Fire and Logging Decrease Soil CO2 Efflux in Siberian Central Taiga Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
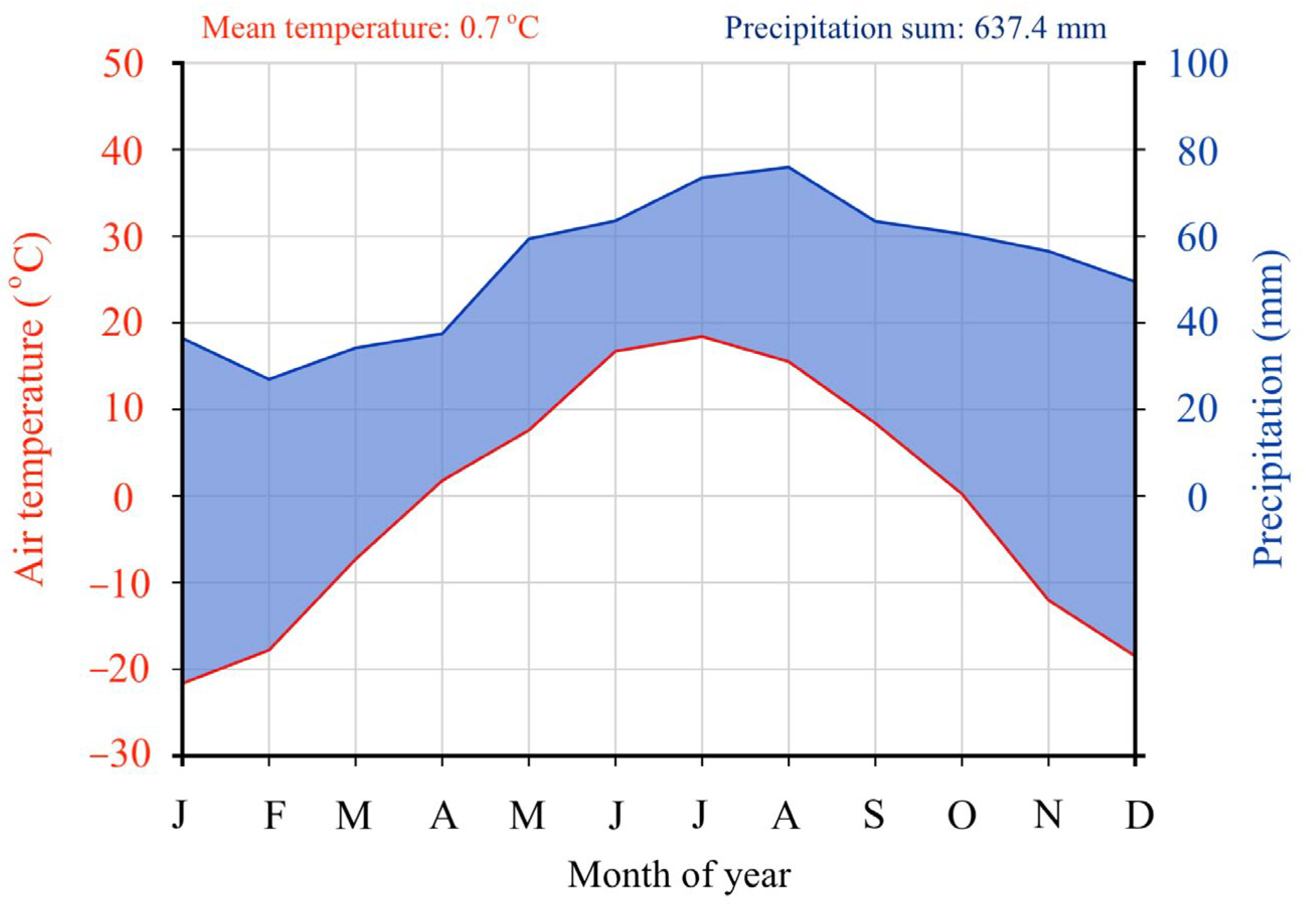
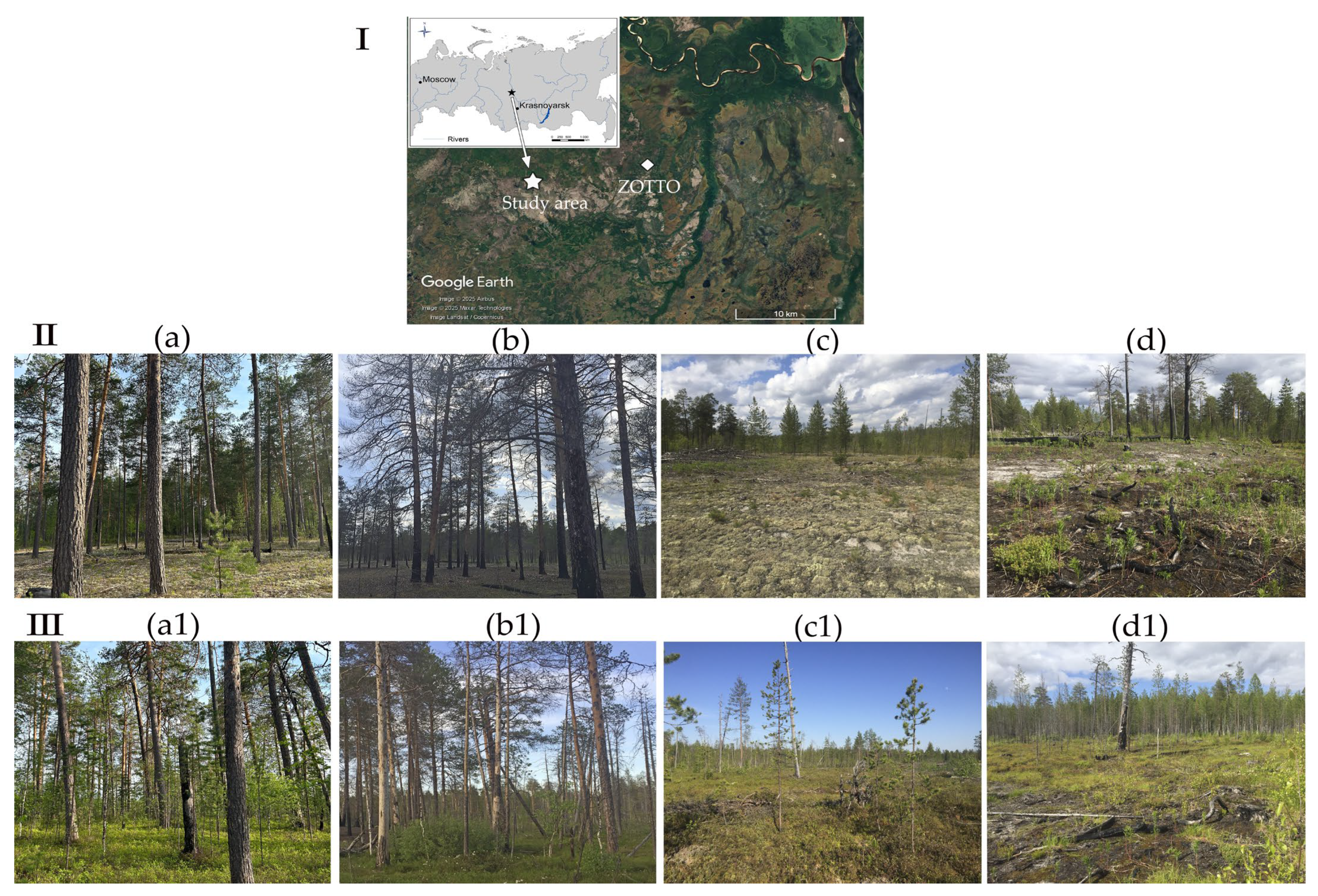
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Soil CO2 Efflux Measurements
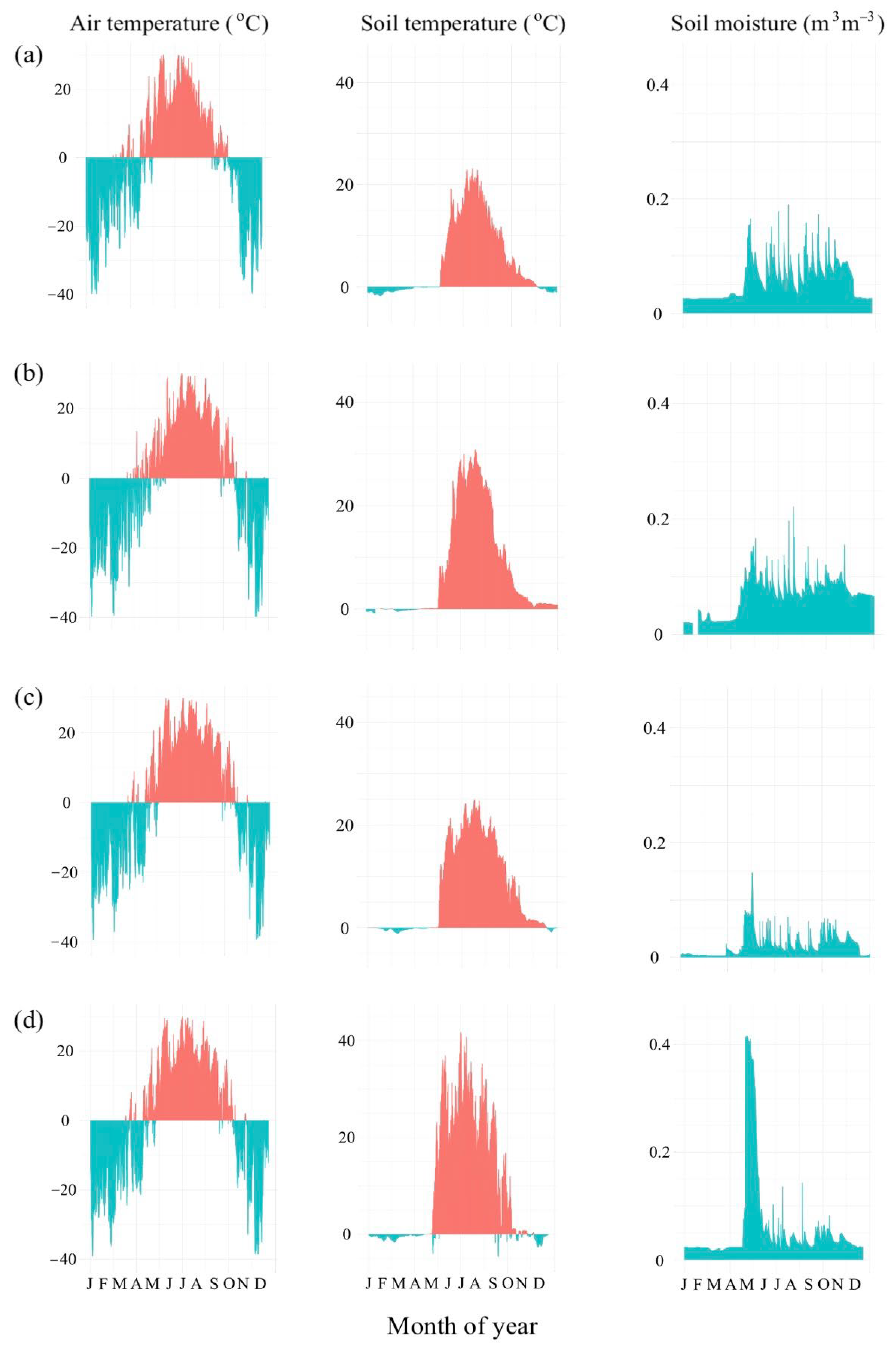
2.3. Weather Station Data
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
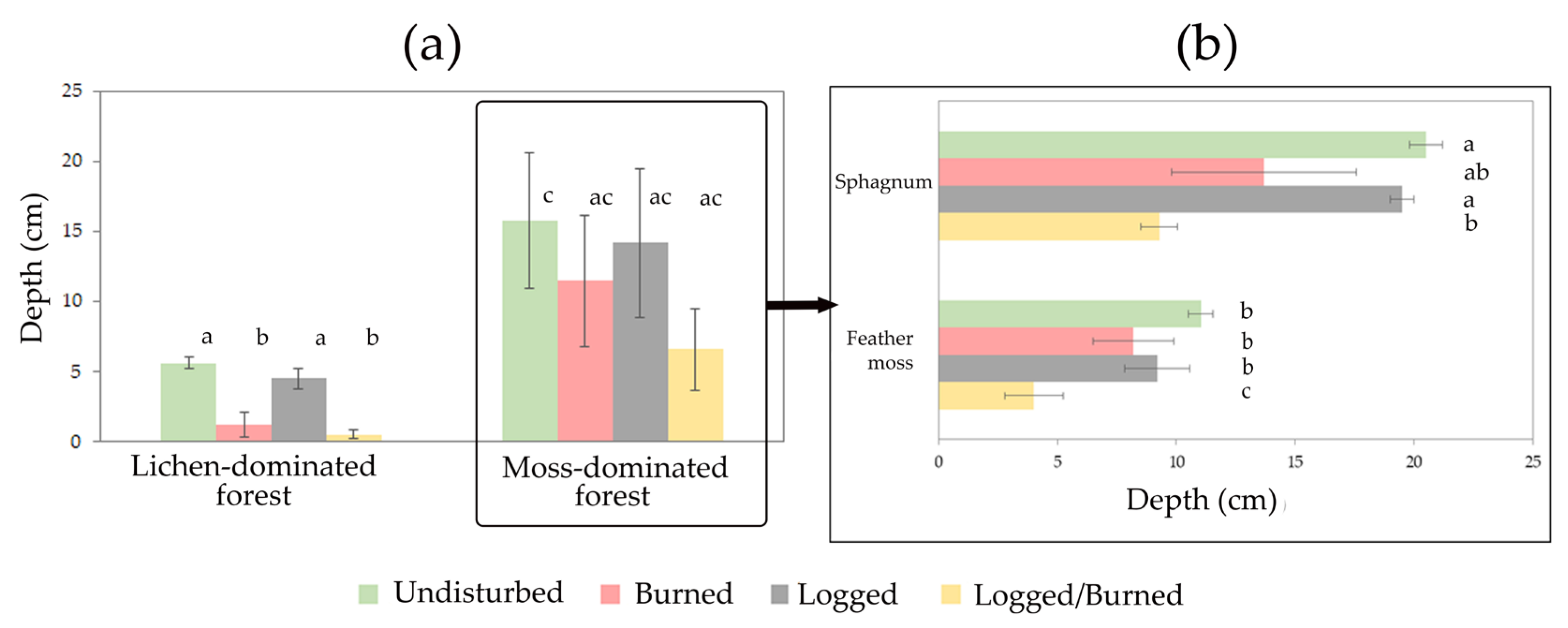
3.1. Weather and Soil Characteristics of the Scots Pine Forests with Different Disturbance Histories
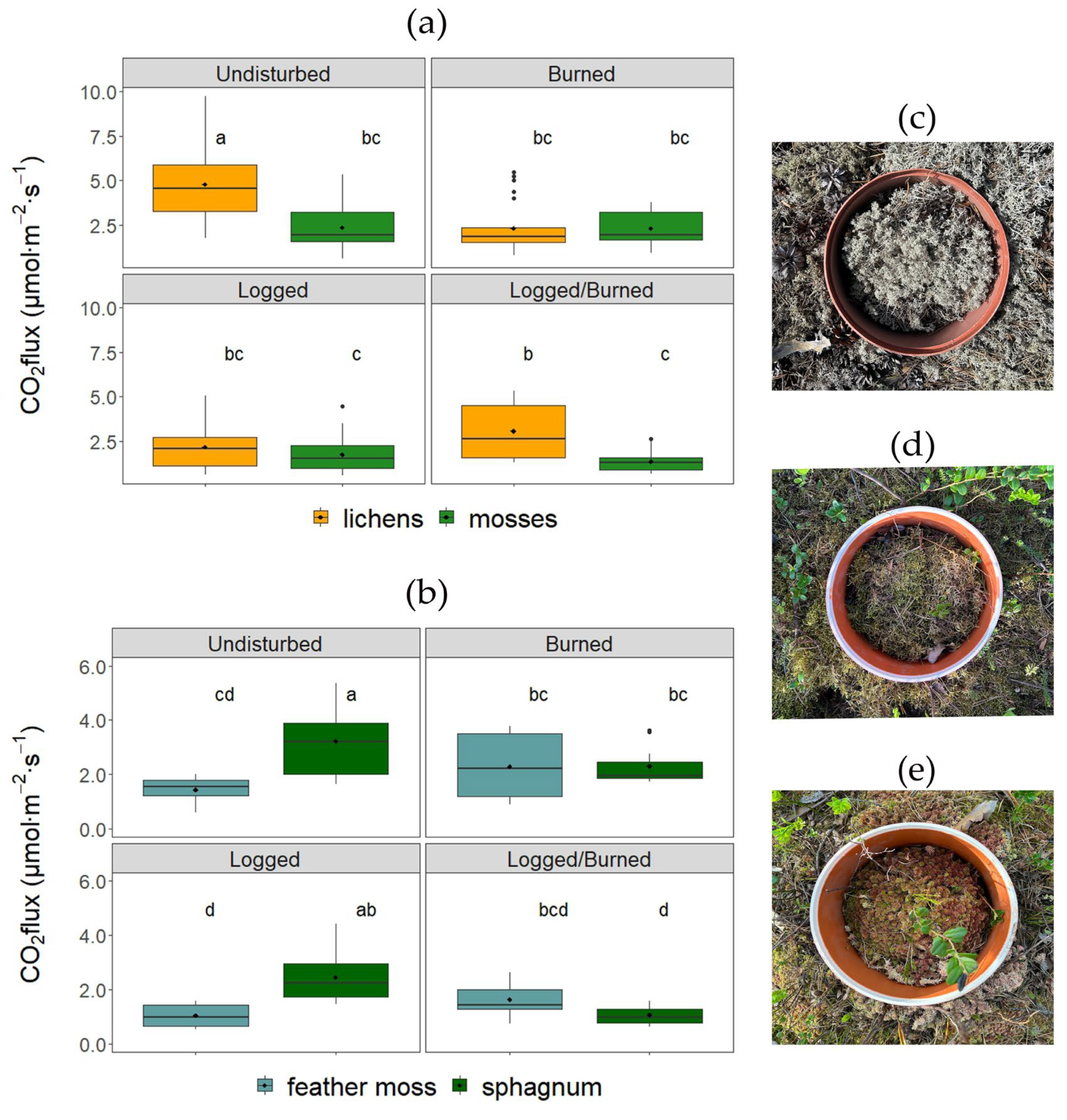
3.2. Wildfire and Clearcut Logging Impact on Soil CO2 Efflux
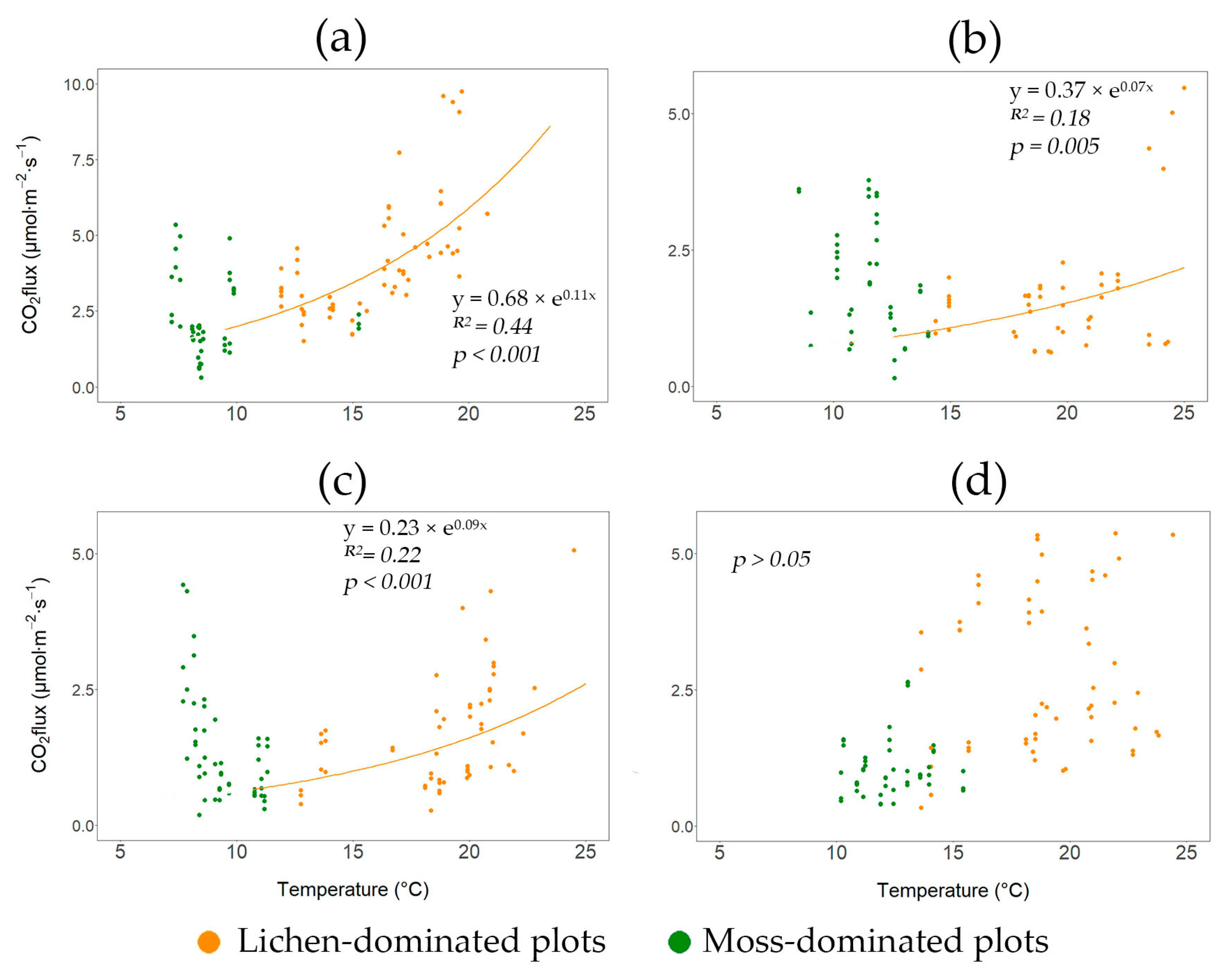
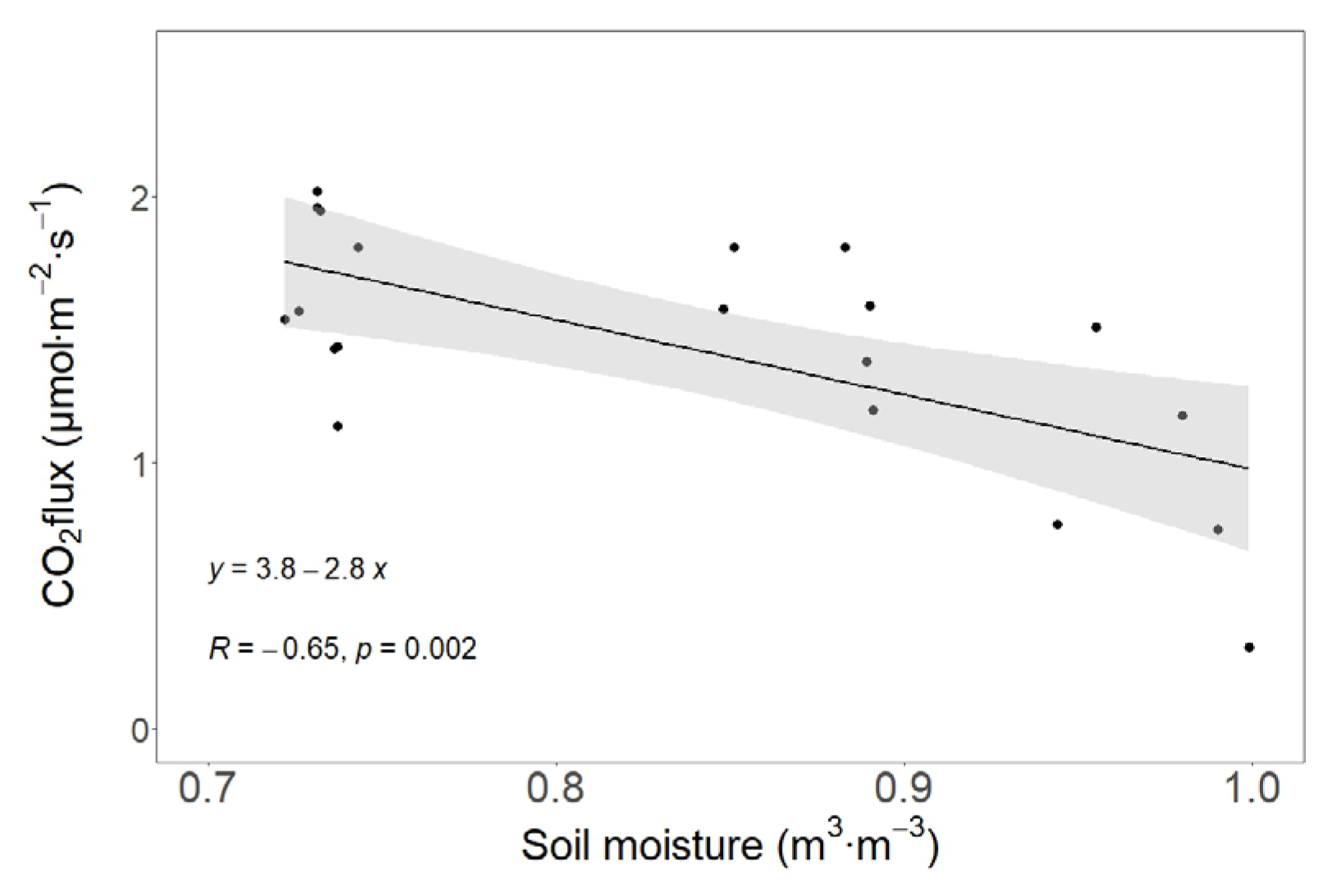
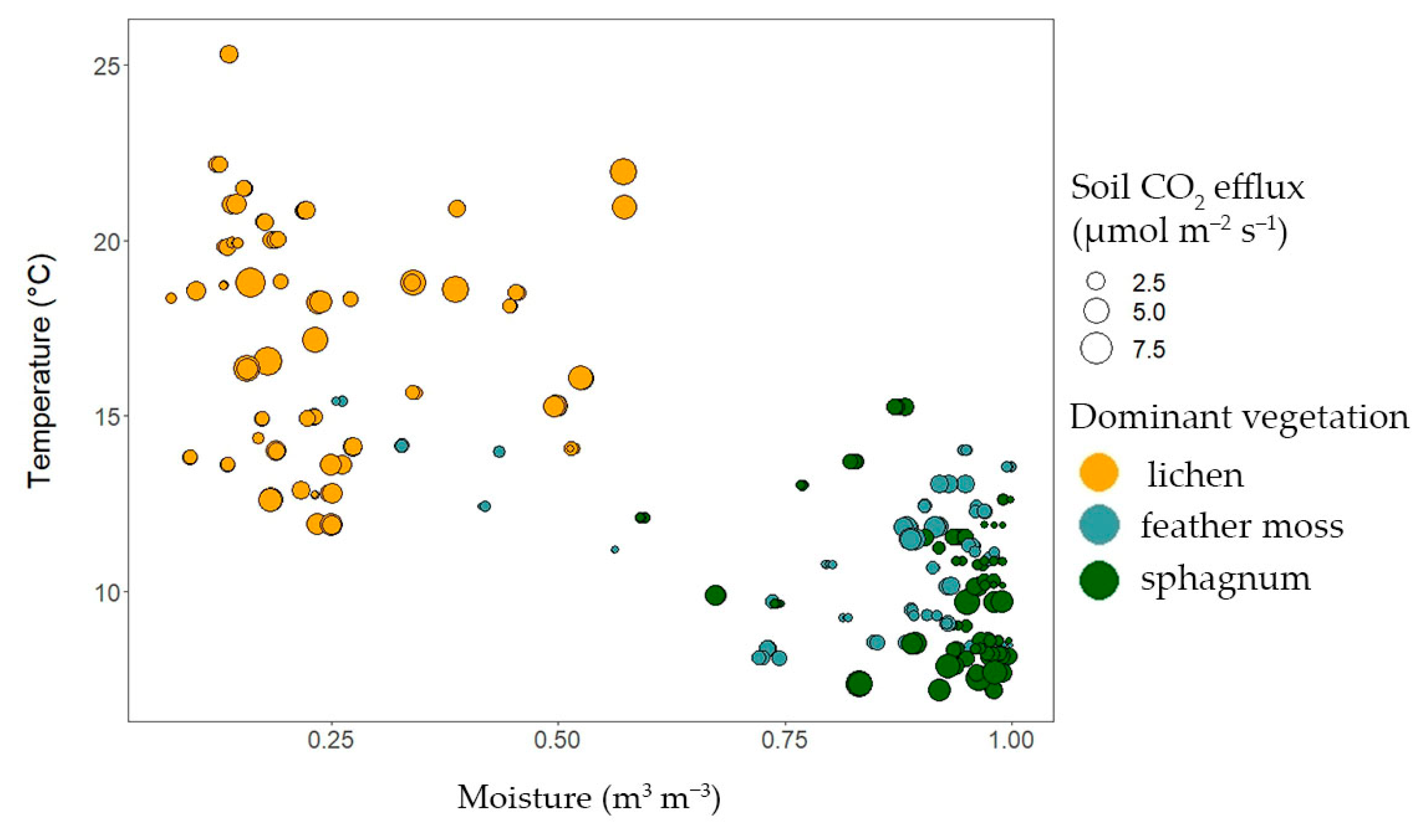
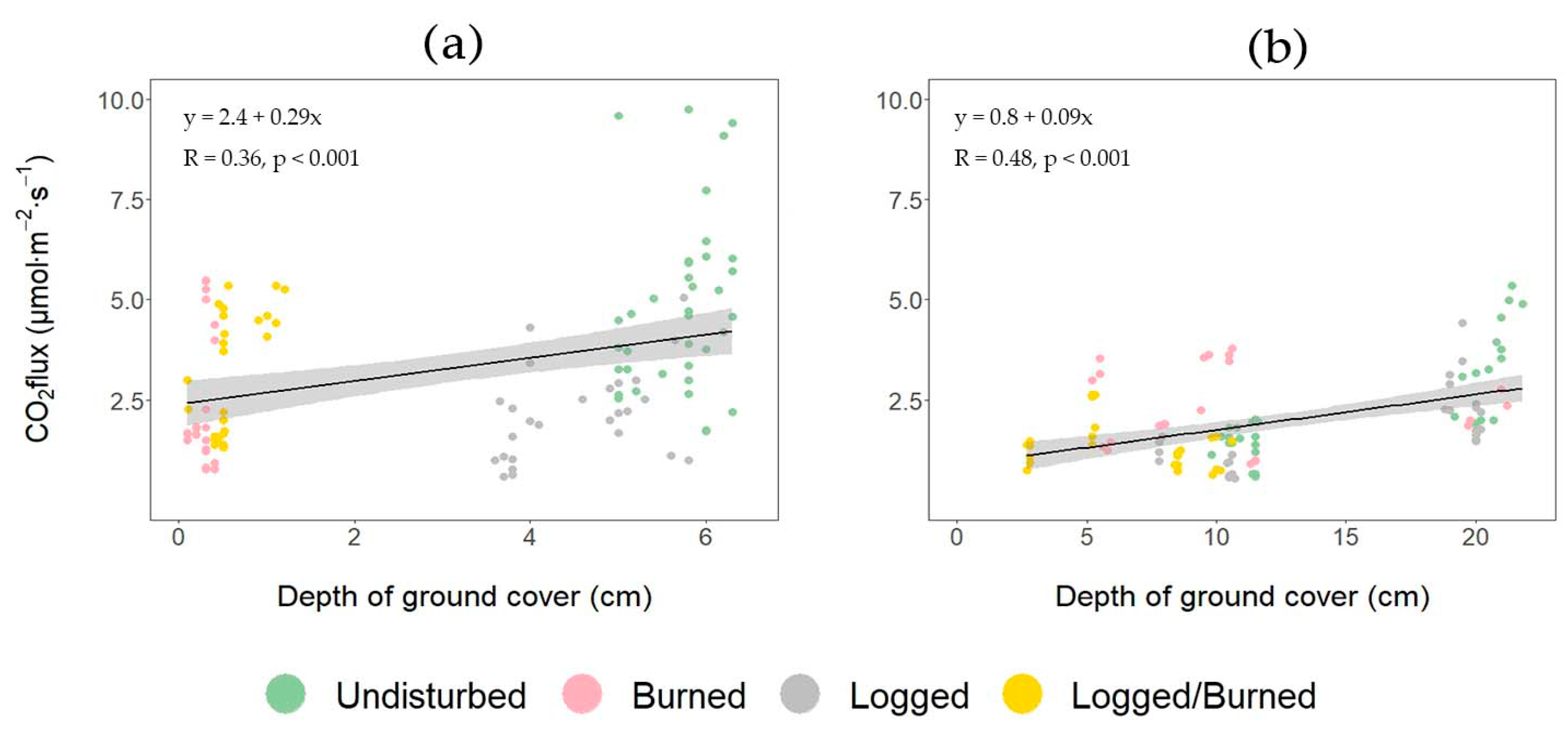
3.3. The Dependences of Soil CO2 Efflux on Soil Temperature, Moisture, and Forest Floor Depth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frelich, L.E.; Johnstone, J.; Kuuluvainen, T. Boreal Forests. In Future Forests; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Stefanski, A.; Eddy, W.C.; Bermudez, R.; Montgomery, R.A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Rich, R.L.; Reich, P.B. Soil respiration response to decade-long warming modulated by soil moisture in a boreal forest. