Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Soil Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C:N:P Stoichiometry in Karst Peak-Cluster Depressions in Southwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Total C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometry
3.2. Soil Microbial C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometry
3.3. Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
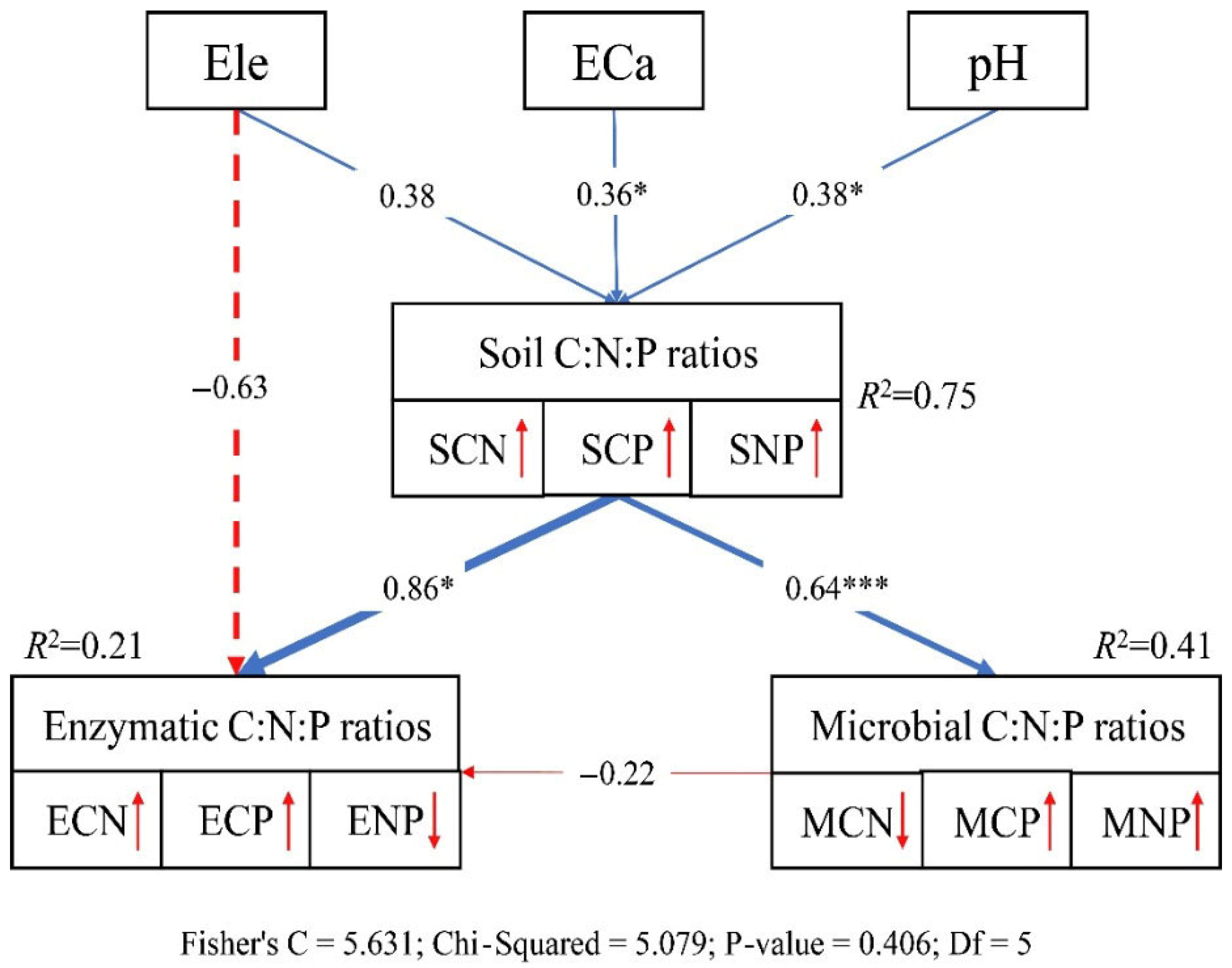
3.4. Drivers of Soil Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C-N-P Contents and Stoichiometry
4. Discussion
4.1. Elevational Patterns of Soil Total C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometry
4.2. Elevational Patterns of Soil Microbial Biomass Stoichiometry
4.3. Elevation Patterns of Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
4.4. Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometry, and Environmental Associations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| BG | β-1,4-glucosidase |
| DBH | Diameter at Breast Height |
| ECa | Soil Exchangeable Calcium |
| EMg | Soil Exchangeable Magnesium |
| Ele | Elevation |
| ECN, ECP, ENP | Enzymatic C:N, C:P, and N:P Ratios, respectively |
| MBC | Microbial Biomass Carbon |
| MBN | Microbial Biomass Nitrogen |
| MBP | Microbial Biomass Phosphorus |
| MCN, MCP, MNP | Microbial Biomass C:N, C:P, and N:P Ratios, respectively |
| NAG + LAP | β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase and L-leucine aminopeptidase |
| RDA | Redundancy Analysis |
| SOC | Soil Organic Carbon |
| SWC | Soil Water Content |
| SR | Species Richness |
| SD | Slope Degree |
| SEM | Structural Equation Modeling |
| SCN, SCP, SNP | Soil C:N, C:P, and N:P Ratios, respectively |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
Appendix A
| Elevation (m) | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | Slope Degree (◦) | Slope Position | Canopy Cover (%) | Bare Rock (%) | Diameter at Breast Height (cm) | Species Richness | Dominant Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 106°49′05.41″~106°56′28.95″ | 22°21′10.09″~22°31′10.40″ | 5.67 ± 0.92 | Depression | 60.00 | 40.00 | 5.60 ± 0.37 | 31.67 ± 5.13 | Litsea variabilis var. oblonga; Catunaregam spinosa; Antidesma bunius; Ficus hispida; Leea indica; Strophioblachia fimbricalyx |
| 300 | 106°56′53.81″~106°57′12.49″ | 22°27′05.32″~22°27′26.82″ | 19.33 ± 1.48 | Downslope | 75.00 | 76.67 | 9.01 ± 1.25 | 19.00 ± 2.28 | Cephalomappa sinensis; Cleistanthus petelotii; Hydnocarpus hainanensis; Excentrodendron tonkinense; Ardisia thyrsiflora |
| 400 | 106°57′00.90″~106°57′04.08″ | 22°27′13.15″~22°27′21.11″ | 34.00 ± 1.32 | Mid-slope | 85.00 | 73.33 | 5.39 ± 0.49 | 24.67 ± 1.65 | Hydnocarpus hainanensis; Cephalomappa sinensis; Orophea polycarpa; Cleistanthus sumatranus; Pterospermum truncatolobatum; Cleistanthus petelotii |
| 500 | 106°58′06.29″~106°58′10.03″ | 22°27′12.82″~22°27′18.38″ | 27.67 ± 0.92 | Upper slope | 65.00 | 58.33 | 3.89 ± 0.09 | 38.67 ± 2.57 | Boniodendron minus; Cephalomappa sinensis; Diospyros siderophylla; Lysidice rhodostegia; Tirpitzia sinensis; Viburnum triplinerve |
| Response Factor | Predictor | PCA1 |
|---|---|---|
| Soil C:N:P ratios | SCP | 0.986 *** |
| SNP | 0.917 *** | |
| SCN | 0.778 *** | |
| Cumulative (%) | 80.583 | |
| Microbial C:N:P ratios | MNP | 0.938 *** |
| MCP | 0.797 *** | |
| MCN | −0.486 *** | |
| Cumulative (%) | 58.335 | |
| Enzymatic C:N:P ratios | ECN | 0.999 *** |
| ECP | 0.815 *** | |
| ENP | −0.649 *** | |
| Cumulative (%) | 69.423 |
| Category | Factor | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | SCN | 10.44 ± 0.56 | 7.92 ± 0.98 |
| SCP | 53.61 ± 7.33 | 32.12 ± 4.25 | |
| SNP | 4.80 ± 0.52 | 3.94 ± 0.41 | |
| Microbe | MCN | 3.84 ± 1.22 | 8.16 ± 3.24 |
| MCP | 47.34 ± 16.28 | 27.42 ± 12.57 | |
| MNP | 12.23 ± 3.12 | 6.42 ± 2.17 | |
| Enzyme | ECN | 1.03 ± 0.05 | 0.91 ± 0.06 |
| ECP | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | |
| ENP | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ± 0.03 |
| Elevation (m) | SWC (%) | pH | ECa (mg·kg−1) | EMg (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 43.29 ± 3.13 a | 7.59 ± 0.10 a | 22.09 ± 0.83 b | 1.05 ± 0.07 b |
| 300 | 39.06 ± 2.61 a | 7.16 ± 0.03 b | 22.58 ± 1.34 b | 1.16 ± 0.02 ab |
| 400 | 37.83 ± 2.66 a | 7.09 ± 0.06 b | 24.62 ± 0.97 b | 1.21 ± 0.04 a |
