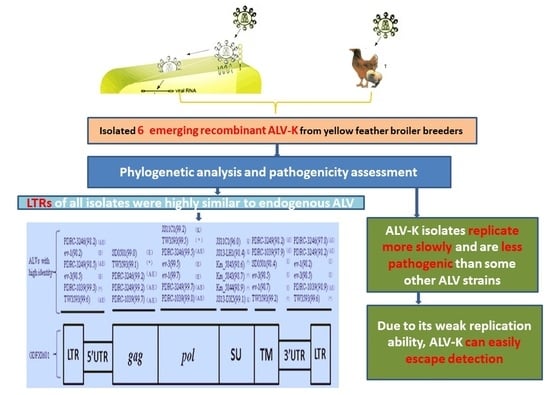
Phylogenetic Analysis and Pathogenicity Assessment of the Emerging Recombinant Subgroup K of Avian Leukosis Virus in South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Cells
2.2. Virus Isolation
2.3. Extraction of Proviral DNA and Primers
2.4. Genomic DNA Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Sequence Analysis
2.6. Evaluation ofthe Replication Ability of ALV-KIsolates In Vitro
2.7. Animal Experiments
2.8. Ethics Approval
3. Results
3.1. Virus Isolation
3.2. Amplification of Proviral Genomes
3.3. Complete Genome Sequences Analysis of ALV Isolates
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of 6 ALV Isolates
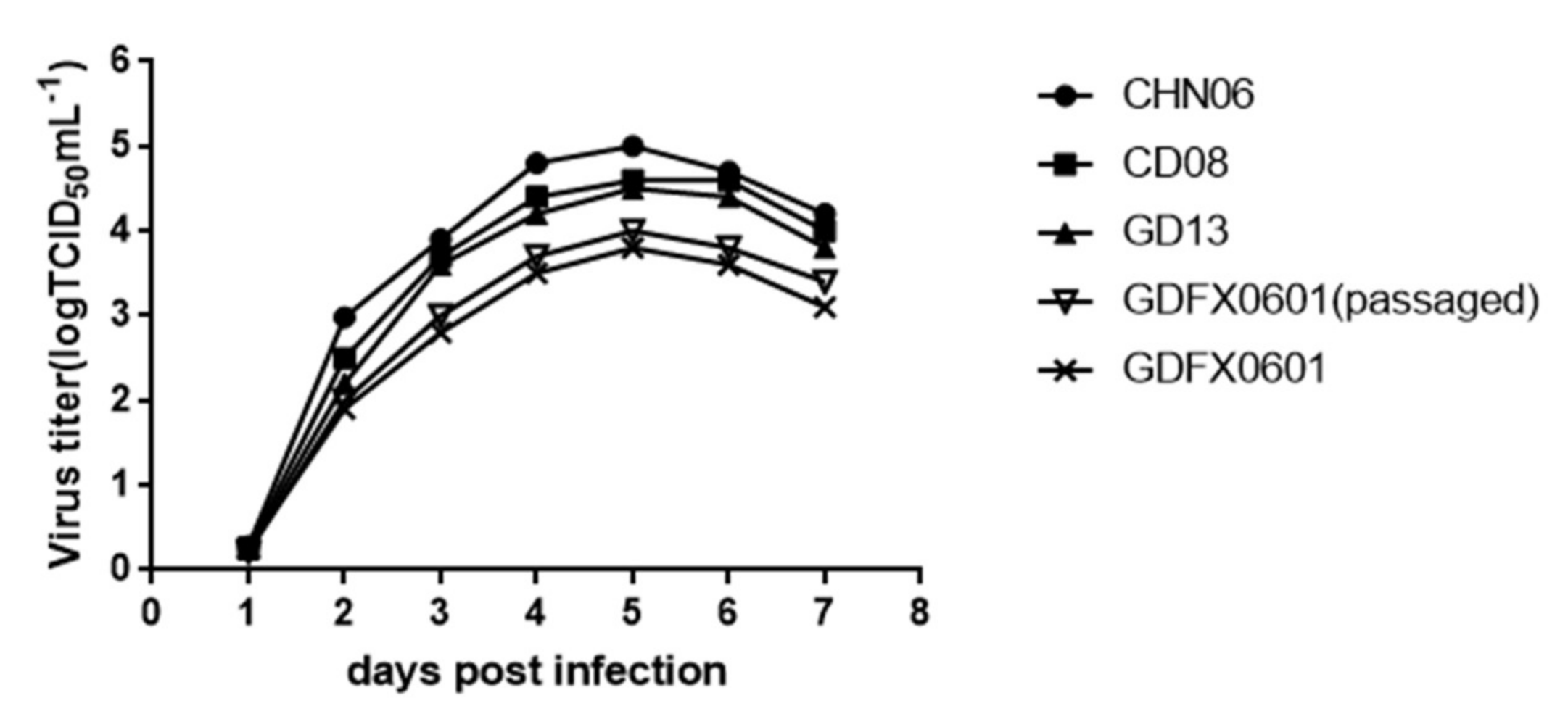
3.5. Evaluation ofthe Replication Ability of Subgroup K ALV Isolates in DF-1 Cells
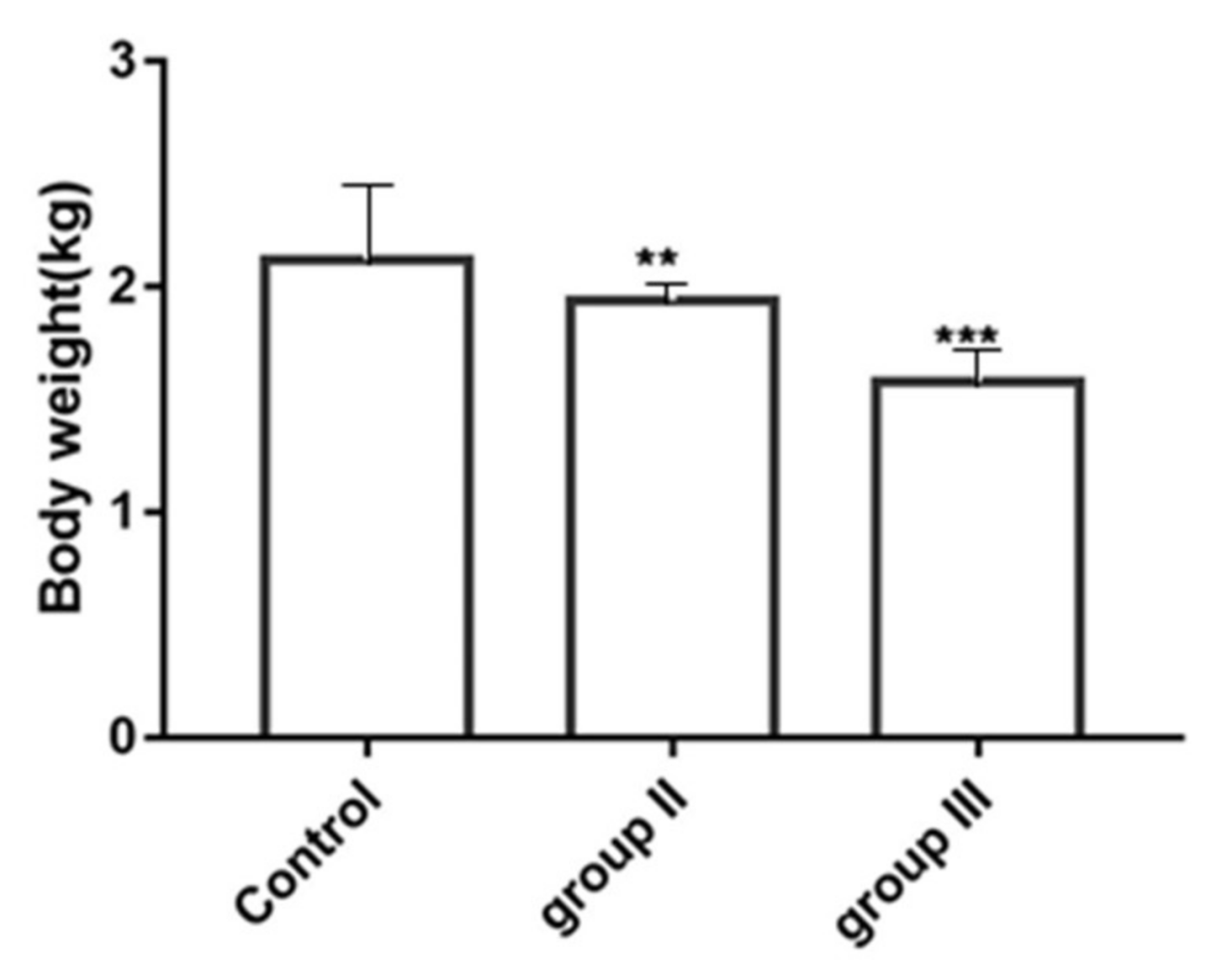
3.6. Influence of ALV-K Infection on Growth Rates of SPF Chickens
3.7. The Influence of ALV-K Infection on Mortality
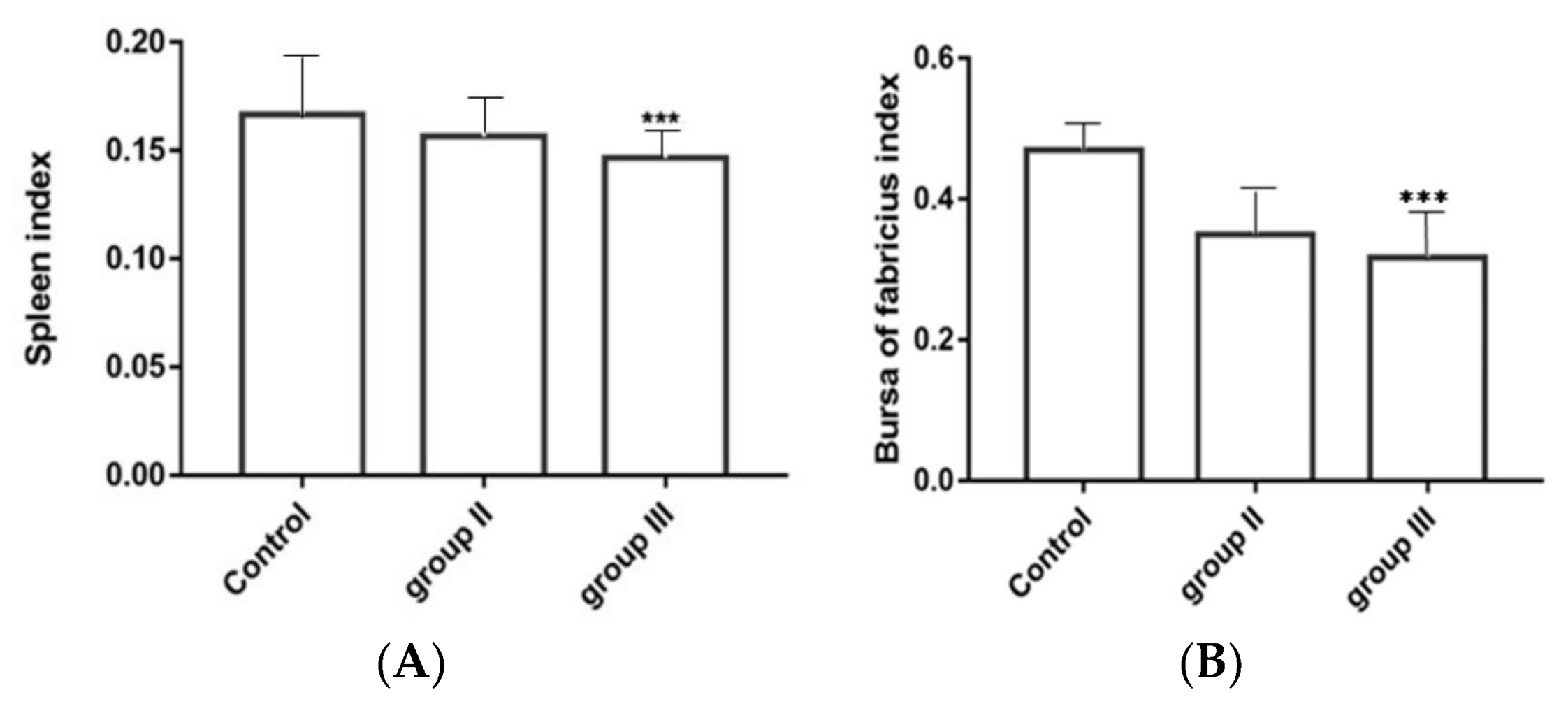
3.8. Influence of ALV-K Infection on Spleen and Bursa
3.9. Detection of Viremia and Cloacal Swabs ALV p27 Antigens
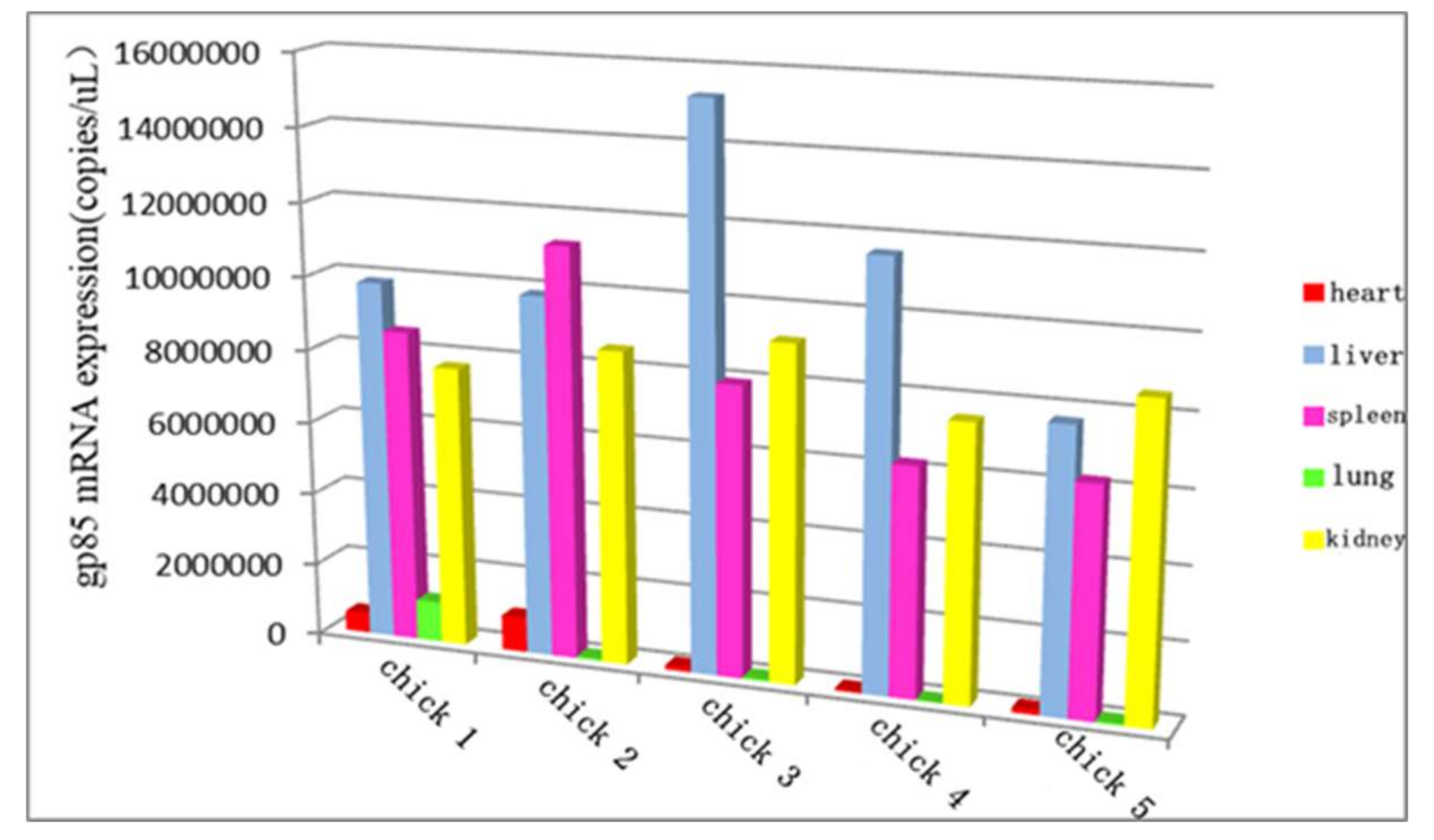
3.10. The Distribution of ALV-K in Different Organs at the Later Stage of Infection
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajabzadeh, M.; Dadras, H.; Mohammadi, A. Detection of avian leukosis virus subgroups in albumen of commercial and native fowl eggs using RT-PCR in Iran. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.F.; Fadly, A.M.; Taylor, S.P. Development of a polymerase chain reaction to differentiate avian leukosis virus (ALV) subgroups: Detection of an ALV contaminant in commercial Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, L.N.; Brown, S.R.; Bumstead, N.; Howes, K.; Frazier, J.A.; Thouless, M.E. A novel subgroup of exogenous avian leukosis virus in chickens. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, W.; Purchase, H.G.; Crittenden, L.B. Pathogenicity of avian leukosis viruses. Avian Dis. 1982, 26, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, H.R. Avian Leukosis-Sarcoma Virus Antibodies in Wildfowl, Domestic Chickens and Man in Kenya 1. Exp. Biol. Med. 1973, 144, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J. Evaluation of Albumen Samples for Isolation of Avian Leukosis Viruses. China Poult. 2014, 36, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, L.N.; Gillespie, A.M.; Howes, K. Myeloid leukaemogenicity and transmission of the HPRS-103 strain of avian leukosis virus. Leukemia 1992, 6, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yun, B.; Qin, L.; Pan, W.; Qu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, X. Molecular Epidemiology of Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroup J in Layer Flocks in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Dong, X.; Cui, Z. Isolation, identification, and gp85 characterization of a subgroup A avian leukosis virus from a contaminated live Newcastle Disease virus vaccine, first report in China. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Dong, W.; Yu, C.; He, Z.; Lv, Y.; Sun, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, N.; Lee, L.F.; Li, M. Occurrence of avian leukosis virus subgroup J in commercial layer flocks in China. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Qian, K.; Qin, A.; Shen, H.; Wang, P.; Jin, W.; Eltahir, Y.M. Recombinant avian leukosis viruses of subgroup J isolated from field infected commercial layer chickens with hemangioma and myeloid leukosis possess an insertion in the E element. Vet. Res. Commun. 2010, 34, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Zhang, H.; Ning, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.; Qing, A.; Xin, C.; Yu, K.; Cao, W.; Liao, M. Isolation and characterization of emerging subgroup J avian leukosis virus associated with hemangioma in egg-type chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 151, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Cui, Z.Z. Identification of a new subgroup of avian leukosis virus isolated from Chinese indigenous chicken breeds. Chin. J. Virol. 2012, 28, 609–614. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, N.; Su, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Z. Genomic sequence analysis and biological characteristics of a rescued clone of avian leukosis virus strain JS11C1, isolated from indigenous chickens. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.W.; Hsu, M.F.; Wang, C.H. Gene detection, virus isolation, and sequence analysis of avian leukosis viruses in Taiwan country chickens. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Toye, A.A.; Howes, K.; Bumstead, N.; Payne, L.N.; Venugopal, K. Novel endogenous retroviral sequences in the chicken genome closely related to HPRS-103 (subgroup J) avian leukosis virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tomioka, Y.; Ochiai, K.; Ohashi, K.; Kimura, T.; Umemura, T. In ovo infection with an avian leukosis virus causing fowl glioma: Viral distribution and pathogenesis. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Toyoda, T.; Ochiai, K.; Ohashi, K.; Tomioka, Y.; Kimura, T.; Umemura, T. Multiple perineuriomas in chicken (Gallus gallusdomesticus). Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomioka, Y. Genome sequence analysis of the avian retrovirus causing so-called fowl glioma and the promoter activity of the long terminal repeat. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochi, A.; Ochiai, K.; Kobara, A.; Nakamura, S.; Hatai, H.; Handharyani, E.; Tiemann, I.; Tanaka, I.R.; Toyoda, T.; Abe, A.; et al. Epidemiological study of fowl glioma-inducing virus in chickens in Asia and Germany. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, C.; Liao, Y.; Wu, X.; Cao, W.; Liao, M. Isolation, identification, and phylogenetic analysis of two avian leukosis virus subgroup J strains associated with hemangioma and myeloid leukosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, W.; Qing-yuan, L.I.; Shao-qiong, L.; Yong-guang, Z.; Zhi-zhong, C. Evaluation on ALV Infection in Fertilized Eggs from A Wan-nan Yellow-feather Parent Broiler Breeder Flock. Chin. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2011, 42, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, R.; van Zoelen, D.; Oei, H.; Claassen, I. Replacement of primary chicken embryonic fibroblasts (CEF) by the DF-1 cell line for detection of avian leucosis viruses. Biologicals 2006, 34, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, H.; Sun, S. The passage of cells can improve the detection rate of avian leukosis virus to facilitate the elimination of avian leukosis in chickens. Springerplus 2013, 2, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Howes, K.; Payne, L.N.; Skinner, M.A. Sequence