A Novel Benthic Phage Infecting Shewanella with Strong Replication Ability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Benthic Phages
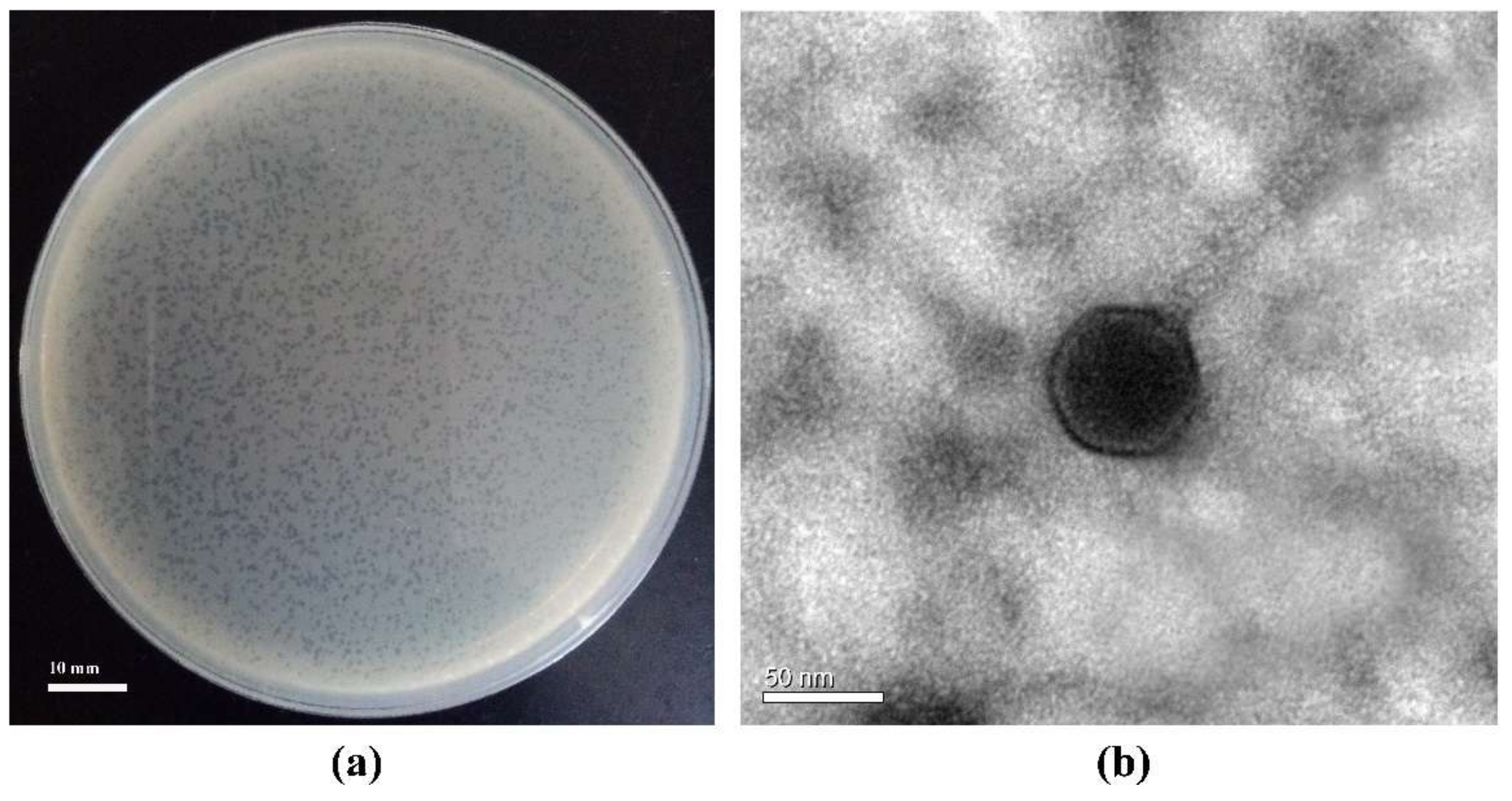
2.2. Phage Morphological Observation Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. Detection of Phage Host Range
2.4. Lipid Detection in the Viral Capsid
2.5. The Influence of the External Factors on Phage Particles Stability
2.6. Lysis Profile Assay
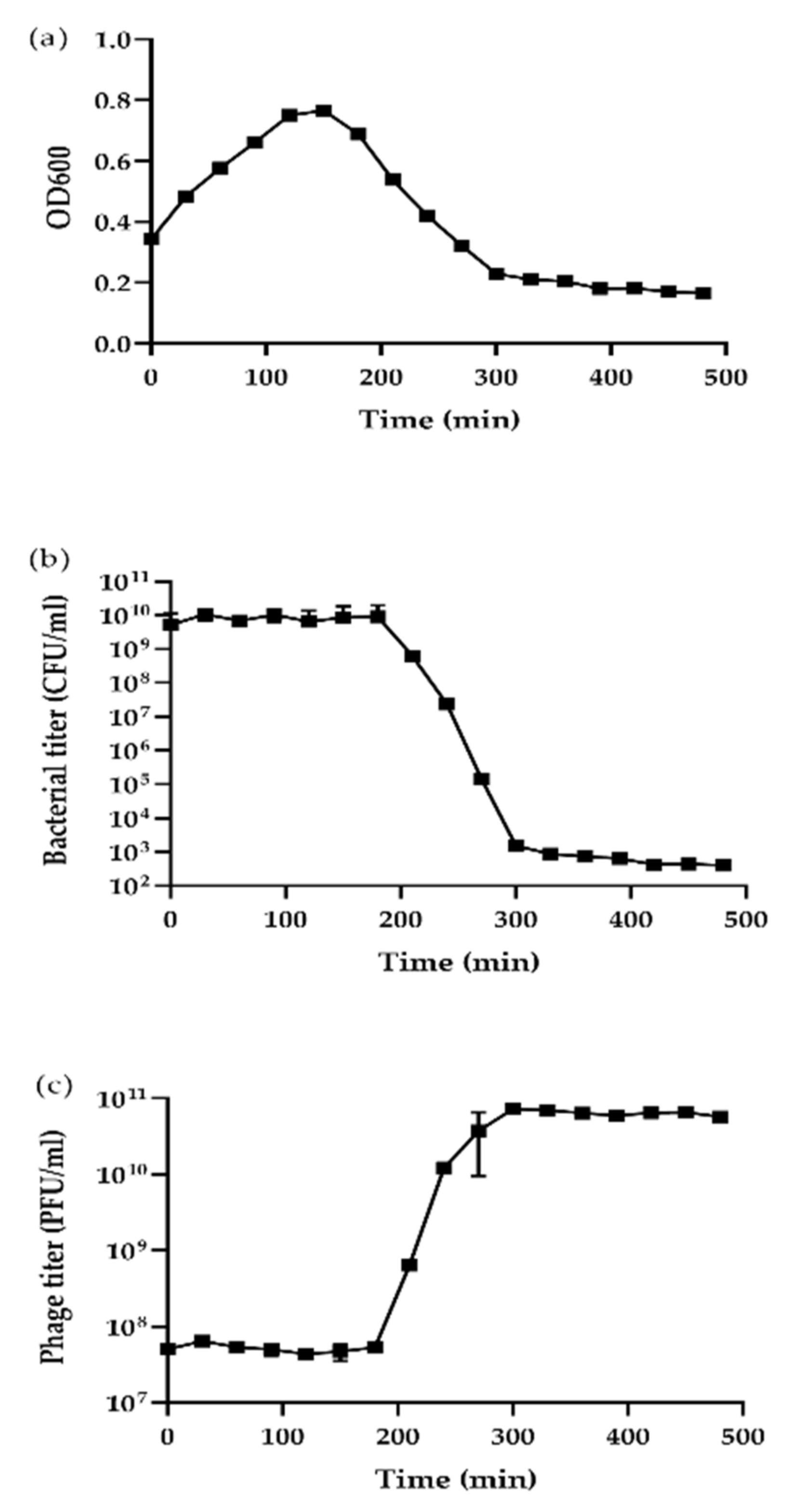
2.7. One-Step Growth Curve
2.8. Phage Genome Extraction
2.9. Genomic Analysis
2.10. Proteomic Analysis
2.11. Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
2.12. Genome Recruitment
2.13. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phage Basic Characteristics: Infection Mode, Morphology, Host Ranges, and Existence or Absence of Lipids in Phage Capsid
3.2. Lysis Profile Assay and Sensitivity of Virions to Physical and Chemical Factors
3.3. High Replication Capability Reflected by the High Burst Size
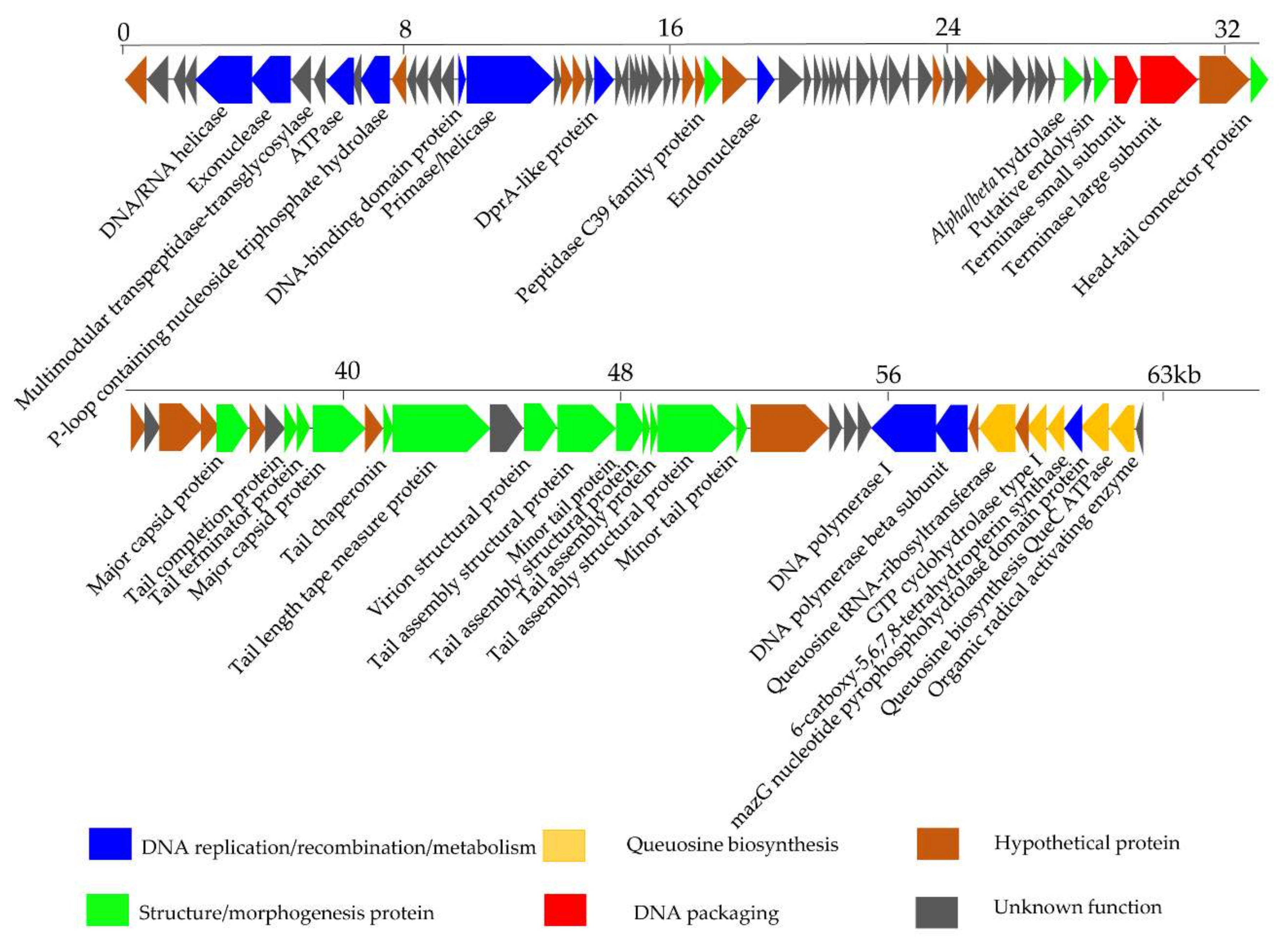
3.4. Genomic Features of the Phage S0112
3.5. Mass-Spectrometric Identification of Phage Proteins
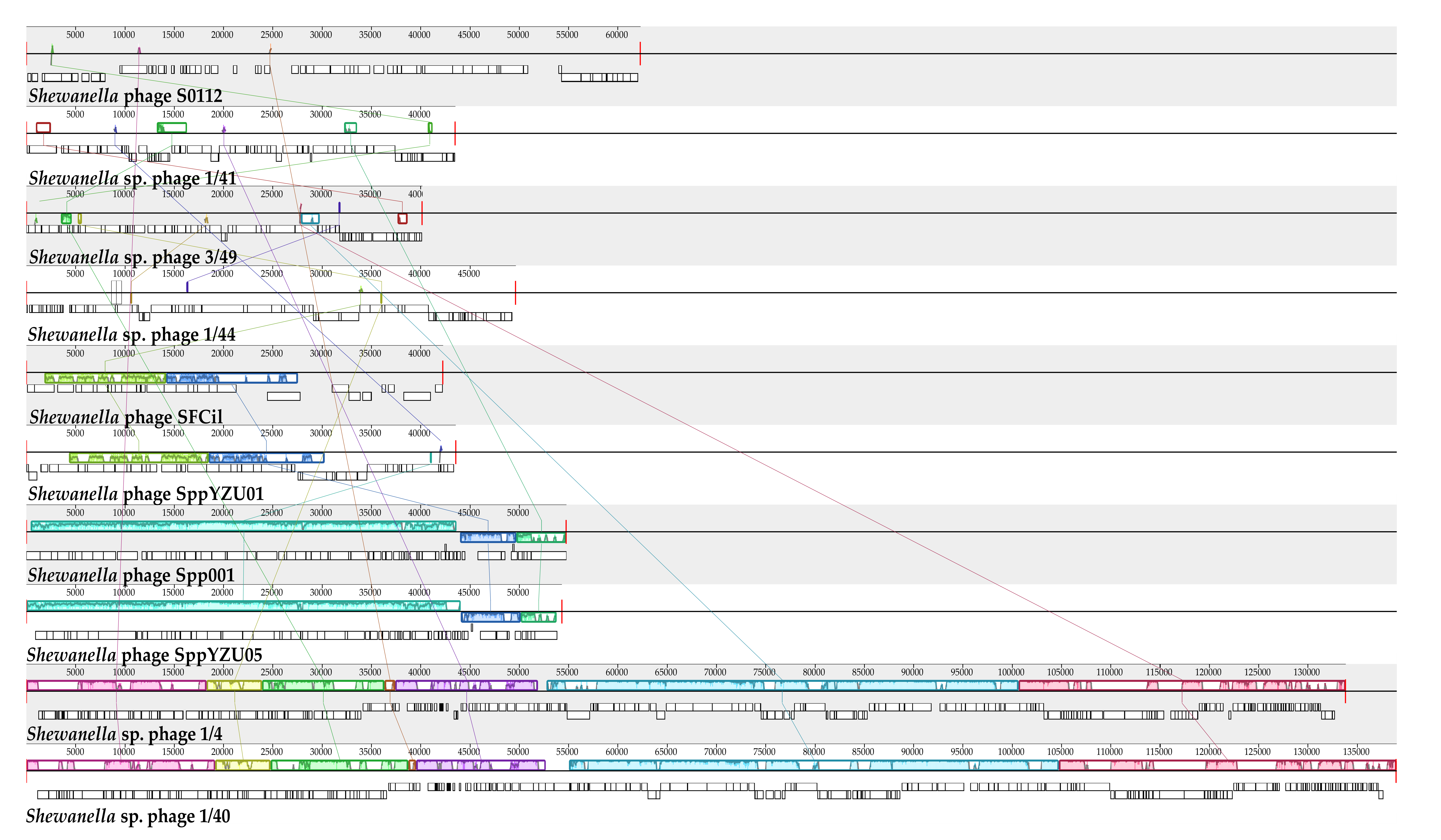
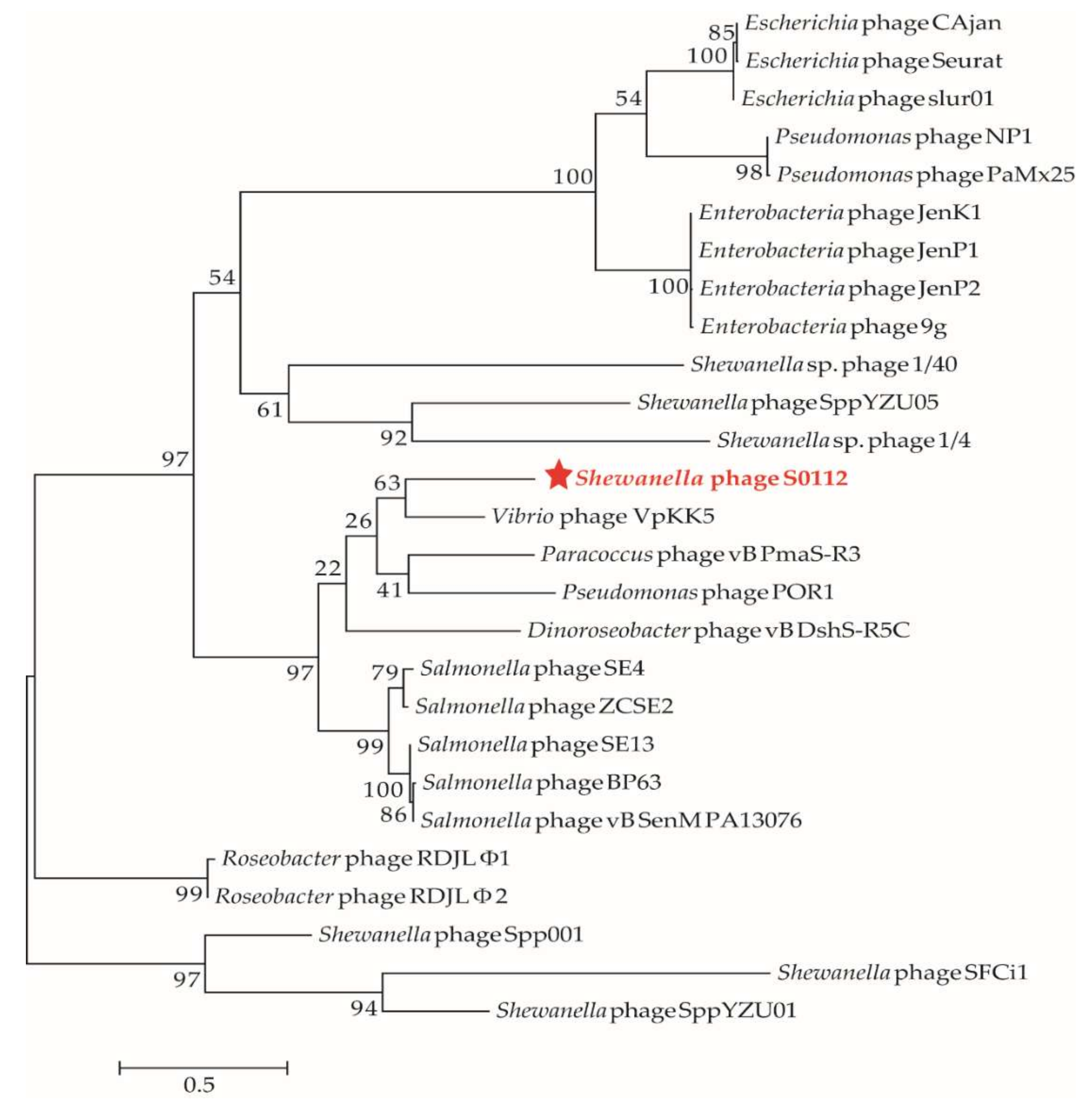
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
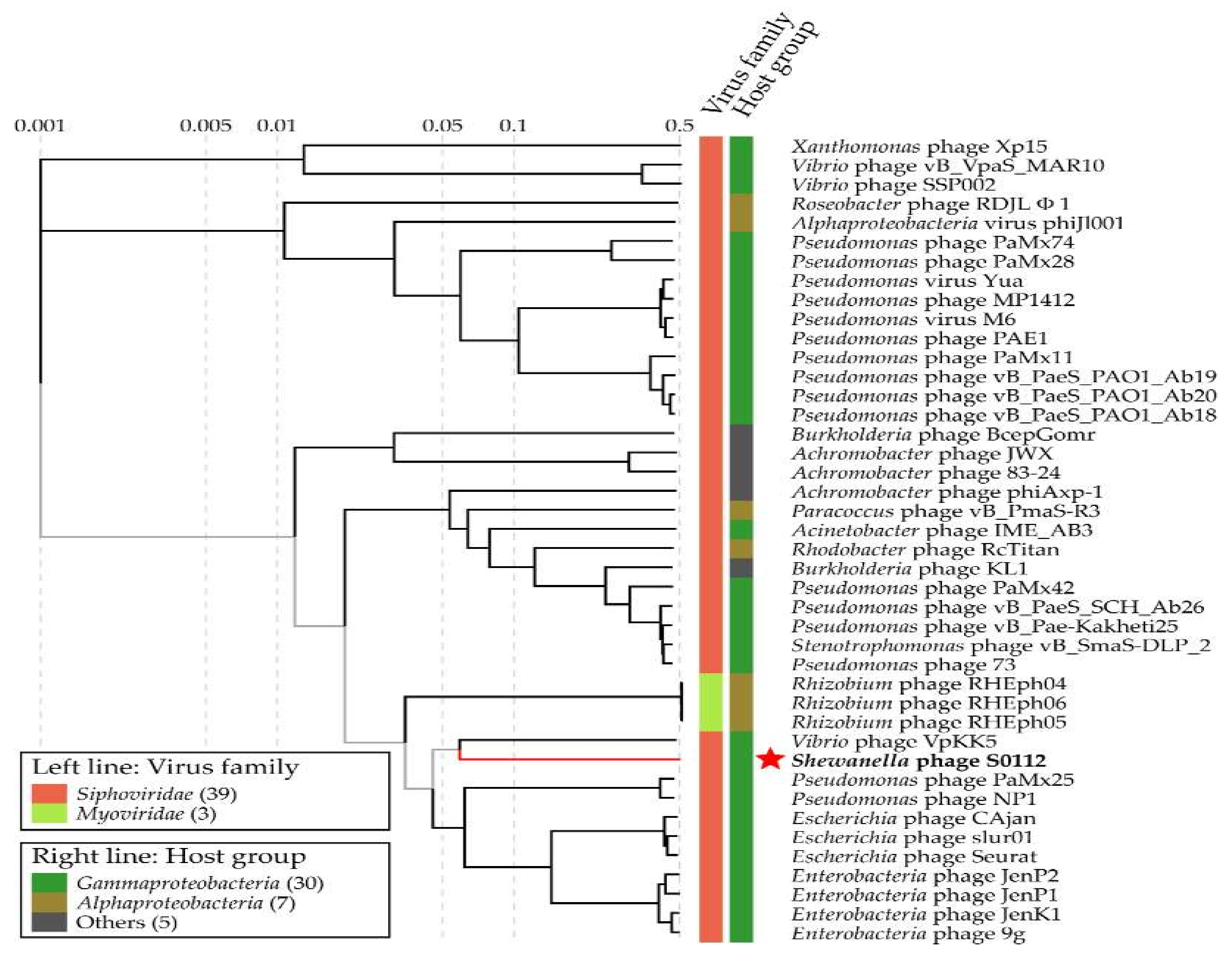
3.7. Environmental Distribution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuhrman, J.A. Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 1999, 399, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses-major players in the global ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A. Viruses in the sea. Nature 2005, 437, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Jiao, N. Interactions between marine microorganisms and their phages. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Temperton, B.; Thrash, J.C.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Vergin, K.L.; Landry, Z.C.; Ellisman, M.; Deerinck, T.; Sullivan, M.B.; Giovannoni, S.J. Abundant SAR11 viruses in the ocean. Nature 2013, 494, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidner, G.; Bielawski, J.P.; Shmoish, M.; Scanlan, D.J.; Sabehi, G.; Beja, O. Potential photosynthesis gene recombination between Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus via viral intermediates. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glud, R.N.; Mathias, M. Virus and bacteria dynamics of a coastal sediment: Implication for benthic carbon cycling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitbart, M.; Felts, B.; Kelley, S.; Mahaffy, J.M.; Nulton, J.; Salamon, P.; Rohwer, F. Diversity and population structure of a near-shore marine-sediment viral community. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hau, H.H.; Gralnick, J.A. Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrickson, J.K.; Romine, M.F.; Beliaev, A.S.; Auchtung, J.M.; Driscoll, M.E.; Gardner, T.S.; Nealson, K.H.; Osterman, A.L.; Pinchuk, G.; Reed, J.L.; et al. Towards environmental systems biology of Shewanella. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, D.; Fang, C.; Wu, C.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Yu, H. Estimates of abundance and diversity of Shewanella genus in natural and engineered aqueous environments with newly designed primers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tao, X.; Zhang, H.; Rao, S.; Gao, L.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. Isolation and characterization of virulent phages infecting Shewanella baltica and Shewanella putrefaciens, and their application for biopreservation of chilled channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Li, M.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Cao, L.; Khan, M.N. The novel Shewanella putrefaciens-infecting bacteriophage Spp001: Genome sequence and lytic enzymes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, B.; Karrer, C.; Cannon, J.P.; Breitbart, M.; Dishaw, L.J. Isolation and characterization of a Shewanella phage-host system from the gut of the tunicate, Ciona intestinalis. Viruses 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencčilo, A.; Luhtanen, A.M.; Saarijӓrvi, M.; Bamford, D.H.; Roine, E. Cold-active bacteriophages from the Baltic Sea ice have diverse genomes and virus-host interactions. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3628–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, L.; Ren, R.; You, W.; Farooq, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Changes in bacterial community structure and humic acid composition in response to enhanced extracellular electron transfer process in coastal sediment. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.S.; Manno, D.; Beaulieu, C.; Paquet, L.; Hawari, J. Shewanella sediminis sp. nov., a novel Na+-requiring and hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine-degrading bacterium from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, T.M.; Sano, M.; Ransangan, J. Genome characterization of a novel vibriophage VpKK5 (Siphoviridae) specific to fish pathogenic strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liang, L.; Lin, S.; Jia, S. Isolation and characterization of a virulent bacteriophage AB1 of Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Pandey, P.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Kim, H.J.; Baik, K.S.; Seong, C.N.; Patole, M.S.; Shouche, Y.S. Shewanella indica sp. nov., isolated from sediment of the Arabian Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, N. Roseophage RDJL Ф1, infecting the aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium Roseobacter denitrificans OCh114. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinbauer, M.G.; Rowe, J.M.; Wilhelm, S. Determining rates of virus production in aquatic systems by the virus reduction approach. In Manual of Aquatic Viral Ecology; Suttle, C.A., Wilhelm, S.W., Weinbauer, M.G., Eds.; American Society of Limnology and Oceanography: Waco, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M.D.C.; Rodríguez, J.; Borrego, J.J. Characterization of marine bacteriophages isolated from the Alboran Sea (Western Mediterranean). J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak-Kurek, A.; Gasior, T.; Nejman-Falenczyk, B.; Bloch, S.; Dydecka, A.; Topka, G.; Necel, A.; Jakubowska-Deredas, M.; Narajczyk, M.; Richert, M.; et al. Biodiversity of bacteriophages: Morphological and biological properties of a large group of phages isolated from urban sewage. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelboe, M.; Chan, A.M.; Bertelsen, S.K. Isolation and life cycle characterization of lytic viruses infecting heterotrophic bacteria and cyanobacteria. In Manual of Aquatic Viral Ecology; Wilhelm, S.W., Weinbauer, M.G., Suttle, C.A., Eds.; American Society of Limnology and Oceanography: Waco, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 118–133. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.F. Bacteriophages. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1950, 4, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Cai, L.