| 500 | 36.50 ± 1.53 a | 6.86 ± 0.22 b | 31.78 ± 3.91 a | 1.21 ± 0.04 a |
References
- Elser, J.J.; Sterner, R.W.; Gorokhova, E.; Fagan, W.F.; Markow, T.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Harrison, J.F.; Hobbie, S.E.; Odell, G.M.; Weider, L.W. Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Ecological stoichiometry: The biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Nature 2003, 423, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Enquist, B.J. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: Metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Duan, Y.; Yao, B.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects microbial metabolic limitations in different desert types of northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 161929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Peng, W.; Du, H.; Xu, Q. Responses of soil and microbial C:N:P stoichiometry to vegetation succession in a karst region of Southwest China. Forests 2019, 10, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Qin, X. Stoichiometry of soil microbial biomass carbon and microbial biomass nitrogen in China′s temperate and alpine grasslands. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 83, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hou, E.; Veen, G.F.; Ellwood, M.D.F.; Dijkstra, P.; Sui, X.; Zhang, S.; Wen, D.; Chu, C. Soil microbial biomass increases along elevational gradients in the tropics and subtropics but not elsewhere. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, J.-D. Microbial extracellular enzymes in biogeochemical cycling of ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; He, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhao, N.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the North–South Transect in eastern China (NSTEC). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Mao, Q.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Resource limitation of soil microbes in karst ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, B.; Zeng, H. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects the unique habitat of karst tiankeng and helps to alleviate the P-limitation of soil microbes. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ning, J. The characteristics of soil C, N and P and stoichiometric ratios as affected by land-use in a karst area, Southwest China. Land 2023, 12, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, F. Soil stoichiometry modulates effects of shrub encroachment on soil carbon concentration and stock in a subalpine grassland. Iforest-Biogeosciences For. 2020, 13, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhou, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, W.; Hou, Y.; Tan, C.; Yang, G.; Ding, F. Stoichiometric characteristics of leaf, litter and soil during vegetation succession in Maolan National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sheng, M. Responses of soil C, N, and P stoichiometrical characteristics, enzyme activities and microbes to land use changes in Southwest China Karst. Forests 2023, 14, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yang, R.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Hu, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, K. Lithologic control of soil C:N:P stoichiometry across a climatic gradient in southwest China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feudis, M.; Cardelli, V.; Massaccesi, L.; Lagomarsino, A.; Fornasier, F.; Westphalen, D.J.; Cocco, S.; Corti, G.; Agnelli, A. Influence of altitude on biochemical properties of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forest soils. Forests 2017, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; Yongkuan, C. Using ecological stoichiometric characteristics to inform grassland management in the karst desertification area. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sheng, M.; Bai, Y.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Li, H. Altitude dependence of soil ecological stoichiometry and enzyme activities in a karst region of Southwest China. J. Forest Environ. 