Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA Detection in Respiratory Samples: Study of a Cohort of Patients Affected by Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Sample Collection
2.2. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
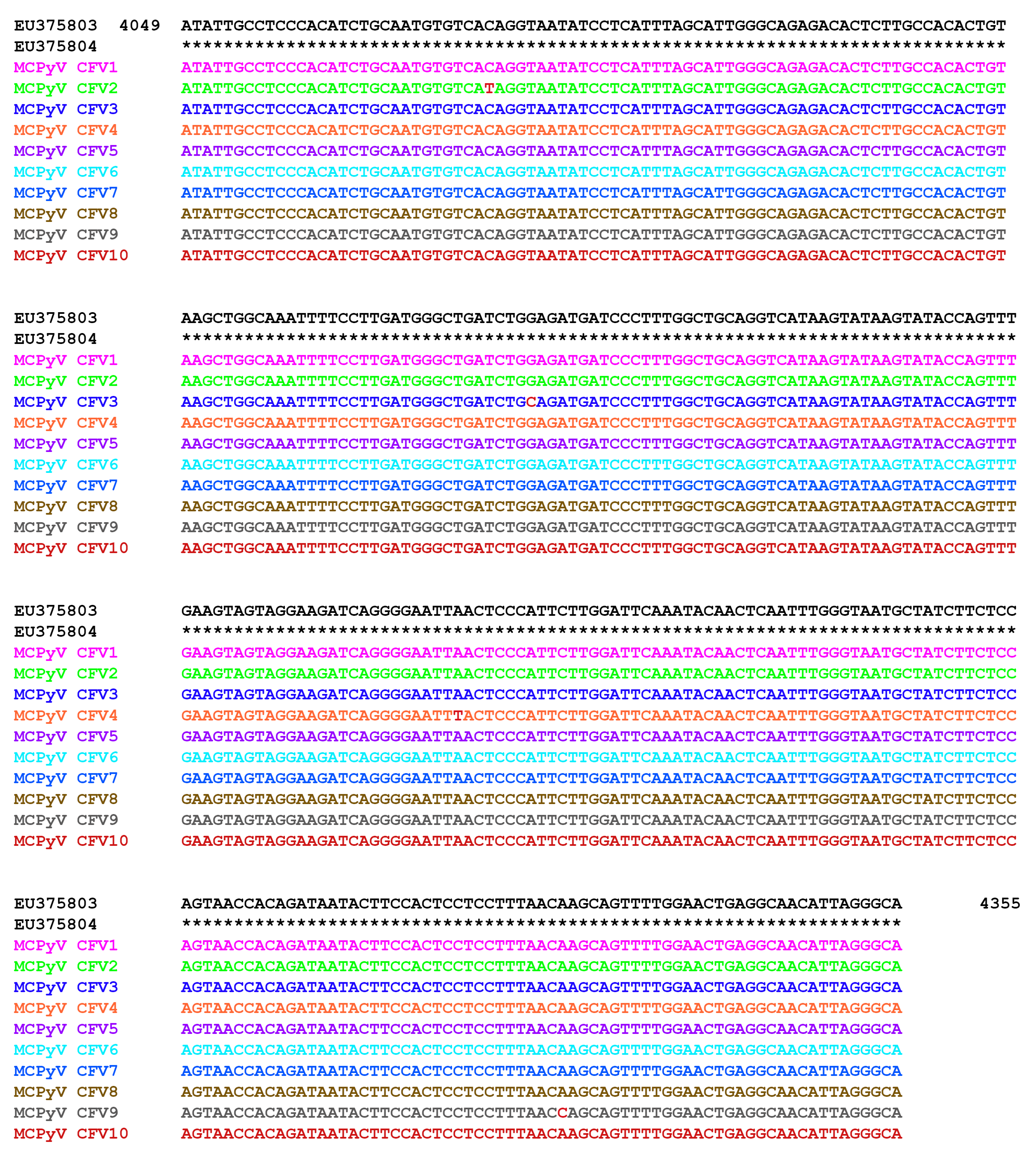
2.3. MCPyV DNA Sequencing
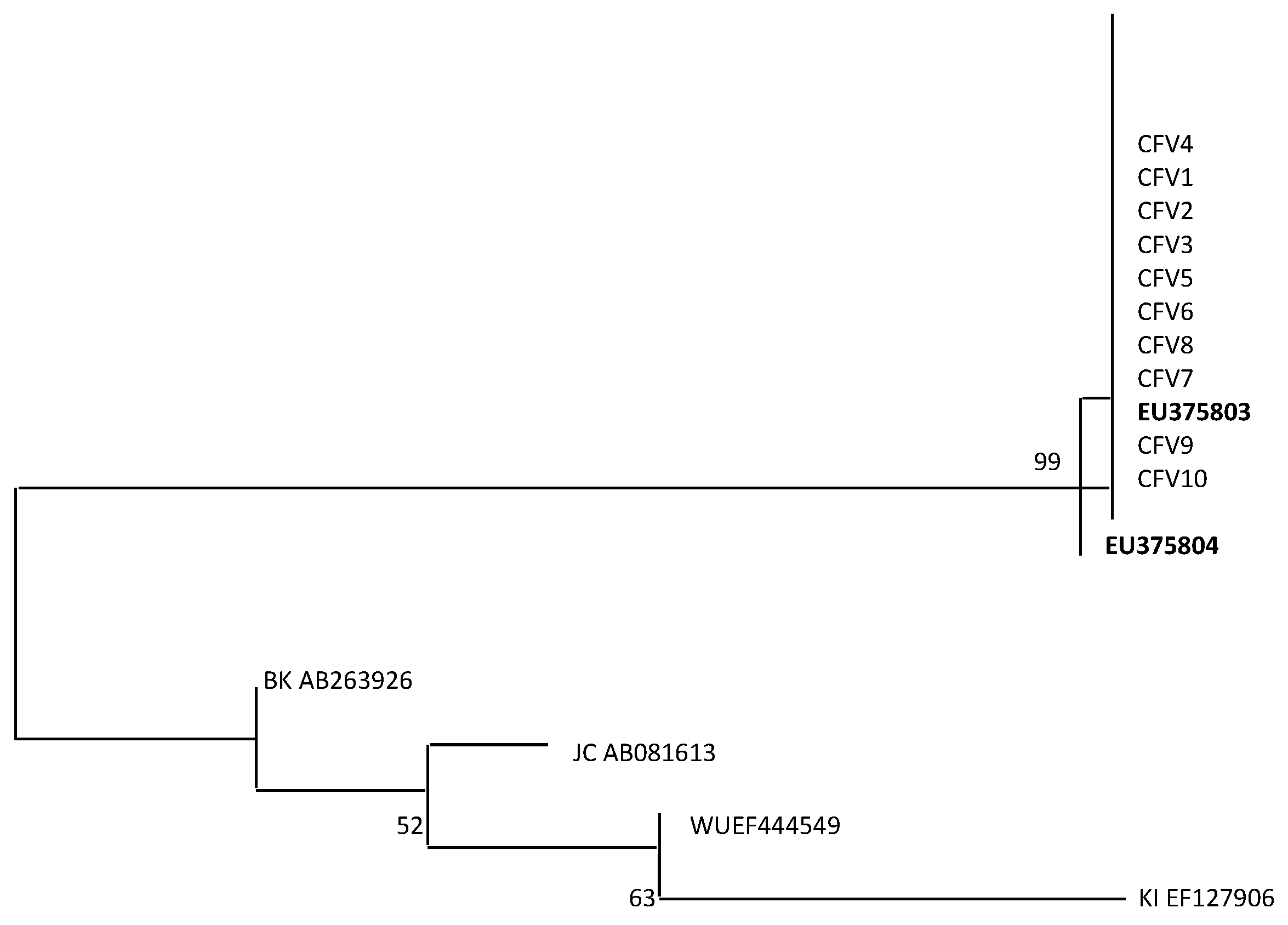
2.4. Viral Capsid Protein 1 (VP1) Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
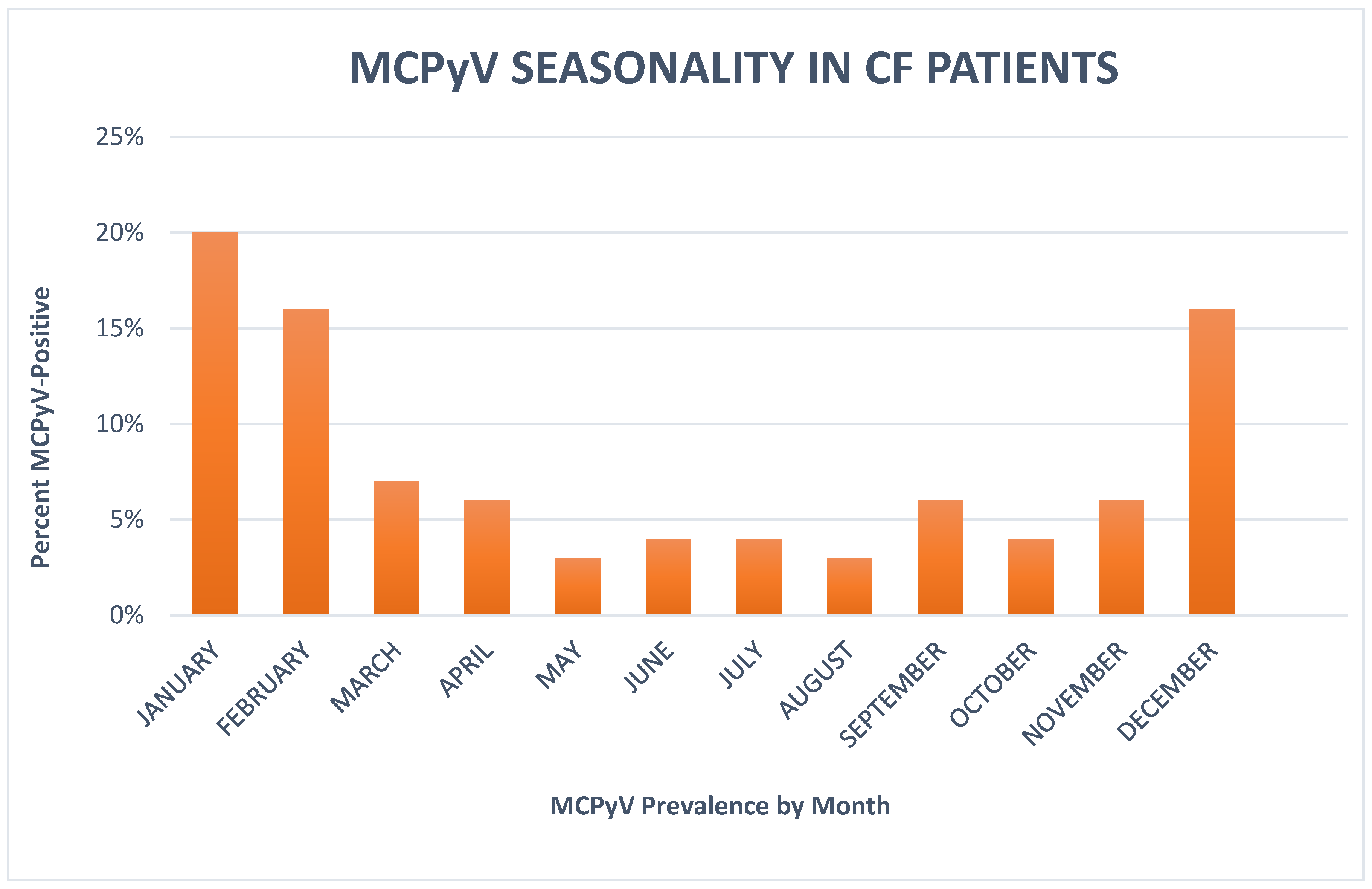
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstov, Y.L.; Pastrana, D.V.; Feng, H.; Becker, J.C.; Jenkins, F.J.; Moschos, S.; Chang, Y.; Buck, C.B.; Moore, P.S. Human Merkel cell polyomavirus infection II: MCV is a common human infection that can be detected by conformational capsid epitope immunoassays. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscidi, R.P.; Rollison, D.E.; Sondak, V.K.; Silver, B.; Messina, J.L.; Giuliano, A.R.; Fulp, W.; Ajidahun, A.; Rivanera, D. Age-specific seroprevalence of Merkel cell polyomavirus, BK virus, and JC virus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashida, Y.; Kamioka, M.; Tanaka, M.; Hosokawa, S.; Murakami, M.; Nakajima, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Fujieda, M.; Sano, S.; Daibata, M. Ecology of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Healthy Skin Among Individuals in an Asian Cohort. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, C.; Belloni, B.; Puchta, U.; Sander, C.A.; Flaig, M.J. Prevalence of MCPyV in Merkel cell carcinoma and non-MCC tumors. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2010, 37, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comar, M.; Cuneo, A.; Maestri, I.; Melloni, E.; Pozzato, G.; Soffritti, O.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G. Merkel-cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) is rarely associated to Bchronic lymphocytic leukemia (1 out of 50) samples and occurs late in the natural history of the disease. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberhold, S.; Hellmich, M.; Panning, M.; Bartok, E.; Silling, S.; Akgul, B.; Wieland, U. Human polyomavirus and human papillomavirus prevalence and viral load in non-malignant tonsillar tissue and tonsillar carcinoma. