Integrating a Newcomer: Niche Differentiation and Habitat Use of Eurasian Red Squirrels and Native Species in a Forest Reserve Under Human Disturbance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
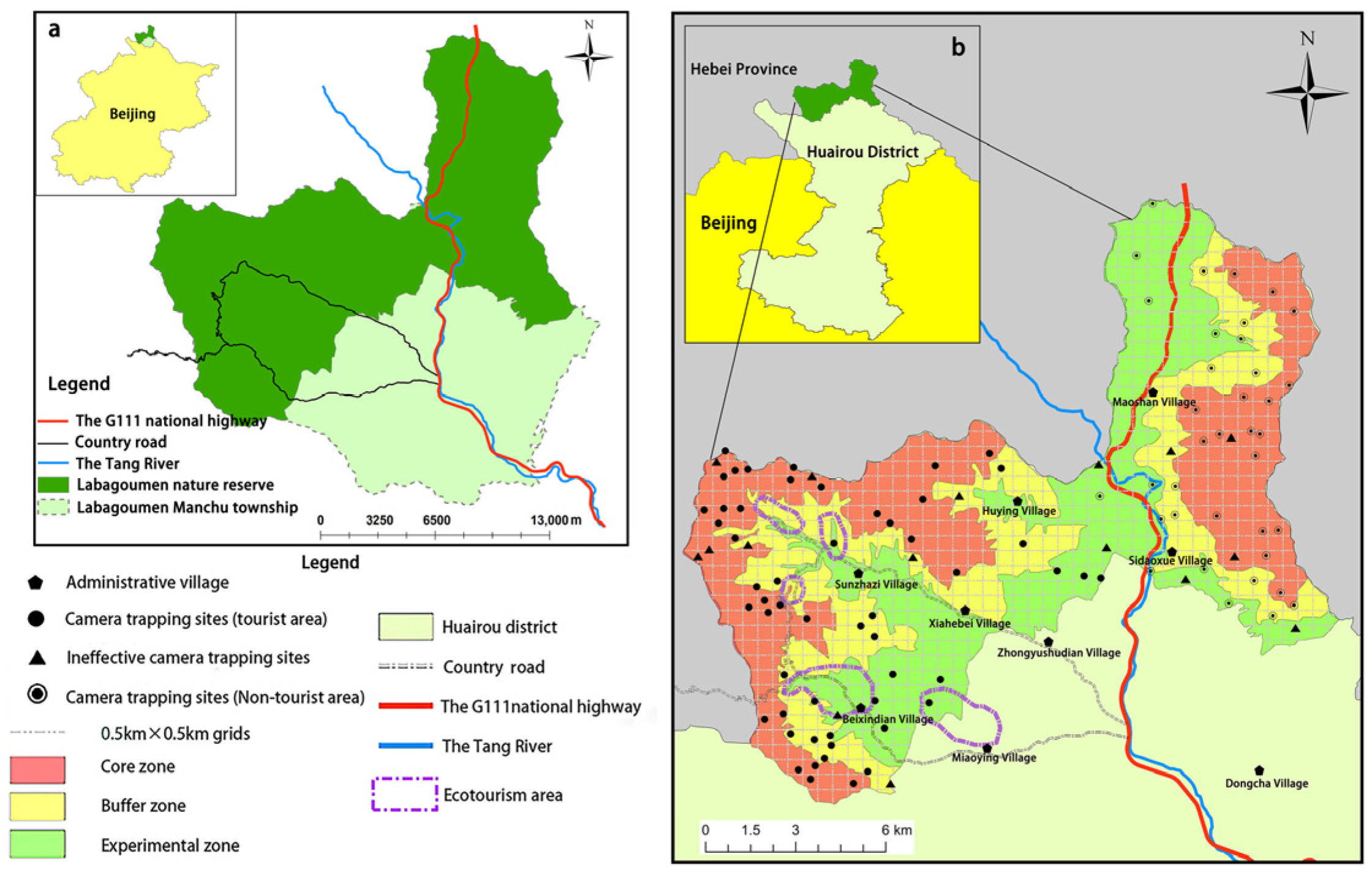
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Deployment of Camera Trapping
2.3. Data Filtering and Species Classification
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4.1. Species Abundance
2.4.2. Annual Activity Patterns
2.4.3. Temporal Niche Overlap Index
2.4.4. Daily Activity Patterns of Eurasian Red Squirrels with the Two Native Squirrel Species
2.4.5. Spatial Niche Breadth
2.4.6. Spatial Niche Differentiation and Community Structure
3. Results
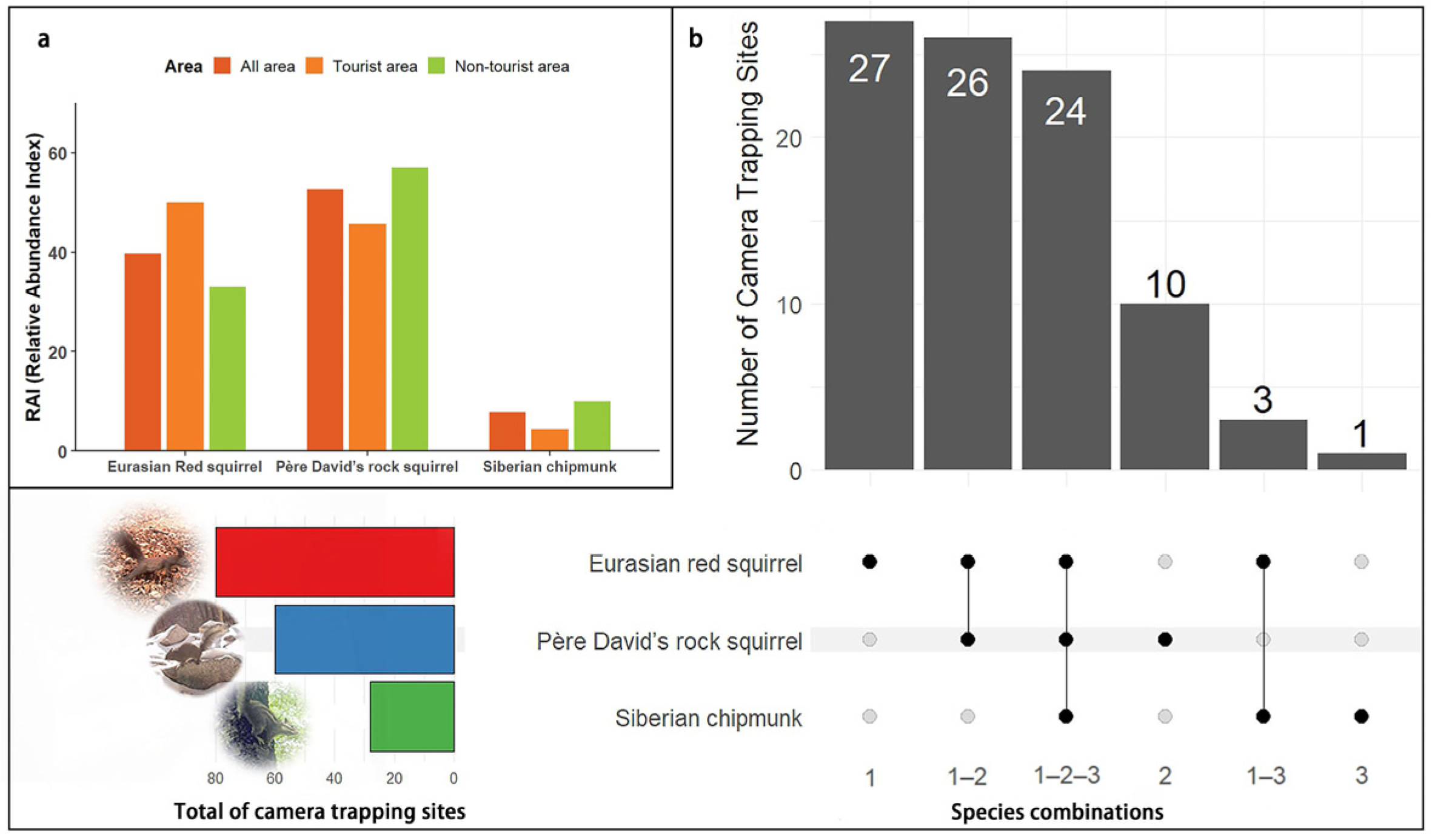
3.1. Overview of Camera Trapping Monitoring
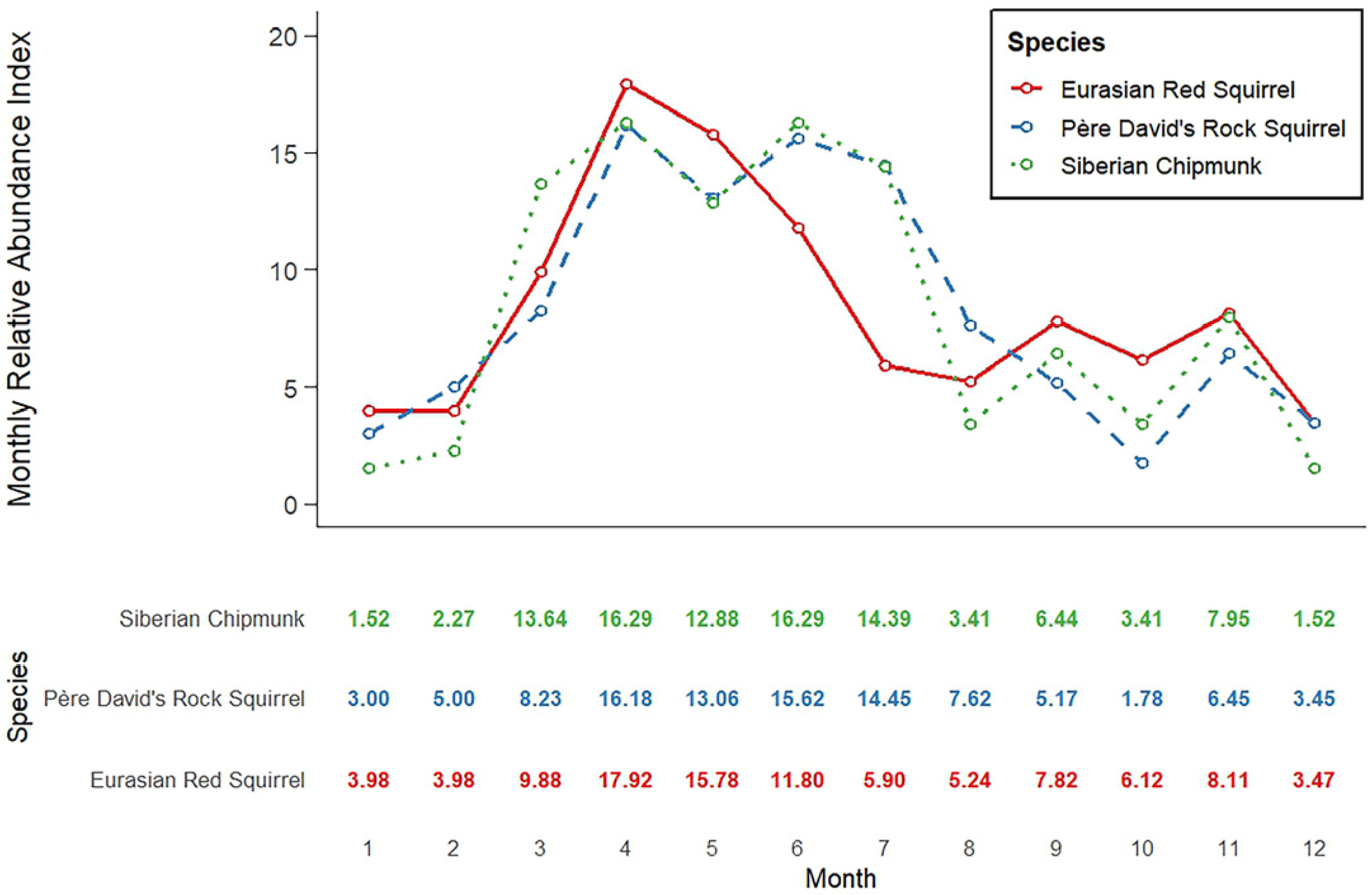
3.2. Analysis of Annual Activity Patterns
3.3. Analysis of the Temporal Niche Overlap Index
3.4. Daily Activity Rhythms of Three Squirrel Species
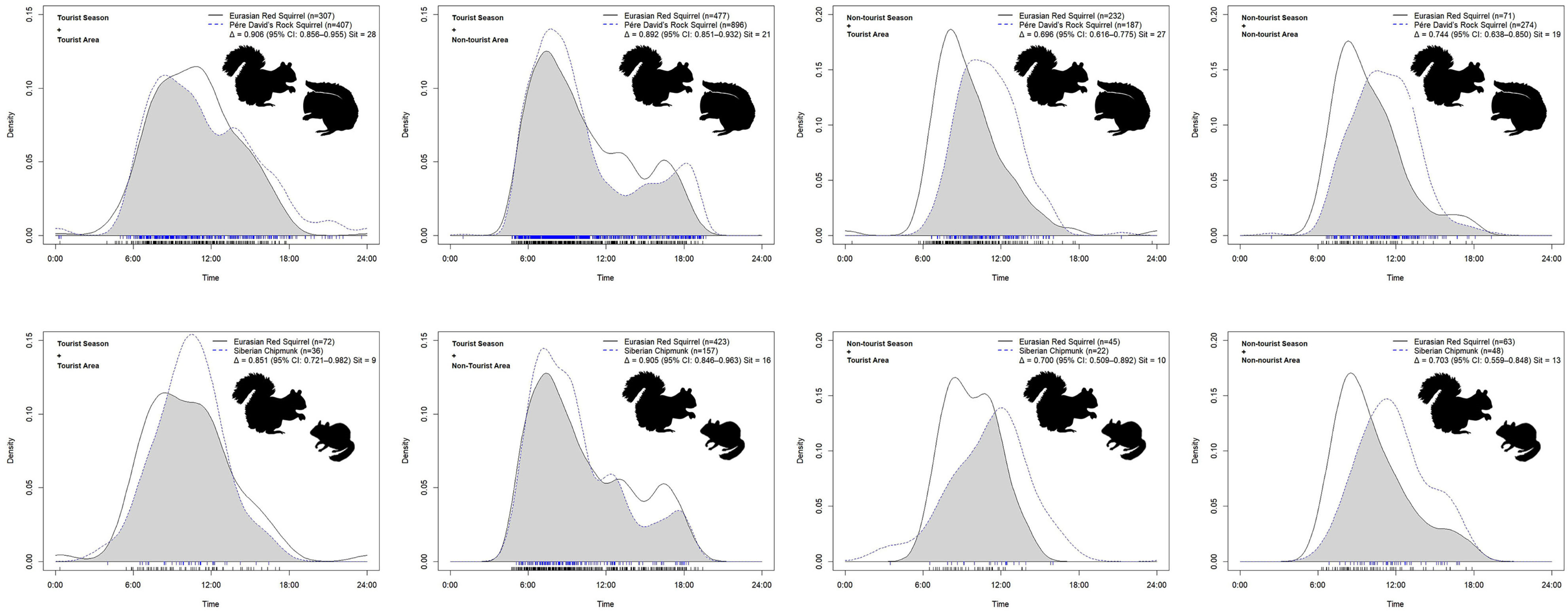
3.5. Overlap Between Eurasian Red Squirrels and Native Species Across Seasons and Areas
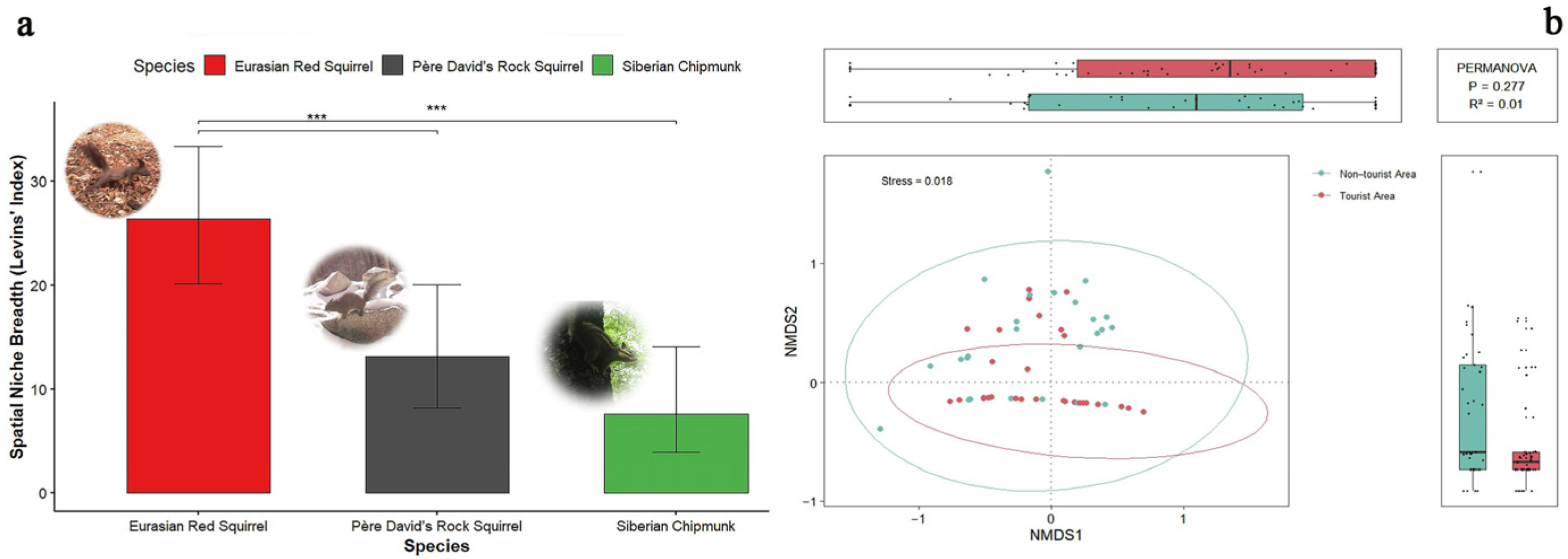
3.6. Differences in the Spatial Niche Breadth
3.7. Analysis of the Spatial Community Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. Competitive Advantages of Eurasian Red Squirrels in Forest Ecosystems
4.2. Interactive Effects of Human Disturbance and Competitive Exclusion
4.3. Temporal Niche Shifts of Native Squirrels in Response to the Eurasian Red Squirrel
4.4. Niche Compression
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salinas-Ramos, V.B.; Ancillotto, L.; Cistrone, L.; Nastasi, C.; Bosso, L.; Smeraldo, S.; Sánchez Cordero, V.; Russo, D. Artificial illumination influences niche segregation in bats. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; He, F.L. Advances in species coexistence theory. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronfeld-Schor, N.; Dayan, T. Partitioning of time as an ecological resource. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 34, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.X.; Yang, H.L.; Zhang, G.Q.; Yang, J.; Feng, X.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, Y.H.; Zhang, J.D.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C.Q. Temporal and spatial niche differentiation among three alpine Galliformes with sympatric distribution in the Wolong National Nature Reserve, Sichuan Province. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 22026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Luna, C.R.; Servin, J.; Valenzuela-Galván, D.; List, R. A matter of time: Temporal partitioning facilitates coexistence between coyotes (Canis latrans) and gray foxes (Urocyon cinereoargenteus) in temperate forests of Mexico. Mamm. Biol. 2024, 104, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, T.W. Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science 1974, 185, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Dahners, H.W. Resource utilization and environmental and spatio-temporal overlap of a hilltopping lycaenid butterfly community in the Colombian Andes. J. Insect Sci. 2009, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pynne, J.T.; Stober, J.M.; Edelman, A.J. Eastern Fox Squirrel (Sciurus niger) occupancy in fragmented montane longleaf pine forests. Southeast. Nat. 2020, 19, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnot, N.C.; Couriot, O.; Berger, A.; Cagnacci, F.; Ciuti, S.; De Groeve, J.E.; Gehr, B.; Heurich, M.; Kjellander, P.; Kröschel, M.; et al. Fear of the dark? Contrasting impacts of humans versus lynx on diel activity of roe deer across Europe. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murru, V.; Farris, E.; Santo, A.; Grillo, O.; Piazza, C.; Gaio, A.; Bacchetta, G.; Thompson, J.D. Niche Differentiation at Multiple Spatial Scales on Large and Small Mediterranean Islands for the Endemic Silene velutina Pourr. ex Loisel. (Caryophyllaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, O.; Jones, M.E.; Ruiz-Aravena, M.; Hamilton, D.G.; Comte, S.; Hamer, R.; Hamede, R.K.; Newton, J.; Bearhop, S.; McDonald, R.A. Human habitat modification, not apex scavenger decline, drives isotopic niche variation in a carnivore community. Oecologia 2024, 204, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Říha, M.; Vejřík, L.; Rabaneda-Bueno, R.; Jarić, I.; Prchalová, M.; Vejříková, I.; Šmejkal, M.; Blabolil, P.; Čech, M.; Draštík, V.; et al. Ecosystem, spatial and trophic dimensions of niche partitioning among freshwater fish predators. Mov. Ecol. 2025, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaniscotte, A.; Pleydell, D.; Raoul, F.; Quéré, J.P.; Jiamin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tiaoying, L.; Bernard, N.; Coeurdassier, M.; Delattre, P.; et al. Modelling and spatial discrimination of small mammal assemblages: An example from western Sichuan (China). Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, R.G.; Leite, Y.L.R.; Costa, L.P.; Rojas, D. Independent reversals to terrestriality in squirrels (Rodentia: Sciuridae) support ecologically mediated modes of adaptation. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhalap, S.G.; Istomin, A.V. Modeling Spatial Niches of Small Mammals Using the Example of Myodes glareolus in Mosaic Southern Taiga Forests. Biol. Bull. 2023, 50, S156–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelt, D.A.; Coppeto, S.A.; Van Vuren, D.H.; Sullivan, J.; Wilson, J.A.; Reid, N.M. Niche conservatism versus niche differentiation in sympatric chipmunks in the northern Sierra Nevada. J. Mammal. 2023, 104, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.J.; Klinger, R.C.; Hellwig, E.C.; Van Vuren, D.H. Niches of three sympatric montane ground-dwelling squirrels: Relative importance of climate, topography, and landcover. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingland, K.; Ward, S.J.; Bates, A.J.; Bremner-Harrison, S. A systematic review into the suitability of urban refugia for the Eurasian red squirrel Sciurus vulgaris. Mammal. Rev. 2021, 52, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T. A new record for the Sciurus vulgaris chiliensis in Beijing. Chin. J. Zool. 2008, 43, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.H. Comprehensive Scientific Survey Report of Beijing Songshan Nature Reserve; China Foresty Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.Y.; Cui, G.F.; Liu, R.Z.; Qu, H.; Huang, S.X.; Wu, J.G.; Fan, Y.Q. Distribution of wildlife along tourism routes in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 38, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, W.J.; Wang, D.; Fan, Y.Q.; Tang, X.M.; Bao, W.D. Activity Patterns of Mammals in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Sichuan J. Zool. 2017, 36, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, Q.C.; Cui, G.F.; Yang, N.; Zhen, C.Y.; Liu, D. Preliminary investigation of wildlife using camera traps along tourism routes in Beijing Baihua Mountain National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8324–8335. Available online: https://www.ecologica.cn/stxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=stxb201709191671 (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Ji, S.N.; Deng, H.Q.; Fan, P.L.; Liu, R.S.; Zhao, Z.P.; Xiao, N.W.; Liu, X.C. The monitoring research of Sciurinae species in Mentougou district, Beijing. Chin. J. Zool. 2020, 55, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioy, S.; Mori, E.; Wauters, L.A.; Bertolino, S. Weight operated see-saw feeding hoppers are not selective for red squirrels when greys are present. Mamm. Biol. 2016, 81, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, S.; Di Montezemolo, N.C.; Preatoni, D.G.; Wauters, L.A.; Martinoli, A. A grey future for Europe: Sciurus carolinensis is replacing native red squirrels in Italy. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzamuto, M.V.; Bisi, F.; Wauters, L.A.; Preatoni, D.G.; Martinoli, A. Interspecific competittion between alien Pallas’s squirrels and Eurasian red squirrels reduces density of the native species. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, W. Report on Mammal Survey of Beijing Songshan Nature Reserve. J. Beijing Teach. Coll (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 1991, 1, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Li, S.F.; Zhuang, G.L.; Cao, D.Q.; Chu, M.W.; Liu, X.F. Structure of rodent community in Lingshan Mountain area of Mentougou in Beijing. Cap. J. Public Health 2008, 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, D.Q.; Wu, J.G. Using infrared camera to survey wildlife in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.M.; Zhang, D.H.; Ma, Z.H.; Wu, T.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Bao, W.D. Camera trapping survey on ground-dwelling birds and mammals of spring and winter in Beijing Wulingshan Nature Reserve. Chin. J. Zool. 2016, 51, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Jin, K. Infrared-triggered camera technology application in the investigation of mammals in Beijing Wulingshan National Nature Reserve. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2016, 36, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.F.; Li, J.Q.; Niu, S.K.; Hu, D.F.; Lu, D.Z.; Wang, J.Z.; Meng, Z.X.; Li, D.; Yu, B.J.; Yu, B.J.; et al. The establishment and the functional areas’ division of Labagoumen reserve in Beijing. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2000, 22, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.F.; Xing, S.H. Comprehensive Scientific Investigation Report of Labagoumen Nature Reserve in Beijing; China Foresty Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.M.; Li, J.Q. Function of Eco-tourism to the Economy Development of Labagoumen Nature Reserve. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2007, 4, 567–571. Available online: http://www.stae.com.cn/jsygc/article/abstract/200704143?st=search (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Azevedo, F.C.; Lemos, F.G.; Freitas-Junior, M.C.; Rocha, D.G.; Azevedo, F.C.C. Puma activity patterns and temporal overlap with prey in a human-modified landscape at southeastern brazil. J. Zool. 2018, 305, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Fu, M.X.; Qi, D.W.; Song, X.Q.; Wei, W.; Yang, W.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.S.; Liu, J.B.; Ma, R.; et al. Camera-trapping survey of wild mammals and birds in Daxiangling Nature Reserve. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, K.M.; Hojnowski, C.E.; Carter, N.H.; Brashares, J.S. The influence of human disturbance on wildlife nocturnality. Science 2018, 360, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.F.; Li, B.Q.; Liang, D.