Development of a Multiplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Different Clades of Avian Influenza in Poultry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Viruses and Field Samples Collection
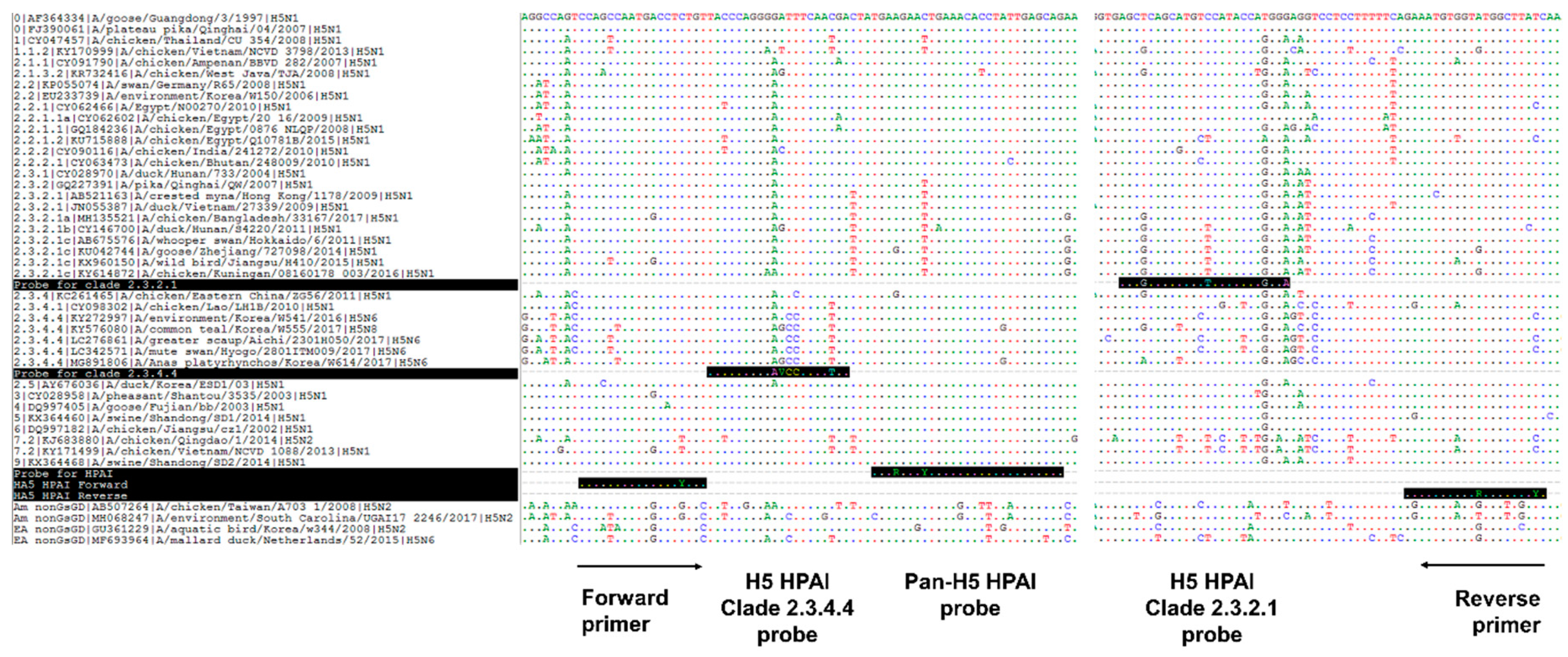
2.2. Primer and Probe Design
2.3. Sensitivity Analyses of One-Step Multiplex RT-qPCR Analysis
2.4. One-Step Multiplex RT-qPCR Analysis
2.5. Specificity Analyses of One-Step Multiplex RT-qPCR Analysis
2.6. H5 HPAI Clade Assignment of Filed Samples
