Evaluation of Baloxavir Marboxil and Peramivir for the Treatment of High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza in Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antiviral Drugs
2.2. Virus
2.3. Animal Experiments
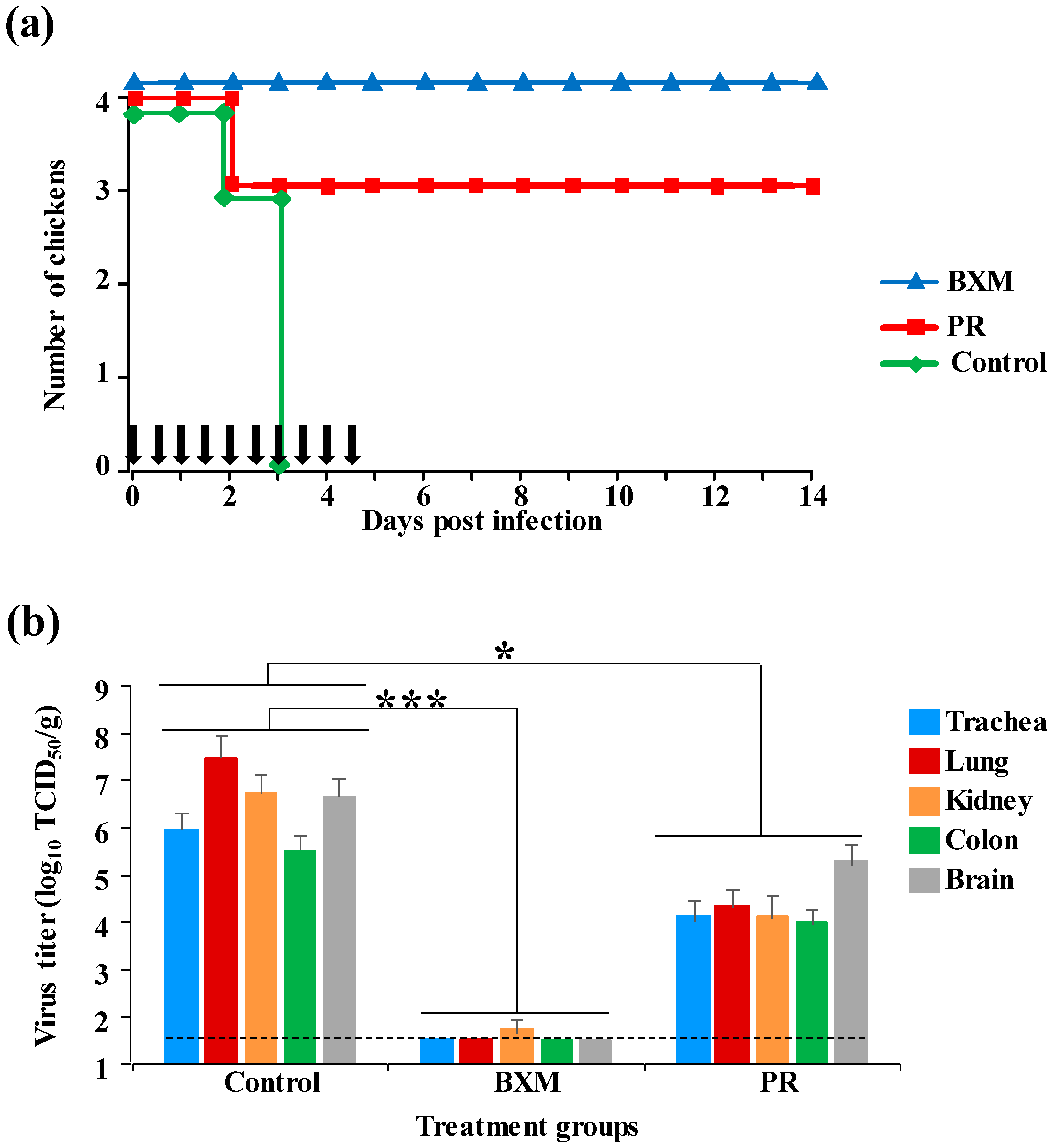
2.3.1. Experiment 1. Simultaneous Treatment with BXM or PR in the Chicken Model
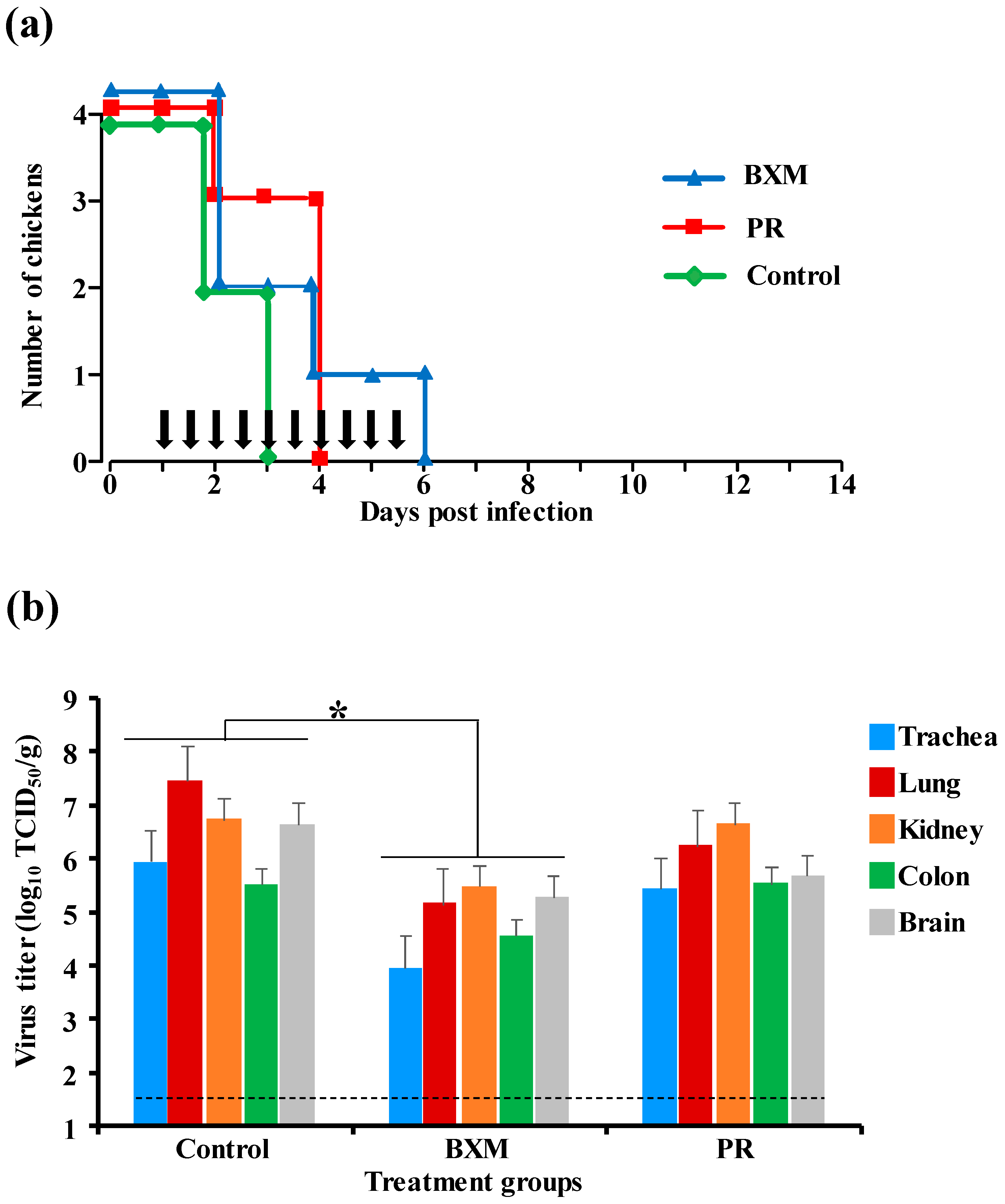
2.3.2. Experiment 2. Delayed Treatment with BXM or PR in the Chicken Model
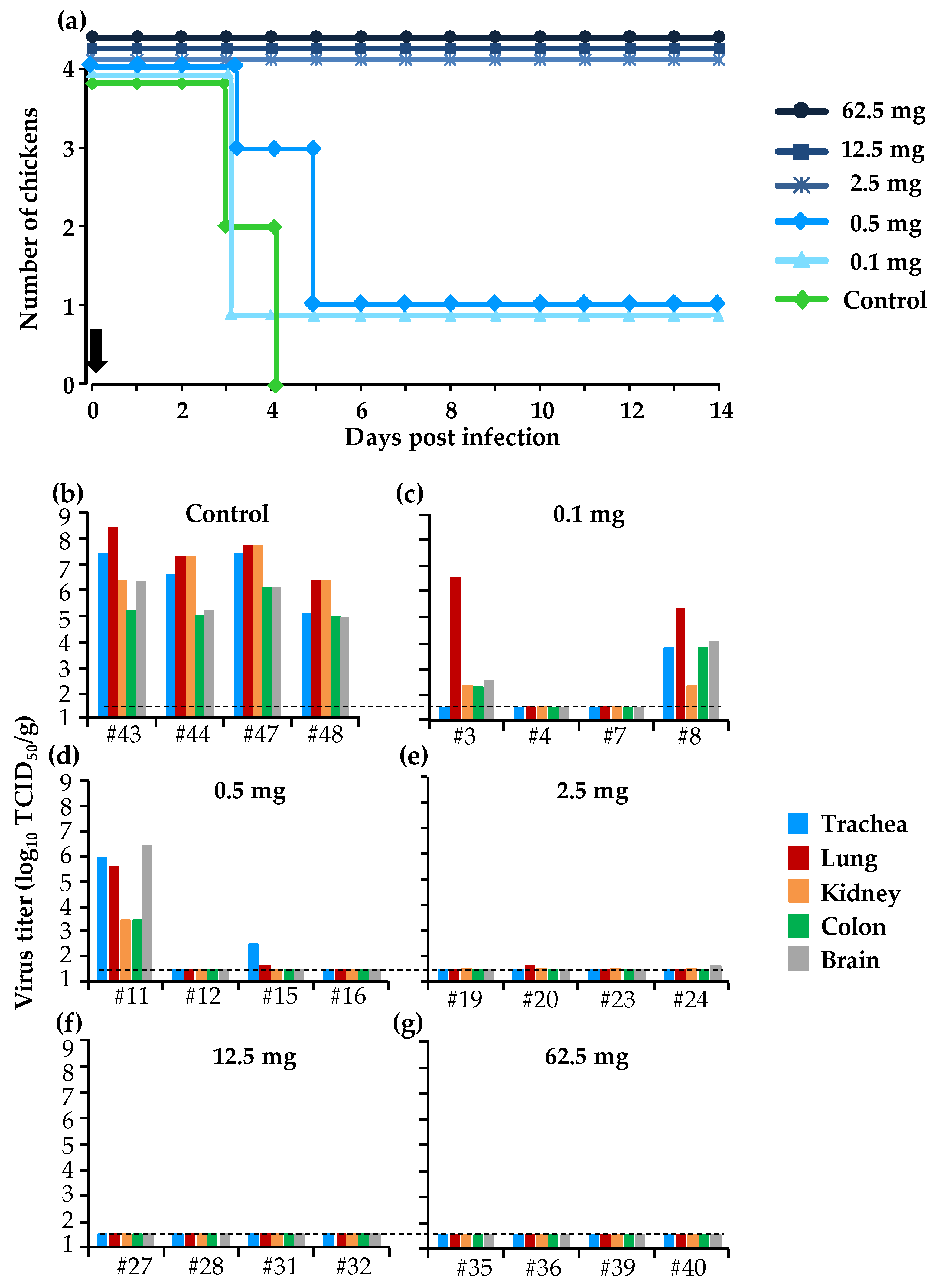
2.3.3. Experiment 3. Assessment of the Minimum Dose of BXM in the Chicken Model
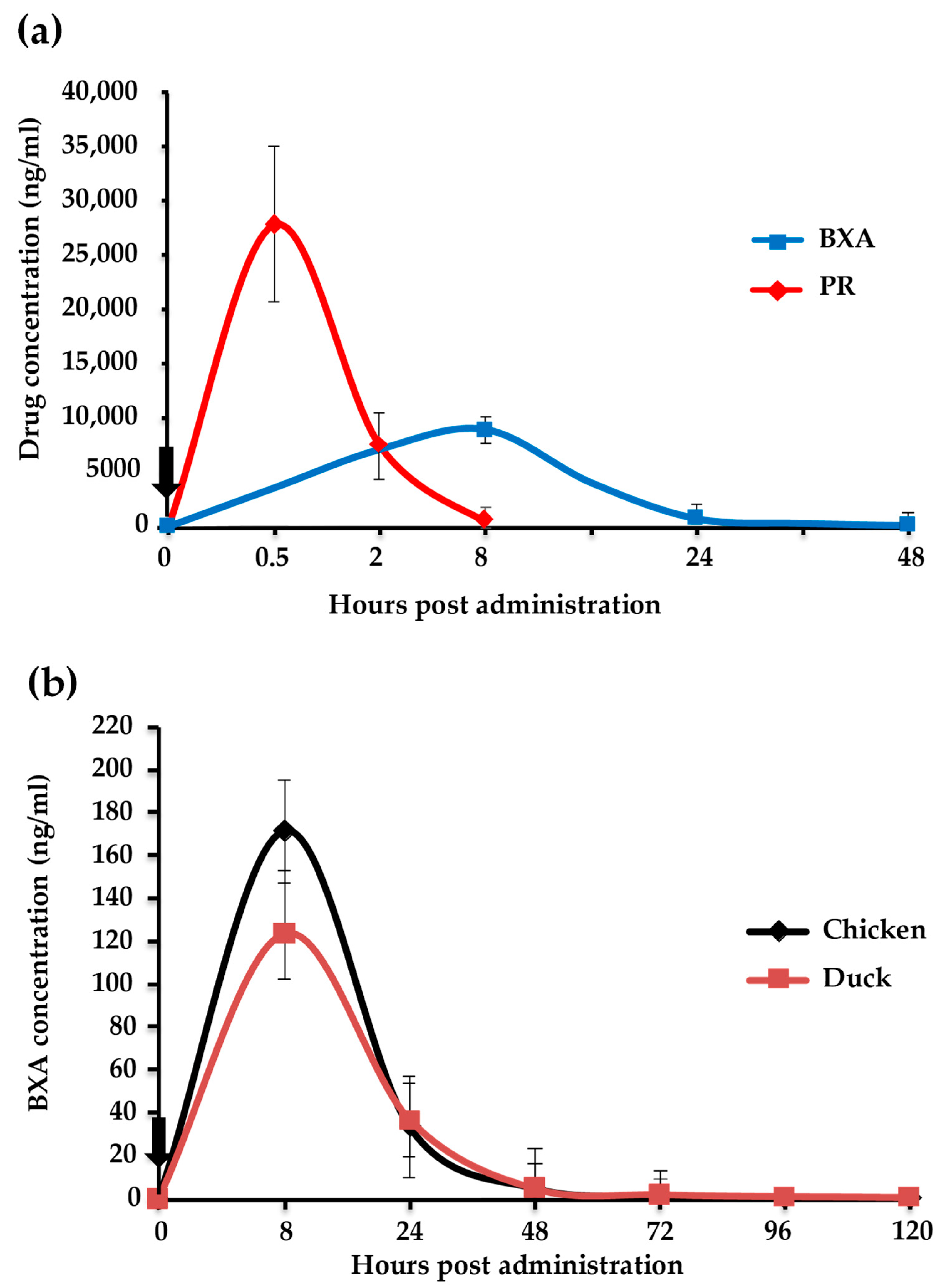
2.3.4. Assessment of BXA and PR Kinetics in Chickens and Ducks
2.3.5. Virus Recovery in Organs and Shedding in Swabs of Chickens
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Multiple Doses of BXM or PR in the Simultaneous Treatment of HPAIV Infection
3.2. Effects of Multiple Doses of BXM or PR in the Delayed Treatment of HPAIV Infection
3.3. Protective Effect of a Single Dose of BXM in the Simultaneous Treatment of HPAI in the Chicken Model
3.4. Kinetics of BXA and PR in Chickens and Ducks
3.5. Virus Shedding and Antibody Response in Chickens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capua, I.; Alexander, D.J. Avian influenza: Recent developments. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, E.; Kawaoka, Y.; de Jong, M.D.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Pathogenicity of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in mammals. Vaccine 2008, 26, D54–D58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.J.; Parsons, G.; Manvell, R.J. Experimental Assessment Of The Pathogenicity Of Eight Avian Influenza A Viruses Of H5 Subtype For Chickens, Turkeys, Ducks And Quail. Avian Pathol. 