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, L.X.; Yang, J.W.; Luo, X. Effect of anthropogenic disturbance on Lady Amherst’s pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae) activity. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 21484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qi, X.H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.G.; Cai, B. Activity Rhythm of Lophura nycthemera and Muntiacus reevesi in Wuyishan National Park and Its Influencing Factors. J. Hainan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 36, 65–72. Available online: https://hsxblk.hainnu.edu.cn/ch/reader/key_query.aspx (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- O’Brien, T.G.; Kinnaird, M.F.; Wibisono, H.T. Crouching tigers, hidden prey: Sumatran tiger and prey populations in a tropical forest landscape. Anim. Conserv. 2003, 6, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.T.; Xie, Y. A Guide to the Mammals of China; Hunan Education Press: Changsha, China, 2009; pp. 31–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.W.; Yang, Q.S.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, X.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Li, B.G.; Yang, G.; Li, M.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; et al. Catalogue of mammals in China (2021). Acta Theriol. Sin. 2021, 41, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Xiao, W.H.; Xiao, Z.S. Limitations of relative abundance indices calculated from camera-trapping data. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, 27, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.F.; Liu, X.H.; Cai, Q.; He, X.B.; Melissa, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, X.M. The application of infrared camera in mammal research in Guanyinshan Nature Reserve, Shaanxi. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2012, 32, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, T.W. The Anolis Lizards of Bimini: Resource Partitioning in a Complex Fauna. Ecology 1968, 49, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.Y. Principles of Animal Ecology, 3rd ed.; Beijing Normal University Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 334–336. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.W.; Ma, J.Z.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, Z. Research on Autumn Time Niche of Five Rodents in Forests Ecosystem. Chin. J. Zool. 2008, 43, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hou, R.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gu, X.D.; Qi, D.W. Study on the Temporal Niche Characteristics and Overlaps of Carnivores and Their Preys Using Infrared Cameras in Xinlong County. Sichuan J. Zool. 2021, 40, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathne, J.A.; Haug, T.; Lydersen, C. Prey preference andniche overlap of ringed seals (Phoca hispida) and harp seals (Phoca groenlandica) in the Barents Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 194, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowcliffe, M. Activity: Animal Activity Statistics. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=activity (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Ridout, M.S.; Linkie, M. Estimating overlap of daily activity patterns from camera trap data. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2009, 14, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, M.; Ridout, M. Overlap: Estimates of Coefficient of Overlapping for Animal Activity Patterns. 2014. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=overlap (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Lynam, A.J.; Jenks, K.E.; Tantipisanuh, N.; Chutipong, W.; Ngoprasert, D.; Steinmetz, R.; Sukmasuang, R.; Jr, L.I.G.; Cutter, P.; Kitamura, S.; et al. Terrestrial Activity patterns of wild cats from camera-trapping. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2013, 61, 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Z.S.; Cao, H.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhang, Z.R.; Teng, L.W. Comparing the activity pattern of red deer (Cervus alashanicus) and blue sheep (Pseudois nayaur) using camera-traps in Helan Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 9365–9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.S.; SenGupta, A. Topics in Circular Statistics; Section 7.5; World Scientific Press: Singapore, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Agnostinelli, C.; Lund, U. Circular Statistics. Package ‘Circular’. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/circular/circular.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations. (MPB-2); Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, L. Bootstrap Confidence intervals for the Shannon biodiversity index: A simulation study. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2004, 9, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, J.X.; Xu, M.Q.; Li, M. Bootstrap Method and its Application in Biology. Sichuan J. Zool. 2010, 29, 638–641. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, M.; Burton, A.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Krishnamurthy, R. Understanding the distribution and fine-scale habitat selection of mesocarnivores along a habitat quality gradient in western Himalaya. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cully, J.F.; Collinge, S.K.; VanNimwegen, R.E.; Ray, C.; Johnson, W.C.; Thiagarajan, B.; Conlin, D.B.; Holmes, B.E. Spatial variation in keystone effects: Small mammal diversity associated with black-tailed prairie dog colonies. Ecography 2010, 33, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. PERMANOVA: A FORTRAN Computer Program for Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J. 2015 Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Commu-Nities in R: Vegan Tutorial. R Package Version 1.7. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Bertolino, S. Animal trade and non-indigenous species introduction: The world-wide spread of squirrels. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.B.; Hughes, N.K. A review of the evidence for potential impacts of black rats (Rattus rattus) on wildlife and humans in Australia. Wildl. Res. 2012, 39, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonesi, L.; MacDonald, D.W. Impact of Released Eurasian Otters on a Population of American Mink: A Test Using an Experimental Approach. Oikos 2004, 106, 9–18. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/3548390 (accessed on 2 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bonesi, L.; Chanin, P.; Macdonald, D.W. Competition between Eurasian otter Lutra lutra and American mink Mustela vison probed by niche shift. Oikos 2004, 106, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, W.; Fu, B.Q. The Mammal Fauna of Beijing; Beijing Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 164–178. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Pereira, R.; Araújo, M.S.; Souza, F.L.; Ingram, T. Competition and resource breadth shape niche variation and overlap in multiple trophic dimensions. Proc. Biol. Scie 2019, 286, 20190369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Feijó, A.; Cheng, J.; Du, Y.; Ge, D.; Xia, L.; Yang, Q. Explaining mammalian abundance and elevational range size with body mass and niche characteristics. J. Mammal. 