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Ochege, F.U.; Hamdi, R.; Tabari, H.; Li, B.; He, B.; Zhang, C.; De Maeyer, P.; Luo, G. Weakening of global terrestrial carbon sequestration capacity under increasing intensity of warm extremes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 9, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descals, A.; Gaveau, D.L.; Verger, A.; Sheil, D.; Naito, D.; Peñuelas, J. Unprecedented fire activity above the Arctic Circle linked to rising temperatures. Science 2022, 378, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venäläinen, A.; Lehtonen, I.; Laapas, M.; Ruosteenoja, K.; Tikkanen, O.-P.; Viiri, H.; Ikonen, V.; Peltola, H. Climate change induces multiple risks to boreal forests and forestry in Finland: A literature review. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4178–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, A.L.; Sun, Q.; Baxter, R.; Kukavskaya, E.A.; Zhila, S.; Shestakova, T.; Rogers, B.M.; Kaduk, J.; Barrett, K. Climate change, fire return intervals and the growing risk of permanent forest loss in boreal Eurasia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, F. Satellite Observational evidence of contrasting changes in Northern Eurasian wildfires from 2003 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Ciais, P.; Chevallier, F.; Yang, H.; Canadell, J.G.; Chen, Y.; van der Velde, I.R.; Aben, I.; Chuvieco, E.; Davis, S.J.; et al. Record-high CO2 emissions from boreal fires in 2021. Science 2023, 379, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achard, F.; Mollicone, D.; Stibig, H.-J.; Aksenov, D.; Laestadius, L.; Li, Z.; Popatov, P.; Yaroshenko, A. Areas of rapid forest-cover change in boreal Eurasia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 237, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukavskaya, E.A.; Shvetsov, E.G.; Buryak, L.V.; Tretyakov, P.D.; Groisman, P.Y. Increasing fuel loads, fire hazard, and carbon emissions from fires in Central Siberia. Fire 2023, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Bernier, P.; Kuuluvainen, T.; Shvidenko, A.Z.; Schepaschenko, D.G. Boreal forest health and global change. Science 2015, 349, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, J.F.; Allen, C.D.; Franklin, J.F.; Frelich, L.E.; Harvey, B.J.; Higuera, P.E.; Mack, M.C.; Meentemeyer, R.K.; Metz, M.R.; Perry, G.L. Changing disturbance regimes, ecological memory, and forest resilience. