Interferon-Independent Upregulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection is Dependent on IRF3 Expression
Abstract
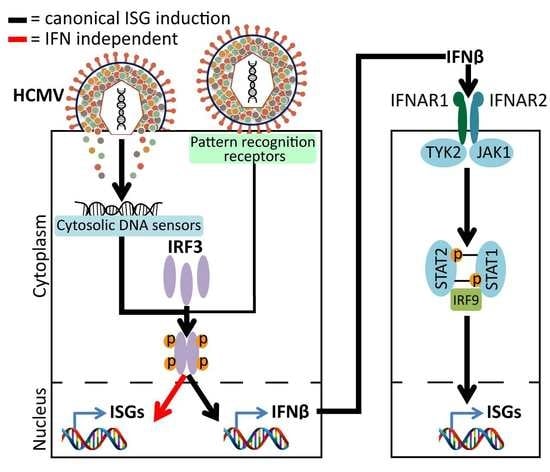
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Viral Infection and Treatment of Cells with Conditioned Supernatants
2.2. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. CRISPR/Cas-9
3. Results
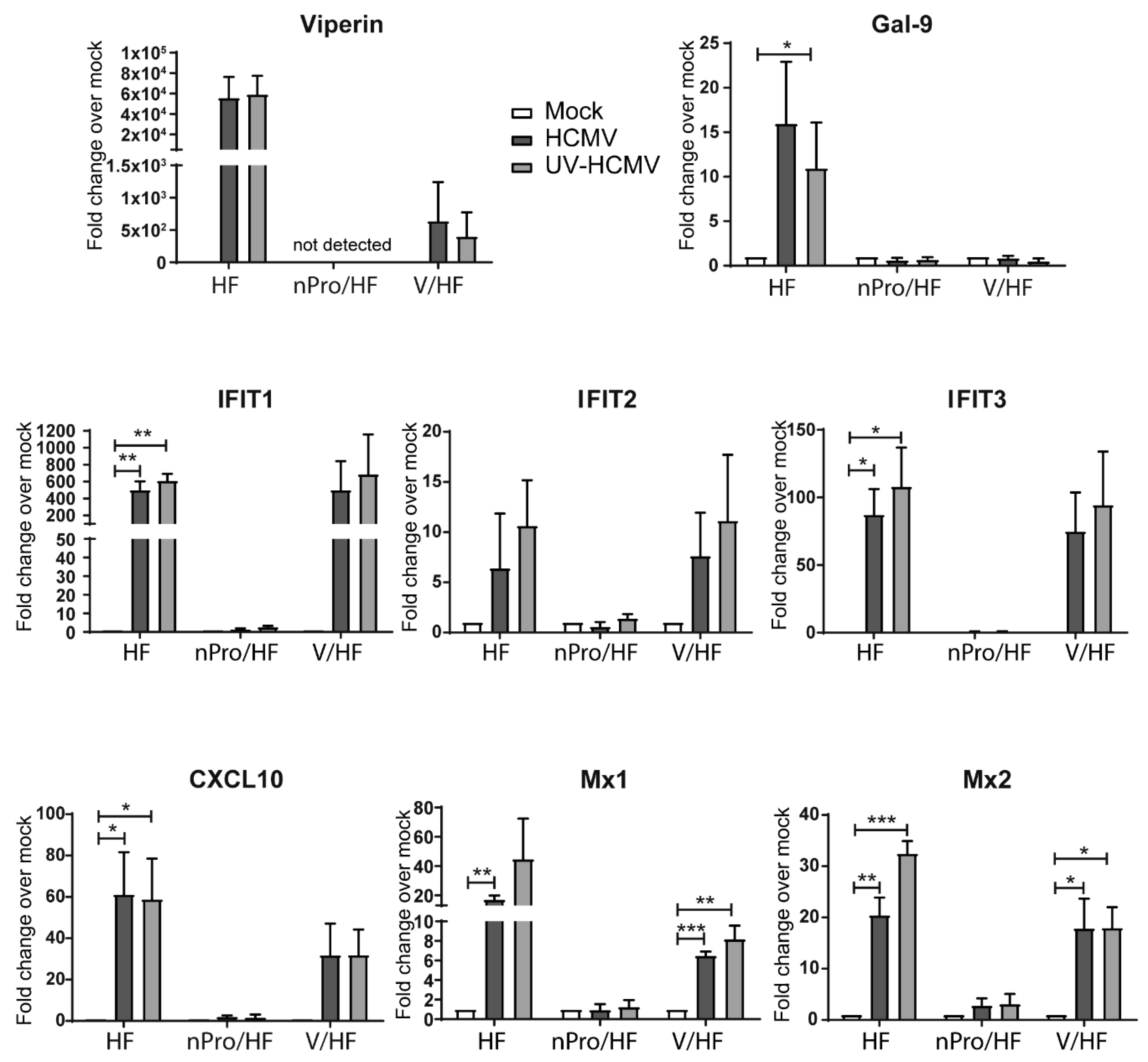
3.1. Transcript Upregulation of Interferon (IFN)-Independent Interferon-Stimulated Genes (ISGs) Following Infection with Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and Ultraviolet-Irradiated HCMV (UV-HCMV) in IRF3-Deficient Human Foreskin Fibroblasts (HFs)
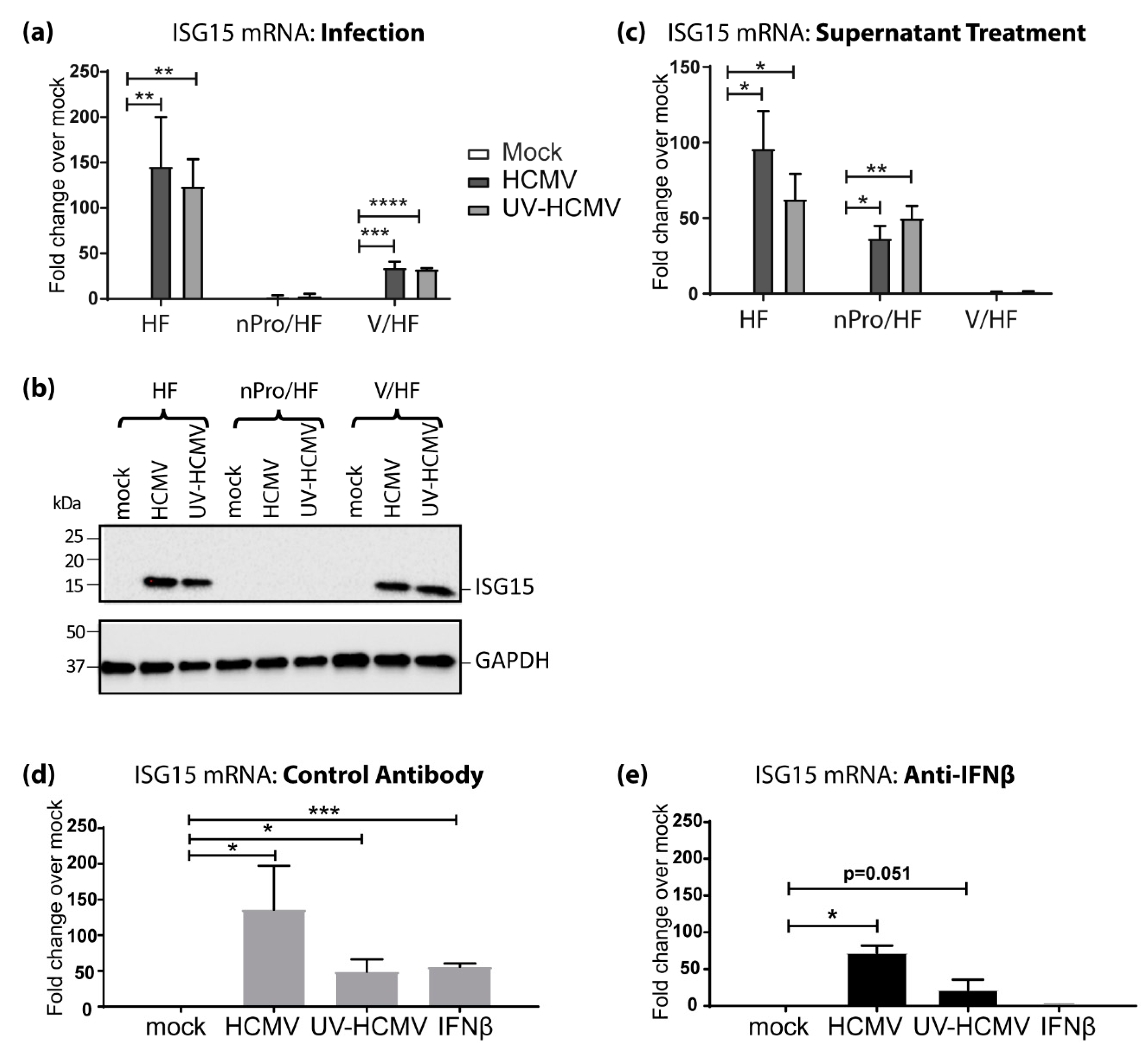
3.2. IFN-Independent, IRF3-Dependent Induction of ISG15 Expression Contributes Significantly to Its Upregulation by HCMV Infection
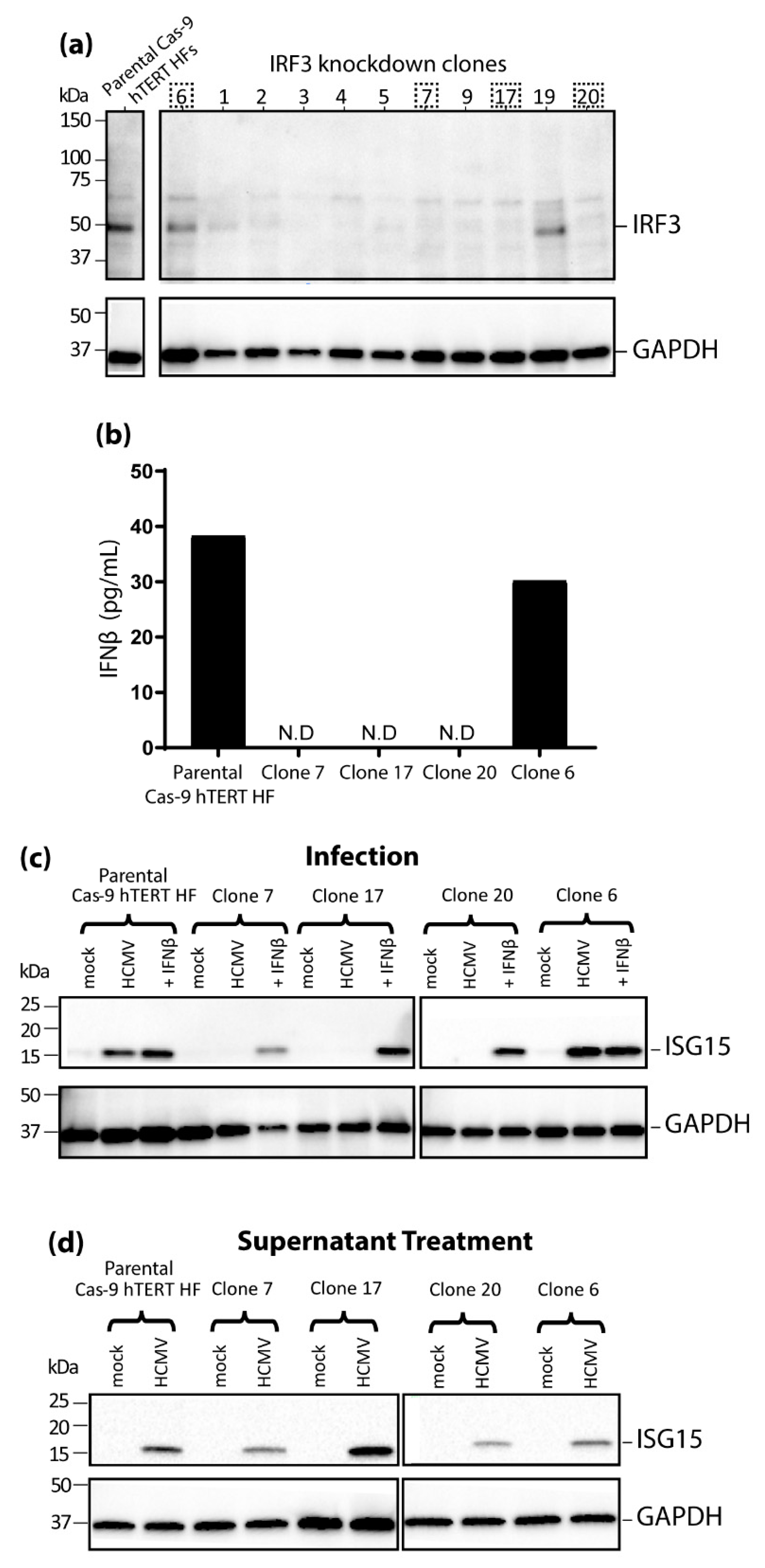
3.3. IRF3 Knockout (KO) by CRISPR/Cas-9 Inhibits ISG15 Protein Expression during HCMV Infection Mirroring the Phenotype Seen in nPro/HFs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seale, H.; MacIntyre, C.R.; Gidding, H.F.; Backhouse, J.L.; Dwyer, D.E.; Gilbert, L. National Serosurvey of Cytomegalovirus in Australia. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, R.; Loenenbach, A.; Waterboer, T.; Brenner, N.; Pawlita, M.; Michel, A.; Thamm, M.; Poethko-Müller, C.; Wichmann, O.; Wiese-Posselt, M. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) seroprevalence in the adult population of Germany. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staras, S.A.S.; Dollard, S.C.; Radford, K.W.; Flanders, W.D.; Pass, R.F.; Cannon, M.J. Seroprevalence of Cytomegalovirus Infection in the United States, 1988–1994. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujtaba, G.; Shaukat, S.; Angez, M.; Alam, M.M.; Hasan, F.; Zahoor Zaidi, S.S.; Shah, A.A. Seroprevalence of Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection in pregnant women and outcomes of pregnancies with active infection. JPMA J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, C.B.; Kourí, V.; Verdasquera, D.; Martínez, P.A.; Alvarez, A.; Alemán, Y.; Pérez, L.; Viera, J.; González, R.; Pérez, E.; et al. HCMV seroprevalence and associated risk factors in pregnant women, Havana City, 2007 to 2008. Prenat. Diagn. 2010, 30, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, M.J.; Schmid, D.S.; Hyde, T.B. Review of cytomegalovirus seroprevalence and demographic characteristics associated with infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, P.; Baraniak, I.; Reeves, M. The pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, B.J.; Palasanthiran, P.; Jones, C.L.A.; Hall, B.P.M.; Robertson, P.W.; Howard, J.; Rawlinson, W.D. Congenital cytomegalovirus–time to diagnosis, management and clinical sequelae in Australia: Opportunities for earlier identification. Med. J. Aust. 2011, 194, 625–629. