Changes in the EV-A71 Genome through Recombination and Spontaneous Mutations: Impact on Virulence
Abstract
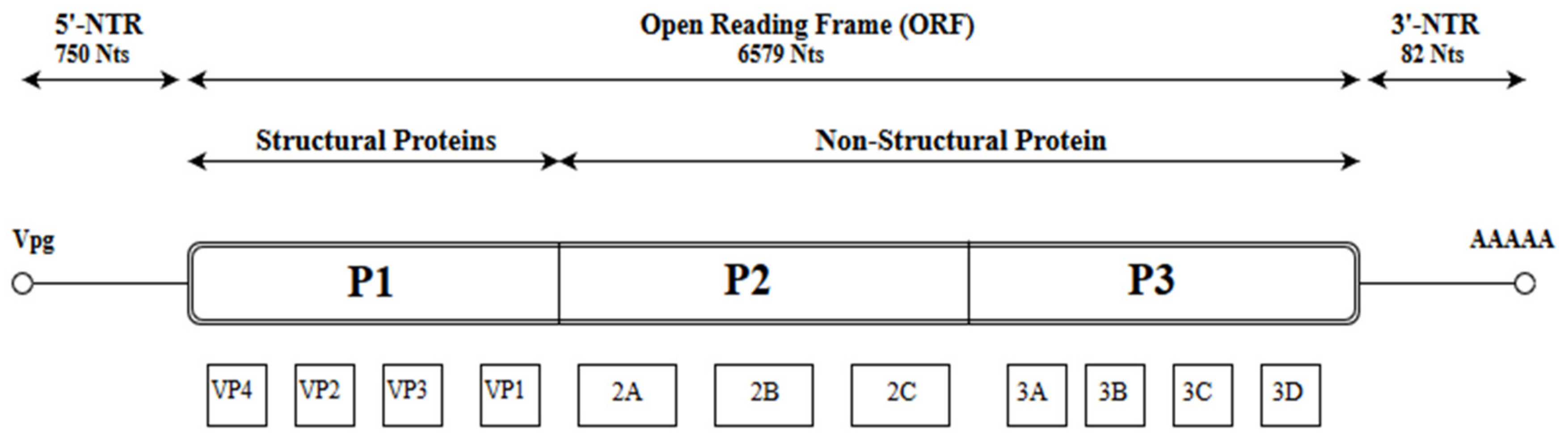
1. Introduction
2. Recombination
2.1. Recombination between EV-A71 and Other Enteroviruses
2.2. Recombination of Poliovirus and Its Implication for EV-A71
3. Spontaneous Mutations
3.1. Spontaneous Mutations in the 5′-NTR of EV-A71
3.2. Spontaneous Mutations in the VP1 of EV-A71
3.3. Spontaneous Mutations in the 2A and 3C of EV-A71
4. The Phenomenon of Quasispecies
Quasispecies through the Morphology of Plaques
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, B.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Alexander, J.P., Jr.; Kennett, M.L.; Pallansch, M.A. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of enterovirus 71 strains isolated from 1970 to 1998. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9969–9975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bessaud, M.; Razafindratsimandresy, R.; Nougairede, A.; Joffret, M.L.; Deshpande, J.M.; Dubot-Peres, A.; Heraud, J.M.; de Lamballerie, X.; Delpeyroux, F.; Bailly, J.L. Molecular comparison and evolutionary analyses of VP1 nucleotide sequences of new African human enterovirus 71 isolates reveal a wide genetic diversity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.J.; Lennette, E.H.; Ho, H.H. An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 129, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease Situation Update Number 511. Available online: http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/HFMD.situation.updates.2017/en/ (accessed on 11 April 2017).
