In Vivo Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Bank Voles (Myodes glareolus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TBEV-Eu Strains
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
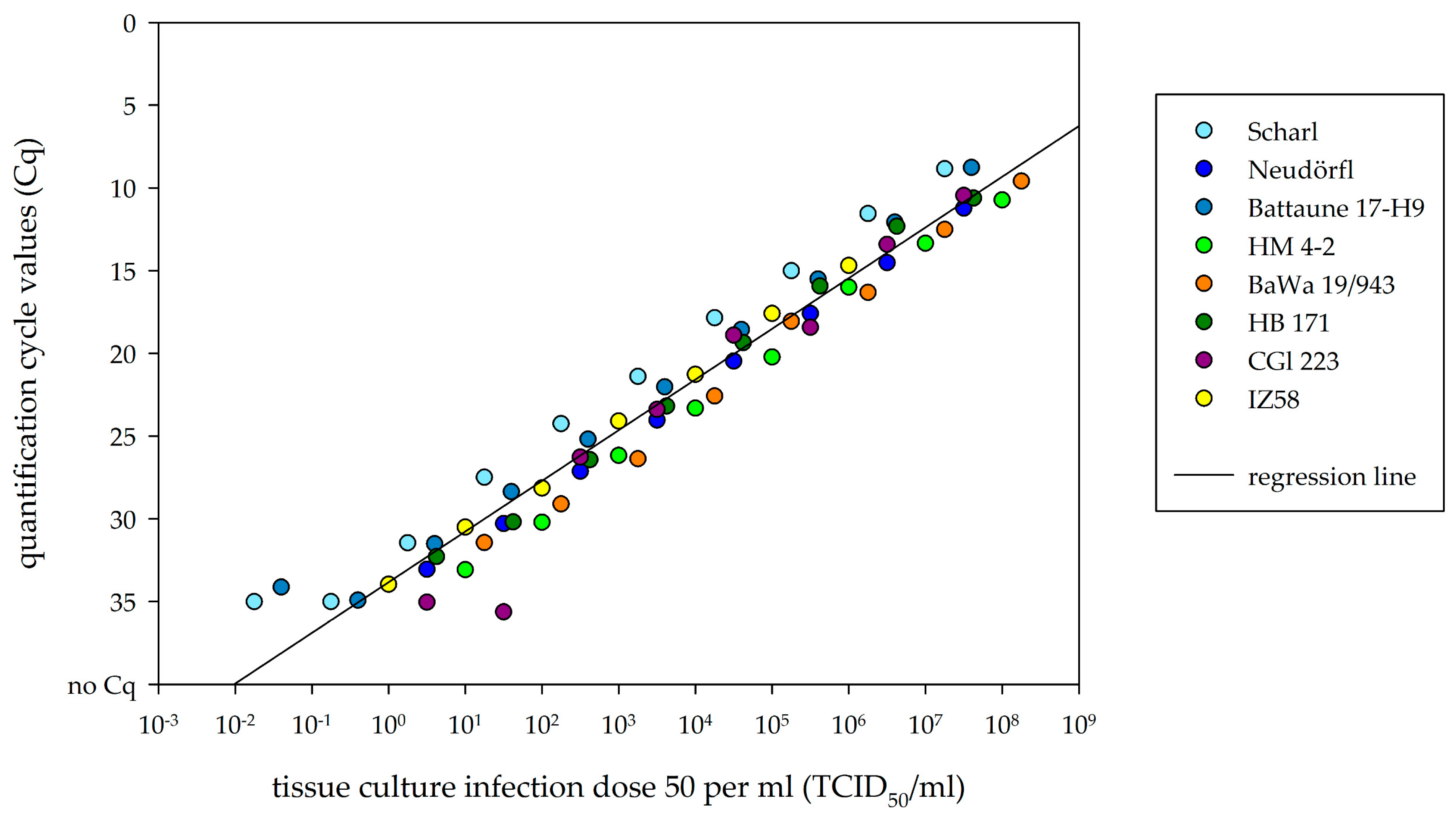
2.4. Comparison of Real-Time RT-PCR to Cell-Culture Infectivity
2.5. Virus Isolation
2.6. Antibody Detection
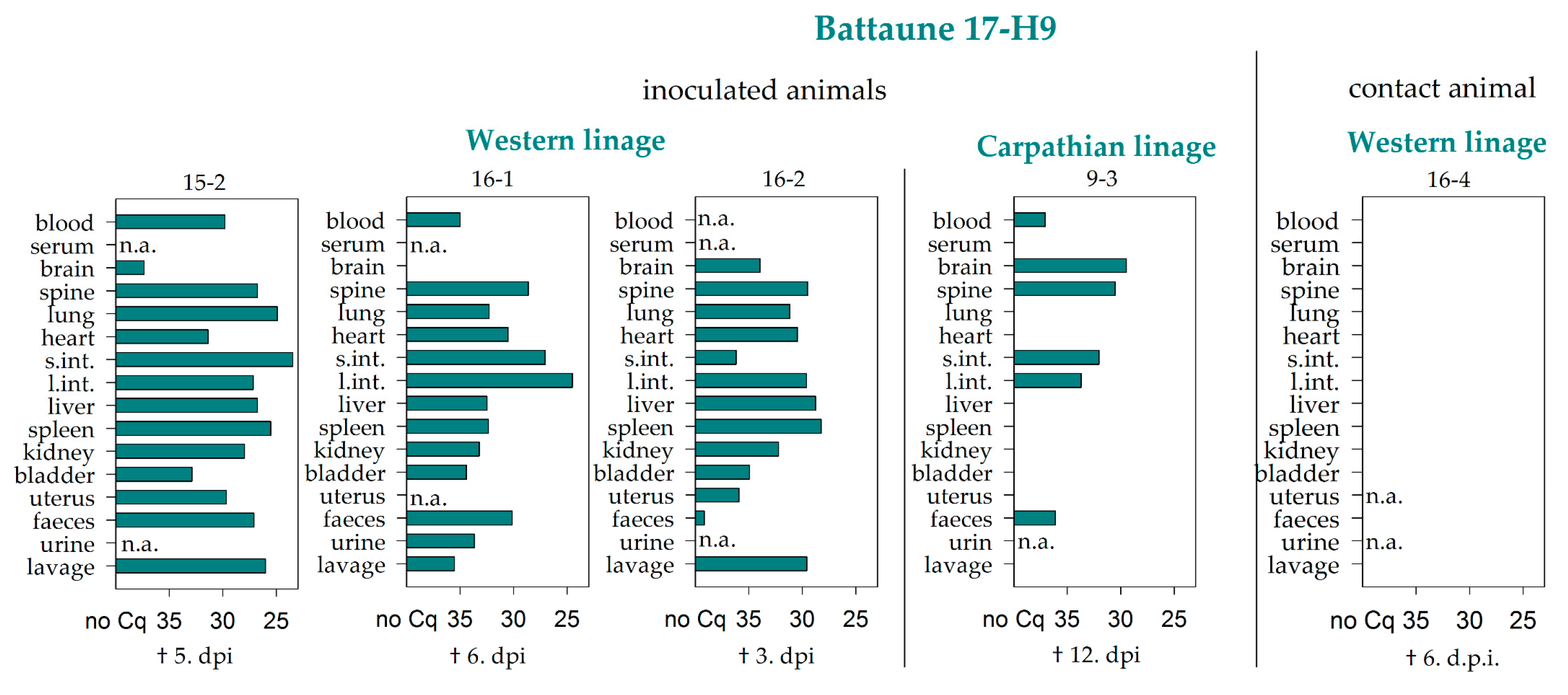
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Manifestation
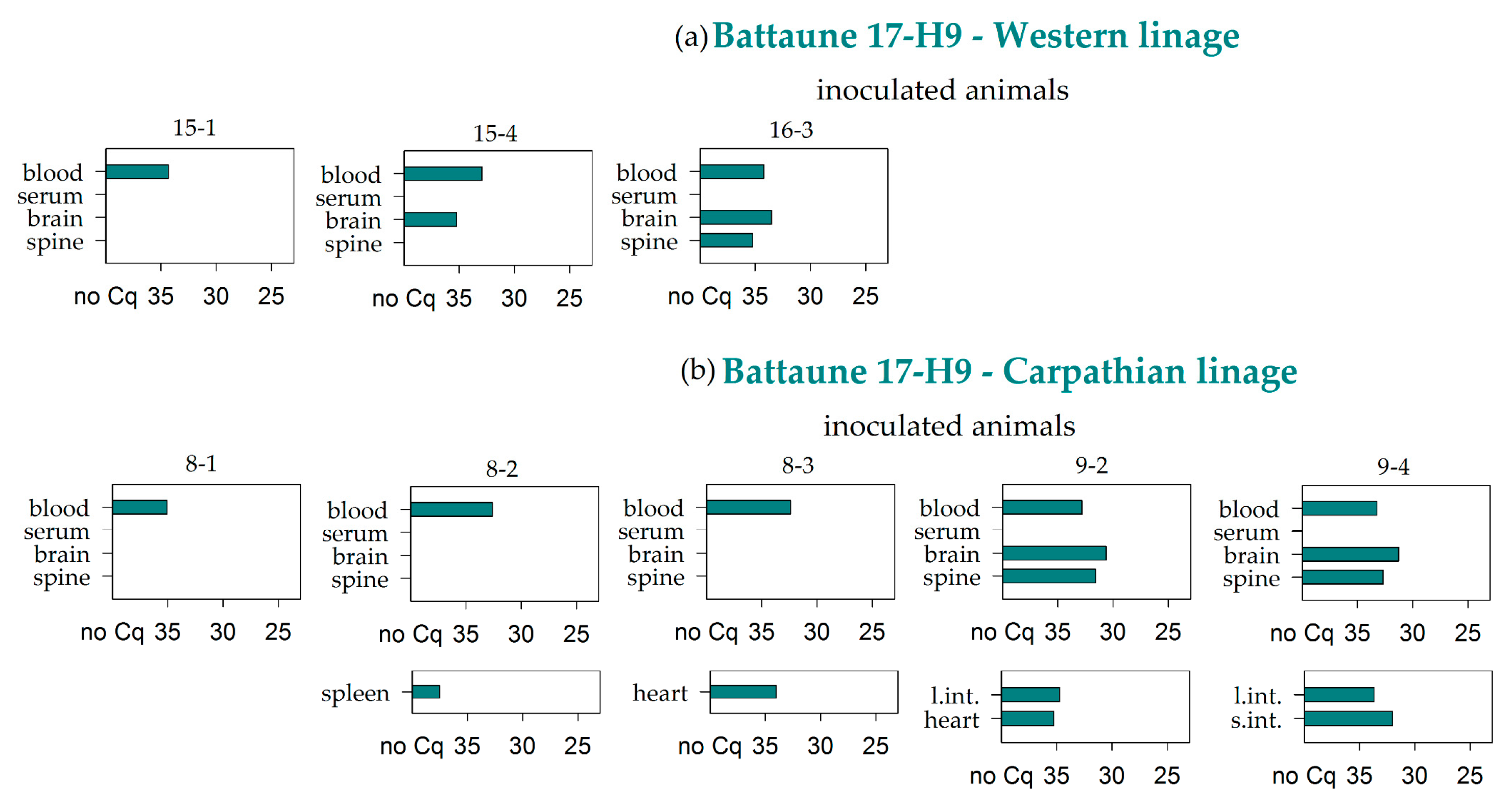
3.2. Virus RNA Detection
3.3. Comparison of Viral RNA Detection and Cell-Culture Infectivity
3.4. Virus Isolation
3.5. Comparative Antibody Detection between Sera and Lavages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taba, P.; Schmutzhard, E.; Forsberg, P.; Lutsar, I.; Ljøstad, U.; Mygland, A.; Levchenko, I.; Strle, F.; Steiner, I. EAN consensus review on prevention, diagnosis and management of tick-borne encephalitis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauté, J.; Spiteri, G.; Warns-Petit, E.; Zeller, H. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe, 2012 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1800201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K.; Song, J.Y.; Park, S.B.; Yang, J.; Schmitt, H.J. Tick-borne encephalitis in Japan, Republic of Korea and China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Bröker, M.; Liang, G. Tick-borne encephalitis in mainland China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, K.L.; Johnson, N.; Phipps, L.P.; Stephenson, J.R.; Fooks, A.R.; Solomon, T. Tick-borne encephalitis virus—A review of an emerging zoonosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süss, J. Epidemiology and ecology of TBE relevant to the production of effective vaccines. Vaccine 2003, 21, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.; Danielová, V.; Fialová, A.; Malý, M.; Kříž, B.; Nuttall, P.A. Increased relative risk of tick-borne encephalitis in warmer weather. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, S.E. Tick-borne encephalitis virus, ticks and humans: Short-term and long-term dynamics. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Petersson, E.H.; Jaenson, D.G.E.; Kindberg, J.; Pettersson, J.H.; Hjertqvist, M.; Medlock, J.M.; Bengtsson, H. The importance of wildlife in the ecology and epidemiology of the TBE virus in Sweden: Incidence of human TBE correlates with abundance of deer and hares. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, G. Zoonotic tick-borne flaviviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, M.; Allison, S.L.; Meixner, T.; Heinz, F.X. Sequence analysis and genetic classification of tick-borne encephalitis viruses from Europe and Asia. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Shang, G.; Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. A new subtype of eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus discovered in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalev, S.Y.; Mukhacheva, T.A. Reconsidering the classification of tick-borne encephalitis virus within the Siberian subtype gives new insights into its evolutionary history. