HIV-1 Impairment via UBE3A and HIV-1 Nef Interactions Utilizing the Ubiquitin Proteasome System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents.
2.2. Plasmids.
2.3. Yeast and Mammalian Two-Hybrid Assays
2.4. β-galactosidase (β-gal) Assay
2.5. Transfection and Infection
2.6. Cycloheximide Determination of Protein Half-Life
2.7. Immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western Blot (WB) Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
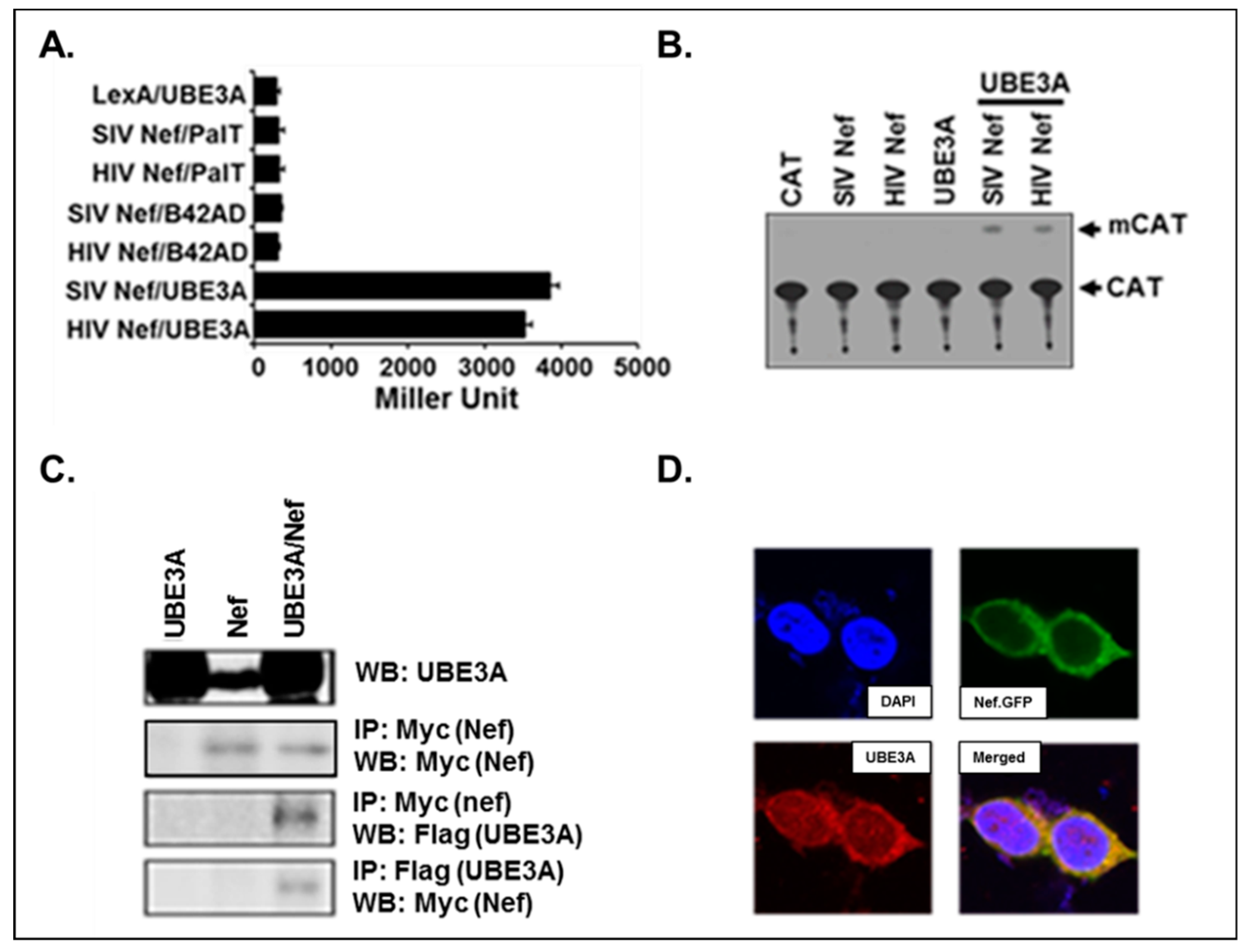
