ding, X.; Xu, C.; Pauza, C.D.; Shao, Y. Association between Vgamma2Vdelta2 T-cells and disease progression after infection with closely related strains of HIV in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, S.; Cairo, C.; Venturi, V.; Pauza, C.D. The gammadelta T-cell receptor repertoire is reconstituted in HIV patients after prolonged antiretroviral therapy. Aids 2013, 27, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Pauza, C.D. HIV envelope-mediated, CCR5/alpha4beta7-dependent killing of CD4-negative gammadelta T-cells which are lost during progression to AIDS. Blood 2011, 118, 5824–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Paiardini, M.; Knox, K.S.; Asher, A.I.; Cervasi, B.; Asher, T.E.; Scheinberg, P.; Price, D.A.; Hage, C.A.; Kholi, L.M.; et al. Differential Th17 CD4 T-cell depletion in pathogenic and nonpathogenic lentiviral infections. Blood 2008, 112, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Schacker, T.W.; Asher, T.E.; Silvestri, G.; Rao, S.; Kazzaz, Z.; Bornstein, E.; Lambotte, O.; Altmann, D.; et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, D.; Cui, L.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H.; He, W. gammadelta T-cells are involved in acute HIV infection and associated with AIDS progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poccia, F.; Boullier, S.; Lecoeur, H.; Cochet, M.; Poquet, Y.; Colizzi, V.; Fournie, J.J.; Gougeon, M.L. Peripheral V gamma 9/V delta 2 T-cell deletion and anergy to nonpeptidic mycobacterial antigens in asymptomatic HIV-1-infected persons. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 449–461. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, M.; Scharko, A.M.; Pauza, C.D.; Fisch, P.; Imaoka, K.; Kawabata, S.; Fujihashi, K.; Kiyono, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Bloom, B.R.; et al. Functional gamma delta T-lymphocyte defect associated with human immunodeficiency virus infections. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilssen, D.E.; Müller, F.; Oktedalen, O.; Frøland, S.S.; Fausa, O.; Halstensen, T.S.; Brandtzaeg, P. Intraepithelial gamma/delta T-cells in duodenal mucosa are related to the immune state and survival time in AIDS. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3545–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imlach, S.; Leen, C.; Bell, J.E.; Simmonds, P. Phenotypic analysis of peripheral blood gammadelta T lymphocytes and their targeting by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 In Vivo. Virology 2003, 305, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klatt, N.R.; Funderburg, N.T.; Brenchley, J.M. Microbial translocation, immune activation, and HIV disease. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacchi, A.; Rinaldi, A.; Tumino, N.; Casetti, R.; Agrati, C.; Turchi, F.; Bordoni, V.; Cimini, E.; Martini, F. HIV infection of monocytes-derived dendritic cells inhibits Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells functions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poccia, F.; Battistini, L.; Cipriani, B.; Mancino, G.; Martini, F.; Gougeon, M.L.; Colizzi, V. Phosphoantigen-reactive Vgamma9Vdelta2 T lymphocytes suppress in vitro human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by cell-released antiviral factors including CC chemokines. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, M.; Willimann, K.; Lang, A.B.; Nam, K.H.; Jin, C.; Brenner, M.B.; Morita, C.T.; Moser, B. Flexible migration program regulates gamma delta T-cell involvement in humoral immunity. Blood 2003, 102, 3693–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.R.; Mackay, C.R.; Moser, B.; Eberl, M. IL-21 enhances the potential of human gammadelta T-cells to provide B-cell help. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, N.; Battistini, L.; Bonneville, M.; Poccia, F.; Fournié, J.J.; Meraviglia, S.; Borsellino, G.; Kroczek, R.A.; La Mendola, C.; Scotet, E.; et al. CXCR5 identifies a subset of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells which secrete IL-4 and IL-10 and help B cells for antibody production. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5290–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mingari, M.C.; Varese, P.; Bottino, C.; Melioli, G.; Moretta, A.; Moretta, L. Clonal analysis of CD4-CD8- human thymocytes expressing a T-cell receptor gamma/delta chain. Direct evidence for the de novo expression of CD8 surface antigen and of cytolytic activity against tumor targets. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkina, A.C.; Starchenko, A.; Drake, K.A.; Proctor, E.A.; Pihl, R.M.F.; Olson, A.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Lin, N.; Snyder-Cappione, J.E. Multivariate Computational Analysis of Gamma Delta T-cell Inhibitory Receptor Signatures Reveals the Divergence of Healthy and ART-Suppressed HIV+ Aging. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwale, A.; Hummel, A.; Mvaya, L.; Kamng’ona, R.; Chimbayo, E.; Phiri, J.; Malamba, R.; Kankwatira, A.; Mwandumba, H.C.; Jambo, K.C. B cell, CD8 (+) T-cell and gamma delta T-cell infiltration alters alveolar immune cell homeostasis in HIV-infected Malawian adults. Wellcome Open Res. 2017, 2, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.; Stanwick, T.L.; Dempsey, M.P.; Lamonica, C.A. HIV-1 replication is controlled at the level of T-cell activation and proviral integration. Embo J. 1990, 9, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Kajdas, J.; Finzi, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.B.; Kovacs, C.; Gange, S.J.; Siliciano, R.F. Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T-cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Sarabia, N.; Archin, N.M.; Bateson, R.; Dahl, N.P.; Crooks, A.M.; Kuruc, J.D.; Garrido, C.; Margolis, D.M. Peripheral Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells Are a Novel Reservoir of Latent HIV Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biradar, S.; Mailliard, R.B.; et al. Adoptive transfer of allogeneic expanded gamma delta T cells promotes HIV replication in a humanized mouse model. (Manuscript in preparation).
