Unraveling Interactive Effects of Climate, Hydrology, and CO2 on Ecological Drought with Interpretable Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
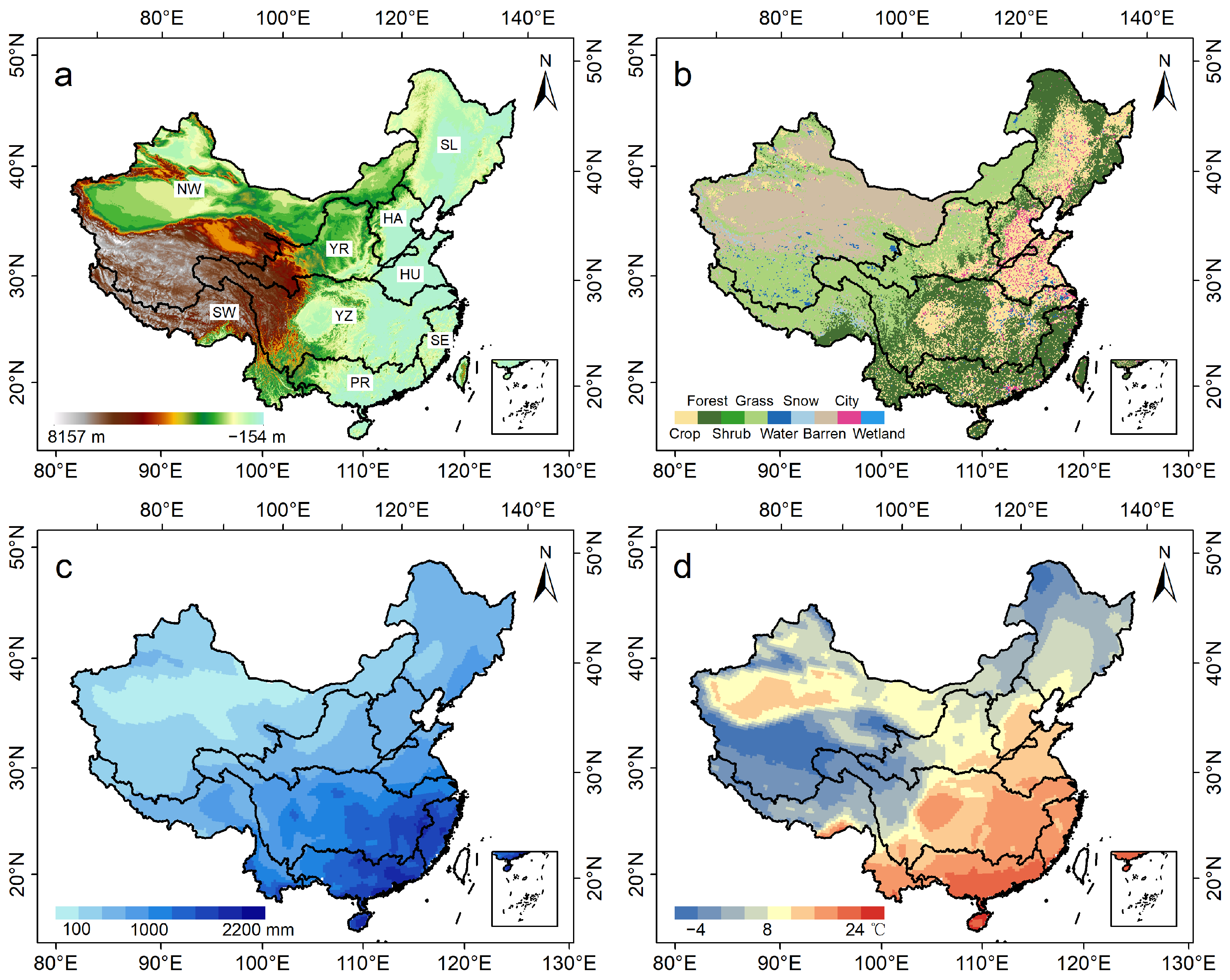
2.1. Study Area
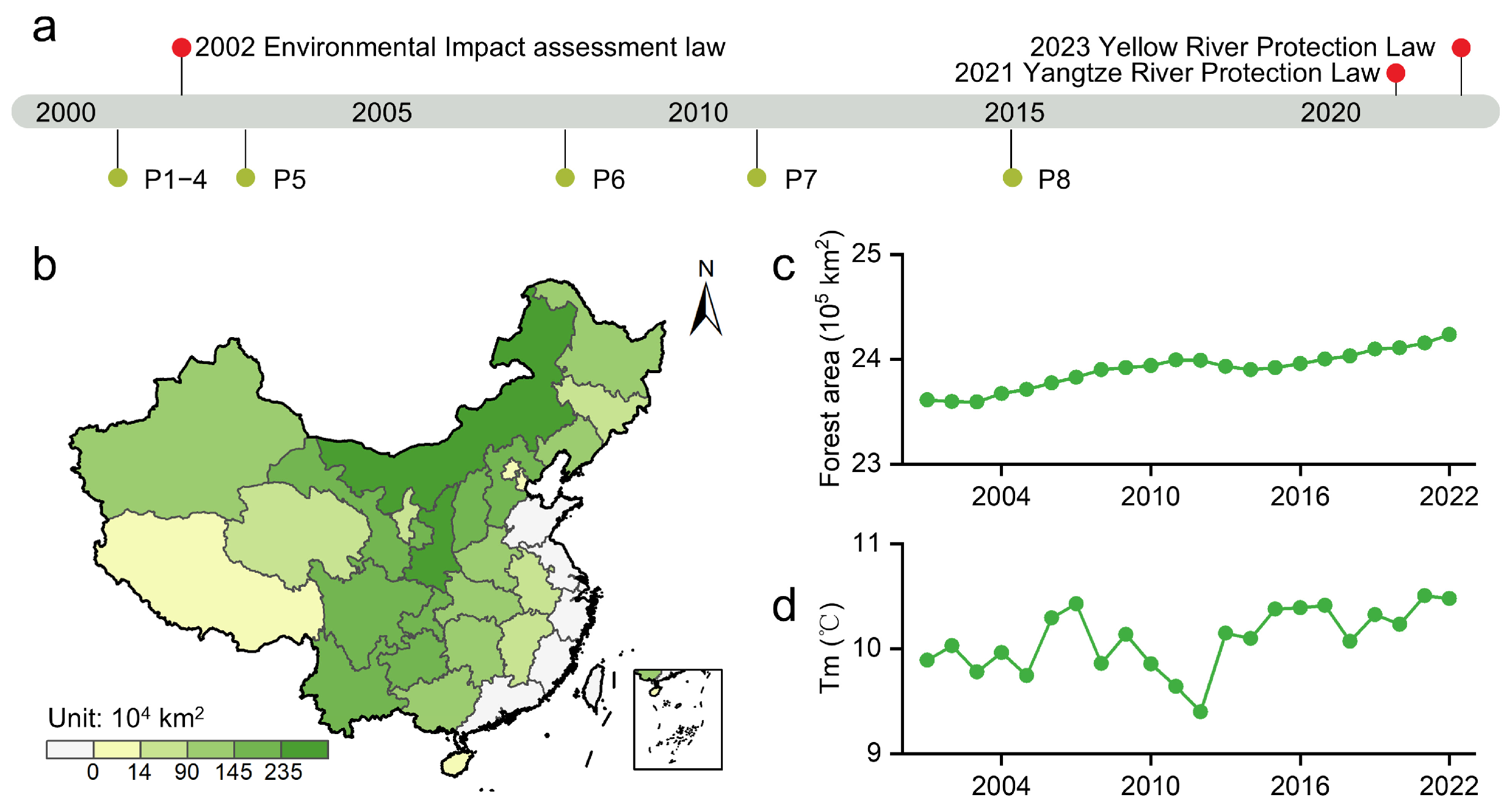
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Land Cover and SIF Dataset
2.2.2. Climate and Hydrological Dataset
2.2.3. CO2 Dataset
2.3. Spatial Trend Analysis
2.4. Characteristics of Ecological Drought
2.5. Interpretable Machine Learning (IML) Model
2.5.1. Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM)
2.5.2. Model Verification
2.5.3. SHAP Additive Explanations
3. Results
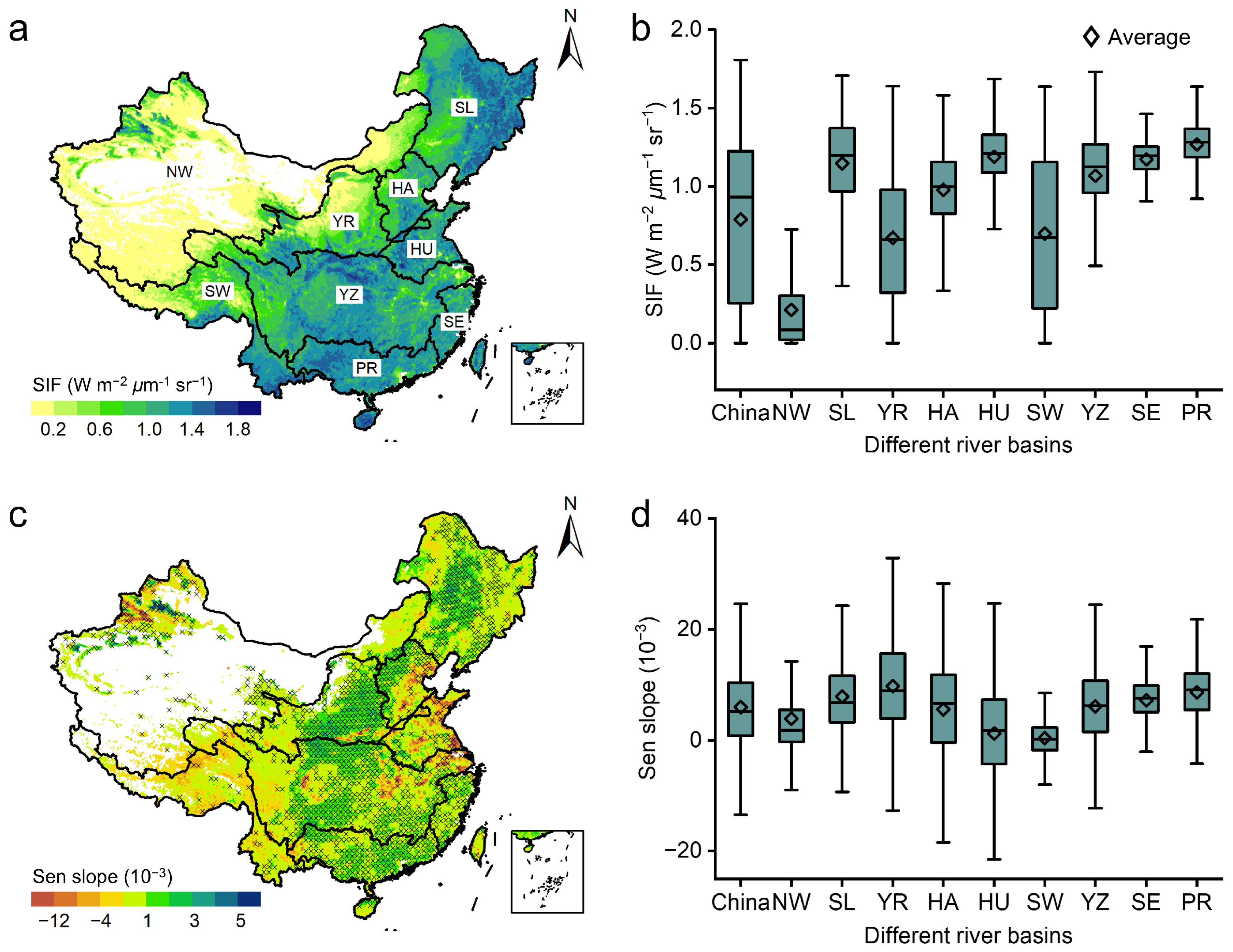
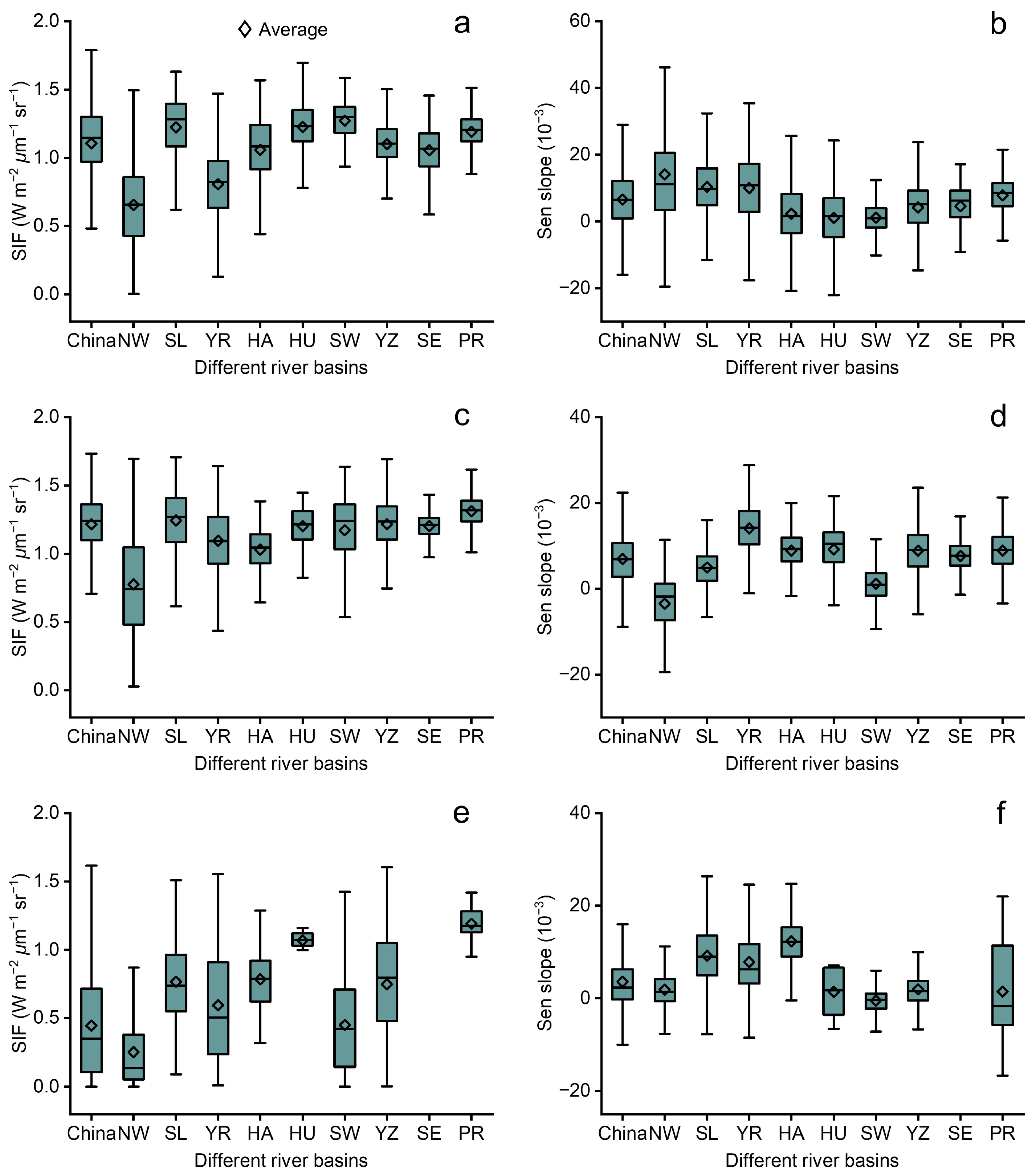
3.1. Spatiotemporal Analysis of SIF
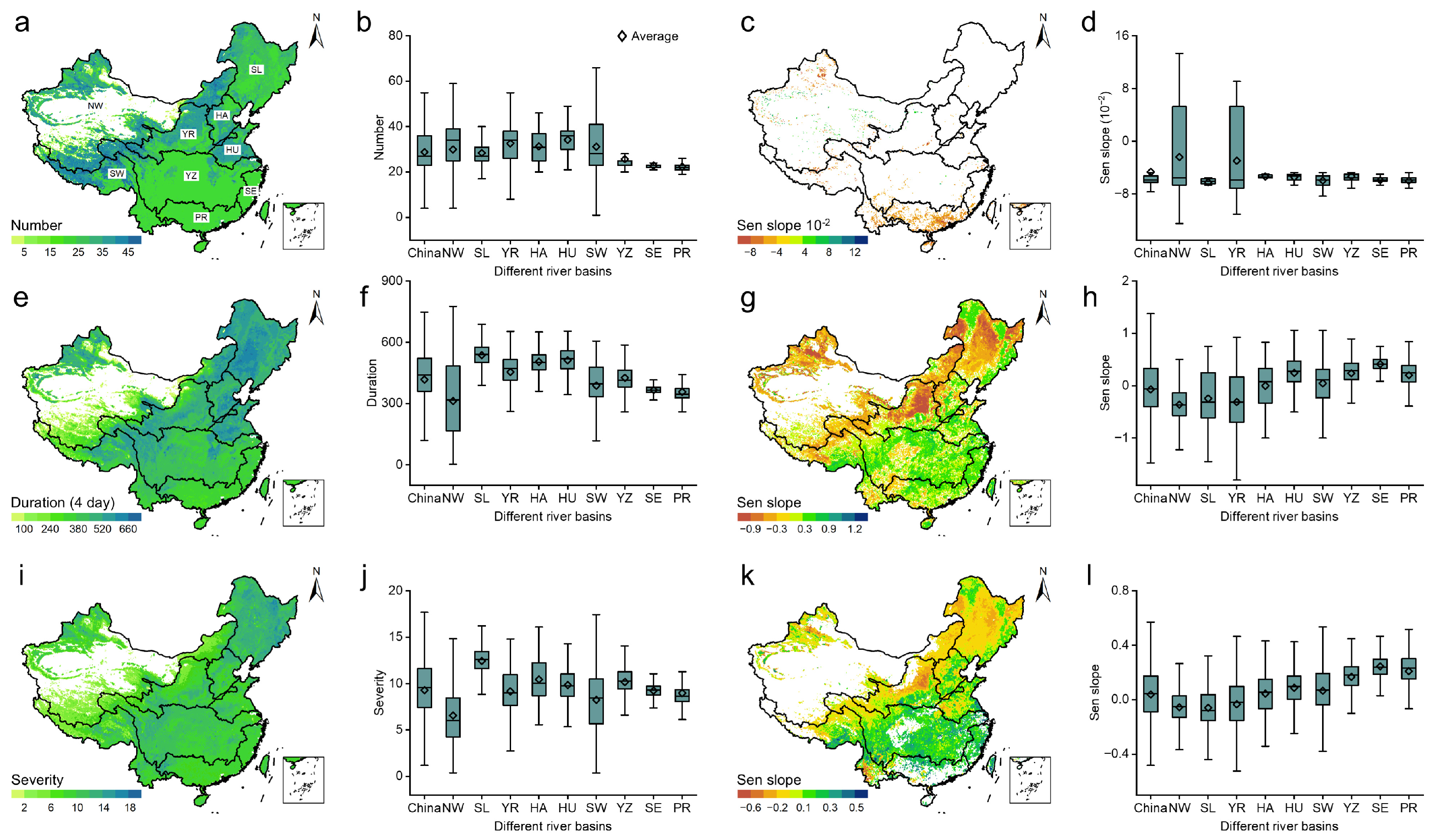
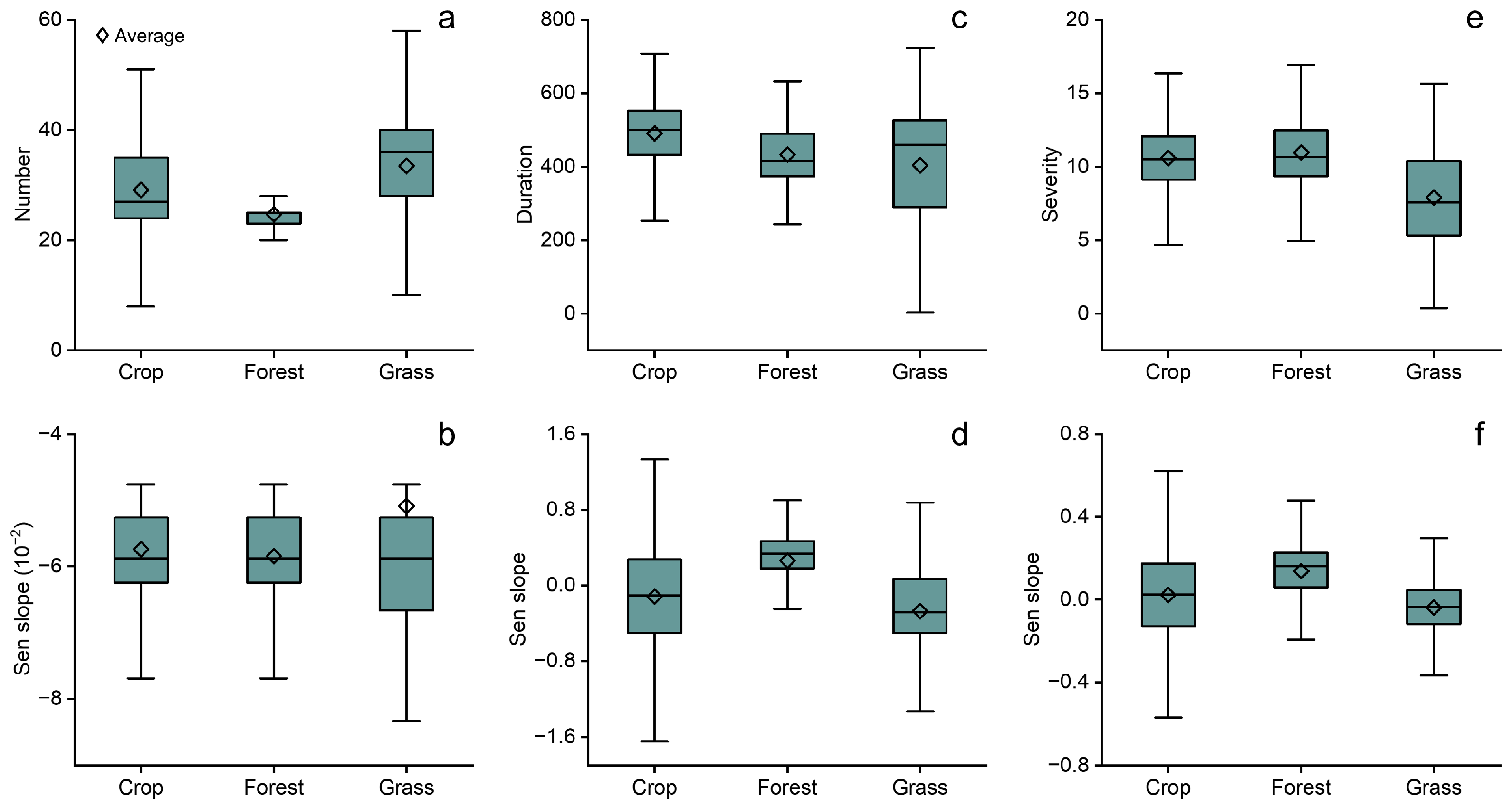
3.2. Evolution Characteristics of Ecological Drought
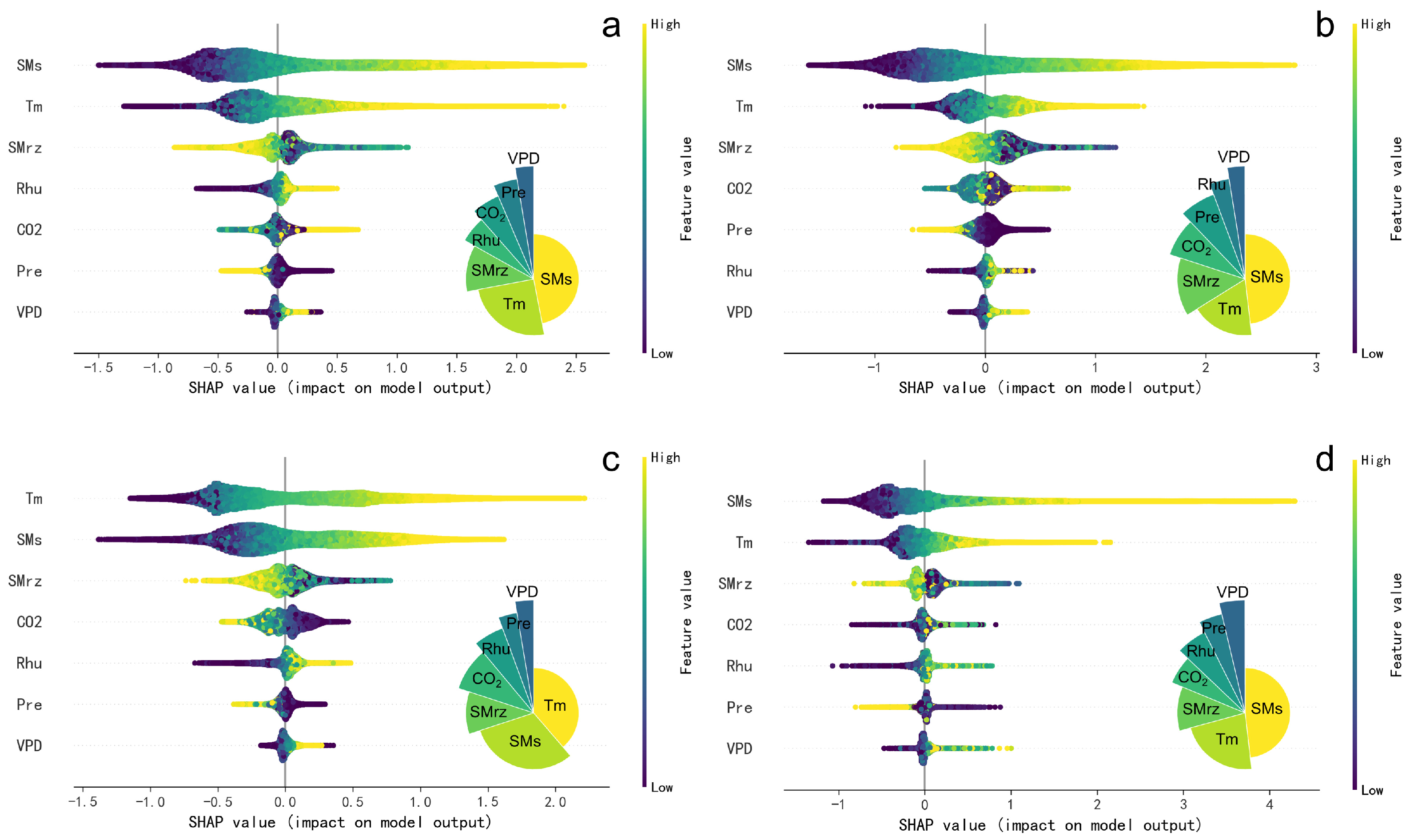
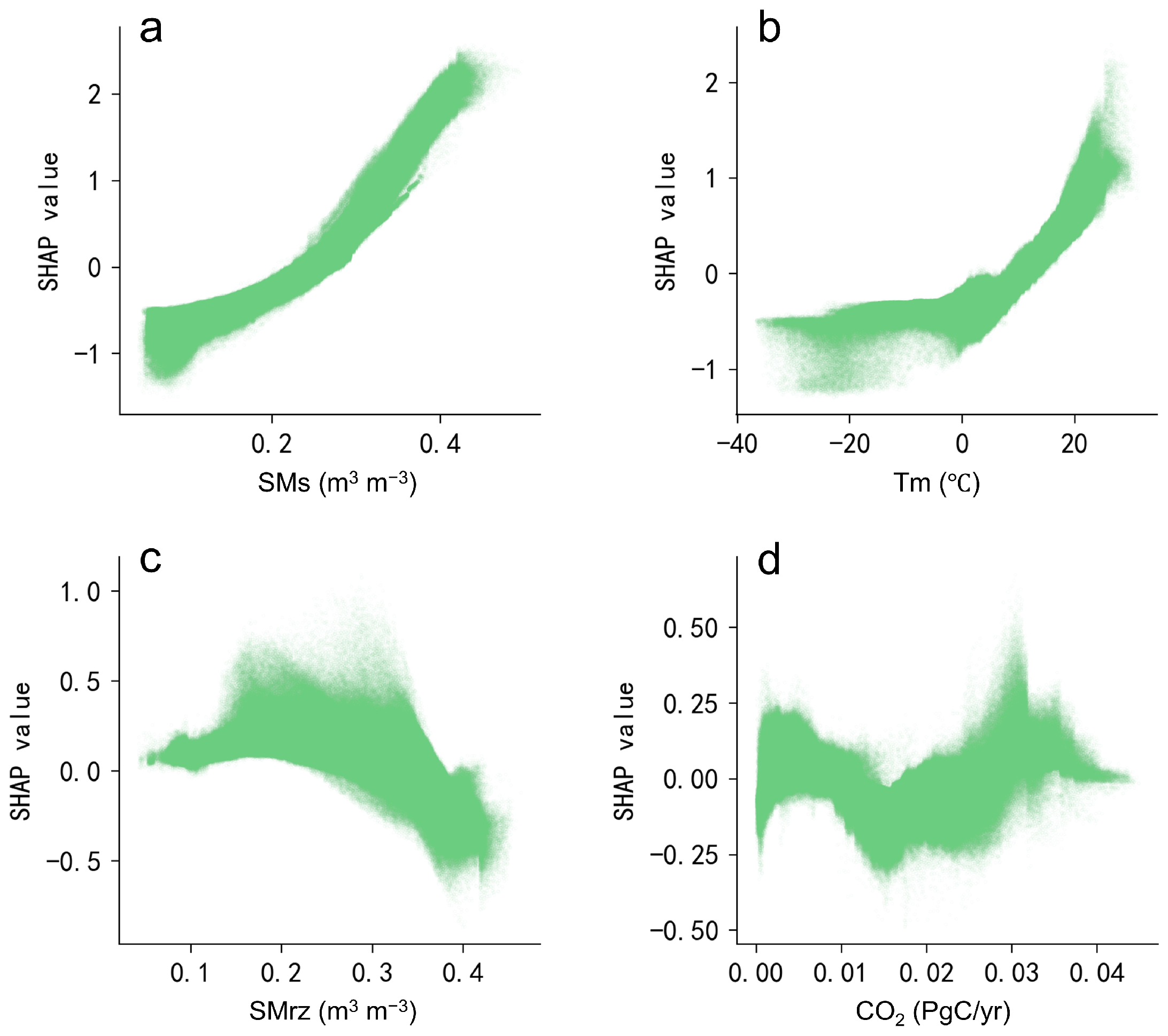
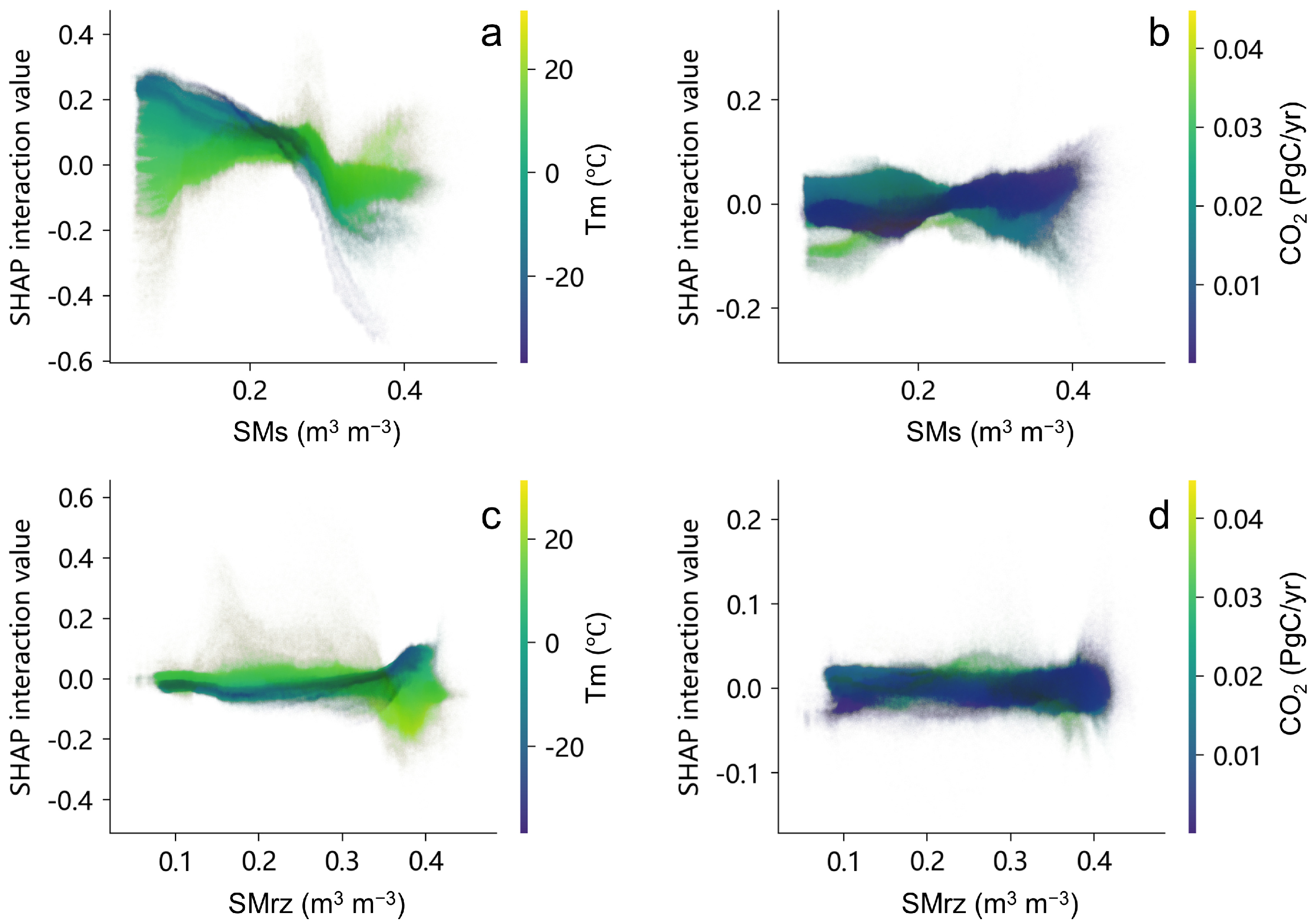
3.3. Interpretable Driving Mechanism of Ecological Drought
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of SIF Changes
4.2. Rationality of the Evolution Characteristics of Ecological Drought
4.3. Driving Mechanism of Ecological Drought
4.4. Uncertainties and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gampe, D.; Zscheischler, J.; Reichstein, M.; O’Sullivan, M.; Smith, W.K.; Sitch, S.; Buermann, W. Increasing impact of warm droughts on northern ecosystem productivity over recent decades. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.C.; Hao, F.H.; Xia, Y.L.; Feng, S.F.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.S.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y. Compound droughts and hot extremes: Characteristics, drivers, changes, and impacts. Earth Sci. Rev. 2022, 235, 104241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Wilkins, K.D.; Holdrege, M.C.; Wilfahrt, P.; Collins, S.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Sala, O.E.; Dukes, J.S.; Phillips, R.P.; Yahdjian, L.; et al. Extreme drought impacts have been underestimated in grasslands and shrublands globally. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2309881120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, A.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Sitch, S.; Pongratz, J.; Fan, L.; Wigneron, J.P.; Weber, U.; Reichstein, M.; Fu, Z.; et al. Direct and seasonal legacy effects of the 2018 heat wave and drought on European ecosystem productivity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, Y.; Felfelani, F.; Satoh, Y.; Boulange, J.; Burek, P.; Gädeke, A.; Gerten, D.; Gosling, S.N.; Grillakis, M.; Gudmundsson, L.; et al. Global terrestrial water storage and drought severity under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.C.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Ciais, P.; Babst, F.; Guo, W.C.; Zhang, C.C.; Magliulo, V.; Pavelka, M.; Liu, S.M.; et al. Differentiating drought legacy effects on vegetation growth over the temperate Northern Hemisphere. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, C.; Rowhani, P.; Ramankutty, N. Influence of extreme weather disasters on global crop production. Nature 2016, 529, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.B.; Slater, L.; Gu, L.; Liao, Z.; Guo, S.L.; Gentine, P. Global Increases in Lethal Compound Heat Stress: Hydrological Drought Hazards Under Climate Change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Wang, X.H.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Lian, X.; He, Y.; Bjerke, J.W.; Chen, A.P.; Ciais, P.; Tommervik, H.; et al. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.C.; Piao, S.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Huang, M.T.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Arneth, A.; et al. Greening of the Earth and its drivers. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungmin, O.; Park, S.K. Global ecosystem responses to flash droughts are modulated by background climate and vegetation conditions. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiqi, S.S.J.; Hong, E.M.; Nam, W.H.; Kim, T. Review: An integrated framework for understanding ecological drought and drought resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.L.; Su, X.L.