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 206, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajoh, M.; Hashida, Y.; Nemoto, Y.; Oguri, H.; Maeda, N.; Furihata, M.; Fukaya, T.; Daibata, M. Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in cervical squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas from Japanese patients. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, M.E.; Lambert, P.F. Merkel cell polyomavirus: A newly discovered human virus with oncogenic potential. Virology 2013, 435, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salakova, M.; Koslabova, E.; Vojtechova, Z.; Tachezy, R.; Sroller, V. The detection of human polyomavirus MCPyV, HPyV6 and HPyV7 in malignant and non-malignant tonsillar tissues. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 88, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulongne, V.; Dereure, O.; Kluger, N.; Molès, J.P.; Guillot, B.; Segondy, M. Merkel cell polyomavirus DNA detection in lesional and non-lesional skin from patients with Merkel cell carcinoma or other skin diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialasiewicz, S.; Lampert, S.B.; Whiley, D.M.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P. Merkel cell polyomavirus DNA in respiratory specimens from children and adults. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, S.; Lindau, C.; Tiveljung-Lindell, A.; Allander, T. Merkel cell polyomavirus in respiratory tract secretions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantola, K.; Sadeghi, M.; Lahtinen, A.; Koskenvuo, M.; Aaltonen, L.M.; Möttönen, M.; Rahiala, J.; Saarinen-Pihkala, U.; Riikonen, P.; Jartti, T.; et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus DNA in tumor-free tonsillar tissues and upper respiratory tract samples: Implications for respiratory transmission and latency. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 45, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi Kiasari, B.; Vallery, P.J.; Klapper, P.E. Merkel cell polyomavirus DNA in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients with respiratory disease. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaria, M.; Caccuri, F.; Apostoli, P.; Giagulli, C.; Pelucchi, F.; Padoan, R.F.; Caruso, A.; Fiorentini, S. Detection of KI WU and Merkel cell polyomavirus in respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, e9–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Babakir-Mina, M.; Ciccozzi, M.; Presti, A.; Greco, F.; Perno, C.F.; Ciotti, M. Identification of Merkel cell polyomavirus in the lower respiratory tract of Italian patients. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.B.; Lowy, D.R. Getting stronger: The relationship between a newly identified virus and Merkel cell carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourez, T.; Bergeron, A.; Ribaud, P.; Scieux, C.; de Latour, R.P.; Tazi, A.; Socié, G.; Simon, F.; LeGoff, J. Polyomaviruses KI and WU in immunocompromised patients with respiratory disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Garcea, R.L.; Robinson, C.C.; Simões, E.A. WU and KI polyomavirus infections in pediatric hematology/oncology patients with acute respiratory tract illness. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, V.; Prezioso, C.; Bagnato, F.; Antonelli, G. John Cunningham virus: An overview on biology and disease of the etiological agent of the progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. New Microbiol. 2018, 41, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.E.; Prober, C.G.; Manson, B.; Corey, M.; Levison, H. Association of respiratory viral infections with pulmonary deterioration in patients with cystic fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.L.; Burns, J.L.; Ramsey, B.W. Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 918–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wat, D.; Gelder, C.; Hibbitts, S.; Cafferty, F.; Bowler, I.; Pierrepoint, M.; Evans, R.; Doull, I. The role of respiratory viruses in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2008, 7, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiki, R.K.; Bugawan, T.L.; Horn, G.T.; Mullis, K.B.; Erlich, H.A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature 1986, 324, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikova, E.; Emin, D.; Alexandrova, D.; Shindov, M.; Kumanova, A.; Lekov, A.; Moens, U. Detection of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Respiratory Tract Specimens. Intervirology 2017, 60, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClustalW2-Multiple Sequence Alignment. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Dudley, J.; Tamura, K. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform. 2008, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrovecchio, R.; Babakir-Mina, M.; Rapanotti, M.C.; Arcese, W.; Perno, C.F.; Ciotti, M. Monitoring of KI and WU polyomaviruses in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1122–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, C.P.; Norja, P.; Anthony, I.; Bell, J.E.; Simmonds, P. Reactivation and mutation of newly discovered WU, KI, and Merkel cell carcinoma polyomaviruses in immunosuppressed individuals. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, M.N.; Fogarty, A.; McKeever, T.M.; Goss, C.H.; Rosenfeld, M.; Smyth, A.R. Early respiratory bacterial detection and anti-staphylococcal antibiotic prophylaxis in young children with cystic fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoli, D.H.; Hoffman, L.R. Help, hinder, hide and harm: What can we learn from the interactions between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus during respiratory infections? Thorax 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Subject Category | CF Patients N = 249 | p-Value | Non-CF Patients N = 124 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 1–62, 18.4 ± 14.3 | NS | 1–63,18.7 ± 14 | NS |
| Age ≤ 6 years, n (%) | 48 (19%) | 24 (19%) | ||
| Age 6–17 years, n (%) | 113 (45%) | 56 (45%) | ||
| Age > 18 years, n (%) | 88 (35%) | 44 (35%) | ||
| Sex, n female (%) | 152 (61%) | NS | 73 (59%) | NS |
| Among ≤ 6 year olds, n (%) | 32 (21%) | 15 (8%) | ||
| Among 7–17 year olds, n (%) | 65 (43%) | 32 (7%) | ||
| Among >18 year olds, n (%) | 55 (36%) | 26 (11%) | ||
| Sex, n male (%) | 97 (39%) | NS | 51 (41%) | NS |
| Among ≤ 6 year olds, n (%) | 16 (17%) | 9 (18%) | ||
| Among 7–17 year olds, n (%) | 48 (49.4%) | 24 (47%) | ||
| Among >18 year olds, n (%) | 33 (34%) | 18 (35%) | ||
| MCPyV-positive, n (%) | 65 (26%) | 11 (9%) | ||
| Among ≤ 6 year olds, n (%) | 11 (23%) | NS | 2 (8%) | NS |
| Among 7–17 year olds, n (%) | 28 (25%) | NS | 4 (7%) | NS |
| Among >18 year olds, n (%) | 26 (30%) | p = 0.037 | 5 (11%) | NS |
| MCPyV-positive, n (%) female | 43 (66%) | NS | 6 (8%) | NS |
| Among ≤ 6 year olds, n (%) | 7 (22%) | 1 (7%) | ||
| Among 7–17 year olds, n (%) | 17 (26%) | 2 (6%) | ||
| Among >18 year olds, n (%) | 19 (34%) | 3 (11%) | ||
| MCPyV-positive, n (%) male | 22 (34%) | NS | 5 (10%) | NS |
| Among ≤ 6 year olds, n (%) | 4 (25%) | 1 (1%) | ||
| Among 7–17 year olds, n (%) | 11 (23%) | 2 (8.3%) | ||