of host-range determinants in the ENV gene of a full-length, infectious proviral clone of exogenous avian leukosis virus HPRS-103 confirms that it represents a new subgroup (designated J). J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, M.A.; Flannery, D.M.; Howes, K.; Venugopal, K. Avian endogenous retrovirus EAV-HP shares regions of identity with avian leucosis virus subgroup J and the avian retrotransposon ART-CH. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Zhao, D.M.; Guo, H.J.; Cui, Z.Z. Isolation and identification of a subgroup A avian leukosis virus from imported meat-type grand-parent chickens. Virol. Sin. 2010, 25, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.M.; Zhang, Q.C.; Cui, Z.Z. Isolation and identification of a subgroup B avian leukosis virus from chickens of Chinese native breed Luhua. Chin. J. Virol. 2010, 26, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Qu, H.; Li, C.; Luo, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Shu, D. Polymorphism of avian leukosis virus subgroup E loci showing selective footprints in chicken. Biochem. Genet. 2014, 52, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Hao, R.; Han, C. Detection and molecular characterization of J subgroup avian leukosis virus in wild ducks in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, T.; Zavala, G.; Cheng, S. Molecular characterization of three recombinant isolates of avian leukosis virus obtained from contaminated Marek’s disease vaccine. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddell, A. Transcription regulatory elements of the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Virology 1995, 206, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, T.A.; Beemon, K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol. Cell Biol. 1989, 9, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