3. Results
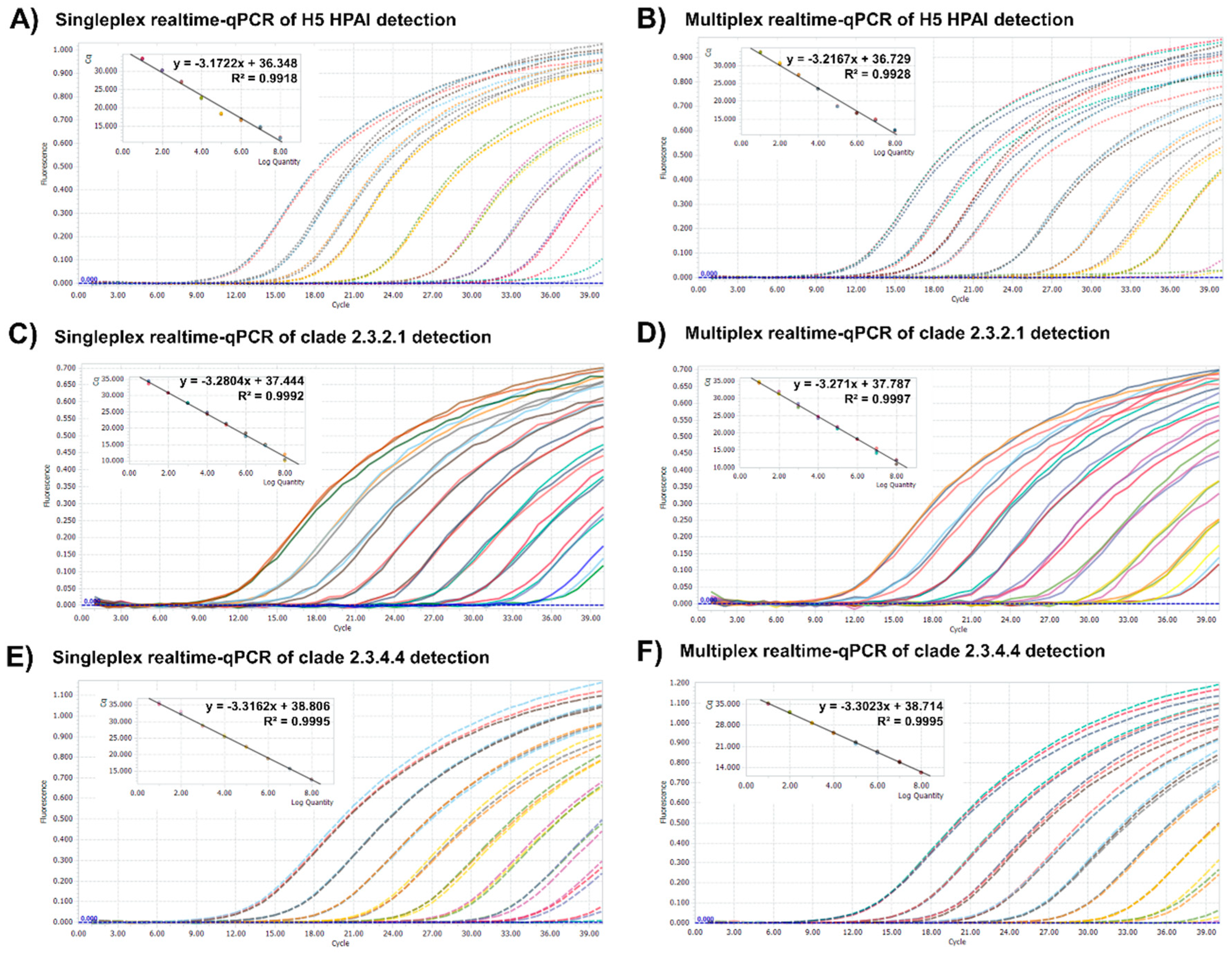
3.1. Sensitivity of One-Step Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay
3.2. Specificity of One-Step Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay
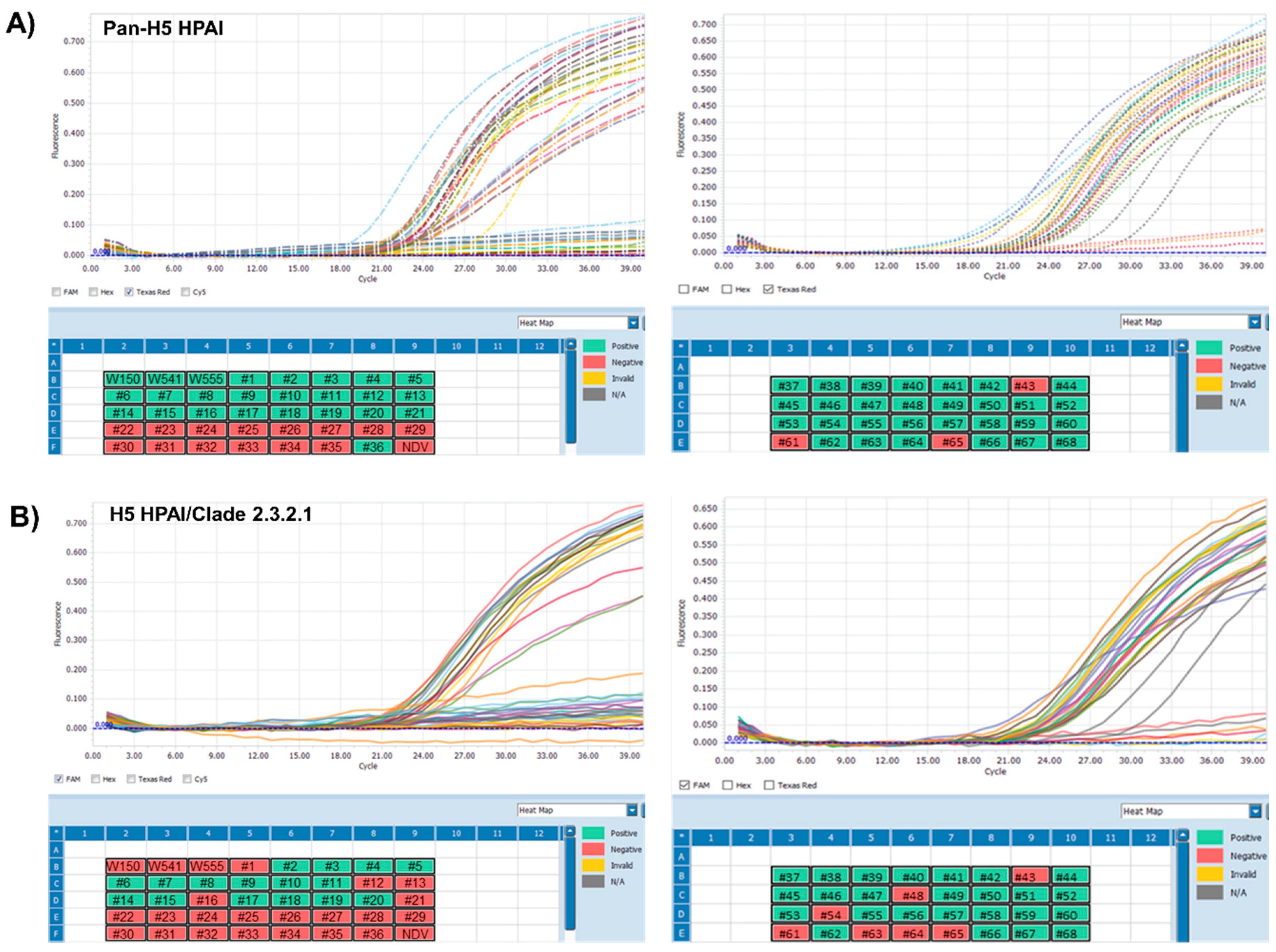
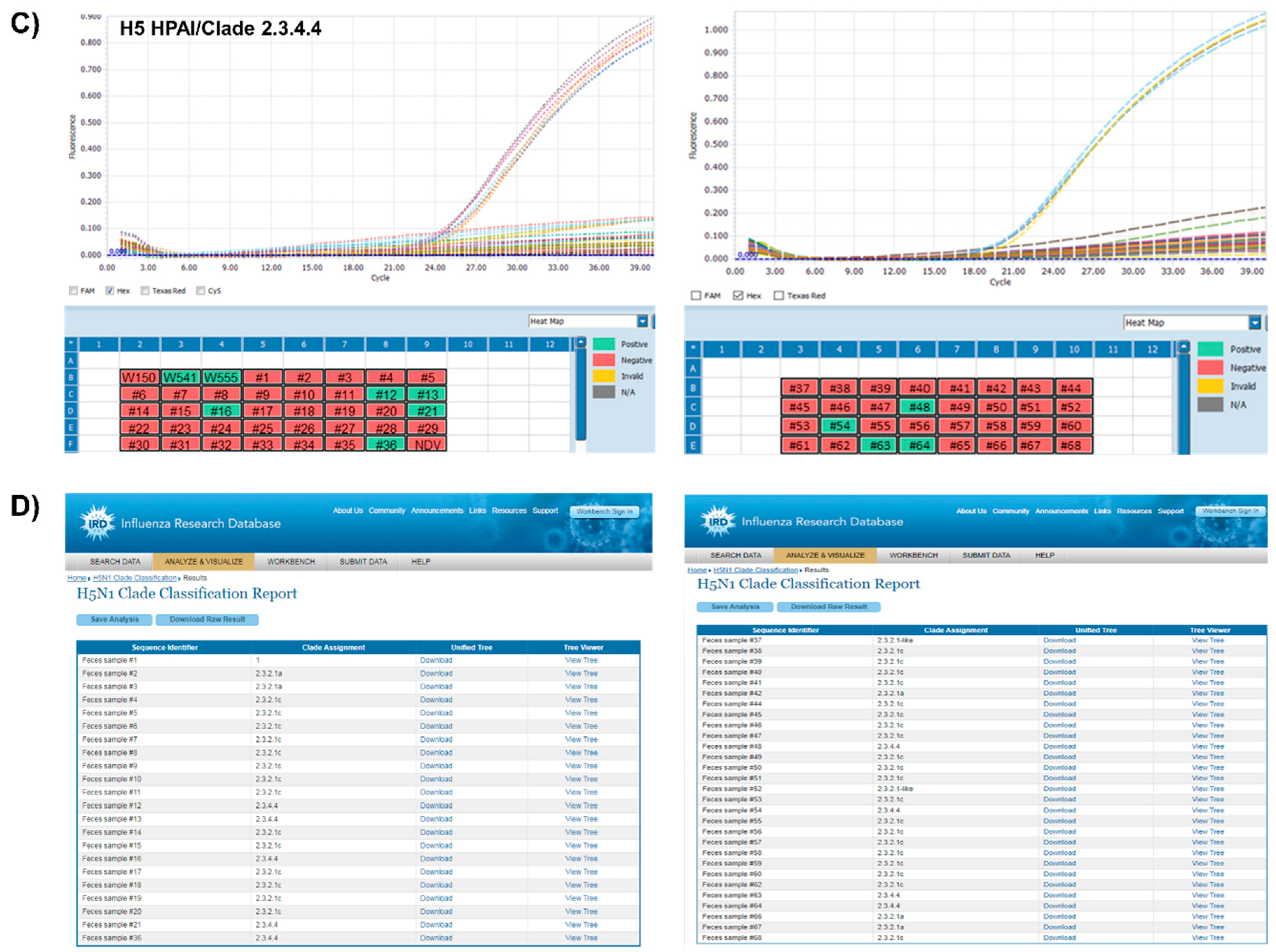
3.3. Application of One-Step Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay Using Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, S.W.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G. Evolution and Ecology of Influenza A Viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 385, 359–375. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Bourgeois, M.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Recuenco, S.; Gomez, J.; et al. New World Bats Harbor Diverse Influenza A Viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.J.; Donis, R.O. Nomenclature Updates Resulting from the Evolution of Avian Influenza A(H5) Virus Clades 2.1.3.2a, 2.2.1, and 2.3.4 During 2013–2014. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2015, 9, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolnik, C. Evolution of H5 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza: Sequence Data Indicate Stepwise Changes in the Cleavage Site. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO Report. Available online: http://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/H5N1_cumulative_table_archives/en/) (accessed on 25 November 2019).
