Understanding the Determinants of BnAb Induction in Acute HCV Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Anti-Envelope Antibody ELISA
2.4. HCVpp Production and Neutralisation Assay
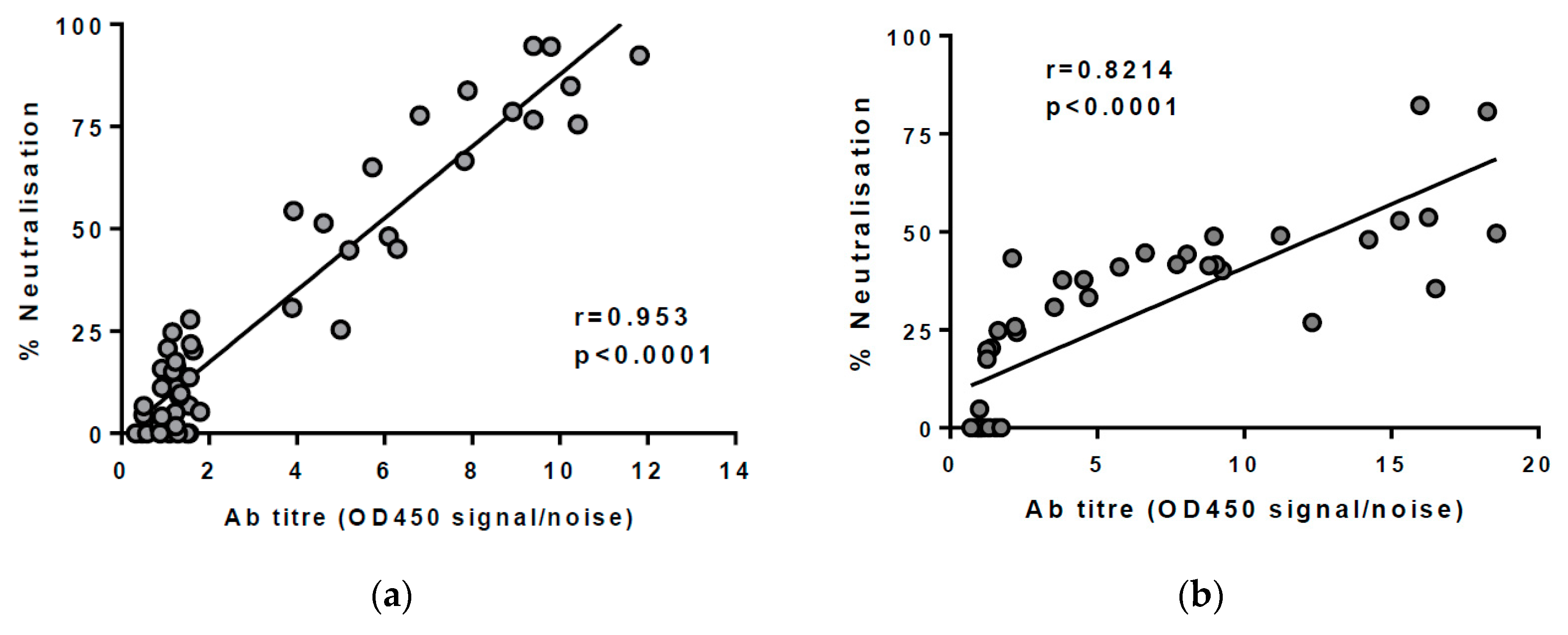
2.5. Measuring Breadth of nAbs in Plasma
2.6. Statistical Tests
3. Results
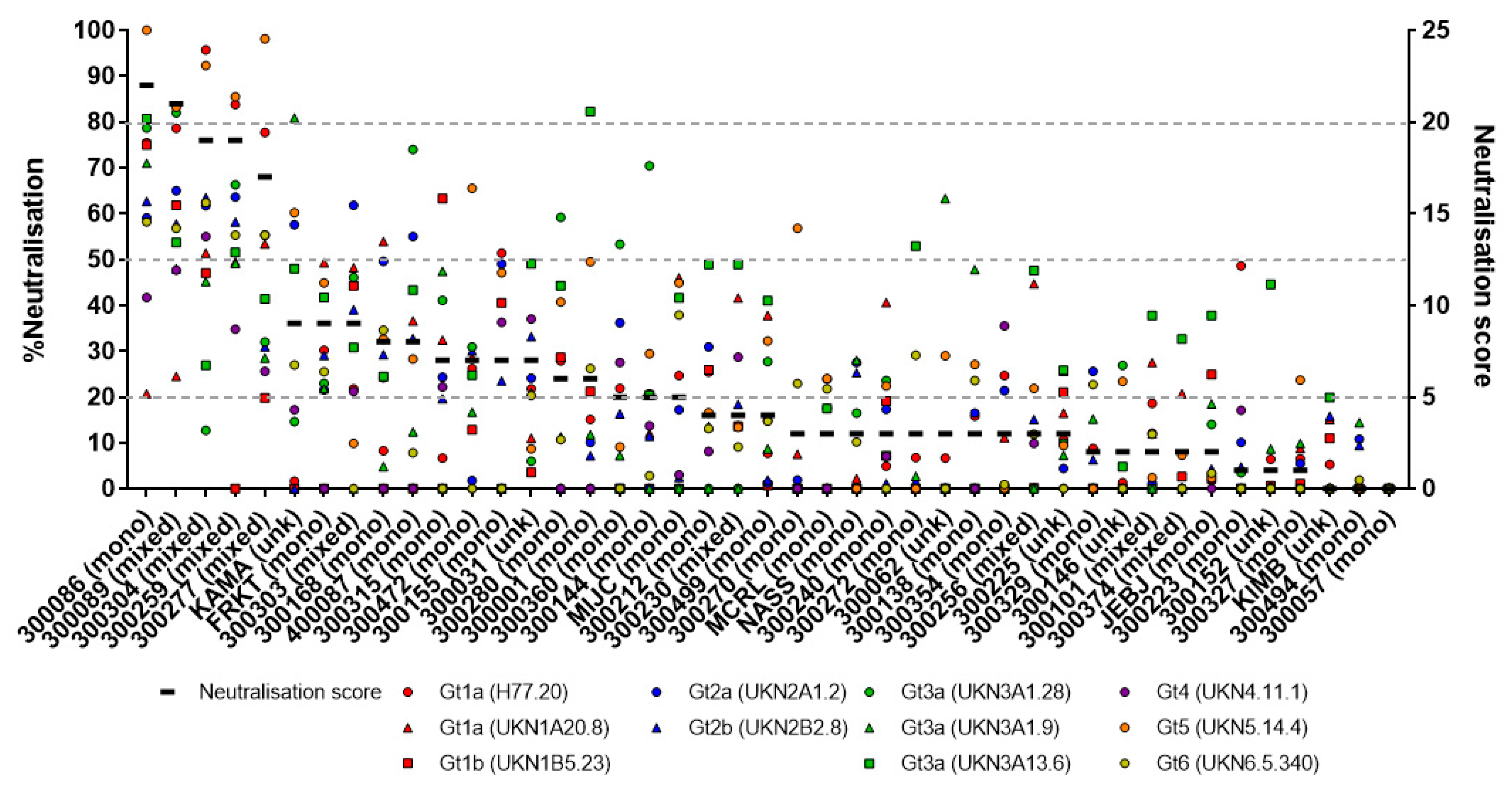
3.1. Assessing the Breadth of nAbs in HCV Infection
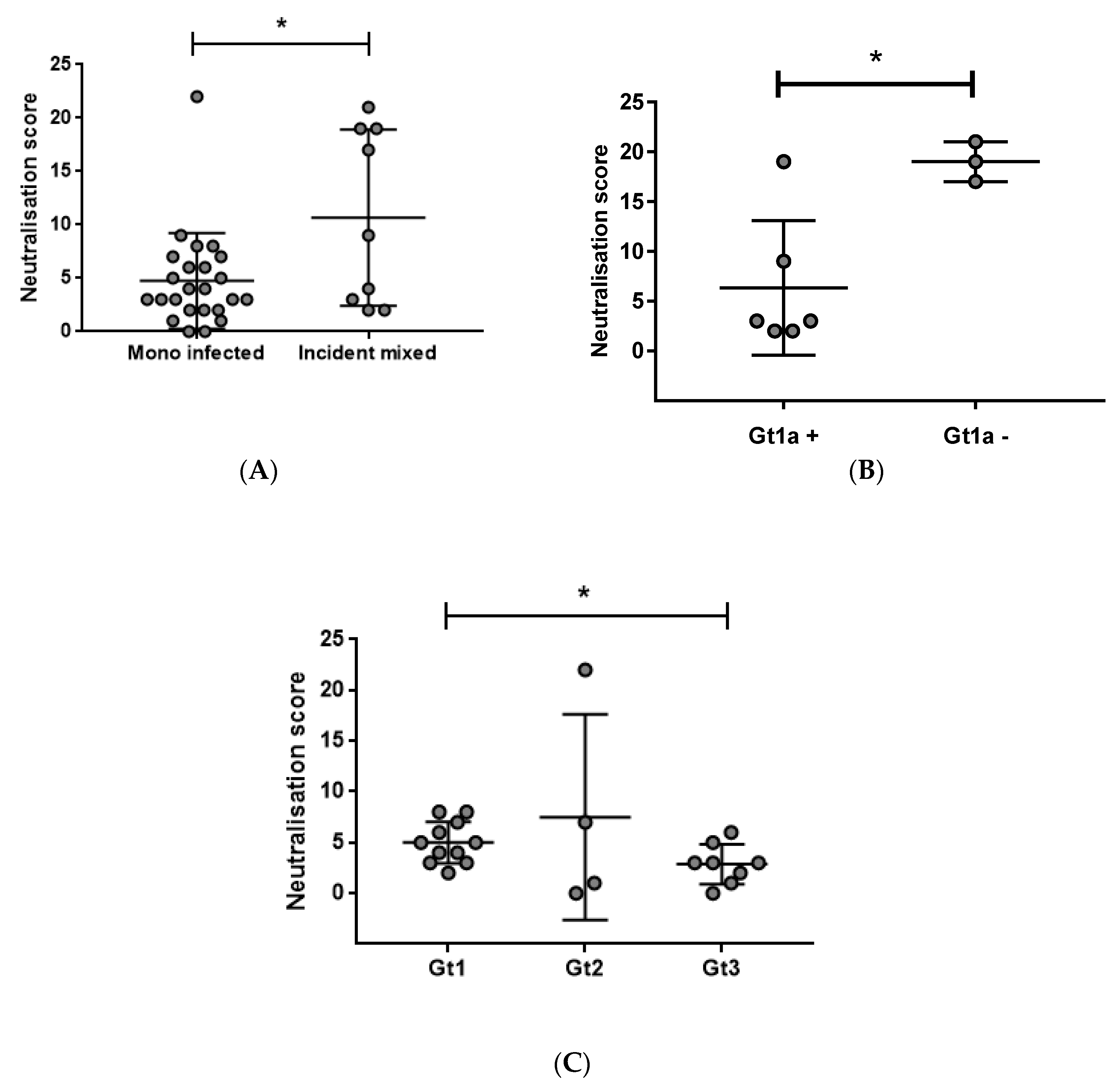
3.2. Early Induction of Broad nAbs Was Associated with Incident Mixed Infections
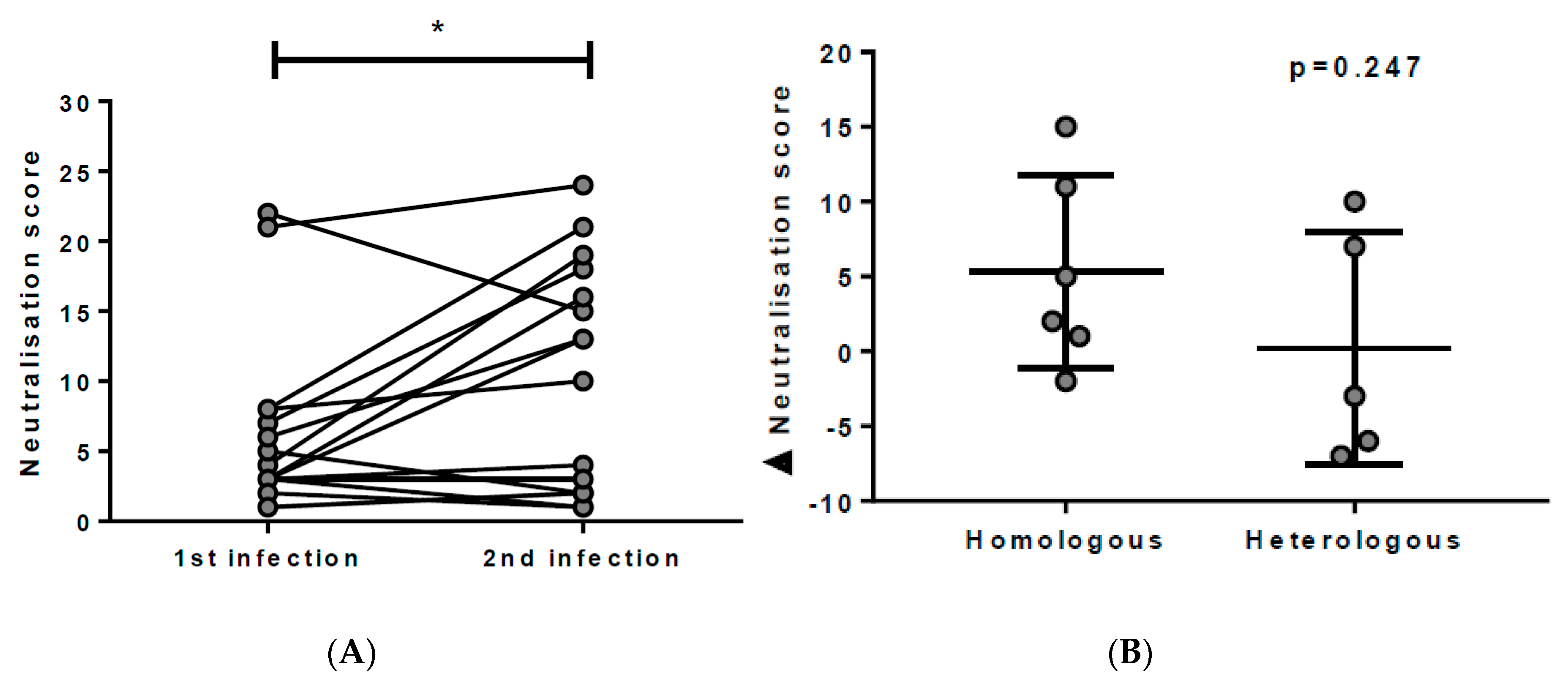
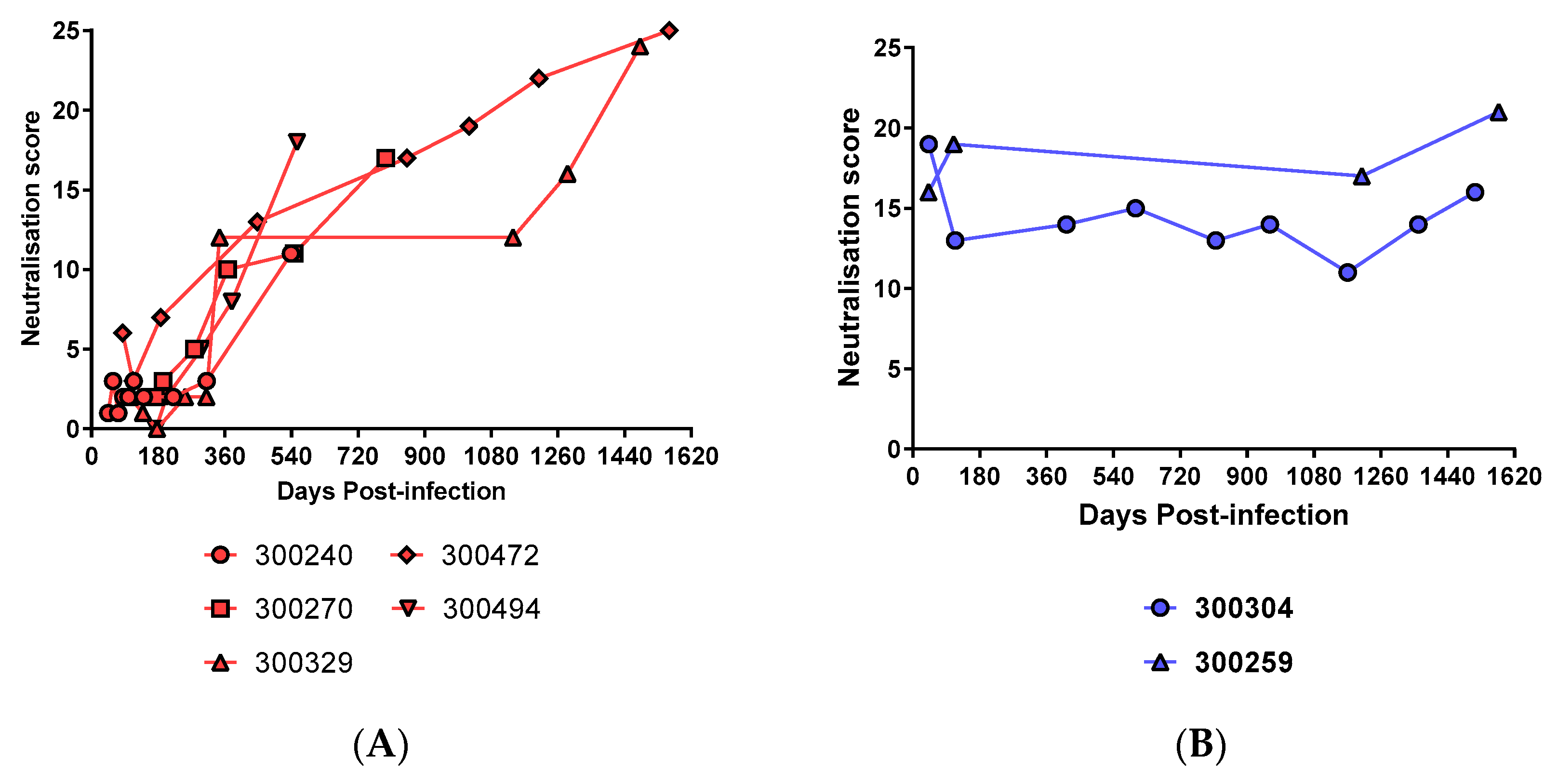
3.3. Breadth of nAbs is Boosted with Re-Exposure to HCV
3.4. Prolonged Antigen Exposure Is Associated with Broader nAb Development in Mono-Infection
3.5. Breadth Is Not Associated with Viral Load
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blach, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Manns, M.; Altraif, I.; Duberg, A.S.; Muljono, D.H.; Waked, I.; Alavian, S.M.; Lee, M.H.; Negro, F.; et al. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, D.G.; Walker, C.M. The origin of quasispecies: Cause or consequence of chronic hepatitis C viral infection? J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebely, J.; Dore, G.J.; Morin, S.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Klein, M.B. Elimination of HCV as a public health concern among people who inject drugs by 2030—What will it take to get there? J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2017, 20, 22146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, K.; Morris, M.D.; Hahn, J.A.; Maher, L.; Prins, M. Injection drug use and hepatitis C virus infection in young adult injectors: Using evidence to inform comprehensive prevention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57 Suppl. S2, S32–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiessing, L.; Ferri, M.; Grady, B.; Kantzanou, M.; Sperle, I.; Cullen, K.J.; EMCDDA DRID Group; Hatzakis, A.; Prins, M.; Vickerman, P.; et al. Hepatitis C virus infection epidemiology among people who inject drugs in europe: A systematic review of data for scaling up treatment and prevention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinello, M.; Grebely, J.; Petoumenos, K.; Gane, E.; Hellard, M.; Shaw, D.; Sasadeusz, J.; Applegate, T.L.; Dore, G.J.; Matthews, G.V. HCV reinfection incidence among individuals treated for recent infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinello, M.