2022, 42, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Xue, X.; Zou, S.; Zhang, Q. Effects of elevation on ecological stoichiometry of plant leaves, litter, and soils in Pseudotsuga sinensis forest in the karst mountain region, Southwest China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3582–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Yu, Y.H. Soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus fractions and response to microorganisms and mineral elements in Zanthoxylum planispinum ‘Dintanensis’ plantations at different altitudes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhou, M.; Xu, N. Soil enzyme activity and microbial carbon metabolism along an altitudinal gradient in grasslands of karst mountain. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Qi, X.; Fu, Z. Karst landscapes of China: Patterns, ecosystem processes and services. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2743–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, X.; Zhang, W.; Hu, P.; Sun, M.; Wang, K. Comparison of bacterial and fungal diversity and network connectivity in karst and non-karst forests in southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-J.; Liu, Q.-M.; Zhang, D.-F. Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: Geomorphology, land use, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Li, Q.Y.; Luo, G.J.; Bai, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xie, J.; Yang, G.B. Discussing the genesis of karst rocky desertification research based on the correlations between cropland and settlements in typical peak-cluster depressions. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Mallik, A.U.; Huang, F.; Xiang, W.; Ding, T.; Wen, S.; Lu, S.; Li, D.; He, Y.; et al. Topographic species–habitat associations of tree species in a heterogeneous tropical karst seasonal rain forest, China. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 10, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, B.; Xiang, W.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Mallik, A.U.; Ding, T.; Huang, F.; Lu, S.; et al. Conspecific and heterospecific crowding facilitate tree survival in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 481, 118700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Chen, T.; Lu, F.; Xiang, W.; Huang, F.; Liu, S.; et al. Analysis of the leaf litter decomposition rate and nutrient content in a karst seasonal rainforest in southwest Guangxi. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2022, 43, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Bai, K.; Xiang, W.; Li, X. C, N and P stoichiometric characteristics of soil and litterfall for six common tree species in a northern tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodivers. Sci. 2017, 25, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Lv, S.; Ning, S.; Zeng, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, B. Leaf nutrient concentrations associated with phylogeny, leaf habit and soil chemistry in tropical karst seasonal rainforest tree species. Plant Soil 2019, 434, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, T.; Guo, Y.; Li, X. Revealing the relative importance among plant species, slope positions, and soil types on rhizosphere microbial communities in northern tropical karst and non-karst seasonal rainforests of China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1135197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xiang, W.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Mallik, A.U.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Huang, F.; Ding, T.; Wen, S.; Lu, S.; et al. Partitioning beta diversity in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Southern China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiya-Cork, K.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Zak, D.R. The effects of long-term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseel, Y. Lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Xing, H. Elevation gradient altered soil C, N, and P stoichiometry of Pinus taiwanensis forest on Daiyun Mountain. Forests 2019, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wen, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Xiao, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, K. Afforestation effects on soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools modulated by lithology. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 400, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hou, E.; Liu, Y.; Wen, D. Altitudinal patterns and controls of plant and soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, C.E.; Hobbie, S.E. Mechanisms driving the soil organic matter decomposition response to nitrogen enrichment in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K. Soil nutrients and stoichiometric ratios as affected by land use and lithology at county scale in a karst area, southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, F.; Song, T.; Peng, W.; Du, H. Stoichiometric variation in soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus following cropland conversion to forest in Southwest China. Forests 2022, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Soil microbial processes and resource limitation in karst and non-karst forests. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Oelmann, Y.; Schickhoff, U.; Böhner, J.; Scholten, T. Himalayan treeline soil and foliar C:N:P stoichiometry indicate nutrient shortage with elevation. Geoderma 2017, 291, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Tognetti, R.; Lei, J.-P.; Pan, H.-L.; Liu, X.-L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; He, P.; Yu, F.-H.; et al. Elevation alters carbon and nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in Quercus aquifolioides in southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Jiao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Che, X. Elevation affects the ecological stoichiometry of Qinghai spruce in the Qilian Mountains of northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1024626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation in rhizosphere soil in the arid area of the northern Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, B.; Yue, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Zamanian, K.; et al. Effects of plastic and straw mulching on soil microbial P limitations in maize fields: Dependency on soil organic carbon demonstrated by ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Geoderma 2021, 388, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Du, H.; Zeng, F.; Peng, W.; Rizwan, M.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Zhou, Y.; Song, T.; Wang, H. Soil and fine roots ecological stoichiometry in different vegetation restoration stages in a karst area, southwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.L.; Fu, X.X.; Lu, Y.; Wei, X.H.; Li, B.; Jia, J.C.; Jiang, K. Soil C:N:P stoichiometry at different altitudes in Mao’er Mountain, Guangxi, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Ding, Z.; Tang, M.; Zhu, B. Changes in soil total, microbial and enzymatic C-N-P contents and stoichiometry with depth and latitude in forest ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ahmad, B.; Ali, A.; Ahamd, A.; Muhammad, D.; Afzaal, M.; Zhang, Z.; Bohnett, E. Variations in soil C, N, P stocks and stoichiometry with soil depth and forest types in Qilian Mountains of Northwest China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 893981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ai, Z.; Liang, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. How microbes cope with short-term N addition in a Pinus tabuliformis forest—Ecological stoichiometry. Geoderma 2019, 337, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Pang, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X. Elevation gradient shapes microbial carbon and phosphorous limitations in the Helan Mountains, Northwest China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 944081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Wieneke, X.; Tao, J.; Zhou, X.; Desilva, U. Soil pH is the primary factor correlating with soil microbiome in karst rocky desertification regions in the Wushan County, Chongqing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; An, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Lian, B. Organomineral fertilizer application enhances Perilla frutescens nutritional quality and rhizosphere microbial community stability in karst mountain soils. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 966035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.M.