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, M.J.; Griffiths, P.D.; Aston, V.; Rawlinson, W.D. Universal newborn screening for congenital CMV infection: What is the evidence of potential benefit? Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.J. Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) epidemiology and awareness. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46 (Suppl. 4), S6–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeran, M.C.J.; Lokensgard, J.R.; Schleiss, M.R. Neuropathogenesis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Disease mechanisms and prospects for intervention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, M.J.; Westbrook, K.; Levis, D.; Schleiss, M.R.; Thackeray, R.; Pass, R.F. Awareness of and behaviors related to child-to-mother transmission of cytomegalovirus. Prev. Med. 2012, 54, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Eizuru, Y.; Minamishima, Y. Effect of natural human interferon-beta on the replication of human cytomegalovirus. J. Med. Virol. 1988, 26, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, A.S.; Hober, D.; Bouzidi, A.; Wattre, P. Role of interferon alpha (IFN-alpha) and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) in the control of the infection of monocyte-like cells with human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Microbiol. Immunol. 1999, 43, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, B.; LaMarca, H.; Garry, R.; Morris, C. Synergistic inhibition of human cytomegalovirus replication by interferon-alpha/beta and interferon-gamma. Virol. J. 2005, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSharry, B.P.; Forbes, S.K.; Avdic, S.; Randall, R.E.; Wilkinson, G.W.; Abendroth, A.; Slobedman, B. Abrogation of the interferon response promotes more efficient human cytomegalovirus replication. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, T.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Boehme, K.W.; Belko, J.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Finberg, R.W. Human cytomegalovirus activates inflammatory cytokine responses via CD14 and Toll-like receptor 2. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4588–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, K.W.; Guerrero, M.; Compton, T. Human cytomegalovirus envelope glycoproteins B and H are necessary for TLR2 activation in permissive cells. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 2006, 177, 7094–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.C.; Moore, P.A.; Lowther, W.; Juang, Y.T.; Pitha, P.M. Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferon-induced genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11657–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFilippis, V.R.; Robinson, B.; Keck, T.M.; Hansen, S.G.; Nelson, J.A.; Früh, K.J. Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Is Necessary for Induction of Antiviral Genes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Durbin, J.E.; Levy, D.E. Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-alpha genes by positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. Embo J. 1998, 17, 6660–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurochko, A.D.; Hwang, E.S.; Rasmussen, L.; Keay, S.; Pereira, L.; Huang, E.S. The human cytomegalovirus UL55 (gB) and UL75 (gH) glycoprotein ligands initiate the rapid activation of Sp1 and NF-kappaB during infection. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5051–5059. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, G.R.; Dell’Oste, V.; Bronzini, M.; Gatti, D.; Luganini, A.; De Andrea, M.; Gribaudo, G.; Gariglio, M.; Landolfo, S. The intracellular DNA sensor IFI16 gene acts as restriction factor for human cytomegalovirus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFilippis, V.R.; Alvarado, D.; Sali, T.; Rothenburg, S.; Fruh, K. Human cytomegalovirus induces the interferon response via the DNA sensor ZBP1. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.T.; Grishin, N.V.; et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2015, 347, aaa2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, C.; Mohr, I. Restriction of Human Cytomegalovirus Replication by ISG15, a Host Effector Regulated by cGAS-STING Double-Stranded-DNA Sensing. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02483-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell 1992, 70, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, M.K.; Juckem, L.K.; Compton, T. Virus Entry and Innate Immune Activation. In Human Cytomegalovirus; Shenk, T.E., Stinski, M.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholl, M.J.; Robinson, L.H.; Preston, C.M. Activation of cellular interferon-responsive genes after infection of human cells with herpes simplex virus type 1. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cong, J.