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Grebely, J.; Dore, G.J.; Matthews, G.V. HCV cure and reinfection among people with HIV/HCV coinfection and people who inject drugs. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2017, 14, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, K.A.; Netski, D.M.; Wang, X.H.; Cox, A.L.; Ray, S.C. Selection pressure from neutralizing antibodies drives sequence evolution during acute infection with hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, W.O.; Fisher, B.E.; Dowd, K.A.; Urban, G.; Liu, L.; Ray, S.C.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L. Spontaneous control of primary hepatitis C virus infection and immunity against persistent reinfection. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, W.O.; Snider, A.E.; Wells, B.L.; Latanich, R.; Bailey, J.R.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L.; Ray, S.C. Clearance of hepatitis C infection is associated with the early appearance of broad neutralizing antibody responses. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, J.M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Blaser, E.; Schurmann, P.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.L.; Patel, A.H.; Meisel, H.; Baumert, J.; Viazov, S.; et al. Rapid induction of virus-neutralizing antibodies and viral clearance in a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6025–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuraman, S.; Park, H.; Osburn, W.O.; Winkelstein, E.; Edlin, B.R.; Rehermann, B. Spontaneous clearance of chronic hepatitis C virus infection is associated with appearance of neutralizing antibodies and reversal of T-cell exhaustion. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Wang, R.Y.; Farci, P.; Alter, H.J.; Purcell, R.H. Immunoglobulin with high-titer in vitro cross-neutralizing hepatitis C virus antibodies passively protects chimpanzees from homologous, but not heterologous, challenge. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9128–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, T.J.; Broering, T.J.; Leav, B.A.; Blair, B.M.; Rowley, K.J.; Boucher, E.N.; Wang, Y.; Cheslock, P.S.; Knauber, M.; Olsen, D.B.; et al. Human monoclonal antibody HCV1 effectively prevents and treats HCV infection in chimpanzees. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, C.; Butt, Z.; Wong, S.; Buxton, J.; Islam, N.; Yu, A.; Darvishian, M.; Gilbert, M.; Wong, J.; Chapinal, N.; et al. Hepatitis C virus reinfection after successful treatment with direct-acting antiviral therapy in a large population-based cohort. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.L. Hepatitis C virus genotypes and quasispecies. Am. J. Med. 1999, 107, 21S–26S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Alter, H.J.; Govindarajan, S.; Wong, D.C.; Engle, R.; Lesniewski, R.R.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Desai, S.M.; Miller, R.H.; Ogata, N.; et al. Lack of protective immunity against reinfection with hepatitis C virus. Science 1992, 258, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuerst, T.R.; Pierce, B.G.; Keck, Z.Y.; Foung, S.K.H. Designing a B cell-based vaccine against a highly variable hepatitis C virus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinchen, V.J.; Cox, A.L.; Bailey, J.R. Can broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies lead to a hepatitis C virus vaccine? Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, M.; Maruyama, T.; Lewis, J.; Giang, E.; Tarr, A.W.; Stamataki, Z.; Gastaminza, P.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, I.M.; Fox, R.I.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies protect against hepatitis C virus quasispecies challenge. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiano, T.D.; Charlton, M.; Younossi, Z.; Galun, E.; Pruett, T.; Tur-Kaspa, R.; Eren, R.; Dagan, S.; Graham, N.; Williams, P.V.; et al. Monoclonal antibody HCV-ABXTL68 in patients undergoing liver transplantation for HCV: Results of a phase 2 randomized study. Liver Transpl. 2006, 12, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.; Meyer, K.; Banerjee, A.; Basu, A.; Coates, S.; Abrignani, S.; Houghton, M.; Frey, S.E.; Belshe, R.B. Characterization of antibodies induced by vaccination with hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Gan, T.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Sun, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, J. A trivalent HCV vaccine elicits broad and synergistic polyclonal antibody response in mice and rhesus monkey. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrone, P.; Fluckiger, A.C.; Mangeot, P.E.; Gauthier, E.; Dupeyrot-Lacas, P.; Mancip, J.; Cangialosi, A.; Du Chene, I.; LeGrand, R.; Mangeot, I.; et al. A prime-boost strategy using virus-like particles pseudotyped for HCV proteins triggers broadly neutralizing antibodies in macaques. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 94ra71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.X.; Lynch, R.; Zhou, T.; Gao, F.; Alam, S.M.; Boyd, S.D.; Fire, A.Z.; Roskin, K.M.; Schramm, C.A.