- Sonnberg, S.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G. Natural History of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, E.; Guo, H.; Dai, M.; Rottier, P.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; de Haan, C.A. Rapid Emergence of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Subtypes from a Subtype H5N1 Hemagglutinin Variant. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Swayne, D.E.; Noh, J.Y.; Yuk, S.S.; Erdene-Ochir, T.O.; Hong, W.T.; Jeong, J.H.; Jeong, S.; Gwon, G.B.; et al. Reassortant Clade 2.3.4.4 Avian Influenza A(H5N6) Virus in a Wild Mandarin Duck, South Korea, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhong, L.; Huang, J.; Wan, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Peng, D.; et al. Novel Variants of Clade 2.3.4 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Viruses, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 2021–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Jeong, D.G.; Yoon, S.W. Recent Outbreaks of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses in South Korea. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2017, 6, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, J.H.; Herfst, S.; Fouchier, R.A. Infectious Disease. How a Virus Travels the World. Science 2015, 347, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Cai, T.; Sharshov, K.; Susloparov, I.; Shestopalov, A.; Wong, G.; He, Y.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 Clade 2.3.2.1c Virus in Migratory Birds, 2014–2015. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Peng, X.; Xu, L.; Jin, C.; Cheng, L.; Lu, X.; Xie, T.; Yao, H.; Wu, N. Novel Reassortant Influenza A(H5N8) Viruses in Domestic Ducks, Eastern China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlhoch, C.; Brown, I.H.; Angelova, S.G.; Balint, A.; Bouwstra, R.; Buda, S.; Castrucci, M.R.; Dabrera, G.; Dan, A.; Grund, C.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Outbreaks: Protection and Management of Exposed People in Europe, 2014/15 and 2016. Eur. Surveill. 2016, 21, 30419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoute, S.; Chin, R.; Crossley, B.; Gabriel Senties-Cue, C.; Bickford, A.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Breitmeyer, R.; Jones, A.; Carnaccini, S.; Shivaprasad, H.L. Highly Pathogenic Eurasian H5N8 Avian Influenza Outbreaks in Two Commercial Poultry Flocks in California. Avian. Dis. 2016, 60, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Tang, H.; Duffy, S.; Hong, Y.; Norman, S.; Ghosh, M.; He, J.; Bose, M.; Henrickson, K.J.; Fan, J.; et al. Multiplex Assay for Simultaneously Typing and Subtyping Influenza Viruses by Use of an Electronic Microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, M.; Ninomiya, A.; Minekawa, H.; Notomi, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Tashiro, M.; Odagiri, T. Development of H5-RT-LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) System for Rapid Diagnosis of H5 Avian Influenza Virus Infection. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6679–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, K.; Harder, T.C.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Karger, A. Diagnosis and Strain Differentiation of Avian Influenza Viruses by Restriction Fragment Mass Analysis. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 158, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, K.; Ashizawa, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Kaji, N.; Suzuki, K.; Okamatsu, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Mase, M. Subtyping of Avian Influenza Viruses H1 to H15 on the Basis of Hemagglutinin Genes by PCR Assay and Molecular Determination of Pathogenic Potential. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3048–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.M.; Graaf, A.; Fortin, A.; Luttermann, C.; Wernery, U.; Amarin, N.; Hussein, H.A.; Sultan, H.; Al Adhadh, B.; Hassan, M.K.; et al. Novel Real-Time PCR-Based Patho- and Phylotyping of Potentially Zoonotic Avian Influenza A Subtype H5 Viruses at Risk of Incursion into Europe in 2017. Eur. Surveill. 2017, 22, 30435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO Manual on Animal Influenza Diagnosis and Surveillance. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/influenza/whocdscsrncs20025rev (accessed on 1 May 2002).