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, K.L. Increased associated effects of topography and litter and soil nutrients on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass along vegetation successions in karst ecosystem, southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16979–16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Dynamics of soil microbial C:N:P stoichiometry and its driving mechanisms following natural vegetation restoration after farmland abandonment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Song, S.; Xiong, K.; Albasher, G.; Fang, J. Responses of soil microbial biomass, microbial entropy and soil-microorganism stoichiometry imbalance to different utilization patterns in the artificial grassland of karst desertification area. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1195082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Fang, F.; Tang, H. Patterns and internal stability of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soils and soil microbial biomass in terrestrial ecosystems in China: A data synthesis. Forests 2021, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; He, M.; Jiang, C.; Liu, F. Soil microbial stoichiometry and community structure responses to long-term natural forest conversion to plantations in a subtropical region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27560–27570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shangguan, Z. Drivers of soil microbial metabolic limitation changes along a vegetation restoration gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Gong, L.; Yang, L.; He, S.; Liu, X. Dynamics in C, N, and P stoichiometry and microbial biomass following soil depth and vegetation types in low mountain and hill region of China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, B. Changes in microbial biomass, community composition and diversity, and functioning with soil depth in two alpine ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 2021, 459, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.-H.; Chen, T.-H.; Tian, G.; Chiu, C.-Y. The effect of altitudinal gradient on soil microbial community activity and structure in moso bamboo plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; Cajthaml, T.; Minerbi, S.; Margesin, R. Effect of altitude and season on microbial activity, abundance and community structure in Alpine forest soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Wang, W. Vertical pattern and its driving factors in soil extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry along mountain grassland belts. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Wu, D. Land conversion from cropland to grassland alleviates climate warming effects on nutrient limitation: Evidence from soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometry. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Green, S.M.; Dungait, J.A.; Wen, X.; Quine, T.A. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry along a gradient of vegetation restoration at the Karst Critical Zone Observatory in Southwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, Y.; Li, Q.; Cui, H.; Lu, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, Z. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry in the rhizosphere and bulk soil of a Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in North China. Forests 2023, 14, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarini, P.; Asensio, D.; Ogaya, R.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Effects of seasonal and decadal warming on soil enzymatic activity in a P-deficient Mediterranean shrubland. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3698–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, W. Stoichiometry of soil extracellular enzyme activity along a climatic transect in temperate grasslands of northern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, B.A.; Goodale, C.L.; Chin, N.A.; Fuss, C.B.; Lang, A.K.; Ollinger, S.V.; Lovett, G.M. Depth patterns and connections between gross nitrogen cycling and soil exoenzyme activities in three northern hardwood forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 107842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, T.; Li, Q.; Cao, J. The characteristics of soil C, N, and P stoichiometric ratios as affected by geological background in a karst graben area, Southwest China. Forests 2019, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xiong, K.; Chi, Y. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of plant–soil–microorganism of grassland ecosystems under different restoration modes in the karst desertification area. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, B.; Wilhelm, R.C.; Debenport, S.J.; Fahey, T.J.; Buckley, D.H.; Goodale, C.L. Microbial community shifts correspond with suppression of decomposition 25 years after liming of acidic forest soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5399–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ding, S.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, E.; Liu, T.; Duan, X. Microbial and enzymatic C:N:P stoichiometry are affected by soil C:N in the forest ecosystems in southwestern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 443, 116819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergh, A.K.; Bodelier, P.L.E.; Hoogveld, H.L.; Slomp, C.P.; Laanbroek, H.J. Phosphatases relieve carbon limitation of microbial activity in Baltic Sea sediments along a redox-gradient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, A.M.; Lidher, K.K.; Whiteside, M.D.; Jones, M.D. Control of soil phosphatase activities at millimeter scales in a mixed paper birch–Douglas-fir forest: The importance of carbon and nitrogen. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Han, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Ma, D.; Du, Y. Changes of soil bacterial activities and functions after different N additions in a temperate forest. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3853–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Cakmak, E.K.; D'AMico, F.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; Cetecioglu, Z. Phosphorus mining from marine sediments adopting different carbon/nitrogen strategies driven by anaerobic reactors: The exploration of potential mechanism and microbial activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Category | Factors | Elevation | Depth | Elevation × Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | SOC | 3.99 * | 46.53 ** | 0.22 |
| TN | 5.14 * | 35.72 ** | 0.57 | |
| TP | 36.57 ** | 2.32 | 0.07 | |
| SCN | 2.84 | 18.05 ** | 0.96 | |
| SCP | 48.25 ** | 17.26 ** | 1.846 | |
| SNP | 66.44 ** | 4.76 * | 0.43 | |
| Microbe | MBC | 0.87 | 21.74 ** | 0.25 |
| MBN | 0.21 | 16.57 ** | 0.90 | |
| MBP | 20.96 ** | 2.74 | 0.19 | |
| MCN | 2.81 | 3.97 | 3.65 * | |
| MCP | 2.47 | 2.46 | 0.16 | |
| MNP | 3.49 * | 6.35 * | 1.00 | |
| Enzyme | BG | 0.99 | 20.49 ** | 1.00 |
| NAG + LAP | 3.36 * | 4.51 * | 0.16 | |
| AP | 4.43 * | 44.50 ** | 1.02 | |
| ECN | 0.42 | 5.39 * | 0.60 | |
| ECP | 0.23 | 0.48 | 0.47 | |
| ENP | 0.72 | 11.57 ** | 0.63 |
| Environment Factor | Explanatory Contribution (%) | Explanatory Rate (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 23.06 | 33.86 | 0.001 |
| Ele | 16.7 | 24.52 | 0.001 |
| ECa | 8.95 | 13.14 | 0.032 |
| SD | 7.3 | 10.72 | 0.005 |
| EMg | 5.06 | 7.43 | 0.002 |
| SR | 2.71 | 3.98 | 0.033 |
| DBH | 2.51 | 3.69 | 0.170 |
| SWC | 1.78 | 2.61 | 0.006 |
| Total | 68.07 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Hu, C.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, G. Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Soil Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C:N:P Stoichiometry in Karst Peak-Cluster Depressions in Southwestern China. Forests 2025, 16, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081216
Chen S, Xu C, Hu C, Zhong C, Zhang Z, Hu G. Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Soil Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C:N:P Stoichiometry in Karst Peak-Cluster Depressions in Southwestern China. Forests. 2025; 16(8):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081216
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Siyu, Chaohao Xu, Cong Hu, Chaofang Zhong, Zhonghua Zhang, and Gang Hu. 2025. "Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Soil Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C:N:P Stoichiometry in Karst Peak-Cluster Depressions in Southwestern China" Forests 16, no. 8: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081216
APA StyleChen, S., Xu, C., Hu, C., Zhong, C., Zhang, Z., & Hu, G. (2025). Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Soil Total, Microbial, and Enzymatic C:N:P Stoichiometry in Karst Peak-Cluster Depressions in Southwestern China. Forests, 16(8), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16081216