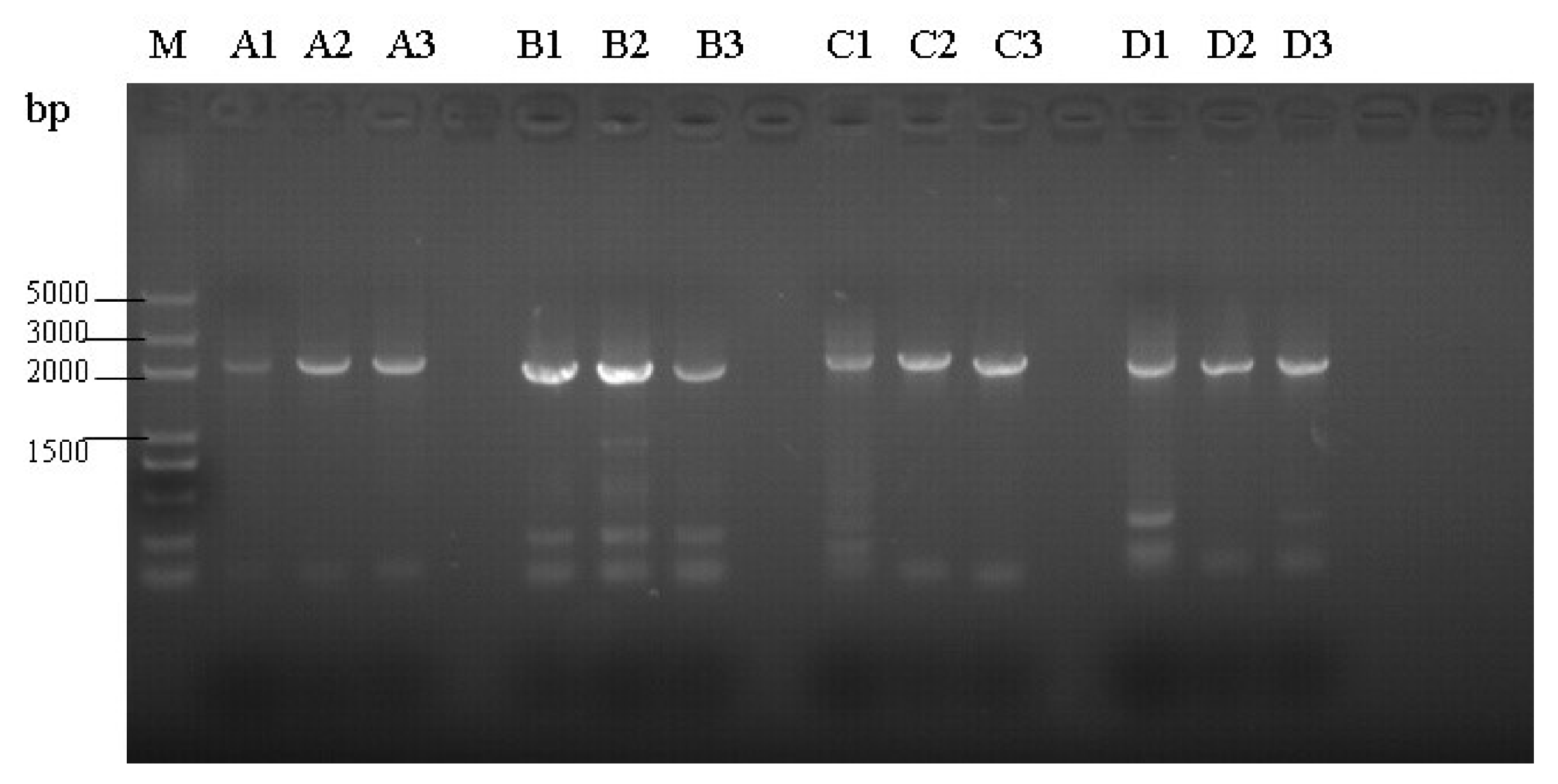
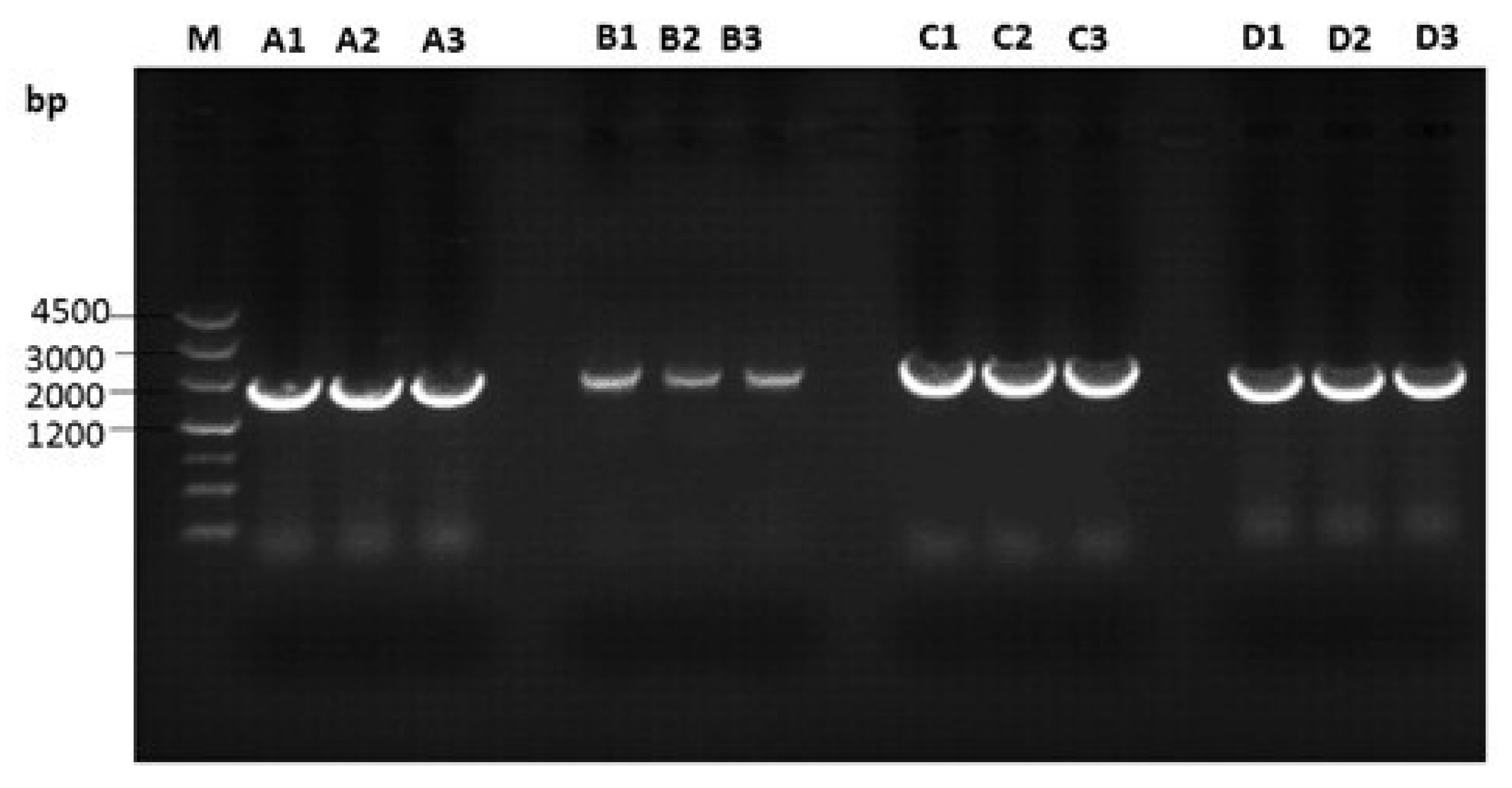
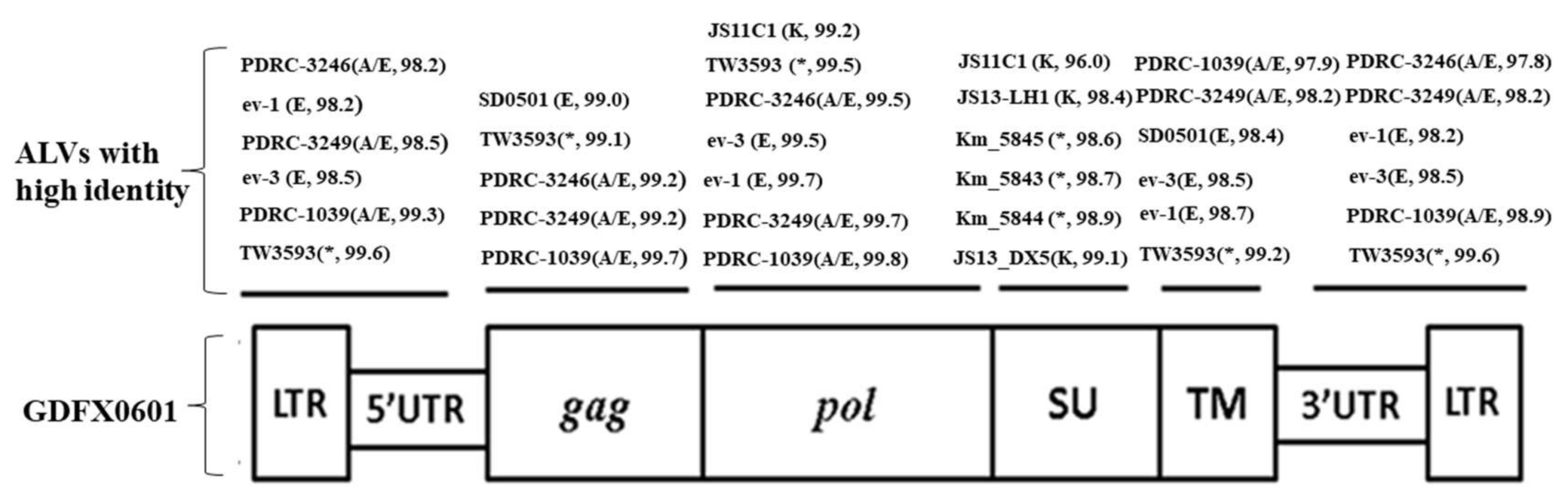



| Primer a | Sequence (5′–3′) {Nucleotide Position of Primer} | Product Size (bp) {Nucleotide Position} |
|---|---|---|
| K-1F | TGTAGTCAAATAGAGCCAG {1–19} | 2147 |
| K-1R | GGCTGTTTCCTGACTTT {2131–2147} | {1–2147} |
| K-2F | GTCACAGCCAGATATTCAG {1858–1876} | 1989 |
| K-2R | AGGCAACAGGAGGATAT {3830–3846} | {1858–3846} |
| K-3F | AGCGTTAGGAATCCCGCCACGA {3468–3489} | 2196 |
| K-3R | TGGTGCTGTTGTCAGGGCCGC {5643–5663} | {3468–5663} |
| K-4F | TCTGCCTCTCTACACAGTCAGCCACCTCCC {5490–5519} | 1993 |
| K-4R | TGAAGCCTTCTGCTTCATTCAGGTGTTCGCAATC {7449–7482} | {5490–7482} |
| Strains | Subgroup | Year | Country | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAV-1 | A | 1993 | France | L10922 |
| MQNCSU | A | 2006 | USA | DQ365814 |
| PDRC-1039 | A/E | 2007 | USA | EU070900 |
| PDRC-3246 | A/E | 2007 | USA | EU070901 |
| PDRC-3249 | A/E | 2007 | USA | EU070902 |
| SDAU09C1 | A | 2009 | China | HM452339 |
| RAV-2 | B | 1986 | USA | M14902 |
| R-S-R B | B | 1998 | USA | AF052428 |
| Prague C | C | 1977 | USA | J02342 |
| R-S-R D | D | 1992 | Japan | D10652 |
| RAV-0 | E | 1985 | USA | M12172 |
| ev-1 | E | 2000 | USA | AY013303 |
| ev-3 | E | 2001 | USA | AY013304 |
| SD0501 | E | 2007 | China | EF467236 |
| HPRS-103 | J | 1995 | UK | Z46390 |
| NX0101 | J | 2005 | China | AY897227 |
| SCAU-HN06 | J | 2006 | China | HQ900844 |
| TW-3593 | * | 2011 | China | HM582658 |
