Viral Metagenomics Revealed Sendai Virus and Coronavirus Infection of Malayan Pangolins (Manis javanica)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Raw Read Filtering and Rapid Identification of Virus Species
2.3.1. Quality Control
2.3.2. Remove Host Contamination
2.3.3. Rapid Identification of Virus Species
2.4. Read Assembly and Species Identification
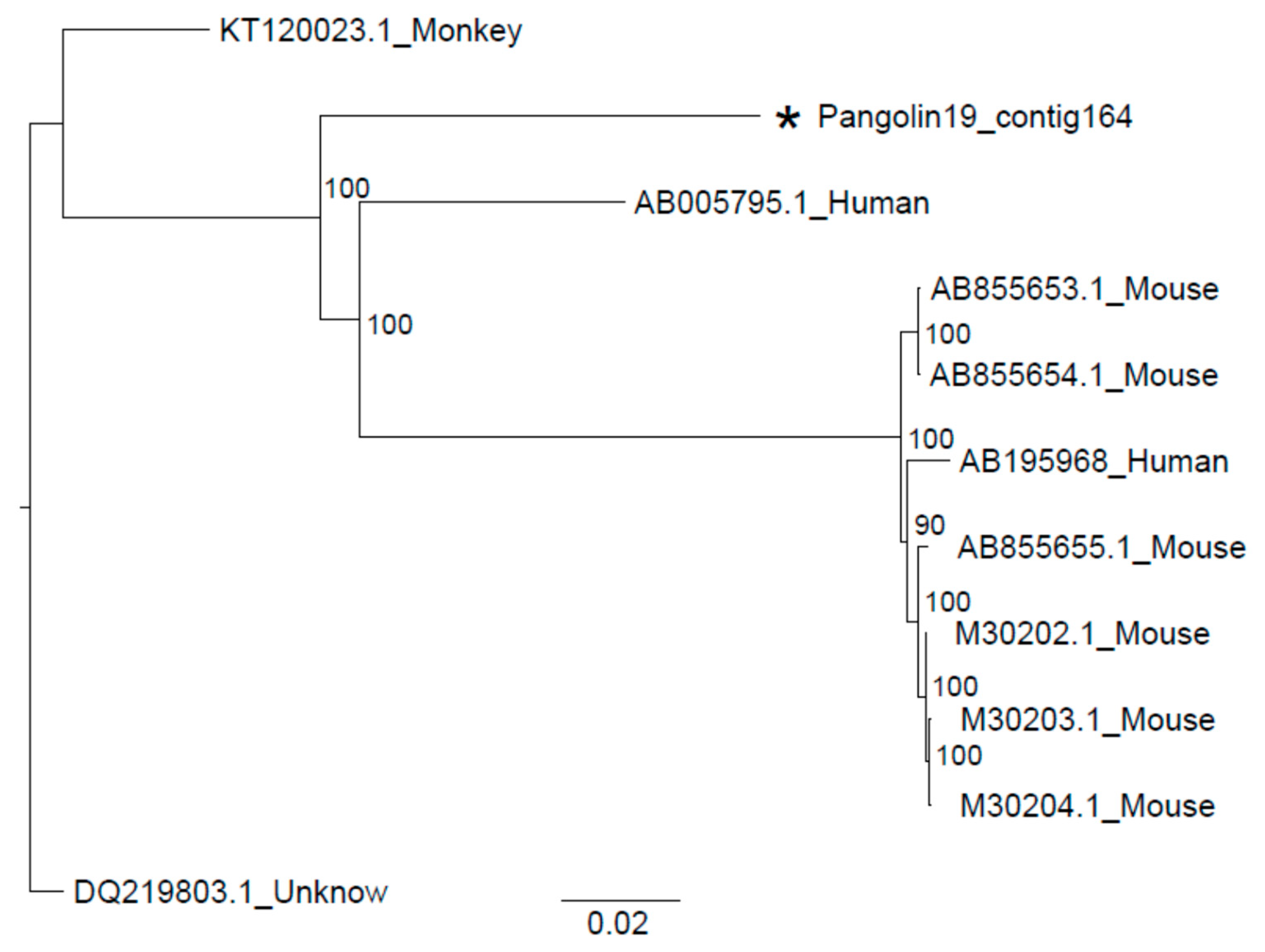
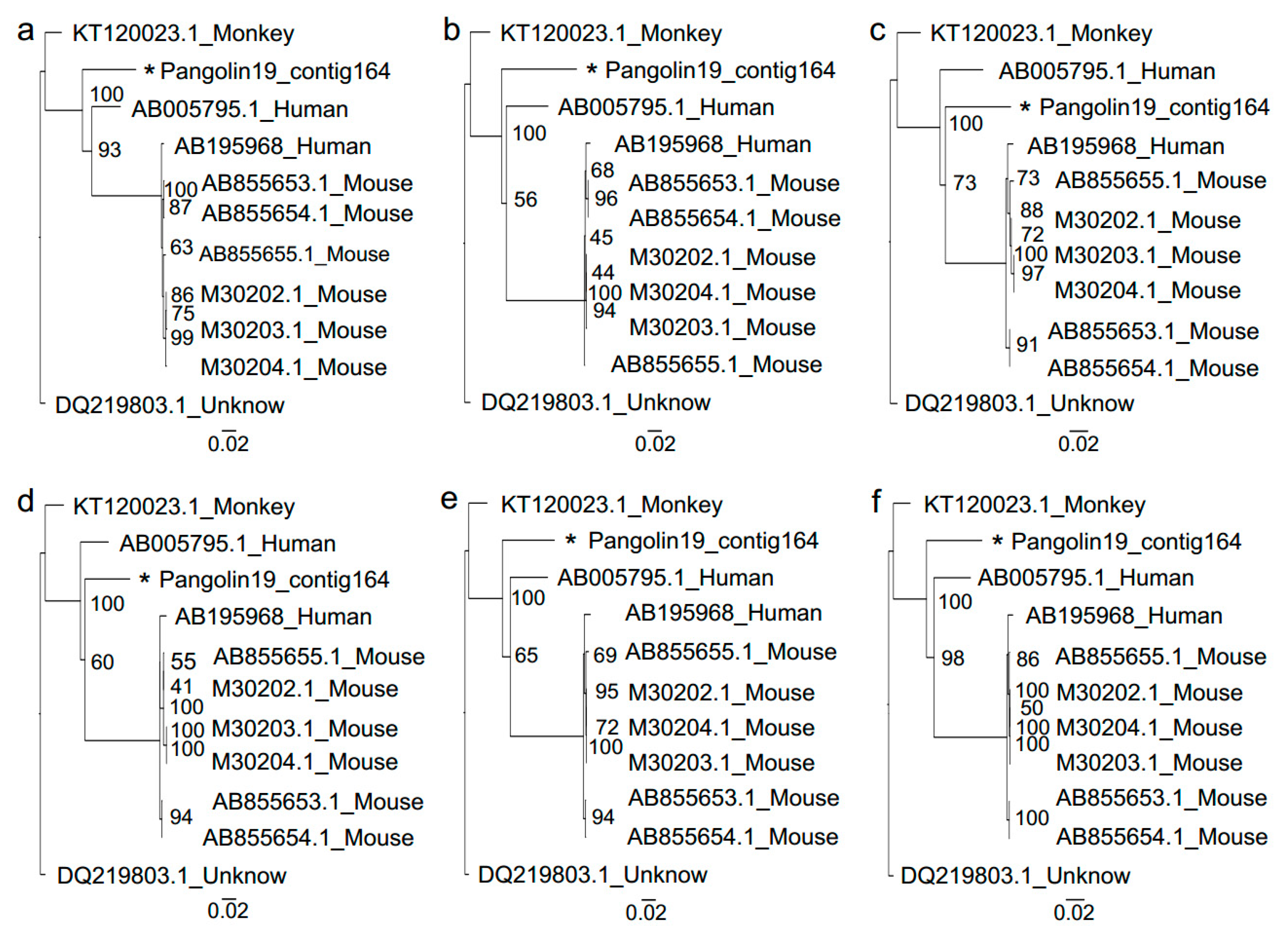
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
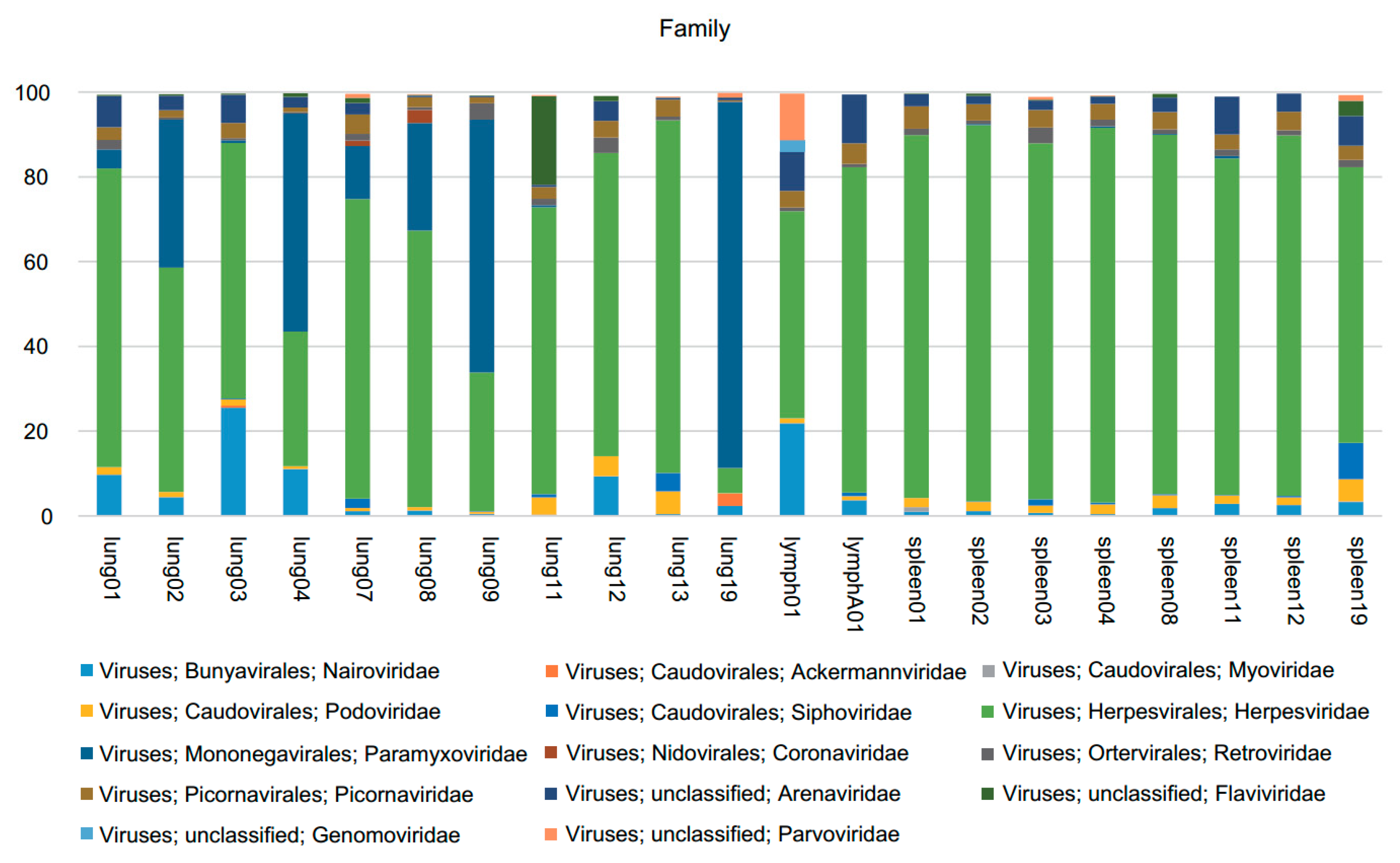
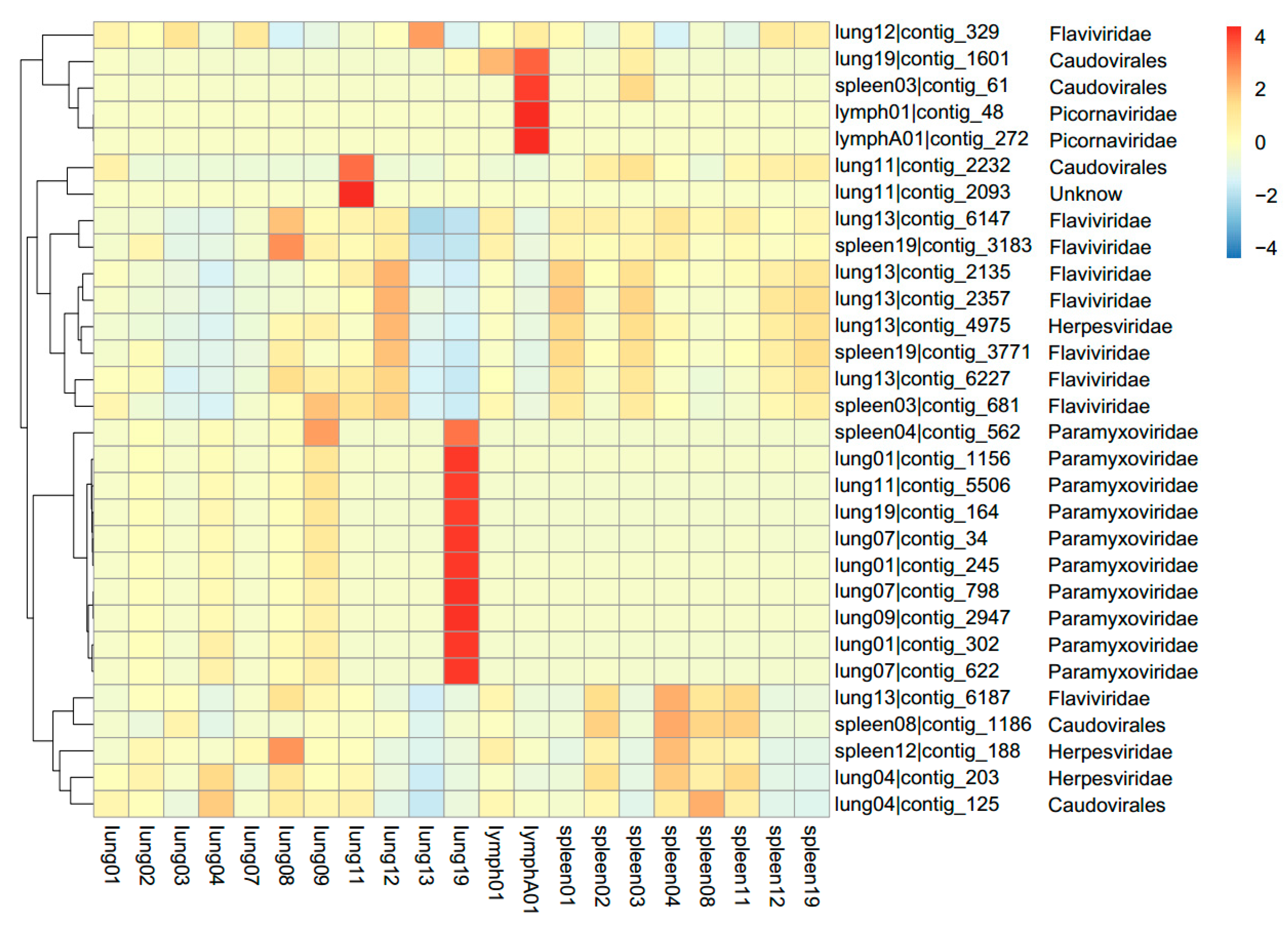
3.1. Viral Metagenomics
3.2. Sendai Virus
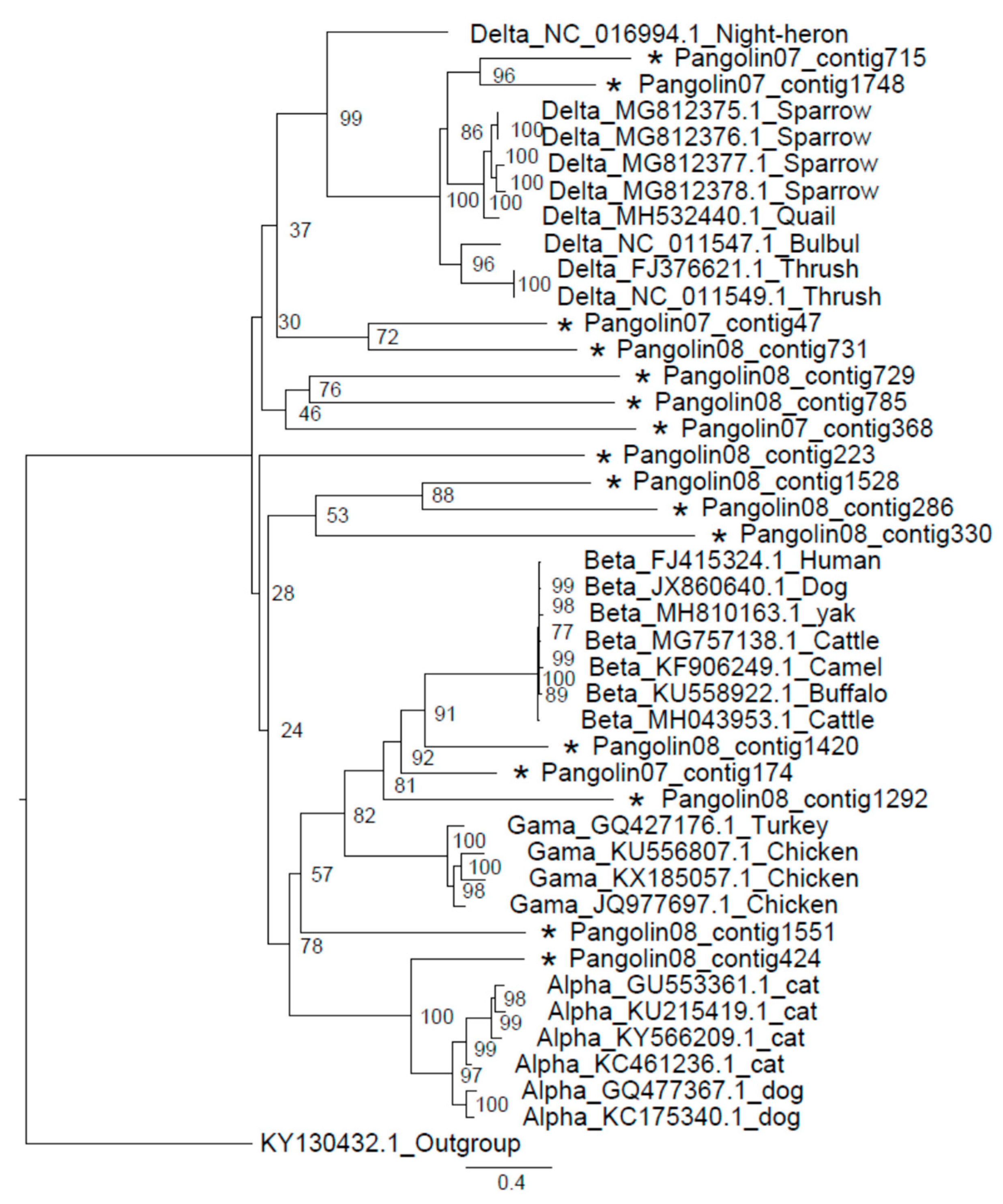
3.3. Coronavirus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaudin, T.J.; Emry, R.J.; Wible, J.R. The phylogeny of living and extinct pangolins (mammalia, pholidota) and associated taxa: A morphology based analysis. J. Mamm. Evol. 2009, 16, 235–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, W.; Liumsiricharoen, M.; Suprasert, A.; Fleischer, L.G.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M. Immunohistochemical demonstration of keratins in the epidermal layers of the Malayan pangolin (Manis javanica), with remarks on the evolution of the integumental scale armour. Eur. J. Histochem. 2013, 57, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Xiang, R.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Zhong, R.; Xiang, H.; Chen, J. Complete Genome Sequence of Parainfluenza Virus 5 (PIV5) from a Sunda Pangolin (Manis javanica) in China. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Ren, X.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Du, J.; et al. Virome Analysis for Identification of Novel Mammalian Viruses in Bat Species from Chinese Provinces. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10999–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Deng, X.; Kapusinszky, B.; Pesavento, P.A.; Delwart, E. Faecal virome of cats in an animal shelter. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2553–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Giannitti, F.; Low, J.; Keyes, C.; Ullmann, L.S.; Deng, X.; Aleman, M.; Pesavento, P.A.; Pusterla, N.; Delwart, E. Exploring the virome of diseased horses. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2721–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.F.F.; Kondov, N.O.; Deng, X.; Van Eenennaam, A.; Neibergs, H.L.; Delwart, E. A Metagenomics and Case-Control Study to Identify Viruses Associated with Bovine Respiratory Disease. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5340–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.A.; Cibulski, S.P.; Finkler, F.; Teixeira, T.F.; Varela, A.P.M.; Cerva, C.; Loiko, M.R.; Scheffer, C.M.; Dos Santos, H.F.; Mayer, F.Q.; et al. Faecal virome of healthy chickens reveals a large diversity of the eukaryote viral community, including novel circular ssDNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomström, A.L.; Ye, X.; Fossum, C.; Wallgren, P.; Berg, M. Characterisation of the virome of tonsils from conventional pigs and from specific pathogen-free pigs. Viruses 2018, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gallego, J.L.; Chou, S.P.; Di Rienzi, S.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Spector, T.D.; Bell, J.T.; Youngblut, N.D.; Hewson, I.; Reyes, A.; Ley, R.E. Virome Diversity Correlates with Intestinal Microbiome Diversity in Adult Monozygotic Twins. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noell, K.; Kolls, J.K. Further Defining the Human Virome using NGS: Identification of Redondoviridae. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Chiu, C. Metagenomics for the discovery of novel human viruses. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.Y. Viral pathogen discovery. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culligan, E.P.; Sleator, R.D.; Marchesi, J.R.; Hill, C. Metagenomics and novel gene discovery: Promise and potential for novel therapeutics. Virulence 2014, 5, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallen, M.J. Diagnostic metagenomics: Potential applications to bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooley, J.C.; Ye, Y. Metagenomics: Facts and artifacts, and computational challenges. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2010, 25, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, E.; Tiedje, J.M. New tools for discovering and characterizing microbial diversity. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.Y.; Huang, S.; Yao, T.; Gao, F.; Jiang, J.Z.; Wang, J.Y. Detection of viruses in abalone tissue using metagenomics technology. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; et al. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. Gigascience 2018, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.M.; Leung, C.M.; Ting, H.F.; Sadakane, K.; Yamashita, H.