-P.; Shenk, T. Use of differential display analysis to assess the effect of human cytomegalovirus infection on the accumulation of cellular RNAs: Induction of interferon-responsive RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13985–13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, C.M.; Harman, A.N.; Nicholl, M.J. Activation of interferon response factor-3 in human cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 or human cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8909–8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, E.P.; Wing, B.; Coleman, D.; Shenk, T. Altered Cellular mRNA Levels in Human Cytomegalovirus-Infected Fibroblasts: Viral Block to the Accumulation of Antiviral mRNAs. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 12319–12330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, M.; Suhara, W.; Fukuhara, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Nishida, E.; Fujita, T. Direct triggering of the type I interferon system by virus infection: Activation of a transcription factor complex containing IRF-3 and CBP/p300. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WATHELET, M.G.; BERR, P.M.; HUEZ, G.A. Regulation of gene expression by cytokines and virus in human cells lacking the type-I interferon locus. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 206, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Peters, K.L.; Sen, G.C. Induction of the human protein P56 by interferon, double-stranded RNA, or virus infection. Virology 2000, 267, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSharry, B.P.; Burgert, H.-G.; Owen, D.P.; Stanton, R.J.; Prod’homme, V.; Sester, M.; Koebernick, K.; Groh, V.; Spies, T.; Cox, S.; et al. Adenovirus E3/19K Promotes Evasion of NK Cell Recognition by Intracellular Sequestration of the NKG2D Ligands Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Chain-Related Proteins A and B. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSharry, B.P.; Forbes, S.K.; Cao, J.Z.; Avdic, S.; Machala, E.A.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Abendroth, A.; Slobedman, B. Human cytomegalovirus upregulates expression of the lectin galectin 9 via induction of beta interferon. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10990–10994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, R.J.; Baluchova, K.; Dargan, D.J.; Cunningham, C.; Sheehy, O.; Seirafian, S.; McSharry, B.P.; Neale, M.L.; Davies, J.A.; Tomasec, P.; et al. Reconstruction of the complete human cytomegalovirus genome in a BAC reveals RL13 to be a potent inhibitor of replication. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3191–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, W. Structure and formation of the cytomegalovirus virion. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 325, 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sali, T.M.; Pryke, K.M.; Abraham, J.; Liu, A.; Archer, I.; Broeckel, R.; Staverosky, J.A.; Smith, J.L.; Al-Shammari, A.; Amsler, L.