Contrasting Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Response to Five-Year Nitrogen Addition in a Pinus tabulaeformis Forest in Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Measurements of Soil Respiration and Its Components, Soil Temperature and Moisture
- (1)
- IT: Subplots in the natural state. Soil respiration measured in IT subplots represented the total respiration (RST);
- (2)
- NL: Subplots subjected to litter layer removal. Litter was excluded from the NL subplots with 1-mm nylon mesh suspended 1 m above the ground. CO2 efflux in NL subplots (RSNL) exclude soil respiration from the litter layer (RSL), thus RSL could be calculated as:RSL = RST − RSNL
- (3)
- NRL: Subplots subjected to both litter removal and trenching. The subplots were trenched to 1 m depth and pieces of polyethylene board were inserted into the inner side of trenches to prevent new roots from growing into the subplots, then the soils were backfilled layer by layer. Two years later after trenching, we found no visual living roots in the trenched subplots by collecting soil cores (4 cm diameter, 1 m depth) in May 2011.
2.3. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Litter Biomass, Fine Root Biomass and Fine Root N Concentration
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Temperature and Moisture
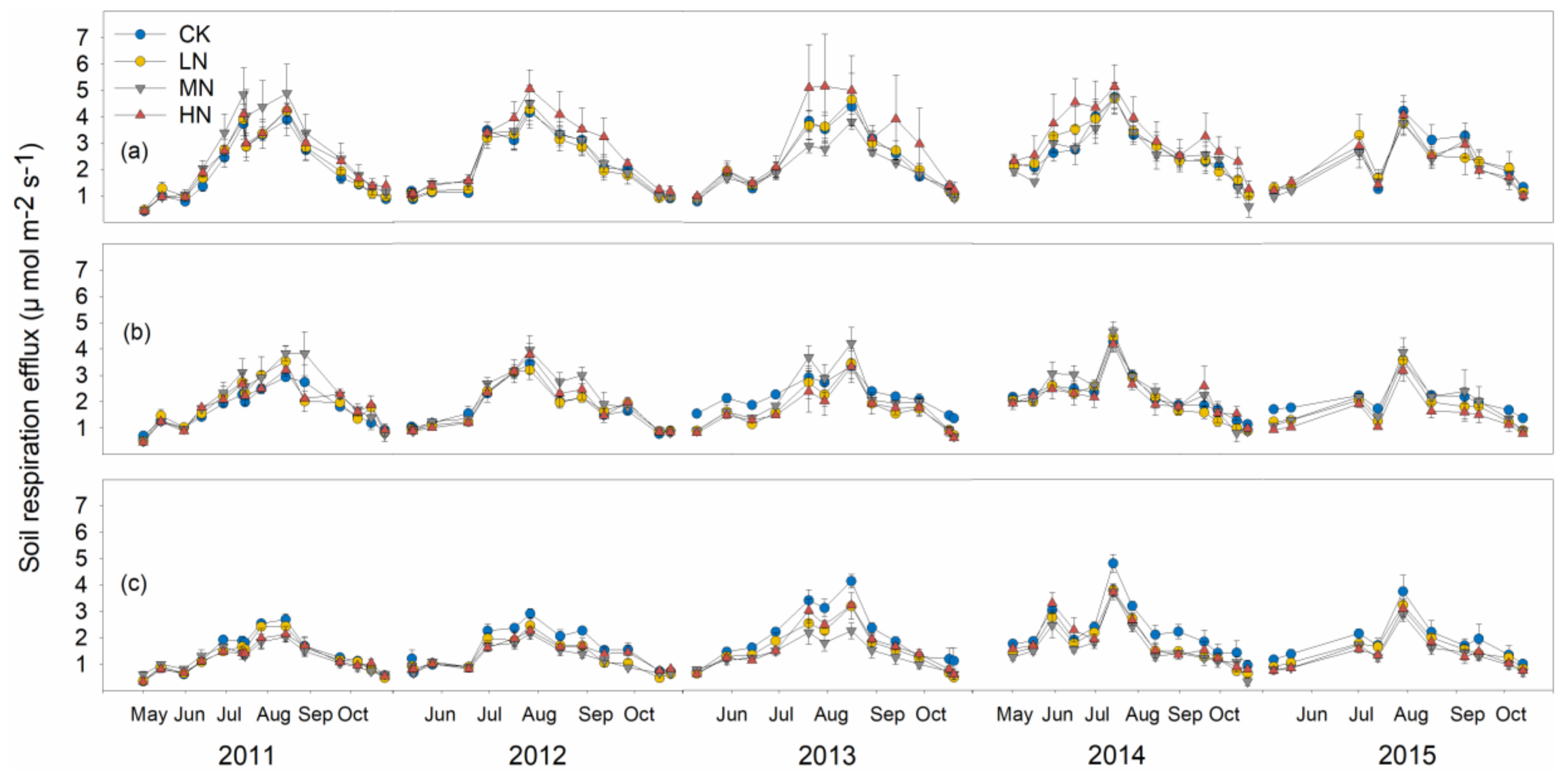
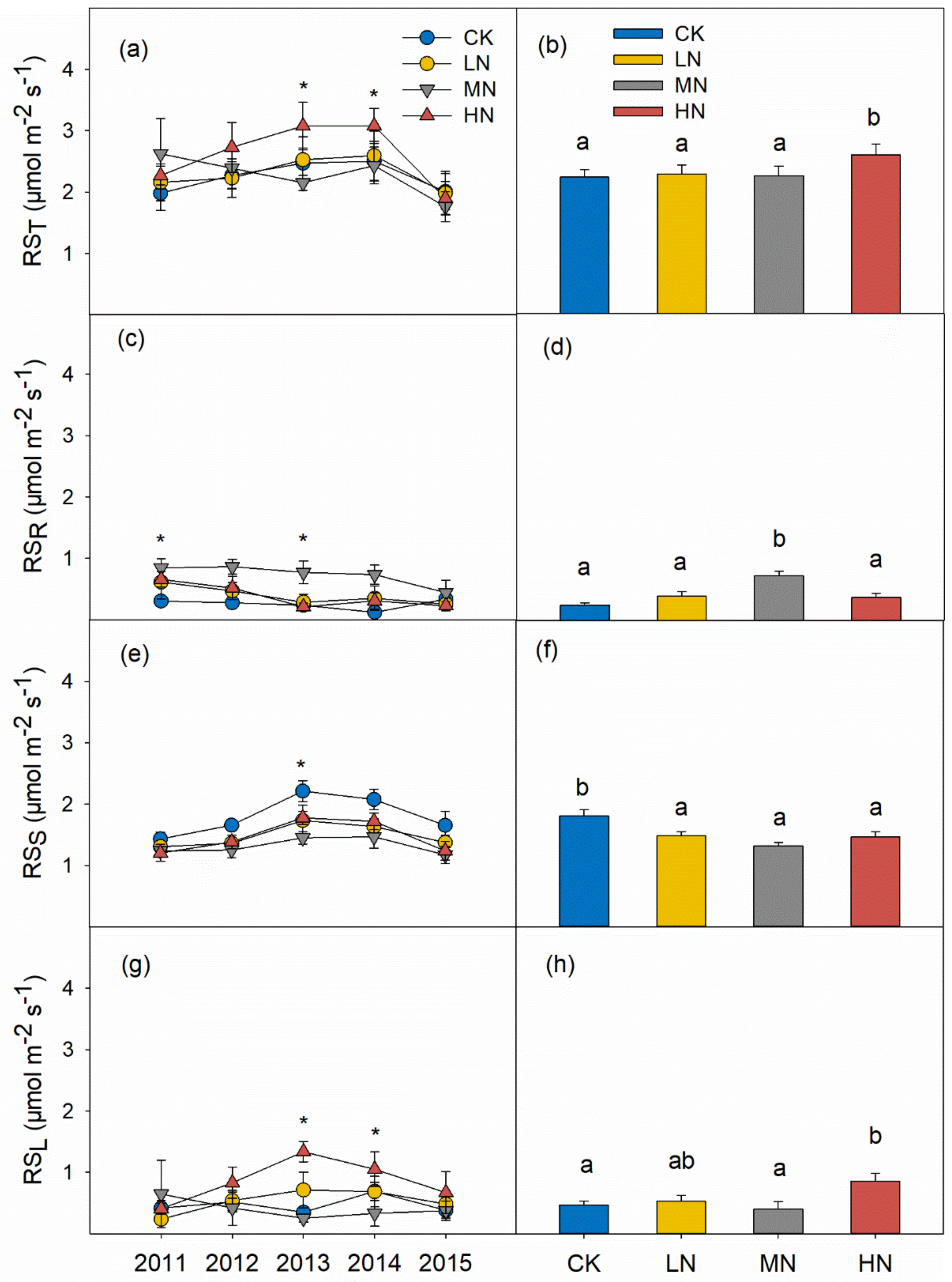
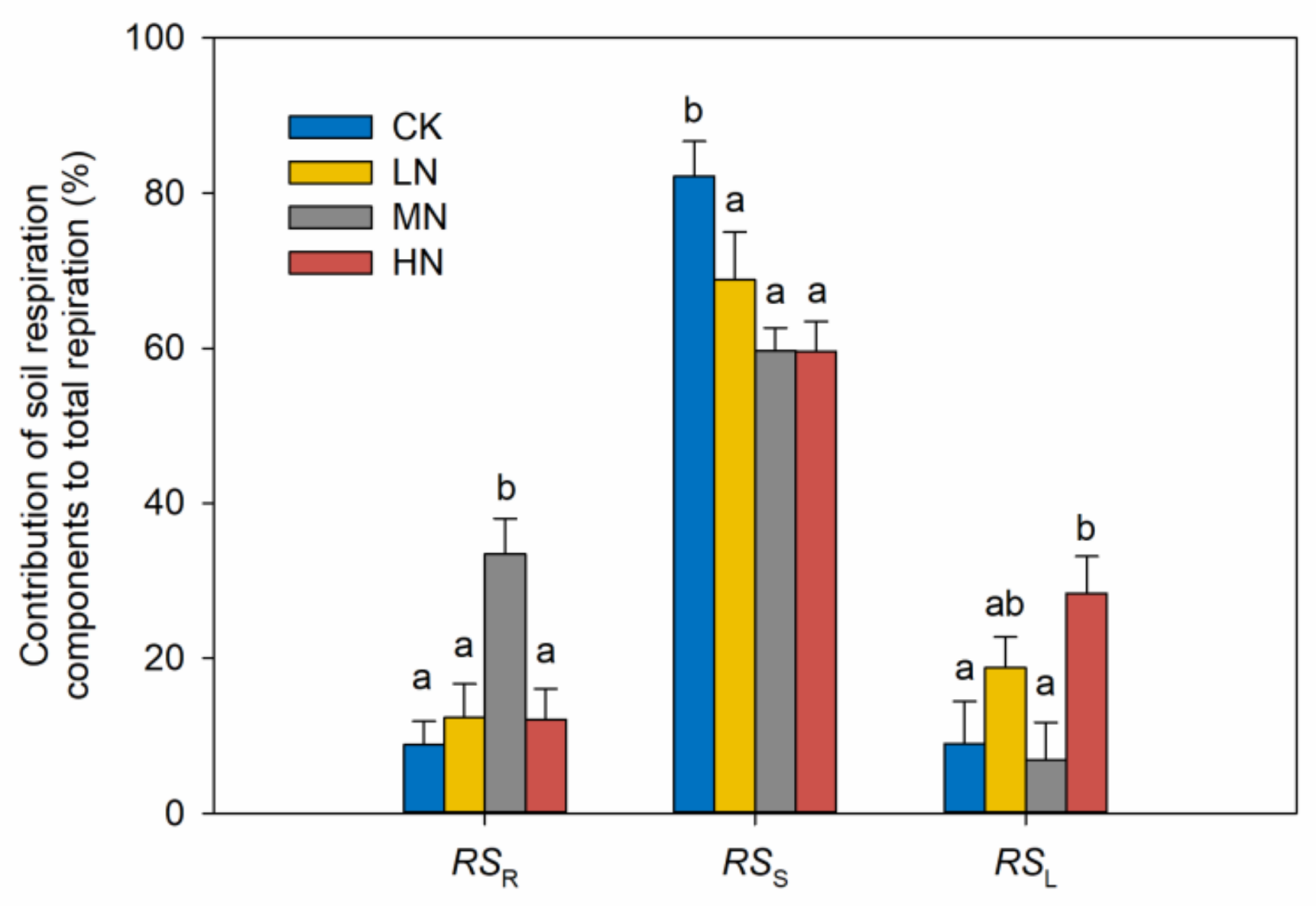
3.2. Soil Respiration and Its Components
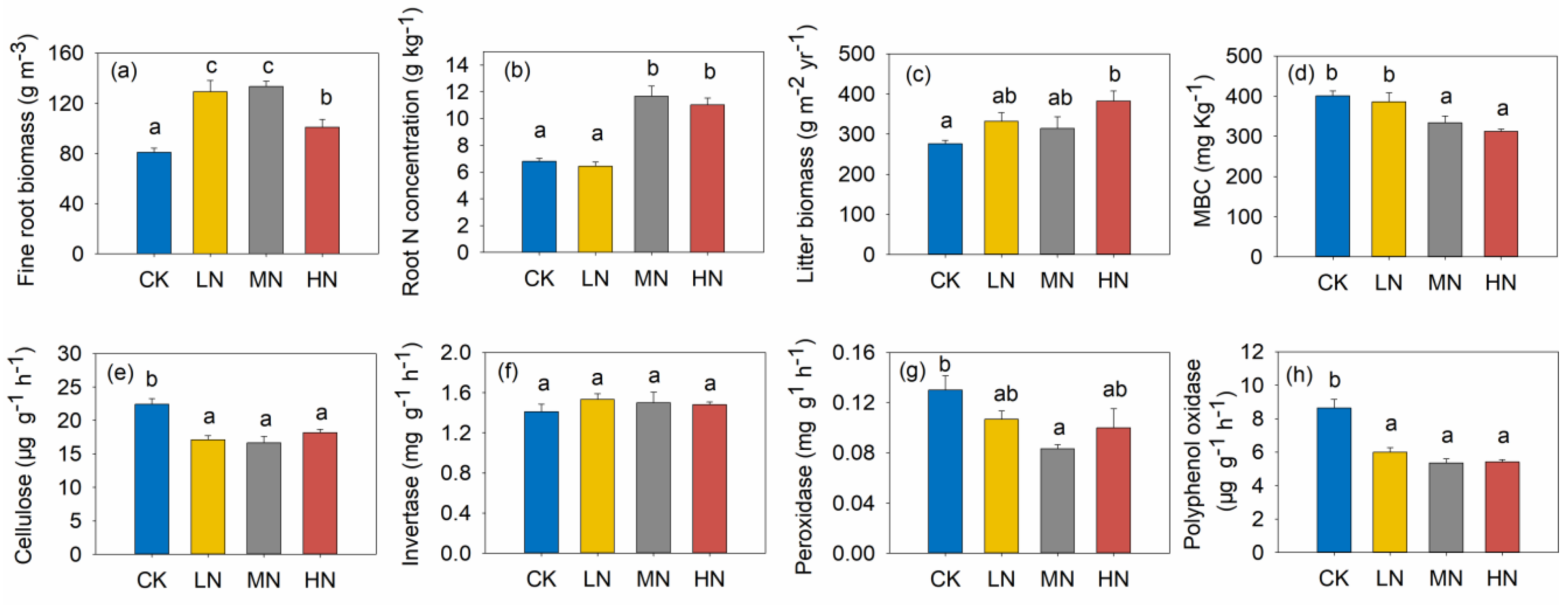
3.3. Litter Biomass, Fine Root Biomass and N Concentration of Fine Root
3.4. Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of N Addition on RST
4.2. Reduction of RSS in Response to N Addition
4.3. Increases of RSL and RSR in Response to N Addition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Lamarque, J.F.; Kiehl, J.; Brasseur, G.; Butler, T.; Cameron-Smith, P.; Collins, W.; Collins, W.; Granier, C.; Hauglustaine, D.; Hess, P. Assessing future nitrogen deposition and carbon cycle feedback using a multimodel approach: Analysis of nitrogen deposition. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dentener, F.; Drevet, J.