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT v1.0: A fast and scalable metagenome assembler driven by advanced methodologies and community practices. Methods 2016, 102, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, I.H.; Wen, D.L.H.; Jayakumar, J.; Gunalan, V.; Wang, L.; Mauer-Stroh, S.; Su, Y.C.F.; Smith, G.J.D. Diversity and Evolution of Viral Pathogen Community in Cave Nectar Bats (Eonycteris spelaea). Viruses 2019, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ai, L.; Yang, L.; Ye, F.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; He, B.; Zhu, J.; et al. Virome analysis for identification of novel mammalian viruses in bats from Southeast China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.M.; Kumulungui, B.; Pourrut, X.; Rouquet, P.; Hassanin, A.; Yaba, P.; Délicat, A.; Paweska, J.T.; Gonzalez, J.P.; Swanepoel, R. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 2005, 438, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Field, H.; Daszak, P.; Eaton, B.T. Review of bats and SARS. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel, R.; Smit, S.B.; Rollin, P.E.; Formenty, P.; Leman, P.A.; Kemp, A.; Burt, F.J.; Grobbelaar, A.A.; Croft, J.; Bausch, D.G.; et al. Studies of reservoir hosts for Marburg virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.K.W.; Poon, L.L.M.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, J.S.M. Novel Astroviruses in Insectivorous Bats. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9107–9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ge, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, L.-F.; Shi, Z. Host Range, Prevalence, and Genetic Diversity of Adenoviruses in Bats. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.; Lau, S.; Woo, P.; Yuen, K.Y. Bats as a continuing source of emerging infections in humans. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freuling, C.M.; Beer, M.; Conraths, F.J.; Finke, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Keller, B.; Kliemt, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Mühlbach, E.; Teifke, J.P.; et al. Novel lyssavirus in Natterer’s bat, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Lai, K.K.Y.; Huang, Y.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Shek, C.-T.; Lee, P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Complete Genome Analysis of Three Novel Picornaviruses from Diverse Bat Species. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8819–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Li, K.S.M.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.W.; Wong, B.H.L.; Wong, S.S.Y.; Leung, S.Y.