Short-Term Changes in the Soil Respiration of Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Severe Typhoon Disturbance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
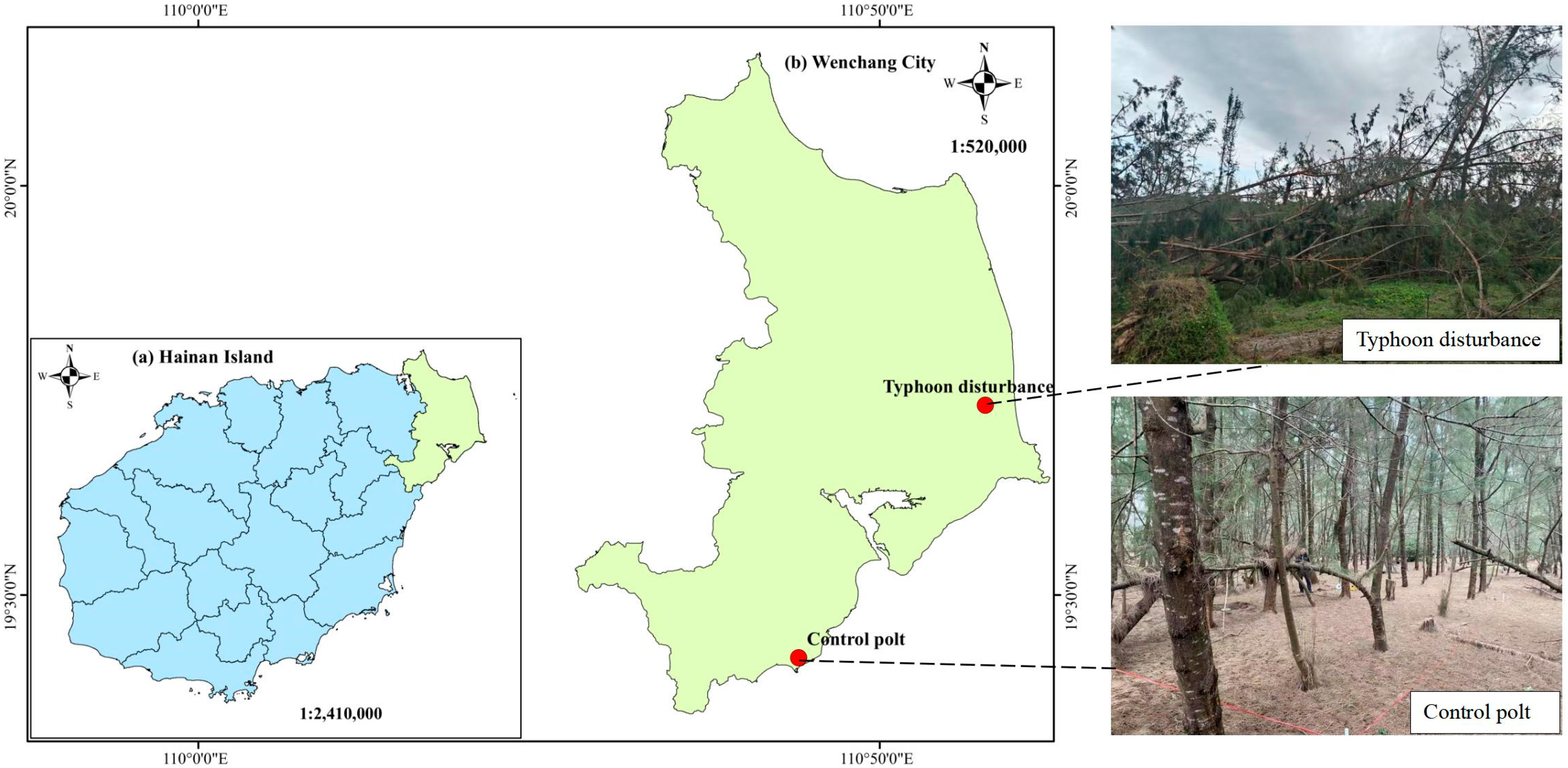
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Plot Arrangement
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Soil Respiration Measurement
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
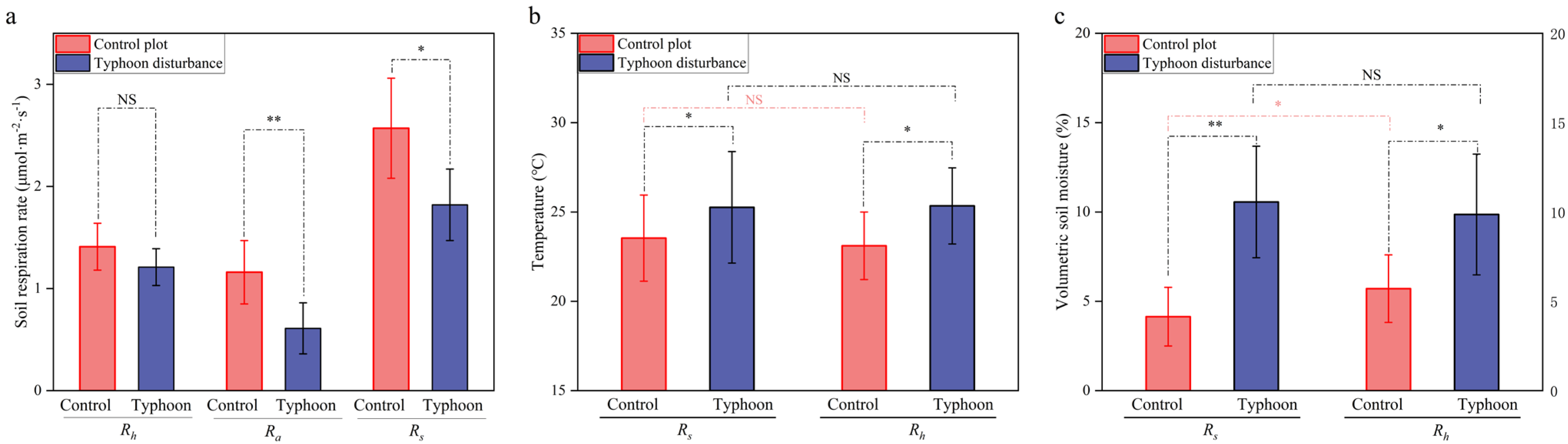
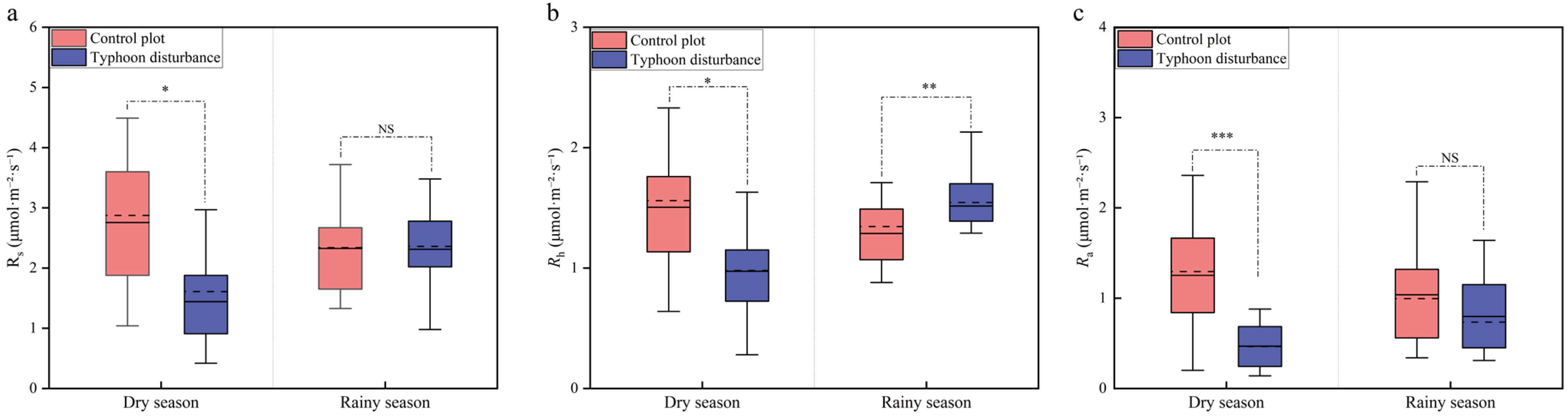
3.1. Changes in Soil Respiration, Soil Temperature, and Soil Moisture in Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Severe Typhoon Disturbance
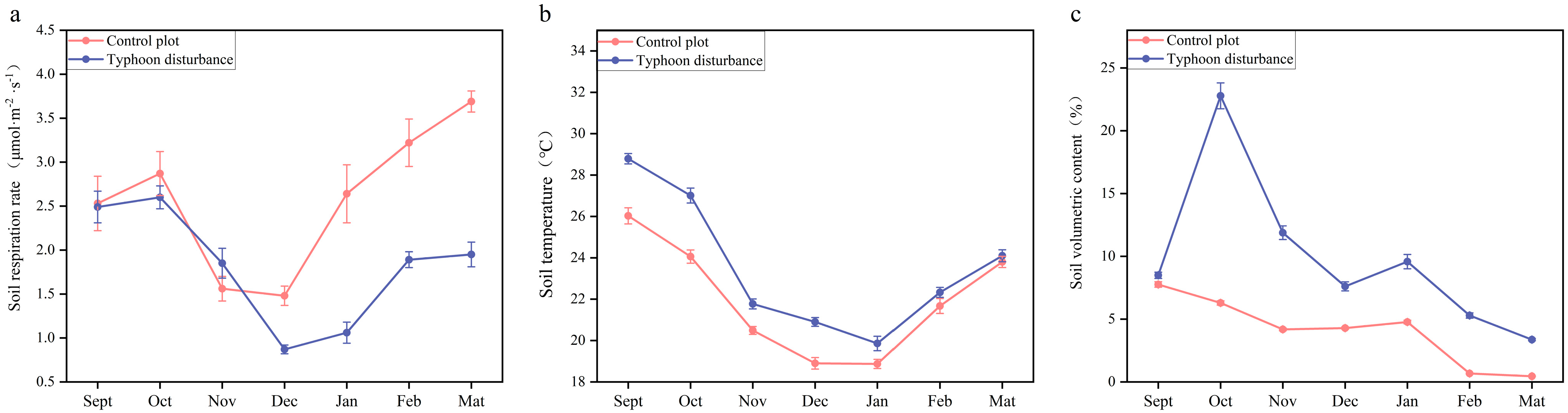
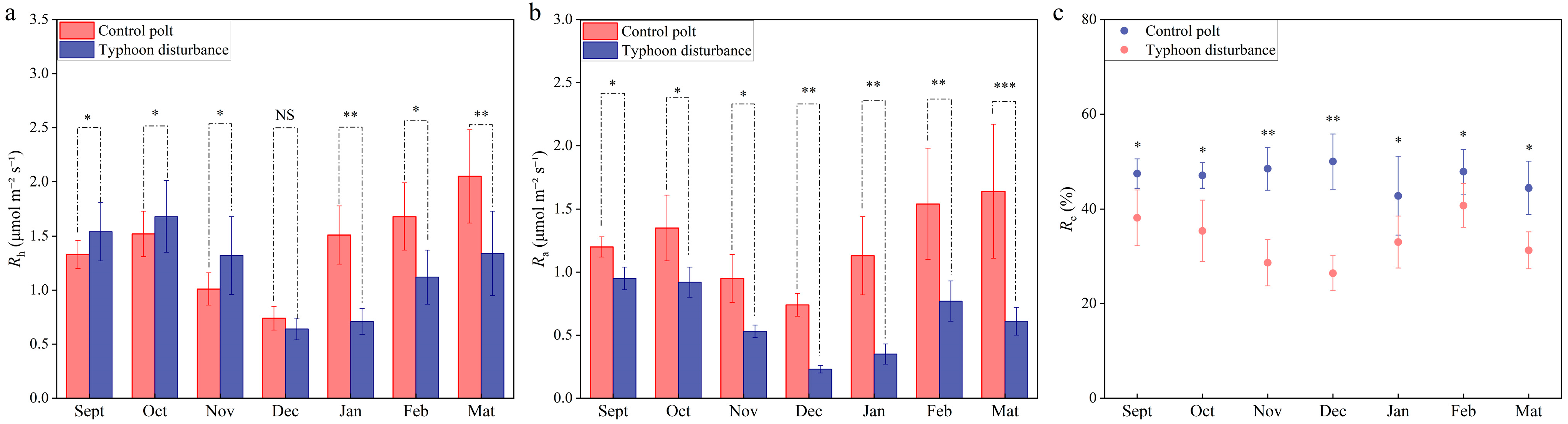
3.2. Dynamic Trends of Soil Respiration in Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Typhoon Disturbance
3.3. Correlations Between Soil Respiration and Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture of the Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Short-Term Effects of Typhoon Disturbance on Soil Respiration
4.2. Seasonal Effects of Typhoon Disturbance on Soil Respiration
4.3. Relationships Between Soil Respiration and Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture After Typhoon Disturbance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Peng, C.; Luo, Y.; Terrer, C.; Yue, C.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Shangguan, Z.; et al. Future soil organic carbon stocks in China under climate change. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2024, 1, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ding, S.; Liu, N.; Mo, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ma, J. Soil Microbial Community in Relation to Soil Organic Carbon and Labile Soil Organic Carbon Fractions under Detritus Treatments in a Subtropical Karst Region during the Rainy and Dry Seasons. Forests 2023, 14, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Liu, Z.; Haghipour, N.; Wacker, L.; Zhang, H.; Sierra, C.A.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Luo, A.; et al. Molecular 14C evidence for contrasting turnover and temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter components. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Responses of tree leaf gas exchange to elevated CO2 combined with changes in temperature and water availability: A global synthesis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 2500–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gillett, N.P.; Monahan, A.H. Climate Model Projections of 21st Century Global Warming Constrained Using the Observed Warming Trend. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Pokharel, P.; Liu, L.