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, R. Isolation and characterization of the first phage infecting ecologically important marine bacteria Erythrobacter. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Yoshikawa, G.; Mihara, T.; Chatchawankanphanich, O.; Kawasaki, T.; Nakano, M.; Fujie, M.; Ogata, H.; Yamada, T. Replications of two closely related groups of Jumbo phages show different level of dependence on host-encoded RNA polymerase. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; An, X.; Pei, G.; Huang, Y.; Fan, H.; Mi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. A novel termini analysis theory using HTS data alone for the identification of Enterococcus phage EF4-like genome termini. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneau, J.; Depardieu, F.; Fortier, L.C.; Bikard, D.; Monot, M. PhageTerm: A fast and user-friendly software to determine bacteriophage termini and packaging mode using randomly fragmented NGS data. bioRxiv 2017, 108100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattner, P.; Brooks, A.N.; Lowe, T.M. The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucl. Acids Res. 2005, 33, W686–W689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajich, J.E.; Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar]
- Paez-Espino, D.; Roux, S.; Chen, I.A.; Palaniappan, K.; Ratner, A.; Chu, K.; Huntemann, M.; Reddy, T.B.K.; Pons, J.C.; Llabrés, M.; et al. IMG/VR v.2.0: An integrated data management and analysis system for cultivated and environmental viral genomes. Nucl. Acids Res. 2018, 47, D678–D686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grissa, I.; Vergnaud, G.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRcompar: A website to compare clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucl. Acids Res. 2008, 36, W145–W148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kuronishi, M.; Uehara, H.; Ogata, H.; Goto, S. ViPTree: The viral proteomic tree server. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2379–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, B.L.; Sullivan, M.B. The Pacific Ocean Virome (POV): A marine viral metagenomic dataset and associated protein clusters for quantitative viral ecology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K.; et al. The sorcerer II global ocean sampling expedition: Northwest Atlantic through eastern tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T. Selection for bacteriophage latent period length by bacterial density: A theoretical examination. Microb. Ecol. 1989, 18, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børsheim, K.Y. Native marine bacteriophages. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1993, 11, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, M.L.; Danovaro, R. Virus production and life strategies in aquatic sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, S.; Rousseau, G.M.; Labrie, S.J.; Tremblay, D.M.; Kourda, R.S.; Ben Slama, K.; Moineau, S. Characterization of two polyvalent phages infecting Enterobacteriaceae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahony, J.; Alqarni, M.; Stockdale, S.; Spinelli, S.; Feyereisen, M.; Cambillau, C.; Sinderen, D.V. Functional and structural dissection of the tape measure protein of lactococcal phage TP901-1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.L.; Struck, D.K.; Scholtz, J.M.; Young, R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the lambda holin. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filée, J.; Forterre, P.; Sen-Lin, T.; Laurent, J. Evolution of DNA polymerase families: Evidences for multiple gene exchange between cellular and viral proteins. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matson, S.W.; Bean, D.W.; George, J.W. DNA helicases: Enzymes with essential roles in all aspects of DNA metabolism. Bioessays 1994, 16, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, K.; Rutvisuttinunt, W.; Scott, W.; Myers, R.S. The enzymatic basis of processivity in lambda exonuclease. Nucl. Acids Res. 2003, 31, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rihtman, B.; Bowman-Grahl, S.; Millard, A.; Corrigan, R.M.; Clokie, M.R.J.; Scanlan, D.J. Cyanophage MazG is a pyrophosphohydrolase but unable to hydrolyse magic spot nucleotides. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnusson, L.U.; Farewell, A.; Nystrom, T. ppGpp: A global regulator in Escherichia coli. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Marianovsky, I.; Glaser, G. MazG—A regulator of programmed cell death in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clokie, M.R.; Mann, N.H. Marine cyanophages and light. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría, R.I.; Bustos, P.; Sepúlveda-Robles, O.; Lozano, L.; Rodríguez, C.; Fernández, J.L.; Juárez, S.; Kameyama, L.; Guarneros, G.; Dávila, G.; et al. Narrow-host-range bacteriophages that infect Rhizobium etli associate with distinct genomic types. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, L.; Ma, R.; Xu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, R. A novel roseosiphophage isolated from the oligotrophic South China Sea. Viruses 2017, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulikov, E.E.; Golomidova, A.K.; Letarova, M.A.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Zelenin, A.S.; Prokhorov, N.S.; Letarov, A.V. Genomic sequencing and biological characteristics of a novel Escherichia coli bacteriophage 9g, a putative representative of a new Siphoviridae genus. Viruses 2014, 6, 5077–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sazinas, P.; Redgwell, T.; Rihtman, B.; Grigonyte, A.; Michniewski, S.; Scanlan, D.J.; Hobman, J.; Millard, A. Comparative genomics of bacteriophage of the genus Seuratvirus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiaville, J.J.; Kellner, S.M.; Yuan, Y.; Hutinet, G.; Thiaville, P.C.; Jumpathong, W.; Mohapatra, S.; Brochier-Armanet, C.; Letarov, A.V.; Hillebrand, R.; et al. Novel genomic island modifies DNA with 7-deazaguanine derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1452–E1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Hutinet, G.; Valera, J.G.; Hillebrand, R.; Gustafson, A.; Iwata-Reuyl, D.; Dedon, P.C.; de Crécy-Lagard, V. Identification of the minimal bacterial 2′-deoxy-7-amido-7-deazaguanine synthesis machinery. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 110, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbonavičius, J.; Qian, Q.; Durand, J.M.; Hagervall, T.G.; Björk, G.R. Improvement of reading frame maintenance is a common function for several tRNA modifications. EMBO. J. 2001, 20, 4863–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Chen, M.; He, L.; Zhang, S.; Ding, T.; Yao, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W. Isolation and characterization of a T4-like phage with a relatively wide host range within Escherichia coli. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Mestre, M.R.; Martinez-Abarca, F.; Gonzalez-Delgado, A. Recruitment of reverse transcriptase-cas1 fusion proteins by type VI-A CRISPR-Cas Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genus and Species | Strain | Source | Strains Lysed by Phage S0112 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shewanella indica | KJW27 a | sediment | + |