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzek, D.; Avšič Županc, T.; Borde, J.; Chrdle, A.; Eyer, L.; Karganova, G.; Kholodilov, I.; Knap, N.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Matveev, A.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of pathogenesis, clinical features, therapy, and vaccines. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoso Mantke, O.; Schadler, R.; Niedrig, M. A survey on cases of tick-borne encephalitis in European countries. Euro Surveill. 2008, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsun, T.S.; Lashkevich, V.A.; Gould, E.A. Tick-borne encephalitis. Antivir. Res. 2003, 57, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenberg, E.; Kovalevskii, Y.V. A model for relationships among the tick-borne encephalitis virus, its main vectors, and hosts. Zool Zhurnal 1994, 10, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, A.; Silaghi, C.; Obiegala, A.; Rudolf, I.; Hubalek, Z.; Foldvari, G.; Plantard, O.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Bonnet, S.; Spitalska, E.; et al. Ixodes ricinus and Its Transmitted Pathogens in Urban and Peri-Urban Areas in Europe: New Hazards and Relevance for Public Health. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, B.; Schade, B.; Bauer, B.; Hoffmann, B.; Hoffmann, D.; Ziegler, U.; Beer, M.; Klaus, C.; Weissenböck, H.; Böttcher, J. Tick-borne encephalitis in a naturally infected sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindel, W.; Wyler, R. Tick-borne encephalitis in a goat in lower Prätigau. Schweiz Arch. Tierheilkd 1983, 125, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bagó, Z.; Bauder, B.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Weissenböck, H. Tickborne encephalitis in a mouflon (Ovis ammon musimon). Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.; Dobler, G. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in dogs—Is this an issue? Parasit Vectors 2011, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaus, C.; Hörügel, U.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) infection in horses: Clinical and laboratory findings and epidemiological investigations. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 163, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowiak, G.; Biernat, B. The role of particular tick developmental stages in the circulation of tick-borne pathogens affecting humans in Central Europe. 2. Tick-borne encephalitis virus. Ann. Parasitol. 2016, 62, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuda, M.; Nuttall, P.A. Tick-borne viruses. Parasitology 2005, 129, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Arboviruses and Human Disease: Report of a WHO Scientific Group; World Health Organization Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneve, Switzerland, 1967; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- Haydon, D.T.; Cleaveland, S.; Taylor, L.H.; Laurenson, M.K. Identifying reservoirs of infection: A conceptual and practical challenge. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, G.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Junglen, S.; Hubálek, Z.; Plyusnin, A.; Gubler, D.J. Vertebrate Reservoirs of Arboviruses: Myth, Synonym of Amplifier, or Reality? Viruses 2017, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosek, J.; Grulich, I. The relationship between the tick-borne encephalitis virus and the ticks and mammals of the Tribec mountain range. Bull. World Health Organ. 1967, 36 (Suppl. 1), 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Labuda, M.; Nuttall, P.A.; Kožuch, O.; Elečková, E.; Williams, T.; Žuffová, E.; Sabó, A. Non-viraemic transmission of tick-borne encephalitis virus: A mechanism for arbovirus survival in nature. Experientia 1993, 49, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso Mantke, O.; Karan, L.S.; Ruzek, D. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A General Overview. In Flavivirus Encephalitis; Ruzek, D., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, S.E. Transmission of tick-borne pathogens between co-feeding ticks: Milan Labuda’s enduring paradigm. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2011, 2, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernek, E.; Kožuch, O.; Lichard, M.; Nosek, J.; Albrecht, P. Experimental infection of Clethrionomys glareolus and Apodemus flavicollis with tick-borne encephalitis virus. Acta Virol. 1963, 7, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kopecký, J.; Tomková, E.; Vlček, M. Immune response of the long-tailed field mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus) to tick-borne encephalitis virus infection. Folia Parasitol. (Praha) 1991, 38, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Heigl, Z.; Zeipel, G.V. Experimental infection with tick-borne encephalitis virus in Clethrionomys glareolus, Apodemus flavicollis, Apodemus sylvaticus and Mus musculus. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1966, 66, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achazi, K.; Růžek, D.; Donoso-Mantke, O.; Schlegel, M.; Ali, H.; Wenk, M.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Ohlmeyer, L.; Rühe, F.; Vor, T.; et al. Rodents as sentinels for the prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunikhin, S.P.; Kurenkov, V.B. Viraemia in Clethrionomys glareolus—A new ecological marker of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Acta Virol. 1979, 23, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tonteri, E.; Kipar, A.; Voutilainen, L.; Vene, S.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O.; Lundkvist, A. The three subtypes of tick-borne encephalitis virus induce encephalitis in a natural host, the bank vole (Myodes glareolus). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knap, N.; Korva, M.; Dolinšek, V.; Sekirnik, M.; Trilar, T.; Avšič-Županc, T. Patterns of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection in rodents in Slovenia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelitsch, A.; Wernike, K.; Klaus, C.; Dobler, G.; Beer, M. Exploring the Reservoir Hosts of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipi, K.; Markova, S.; Searle, J.B.; Kotlik, P. Mitogenomic phylogenetics of the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus, a model system for studying end-glacial colonization of Europe. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 82(Pt. A), 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E. A virus resembling Russian spring-summer encephalitis virus from an ixodid tick in Malaya. Nature 1956, 178, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumyantsev, A.A.; Murphy, B.R.; Pletnev, A.G. A tick-borne Langat virus mutant that is temperature sensitive and host range restricted in neuroblastoma cells and lacks neuroinvasiveness for immunodeficient mice. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewes, S.; Ali, H.S.; Saxenhofer, M.; Rosenfeld, U.M.; Binder, F.; Cuypers, F.; Schlegel, M.; Röhrs, S.; Heckel, G.; Ulrich, R.G. Host-associated absence of human Puumala virus infections in northern and eastern Germany. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobler, G.; Bestehorn, M.; Antwerpen, M.; Överby-Wernstedt, A. Complete genome sequence of a low-virulence tick-borne encephalitis virus strain. Genome Announc. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apitzsch, L.; Sinnecker, H.; Wigand, R.; Berndt, D. Zeckencephalitis-Virusisolierungen in der DDR 1965/66 und einige Stammdifferenzierungen. Zbl. Bakt. I. Abt. Orig. 1968, 207, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Mandl, C.W.; Heinz, F.X.; Kunz, C. Sequence of the structural proteins of tick-borne encephalitis virus (western subtype) and comparative analysis with other flaviviruses. Virology 1988, 166, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuch, O.; Gurycova, D.; Lysy, J.; Labuda, M. Mixed natural focus of tick-borne encephalitis, tularemia and haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in west Slovakia. Acta Virol. 1995, 39, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, A.; Ulrich, R.G.; Weber, S.; Osterrieder, N.; Keller, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Beer, M. Experimental Cowpox Virus (CPXV) Infections of Bank Voles: Exceptional Clinical Resistance and Variable Reservoir Competence. Viruses 2017, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, M.; Ali, H.S.; Stieger, N.; Groschup, M.H.; Wolf, R.; Ulrich, R.G. Molecular identification of small mammal species using novel cytochrome B gene-derived degenerated primers. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, M.; Cassinotti, P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J. Clin. Virol. 