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Co-evolution of a broadly neutralizing HIV-1 antibody and founder virus. Nature 2013, 496, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusert, P.; Kouyos, R.D.; Kadelka, C.; Ebner, H.; Schanz, M.; Huber, M.; Braun, D.L.; Hoze, N.; Scherrer, A.; Magnus, C.; et al. Determinants of HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody induction. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sather, D.N.; Carbonetti, S.; Malherbe, D.C.; Pissani, F.; Stuart, A.B.; Hessell, A.J.; Gray, M.D.; Mikell, I.; Kalams, S.A.; Haigwood, N.L.; et al. Emergence of broadly neutralizing antibodies and viral coevolution in two subjects during the early stages of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12968–12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logvinoff, C.; Major, M.E.; Oldach, D.; Heyward, S.; Talal, A.; Balfe, P.; Feinstone, S.M.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; McKeating, J.A. Neutralizing antibody response during acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10149–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binley, J.M.; Lybarger, E.A.; Crooks, E.T.; Seaman, M.S.; Gray, E.; Davis, K.L.; Decker, J.M.; Wycuff, D.; Harris, L.; Hawkins, N.; et al. Profiling the specificity of neutralizing antibodies in a large panel of plasmas from patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11651–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Klein, R.M.; Daniels, M.G.; O’Dell, S.; Nason, M.; Lapedes, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Migueles, S.A.; Wyatt, R.T.; Korber, B.T.; et al. Breadth of human immunodeficiency virus-specific neutralizing activity in sera: Clustering analysis and association with clinical variables. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretana, N.A.; Boelen, L.; Bull, R.; Teutsch, S.; White, P.A.; Lloyd, A.R.; Luciani, F.; HITS-p Investigators. Transmission of hepatitis C virus among prisoners, Australia, 2005–2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, K.; Teutsch, S.; Scheuer, N.; Levy, M.; Rawlinson, W.; Kaldor, J.; Lloyd, A.; Haber, P. Incidence and risk for acute hepatitis C infection during imprisonment in Australia. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciani, F.; Bretana, N.A.; Teutsch, S.; Amin, J.; Topp, L.; Dore, G.J.; Maher, L.; Dolan, K.; Lloyd, A.R.; HITS-p Investigators. A prospective study of hepatitis C incidence in Australian prisoners. Addiction 2014, 109, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, S.T.; Bull, R.A.; Bennett, J.M.