Inhibition of Influenza A Virus by Human Infant Saliva
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Collection of Saliva
2.3. Treatment of Saliva with Receptor-Destroying Enzyme (RDE)
2.4. Virus Neutralization Assay
2.5. Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Assay
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
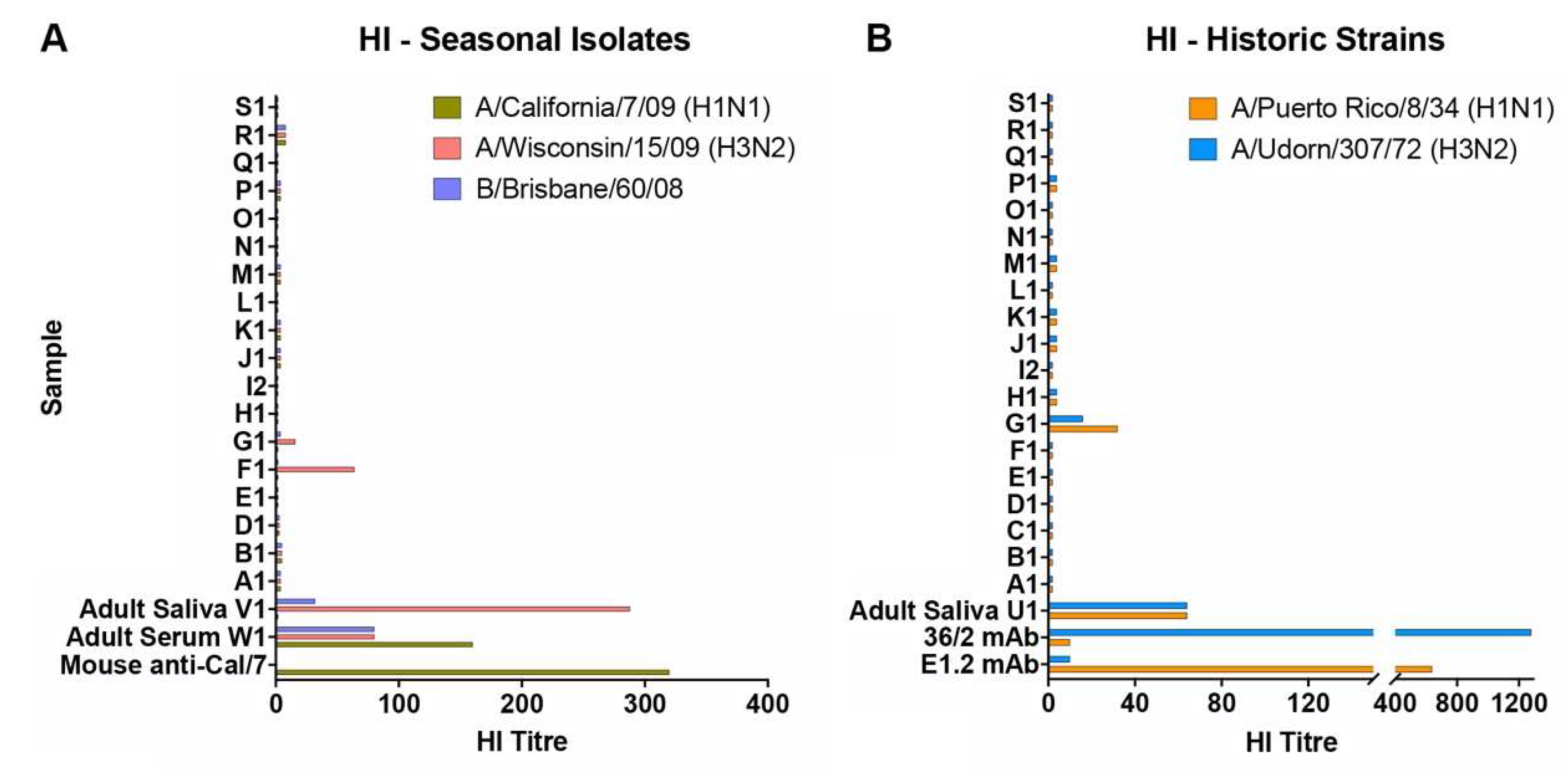
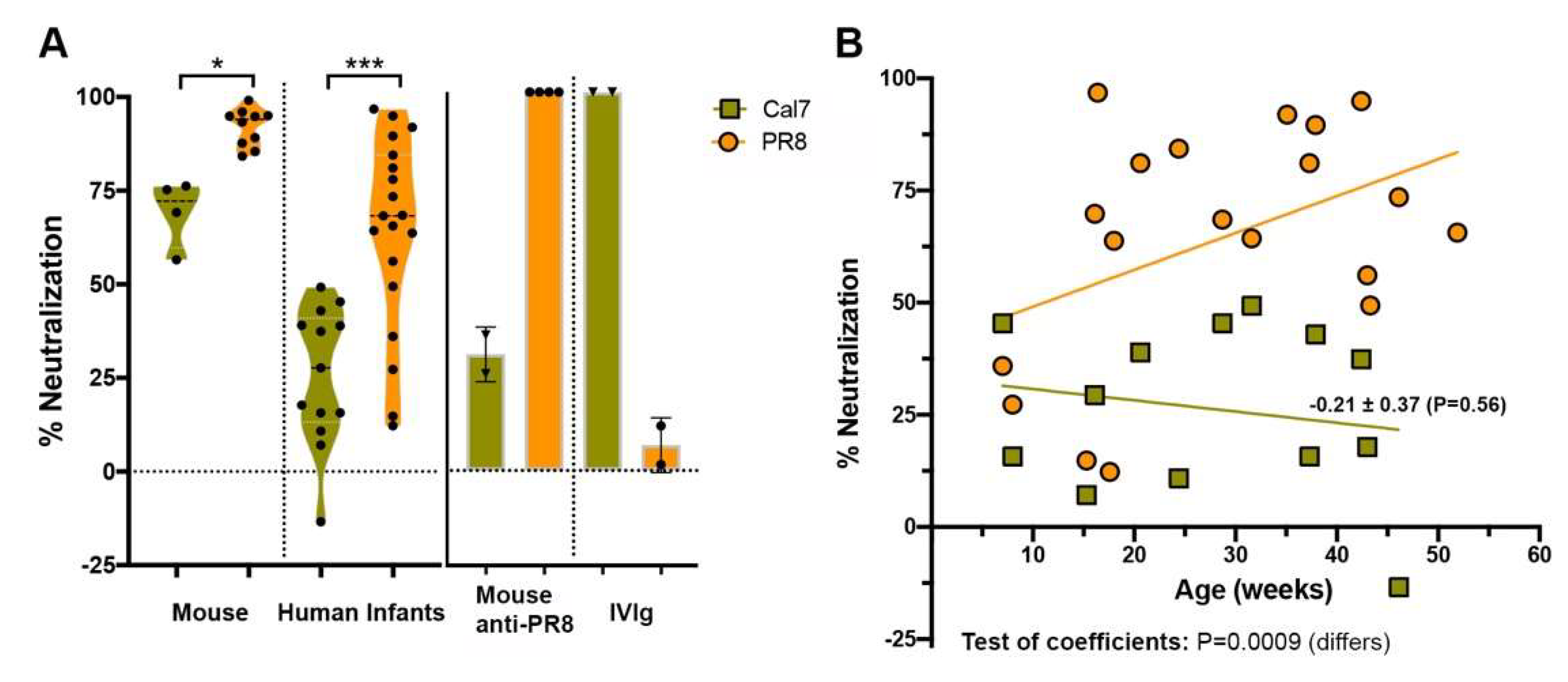
3.1. Infant Saliva Is Largely Devoid of Antibodies to Current and Historic Influenza Strains
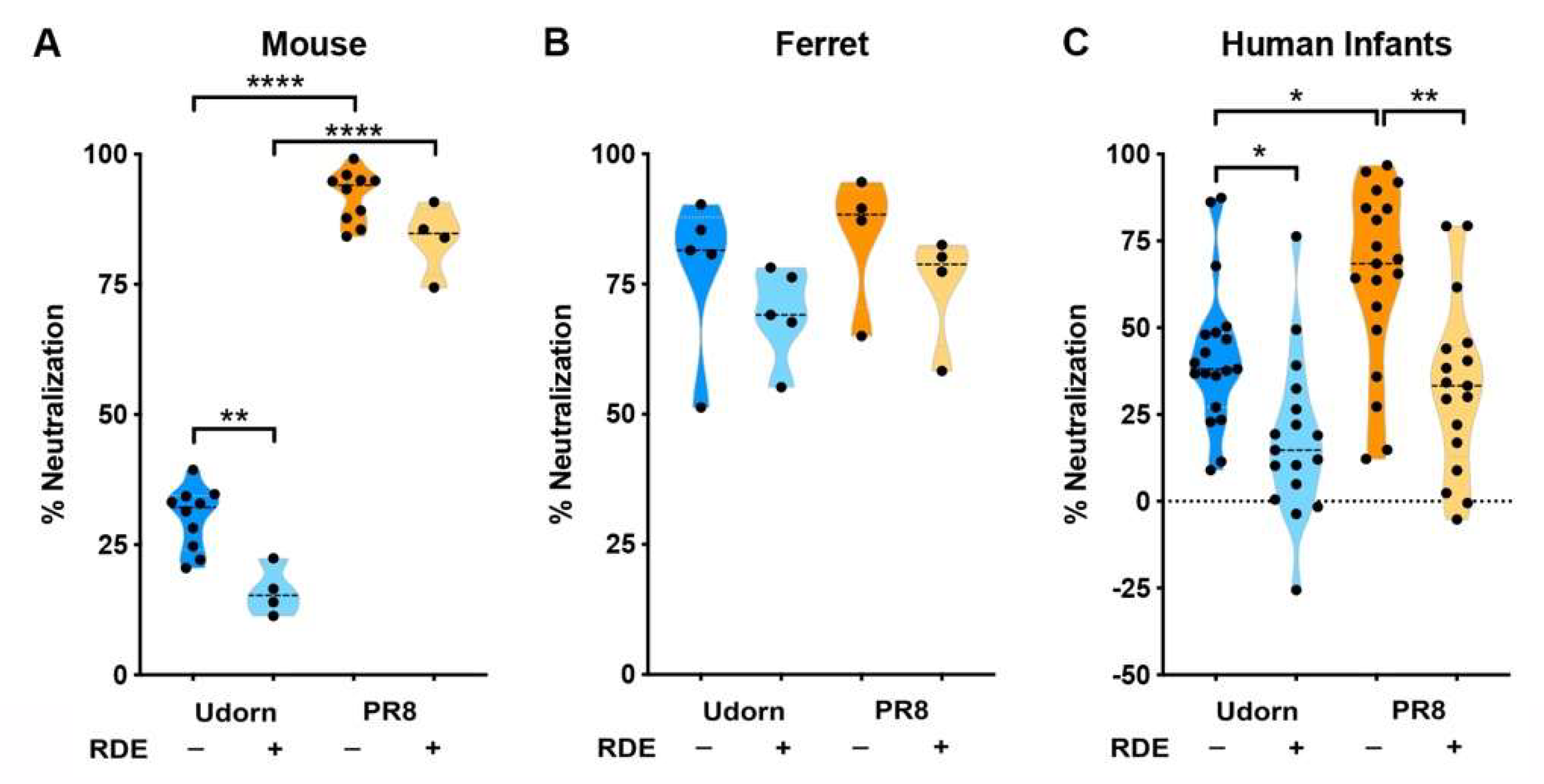
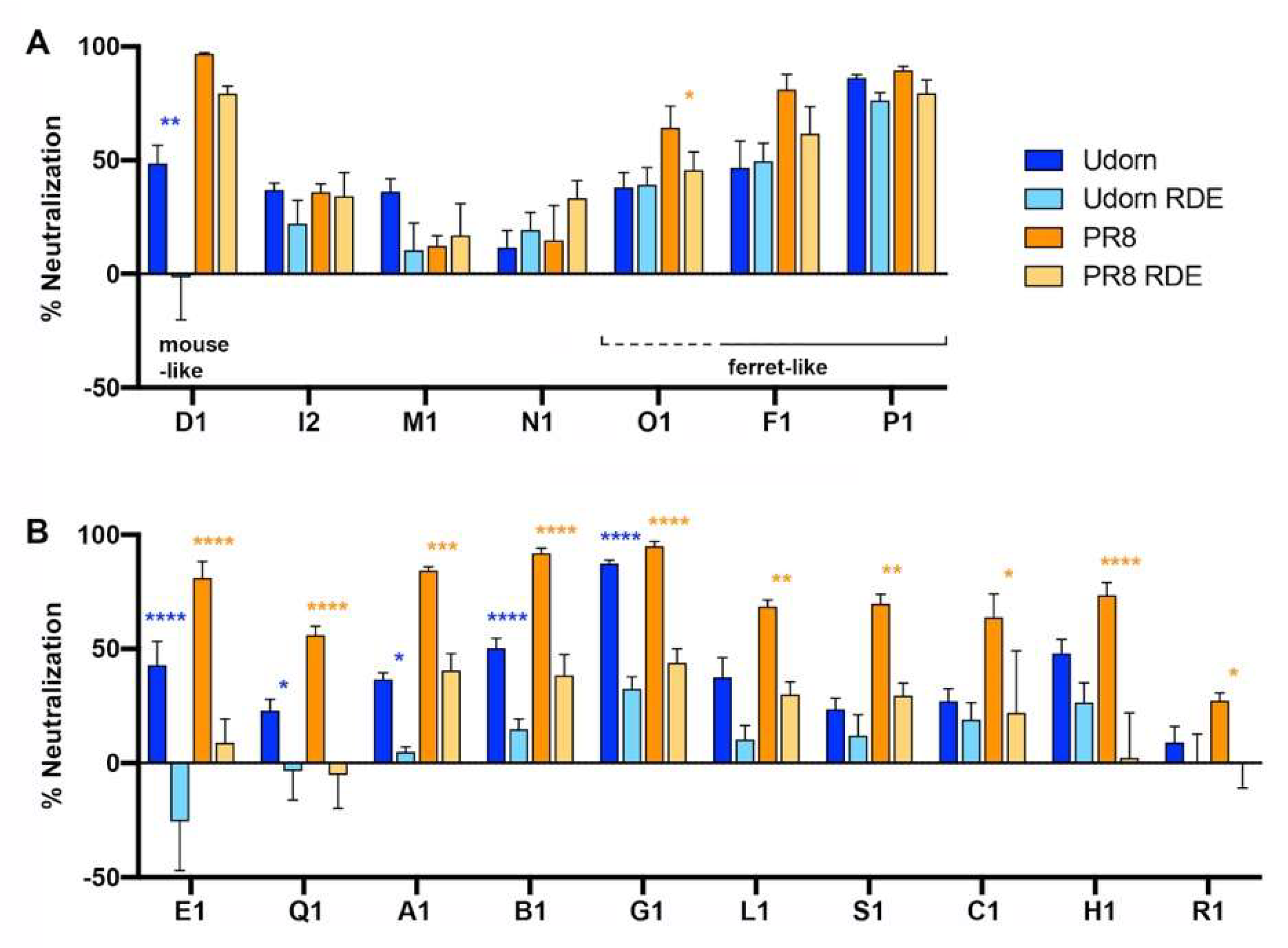
3.2. Infant Saliva Showed a Complex Pattern of Inhibition Unlike That Seen in the Mouse or Ferret
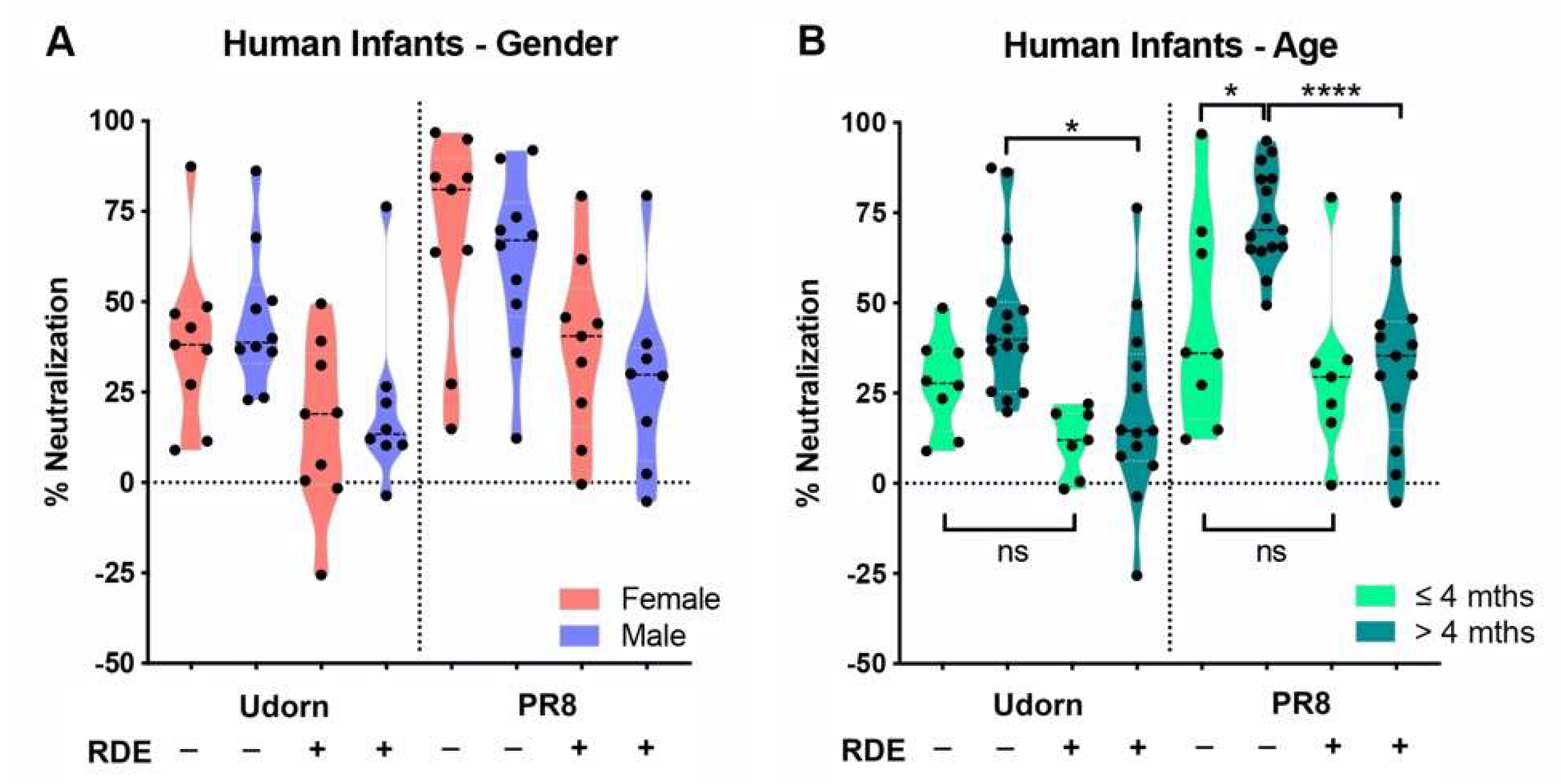
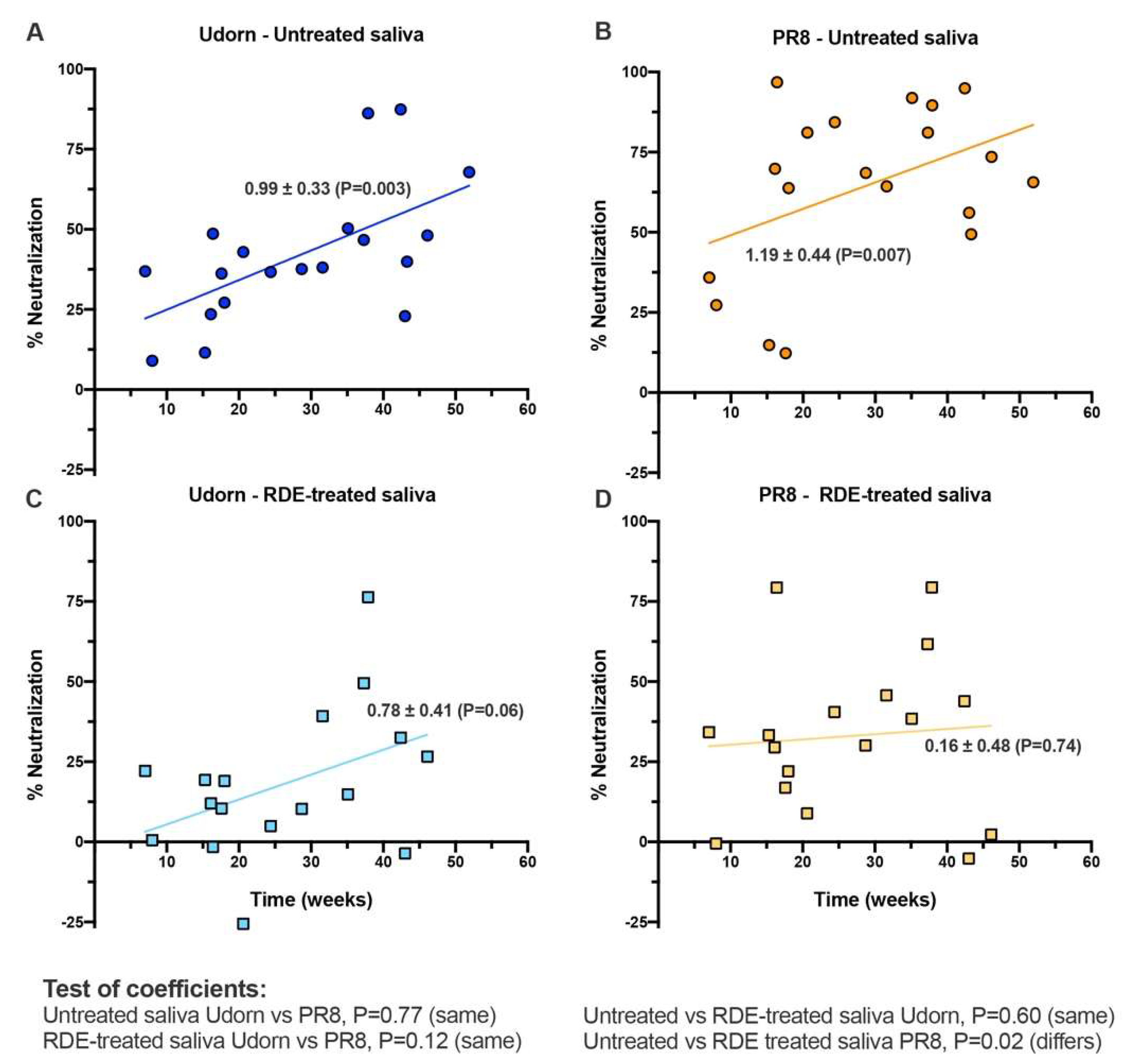
3.3. Inhibitors in Infant Saliva Differed with Age But Not Gender
3.4. Inhibition of the 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Virus by Infant Saliva Is Less Than That of PR8
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Infant ID | Age (weeks) | Gender |
|---|---|---|
| I1 | 6.1 | Male |
| I21 | 7.0 | Male |
| R1 | 8.0 | Female |
| N1 | 15.3 | Female |
| S1 | 16.1 | Male |
| D1 | 16.4 | Female |
| M1 | 17.6 | Male |
| C1 | 18.0 | Female |
| E1 | 20.6 | Female |
| A1 | 24.4 | Female |
| L1 | 28.7 | Male |
| S2 | 31.1 | Male |
| O1 | 31.6 | Female |
| B1 | 35.1 | Male |
| F1 | 37.3 | Female |
| S3 | 37.6 | Male |
| P1 | 37.9 | Male |
| G1 | 42.4 | Female |
| Q1 | 43.0 | Male |
| J1 | 43.3 | Male |