2003, 27, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, J.F.; Sailleau, C.; Breard, E.; Zientara, S.; De Clercq, K. Bluetongue virus detection by two real-time RT-qPCRs targeting two different genomic segments. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 140, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amicizia, D.; Domnich, A.; Panatto, D.; Lai, P.L.; Cristina, M.L.; Avio, U.; Gasparini, R. Epidemiology of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in Europe and its prevention by available vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzmann, H.; Kundi, M.; Stiasny, K.; Clement, J.; McKenna, P.; Kunz, C.; Heinz, F.X. Correlation between ELISA, hemagglutination inhibition, and neutralization tests after vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 48, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, Y.; Rojas, M.; Gershwin, M.E.; Anaya, J.M. Tick-borne diseases and autoimmunity: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlera, L.; Bloom, M.E. The role of mammalian reservoir hosts in tick-borne flavivirus biology. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhvalova, V.N.; Potapova, O.F.; Panov, V.V.; Morozova, O.V. Vertical transmission of tick-borne encephalitis virus between generations of adapted reservoir small rodents. Virus Res. 2009, 140, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, N.V.; Smolina, T.P.; Leonova, G.N. Molecular Mechanisms of Interaction Between Human Immune Cells and Far Eastern Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Strains. Viral. Immunol. 2015, 28, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overby, A.K.; Popov, V.L.; Niedrig, M.; Weber, F. Tick-borne encephalitis virus delays interferon induction and hides its double-stranded RNA in intracellular membrane vesicles. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8470–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miorin, L.; Albornoz, A.; Baba, M.M.; D’Agaro, P.; Marcello, A. Formation of membrane-defined compartments by tick-borne encephalitis virus contributes to the early delay in interferon signaling. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuda, M.; Kozuch, O.; Zuffova, E.; Elecková, E.; Hails, R.S.; Nuttall, P.A. Tick-borne encephalitis virus transmission between ticks cofeeding on specific immune natural rodent hosts. Virology 1997, 235, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuda, M.; Austyn, J.M.; Zuffova, E.; Kozuch, O.; Fuchsberger, N.; Lysy, J.; Nuttall, P.A. Importance of localized skin infection in tick-borne encephalitis virus transmission. Virology 1996, 219, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plekhova, N.G.; Pustovalov, E.V.; Somova, L.M.; Leonova, G.N.; Drobot, E.I.; Lyapun, I.N. The structural changes of macrophages infected with tick-borne encephalitis virus. Tsitologiia 2017, 59, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreil, T.R.; Burger, I.; Bachmann, M.; Fraiss, S.; Eibl, M.M. Antibodies