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Dore, G.J.; Lloyd, A.R.; White, P.A. Frequent multiple hepatitis C virus infections among injection drug users in a prison setting. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.R.; Li, H.; Teutsch, S.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Luciani, F.; Lloyd, A.R.; Bull, R.A. Incident hepatitis C virus genotype distribution and multiple infection in australian prisons. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.; Madden, A.; Hellard, M.; Kerr, T.; Prins, M.; Page, K.; Dore, G.J.; Maher, L. Increased hepatitis C virus vaccine clinical trial literacy following a brief intervention among people who inject drugs. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2013, 32, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.; Madden, A.; Prins, M.; Hellard, M.; Wand, H.; Dore, G.J.; Page, K.; Maher, L. Assessing the feasibility of hepatitis C virus vaccine trials: Results from the hepatitis C incidence and transmission study-community (hits-C) vaccine preparedness study. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5460–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.; Dore, G.J.; Lloyd, A.R.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Maher, L. Opioid substitution therapy protects against hepatitis C virus acquisition in people who inject drugs: The hits-C study. Med. J. Aust. 2014, 201, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, E.B.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Bretana, N.A.; Amin, J.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Dore, G.J.; Luciani, F.; Teutsch, S.; Dolan, K.; Lloyd, A.R.; et al. Ongoing incident hepatitis C virus infection among people with a history of injecting drug use in an Australian prison setting, 2005–2014: The hits-p study. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Li, S.H.; Xia, J.; von Hahn, T.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A.; Witteveldt, J.; Patel, A.H.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M.; et al. Mutations in hepatitis C virus E2 located outside the CD81 binding sites lead to escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies but compromise virus infectivity. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6149–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, A.W.; Owsianka, A.M.; Szwejk, A.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Cloning, expression, and functional analysis of patient-derived hepatitis C virus glycoproteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 379, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urbanowicz, R.A.; McClure, C.P.; King, B.; Mason, C.P.; Ball, J.K.; Tarr, A.W. Novel functional hepatitis C virus glycoprotein isolates identified using an optimized viral pseudotype entry assay. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Dubuisson, J.; Cosset, F.L. Infectious hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles containing functional E1-E2 envelope protein complexes. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, K.A.; Hershow, R.C.; Yawetz, S.; Larussa, P.; Diaz, C.; Landesman, S.H.; Paul, M.E.; Read, J.S.; Lu, M.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Maternal neutralizing antibody and transmission of hepatitis C virus to infants. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 1651–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, R.A.; Leung, P.; Gaudieri, S.; Deshpande, P.; Cameron, B.; Walker, M.; Chopra, A.; Lloyd, A.R.; Luciani, F. Transmitted/founder viruses rapidly escape from CD8+ T cell responses in acute hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5478–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease; Garland Science Publishing: Abingdon, Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nachbagauer, R.; Choi, A.; Hirsh, A.; Margine, I.; Iida, S.; Barrera, A.; Ferres, M.; Albrecht, R.A.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Bouvier, N.M.; et al. Defining the antibody cross-reactome directed against the influenza virus surface glycoproteins. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.L.; Chen, C.; Wong, J.; Hockman, D.; Santer, D.M.; Frey, S.E.; Belshe, R.B.; Wakita, T.; Bukh, J.; Jones, C.T.; et al. A hepatitis C virus (HCV) vaccine comprising envelope glycoproteins GPE1/GPE2 derived from a single isolate elicits broad cross-genotype neutralizing antibodies in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, C.; Leung, P.; Lloyd, A.R.; Bull, R.A.; Luciani, F.; Grebely, J.; Dore, G.J.; Applegate, T.; Page, K.; Bruneau, J.; et al. Genetic variability of within-host hepatitis C variants in acute infection. J. Viral Hepat. accepted for publication 2018.
- Bailey, J.R.; Flyak, A.I.; Cohen, V.J.; Li, H.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Snider, A.E.; Wang, S.; Learn, G.H.; Kose, N.; Loerinc, L.; et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies with few somatic mutations and hepatitis C virus clearance. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikell, I.; Sather, D.N.; Kalams, S.A.; Altfeld, M.; Alter, G.; Stamatatos, L. Characteristics of the earliest cross-neutralizing antibody response to HIV-1. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLinden, R.; Paris, R.; Polonis, V.; Close, N.; Su, Z.; Shikuma, C.; Margolis, D.; Kim, J. Association of HIV neutralizing antibody with lower viral load after treatment interruption in a prospective trial (a5170). AIDS 2012, 26, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piantadosi, A.; Panteleeff, D.; Blish, C.A.; Baeten, J.M.; Jaoko, W.; McClelland, R.S.; Overbaugh, J. Breadth of neutralizing antibody response to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is affected by factors early in infection but does not influence disease progression. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10269–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, R.E.; Cowton, V.M.; Robinson, M.W.; Cole, S.J.; Barclay, S.T.; Mills, P.R.; Thomson, E.C.; McLauchlan, J.; Patel, A.H. Broad anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibody responses are associated with improved clinical disease parameters in chronic hcv infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4530–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Subject ID | Gender | Age | Estimated Days Since First Viraemic Time Point | Infecting Subtype a | Peak Viral Load (IU/mL) | Time at Peak Viral Load (DPI) b | Persistent Infection | Reinfecting Subtype | Estimated Days Since First Infection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300001 | F | 26 | 155 | 3a | 86,443 | 155 | - | 1a | 448 |
| 300031 | M | 22 | 51 | Unk | 861,000 | 51 | - | - | - |
| 300057 | M | 22 | 51 | 3a | 1254 | 51 | - | - | - |
| 300062 | F | 25 | 95 | Unk | <15 | 95 | - | 1b | 1079 |
| 300086 | M | 22 | 51 | 2a | 26,953 | 51 | - | 3a | 820 |
| 300089 | M | 23 | 179 | 1b/3a | 70,737 | 179 | - | 3a | 866 |
| 300101 | M | 23 | 179 | 1a/3a | 11,441,811 | 179 | - | - | - |
| 300138 | M | 21 | 191 | 3a | 582 | 191 | - | 3a | 386 |
| 300144 | F | 20 | 268 | 3a | 1205 | 268 | - | 1a | 630 |
| 300146 | M | 18 | 170 | Unk | <15 | 170 | - | - | - |
| 300152 | M | 19 | 122 | Unk | <15 | 122 | - | 1a | 1157 |
| 300155 | M | 27 | 217 | 3a | 615 | 217 | - | Unk | 1468 |
| 300168 | M | 18 | 4 | 1b | 10,989,916 | 32 | - | 1a | 120 |
| 300212 | M | 19 | 146 | 1b | 8039 | 146 | - | 1a | 358 |
| 300223 | F | 26 | 169 | 3a | 267,750 | 169 | Y | - | - |
| 300225 | M | 22 | 103 | Unk | <15 | 103 | - | 1b | 416 |
| 300230 | F | 26 | 165 | 1a/2a | 2450 | 165 | - | - | - |
| 300240 | M | 18 | 45 | 3a | 54,887 | 58 | Y | - | - |
| 300256 | M | 24 | 44 | 1a/3a | 34,149,824 | 44 | Y | - | - |