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Human-Specific STING Agonist that Elicits Antiviral Activity Against Emerging Alphaviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, L.; Moganeradj, K.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.-H.; Randall, R.E.; McCauley, J.W.; Goodbourn, S. The NPro Product of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Inhibits DNA Binding by Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and Targets It for Proteasomal Degradation. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11723–11732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrejeva, J.; Young, D.F.; Goodbourn, S.; Randall, R.E. Degradation of STAT1 and STAT2 by the V Proteins of Simian Virus 5 and Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 2, Respectively: Consequences for Virus Replication in the Presence of Alpha/Beta and Gamma Interferons. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, K.C.; Cresswell, P. Viperin (cig5), an IFN-inducible antiviral protein directly induced by human cytomegalovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15125–15130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, K.W.; Singh, J.; Perry, S.T.; Compton, T. Human cytomegalovirus elicits a coordinated cellular antiviral response via envelope glycoprotein B. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirnweiss, A.; Ksienzyk, A.; Klages, K.; Rand, U.; Grashoff, M.; Hauser, H.; Kroger, A. IFN regulatory factor-1 bypasses IFN-mediated antiviral effects through viperin gene induction. J. Immunol. (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 2010, 184, 5179–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, C.L.; Glass, M.S.; Abendroth, A.; McSharry, B.P.; Slobedman, B. Nuclear domain 10 components upregulated via interferon during human cytomegalovirus infection potently regulate viral infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandvaux, N.; Servant, M.J.; tenOever, B.; Sen, G.C.; Balachandran, S.; Barber, G.N.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Transcriptional Profiling of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Target Genes: Direct Involvement in the Regulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5532–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinova, I.; Forster, S.; Yu, S.; Kannan, A.; Masse, M.; Cumming, H.; Chapman, R.; Hertzog, P.J. INTERFEROME v2.0: An updated database of annotated interferon-regulated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1040–D1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, E.T.; Kim, Y.-E.; Lee, M.K.; Kwon, K.M.; Kim, K.I.; Stamminger, T.; Ahn, J.