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Yeh, T.F. Neurologic complications in children with enterovirus 71 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakov, M.; Voroshilova, M.; Shindarov, L.; Lavrova, I.; Gracheva, L.; Koroleva, G.; Vasilenko, S.; Brodvarova, I.; Nikolova, M.; Gyurova, S.; et al. Enterovirus 71 isolated from cases of epidemic poliomyelitis-like disease in Bulgaria. Arch. Virol. 1979, 60, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, G. Virological diagnosis of enterovirus type 71 infections: Experiences gained during an epidemic of acute CNS diseases in Hungary in 1978. Virology 1982, 71, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.G. Deaths of children during an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Sarawak, Malaysia: Clinical and pathological characteristics of the disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Tuan, Y.C.; Tsai, H.P.; Yan, J.J.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J. Change of major genotype of enterovirus 71 in outbreaks of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Taiwan between 1998 and 2000. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Liao, Q.; Viboud, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.T.; Chang, Z.; Liu, F.; Fang, V.J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Hand, foot, and mouth disease in China, 2008–12: An epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andino, R.; Böddeker, N.; Silvera, D.; Gamarnik, A.V. Intracellular determinants of picornavirus replication. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.A.; Pallansch, M.A. Complete nucleotide sequence of enterovirus 71 is distinct from poliovirus. Virus Res. 1995, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.J.J.H.; Holland, J.J. RNA virus mutations and fitness for survival. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1997, 51, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, E.; Sabo, D.; Taniguchi, T.; Weissmann, C. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of an RNA phage population. Cell 1978, 13, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.; Spindler, K.; Horodyski, F.; Grabau, E.; Nichol, S.; VandePol, S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science 1982, 215, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Orta, C.; Arias, A.; Escarmis, C.; Verdaguer, N. A comparison of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006, 16, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, G.K. Genetic recombination with newcastle disease virus, polioviruses, and influenza. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1962, 27, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledinko, N. Genetic recombination with poliovirus type 1: Studies of crosses between a normal horse serum-resistant mutant and several guanidine-resistant mutants of the same strain. Virology 1963, 20, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslin, C.; Joffret, M.L.; Pelletier, I.; Blondel, B.; Delpeyroux, F. Evolution and emergence of enteroviruses through intra- and inter-species recombination: Plasticity and phenotypic impact of modular genetic exchanges in the 5’ untranslated region. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessaud, M.; Joffret, M.L.; Blondel, B.; Delpeyroux, F. Exchanges of genomic domains between poliovirus and other cocirculating species C enteroviruses reveal a high degree of plasticity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, K.K.; Lam, T.T.; Chan, Y.F.; Bible, J.M.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Tong, C.Y.; Takebe, Y.; Pybus, O.G. Evolutionary genetics of human enterovirus 71: Origin, population dynamics, natural selection, and seasonal periodicity of the VP1 gene. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Welch, J. Frequency and dynamics of recombination within different species of human enteroviruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Utama, A.; Yoshii, K.; Yoshida, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Sinniah, M.; Yusof, M.A.; Okuno, Y.; Okabe, N.; Shih, S.R.; et al. Enterovirus 71 from fatal and nonfatal cases of hand, foot and mouth disease epidemics in Malaysia, Japan and Taiwan in 1997-1998. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 52, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oberste, M.S.; Penaranda, S.; Maher, K.; Pallansch, M.A. Evidence for frequent recombination within species human Enterovirus B based on complete genomic sequences of all thirty-seven serotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 78, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Holmes, E.C. Why do RNA viruses recombine? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worobey, M.; Holmes, E.C. Evolutionary aspects of recombination in RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Rouzine, I.M.; Bianco, S.; Acevedo, A.; Goldstein, E.F.; Farkov, M.; Brodsky, L.; Andino, R. RNA recombination enhances adaptability and is required for virus spread and virulence. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.C.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Human enterovirus 71 epidemics: What’s next? Emerg. Health Threats J. 2013, 6, 19780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Bao, W.; Zhao, K.; Niu, J.; Yu, X.F.; Zhang, W. Characterization of full-length enterovirus 71 strains from severe and mild disease patients in northeastern China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoke-Fun, C.; AbuBakar, S. Phylogenetic evidence for inter-typic recombination in the emergence of human enterovirus 71 subgenotypes. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, S.W.; Kiang, D.; Tsai, H.P.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Lin, K.H.; Su, I.J.; et al. Appearance of intratypic recombination of enterovirus 71 in Taiwan from 2002 to 2005. Virus Res. 2008, 131, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.; Van der Sanden, S.; Zeng, H.; Li, W.; Zheng, H.; Ma, C.; Su, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Population dynamics and genetic diversity of C4 strains of human enterovirus 71 in Mainland China, 1998–2010. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardosa, M.J.; Perera, D.; Brown, B.A.; Doosung, C.; Chan, H.M.; Chan, K.P.; Cho, H.; McMinn, P. Molecular epidemiology of human enterovirus 71 strains and recent outbreaks in the Asia-Pacific region: Comparative analysis of the VP1 and VP4 genes. J. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, A.; Yeh, M.T.; Zinger, T.; Smith, M.; Wright, C.; Ling, G.; Nielsen, R.; Macadam, A.; Andino, R. The evolutionary pathway to virulence of an RNA Virus. Cell 2017, 169, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danis, C.; Mabrouk, T.; Garzon, S.; Lemay, G. Establishment of persistent reovirus infection in SC1 cells: Absence of protein synthesis inhibition and increased level of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Virus Res. 1993, 27, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kuo, R.; Lin, J.; Huang, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Arnold, J.J.; Chen, S.; Wang, R.Y.; Cameron, C.E.; et al. Cytoplasmic viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase disrupts the intracellular splicing machinery by entering the nucleus and interfering with prp8. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.T.; Wang, S.W.; Yu, C.K.; Lin, K.H.; Lei, H.Y.; Su, I.J.; Wang, J.R. A single nucleotide in stem loop II of 5'-untranslated region contributes to virulence of enterovirus 71 in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.L.; Si, L.Y.; Yuan, X.J.; Hao, S.B.; Gao, F.; Chu, F.L.; Sun, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y. Complete genome sequencing and analysis of six enterovirus 71 strains with different clinical phenotypes. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zou, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Molecular analysis of virulent determinants of enterovirus 71. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, C.; Wu, S.; Xiong, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A novel finding for enterovirus virulence from the capsid protein VP1 of EV71 circulating in mainland China. Virus Genes 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Lee, H.; Hafenstein, S.; Kataoka, C.; Wakita, T.; Bergelson, J.; Shimizu, H. Enterovirus 71 binding to PSGL-1 on leukocytes: VP1-145 acts as a molecular switch to control receptor binding. PloS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Li, W.C.; Chen, G.W.; Tsao, K.C.; Huang, C.G.; Huang, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Kuo, C.Y.; Tsai, K.N.; Shih, S.R.; et al. Genetic characterization of enterovirus 71 isolated from patients with severe disease by comparative analysis of complete genomes. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Altmeyer, R.; Zou, G. Identification of positively charged residues in enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1 essential for production of infectious particles. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caine, E.A.; Moncla, L.H.; Ronderos, M.D.; Friedrich, T.C.; Osorio, J.E. A single mutation in the VP1 of enterovirus 71 is responsible for increased virulence and neurotropism in adult interferon-deficient mice. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8592–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Lee, K.; Chung, N.; Lu, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, C.; Chow, Y. Mutation in VP1 and 5′-NTR affect enterovirus 71 virulence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Tai, C.H.; Fonville, J.M.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J.; Smith, D.J.; Wang, J.R. Mapping enterovirus A71 antigenic determinants from viral evolution. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11500–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, B.H.; Phuektes, P.; Sanders, S.A.; Nicholls, P.K.; McMinn, P.C. The molecular basis of mouse adaptation by human enterovirus 71. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yue, Y.; Song, N.; Li, B.; Meng, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; An, L.; Qin, L. Genome analysis of enterovirus 71 strains differing in mouse pathogenicity. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Poh, C.L.; Chow, V.T. Complete sequence analyses of enterovirus 71 strains from fatal and non-fatal cases of the hand, foot and mouth disease outbreak in Singapore (2000). Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, P.T.; Tan, K.O.; Othman, I.; Poh, C.L. Identification of molecular determinants of cell culture growth characteristics of Enterovirus 71. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauring, A.S.; Andino, R. Quasispecies theory and the behavior of RNA viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Hooper, D.C.; Carbaugh, H.; Fu, Z.F.; Koprowski, H.; Dietzschold, B. Rabies virus quasispecies: Implications for pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3152–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, J.K.; Kirkegaard, K. Bottleneck-mediated quasispecies restriction during spread of an RNA virus from inoculation site to brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsai, H.P.; Kuo, P.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, J.R. A selective bottleneck shapes the evolutionary mutant spectra of enterovirus A71 during viral dissemination in humans. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01062-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignuzzi, M.; Stone, J.K.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. Quasispecies diversity determines pathogenesis through cooperative interactions in a viral population. Nature 2006, 439, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Ramos, M.; Diaz-San Segundo, F.; Escarmis, C.; Domingo, E.; Sevilla, N. Hidden virulence determinants in a viral quasispecies in vivo. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10465–10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignuzzi, M.; Wendt, E.; Andino, R. Engineering attenuated virus vaccines by controlling replication fidelity. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moratorio, G.; Henningson, R.; Barbezange, C.; Carrau, L.; Borderia, A.V.; Blanc, H.; Beaucourt, S.; Poirier, E.; Vallet, T.; Boussier, J.; et al. Attenuation of RNA viruses by redirecting their evolution in sequence space. Nat. Microb. 2017, 2, 17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsingh, A.I.; Caggana, M.; Ronstrom, S. Genetic mapping of the determinants of plaque morphology of coxsackievirus B4. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, J.H.; Hatch, M.H.; Thieme, M.L.; Nottay, B. Parameters for differentiating vaccine-derived and wild poliovirus strains. Prog. Med. Virol. 1978, 24, 178–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, E.R.; Erickson, A.K.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Robinson, C.M.; Pfeiffer, J.K. Plaques formed by mutagenized viral populations have elevated coinfection frequencies. MBio 2017, 8, e02020-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Recombinants of EV-A71 | Genes of the EV-A71 Involved in Recombination | Significance of the Recombination Events | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| EV-A71 strains SZ/HK08-5 and SZ/KH08-6 | 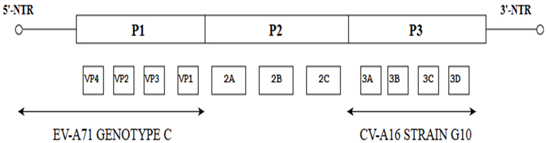 | Both EV-A71 strains have >80% similarity to the EV-A71 genotype C strain (Tainan/4643/98). Both EV-A71 strains showed similarity of ≥80% to the G-10 prototype strain of CV-A16. | [29] |
| Recombination between species A and B human enteroviruses |  | Enterovirus species B showed more recombination events between VP1 and 3Dpol as well as between VP1 and VP4. | [23] |