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Y.; An, S.; Chang, S.X. Global effects on soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity depend on nitrogen addition rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 174, 108814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. Diurnal Dynamics of Soil Respiration: Relationship with Temperature and the Most Suitable Measuring Time. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2015, 1, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Jia, B.R. A compiled soil respiration dataset at different time scales for forest ecosystems across China from 2000 to 2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, M.; Campbell, M.J.; Turton, S.M.; Pert, P.L.; Edwards, W.; Laurance, W.F. Degraded tropical rain forests possess valuable carbon storage opportunities in a complex, forested landscape. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Pan, L.; Xue, L. Effects of typhoons on forests. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Su, T.; Fu, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, W. Effects of forest gaps in tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan on soil respiration. Chin. J. Trop. Crop. 2021, 12, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Cao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, W. The immediate effect of typhoon disturbance on soil carbon fractions along a subtropical forest gap gradient. Catena 2025, 254, 108986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Hui, D.; Chu, G.; Han, X.; Zhang, Q. Rain-induced changes in soil CO2 flux and microbial community composition in a tropical forest of China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.E.; Davidson, E.A.; Abramoff, R.Z.; Finzi, A.C.; Giasson, M.A. Partitioning soil respiration: Quantifying the artifacts of the trenching method. Biogeochemistry 2018, 140, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.Y.; Lau, S.Y.L.; Midot, F.; Jee, M.S.; Lo, M.L.; Sangok, F.E.; Melling, L. Root exclusion methods for partitioning of soil respiration: Review and methodological considerations. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, E.J.; Tanner, E.V.J. A new approach to trenching experiments for measuring root–rhizosphere respiration in a lowland tropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiang, D.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, L. Biophysical control of daytime and nighttime soil respiration during growing and non-growing seasons in a temperate deciduous forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 350, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Zeng, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Lyu, Y.; Cheng, A.; Zhang, L.; Cai, X.; Chen, J.; et al. CO2 flux of soil respiration in natural recovering karst abandoned farmland in Southwest China. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, W.; Wang, B.; Hu, H.; Tian, F. The characteristics of ecosystem respiration and its components of a representative film-mulched and drip-irrigated cotton field in Northwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 352, 108506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromova, M.S.; Matvienko, A.I.; Makarov, M.I.; Cheng, C.H.; Menyailo, O.V. Temperature Sensitivity (Q10) of Soil Basal Respiration as a Function of Available Carbon Substrate, Temperature, and Moisture. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, S. Temperature response of soil respiration decreases with latitude and elevation in abandoned croplands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 363, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Friend, A.; Huang, C. Simulating the effects of typhoon-induced defoliation on forest dynamics using a process-based model in a subtropical forest. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 3503–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, K.; Sun, X.; Sun, H.; Xia, J. Modeling the typhoon disturbance effect on ecosystem carbon storage dynamics in a subtropical forest of China’s coastal region. Ecol. Model. 2021, 455, 109636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, P.N.; Yu, J.C.; Lai, Y.J. Soil Respiration Variation among Four Tree Species at Young Afforested Sites under the Influence of Frequent Typhoon Occurrences. Forests 2021, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneke-Fiegenbaum, F.; Santos, S.H.; Klemm, O.; Yu, J.; Chiang, P.; Lai, Y. Carbon Dioxide Fluxes of a Young Deciduous Afforestation Under the Influence of Seasonal Precipitation Patterns and Frequent Typhoon Occurrence. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG005996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Wang, X. Contrasting Rhizospheric and Heterotrophic Components of Soil Respiration during Growing and Non-Growing Seasons in a Temperate Deciduous Forest. Forests 2018, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, L. Quantifying Components of Soil Respiration and Their Response to Abiotic Factors in Two Typical Subtropical Forest Stands, Southwest China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phyo, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liang, N.; Myo, S.T.Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, K.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Soil Respiration Dynamics and Heterotrophic Respiration Sensitivity to Warming in a Subalpine Coniferous Forest and a Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forest in Southwest China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 4522–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; See, C.R.; Wang, H.; Cao, R.; Liang, G.; Zhang, A.