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14040–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.; Broos, A.; de Jong, C.; Zeddeman, A.; Smith, C.; Smith, G.; Moore, F.; Barr, J.; Crameri, G.; Marsh, G.; et al. Identifying hendra virus diversity in pteropid bats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, A.D.; Hayman, D.T.S.; O’Shea, T.J.; Cryan, P.M.; Gilbert, A.T.; Pulliam, J.R.C.; Mills, J.N.; Timonin, M.E.; Willis, C.K.R.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. A comparison of bats and rodents as reservoirs of zoonotic viruses: Are bats special? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20122753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Li, L.; Simmonds, P.; Wang, C.; Moeser, A.; Delwart, E. The Fecal Virome of Pigs on a High-Density Farm. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11697–11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, K.M.; Ng, T.F.; Bayles, D.O.; Alt, D.P.; Delwart, E.L.; Cheung, A.K. Diversity of viruses detected by deep sequencing in pigs from a common background. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amimo, J.O.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Githae, D.; Wamalwa, M.; Djikeng, A.; Nasrallah, G.K. Metagenomic analysis demonstrates the diversity of the fecal virome in asymptomatic pigs in East Africa. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faísca, P.; Desmecht, D. Sendai virus, the mouse parainfluenza type 1: A longstanding pathogen that remains up-to-date. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 82, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumi, H.; Fumio, T.; Nishikawa, T. A pneumotropic virus from mice causing hemagglutination. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1954, 7, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Parker, J.C.; Tennant, R.W.; Ward, T.G.; Rowe, W.P. Enzootic sendai virus infections in mouse breeder colonies within the United States. Science 1964, 146, 936–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurcher, C.; Burek, J.D.; van, M.N.; Meihuizen, S.P. A naturally occurring epizootic caused by Sendai virus in breeding and aging rodent colonies. I. Infection in the mouse. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1977, 27, 955–962. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.C.; Reynolds, R.K. Natural history of sendai virus infection in mice. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1968, 88, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.Y.; Jeong, D.G.; Yoon, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.G.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, H.K. Isolation and characterization of novel bat paramyxovirus B16-40 potentially belonging to the proposed genus Shaanvirus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.R.; Navas-Martin, S. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.V.; Lai, M.M.C. Coronaviridae: The viruses and their replication. Fields Virol. 1996, 1, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, J.S.; Breslin, J.J.; Breuhaus, B.; Vivrette, S.; Smith, L.G. Characterization of a coronavirus isolated from a diarrheic foal. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4523–4526. [Google Scholar]
- Assiri, A.; McGeer, A.; Perl, T.M.; Price, C.S.; Al Rabeeah, A.A.; Cummings, D.A.T.; Alabdullatif, Z.N.; Assad, M.; Almulhim, A.; Makhdoom, H.; et al. Hospital outbreak of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, J.S.M.; Lam, T.T.; Mohamed, M.M.; Li, L.; Shen, Y.; Abo-aba, S.E.M.; Qureshi, M.I.; Abu-zeid, M.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, D.K.; et al. Co-circulation of three camel coronavirus species and recombination of MERS-CoVs in Saudi Arabia. Science 2015, 351, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.H.; McEachern, J.; Zhang, J.; Daszak, P.; Wang, H.; Field, H.; Li, W.; Eaton, B.T.; Wang, L.-F.; Yu, M.; et al. Bats Are Natural Reservoirs of SARS-Like Coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Eaton, B.T. Bats, civets and the emergence of SARS. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 315, 325–344. [Google Scholar]
| Sample ID | Raw Reads (PE) | Number of Reads Remaining after Filtering (%) | Assembly Data on Filtered Reads | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Reads (PE) | Rm. rRNA Clean (PE) | Rm. Host Clean (PE) | Virus Reads (PE) | Total No. | Max Len. | Min Len. | N50 | GC (%) | ||
| lung01 | 53,970,685 | 22,900,426 (42.43) | 13,929,751 (60.83) | 13,784,503(60.19) | 8945 (0.04) | 2395 | 7054 | 300 | 471 | 51.08 |
| lung02 | 39,738,679 | 16,573,376 (41.71) | 10,760,690 (64.93) | 10,580,567 (63.84) | 10,242 (0.06) | 3828 | 7638 | 300 | 534 | 51.02 |
| lung03 | 29,005,761 | 12,967,281 (44.71) | 7,511,236 (57.92) | 7,427,749 (57.28) | 7456 (0.06) | 3380 | 5192 | 300 | 490 | 47.60 |
| lung04 | 32,420,343 | 13,527,964 (41.73) | 8,156,824 (60.30) | 7,838,436 (57.94) | 15,539 (0.11) | 6047 | 7392 | 300 | 559 | 50.72 |