-H. Consecutive Inhibition of ISG15 Expression and ISGylation by Cytomegalovirus Regulators. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.-E.; Han, T.-H.; Milbradt, J.; Marschall, M.; Ahn, J.-H. Transmembrane protein pUL50 of human cytomegalovirus inhibits ISGylation by downregulating UBE1L. J. Virol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, C.; Büscher, N.; Krauter, S.; Krämer, N.; Wolfrum, U.; Sehn, E.; Tenzer, S.; Plachter, B. The abundant tegument protein pUL25 of human cytomegalovirus prevents proteasomal degradation of pUL26 and supports its suppression of ISGylation. J. Virol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.E.; Noyce, R.S.; Mossman, K.L. Innate cellular response to virus particle entry requires IRF3 but not virus replication. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baca, L.M.; Genis, P.; Kalvakolanu, D.; Sen, G.; Meltzer, M.S.; Zhou, A.; Silverman, R. Regulation of interferon-α-inducible cellular genes in human immunodeficiency virus-infected monocytes. J. Leukocyte Biol. 1994, 55, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-Y.; Cresswell, P. Viperin Regulates Cellular Lipid Metabolism during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, K.J.; Beard, M.R. The Role of Viperin in the Innate Antiviral Response. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-Y.; Yaneva, R.; Cresswell, P. Viperin: A Multifunctional, Interferon-Inducible Protein that Regulates Virus Replication. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashley, C.L.; Abendroth, A.; McSharry, B.P.; Slobedman, B. Interferon-Independent Upregulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection is Dependent on IRF3 Expression. Viruses 2019, 11, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030246
Ashley CL, Abendroth A, McSharry BP, Slobedman B. Interferon-Independent Upregulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection is Dependent on IRF3 Expression. Viruses. 2019; 11(3):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030246
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshley, Caroline L., Allison Abendroth, Brian P. McSharry, and Barry Slobedman. 2019. "Interferon-Independent Upregulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection is Dependent on IRF3 Expression" Viruses 11, no. 3: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030246
APA StyleAshley, C. L., Abendroth, A., McSharry, B. P., & Slobedman, B. (2019). Interferon-Independent Upregulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection is Dependent on IRF3 Expression. Viruses, 11(3), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11030246