1986, 15, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, R.G.; Bean, W.J.; Gorman, O.T.; Chambers, T.M.; Kawaoka, Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottis, K.; Bachmann, P.A. Isolation and characterization of ortho- and paramyxoviruses from feral birds in Europe. Zent. Vet. B 1983, 30, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Martelli, P.; Hock, O.S.; Luz, S.; Furley, C.; Chiek, E.J.; Wee, L.C.; Keun, N.M. Field study on the use of inactivated H5N2 vaccine in avian species. Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krone, O.; Globig, A.; Ulrich, R.; Harder, T.; Schinköthe, J.; Herrmann, C.; Gerst, S.; Conraths, F.J.; Beer, M. White-Tailed Sea Eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) Die-Off Due to Infection with Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus, Subtype H5N8, in Germany. Viruses 2018, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyre, M.; Fusheng, G.; Desvaux, S.; Roger, F. Avian influenza vaccines: A practical review in relation to their application in the field with a focus on the Asian experience. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swayne, D.E. Impact of Vaccines and Vaccination on Global Control of Avian Influenza. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swayne, D.E.; Spackman, E. Current status and future needs in diagnostics and vaccines for high pathogenicity avian influenza. Dev. Biol. 2013, 135, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawara, A.; Okamatsu, M.; Ozawa, M.; Chu, D.-H.; Nguyen, L.T.; Hiono, T.; Matsuno, K.; Kida, H.; Sakoda, Y. Antigenic diversity of H5 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses of clade 2.3.4.4 isolated in Asia. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 61, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Antigenic and Genetic Characteristics of Zoonotic Influenza Viruses and Development of Candidate Vaccine Viruses for Pandemic Preparedness; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gulbudak, H.; Martcheva, M. A Structured Avian Influenza Model with Imperfect Vaccination and Vaccine-Induced Asymptomatic