| Among >18 year olds, n (%) | 7 (21%) | 2 (4%) |
| Subject Category | CF Patients N = 249 | S. aureus Colonization Status | p-Value | P. aeruginosa Colonization Status | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCPyV-positive, n (%) | 65 (26%) | 47 (72%) | p = 0.001 | 12 (18.5%) | NS |
| Among ≤ 6 year olds, n (%) | 11 (23%) | 9 (19%) | p = 0.030 | 2 (16%) | NS |
| Among 7–17 year olds, n (%) | 28 (25%) | 18 (38%) | p = 0.001 | 3 (25%) | NS |
| Among >18 year olds, n (%) | 26 (30%) | 20 (43%) | NS | 7 (59%) | NS |
| Subject Category | CF Patients N= 249 | p-Value | S. aureus Colonization Status | p-Value |
| MCPyV-positive, n (%) | 65 (26%) | p = 0.001 | 47 | p = 0.001 |
| non-CF patients N= 124 | p-value | S. aureus colonization status | p-value | |
| MCPyV-positive, n (%) | 11 (9%) | NS | 12 | NS |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prezioso, C.; Di Lella, F.M.; Rodio, D.M.; Bitossi, C.; Trancassini, M.; Mele, A.; de Vito, C.; Antonelli, G.; Pietropaolo, V. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA Detection in Respiratory Samples: Study of a Cohort of Patients Affected by Cystic Fibrosis. Viruses 2019, 11, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060571
Prezioso C, Di Lella FM, Rodio DM, Bitossi C, Trancassini M, Mele A, de Vito C, Antonelli G, Pietropaolo V. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA Detection in Respiratory Samples: Study of a Cohort of Patients Affected by Cystic Fibrosis. Viruses. 2019; 11(6):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060571
Chicago/Turabian StylePrezioso, Carla, Federica Maria Di Lella, Donatella Maria Rodio, Camilla Bitossi, Maria Trancassini, Annamaria Mele, Corrado de Vito, Guido Antonelli, and Valeria Pietropaolo. 2019. "Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA Detection in Respiratory Samples: Study of a Cohort of Patients Affected by Cystic Fibrosis" Viruses 11, no. 6: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060571
APA StylePrezioso, C., Di Lella, F. M., Rodio, D. M., Bitossi, C., Trancassini, M., Mele, A., de Vito, C., Antonelli, G., & Pietropaolo, V. (2019). Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA Detection in Respiratory Samples: Study of a Cohort of Patients Affected by Cystic Fibrosis. Viruses, 11(6), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11060571