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Bey, I.; Eickhout, B.; Fiore, A.M.; Hauglustaine, D.; Horowitz, L.W.; Krol, M.; Kulshrestha, U. Nitrogen and sulfur deposition on regional and global scales: A multimodel evaluation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, R.; Wallen, B.; Malmer, N. Growth-limiting nutrients in sphagnum-dominated bogs subject to low and high atmospheric nitrogen supply. J. Ecol. 1992, 80, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, A.; Pregitzer, K.; Ruess, R.; Hendrick, R.; Allen, M. Root respiration in North American forests: Effects of nitrogen concentration and temperature across biomes. Oecologia 2002, 131, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reay, D.S.; Dentener, F.; Smith, P.; Grace, J.; Feely, R.A. Global nitrogen deposition and carbon sinks. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Greaver, T.L. A global perspective on belowground carbon dynamics under nitrogen enrichment. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, I.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.-A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, B. Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen addition among biomes: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, L.; Yao, P.; Qiao, M.; Yao, S. Meta-analyses of the effects of major global change drivers on soil respiration across China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, T.; Chen, L.; Pang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, F. N and P fertilization reduced soil autotrophic and heterotrophic respiration in a young cunninghamia lanceolata forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, D.; Hall, S.J.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Fu, H.; Wan, C.; Elser, J.J. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil respiration components and their temperature sensitivities in a semiarid grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Wan, S. Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Lin, T.