protect mice against challenge with tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV)-infected macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 110, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, J.M.; Kawałko, A.; Marková, S.; Searle, J.B.; Kotlík, P. Phylogeographic signatures of northward post-glacial colonization from high-latitude refugia: A case study of bank voles using museum specimens. J. Zool. 2010, 281, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offerdahl, D.K.; Clancy, N.G.; Bloom, M.E. Stability of a tick-borne flavivirus in milk. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Essbauer, S.; Petraityte, R.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Tackmann, K.; Conraths, F.J.; Sasnauskas, K.; Arikawa, J.; Thomas, A.; Pfeffer, M.; et al. Extensive host sharing of central European Tula virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain | First Isolation | Passage on Cell Culture | Accession Number (NCBI GenBank) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Country | Location | Species | ||||
| BaWa 15/943 | 2015 | GER | Haselmühl | tick | 1× | - | - |
| HB 171/11 | 2011 | GER | Heselbach | tick | 2× | KX268728 | Dobler et al., 2016 [46] |
| IZ58 | 1965 | GER | Schorfheide | tick | 3× | - | Apitzsch et al., 1968 [47] |
| Neudörfl | 1970 | AUT | Neudörfl | tick | n.a. | U27495 | Mandl et al., 1988 [48] |
| Battaune 17-H9 | 2017 | GER | Leipzig | bank vole | 1× | - | - |
| CGl 223 | 1990 | SVK | Záhorská Ves | bank vole | 1× | KC835597 | Kozuch et al., 1995 [49] |
| HM 4-2 | 2015 | GER | Haselmühl | bank vole | 2× | - | - |
| Scharl | 1956 | AUT | Lower Austria | human | n.a. | - | Ecker et al., 1999 [12] |
| Langat virus | 1956 | MYS | Kuala Lumpur | tick | 3× | - | Smith 1956 [43] |
| Virus Strain | Bank Vole Lineage | Number of Positive Samples/Total Number | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | Serum | Brain | Spine | Lung | Heart | s. int. | l. int. | Liver | Spleen | Kidney | Bladder | Uterus | Faeces | Urine | Lavage | ||
| HM 4-2 | Western | 6/6 | 1/6 | 3/6 | 3/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 2/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 1 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 |
| BaWa 15/943 | Western | 1/6 | 0/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/4 | 0/6 |
| Neudörfl | Western | 4/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/2 | 0/6 |
| HB 171/11 | Western | 6/6 | 0/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/5 | 0/6 |
| Langat virus | Western | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 1 | 0/5 | 0/1 | 0/6 |
| Battaune 17-H9 | Western | 3/3 | 0/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 0/3 |
| Carparthian | 5/5 | 0/5 | 2/5 | 2/5 | 0/5 | 2/5 | 1/5 | 2/5 | 0/5 | 1/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/4 | 0/1 | 0/5 | |
| CGl 223 | Western | 2/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/2 | 0/6 |