| lung07 | 44,500,928 | 19,045,923 (42.80) | 12,466,935 (65.46) | 12,339,084 (64.79) | 6056 (0.03) | 2539 | 2541 | 300 | 429 | 47.50 |
| lung08 | 39,624,368 | 16,414,925 (41.43) | 10,655,020 (64.91) | 10,555,677 (64.31) | 9139 (0.06) | 2196 | 6969 | 300 | 514 | 50.72 |
| lung09 | 42,219,253 | 18,067,615 (42.79) | 11,552,994 (63.94) | 11,442,175 (63.33) | 13,146 (0.07) | 4903 | 13,503 | 300 | 623 | 46.97 |
| lung11 | 52,714,790 | 22,220,187 (42.15) | 15,402,765 (69.32) | 14,227,635 (64.03) | 11,877 (0.05) | 9668 | 4560 | 300 | 394 | 49.82 |
| lung12 | 17,630,092 | 9,275,501 (52.61) | 5,425,644 (58.49) | 5,368,963 (57.88) | 2856 (0.03) | 638 | 2866 | 300 | 422 | 52.31 |
| lung13 | 25,571,230 | 16,491,648 (64.49) | 14,588,679 (88.46) | 10,591,839 (64.23) | 7447 (0.05) | 7557 | 8164 | 300 | 495 | 62.37 |
| lung19 | 39,314,715 | 19,986,780 (50.84) | 9,028,100 (45.17) | 8,889,856 (44.48) | 78,052 (0.39) | 2,469 | 13,232 | 300 | 509 | 51.16 |
| lymph01 | 40,842,452 | 18,903,834 (46.28) | 11,243,800 (59.48) | 11,117,284 (58.81) | 7158 (0.04) | 1575 | 3442 | 300 | 477 | 46.47 |
| lymphA01 | 44,848,973 | 20,045,443 (44.70) | 12,675,354 (63.23) | 12,580,282 (62.76) | 6081 (0.03) | 2373 | 3651 | 300 | 421 | 48.74 |
| spleen01 | 20,058,026 | 11,527,782 (57.47) | 7,566,895 (65.64) | 7,422,262 (64.39) | 3161 (0.03) | 945 | 1445 | 300 | 382 | 49.79 |
| spleen02 | 35,359,899 | 15,350,468 (43.41) | 9,888,746 (64.42) | 9,739,169 (63.45) | 7955 (0.05) | 1857 | 6119 | 300 | 436 | 47.94 |
| spleen03 | 34,350,848 | 19,055,973 (55.47) | 11,356,082 (59.59) | 11,244,710 (59.01) | 5405 (0.03) | 1194 | 4290 | 300 | 353 | 51.60 |
| spleen04 | 42,861,276 | 19,038,817 (44.42) | 12,498,406 (65.65) | 12,394,988 (65.10) | 7616 (0.04) | 1442 | 4162 | 300 | 481 | 51.78 |
| spleen08 | 37,544,029 | 15,975,904 (42.55) | 10,761,939 (67.36) | 10,516,975 (65.83) | 7191 (0.05) | 3516 | 5176 | 300 | 386 | 47.06 |
| spleen11 | 35,405,980 | 15,273,939 (43.14) | 9,877,753 (64.67) | 9,726,051 (63.68) | 6596 (0.04) | 1351 | 5266 | 300 | 480 | 51.27 |
| spleen12 | 21,926,554 | 12,590,769 (57.42) | 8,383,040 (66.58) | 8,298,012 (65.91) | 5381 (0.04) | 1298 | 989 | 300 | 415 | 58.16 |
| spleen19 | 27,820,892 | 16,068,654 (57.76) | 11,459,934 (71.32) | 10,570,867 (65.79) | 6288 (0.04) | 6367 | 1553 | 300 | 381 | 42.60 |
| Mean | 36,082,370 | 16,728,724 | 10,723,361 | 10,317,004 | 11,123 | 3216 | 5486 | 300 | 460 | 50.32 |
| Standard Deviation | 9,831,029 | 3,477,218 | 2,487,225 | 2,214,377 | 15,630 | 2408 | 3348 | 0 | 67 | 4.11 |