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, G.X. A novel index for ecological drought monitoring based on ecological water deficit. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Sur, C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Ecological drought monitoring through fish habitat-based flow assessment in the Gam river basin of Korea. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crausbay, S.D.; Betancourt, J.; Bradford, J.; Cartwright, J.; Dennison, W.C.; Dunham, J.; Enquist, C.A.F.; Frazier, A.G.; Hall, K.R.; Littell, J.S.; et al. Unfamiliar Territory: Emerging Themes for Ecological Drought Research and Management. One Earth 2020, 3, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, J.B.; Schlaepfer, D.R.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Palmquist, K.A. Robust ecological drought projections for drylands in the 21st century. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3906–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lai, H.X.; Li, Y.B.; Feng, K.; Tian, Q.Q.; Guo, W.X.; Zhang, W.J.; Di, D.Y.; Yang, H.B. Dynamic variations of terrestrial ecological drought and propagation analysis with meteorological drought across the mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crausbay, S.D.; Ramirez, A.R.; Carter, S.L.; Cross, M.S.; Hall, K.R.; Bathke, D.J.; Betancourt, J.L.; Colt, S.; Cravens, A.E.; Dalton, M.S.; et al. Defining Ecological Drought for the Twenty-First Century. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 2543–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Wang, M.H.; Ren, L.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhou, L.; Cui, H.; Xu, C.Y. An integrated approach for identification and quantification of ecological drought in rivers from an ecological streamflow perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovach, R.P.; Dunham, J.B.; Al-Chokhachy, R.; Snyder, C.D.; Letcher, B.H.; Young, J.A.; Beever, E.A.; Pederson, G.T.; Lynch, A.J.; Hitt, N.P.; et al. An Integrated Framework for Ecological Drought across