| Carparthian | 4/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 1/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/5 | 0/1 | 1/6 | |
| IZ58 | Western | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 1 | 0/6 | 0/2 | 0/6 |
| Carparthian | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/0 | 0/6 | |
| Scharl | Western | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/2 | 0/6 |
| Carparthian | 0/6 | 0/6 | 2/6 | 2/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | |
| Σ | Σ | 31/74 | 2/74 | 11/74 | 8/74 | 1/74 | 2/74 | 3/74 | 2/74 | 0/74 | 2/74 | 1/74 | 0/74 | 0/74 | 0/71 | 0/33 | 1/74 |
| HM 4-2 | BaWa 15/943 | Neudörfl | ||||||
| ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage |
| ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | |||
| 2-1 | 1:960 | 1:5 | 24-1 | 1:480 | 1:10 | 1-1 | 1:1280 | 1:5 |
| 2-2 | 1:240 | neg. 1 | 24-3 | 1:240 | 1:5 | 1-2 | 1:640 | 1:10 |
| 2-3 | 1:1280 | 1:7.5 | 24-4 | 1:320 | 1:20 | 1-3 | 1:240 | 1:5 |
| 2-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 24-2 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 1-4 | neg.1 | neg. 1 |
| 3-1 | 1:1280 | 1:40 | 25-1 | 1:80 | 1:5 | 6-1 | 1:960 | 1:10 |
| 3-2 | 1:1280 | 1:40 | 25-2 | 1:120 | 1:5 | 6-2 | 1:1280 | 1:7.5 |
| 3-3 | 1:1280 | 1:10 | 25-3 | 1:160 | 1:15 | 6-3 | 1:1280 | 1:30 |
| 3-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 25-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 6-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 |
| HB 171/11 | Langat virus | |||||||
| ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage | |||
| ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | |||||
| 4-1 | 1:640 | 1:10 | 26-1 | 1:120 | neg. 1 | |||
| 4-2 | 1:1280 | 1:40 | 26-2 | 1:160 | 1:2.5 | |||
| 4-3 | 1:640 | 1:5 | 26-3 | 1:240 | 1:2.5 | |||
| 4-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 26-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | |||
| 5-1 | 1:160 | 1:2.5 | 27-1 | 1:160 | neg. 1 | |||
| 5-2 | 1:1280 | 1:5 | 27-3 | 1:320 | 1:10 | |||
| 5-3 | 1:1280 | 1:40 | 27-4 | 1:320 | 1:7.5 | |||
| 5-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 27-2 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | |||
| Battaune 17-H9 | CGl 223 | ||||||||||
| Western lineage | Carpathian lineage | Western lineage | Carpathian lineage | ||||||||
| ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage |
| ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ||||
| 15-1 | 1:40 | 1:10 | 8-1 | 1:160 | 1:2.5 | 17-1 | 1:60 | 1:2.5 | 10-1 | 1:30 | 1:7.5 |
| 15-2 | n.a. 2 | 1:10 | 8-2 | 1:120 | neg. 1 | 17-2 | 1:80 | 1:10 | 10-2 | 1:80 | 1:10 |
| 15-4 | 1:240 | 1:10 | 8-3 | 1:40 | 1:5 | 17-4 | 1:160 | 1:2.5 | 10-3 | 1:20 | neg. 1 |
| 15-3 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 8-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 17-3 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 10-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 |