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, X. Soil Respiration and the Environment; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change. 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Thomson, A. A global database of soil respiration data. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, K.; Wickland, K.; Striegl, R.; Neff, J. Variation in soil carbon dioxide efflux at two spatial scales in a topographically complex boreal forest. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2012, 44, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.E.; Detto, M.; Silver, W.L. Sensitivity of soil respiration to variability in soil moisture and temperature in a humid tropical forest. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Ida, H.; Hirota, M. Spatial variation in soil respiration is determined by forest canopy structure through soil water content in a mature beech forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 501, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Sawada, K.; Hirota, M. Spatial variation in forest soil respiration: A systematic review of field observations at the global scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugelius, G.; Strauss, J.; Zubrzycki, S.; Harden, J.W.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Ping, C.-L.; Schirrmeister, L.; Grosse, G.; Michaelson, G.J.; Koven, C.D.; et al. Estimated stocks of circumpolar permafrost carbon with quantified uncertainty ranges and identified data gaps. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 6573–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, T.V.; Shaduyko, O.; Kirpotin, S.N.; Gordov, E. Siberian environmental change: Synthesis of recent studies and opportunities for networking. Ambio 2021, 50, 2104–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyagina, O.V.; Menyailo, O.V.; Prokushkin, A.S.; Matvienko, A.I.; Makhnykina, A.V.; Evgrafova, S.Y.; Mori, S.; Koike, T.; Prokushkin, S.G. Soil respiration in larch and pine ecosystems of the Krasnoyarsk region (Russian Federation): A latitudinal comparative study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.; Prokushkin, A.; Korets, M.; Putilin, I.; Zrazhevskaya, G.; Kolosov, R.; Bondar, M. Variation in soil CO2 fluxes across land cover mosaic in typical tundra of the Taimyr Peninsula, Siberia. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, A.F. Influence of forest growth conditions on the CO2 emissions from the soil surface in the middle taiga pine forests of the Komi