- The WHO Report. Available online: https://www.who.int/influenza/gisrs_laboratory/H5CompleteTree.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 16 October 2015).
- Hu, T.; Song, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.; Duan, B.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, W.; Qiu, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Emergence of Novel Clade 2.3.4 Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Subgroups in Yunnan Province, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 33, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Song, B.M.; Jeong, J.; Kwon, Y.K.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, K.J.; Hong, M.S.; Jang, I.; et al. Novel Reassortant Influenza A(H5N8) Viruses, South Korea, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Jang, Y.; Nguyen, T.D.; Jones, J.; Shepard, S.S.; Yang, H.; Gerloff, N.; Fabrizio, T.; Nguyen, L.V.; Inui, K.; et al. Shifting Clade Distribution, Reassortment, and Emergence of New Subtypes of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5) Viruses Collected from Vietnamese Poultry from 2012 to 2015. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.Y.; Phommachanh, P.; Kalpravidh, W.; Chanthavisouk, C.; Gilbert, J.; Bingham, J.; Davies, K.R.; Cooke, J.; Eagles, D.; Phiphakhavong, S.; et al. Reassortant Highly Pathogenic Influenza A(H5N6) Virus in Laos. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapczynski, D.R.; Sylte, M.J.; Killian, M.L.; Torchetti, M.K.; Chrzastek, K.; Suarez, D.L. Protection of Commercial Turkeys Following Inactivated or Recombinant H5 Vaccine Application against the 2015U.S. H5N2 Clade 2.3.4.4 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 191, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wong, G.; Ma, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Lin, J.; et al. Development of a Quadruple qRT-PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Highly and Low Pathogenic H7N9 Avian Influenza Viruses and Characterization against Oseltamivir Resistance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payungporn, S.; Chutinimitkul, S.; Chaisingh, A.; Damrongwantanapokin, S.; Buranathai, C.; Amonsin, A.; Theamboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. Single Step Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR for H5N1 Influenza A Virus Detection. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, E.; Senne, D.A.; Myers, T.J.; Bulaga, L.L.; Garber, L.P.; Perdue, M.L.; Lohman, K.; Daum, L.T.; Suarez, D.L. Development of a Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assay for Type A Influenza Virus and the Avian H5 and H7 Hemagglutinin Subtypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3256–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Hu, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Jiang, D.; et al. Multiplex One-Step Real-Time PCR Assay for Rapid Simultaneous Detection of Velogenic and Mesogenic Newcastle Disease Virus and H5-Subtype Avian Influenza Virus. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, H.G.; Foord, A.J.; Wang, J.; Valdeter, S.; Walker, S.; Morrissy, C.; Wong, F.Y.; Meehan, B. A Detection of highly pathogenic zoonotic influenza virus H5N6 by reverse-transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Specificity | Fluorescence Dye | Singleplex Assay | Multiplex Assay | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limit of Detection | Mean ct Value | SD | Limit of Detection | Mean ct Value | SD | ||
| Clade 2.3.4.4 | Hex | 5 × 101 | 34.39 | 0.025 | 5 × 101 | 33.84 | 0.03 |
| Clade2.3.2.1 | FAM | 5 × 101 | 33.83 | 0.020 | 5 × 101 | 34.5 | 0.025 |
| Pan-H5 HPAI | Texas red | 5 × 101 | 34.12 | 0.061 | 5 × 101 | 33.89 | 0.06 |
| Virus Name | Host | Accession Number | Subtype | Mean ct Value | Comments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 HPAI | 2.3.2.1c Clade | 2.3.4.4 Clade | |||||
| A/California/04/2009 | Human | GQ280797 | H1N1 | ND | ND | ND | |
| A/wild bird/Korea/SK14/2014 | Avian | KX066871 | H1N1 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| A/swine/Korea/CAN04/2005 | Swine | EU798790 | H3N2 | ND | ND | ND | |
| A/canine/Korea/01/2007 | Canine | JX163256 | H3N2 | ND | ND | ND | |
| A/aquatic bird/SouthKorea/sw006/2016 | Avian | MG386182 | H3N3 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| A/equine/Kyonggi/SA1/2011 | Equine | JX844146 | H3N8 | ND | ND | ND | |