| Sp-53 | * | 2012 | Japan | AB617820 |
| Oki_009 | * | 2012 | Japan | AB669433 |
| Km_5844 | * | 2012 | Japan | AB670312 |
| Km_5943 | * | 2012 | Japan | AB669897 |
| Km_5845 | * | 2012 | Japan | AB670314 |
| JS13-DX5 | K | 2014 | China | KF999961 |
| JS13-LH1 | K | 2014 | China | KF999962 |
| JS11C1 | K | 2014 | China | KF746200 |
| GDFX0601 | K/E | 2014 | China | KP686142 |
| GDFX0602 | K/E | 2014 | China | KP686143 |
| GDFX0603 | K/E | 2014 | China | KP686144 |
| GD150509 | K/E | 2015 | China | — |
| GD160403 | K/E | 2016 | China | — |
| GD160607 | K/E | 2016 | China | — |
| ALV Strains | GDFX0601 | GDFX0602 | GDFX0603 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gp85 | gp37 | LTR | gp85 | gp37 | LTR | gp85 | gp37 | LTR | |
| MQNSU (A) | 85.1 | 94.4 | 68.1 | 85.2 | 94.6 | 67.8 | 84.9 | 94.7 | 67.4 |
| R-S-RB (B) | 83.2 | 93.6 | 59.0 | 83.2 | 93.8 | 59.5 | 82.9 | 93.9 | 59.0 |
| Prague C (C) | 88.4 | 93.7 | 70.0 | 88.5 | 93.9 | 70.3 | 88.2 | 94.1 | 70.0 |
| R-S-RD (D) | 78.2 | 94.3 | 57.2 | 78.4 | 94.4 | 57.7 | 78.1 | 94.6 | 57.2 |
| HPRS-103 (J) | 51.5 | 58.7 | 67.0 | 51.7 | 59.0 | 67.4 | 51.5 | 59.2 | 67.0 |
| ev-1 (E) | 87.8 | 98.7 | 98.2 | 87.9 | 98.9 | 98.5 | 87.7 | 99.0 | 98.2 |
| ev-3 (E) | 87.7 | 98.7 | 98.5 | 87.8 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 87.6 | 99.0 | 98.5 |
| SD0501 (E) | 87.8 | 98.4 | 96.5 | 87.9 | 98.5 | 96.9 | 87.6 | 98.7 | 96.5 |
| TW3593 (*) | 95.8 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 95.9 | 99.3 | 100 | 95.6 | 99.5 | 99.6 |
| PDRC-1039 (A/E) | 86.0 | 97.9 | 98.9 | 86.1 | 98.0 | 99.3 | 86.1 | 98.2 | 98.9 |
| PDRC-3246 (A/E) | 86.4 | 97.7 | 97.8 | 86.5 | 97.9 | 98.2 | 86.5 | 98.0 | 97.8 |
