Mutation of CD2AP and SH3KBP1 Binding Motif in Alphavirus nsP3 Hypervariable Domain Results in Attenuated Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
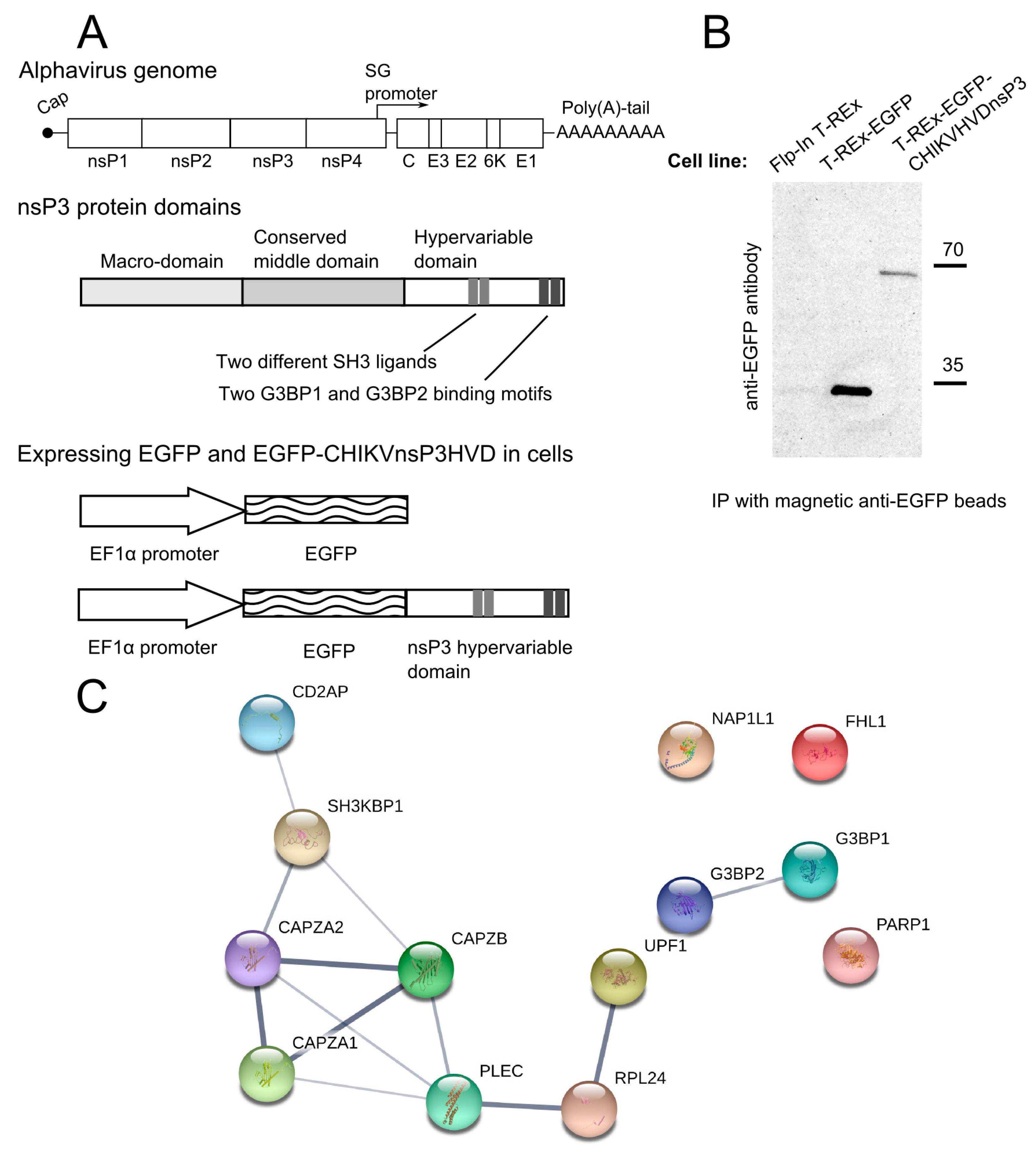
2.2. Construction of Expression Constructs for HVD Domains of Different Alphaviruses and Making of the Stable Transgenic Cell Lines
2.3. Virological Methods
2.4. Immunoprecipitation and Proteomics Analysis
2.5. Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
3. Results
3.1. CHIKV nsP3 Hypervariable Domain Binds CD2AP and Other Host Proteins
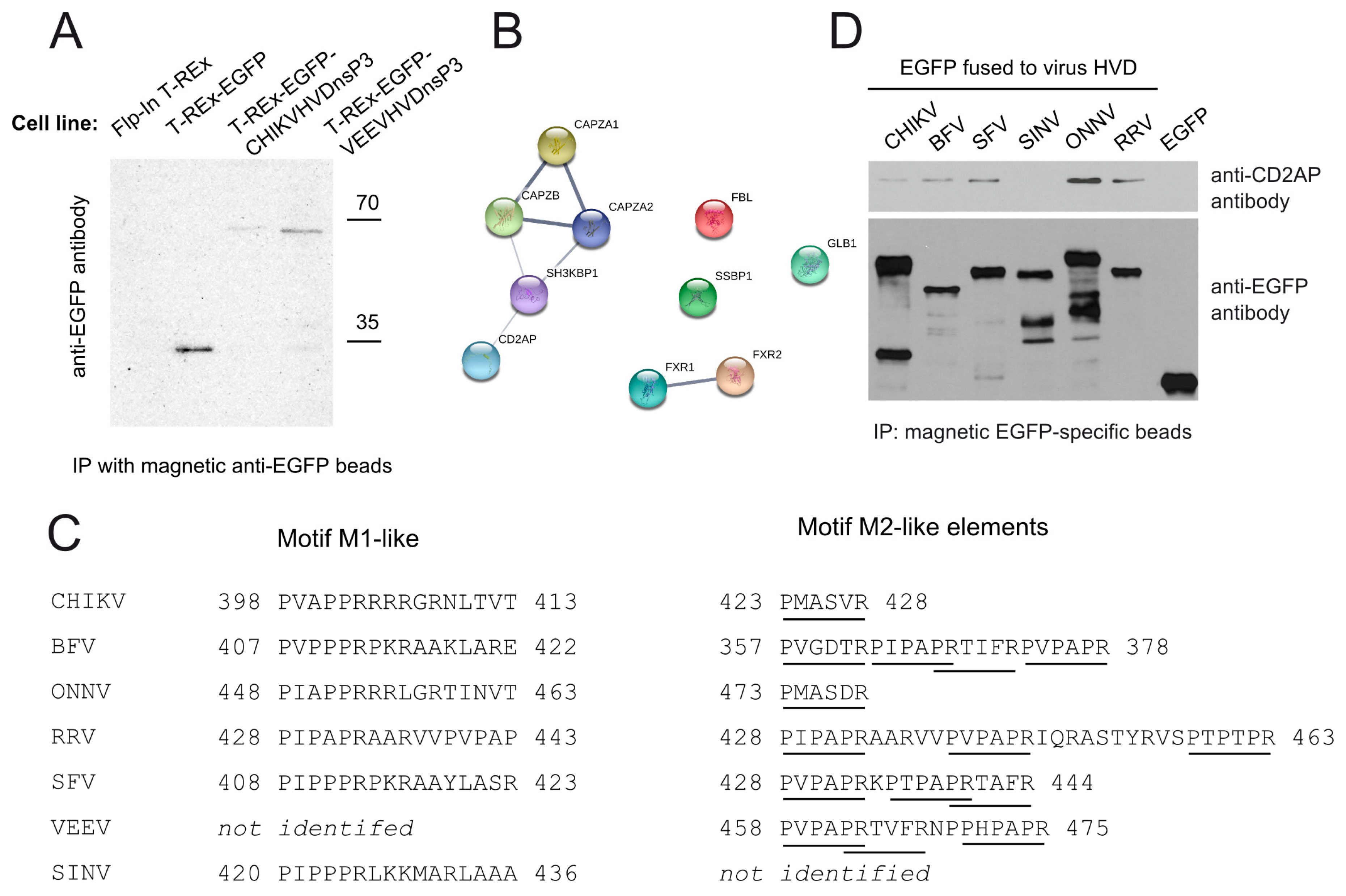
3.2. CD2AP Interacts with HVD of nsP3 from Many, but Not All Alphaviruses
3.3. CD2AP Binding Motif Mediates nsP3 HVD Interaction with Multiple Cellular Proteins
3.4. Mutations in M2 Motif of nsP3 Affects RNA Infectivity and Replication of Alphaviruses
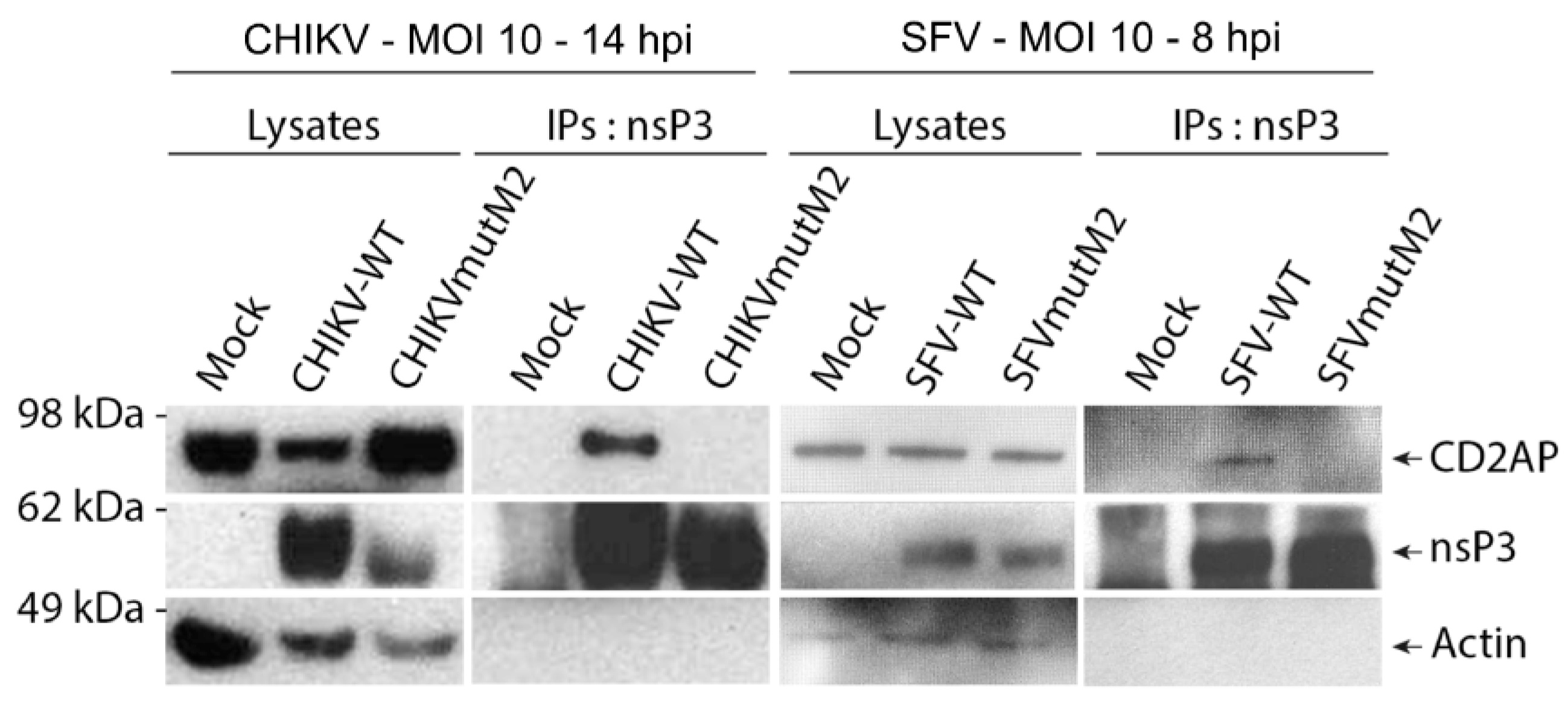
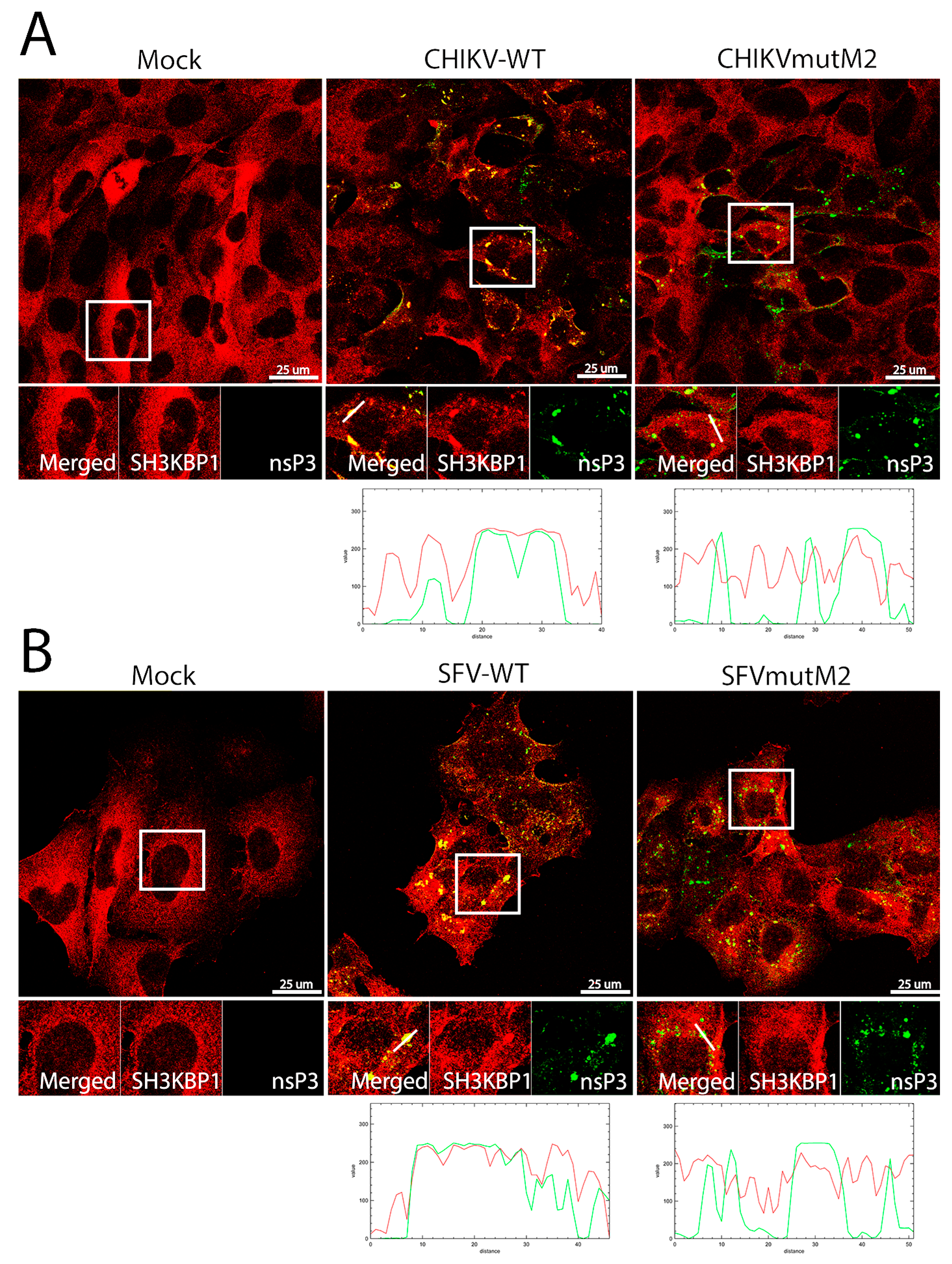
3.5. CD2AP and SH3KBP1 Interact with Viral nsP3 and Co-Localise with Replication Complexes in CHIKV and SFV Infected Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The alphaviruses: Gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryman, K.D.; Klimstra, W.B. Host responses to alphavirus infection. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 225, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, J.; Snyder, J.E.; Kuhn, R.J. A structural and functional perspective of alphavirus replication and assembly. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 837–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, K.E.; Blair, C.D. Arbovirus-mosquito interactions: RNAi pathway. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, F.J.; Chen, W.; Miner, J.J.; Lenschow, D.J.; Merits, A.; Schnettler, E.; Kohl, A.; Rudd, P.A.; Taylor, A.; Herrero, L.J.; et al. Chikungunya virus: An update on the biology and pathogenesis of this emerging pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e107–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmashova, N.; Gorchakov, R.; Volkova, E.; Paessler, S.; Frolova, E.; Frolov, I. The Old World and New World alphaviruses use different virus-specific proteins for induction of transcriptional shutoff. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2472–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Reynaud, J.M.; Rasalouskaya, A.; Akhrymuk, I.; Mobley, J.A.; Frolov, I.; Frolova, E.I. New World and Old World Alphaviruses Have Evolved to Exploit Different Components of Stress Granules, FXR and G3BP Proteins, for Assembly of Viral Replication Complexes. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaa, B.; Biasiotto, R.; Eng, K.; Neuvonen, M.; Götte, B.; Rheinemann, L.; Mutso, M.; Utt, A.; Varghese, F.; Balistreri, G.; et al. Differential Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase-Akt-mTOR Activation by Semliki Forest and Chikungunya Viruses Is Dependent on nsP3 and Connected to Replication Complex Internalization. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11420–11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjak, M.; Saul, S.; Arike, L.; Lulla, A.; Peil, L.; Merits, A. Magnetic fractionation and proteomic dissection of cellular organelles occupied by the late replication complexes of Semliki Forest virus. J. Virol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolov, I.; Kim, D.Y.; Akhrymuk, M.; Mobley, J.A.; Frolova, E.I. Hypervariable Domain of Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP3 Redundantly Utilizes Multiple Cellular Proteins for Replication Complex Assembly. J. Virol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietilä, M.K.; Hellström, K.; Ahola, T. Alphavirus polymerase and RNA replication. Virus Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemm, J.A.; Rümenapf, T.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H.; Rice, C.M. Polypeptide requirements for assembly of functional Sindbis virus replication complexes: A model for the temporal regulation of minus- and plus-strand RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shirako, Y.; Strauss, J.H. Regulation of Sindbis virus RNA replication: Uncleaved P123 and nsP4 function in minus-strand RNA synthesis, whereas cleaved products from P123 are required for efficient plus-strand RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1874–1885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spuul, P.; Balistreri, G.; Kääriäinen, L.; Ahola, T. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-, actin-, and microtubule-dependent transport of Semliki Forest Virus replication complexes from the plasma membrane to modified lysosomes. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7543–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolova, E.I.; Gorchakov, R.; Pereboeva, L.; Atasheva, S.; Frolov, I. Functional Sindbis virus replicative complexes are formed at the plasma membrane. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11679–11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Sawicki, S.G.; Sawicki, D.L. Alphavirus nsP3 functions to form replication complexes transcribing negative-strand RNA. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6466–6475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Firth, A.E.; Chung, B.Y.; Fleeton, M.N.; Atkins, J.F. Discovery of frameshifting in Alphavirus 6K resolves a 20-year enigma. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.A.; Castelló, A.; Carrasco, L. Viral translation is coupled to transcription in Sindbis virus-infected cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7061–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-L.; Stollar, V. Identification of the amino acid sequence in Sindbis virus nsP4 that binds to the promoter for the synthesis of the subgenomic RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9429–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, R.; Huang, H.V. Analysis of Sindbis virus promoter recognition in vivo, using novel vectors with two subgenomic mRNA promoters. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2501–2510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rausalu, K.; Iofik, A.; Ulper, L.; Karo-Astover, L.; Lulla, V.; Merits, A. Properties and use of novel replication-competent vectors based on Semliki Forest virus. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, A.; Vasiljeva, L.; Merits, A.; Magden, J.; Jokitalo, E.; Kääriäinen, L. Properly folded nonstructural polyprotein directs the semliki forest virus replication complex to the endosomal compartment. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakkonen, P.; Auvinen, P.; Kujala, P.; Kääriäinen, L. Alphavirus replicase protein NSP1 induces filopodia and rearrangement of actin filaments. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 10265–10269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahola, T.; Kääriäinen, L. Reaction in alphavirus mRNA capping: Formation of a covalent complex of nonstructural protein nsP1 with 7-methyl-GMP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulla, A.; Lulla, V.; Tints, K.; Ahola, T.; Merits, A. Molecular determinants of substrate specificity for Semliki Forest virus nonstructural protease. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5413–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljeva, L.; Merits, A.; Golubtsov, A.; Sizemskaja, V.; Kääriäinen, L.; Ahola, T. Regulation of the sequential processing of Semliki Forest virus replicase polyprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41636–41645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljeva, L.; Merits, A.; Auvinen, P.; Kääriäinen, L. Identification of a novel function of the alphavirus capping apparatus. RNA 5’-triphosphatase activity of Nsp2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17281–17287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.K.; Merits, A.; Lulla, A. Functional cross-talk between distant domains of chikungunya virus non-structural protein 2 is decisive for its RNA-modulating activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5635–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez de Cedrón, M.; Ehsani, N.; Mikkola, M.L.; García, J.A.; Kääriäinen, L. RNA helicase activity of Semliki Forest virus replicase protein NSP2. FEBS Lett. 1999, 448, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-L.; Wang, H.; Stollar, V. In vitro synthesis of Sindbis virus genomic and subgenomic RNAs: Influence of nsP4 mutations and nucleoside triphosphate concentrations. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubach, J.K.; Wasik, B.R.; Rupp, J.C.; Kuhn, R.J.; Hardy, R.W.; Smith, J.L. Characterization of purified Sindbis virus nsP4 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in vitro. Virology 2009, 384, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, S.; Hardy, R.W.; Smith, J.L.; Kuhn, R.J. Catalytic core of alphavirus nonstructural protein nsP4 possesses terminal adenylyltransferase activity. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9962–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, G.; Yost, S.A.; Miller, M.T.; Elrod, E.J.; Grakoui, A.; Marcotrigiano, J. Structural and functional insights into alphavirus polyprotein processing and pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16534–16539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malet, H.; Coutard, B.; Jamal, S.; Dutartre, H.; Papageorgiou, N.; Neuvonen, M.; Ahola, T.; Forrester, N.; Gould, E.A.; Lafitte, D.; et al. The crystal structures of Chikungunya and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus nsP3 macro domains define a conserved adenosine binding pocket. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6534–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panas, M.D.; Schulte, T.; Thaa, B.; Sandalova, T.; Kedersha, N.; Achour, A.; McInerney, G.M. Viral and Cellular Proteins Containing FGDF Motifs Bind G3BP to Block Stress Granule Formation. PLOS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuvonen, M.; Ahola, T. Differential activities of cellular and viral macro domain proteins in binding of ADP-ribose metabolites. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Debing, Y.; Jankevicius, G.; Neyts, J.; Ahel, I.; Coutard, B.; Canard, B. Viral Macro Domains Reverse Protein ADP-Ribosylation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8478–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, R.L.; Abraham, R.; Sreekumar, E.; Ong, S.-E.; Cheng, S.-J.; Baxter, V.K.; Kistemaker, H.A.V.; Filippov, D.V.; Griffin, D.E.; Leung, A.K.L. ADP-ribosylhydrolase activity of Chikungunya virus macrodomain is critical for virus replication and virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjak, M.; Zusinaite, E.; Merits, A. Novel functions of the alphavirus nonstructural protein nsP3 C-terminal region. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2352–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vihinen, H.; Saarinen, J. Phosphorylation site analysis of Semliki forest virus nonstructural protein 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27775–27783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dé, I.; Fata-Hartley, C.; Sawicki, S.G.; Sawicki, D.L. Functional Analysis of nsP3 Phosphoprotein Mutants of Sindbis Virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13106–13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Foy, N.J.; Akhrymuk, M.; Akhrymuk, I.; Atasheva, S.; Waffo, A.B.; Frolov, I.; Frolova, E.I. Hypervariable domains of nsP3 proteins of the New World and the Old World alphaviruses mediate formation of distinct, virus-specific protein complexes. J. Virol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, I.M.; Carroll, J.