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; et al. Soil fauna trophic multifunctionality mediates the release of elements from decomposing typhoon-generated leaf litter. Funct. Ecol. 2025, 39, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Ye, G.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Z.; Liu, L. Soil heterotrophic respiration in Casuarina equisetifolia plantation at different stand ages. J. For. Res. 2009, 20, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S.; Kongsurakan, P.; Yuttitham, M.; Hatano, R. Variations of soil properties and soil surface loss after fire in rotational shifting cultivation in Northern Thailand. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1213181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Kumar, P. Impacts of Landscape Evolution on Heterotrophic Carbon Loss in Intensively Managed Landscapes. Front. Water 2021, 3, 666278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, K.; Tsubota, H.; Yamamoto, M. Cycling of soil carbon in a Japanese red pine forest II. Changes occurring in the first year after a clear-felling. Ecol. Res. 1986, 1, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.; Kariyawasam Hetti Gamage, L.; Thapa, V.R. Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, Q.; Chen, F.; Jin, G.; Lu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Q. Characteristics and mechanisms of typhoon-induced decomposition of organic matter and its implication for climate change. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2023, 128, e2023JG007518. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Ji, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, L. A super typhoon disturbs organic contamination in agricultural soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Stefanski, A.; Eddy, W.C.; Bermudez, R.; Montgomery, R.A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Rich, R.L.; Reich, P.B. Soil respiration response to decade-long warming modulated by soil moisture in a boreal forest. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, M.; Tappe, W.; Kummer, S.; Vereecken, H. The influence of soil structure on heterotrophic respiration response to soil water content. In Proceedings of the 22nd EGU General Assembly, Online, 4–8 May 2020; p. 3365. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado, I.I.M. Diversity and Dynamics of Arthropods and Microbes, and Nutrient Release during Green Litter Decomposition in a Simulated Hurricane Experiment. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad del Turabo, Gurabo, Puerto Rico, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.N.; Cui, R.; Chi, C.L.; Dong, L.B.; Zhang, J.L. The effect of experimental warming on soil respiration and its components of Quercus mongolica forest. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 22, 10367–10376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Zhao, R.F.; Li, W.H. Impact of temperature and soil water content on soil respiration in temperate deserts, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2009, 33, 936–949. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.; Zhu, X.; Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Rui, Y.; Cui, X. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on soil respiration on the tibetan plateau. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, A.Y.; Narayanan, A.; Alster, C.J.; DeAngelis, K.M. Thermal adaptation of soil microbial growth traits in response to chronic warming. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0082523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.A.; Sharpe, J.; Van Beusekom, A.; Stankavich, S.; Matta Carmona, S.; Bithorn, J.E.; Shiels, A.B. Solar radiation and soil moisture drive tropical forest understory responses to experimental and natural hurricanes. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, R.T.; Ryan, M.G.; Birge, H.E.; Davidson, E.A.; Eliasson, P.E.; Evans, S.E.; Frey, S.D.; Giardina, C.P.; Hopkins, F.M.; Hyvnen, R.; et al. Temperature and soil organic matter decomposition rates—Synthesis of current knowledge and a way forward. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 3392–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Sun, B.; Chu, X.; Xing, Q.; Song, W.; Xia, J. Precipitation events reduce soil respiration in a coastal wetland based on four-year continuous field measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.X.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.J.; Ding, G. Response of soil respiration and Q10 to temperature and moisture in naturally regenerated and bare lands based on an 11-year observation period. Catena 2022, 208, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.X.; Li, H.J.; Li, J.J.; Xue, Y.T.; Ding, G.W.; Shao, H.B. Response of soil respiration to temperature and soil moisture: Effects of different vegetation types on a small scale in the eastern loess plateau of China. Plant Biosyst. 2013, 147, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Shen, G.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, L. Soil Respiration Components and Their Sensitivity to Temperature in Four Typical Forests along an Altitudinal Gradient in Shennongjia. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiong, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Analysis of Soil Respiration and Its Components in Castanopsis carlesii and Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 38, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Pang, D.