| A/environment/Korea/W150/2006 | Avian | EU233739 | H5N1 | 21.55 | ND | ND | Clade 2.2 |
| A/duck/Vietnam/NCVD-1648/2012 | Avian | KY171342 | H5N1 | 20.58 | 21.6 | ND | Clade 2.3.2.1c |
| A/aquatic bird/Korea/CN2/2009 | Avian | KY584075 | H5N2 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| A/aquatic bird/ South Korea/sw007/2015 | Avian | MG386197 | H5N3 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| A/Environment/Korea/W541/2016 | Avian | KY272997 | H5N6 | 22.13 | ND | 21.36 | Clade 2.3.4.4 |
| A/Common Teal/Korea/W555/2017 | Avian | KY576080 | H5N8 | 20.82 | ND | 19.02 | Clade 2.3.4.4 |
| A/aquatic bird/ South Korea/sw001/2015 | Avian | MF987893 | H7N1 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| A/Chicken/Korea/MS96/1996 | Avian | GU053186 | H9N2 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| A/Aquatic bird/South Korea/SW1/2018 | Avian | MK539837 | H10N1 | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Infectious bronchitis virus | Avian | KY992863 | VNUA3 | ND | ND | ND | |
| Newcastle disease virus | Avian | KC607878 | VN1 | ND | ND | ND | |
| Coronavirus-229E, strain | Human | AY386391 | KUMC-9 | ND | ND | ND | |
| Parainfluenza virus 1 | Human | MG255129 | KUMC-44 | ND | ND | ND | |
| Samples Description | ct Value | Clade ** | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAV * | HPAI | 2.3.2.1 | 2.3.4.4 | |||||
| Singleplex | Multiplex | Singleplex | Multiplex | Singleplex | Multiplex | |||
| A/environment/Korea/W150/2006 | + | 20.32 | 20.04 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 2.2 |
| A/Environment/Korea/W541/2016 | + | 20.68 | 21.33 | ND | ND | 21.32 | 22.09 | 2.3.4.4 |
| A/Common Teal/Korea/W555/2017 | + | 19.79 | 21.81 | ND | ND | 21.62 | 22.01 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #1 | + | 25.35 | 26.3 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 |
| Feces sample #2 | + | 21.82 | 21.29 | 23.72 | 24.07 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1a |
| Feces sample #3 | + | 19.5 | 19.32 | 20.97 | 22.12 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1a |
| Feces sample #4 | + | 19.84 | 19.72 | 20.05 | 20.93 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #5 | + | 19.99 | 19.2 | 19.89 | 21.32 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #6 | + | 21.37 | 21.53 | 22.18 | 21.9 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #7 | + | 20.24 | 20.35 | 21.07 | 20.75 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #8 | + | 19.88 | 19.57 | 19.93 | 20.49 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #9 | + | 23.13 | 22.63 | 23.19 | 23.56 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #10 | + | 22.29 | 22.15 | 22.64 | 23.26 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #11 | + | 20.33 | 19.68 | 20.4 | 21.1 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #12 | + | 20.13 | 21 | ND | ND | 20.7 | 21.97 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #13 | + | 19.48 | 22.59 | ND | ND | 22.33 | 21.24 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #14 | + | 20.2 | 19.97 | 20.54 | 20.45 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #15 | + | 22.05 | 21.58 | 21.93 | 22.31 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #16 | + | 21.64 | 23.66 | ND | ND | 23.54 | 23.45 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #17 | + | 20.85 | 20.56 | 20.88 | 21.44 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #18 | + | 19.49 | 19.65 | 20.15 | 20.78 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #19 | + | 20.92 | 21.02 | 21.6 | 21.98 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #20 | + | 20.68 | 20.31 | 20.87 | 21.26 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #21 | + | 22.04 | 23.54 | ND | ND | 23.15 | 23.13 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #22 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #23 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #24 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #25 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #26 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #27 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #28 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #29 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #30 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #31 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #32 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #33 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #34 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #35 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #36 | + | 23.21 | 24.33 | ND | ND | 23.86 | 23.92 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #37 | + | 26.71 | 27.4 | 27.01 | 27.48 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1 |