| Query ID | Subject ID | Identity (%) | Alignment Length | Mismatches | Gap Openings | q Start | q End | s Start | s End | e-Value | Bit Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lung01|contig_245 | AB005795.1 | 90.15 | 2072 | 204 | 0 | 1060 | 3131 | 4378 | 6449 | 0.0 | 2818 |
| lung01|contig_302 | AB005795.1 | 86.03 | 594 | 83 | 0 | 207 | 800 | 1451 | 2044 | 0.0 | 697 |
| lung01|contig_307 | DQ219803.1 | 90.06 | 513 | 50 | 1 | 22 | 534 | 9315 | 8804 | 0.0 | 691 |
| lung01|contig_507 | DQ219803.1 | 92.27 | 1747 | 135 | 0 | 99 | 1845 | 11,967 | 13,713 | 0.0 | 2542 |
| lung01|contig_1156 | DQ219803.1 | 87.60 | 500 | 62 | 0 | 99 | 598 | 7149 | 6650 | 1.5 × 10−176 | 623 |
| lung01|contig_2161 | AB005795.1 | 90.46 | 1362 | 130 | 0 | 101 | 1462 | 147 | 1508 | 0.0 | 1871 |
| lung02|contig_1124 | DQ219803.1 | 91.41 | 7028 | 602 | 2 | 1 | 7027 | 8306 | 15,332 | 0.0 | 9945 |
| lung07|contig_34 | DQ219803.1 | 91.44 | 596 | 51 | 0 | 1 | 596 | 5376 | 5971 | 0.0 | 845 |
| lung07|contig_45 | DQ219803.1 | 91.46 | 515 | 44 | 0 | 1 | 515 | 4576 | 4062 | 0.0 | 731 |
| lung07|contig_444 | DQ219803.1 | 89.01 | 1128 | 124 | 0 | 91 | 1218 | 2750 | 3877 | 0.0 | 1476 |
| lung07|contig_506 | DQ219803.1 | 90.68 | 794 | 74 | 0 | 2 | 795 | 976 | 183 | 0.0 | 1099 |
| lung07|contig_798 | DQ219803.1 | 92.43 | 1202 | 91 | 0 | 104 | 1305 | 14,131 | 15,332 | 0.0 | 1757 |
| lung07|contig_1426 | AB005795.1 | 91.60 | 607 | 51 | 0 | 131 | 737 | 10,163 | 9557 | 0.0 | 865 |
| lung09|contig_2947 | DQ219803.1 | 91.74 | 1550 | 122 | 4 | 1 | 1547 | 13,835 | 15,381 | 0.0 | 2206 |
| lung11|contig_5506 | DQ219803.1 | 91.31 | 656 | 57 | 0 | 72 | 727 | 5180 | 5835 | 0.0 | 926 |
| lung19|contig_164 | AB005795.1 | 89.76 | 13,231 | 1355 | 0 | 1 | 13,231 | 19 | 13,249 | 0.0 | 17,751 |
| Query ID | Subject ID | Identity (%) | Alignment Length | Mismatches | Gap Openings | q Start | q End | s Start | s End | e-Value | Bit Score | Taxonomy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lung07|contig_47 | JX993987.1 | 80.24 | 506 | 100 | 0 | 2 | 507 | 7611 | 7106 | 2.28 × 10−128 | 462 | Bat coronavirus Rp/Shaanxi2011 |
| lung07|contig_174 | KJ473815.1 | 87.16 | 1262 | 162 | 0 | 19 | 1280 | 15,069 | 16,330 | 0.0 | 1546 | BtRs-BetaCoV/GX2013 |
| lung07|contig_368 | KC881006.1 | 88.93 | 1057 | 117 | 0 | 1 | 1057 | 28,204 | 29,260 | 0.0 | 1379 | Bat SARS-like coronavirus Rs3367 |
| lung07|contig_715 | AY394981.1 | 88.68 | 521 | 59 | 0 | 96 | 616 | 17,937 | 17,417 | 0.0 | 673 | SARS coronavirus HGZ8L1-A |