3.1. Nef Interacted with UBE3A
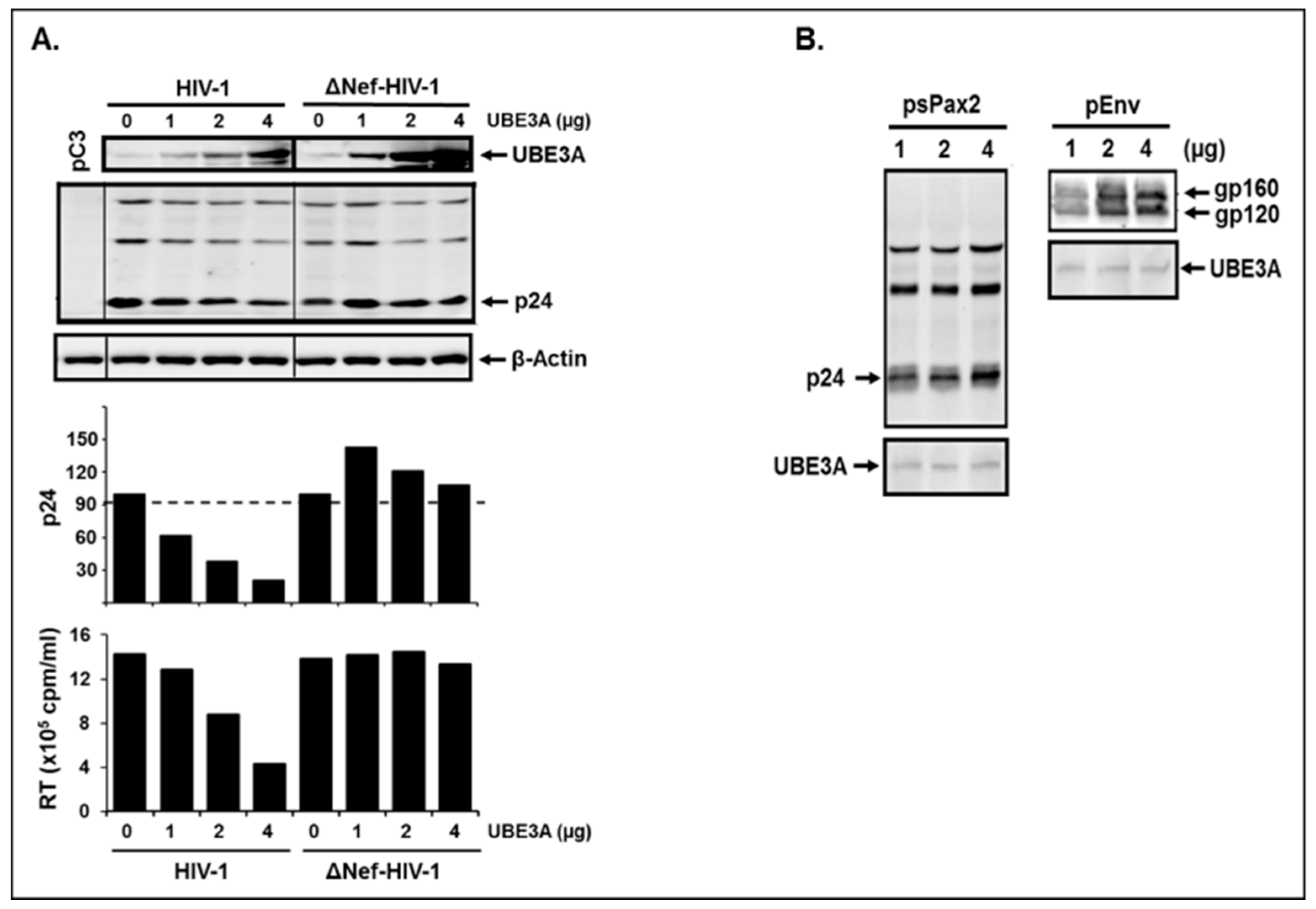
3.2. UBE3A Inhibited HIV-1 Replication.
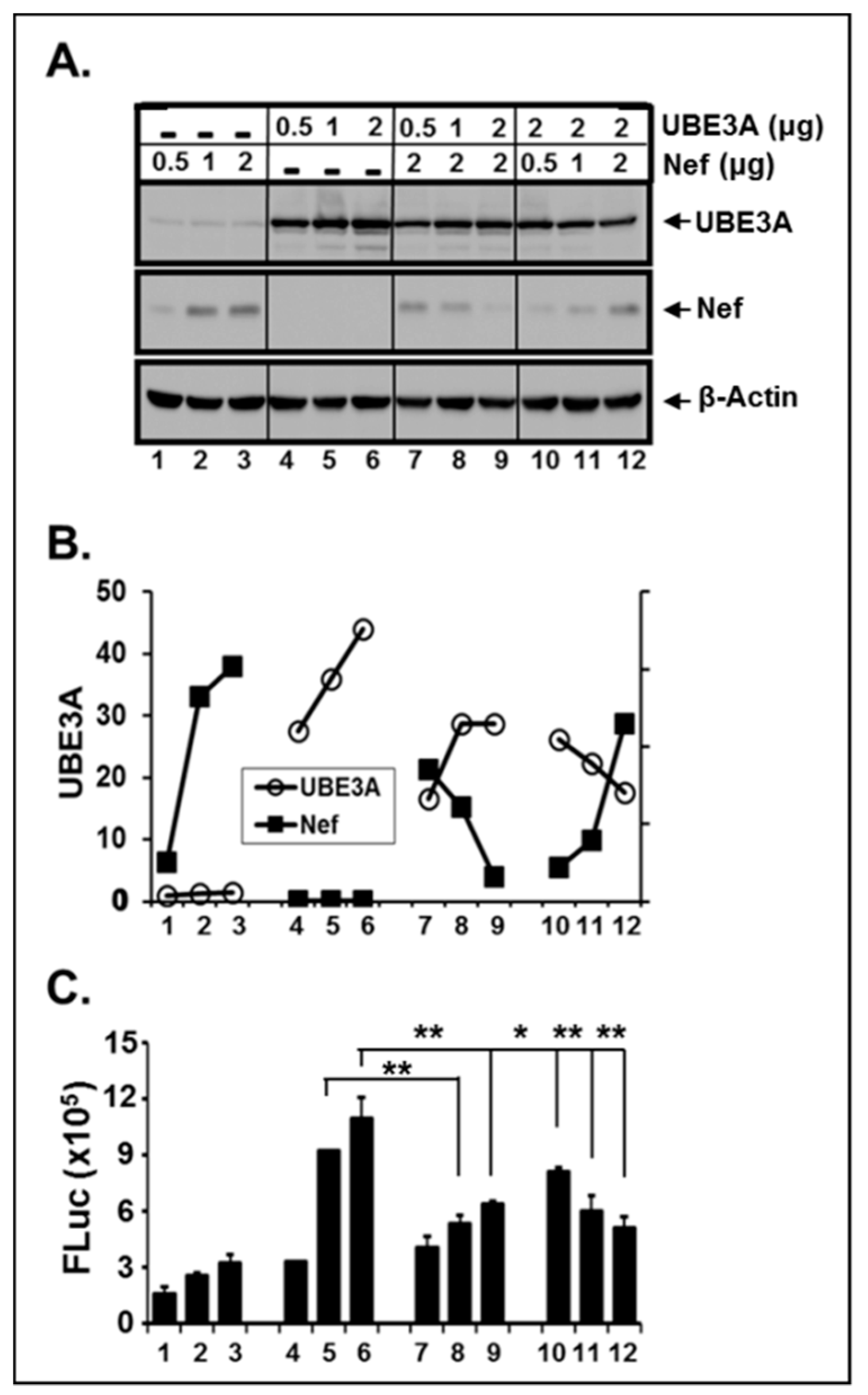
3.3. UBE3A Required Nef for UBE3A-Mediated Inhibition of HIV-1 Replication