-W.N.; Rout, M.P.; Rice, C.M.; Chait, B.T.; MacDonald, M.R. Tracking and elucidating alphavirus-host protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 30269–30278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolova, E.; Gorchakov, R.; Garmashova, N.; Atasheva, S.; Vergara, L.A.; Frolov, I. Formation of nsP3-specific protein complexes during Sindbis virus replication. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4122–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foy, N.J.; Akhrymuk, M.; Shustov, A.V.; Frolova, E.I.; Frolov, I. Hypervariable domain of nsP3 protein of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus determines cell-specific mode of virus replication. J. Virol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panas, M.D.; Varjak, M.; Lulla, A.; Eng, K.E.; Merits, A.; Hedestam, G.B.K.; McInerney, G.M. Sequestration of G3BP coupled with efficient translation inhibits stress granules in Semliki Forest virus infection. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panas, M.D.; Ahola, T.; McInerney, G.M. The C-terminal repeat domains of nsP3 from the Old World alphaviruses bind directly to G3BP. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5888–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholte, F.E.M.; Tas, A.; Albulescu, I.C.; Žusinaite, E.; Merits, A.; Snijder, E.J.; van Hemert, M.J. Stress granule components G3BP1 and G3BP2 play a proviral role early in Chikungunya virus replication. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4457–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, T.; Liu, L.; Panas, M.D.; Thaa, B.; Dickson, N.; Götte, B.; Achour, A.; McInerney, G.M. Combined structural, biochemical and cellular evidence demonstrates that both FGDF motifs in alphavirus nsP3 are required for efficient replication. Open Biol. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuvonen, M.; Kazlauskas, A.; Martikainen, M.; Hinkkanen, A.; Ahola, T.; Saksela, K. SH3 domain-mediated recruitment of host cell amphiphysins by alphavirus nsP3 promotes viral RNA replication. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzon, M.; Castro, C.; Thaa, B.; Liu, L.; Mutso, M.; Liu, X.; Mahalingam, S.; Griffin, J.L.; Marsh, M.; McInerney, G.M. Alphavirus-induced hyperactivation of PI3K/AKT directs pro-viral metabolic changes. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götte, B.; Liu, L.; McInerney, G.M. The Enigmatic Alphavirus Non-Structural Protein 3 (nsP3) Revealing Its Secrets at Last. Viruses 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulper, L.; Sarand, I.; Rausalu, K.; Merits, A. Construction, properties, and potential application of infectious plasmids containing Semliki Forest virus full-length cDNA with an inserted intron. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 148, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.-E.; Mann, M. A practical recipe for stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC). Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Griffin, D.E. Interaction of Sindbis virus non-structural protein 3 with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 in neuronal cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaidos, G.; Soni, S.; Oswald, D.J.; Toselli, P.A.; Kirsch, K.H. Structure and function analysis of the CMS/CIN85 protein family identifies actin-bundling properties and heterotypic-complex formation. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 2366–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouka, E.; Simister, P.C.; Janning, M.; Kumbrink, J.; Konstantinou, T.; Muniz, J.R.C.; Joshi, D.; O’Reilly, N.; Volkmer, R.; Ritter, B.; et al. Differential Recognition Preferences of the Three Src Homology 3 (SH3) Domains from the Adaptor CD2-associated Protein (CD2AP) and Direct Association with Ras and Rab Interactor 3 (RIN3). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25275–25292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, V.W.; Brieher, W.M. FSGS3/CD2AP is a barbed-end capping protein that stabilizes actin and strengthens adherens junctions. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 203, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remenyi, R.; Roberts, G.C.; Zothner, C.; Merits, A.; Harris, M. SNAP-tagged Chikungunya Virus Replicons Improve Visualisation of Non-Structural Protein 3 by Fluorescence Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bruck, S.; Cemerski, S.; Zhang, L.; Butler, B.; Dani, A.; Cooper, J.A.; Shaw, A.S. CD2AP Links Cortactin and Capping Protein at the Cell Periphery To Facilitate Formation of Lamellipodia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, D.K.; Winata, S.C.; Lyons, R.J.; Hughes, W.E.; Lehrbach, G.M.; Wasinger, V.; Corthals, G.; Cordwell, S.; Daly, R.J. A Cortactin-CD2-associated Protein (CD2AP) Complex Provides a Novel Link between Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Endocytosis and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21805–21813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roques, P.; Ljungberg, K.; Kümmerer, B.M.; Gosse, L.