-C.; Yang, Z.; Vadeboncoeur, M.A.; Lin, C.; Xiong, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Xie, J.; Li, Y. Increased litter in subtropical forests boosts soil respiration in natural forests but not plantations of castanopsis carlesii. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, L.J.; Dorland, E.; Vergeer, P.; Hart, M.A.; Bobbink, R.; Roelofs, J.G. Decline of acid-sensitive plant species in heathland can be attributed to ammonium toxicity in combination with low pH. New Phytol. 2005, 166, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.; Vitousek, P.; Zhang, F. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Gallo, M.E.; Lauber, C.; Waldrop, M.P.; Zak, D.R. Extracellular enzyme activities and soil organic matter dynamics for northern hardwood forests receiving simulated nitrogen deposition. Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: Implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, I.P.; Zak, D.R.; Kellner, H.; Eisenlord, S.D.; Pregitzer, K.S. Simulated atmospheric n deposition alters fungal community composition and suppresses ligninolytic gene expression in a northern hardwood forest. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, J.E.; Watrud, L.S.; Porteous, L.A.; Degrood, S. Response of soil microbial biomass and community composition to chronic nitrogen additions at Harvard forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Simpson, A.J.; Wilson, K.P.; Williams, D.D.; Simpson, M.J. Increased cuticular carbon sequestration and lignin oxidation in response to soil warming. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.-H.; Hu, T.-X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.-W.; Hu, H.-L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.-L. Nitrogen addition stimulates different components of soil respiration in a subtropical bamboo ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, J.; Lan, Z.; Hu, S.; Bai, Y. Soil acidification exerts a greater control on soil respiration than soil nitrogen availability in grasslands subjected to long-term nitrogen enrichment. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, R.D.