2021, 102, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorboy, D.M.; Calède, J.J.M.; Chavez, A.S. Craniodental divergence associated with bite force between hybridizing pine squirrels (Tamiasciurus). PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.R. Body size, energy metabolism and lifespan. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurnell, J.; Wauters, L.A.; Lurz, P.W.W.; Tosi, G. Alien species and interspecific competition: Effects of introduced eastern grey squirrels on red squirrel population dynamics. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.K.Y.; Uchida, K.; von Bayern, A.M.P.; Koizumi, I. Characteristics of urban environments and novel problem-solving performance in Eurasian red squirrels. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20202832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzamuto, M.V.; Merrick, M.J.; Bisi, F.; Koprowski, J.L.; Wauters, L.; Martinoli, A. Timing of Resource Availability Drives Divergent Social Systems and Home Range Dynamics in Ecologically Similar Tree Squirrels. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Wen, Y.X. Rodents of China; Fudan University Press: Shanghai, China, 1995; pp. 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.W. Coexistence Mechanisms of Five Rodent Species in Major Forest Regions of Northeast China. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.S. Study on Nutritional Adaptation Strategies of the Red Squirrel (Sciurus Vulgaris Mantchuricus). Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Hu, J.C. Study of Spatial Memory in Seed-caching Sciurotamias davidianus. Sichuan J. Zool. 2013, 32, 658–663. Available online: http://www.scdwzz.com/thesisDetails?columnId=29112746&Fpath=home&index=0&lang=zh (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Wei, S.; Liang, Z.L.; Teng, W.; Jing, Y.; Yu, M.C.; Rong, K. Food Composition and Feeding Preference of Chipmunks in a Broadleaved Red Pine Forest. Chin. J. Wildl. 2023, 44, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucherini, M.; Reppucci, J.I.; Walker, R.S.; Villalba, M.L.; Wurstten, A.; Gallardo, G.; Iriarte, A.; Villalobos, R.; Perovic, P. Activity Pattern Segregation of Carnivores in the High Andes. J. Mammal. 2009, 90, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Shi, X.Y.; Hu, Q.; Feng, X.; Jin, S.L.; Cheng, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, M.; Li, S. Spatiotemporal relationships between snow leopard (Panthera uncia) and red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in Qionglai Mountains, Sichuan Province. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2021, 41, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, L.A.; Lurz, P.W.W.; Santicchia, F.; Romeo, C.; Ferrari, N.; Martinoli, A.; Gurnell, J. Interactions between native and invasive species: A systematic review of the red squirrel-gray squirrel paradigm. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1083008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, E.; Zozzoli, R.; Mazza, G. Coming in like a wrecking-ball: Are native Eurasian red squirrels displacing invasive Siberian chipmunks? A study from an urban park. Urban. Ecosyst. 