- Negash, M.; Tsegaye, A.; Wassie, L.; Howe, R. Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of peripheral gammadelta T-cells in pulmonary TB and HIV patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.S.; Cairo, C.; Armstrong, C.; Davis, C.E.; Pauza, C.D. Impacts of HIV infection on Vgamma2Vdelta2 T-cell phenotype and function: A mechanism for reduced tumor immunity in AIDS. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, G.S.; Moore, S.W.; Richter, J.M.; Garber, J.J.; Bowman, B.A.; Rawlings, C.A.; Flagg, M.; Corleis, B.; Kwon, D.S. Increased frequency of systemic pro-inflammatory Vdelta1(+) gammadelta T-cells in HIV elite controllers correlates with gut viral load. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, D.J.; Sajadi, M.M.; Armstrong, C.L.; Cummings, J.S.; Cairo, C.; Redfield, R.R.; Pauza, C.D. Natural viral suppressors of HIV-1 have a unique capacity to maintain gammadelta T-cells. Aids 2009, 23, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevalier, M.F.; Bhatnagar, N.; Didier, C.; Lopez-Gonzalez, M.; Pavie, J.; Bollens, D.; Duvivier, C.; Collias, L.; Jung, C.; Scott-Algara, D.; et al. gammadelta T-cell subsets in HIV controllers: Potential role of Tgammadelta17 cells in the regulation of chronic immune activation. Aids 2019, 33, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, A.J.; Jauhiainen, M.; Monkkonen, H.; Rogers, M.J.; Monkkonen, J.; Thompson, K. Peripheral blood monocytes are responsible for gammadelta T-cell activation induced by zoledronic acid through accumulation of IPP/DMAPP. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, A.R.; Correia, D.V.; Fernandes-Platzgummer, A.; da Silva, C.L.; da Silva, M.G.; Anjos, D.R.; Silva-Santos, B. Delta One T-cells for Immunotherapy of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Clinical-Grade Expansion/Differentiation and Preclinical Proof of Concept. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5795–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegers, G.M.; Dhamko, H.; Wang, X.H.; Mathieson, A.M.; Kosaka, Y.; Felizardo, T.C.; Medin, J.A.; Tohda, S.; Schueler, J.; Fisch, P.; et al. Human Vδ1 γδ T-cells expanded from peripheral blood exhibit specific cytotoxicity against B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia-derived cells. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Borowska, M.T.; Boughter, C.T.; Adams, E.J. Butyrophilin3A proteins and Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell activation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 84, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poccia, F.; Gioia, C.; Martini, F.; Sacchi, A.; Piacentini, P.; Tempestilli, M.; Agrati, C.; Amendola, A.; Abdeddaim, A.; Vlassi, C.; et al. Zoledronic acid and interleukin-2 treatment improves immunocompetence in HIV-infected persons by activating Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells. Aids 2009, 23, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murday, A.S.; Chaudhry, S.; Pauza, C.D. Interleukin-18 activates Vgamma9Vdelta2(+) T-cells from HIV-positive individuals: Recovering the response to phosphoantigen. Immunology 2017, 151, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawanishi, Y.; Passweg, J.; Drobyski, W.R.; Rowlings, P.; Cook-Craig, A.; Casper, J.; Pietryga, D.; Garbrecht, F.; Camitta, B.; Horowitz, M.; et al. Effect of T-cell subset dose on outcome of T-cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997, 19, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poonia, B. Adoptive transfer of aminobisphonate-expanded Vgamma9Vdelta2+ T-cells does not control HIV replication in a humanized mouse model. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, Z.; Yan, L.; Plagman, N.; Reichenberg, A.; Hintz, M.; Jomaa, H.; Villinger, F.; Chen, Z.W. Gammadelta T-cell immune manipulation during chronic phase of simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection [corrected] confers immunological benefits. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5407–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrido, C.; Clohosey, M.L.; Whitworth, C.P.; Hudgens, M.; Margolis, D.M.; Soriano-Sarabia, N. γδ T-cells: An immunotherapeutic approach for HIV cure strategies. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liang, H.; Hong, K.; Li, H.; Peng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, M.; Ruan, Y.; Shao, Y. The potential role of CD16+ Vgamma2Vdelta2 T-cell-mediated antibody-dependenT-cell-mediated cytotoxicity in control of HIV type 1 disease. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2013, 29, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijting, I.E.A.; Wit, F.; Rokx, C.; Leyten, E.M.S.; Lowe, S.H.; Brinkman, K.; Bierman, W.F.W.; van Kasteren, M.E.E.; Postma, A.M.; Bloemen, V.C.M.; et al. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV infected late presenters starting integrase inhibitor containing antiretroviral therapy. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 17, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dieli, F.; Vermijlen, D.; Fulfaro, F.; Caccamo, N.; Meraviglia, S.; Cicero, G.; Roberts, A.; Buccheri, S.; D’Asaro, M.; Gebbia, N.; et al. Targeting human {gamma}delta} T-cells with zoledronate and interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Pauza, C.D. Rapamycin increases the yield and effector function of human gammadelta T-cells stimulated In Vitro. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Chaudhry, S.; Poonia, B.; Shao, Y.; Pauza, C.D. Depletion and dysfunction of Vγ2Vδ2 T-cells in HIV disease: Mechanisms, impacts and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| γδ Subtypes | Vδ1 | Vδ2 | Vδ3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Dermis, spleen, liver, gut epithelia, lung, peripheral blood, and other mucosal sites | Peripheral blood and lymphatics | Peripheral blood, liver, and gut |
| Function | Maintain epithelial tissue integrity by recognizing stress-induced MICA/B [4] Major source of IL-17 [14] Lyse autologous tumor [15] Opsonization of CMV through CD16 induce IFN-γ response [16]. Cytotoxicity against HIV infected cells through NKG2C triggering [17]. Recognize lipid antigens presented by CD1d [4]. | Recognize phosphoantigens produced by various microbes and transformed host cells in an MHC-independent manner and induce cytotoxicity [1]. Promote Th1 response by IFN-γ and TNF-α production [13]. Produce chemokines CCL-4 and CCL-5, which block HIV co-receptor CCR-5 [18]. Modulate B cell and DC maturation [19]. Enhance NK cell cytotoxicity via CD137 Interaction [20]. Antibody-dependent cellular Cytotoxicity [18]. | Function through cognate interaction with HLA-A2 and CD1d [7]. Expand in peripheral blood of renal and stem cell transplant recipients with CMV reactivation and B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia [9]. Modulate B cell and DC maturation [10,11]. |
| Treatment | Participant Status | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adoptive transfer of zoledronate + IL-2 expanded PBMCs | HIV infected humanized mice | No impact of Vδ2 T cell on HIV induced CD4+ depletion or plasma viremia | [108] |
| HMBPP + IL-2 injected in Macaque | SHIV infected Macaque | Expansion and activation of Vδ2 T cell. Increase in Env specific antibody but no impact on viral load. | [109] |
| Pamidronate + IL-2 expanded PBMCs | Human HIV + ART | Inhibition of HIV replication in vitro. PAM expanded Vδ2 T cells suppress p24 production by infected CD4+ T cells in the presence of vorinostat. | [110] |
| Ex vivo Vδ2 T cells | Human HIV + ART | CD16 activation on Vδ2 T cells from HIV infected individuals on ART promote ADCC in vitro. | [111] |
| Ex vivo IPP + IL-18 | Human HIV + ART | IL-18 improves IPP induced Vδ2 activation, proliferation, and degranulation in HIV infected individuals | [106] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biradar, S.; Lotze, M.T.; Mailliard, R.B. The Unknown Unknowns: Recovering Gamma-Delta T Cells for Control of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Viruses 2020, 12, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121455
Biradar S, Lotze MT, Mailliard RB. The Unknown Unknowns: Recovering Gamma-Delta T Cells for Control of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121455
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiradar, Shivkumar, Michael T. Lotze, and Robbie B. Mailliard. 2020. "The Unknown Unknowns: Recovering Gamma-Delta T Cells for Control of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121455
APA StyleBiradar, S., Lotze, M. T., & Mailliard, R. B. (2020). The Unknown Unknowns: Recovering Gamma-Delta T Cells for Control of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Viruses, 12(12), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121455