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Canary, J.D.; Kaye, J.P. Roots exert a strong influence on the temperature sensitivityof soil respiration. Nature 1998, 396, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, P.; Nordgren, A.; Buchmann, N.; Taylor, A.F.; Ekblad, A.; Högberg, M.N.; Nyberg, G.; Ottosson-Löfvenius, M.; Read, D.J. Large-scale forest girdling shows that current photosynthesis drives soil respiration. Nature 2001, 411, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, L.; Mathew, R.; Stokes, T.; Feng, Y.; Aubrey, D.; Coleman, M. Soil and microbial respiration in a loblolly pine plantation in response to seven years of irrigation and fertilization. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.G.; Law, B.E. Interpreting, measuring, and modeling soil respiration. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leff, J.W.; Wieder, W.R.; Taylor, P.G.; Townsend, A.R.; Nemergut, D.R.; Grandy, A.S.; Cleveland, C.C. Experimental litterfall manipulation drives large and rapid changes in soil carbon cycling in a wet tropical forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhao, X.; Gadow, K.V. Inconsistent autotrophic respiration but consistent heterotrophic respiration responses to 5-years nitrogen addition under natural and planted pinus tabulaeformis forests in northern China. Plant Soil 2018, 429, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Biochem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J. Origin and Range of Enzymes in Soil; Soil Enzymes Academic Press: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, R.D.; Davidson, E.; Savage, K.; Arabia, C.; Steudler, P. Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Czimczik, C.I.; Treseder, K.K. Microbial activity and soil respiration under nitrogen addition in Alaskan boreal forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggs, C.E.; Hobbie, S.E. Mechanisms driving the soil organic matter decomposition response to nitrogen enrichment in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archmiller, A.A.; Samuelson, L.J. Intra-annual variation of soil respiration across four heterogeneous longleaf pine forests in the Southeastern United States. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 359, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Belk, E.; Boone, R.D. Soil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest. Glob. Chang. Boil. 1998, 4, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoling, F.; Nilsson, L.O.; Bååth, E. Bacterial and fungal response to nitrogen fertilization in three coniferous forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treseder, K.K. Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: A meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Bååth, E. Contrasting soil pH effects on fungal and bacterial growth suggest functional redundancy in carbon mineralization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Oba, Y. Effect of fungal to bacterial biomass ratio on the relationship between CO2 evolution and total soil microbial biomass. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 17, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.-H.; Hu, T.-X.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.-H.; Dai, H.-Z.; Luo, S.-H. Short-term simulated nitrogen deposition increases carbon sequestration in a pleioblastus amarus plantation. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Potter, C.S. Global patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, G.; Fang, K.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Mohammat, A. Nonlinear response of soil respiration to increasing nitrogen additions in a Tibetan alpine steppe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 024018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Han, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Hui, D.; Niu, S.; Wan, S. Plant functional groups regulate soil respiration responses to nitrogen addition and mowing over a decade. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; Burton, A.J.; King, J.S.; Zak, D.R. Soil respiration, root biomass, and root turnover following long-term exposure of northern forests to elevated atmospheric CO2 and tropospheric O3. New Phytol. 2008, 180, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.J.; Yavitt, J.B.; Wurzburger, N.; Turner, B.L.; Tanner, E.V.; Sayer, E.J.; Santiago, L.S.; Kaspari, M.; Hedin, L.O.; Harms, K.E. Potassium, phosphorus, or nitrogen limit root allocation, tree growth, or litter production in a lowland tropical forest. Ecology 2011, 92, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Houdijk, A.L.F.M.; Verbeek, P.J.M.; Dijk, H.F.G.V.; Roelofs, J.G.M. Distribution and decline of endangered herbaceous heathland species in relation to the chemical composition of the soil. Plant Soil 1993, 148, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Ha, D.; Qu, Y.; Jing, G.; Niu, S. Soil acid cations induced reduction in soil respiration under nitrogen enrichment and soil acidification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 615, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aber, J.D.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Steudler, P.; Melillo, J.M. Nitrogen saturation in northern forest ecosystems. BioScience 1989, 39, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Properties | Forest Characteristics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N Treatment | SOC (g kg−1) | Total N (g kg−1) | pH | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Density (stem ha−1) | Average DBH (cm) |
| CK | 30.75 ± 3.06 | 2.04 ± 0.23 | 6.91 ± 0.18 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 1267 | 25.2 |
| LN | 31.57 ± 3.74 | 1.91 ± 0.22 | 6.79 ± 0.19 | 1.02 ± 0.05 | 1567 | 24.6 |
| MN | 32.45 ± 3.75 | 1.66 ± 0.13 | 6.86 ± 0.09 | 1.08 ± 0.02 | 1208 | 24.1 |
| HN | 29.04 ± 4.69 | 2.35 ± 0.07 | 6.61 ± 0.10 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 1225 | 23.9 |
| N Treatment | SOC (g kg−1) | Total N (g kg−1) | Soil Extractable N (mg kg−1) | pH | Soil Temperature (°C) | Soil Moisture (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 34.85 ± 5.77a | 1.87 ± 0.22a | 186.89 ± 11.54a | 7.25 ± 0.15b | 11.42 ± 0.19a | 33.15 ± 0.35a |
| LN | 26.51 ± 3.55a | 1.59 ± 0.14a | 228.89 ± 16.61b | 6.55 ± 0.13ab | 11.58 ± 0.22a | 33.72 ± 0.32a |
| MN | 28.45 ± 2.67a | 1.57 ± 0.10a | 261.33 ± 23.34c | 6.22 ± 0.13a | 11.11 ± 0.18a | 33.68 ± 0.31a |
| HN | 25.17 ± 4.42a | 1.66 ± 0.18a | 279.66 ± 20.16c | 5.79 ± 0.16a | 11.33 ± 0.18a | 33.00 ± 0.31a |