3.4. The Amount of the Intracellular UBE3A and Nef was Mutually Regulated.
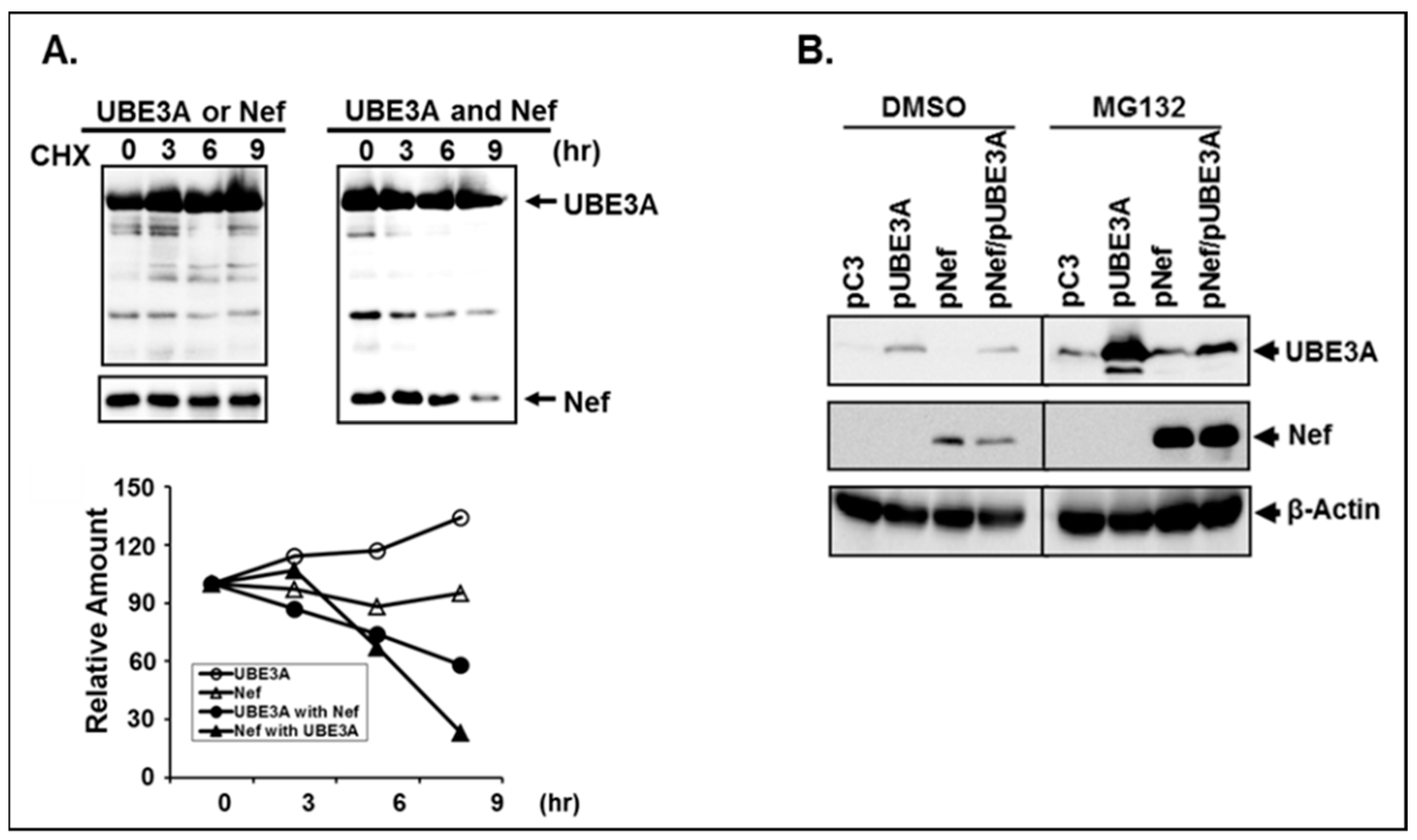
3.5. Reciprocal Reduction of Nef and UBE3A was due to Degradation of the Expressed Proteins.
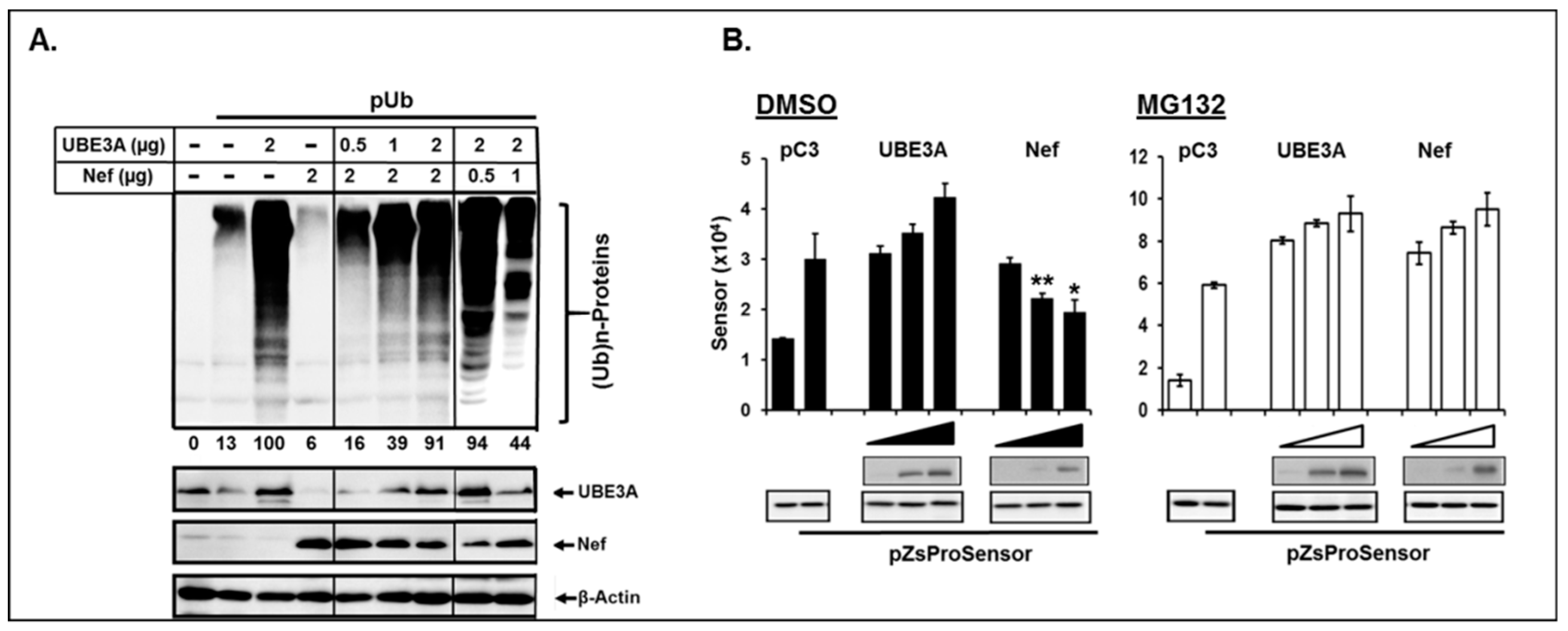