| Shewanella basaltis | CJW-54 | sediment | - |
| Shewanella chilikensis | JC5 | sediment | - |
| Shewanella japonica | KCTC22435 | sediment | - |
| Shewanella algae | JCM 21037 | seawater | - |
| Alginatibacterium sediminis | ALS 81 | sediment | - |
| Woeseia oceani | SDUM189001 | sediment | - |
| Sediminicola luteus | SDUM701001 | sediment | - |
| Kordiimonas sediminis | N39 | sediment | - |
| Roseobacter denitrificans | OCH114 | seawater | - |
| Marinobacter vinifirmus | D7035 | wastewater | - |
| Halomonas denitrificans | D7027 | saline water | - |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | CIP 82.01 | seawater | - |
| Vibrio neocaledonicus | NC 470 | seawater | - |
| Vibrio azureus | NBRC 104587 | seawater | - |
| Vibrio harveyi | NBRC 15634 | seawater | - |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | NBRC 12711 | seawater | - |
| Vibrio campbellii | CAIM 519 | seawater | - |
| Phage Name | −20 °C | 15 °C | 20 °C | 28 °C | 30 °C | 37 °C | 40 °C | 50 °C | 60 °C | 95 °C | 100 °C | pH 2 | pH 4 | pH 10 | pH 12 | Osmotic Shock | 0.1% CTAB | 0.09% SDS | 0.1% Sarkosyl | 63% Ethanol | 90% Acetone | 50% DMSO | Chloroform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phage S0112 | 95 | 1.3 | 4.5 | 99.2 | 100 | 86.7 | 72.9 | 1.4 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.8 | 82.1 | 0.3 | 30.4 | 52.5 | 0 | 12.7 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 30.9 | 91.9 |
| Shewanella Phages a | Host Strains | Family | Size (Kb) | GC% | Protein | No. of tRNAs | Isolation Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0112 | Shewanella indica | Siphoviridae | 62.286 | 44.7 | 102 | 0 | Coastal sediment |
| Spp001 | S. putrefaciens | Siphoviridae | 54.789 | 49.4 | 67 | 0 | Sewage |
| 3/49 | S. baltica | Siphoviridae | 40.161 | 42 | 70 | 0 | Baltic Sea ice |
| 1/44 | S. frigidimarina | Siphoviridae | 49.64 | 39.8 | 75 | 0 | Baltic Sea ice |
| SppYZU05 | S. putrefaciens | Siphoviridae | 54.319 | 50.63 | 65 | 0 | Waste effluents |
| 1/41 | S. baltica | Myoviridae | 43.51 | 42.7 | 69 | 0 | Baltic Sea ice |
| SFCi1 | S. fidelis | Myoviridae | 42.279 | 59.1 | 40 | 0 | Seawater |
| SppYZU01 | S. baltica | Myoviridae | 43.567 | 55.72 | 49 | 0 | Waste effluents |