Riverscapes of North America. Bioscience 2019, 69, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, N.; Cravens, A.E.; Cross, M.S.; Crausbay, S.; Ramirez, A.; McEvoy, J.; Zoanni, D.; Bathke, D.J.; Hayes, M.; Carter, S.; et al. Planning for ecological drought: Integrating ecosystem services and vulnerability assessment. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lai, H.X.; Men, R.Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Li, Y.B.; Qu, Y.P.; Feng, K.; Guo, W.X.; Jiang, Y.Z. Dynamic Variations of Agricultural Drought and Its Response to Meteorological Drought: A Drought Event-Based Perspective. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2024JD041044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, H.; Huang, J.J.; Yu, J.X.; Yuan, Y.B. A framework for identifying propagation from meteorological to ecological drought events. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Ficklin, D.L.; Jiao, W.Z.; Denham, S.O.; Wood, J.D.; Brunsell, N.A.; Matamala, R.; Cook, D.R.; Wang, L.X.; Novick, K.A. Earlier Ecological Drought Detection by Involving the Interaction of Phenology and Eco-Physiological Function. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2022EF002667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Zolin, C.A.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Hain, C.R.; Semmens, K.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Gao, F.; Otkin, J.A.; Tetrault, R. The Evaporative Stress Index as an indicator of agricultural drought in Brazil: An assessment based on crop yield impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chang, J.X.; Guo, A.J.; Zhou, K.; Yang, G.B.; Zou, D.J. Ecological drought evolution characteristics under different climatic regions in the Yangtze River basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Jiang, S.H.; Ren, L.L.; Guo, J.Y.; Zhong, F.; Du, S.P.; Cui, H.; He, M.; Duan, Z. Three-dimensional ecological drought identification and evaluation method considering eco-physiological status of terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D. Propagation in the Drought Cascade: Observational Analysis Over the Continental US. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR032608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, S.M.; Bradford, J.B.; Hultine, K.R. An Integrative Ecological Drought Framework to Span Plant Stress to Ecosystem Transformation. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Alonso, L.; Gómez-Chova, L.; Amorós-López, J.; Vila, J.; Moreno, J. Estimation of solar-induced vegetation fluorescence from space measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L08401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentine, P.; Alemohammad, S.H. Reconstructed Solar-Induced Fluorescence: A Machine Learning Vegetation Product Based on MODIS Surface Reflectance to Reproduce GOME-2 Solar-Induced Fluorescence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3136–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.J.; Feng, Z.Q.; Chen, H.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Xiong, T.; Xiao, J.F.; Li, X. Evaluation of photosynthesis estimation from machine learning-based solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence downscaling from canopy to leaf level. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehr, S.; Gerlein-Safdi, C.; Falco, N.; Seibert, P.O.; Chou, C.W.; Albert, L.; Keenan, T.F. Quantifying Seasonal and Diurnal Cycles of Solar-Induced Fluorescence With a Novel Hyperspectral Imager. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.A.; Li, X.; Han, G.; Xiao, J.F.; Ma, X.; Gong, W. Monitoring drought impacts on crop productivity of the US Midwest with solar-induced fluorescence: GOSIF outperforms GOME-2 SIF and MODIS NDVI, EVI, and NIRv. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.Y.; Bai, X.Y.; Zhao, C.W.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.B.; Luo, G.J.; Wu, L.H.; Chen, F.; Li, C.J.; Ran, C.; et al. Spring photosynthetic phenology of Chinese vegetation in response to climate change and its impact on net primary productivity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 342, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Elakkiyaa, T.L.; Sarkar, A.; Dutta, D. Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence Yield Holds the Potential for Drought Early Warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL113419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.A.; Wang, Q.M.; Muneer, S.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Baig, F.; Naz, F. Probabilistic approach to monitoring vegetation water stress using solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence data. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 315, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.G. Large-scale diurnal responses of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) to varying heat and water stresses: Implications for monitoring SIF variations from satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 324, 114748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.Z.; Chang, Q.; Wang, L.X. The Sensitivity of Satellite Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence to Meteorological Drought. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Gao, L.; Ye, Y.Q.; Sun, X.F.; Connor, J.D.; Crossman, N.D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wu, J.G.; He, C.Y.; Yu, D.Y.; et al. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Meadows, M.E. Ecological restoration for sustainable development in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Jiang, S.H.; Ren, L.L.; Yan, Y.Q.; Zhu, Q.A.; Yang, X.L.; Fang, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.Y. Identifying cumulative transition effects of large-scale vegetation restoration on climate and hydrology via a dynamically separating framework. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 366, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Joiner, J.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Zhou, S.; Gentine, P. A global spatially contiguous solar-induced fluorescence (CSIF) dataset using neural networks. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 5779–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.J.; Sweet, L.B.; Blougouras, G.; Brenning, A.; Li, W.T.; Reichstein, M.; Denzler, J.; Wei, S.G.; Yu, G.; Huang, F.N.; et al. How Interpretable Machine Learning Can Benefit Process Understanding in the Geosciences. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani-Sadat, Y.; Safari, A.; Nasseri, M.; Homayouni, S. A novel explainable PSO-XGBoost model for regional flood frequency analysis at a national scale: Exploring spatial heterogeneity in flood drivers. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 130753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Ma, X.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, F.C.; Yu, X.; Zeng, W.Z. Light Gradient Boosting Machine: An efficient soft computing model for estimating daily reference evapotranspiration with local and external meteorological data. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 225, 105758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.I. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.X.; Wang, R.Y.; Li, X.T. Temporal and spatial evolution simulation and attribution analysis of vegetation photosynthesis over the past 21 years based on satellite SIF data: A case study from Asia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.Y.; Tang, Q.H.; Rayburg, S. Climate change impacts on meteorological, agricultural and hydrological droughts in China. Glob. Planet. Change 2015, 126, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.; Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A. Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.L.; Ma, J.; Yan, P.; Tian, F.; Peñuelas, J.; Rao, M.P.; Fu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.H. Planted Forests in China Have Higher Drought Risk Than Natural Forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.L.; Su, X.L.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.J. Estimating propagation probability from meteorological to ecological droughts using a hybrid machine learning copula method. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.L.; Su, X.L.; Qu, Y.P.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, T.; Chu, J.D.; Hu, X.X. Determining the response of ecological drought to meteorological and groundwater droughts in Northwest China using a spatio-temporal matching method. J. Hydrol. 