3.6. Nef and UBE3A were Antagonistic in Ubiquitination of Cellular Proteins and Regulation of Proteasome Complex
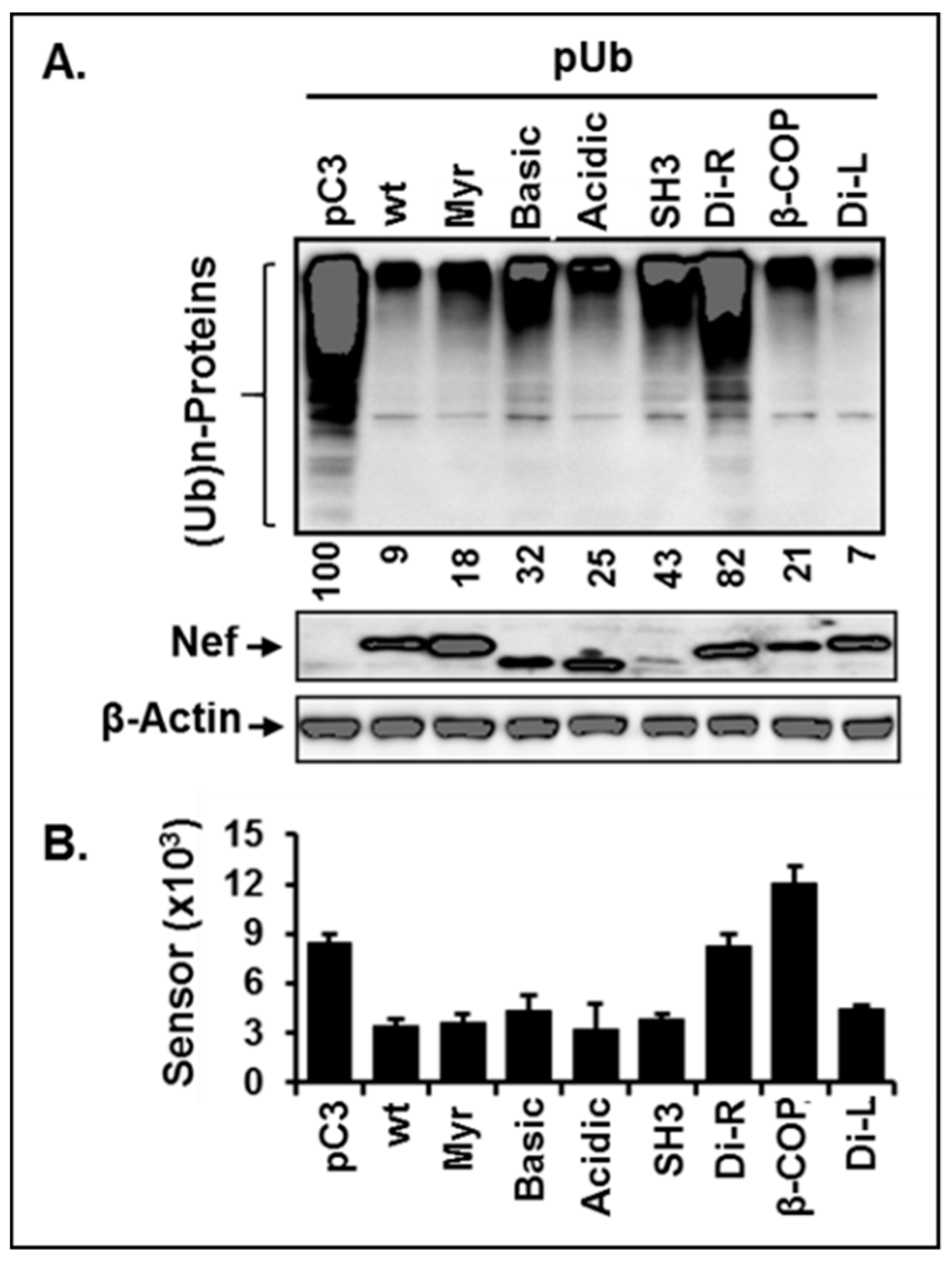
3.7. Di-Acidic and Di-Leucine Motifs in Nef Play an Essential Role in Regulation of Ubiquitination and Proteasome Function