| PDRC-3249 (A/E) | 87.6 | 98.2 | 98.2 | 87.7 | 98.4 | 98.5 | 87.5 | 98.5 | 98.2 |
| JS11C1 (K) | 96.0 | 95.7 | 71.1 | 96.1 | 95.9 | 71.4 | 95.8 | 96.1 | 71.1 |
| Km_5844 (*) | 98.9 | 96.7 | 59.0 | 99.0 | 96.9 | 59.5 | 98.7 | 97.0 | 59.0 |
| Sp_53 (*) | 94.7 | 94.1 | 64.8 | 94.8 | 94.2 | 65.2 | 94.5 | 94.1 | 64.8 |
| JS13-DX5 (K) | 99.1 | - | - | 99.2 | - | - | 98.9 | - | - |
| Mortality Rate * | Control | Group II | Group III |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| 14 d | 0% | 0% | 3% |
| 21 d | 0% | 0% | 3.4% |
| 28 d | 0% | 0% | 3.6% |
| 35 d | 0% | 0% | 0% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Rao, M.; Liao, M.; Cao, W. Phylogenetic Analysis and Pathogenicity Assessment of the Emerging Recombinant Subgroup K of Avian Leukosis Virus in South China. Viruses 2018, 10, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040194
Zhao Z, Rao M, Liao M, Cao W. Phylogenetic Analysis and Pathogenicity Assessment of the Emerging Recombinant Subgroup K of Avian Leukosis Virus in South China. Viruses. 2018; 10(4):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040194
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zijun, Mingzhang Rao, Ming Liao, and Weisheng Cao. 2018. "Phylogenetic Analysis and Pathogenicity Assessment of the Emerging Recombinant Subgroup K of Avian Leukosis Virus in South China" Viruses 10, no. 4: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040194
APA StyleZhao, Z., Rao, M., Liao, M., & Cao, W. (2018). Phylogenetic Analysis and Pathogenicity Assessment of the Emerging Recombinant Subgroup K of Avian Leukosis Virus in South China. Viruses, 10(4), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10040194