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Tchitchek, N.; Hallengärd, D.; García-Arriaza, J.; Meinke, A.; Esteban, M.; et al. Attenuated and vectored vaccines protect nonhuman primates against Chikungunya virus. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e83527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Protein Name | Fold Difference in the Amounts Host Proteins Captured by HVD and HVD-mutM2 of SFV nsP3 |
|---|---|
| SH3KBP1 | 11.0 |
| CD2AP | 8.1 |
| CAPZB | 4.7 |
| CAPZA1 | 4.7 |
| CAPZA2 | 2.6 |
| G3BP1 | 0.9 |
| G3BP2 | 0.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mutso, M.; Morro, A.M.; Smedberg, C.; Kasvandik, S.; Aquilimeba, M.; Teppor, M.; Tarve, L.; Lulla, A.; Lulla, V.; Saul, S.; et al. Mutation of CD2AP and SH3KBP1 Binding Motif in Alphavirus nsP3 Hypervariable Domain Results in Attenuated Virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10050226
Mutso M, Morro AM, Smedberg C, Kasvandik S, Aquilimeba M, Teppor M, Tarve L, Lulla A, Lulla V, Saul S, et al. Mutation of CD2AP and SH3KBP1 Binding Motif in Alphavirus nsP3 Hypervariable Domain Results in Attenuated Virus. Viruses. 2018; 10(5):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10050226
Chicago/Turabian StyleMutso, Margit, Ainhoa Moliner Morro, Cecilia Smedberg, Sergo Kasvandik, Muriel Aquilimeba, Mona Teppor, Liisi Tarve, Aleksei Lulla, Valeria Lulla, Sirle Saul, and et al. 2018. "Mutation of CD2AP and SH3KBP1 Binding Motif in Alphavirus nsP3 Hypervariable Domain Results in Attenuated Virus" Viruses 10, no. 5: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10050226
APA StyleMutso, M., Morro, A. M., Smedberg, C., Kasvandik, S., Aquilimeba, M., Teppor, M., Tarve, L., Lulla, A., Lulla, V., Saul, S., Thaa, B., McInerney, G. M., Merits, A., & Varjak, M. (2018). Mutation of CD2AP and SH3KBP1 Binding Motif in Alphavirus nsP3 Hypervariable Domain Results in Attenuated Virus. Viruses, 10(5), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10050226