| A2 | 44.1 | Female |
| H1 | 46.1 | Male |
| K1 | 51.9 | Male |
References
- White, M.R.; Crouch, E.; van Eijk, M.; Hartshorn, M.; Pemberton, L.; Tornoe, I.; Holmskov, U.; Hartshorn, K.L. Cooperative anti-influenza activities of respiratory innate immune proteins and neuraminidase inhibitor. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 288, L831–L840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reading, P.C.; Morey, L.S.; Crouch, E.C.; Anders, E.M. Collectin-mediated antiviral host defense of the lung: Evidence from influenza virus infection of mice. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8204–8212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; White, M.R.; Tecle, T.; Holmskov, U.; Crouch, E.C. Innate defense against influenza A virus: Activity of human neutrophil defensins and interactions of defensins with surfactant protein D. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6962–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; White, M.R.; Shepherd, V.; Reid, K.; Jensenius, J.C.; Crouch, E.C. Mechanisms of anti-influenza activity of surfactant proteins A and D: Comparison with serum collectins. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273 Pt 1, L1156–L1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; White, M.R.; Mogues, T.; Ligtenberg, T.; Crouch, E.; Holmskov, U. Lung and salivary scavenger receptor glycoprotein-340 contribute to the host defense against influenza a viruses. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L1066–L1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; Reid, K.B.; White, M.R.; Jensenius, J.C.; Morris, S.M.; Tauber, A.I.; Crouch, E. Neutrophil deactivation by influenza a viruses: Mechanisms of protection after viral opsonization with collectins and hemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies. Blood 1996, 87, 3450–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; Liou, L.S.; White, M.R.; Kazhdan, M.M.; Tauber, J.L.; Tauber, A.I. Neutrophil deactivation by influenza A virus. Role of hemagglutinin binding to specific sialic acid-bearing cellular proteins. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 3952–3960. [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; Crouch, E.C.; White, M.R.; Eggleton, P.; Tauber, A.I.; Chang, D.; Sastry, K. Evidence for a protective role of pulmonary surfactant protein D (SP-D) against influenza a viruses. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, E.M.; Hartley, C.A.; Jackson, D.C. Bovine and mouse serum beta inhibitors of influenza a viruses are mannose-binding lectins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; Sastry, K.; White, M.R.; Anders, E.M.; Super, M.; Ezekowitz, R.A.; Tauber, A.I. Human Mannose-Binding Protein Functions as an Opsonin for Influenza-a Viruses. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; Sastry, K.; Brown, D.; White, M.R.; Okarma, T.B.; Lee, Y.M.; Tauber, A.I. Conglutinin Acts as an Opsonin for Influenza-a Viruses. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 6265–6273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pritchett, T.J.; Paulson, J.C. Basis for the Potent Inhibition of Influenza-Virus Infection by Equine and Guinea-Pig Alpha-2-Macroglobulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 9850–9858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanaoka, K.; Pritchett, T.J.; Takasaki, S.; Kochibe, N.; Sabesan, S.; Paulson, J.C.; Kobata, A. 4-O-acetyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid in the N-linked carbohydrate structures of equine and guinea pig alpha 2-macroglobulins, potent inhibitors of influenza virus infection. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 9842–9849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benne, C.A.; Kraaijeveld, C.A.; Vanstrijp, J.A.G.; Brouwer, E.; Harmsen, M.; Verhoef, J.; Vangolde, L.M.G.; Vaniwaarden, J.F. Interactions of Surfactant Protein-a with Influenza-a Viruses—Binding and Neutralization. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reading, P.C.; Bozza, S.; Gilbertson, B.; Tate, M.; Moretti, S.; Job, E.R.; Crouch, E.C.; Brooks, A.G.; Brown, L.E.; Bottazzi, B.; et al. Antiviral activity of the long chain pentraxin PTX3 against influenza viruses. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3391–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.R.; Helmerhorst, E.J.; Ligtenberg, A.; Karpel, M.; Tecle, T.; Siqueira, W.L.; Oppenheim, F.G.; Hartshorn, K.L. Multiple components contribute to ability of saliva to inhibit influenza viruses. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 24, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamud, D.; Abrams, W.R.; Barber, C.A.; Weissman, D.; Rehtanz, M.; Golub, E. Antiviral activities in human saliva. Adv. Dent. Res. 2011, 23, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limsuwat, N.; Suptawiwat, O.; Boonarkart, C.; Puthavathana, P.; Auewarakul, P.; Wiriyarat, W. Susceptibility of human and avian influenza viruses to human and chicken saliva. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorn, K.L.; Ligtenberg, A.; White, M.R.; Van Eijk, M.; Hartshorn, M.; Pemberton, L.; Holmskov, U.; Crouch, E. Salivary agglutinin and lung scavenger receptor cysteine-rich glycoprotein 340 have broad anti-influenza activities and interactions with surfactant protein D that vary according to donor source and sialylation. Biochem. J. 2006, 393 Pt 2, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Lo, C.W.; Liu, P.F.; Liu, Y.T.; Gallo, R.L.; Hsieh, M.F.; Schooley, R.T.; Huang, C.M. The essentiality of alpha-2-macroglobulin in human salivary innate immunity against new H1N1 swine origin influenza A virus. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2396–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergey, E.J.; Cho, M.I.; Hammarskjold, M.L.; Rekosh, D.; Levine, M.J.; Blumberg, B.M.; Epstein, L.G. Aggregation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by human salivary secretions. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1993, 4, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergey, E.J.; Gu, M.; Collins, A.R.; Bradway, S.D.; Levine, M.J. Modulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication by human salivary secretions. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1993, 8, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivinson, K.; Deliyannis, G.; McNabb, L.; Grollo, L.; Gilbertson, B.; Jackson, D.; Brown, L.E. Salivary Blockade Protects the Lower Respiratory Tract of Mice from Lethal Influenza Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00624-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbertson, B.; Ng, W.C.; Crawford, S.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L.; Brown, L.E. Mouse saliva inhibits transit of influenza virus to the lower respiratory tract by efficiently blocking influenza virus neuraminidase activity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00145-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Cai, T.; Wu, P.; Yang, F.; Li, Z. Analysis of age and gender associated N-glycoproteome in human whole saliva. Clin. Proteom. 2014, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonesson, M.; Wickstrom, C.; Kinnby, B.; Ericson, D.; Matsson, L. Mucins MUC5B and MUC7 in minor salivary gland secretion of children and adults. Arch. Oral Biol. 2008, 53, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonesson, M.; Hamberg, K.; Wallengren, M.L.; Matsson, L.; Ericson, D. Salivary IgA in minor-gland saliva of children, adolescents, and young adults. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonesson, M.; Ericson, D.; Kinnby, B.; Wickstrom, C. Glycoprotein 340 and sialic acid in minor-gland and whole saliva of children, adolescents, and adults. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, M.; Dang, L.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Age- and sex-associated differences in the glycopatterns of human salivary glycoproteins and their roles against influenza A virus. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2742–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashunmugam, T.; Malamud, D.; Davis, C.; Abrams, W.R.; Friedman, H.M. Human submandibular saliva inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection by displacing envelope glycoprotein gp120 from the virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limsuwat, N.; Suptawiwat, O.; Boonarkart, C.; Puthavathana, P.; Wiriyarat, W.; Auewarakul, P. Sialic acid content in human saliva and anti-influenza activity against human and avian influenza viruses. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Cui, L.; Huo, X.; Xia, M.; Shi, F.; Zeng, X.; Huang, P.; Zhong, W.; Li, W.; Xu, K.; et al. Saliva as a source of reagent to study human susceptibility to avian influenza H7N9 virus infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, G.A.; Paul, J.A.; Barry, R.D. Relative immunogenicity of the cold-adapted influenza virus A/Ann Arbor/6/60 (A/AA/6/60-ca), recombinants of A/AA/6/60-ca, and parental strains with similar surface antigens. Infect. Immun. 1984, 43, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartley, C.A.; Jackson, D.C.; Anders, E.M. Two distinct serum mannose-binding lectins function as beta inhibitors of influenza virus: Identification of bovine serum beta inhibitor as conglutinin. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4358–4363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruhl, S.; Rayment, S.A.; Schmalz, G.; Hiller, K.A.; Troxler, R.F. Proteins in whole saliva during the first year of infancy. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilbertson, B.; Edenborough, K.; McVernon, J.; Brown, L.E. Inhibition of Influenza A Virus by Human Infant Saliva. Viruses 2019, 11, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080766
Gilbertson B, Edenborough K, McVernon J, Brown LE. Inhibition of Influenza A Virus by Human Infant Saliva. Viruses. 2019; 11(8):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080766
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilbertson, Brad, Kathryn Edenborough, Jodie McVernon, and Lorena E. Brown. 2019. "Inhibition of Influenza A Virus by Human Infant Saliva" Viruses 11, no. 8: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080766
APA StyleGilbertson, B., Edenborough, K., McVernon, J., & Brown, L. E. (2019). Inhibition of Influenza A Virus by Human Infant Saliva. Viruses, 11(8), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080766