Infection. B Math. Biol. 2014, 76, 2389–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakogawa, M.O.M.; Kirisawa, R.; Asakawa, M. Countermeasures for avian influenza outbreaks among captive avian collections at zoological gardens and aquariums in Japan. Microbiol. Exp. 2019, 7, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippa, J.D.W.; Munster, V.J.; van Bolhuis, H.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Schaftenaar, W.; Beyer, W.E.P.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Kuiken, T.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Highly pathogenic avian influenza (H7N7): Vaccination of zoo birds and transmission to non-poultry species. Vaccine 2005, 23, 5743–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.-J.; Fang, J.-M. Development of effective anti-influenza drugs: Congeners and conjugates—A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, N.; Camilloni, B.; Alunno, A.; Polinori, I.; Argentiero, A.; Esposito, S. Drugs for Influenza Treatment: Is There Significant News? Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2019, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-N.; Park, J.-K.; Yuk, S.-S.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, J.-I.; Han, J.S.; Lee, J.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, I.-S.; et al. Antiviral Efficacy of Oseltamivir Against Avian Influenza Virus in Avian Species. Avian Dis. 2011, 55, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleta, E.F.; Blanco Peña, K.M.; Yilmaz, A.; Redmann, T.; Hofheinz, S. Avian influenza A viruses in birds of the order Psittaciformes: Reports on virus isolations, transmission experiments and vaccinations and initial studies on innocuity and efficacy of oseltamivir in ovo. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2007, 114, 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Tare, D.S.; Kode, S.S.; Hurt, A.C.; Pawar, S.D. Assessing the susceptibility of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 viruses to oseltamivir using embryonated chicken eggs. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 150, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, A.; van der Goot, J.A.; Koch, G.; van Boven, M.; Kimman, T.G. Oseltamivir reduces transmission, morbidity, and mortality of highly pathogenic avian influenza in chickens. Int. Congr. Ser. 2004, 1263, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamatsu, M.; Ozawa, M.; Soda, K.; Takakuwa, H.; Haga, A.; Hiono, T.; Matsuu, A.; Uchida, Y.; Iwata, R.; Matsuno, K.; et al. Characterization of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A(H5N6), Japan, November 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Miller, P.J.; Grund, C.; Koch, G.; Peeters, B.; Selleck, P.W.; Srinivas, G.B. The Manual of Diagnosis Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 7th ed.; World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 865–878. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; Lee, N.; de Jong, M.D.; Hurt, A.C.; Ishida, T.; Sekino, H.; Yamada, K.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Baloxavir Marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshimichi, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Kawaguchi, N.; Sato, C.; Kawasaki, A.; Wajima, T. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of the Novel Anti-influenza Agent Baloxavir Marboxil in Healthy Adults: Phase I Study Findings. Clin. Drug Investig. 2018, 38, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, N.E.; Linde, N.S.; Zacks, M.A.; Barr, I.G.; Hurt, A.C.; Smith, J.N.; Dziuba, N.; Holbrook, M.R.; Zhang, L.; Kilpatrick, J.M.; et al. Injectable peramivir mitigates disease and promotes survival in ferrets and mice infected with the highly virulent influenza virus, A/Vietnam/1203/04 (H5N1). Virology 2008, 374, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, R.C.; Witcher, R.; Cies, J.J.; Moore, W.S., 