| Seven full-length EV-A71 C4 sequences from HFMD patients who had severe or mild diseases | 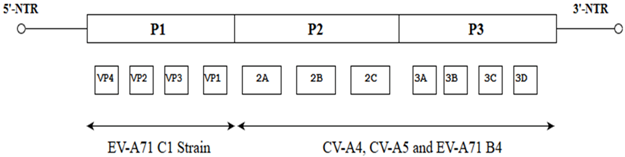 | All seven strains might have originated from the same ancestor as they were found in the same cluster after phylogenetic analysis | [30] |
| EV-A71 subgenotypes A, B (B2, B3 and B4) and C (C2 and C4) |  | These similarity plots support the likelihood of intertypic recombination between EV-A71 and different Human Enteroviruses A (HEV-A) | [31] |
| EV-A71 subgenotype C2, which was observed to be circulating in Taiwan in 1998 |  | Recombination between CV-A8 and EV-A71 shows evidence of intertypic recombination. | [24] |
| C4 isolates, which circulated in China from 2004 to 2005 |  | Proof of intratypic recombination was observed between EV-A71 subgenotype C and B. | [32] |
| Nucleotide Identity of Strain EV71/MS/7423 with Other Enteroviruses | ||||||||
| Whole Genome | 5′-NTR | P1 | P2 | P3 | 3′NTR | |||
| EV-A71/BrCr | 81 | 85 | 82 | 77 | 80 | 92 | ||
| Coxsackie A16 | 77 | 86 | 68 | 82 | 79 | 79 | ||
| Poliovirus | 58 | 71 | 53 | 58 | 61 | 41 | ||
| Amino Acid Identity of Strain EV71/MS/7423 with Other Enteroviruses | ||||||||
| Whole Genome | P1 | P2 | P3 | VP1 | VP2 | VP3 | VP4 | |
| EV-A71/BrCr | 95 | 97 | 94 | 94 | 93 | 99 | 99 | 100 |
| Coxsackie A16 | 89 | 79 | 95 | 95 | 71 | 84 | 84 | 78 |
| Poliovirus | 55 | 46 | 59 | 62 | 36 | 55 | 45 | 58 |
| Mutant Strains of EV-A71 | Position of Amino Acid(s) on the EV-A71 Genomes of Mutants | Significance of the Mutations in the EV-A71 Genome | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis of EV-A71 subgenotype C4 showed changes in the 5′-NTR and the VP1. |  | When the nucleotide cytosine was substituted with uridine at position 158, the conformation of the RNA secondary structure of stem loop II in the 5′-NTR changed, leading to a decrease in viral translation and virulence in mice. | [38] |
| Nucleotide and amino acid changes in neuro-virulent strains of EV-A71 subgenotype C4a. |  | These amino acids are potential molecular determinants of virulence. Variations in the secondary structure of the 5′-NTR at three positions (CP241/TP241, AP571/TP571 and CP579/TP579) and one position in the 3′-NTR(TP7335/CP7335) might confer fatality. | [39] |
| Comparisons of EV-A71 across different genotypes (BrCr, B1-B5 and C1-C5) |  | These amino acid residues might be associated with the EV-A71 virulentphenotype. | [40] |
| Changes in VP1 sequences of EV-A71 subgenotype C4 causing severe HFMD |  | E145Q/G interacts with residues of the PSGL-1 N-terminus and acts as a molecular switch to modulate binding to the cell receptor by controlling the exposure of the amino acid (VP1-244K) on the VP1 surface. | [41,42] |
| Analysis of EV-A71 subgenotype C4 showed changes in the 5′-NTR and the VP1 |  | K215A located at the VP1 GH loop increased the thermal stability of the virus. | [44] |
| Roles of K244E and H37R were investigated by reverse engineering in the EV71-B2 isolate, MS/7423/87 |  | It was postulated that H37E and K244E interactions were important for replication in primate cells but K244E alone was able to confer the ability of the virus to replicate alone in a murine model | [45] |
| Role of K216→R, G145→E and K129→I in the mouse-adapted strain of EV-A71 26M/AUS/4/99 |  | G145→E mutation was solely responsible for an increase in virulence in mice whilst K129→I led to an improved growth of the strain in vitro but did not lead to increased virulence in mice | [48] |
| Analysis of the genomes of six EV-A71 strains of subgenotype C4a identified the only change of amino acid Asn 1617 in the 3C gene |  | This specific amino acid led to conformational change at the active centre of the 3C proteinase (3Cpro) and this could be a potential molecular determinant for the EV-A71. | [49] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandary, M.B.; Poh, C.L. Changes in the EV-A71 Genome through Recombination and Spontaneous Mutations: Impact on Virulence. Viruses 2018, 10, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10060320
Mandary MB, Poh CL. Changes in the EV-A71 Genome through Recombination and Spontaneous Mutations: Impact on Virulence. Viruses. 2018; 10(6):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10060320
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandary, Madiiha Bibi, and Chit Laa Poh. 2018. "Changes in the EV-A71 Genome through Recombination and Spontaneous Mutations: Impact on Virulence" Viruses 10, no. 6: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10060320
APA StyleMandary, M. B., & Poh, C. L. (2018). Changes in the EV-A71 Genome through Recombination and Spontaneous Mutations: Impact on Virulence. Viruses, 10(6), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10060320