2018, 21, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, E.E.; Goodenough, A.E. Effects of visitor numbers on captive European red squirrels (Sciurus vulgaris) and impacts on visitor experience. Zoo Biol. 2017, 36, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauze-Gryz, D.; Gryz, J.; Brach, M. Spatial organization, behaviour and feeding habits of red squirrels: Differences between an urban park and an urban forest. J. Zool. 2021, 315, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bitetti, M.S.; De Angelo, C.; Di Blanco, Y.E.; Paviolo, A. Niche partitioning and species coexistence in a Neotropical felid assemblage. Acta Oecol. 2010, 36, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Cao, G.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Quan, R.C. Macaca leonina has a wider niche breadth than sympatric M. mulatta in a fragmented tropical forest in southwest China. Am. J. Primatol. 2020, 82, e23100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.X.; Sun, N.; Gu, B.J.; He, R.C.; Liu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Niche Differentiation of Sympatric Green Peafowl (Pavo muticus) and Silver Pheasant (Lophura nycthemera). Sichuan J. Zool. 2021, 40, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Ma, J.Z.; Song, Y.L.; Zeng, Z.G. Comparative Studies on the Seasonal Changes of Some Eco-physiological Indices of Red Squirrels, Sciurus vulgaris mantchuricus, in Northeast Forestry Region, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2002, 22, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Viviano, A.; Mori, E.; Fattorini, N.; Mazza, G.; Lazzeri, L.; Panichi, A.; Strianese, L.; Mohamed, W.F. Spatiotemporal Overlap between the european brown hare and its potential predators and competitors. Animals 2021, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy-Reis, M.B.; Iwakami, V.H.; Estevo, C.A.; Setz, E.Z.F. Temporal and dietary segregation in a neotropical small-felid assemblage and its relation to prey activity. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Kang, M.J.; Deng, W.H. Foraging habitat selection by sympatric Temminck’s tragopan and blood pheasant during breeding season in southwestern China. Biodivers. Sci. 2008, 16, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Ji, L.; Pang, D.; Zhou, M.; Cheng, Y.; Pu, F.; Zhang, B. The Spatial Relationship Between Two Sympatric Pheasant Species and Various Human Disturbance Activities. Animals 2025, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.W.; Rota, C.T.; Forrester, T.; Baker-Whatton, M.C.; McShea, W.J.; Schuttler, S.G.; Millspaugh, J.J.; Kays, R. Urbanization focuses carnivore activity in remaining natural habitats, increasing species interactions. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, N.A.; Stenglein, J.L.; Pauli, J.N.; Zuckerberg, B. Human disturbance compresses the spatiotemporal niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2206339119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sévêque, A.; Gentle, L.K.; López-Bao, J.V.; Yarnell, R.W.; Uzal, A. Human disturbance has contrasting effects on niche partitioning within carnivore communities. Biol.Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2020, 95, 1689–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.W.; Ridlon, A.D.; Gaynor, K.M.; Gaines, S.D.; Stier, A.C.; Halpern, B.S. Ecological impacts of human-induced animal behaviour change. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Sites (All) | Photos (All) | RAI (All) | Sites (Tourist) | Photos (Tourist) | RAI (Tourist) | Sites (Non-Tourist) | Photos (Non-Tourist) | RAI (Non-Tourist) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian red squirrel | 80 | 1356 | 39.66 | 48 | 688 | 50.00 | 32 | 688 | 33.03 |
| Pére David’s rock squirrel | 60 | 1799 | 52.62 | 35 | 610 | 45.66 | 25 | 1189 | 57.08 |
| Siberian chipmunk | 28 | 264 | 7.72 | 10 | 58 | 4.43 | 18 | 206 | 9.89 |