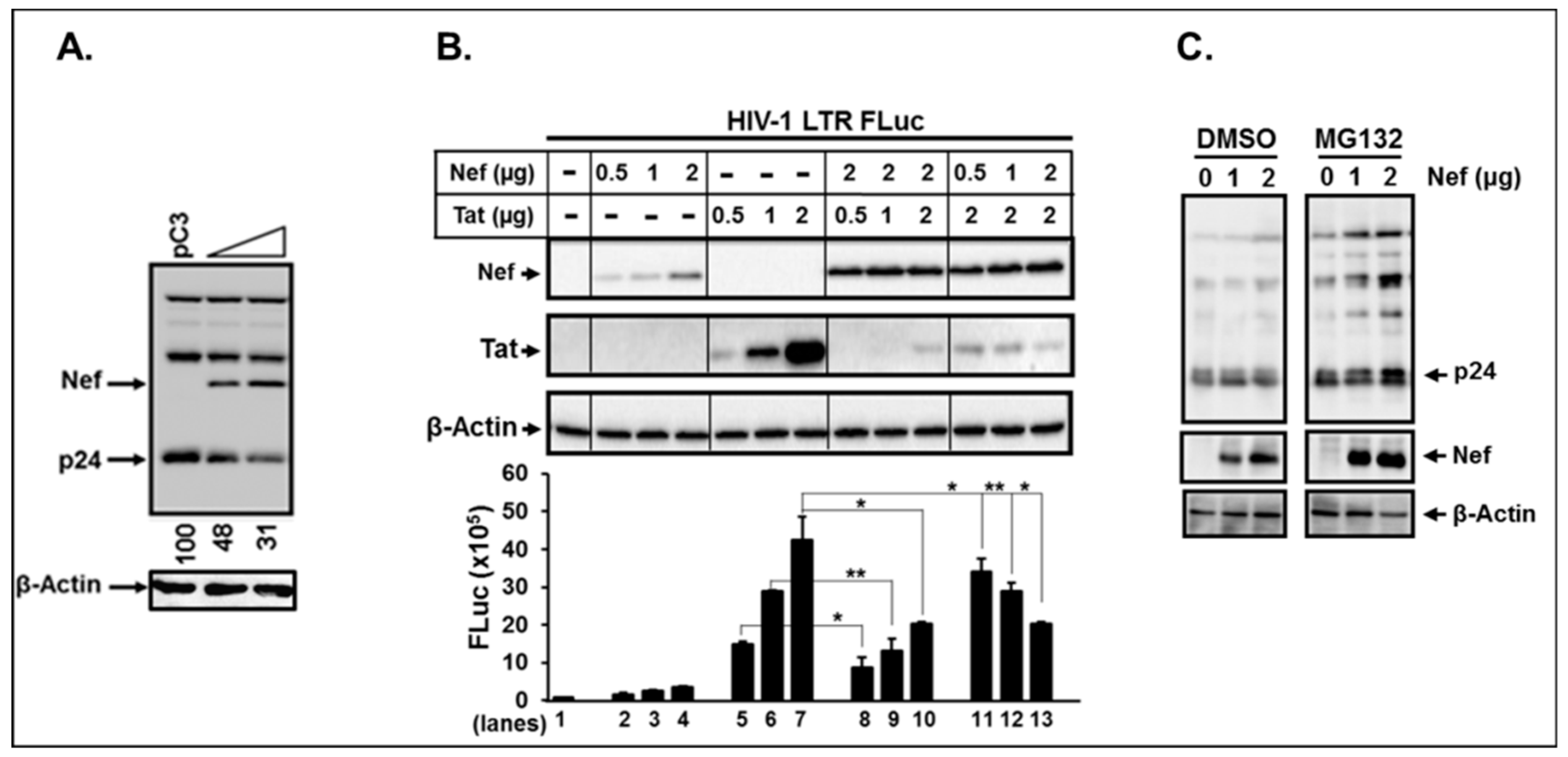
3.8. Nef Itself can Degrade HIV-1 Viral Proteins.
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zolotukhin, A.S.; Valentin, A.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K. Continuous Propagation of Rre(−) and Rev(−)Rre(−) Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Molecular Clones Containing a Cis-Acting Element of Simian Retrovirus Type 1 in Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 7944–7952. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, R.T.; Du, B.; Boldt-Houle, D.; Ferrante, A.; Park, I.W.; Hammer, S.M.; Duan, L.; Groopman, J.E.; Pomerantz, R.J.; Terwilliger, E.F. Potent Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 in Primary T Cells and Alveolar Macrophages by a Combination Anti-Rev Strategy Delivered in an Adeno-Associated Virus Vector. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4071–4078. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zapp, M.L.; Green, M.R. Sequence-Specific Rna Binding by the Hiv-1 Rev Protein. Nature 1989, 342, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malim, M.H.; Tiley, L.S.; McCarn, D.F.; Rusche, J.R.; Hauber, J.; Cullen, B.R. Hiv-1 Structural Gene Expression Requires Binding of the Rev Trans-Activator to Its Rna Target Sequence. Cell 1990, 60, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, B.K.; Drysdale, C.M.; Pavlakis, G.N. Feedback Regulation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Expression by the Rev Protein. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3734–3741. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, J.V.; Miller, A.D. Downregulation of Cell Surface Cd4 by Nef. Res. Virol. 1992, 143, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, R.; Skowronski, J. Cd4 Down-Regulation by Nef Alleles Isolated from Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Infected Individuals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5549–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, C.; Konner, J.; Landau, N.R.; Lenburg, M.E.; Trono, D. Nef Induces Cd4 Endocytosis: Requirement for a Critical Dileucine Motif in the Membrane-Proximal Cd4 Cytoplasmic Domain. Cell 1994, 76, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildum, S.; Schindler, M.; Munch, J.; Kirchhoff, F. Contribution of Vpu, Env, and Nef to Cd4 Down-Modulation and Resistance of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Infected T Cells to Superinfection. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8047–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, J.; Mangasarian, A.; Trono, D. Cell-Surface Expression of Cd4 Reduces Hiv-1 Infectivity by Blocking Env Incorporation in a Nef- and Vpu-Inhibitable Manner. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremlau, M.; Owens, C.M.; Perron, M.J.; Kiessling, M.; Autissier, P.; Sodroski, J. The Cytoplasmic Body Component Trim5alpha Restricts Hiv-1 Infection in Old World Monkeys. Nature 2004, 427, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.; Guatelli, J.C.; Stephens, E.B. The Vpu Protein: New Concepts in Virus Release and Cd4 Down-Modulation. Curr. HIV Res. 2010, 8, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, K.; Finzi, A.; Binette, J.; Cohen, E.A. Role of Cd4 Receptor Down-Regulation During Hiv-1 Infection. Curr. HIV Res. 2004, 2, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Aiken, C. Saturation of Trim5 Alpha-Mediated Restriction of Hiv-1 Infection Depends on the Stability of the Incoming Viral Capsid. Virology 2006, 350, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, R.; Noser, J.A.; Ohmine, S.; Ikeda, Y. Rhesus Monkey Trim5alpha Restricts Hiv-1 Production through Rapid Degradation of Viral Gag Polyproteins. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, U.; Bobardt, M.D.; Gaskill, P.; Sheeter, D.; Fox, H.; Gallay, P.A. Trim5alpha Accelerates Degradation of Cytosolic Capsid Associated with Productive Hiv-1 Entry. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37025–37033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Perez-Caballero, D.; Hatziioannou, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. No Effect of Endogenous Trim5alpha on Hiv-1 Production. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 235–236, author reply 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriagada, G.; Muntean, L.N.; Goff, S.P. Sumo-Interacting Motifs of Human Trim5alpha Are Important for Antiviral Activity. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battivelli, E.; Lecossier, D.; Matsuoka, S.; Migraine, J.; Clavel, F.; Hance, A.J. Strain–Specific Differences in the Impact of Human Trim5alpha, Different Trim5alpha Alleles, and the Inhibition of Capsid–Cyclophilin a Interactions on the Infectivity of Hiv–1. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11010–11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangeat, B.; Turelli, P.; Caron, G.; Friedli, M.; Perrin, L.; Trono, D. Broad Antiretroviral Defence by Human Apobec3g through Lethal Editing of Nascent Reverse Transcripts. Nature 2003, 424, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, R.; Chen, D.; Schrofelbauer, B.; Navarro, F.; Konig, R.; Bollman, B.; Munk, C.; Nymark-McMahon, H.; Landau, N.R. Species-Specific Exclusion of Apobec3g from Hiv-1 Virions by Vif. Cell 2003, 114, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopak, K.; de Noronha, C.; Yonemoto, W.; Greene, W.C. HIV-1 Vif blocks the antiviral activity of APOBEC3G by impairing both its translation and intracellular stability. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Luo, K.; Kong, W.; Mao, P.; Yu, X.F. Induction of APOBEC3G ubiquitination and degradation by an HIV-1 Vif-Cul5-SCF complex. Science 2003, 302, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimmie, B.A.; Delviks-Frankenberrry, K.A.; Burdick, R.C.; Qi, D.; Izumi, T.; Pathak, V.K. Multiple APOBEC3 restriction factors for HIV-1 and one Vif to rule them all. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 1220–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, E.S.; Yu, X.F. Lentiviral Vif: Viral hijacker of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Int. J. Hematol. 2006, 83, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, S.J.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. Tetherin inhibits retrovirus release and is antagonized by HIV-1 Vpu. Nature 2008, 451, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, E.; Andrew, A.J.; Kao, S.; Strebel, K. Vpu enhances HIV-1 virus release in the absence of Bst-2 cell surface down-modulation and intracellular depletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2868–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNatt, M.W.; Zang, T.; Hatziioannou, T.; Bartlett, M.; Fofana, I.B.; Johnson, W.E.; Neil, S.J.; Bieniasz, P.D. Species-specific activity of HIV-1 Vpu and positive selection of tetherin transmembrane domain variants. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.S.; Hultquist, J.F.; Evans, D.T. The restriction factors of human immunodeficiency virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40875–40883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikeakos, J.D.; Thomas, L.; Kwon, G.; Elferich, J.; Shinde, U.; Thomas, G. An interdomain binding site on HIV-1 Nef interacts with PACS-1 and PACS-2 on endosomes to down-regulate MHC-I. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 2184–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueck, T.; Neil, S.J. A cytoplasmic tail determinant in HIV-1 Vpu mediates targeting of tetherin for endosomal degradation and counteracts interferon-induced restriction. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.W.; Fan, Y.; Luo, X.; Ryou, M.G.; Liu, J.; Green, L.; He, J.J. HIV-1 Nef is transferred from expressing T cells to hepatocytic cells through conduits and enhances HCV replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseltine, W.A. Molecular biology of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, E.T.; Baur, A.S.; Peterlin, B.M.; Levy, J.A.; Cheng-Mayer, C. A conserved domain and membrane targeting of Nef from HIV and SIV are required for association with a cellular serine kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15307–15314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Otake, K.; Fujita, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Nagai, Y.; Tashiro, M.; Adachi, A. Clustered localization of oligomeric Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 on the cell surface. FEBS Lett. 1996, 395, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfridson, A.; Hester, S.; Doyle, C. Nef proteins encoded by human and simian immunodeficiency viruses induce the accumulation of endosomes and lysosomes in human T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Pezo, V.; Mallard, F.; Tenza, D.; Wiltz, A.; Saint-Pol, A.; Helft, J.; Antony, C.; Benaroch, P. Effects of HIV-1 Nef on retrograde transport from the plasma membrane to the endoplasmic reticulum. Traffic 2003, 4, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, R.; Naganuma, H.; Nishitsuji, H.; Takaku, H. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 Nef suppresses Hsp70-mediated Tat activation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3367–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.J.; Cai, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Burakoff, S.J. Lysine 144, a ubiquitin attachment site in HIV-1 Nef, is required for Nef-mediated CD4 down-regulation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7878–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xiong, R.; Zhou, T.; Su, P.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, X.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yu, C.; Wang, B.; et al. HIV-1 Nef Antagonizes SERINC5 Restriction by Downregulation of SERINC5 via the Endosome/Lysosome System. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaic, V.; Pim, D.; Thomas, M.; Massimi, P.; Myers, M.P.; Banks, L. Regulation of the human papillomavirus type 18 E6/E6AP ubiquitin ligase complex by the HECT domain-containing protein EDD. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3120–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnle, S.; Kogel, U.; Glockzin, S.; Marquardt, A.; Ciechanover, A.; Matentzoglu, K.; Scheffner, M. Physical and functional interaction of the HECT ubiquitin-protein ligases E6AP and HERC2. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19410–19416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, F.; Schneider, D.; Barbic, T.; Sladewska-Marquardt, A.; Kuhnle, S.; Marx, A.; Scheffner, M. Role of ubiquitin and the HPV E6 oncoprotein in E6AP-mediated ubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9872–9877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirson, J.; Biquand, E.; Straub, M.L.; Cassonnet, P.; Nomine, Y.; Jones, L.; van der Werf, S.; Trave, G.; Zanier, K.; Jacob, Y.; et al. Mapping the interactome of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with the ubiquitin-proteasome system. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3171–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.W.; Sodroski, J. Amino acid sequence requirements for the incorporation of the Vpx protein of simian immunodeficiency virus into virion particles. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1995, 10, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.W.; Ndjomou, J.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ridgway, N.D.; Kao, C.C.; He, J.J. Inhibition of HCV replication by oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 4 (ORP4) through interaction with HCV NS5B and alteration of lipid droplet formation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ikeuchi, K.; Byrn, R.; Groopman, J.; Baltimore, D. Lack of a negative influence on viral growth by the nef gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9544–9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremlau, M.; Perron, M.; Lee, M.; Li, Y.; Song, B.; Javanbakht, H.; Diaz-Griffero, F.; Anderson, D.J.; Sundquist, W.I.; Sodroski, J. Specific recognition and accelerated uncoating of retroviral capsids by the TRIM5alpha restriction factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5514–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, M.; Besche, H.C.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Piccirillo, R.; Edelmann, M.J.; Kessler, B.M.; Goldberg, A.L.; Ulfhake, B. Muscle wasting in aged, sarcopenic rats is associated with enhanced activity of the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39597–39608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimer, N.; Drews, C.M.; Vande Pol, S.B. Association of papillomavirus E6 proteins with either MAML1 or E6AP clusters E6 proteins by structure, function, and evolutionary relatedness. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, A.; Gangadharan, B.; Hodges, A.; Sharrocks, K.; Prabhakar, S.; Garcia, A.; Dwek, R.; Zitzmann, N.; McMichael, A. Nef-mediated lipid raft exclusion of UbcH7 inhibits Cbl activity in T cells to positively regulate signaling. Immunity 2005, 23, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Chavez, L.; Hoh, R.; Deeks, S.G.; Pillai, S.K.; Zhou, Q. Reiterative Enrichment and Authentication of CRISPRi Targets (REACT) identifies the proteasome as a key contributor to HIV-1 latency. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, M.L.; Keiger, K.E.; Lee, C.J.; Huibregtse, J.M. The global transcriptional effects of the human papillomavirus E6 protein in cervical carcinoma cell lines are mediated by the E6AP ubiquitin ligase. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Guroff, M.; Popovic, M.; Gartner, S.; Markham, P.; Gallo, R.C.; Reitz, M.S. Structure and expression of tat-, rev-, and nef-specific transcripts of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in infected lymphocytes and macrophages. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3391–3398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terwilliger, E.F.; Langhoff, E.; Gabuzda, D.; Zazopoulos, E.; Haseltine, W.A. Allelic variation in the effects of the nef gene on replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10971–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talis, A.L.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Howley, P.M. The role of E6AP in the regulation of p53 protein levels in human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive and HPV-negative cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6439–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimi, P.; Shai, A.; Lambert, P.; Banks, L. HPV E6 degradation of p53 and PDZ containing substrates in an E6AP null background. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1800–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, A.L.; McPhee, D.A.; Allen, K.; Johnstone, R.; Holloway, G.; Mills, J.; Azad, A.; Sankovich, S.; Lambert, P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef binds to tumor suppressor p53 and protects cells against p53-mediated apoptosis. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2692–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewski, A.; Sato, K.; Aron, Z.D.; Cohen, F.; Harris, A.; McDougall, B.R.; Robinson, W.E., Jr.; Overman, L.E.; Weiss, G.A. Guanidine alkaloid analogs as inhibitors of HIV-1 Nef interactions with p53, actin, and p56lck. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14079–14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.K.; Shrivastava, G.; Tiwari, S.; Nair, M.P. HIV-1 Nef: Hacker of the host cell. Future Virol. 2012, 7, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Nakabayashi, O.; Nakano, H. FLIP the Switch: Regulation of Apoptosis and Necroptosis by cFLIP. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30321–30341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyeon, D.; Rojas, V.K.; Price, L.; Kim, S.; Singh, M.; Park, I.-W. HIV-1 Impairment via UBE3A and HIV-1 Nef Interactions Utilizing the Ubiquitin Proteasome System. Viruses 2019, 11, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11121098
Pyeon D, Rojas VK, Price L, Kim S, Singh M, Park I-W. HIV-1 Impairment via UBE3A and HIV-1 Nef Interactions Utilizing the Ubiquitin Proteasome System. Viruses. 2019; 11(12):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11121098
Chicago/Turabian StylePyeon, Dohun, Vivian K. Rojas, Lenore Price, Seongcheol Kim, Meharvan Singh, and In-Woo Park. 2019. "HIV-1 Impairment via UBE3A and HIV-1 Nef Interactions Utilizing the Ubiquitin Proteasome System" Viruses 11, no. 12: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11121098
APA StylePyeon, D., Rojas, V. K., Price, L., Kim, S., Singh, M., & Park, I.-W. (2019). HIV-1 Impairment via UBE3A and HIV-1 Nef Interactions Utilizing the Ubiquitin Proteasome System. Viruses, 11(12), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11121098