| lung07|contig_1748 | DQ412042.1 | 87.84 | 584 | 71 | 0 | 46 | 629 | 11,919 | 12,502 | 0.0 | 733 | Bat SARS CoV Rf1/2004 |
| lung08|contig_223 | KJ473814.1 | 85.52 | 2023 | 293 | 0 | 98 | 2120 | 14,509 | 12,487 | 0.0 | 2327 | BtRs-BetaCoV/HuB2013 |
| lung08|contig_286 | KY417145.1 | 82.29 | 559 | 99 | 0 | 1 | 559 | 18,771 | 18,213 | 3.95 × 10−158 | 562 | Bat SARS-like coronavirus |
| lung08|contig_330 | FJ588686.1 | 80.46 | 1167 | 224 | 2 | 153 | 1317 | 1374 | 210 | 0.0 | 1072 | SARS coronavirus Rs_672/2006 |
| lung08|contig_424 | DQ412042.1 | 87.99 | 608 | 73 | 0 | 3 | 610 | 12,054 | 12,661 | 0.0 | 767 | Bat SARS CoV Rf1/2004 |
| lung08|contig_729 | KY417145.1 | 88.06 | 1139 | 136 | 0 | 1 | 1139 | 17,326 | 16,188 | 0.0 | 1442 | Bat SARS-like coronavirus |
| lung08|contig_731 | KF569996.1 | 83.96 | 767 | 123 | 0 | 2 | 768 | 11,978 | 11,212 | 0.0 | 829 | Rhinolophus affinis coronavirus |
| lung08|contig_785 | KF294457.1 | 83.45 | 1722 | 285 | 0 | 608 | 2329 | 21,463 | 19,742 | 0.0 | 1820 | Bat SARS-like coronavirus |
| lung08|contig_1292 | JX993988.1 | 82.61 | 644 | 112 | 0 | 3 | 646 | 24,133 | 24,776 | 0.0 | 657 | Bat coronavirus Cp/Yunnan2011 |
| lung08|contig_1420 | AY394981.1 | 88.39 | 646 | 75 | 0 | 1 | 646 | 17,333 | 17,978 | 0.0 | 827 | SARS coronavirus HGZ8L1-A |
| lung08|contig_1528 | DQ412043.1 | 84.29 | 681 | 107 | 0 | 138 | 818 | 19,339 | 18,659 | 0.0 | 746 | Bat SARS CoV Rm1/2004 |
| lung08|contig_1551 | GQ153548.1 | 82.60 | 500 | 87 | 0 | 2 | 501 | 24,202 | 23,703 | 1.73 × 10−142 | 509 | Bat SARS coronavirus HKU3-13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.-P. Viral Metagenomics Revealed Sendai Virus and Coronavirus Infection of Malayan Pangolins (Manis javanica). Viruses 2019, 11, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110979
Liu P, Chen W, Chen J-P. Viral Metagenomics Revealed Sendai Virus and Coronavirus Infection of Malayan Pangolins (Manis javanica). Viruses. 2019; 11(11):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110979
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ping, Wu Chen, and Jin-Ping Chen. 2019. "Viral Metagenomics Revealed Sendai Virus and Coronavirus Infection of Malayan Pangolins (Manis javanica)" Viruses 11, no. 11: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110979
APA StyleLiu, P., Chen, W., & Chen, J.-P. (2019). Viral Metagenomics Revealed Sendai Virus and Coronavirus Infection of Malayan Pangolins (Manis javanica). Viruses, 11(11), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110979