| Feces sample #38 | + | 20.49 | 21.48 | 21.01 | 20.98 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #39 | + | 22.27 | 22.93 | 22.65 | 23.11 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #40 | + | 21.89 | 22.36 | 21.82 | 22.56 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #41 | + | 22.92 | 23.31 | 22.91 | 23.37 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #42 | + | 19.46 | 19.62 | 19.38 | 19.96 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1a |
| Feces sample #43 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #44 | + | 23.17 | 23.71 | 23.16 | 24.16 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #45 | + | 21.62 | 22.37 | 21.88 | 22.75 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #46 | + | 29.58 | 29.98 | 29.41 | 30.42 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #47 | + | 23.36 | 23.21 | 23.86 | 23.76 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #48 | + | 18.88 | 18.94 | ND | ND | 19.88 | 20.05 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #49 | + | 23.6 | 24.3 | 23.42 | 24.52 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #50 | + | 23.9 | 24.14 | 24.16 | 24.6 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #51 | + | 22.32 | 22.85 | 22.71 | 23.22 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #52 | + | 24.67 | 24.4 | 24.36 | 24.37 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #53 | + | 21.32 | 22.06 | 21.22 | 21.71 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #54 | + | 18.97 | 18.53 | ND | ND | 18.3 | 18.94 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #55 | + | 23.3 | 23.22 | 23.17 | 22.93 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #56 | + | 22.42 | 22.79 | 22.94 | 23 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #57 | + | 22.8 | 22.92 | 22.43 | 22.36 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #58 | + | 25.22 | 25.04 | 24.17 | 25.05 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #59 | + | 23.57 | 23.83 | 23.91 | 23.38 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #60 | + | 23.06 | 23.78 | 23.54 | 23.39 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #61 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #62 | + | 24.81 | 24.75 | 23.93 | 24.55 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
| Feces sample #63 | + | 18.6 | 18.09 | ND | ND | 18.93 | 19.16 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #64 | + | 18.16 | 18.2 | ND | ND | 19.16 | 19.3 | 2.3.4.4 |
| Feces sample #65 | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | LPAI |
| Feces sample #66 | + | 23.79 | 23.94 | 24.28 | 24.4 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1a |
| Feces sample #67 | + | 23.78 | 23.78 | 23.83 | 24.25 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1a |
| Feces sample #68 | + | 24.25 | 24.37 | 24.47 | 24.66 | ND | ND | 2.3.2.1c |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, T.B.; Kim, H.K.; Na, W.; Le, V.P.; Song, M.-S.; Song, D.; Jeong, D.G.; Yoon, S.-W. Development of a Multiplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Different Clades of Avian Influenza in Poultry. Viruses 2020, 12, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010100
Le TB, Kim HK, Na W, Le VP, Song M-S, Song D, Jeong DG, Yoon S-W. Development of a Multiplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Different Clades of Avian Influenza in Poultry. Viruses. 2020; 12(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Tran Bac, Hye Kwon Kim, Woonsung Na, Van Phan Le, Min-Suk Song, Daesub Song, Dae Gwin Jeong, and Sun-Woo Yoon. 2020. "Development of a Multiplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Different Clades of Avian Influenza in Poultry" Viruses 12, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010100
APA StyleLe, T. B., Kim, H. K., Na, W., Le, V. P., Song, M.-S., Song, D., Jeong, D. G., & Yoon, S.-W. (2020). Development of a Multiplex RT-qPCR for the Detection of Different Clades of Avian Influenza in Poultry. Viruses, 12(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010100