2024, 633, 130753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Williams, C.A.; Kauwe, M.G.; Schwalm, C.R.; Medlyn, B.E. Patterns of post-drought recovery are strongly influenced by drought duration, frequency, post-drought wetness, and bioclimatic setting. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 4630–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.C.; Rademacher, T.; Huang, X.R.; Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Prolonged drought duration, not intensity, reduces growth recovery and prevents compensatory growth of oak trees. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 326, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classification | China | Corp | Forest | Grass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 0.832 | 0.797 | 0.869 | 0.764 |
| Test | 0.829 | 0.778 | 0.864 | 0.705 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Guo, J.; Tang, P.; Xu, C.-Y. Unraveling Interactive Effects of Climate, Hydrology, and CO2 on Ecological Drought with Interpretable Machine Learning. Forests 2025, 16, 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081325
Zhu Y, Jiang S, Ren L, Guo J, Tang P, Xu C-Y. Unraveling Interactive Effects of Climate, Hydrology, and CO2 on Ecological Drought with Interpretable Machine Learning. Forests. 2025; 16(8):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081325
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yongwei, Shanhu Jiang, Liliang Ren, Jianying Guo, Pengcheng Tang, and Chong-Yu Xu. 2025. "Unraveling Interactive Effects of Climate, Hydrology, and CO2 on Ecological Drought with Interpretable Machine Learning" Forests 16, no. 8: 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081325
APA StyleZhu, Y., Jiang, S., Ren, L., Guo, J., Tang, P., & Xu, C.-Y. (2025). Unraveling Interactive Effects of Climate, Hydrology, and CO2 on Ecological Drought with Interpretable Machine Learning. Forests, 16(8), 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081325