| Season Type | Area | Species Pair | Δ (95% CI) | Overlap Level | Watson Value | p-Value Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All years | All Area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.947 (0.924–0.970) | High | 0.148 | p > 0.10 |
| All years | All Area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.903 (0.849–0.956) | High | 0.216 | p < 0.05 |
| Tourist season | All Area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.893 (0.858–0.928) | High | 0.551 | p < 0.001 |
| Tourist season | All Area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.910 (0.856–0.963) | High | 0.1985 | p < 0.05 |
| Non-tourist season | All Area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.709(0.649–0.769) | Moderate | 1.650 | p < 0.001 |
| Non-tourist season | All area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.708 (0.589–0.828) | Moderate | 0.415 | p < 0.001 |
| Tourist season | Tourist area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.906 (0.856–0.956) | High | 0.236 | p < 0.05 |
| Tourist season | Tourist area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.851 (0.721–0.982) | High | 0.103 | p > 0.10 |
| Tourist season | Non-tourist area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.892 (0.851–0.932) | High | 0.295 | p < 0.01 |
| Tourist season | Non-tourist area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.905 (0.846–0.963) | High | 0.170 | p > 0.05 |
| Non-tourist season | Tourist area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.696 (0.616–0.775) | Moderate | 1.080 | p < 0.001 |
| Non-tourist season | Tourist area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.700 (0.509–0.892) | Moderate | 0.207 | p < 0.05 |
| Non-tourist season | Non-tourist area | Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 0.744 (0.638–0.850) | Moderate | 0.427 | p < 0.001 |
| Non-tourist season | Non-tourist area | Eurasian red Squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 0.703 (0.559–0.848) | Moderate | 0.318 | p < 0.01 |
| Species Comparison | Bi (±95% CI) | Difference in Bi (±95% CI) | Wilcoxon Test p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian red squirrel vs. Pére David’s rock squirrel | 26.4 (20.2–33.3) vs. 13.1 (8.20–20.1) | 13.3(3.51–20.03) | p < 0.001 *** |
| Eurasian red squirrel vs. Siberian chipmunk | 26.4 (20.2–33.3) vs. 7.63 (3.88–14.0) | 18.77 (9.95–26.42) | p < 0.001 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Cui, G. Integrating a Newcomer: Niche Differentiation and Habitat Use of Eurasian Red Squirrels and Native Species in a Forest Reserve Under Human Disturbance. Forests 2025, 16, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081360
Zhang W, Liu X, Zhang T, Cui G. Integrating a Newcomer: Niche Differentiation and Habitat Use of Eurasian Red Squirrels and Native Species in a Forest Reserve Under Human Disturbance. Forests. 2025; 16(8):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081360
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wuyuan, Xiaoxiao Liu, Tong Zhang, and Guofa Cui. 2025. "Integrating a Newcomer: Niche Differentiation and Habitat Use of Eurasian Red Squirrels and Native Species in a Forest Reserve Under Human Disturbance" Forests 16, no. 8: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081360
APA StyleZhang, W., Liu, X., Zhang, T., & Cui, G. (2025). Integrating a Newcomer: Niche Differentiation and Habitat Use of Eurasian Red Squirrels and Native Species in a Forest Reserve Under Human Disturbance. Forests, 16(8), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081360