| 1/4 | S. frigidimarina | Myoviridae | 133.824 | 36.9 | 235 | 3 | Baltic Sea ice |
| 1/40 | S. baltica | Myoviridae | 139.004 | 36.9 | 236 | 3 | Baltic Sea ice |
| Detected Protein | Predicted Function | Molecular Mass (kDa) | Number of Peptides | Sequence Coverage (%) | Protein Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0112_001 | Uncharacterized protein | 11.2 | 3 | 33.7 | 175 |
| S0112_065 | Uncharacterized protein | 52.6 | 17 | 46.7 | 3837 |
| S0112_066 | Head-tail connector protein | 19.6 | 7 | 49.7 | 1873 |
| S0112_068 | Uncharacterized protein | 16.9 | 5 | 30.1 | 575 |
| S0112_069 | Uncharacterized protein | 43.1 | 4 | 9.4 | 220 |
| S0112_071 | Major capsid protein | 37.3 | 13 | 42.1 | 9723 |
| S0112_074 | Tail completion protein | 13.7 | 4 | 43.7 | 418 |
| S0112_075 | Tail terminator protein | 16.1 | 6 | 44.3 | 694 |
| S0112_076 | Major capsid protein | 54.1 | 17 | 58.7 | 15,158 |
| S0112_079 | Tail length tape measure protein | 99 | 24 | 31.4 | 5007 |
| S0112_080 | Uncharacterized protein | 38.4 | 5 | 27.1 | 1859 |
| S0112_081 | Virion structural protein | 30.8 | 7 | 30.8 | 709 |
| S0112_082 | Tail assembly structural protein | 62.2 | 8 | 27.1 | 1781 |
| S0112_083 | Minor tail protein | 30.8 | 8 | 37.7 | 1024 |
| S0112_086 | Tail assembly structural protein | 83.3 | 12 | 23.9 | 1972 |
| S0112_087 | Minor tail protein | 14.9 | 4 | 45.5 | 696 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Benthic Phage Infecting Shewanella with Strong Replication Ability. Viruses 2019, 11, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111081
Wang Z, Zhao J, Wang L, Li C, Liu J, Zhang L, Zhang Y. A Novel Benthic Phage Infecting Shewanella with Strong Replication Ability. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111081
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zengmeng, Jiulong Zhao, Long Wang, Chengcheng Li, Jianhui Liu, Lihua Zhang, and Yongyu Zhang. 2019. "A Novel Benthic Phage Infecting Shewanella with Strong Replication Ability" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111081
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhao, J., Wang, L., Li, C., Liu, J., Zhang, L., & Zhang, Y. (2019). A Novel Benthic Phage Infecting Shewanella with Strong Replication Ability. Viruses, 11(11), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111081