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Chen, L. Response of soil respiration to short-term changes in precipitation and nitrogen addition in a desert steppe. J. Arid. Land 2023, 15, 1084–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Altitude (m) | Soil Type | Stand Age (Year) | Diameter at Breast Height (cm) | Tree Height (m) | Crown Density | Planting Density (Plant/ha) | Stand Density (Plant/ha) | Understory Vegetation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control plot | 33 | Coastal sandy soil | 10 | 13.46 ± 0.76 | 10.40 ± 0.88 | 0.87 | 1475 | 1401 | Bidens pilosa L. Waltheria indica L. Cyperus rotundus L. Spermacoce pusilla Wallich. |
| Typhoon disturbance plot | 30 | Coastal sandy soil | 10 | 14.17 ± 0.85 | 10.85 ± 0.71 | 0.90 | 1370 | 135 | Bidens pilosa L. Cyperusrotundus L. |
| T5/°C | W10/% | |
|---|---|---|
| Rs of Control plot | 0.524 ** | −0.36 |
| Rs of Typhoon disturbance | 0.889 ** | −0.58 * |
| Rh of Control plot | 0.517 * | −0.27 |
| Rh of Typhoon disturbance | 0.786 * | −0.61 ** |
| N | Fitting Equation Parameter α | Fitting Equation Parameter β | Q10 | R2 | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs of Control plot | 126 | 0.50 ± 0.26 | 0.064 ± 0.020 | 1.90 ± 1.22 | 0.62 | 227.49 | <0.001 |
| Rs of Typhoon disturbance | 126 | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 0.083 ± 0.014 | 2.29 ± 1.15 | 0.47 | 247.04 | <0.001 |
| Rh of Control plot | 84 | 0.35 ± 0.16 | 0.055 ± 0.018 | 1.73 ± 1.20 | 0.20 | 283.63 | <0.001 |
| Rh of Typhoon disturbance | 84 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 0.070 ± 0.015 | 2.01 ± 1.16 | 0.34 | 208.54 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, L.; Su, S.; Lin, Z.; Nong, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; Jia, J.; Chen, H. Short-Term Changes in the Soil Respiration of Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Severe Typhoon Disturbance. Forests 2025, 16, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091451
Du L, Su S, Lin Z, Nong S, Chen Y, Chen Z, Lei X, Jia J, Chen H. Short-Term Changes in the Soil Respiration of Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Severe Typhoon Disturbance. Forests. 2025; 16(9):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091451
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Limin, Shaofeng Su, Zhipan Lin, Shouqian Nong, Yiqing Chen, Zongzhu Chen, Xiangling Lei, Junting Jia, and Haihui Chen. 2025. "Short-Term Changes in the Soil Respiration of Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Severe Typhoon Disturbance" Forests 16, no. 9: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091451
APA StyleDu, L., Su, S., Lin, Z., Nong, S., Chen, Y., Chen, Z., Lei, X., Jia, J., & Chen, H. (2025). Short-Term Changes in the Soil Respiration of Casuarina equisetifolia L. Plantations After Severe Typhoon Disturbance. Forests, 16(9), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16091451