| 300259 | M | 20 | 41 | 3a/2a | 567,122 | 41 | Y | - | - |
| 300270 | M | 25 | 173 | 6a | 10,671 | 173 | Y | - | - |
| 300272 | F | 29 | 61 | 3a | 10,122 | 61 | - | 1a | 2270 |
| 300277 | M | 18 | 39 | 3a/3b | 5,482,503 | 63 | - | - | - |
| 300280 | F | 19 | 176 | 1a | 22,384,668 | 176 | - | - | - |
| 300303 | F | 40 | 48 | 1a/3a | 5,052,079 | 48 | - | - | - |
| 300304 | M | 46 | 43 | 1a/3a | 1,436,063 | 114 | Y | - | - |
| 300315 | M | 21 | 51 | 2b | 872,728 | 51 | Y | - | - |
| 300327 | M | 28 | 101 | 2b | 6748 | 146 | Y | - | - |
| 300329 | M | 19 | 104 | 3a | 9504 | 177 | Y | - | - |
| 300354 | M | 18 | 127 | 1a | 23,573 | 127 | - | 1a | 336 |
| 300360 | M | 23 | 30 | 3a | 5,648,631 | 30 | - | - | - |
| 300374 | M | 23 | 145 | 1a/3a | 44,836 | 145 | - | - | - |
| 300472 | M | 22 | 84 | 1a | 1,263,375 | 84 | Y | - | - |
| 300494 | F | 23 | 174 | 2b | 73,841 | 174 | Y | - | - |
| 300499 | M | 23 | 169 | 1a | 591,430 | 169 | - | - | - |
| 400087 | M | 23 | 31 | 1b | 13,118,082 | 42 | - | 3a | 49 |
| FRKT0686FX | M | 22 | 41 | 1a | 2,404,901 | 41 | - | - | - |
| JEBJ0991MX | M | 18 | 74 | 1a | 1037 | 74 | - | - | - |
| KAMA0984MX | M | 24 | 88 | Unk | <15 | 88 | - | 3a | 591 |
| KIMB0979FX | F | 29 | 98 | Unk | <15 | 98 | - | - | - |
| MCRL0786FX | F | 22 | 81 | 1a | 1846 | 81 | - | - | - |
| MIJC1076FX | F | 32 | 126 | 1a | 15,997 | 175 | - | - | - |
| NASS0384MX | M | 25 | 84 | 3a | 5321 | 94 | - | 3a | 84 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Underwood, A.P.; Walker, M.R.; Brasher, N.A.; Eltahla, A.A.; Maher, L.; Luciani, F.; Lloyd, A.R.; Bull, R.A. Understanding the Determinants of BnAb Induction in Acute HCV Infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110659
Underwood AP, Walker MR, Brasher NA, Eltahla AA, Maher L, Luciani F, Lloyd AR, Bull RA. Understanding the Determinants of BnAb Induction in Acute HCV Infection. Viruses. 2018; 10(11):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110659
Chicago/Turabian StyleUnderwood, Alexander P., Melanie R. Walker, Nicholas A. Brasher, Auda A. Eltahla, Lisa Maher, Fabio Luciani, Andrew R. Lloyd, and Rowena A. Bull. 2018. "Understanding the Determinants of BnAb Induction in Acute HCV Infection" Viruses 10, no. 11: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110659
APA StyleUnderwood, A. P., Walker, M. R., Brasher, N. A., Eltahla, A. A., Maher, L., Luciani, F., Lloyd, A. R., & Bull, R. A. (2018). Understanding the Determinants of BnAb Induction in Acute HCV Infection. Viruses, 10(11), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110659