| 16-1 | n.a. 2 | 1:20 | 9-2 | 1:80 | 1:10 | 18-2 | 1:160 | 1:7.5 | 11-1 | 1:40 | 1:5 |
| 16-2 | n.a. 2 | 1:10 | 9-3 | n.a. 2 | 1:15 | 18-3 | 1:160 | 1:5 | 11-2 | 1:160 | 1:5 |
| 16-3 | 1:160 | 1:15 | 9-4 | 1:240 | 1:2.5 | 18-4 | 1:160 | 1:5 | 11-4 | 1:320 | neg. 1 |
| 16-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 9-1 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 18-1 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 11-3 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 |
| IZ58 | Scharl | ||||||||||
| Western lineage | Carpathian lineage | Western lineage | Carpathian lineage | ||||||||
| ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage | ID | serum | lavage |
| ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ND50 | ||||
| 19-2 | 1:120 | 1:10 | 12-2 | 1:20 | 1:2.5 | 22-2 | 1:240 | 1:7.5 | 29-1 | 1:40 | 1:5 |
| 19-3 | 1:120 | 1:7.5 | 12-3 | 1:20 | neg. 1 | 22-3 | 1:320 | 1:5 | 29-2 | 1:60 | 1:2.5 |
| 19-4 | 1:20 | 1:5 | 12-4 | 1:40 | 1:5 | 22-4 | 1:120 | 1:5 | 29-4 | 1:80 | 1:7.5 |
| 19-1 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 12-1 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 22-1 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 29-3 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 |
| 20-1 | 1:30 | 1:5 | 13-1 | 1:40 | 1:2.5 | 23-1 | 1:160 | 1:7.5 | 30-1 | 1:80 | neg. 1 |
| 20-2 | 1:40 | 1:10 | 13-3 | 1:40 | 1:15 | 23-3 | 1:120 | 1.7.5 | 30-3 | 1:60 | 1:2.5 |
| 20-3 | 1:20 | 1: 5 | 13-4 | 1:80 | neg. 1 | 23-4 | 1:320 | 1:5 | 30-4 | 1:20 | neg. 1 |
| 20-4 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 13-2 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 23-2 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 | 30-2 | neg. 1 | neg. 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michelitsch, A.; Tews, B.A.; Klaus, C.; Bestehorn-Willmann, M.; Dobler, G.; Beer, M.; Wernike, K. In Vivo Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Bank Voles (Myodes glareolus). Viruses 2019, 11, 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111069
Michelitsch A, Tews BA, Klaus C, Bestehorn-Willmann M, Dobler G, Beer M, Wernike K. In Vivo Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Bank Voles (Myodes glareolus). Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111069
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichelitsch, Anna, Birke Andrea Tews, Christine Klaus, Malena Bestehorn-Willmann, Gerhard Dobler, Martin Beer, and Kerstin Wernike. 2019. "In Vivo Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Bank Voles (Myodes glareolus)" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111069
APA StyleMichelitsch, A., Tews, B. A., Klaus, C., Bestehorn-Willmann, M., Dobler, G., Beer, M., & Wernike, K. (2019). In Vivo Characterization of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in Bank Voles (Myodes glareolus). Viruses, 11(11), 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111069