| Source of Variation | RST | RSR | RSS | RSL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F | df | F | df | F | df | F | |
| Year | 4 | 2.88 * | 4 | 3.49 * | 4 | 10.80 *** | 4 | 0.34 |
| Treatment | 3 | 3.22 * | 3 | 7.80 *** | 3 | 15.12 *** | 3 | 2.80 * |
| Year × Treatment | 12 | 1.22 | 12 | 0.47 | 12 | 0.77 | 12 | 0.43 |
| RST | RSR | RSS | RSL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (H2O) | −0.077 | −0.210 | 0.618 * | 0.037 |
| MBC (mg kg−1) | −0.065 | −0.404 | 0.613 * | 0.096 |
| Cellulase (µg g−1 h−1) | 0.164 | −0.466 | 0.811 ** | 0.048 |
| Polyphenol oxidase (µg g−1 h−1) | −0.184 | −0.412 | 0.607 * | −0.068 |
| Fine root biomass (g m−2) | 0.449 | 0.600 * | −0.490 | 0.415 |
| Fine Root N concentration (g kg−1) | 0.195 | 0.635 * | −0.575 | −0.027 |
| Litter biomass (g m−1 year−1) | 0.449 | 0.461 | −0.480 | 0.680 * |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 0.358 ** | −0.163 | 0.456 ** | 0.268 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, B.; Geng, Y.; Cao, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, X. Contrasting Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Response to Five-Year Nitrogen Addition in a Pinus tabulaeformis Forest in Northern China. Forests 2018, 9, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090544
Zhao B, Geng Y, Cao J, Yang L, Zhao X. Contrasting Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Response to Five-Year Nitrogen Addition in a Pinus tabulaeformis Forest in Northern China. Forests. 2018; 9(9):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090544
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Bo, Yan Geng, Jing Cao, Lu Yang, and Xiuhai Zhao. 2018. "Contrasting Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Response to Five-Year Nitrogen Addition in a Pinus tabulaeformis Forest in Northern China" Forests 9, no. 9: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090544
APA StyleZhao, B., Geng, Y., Cao, J., Yang, L., & Zhao, X. (2018). Contrasting Responses of Soil Respiration Components in Response to Five-Year Nitrogen Addition in a Pinus tabulaeformis Forest in Northern China. Forests, 9(9), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9090544