2nd; Chopra, A. Pharmacokinetics of Peramivir in an Adolescent Patient Receiving Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 22, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshimichi, H.; Tsuda, Y.; Ishibashi, T.; Wajima, T. Population Pharmacokinetic and Exposure-Response Analyses of Baloxavir Marboxil in Adults and Adolescents Including Patients With Influenza. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKimm-Breschkin, J.L.; Jiang, S.; Hui, D.S.; Beigel, J.H.; Govorkova, E.A.; Lee, N. Prevention and treatment of respiratory viral infections: Presentations on antivirals, traditional therapies and host-directed interventions at the 5th ISIRV Antiviral Group conference. Antiviral. Res. 2018, 149, 118–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, S.; Speranzini, V.; Hashimoto, T.; Noshi, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kawai, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Uehara, T.; Shishido, T.; Naito, A.; et al. Characterization of influenza virus variants induced by treatment with the endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippa, J.; Baas, C.; Beyer, W.; Bestebroer, T.; Fouchier, R.; Smith, D.; Schaftenaar, W.; Osterhaus, A. Vaccination against highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus in zoos using an adjuvanted inactivated H5N2 vaccine. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3800–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshi, T.; Sato, K.; Ishibashi, T. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of S-033188/S-033447, a novel inhibitor of influenza virus Cap-dependent endonuclease, in mice infected with influenza A virus [P1973]. In Proceedings of the Final Programme of the 27th European congress of clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Vienna, Australia, 22 April 2017; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, B.; Moore, B.M.; Sterner, B.; Peterson, L.R.; Gerding, D.N.; Balfour, H.H. Survival of Influenza Viruses on Environmental Surfaces. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 146, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.P.; Choi, Y.W.; Chappie, D.J.; Rogers, J.V.; Kaye, J.Z. Environmental Persistence of a Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H5N1) Virus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7515–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yamada, M.; Mase, M. Persistence of avian influenza virus (H5N1) in feathers detached from bodies of infected domestic ducks. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 5496–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubareva, L.V.; Mishin, V.P.; Patel, M.C.; Chesnokov, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; De La Cruz, J.; Spencer, S.; Campbell, A.P.; Sinner, M.; Reid, H.; et al. Assessing baloxavir susceptibility of influenza viruses circulating in the United States during the 2016/17 and 2017/18 seasons. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1800666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment (mg/kg) | Chicken ID | Virus Recovery from Swabs on Days Post-Challenge (log10 EID50/mL) a | HI Titer in Serum b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 0 | 14 | ||
| T/C | T/C | T/C | T/C | T/C | ||||
| # 41 | –/– | 5.2/4.8 | † | † | † | <2 | † | |
| Control | # 42 | –/– | 4.9/4.0 | † | † | † | <2 | † |
| # 45 | –/– | 5.5/4.3 | † | † | † | <2 | † | |
| # 46 | –/– | 5.3/4.5 | † | † | † | <2 | † | |
| 0.1 | # 1 | –/– | 4.2/3.5 | † | † | † | <2 | † |
| # 2 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 5 | –/– | 3.8/2.7 | † | † | † | <2 | † | |
| # 6 | –/– | 4.2/3.5 | † | † | † | <2 | † | |
| 0.5 | # 9 | –/– | 3.4/2.7 | † | † | † | <2 | † |
| # 10 | –/– | 3.5/3.5 | 3.7/3.2 | † | † | <2 | † | |
| # 13 | –/– | 3.2/3.0 | 2.6/3.0 | † | † | <2 | † | |
| # 14 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| 2.5 | # 17 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 |
| # 18 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 21 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 22 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| 12.5 | # 25 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 32 |
| # 26 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 29 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 30 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| 62.5 | # 33 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 |
| # 34 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 37 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
| # 38 | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | –/– | <2 | 64 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Twabela, A.; Okamatsu, M.; Matsuno, K.; Isoda, N.; Sakoda, Y. Evaluation of Baloxavir Marboxil and Peramivir for the Treatment of High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza in Chickens. Viruses 2020, 12, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121407
Twabela A, Okamatsu M, Matsuno K, Isoda N, Sakoda Y. Evaluation of Baloxavir Marboxil and Peramivir for the Treatment of High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza in Chickens. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121407
Chicago/Turabian StyleTwabela, Augustin, Masatoshi Okamatsu, Keita Matsuno, Norikazu Isoda, and Yoshihiro Sakoda. 2020. "Evaluation of Baloxavir Marboxil and Peramivir for the Treatment of High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza in Chickens" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121407
APA StyleTwabela, A., Okamatsu, M., Matsuno, K., Isoda, N., & Sakoda, Y. (2020). Evaluation of Baloxavir Marboxil and Peramivir for the Treatment of High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza in Chickens. Viruses, 12(12), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121407