Republic, Russia. Russ. J. Ecol. 2023, 54, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyagina, O.V. Carbon dioxide emissions and vegetation recovery in fire-affected forest ecosystems of Siberia: Recent local estimations. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 23, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Gu, Y.; Wu, L.; Hu, H.-W.; He, J.-Z. Fire decreases soil respiration and its components in terrestrial ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 3124–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhnykina, A.; Panov, A.; Prokushkin, A. The impact of wildfires on soil CO2 emission in middle taiga forests in Central Siberia. Land 2023, 12, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Ibáñez, T.S.; Santín, C.; Doerr, S.H.; Nilsson, M.-C.; Holst, T.; Lindroth, A.; Kljun, N. Boreal forest soil carbon fluxes one year after a wildfire: Effects of burn severity and management. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 4181–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukavskaya, E.A.; Bogorodskaya, A.V.; Buryak, L.V.; Kalenskaya, O.P.; Conard, S.G. Effects of wildfire and logging on soil CO2 efflux in Scots Pine forests of Siberia. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, K.; Köster, E.; Orumaa, A.; Parro, K.; Jõgiste, K.; Berninger, F.; Pumpanen, J.; Metslaid, M. How time since forest fire affects stand structure, soil physical-chemical properties and soil CO2 efflux in hemiboreal Scots pine forest fire chronosequence? Forests 2016, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, A.G.; Kurbatova, Y.A.; Olchev, A.V. Effect of clear-cutting on soil CO2 emission. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2017, 44, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Xiang, Y.Z.; He, Z.B.; Du, J.; Lin, P.F.; Zhu, X. A meta-analysis of the impacts of forest logging on soil CO2 efflux. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2020, 12, 165–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lytle, D.E.; Cronan, C.S. Comparative soil CO2 evolution, litter decay, and root dynamics in clearcut and uncut spruce-fir forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 103, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, M.F.; Duchesne, L.C.; Morrison, I.K. Effect of clearcutting, selection cutting, shelterwood cutting and microsites on soil surface CO2 efflux in a tolerant hardwood ecosystem of northern Ontario. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 174, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridacha, V.B.; Semin, D.E.; Ekimov, D.A. Dynamics of soils properties in disturbed forest ecosystems of southern Karelia. In XV Siberian Meeting and School of Young Scientists on Climate-Ecological Monitoring, Proceedings of the All-Russian Conference with International Participation, Tomsk, Russia, 17–20 October 2023; Golovatskaya, E.A., Ed.; Institute of Monitoring of Climatic and Ecological Systems SB RAS: Tomsk, Russia, 2023; pp. 171–173. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kulmala, L.; Aaltonen, H.; Berninger, F.; Kieloaho, A.-J.; Levula, J.; Bäck, J.; Hari, P.; Kolari, P.; Korhonen, J.F.J.; Kulmala, M.; et al. Changes in biogeochemistry and carbon fluxes in a boreal forest after the clear-cutting and partial burning of slash. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 188, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Doerr, S.H.; Ekroos, J.; Ibáñez, T.S.; Islam, M.R.; Santín, C.; Soares, M.; Kljun, N. No recovery of soil respiration four years after fire and post-fire management in a Nordic boreal forest Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 364, 110454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshurnikova, N.; Verkhovets, S.; Antamoshkina, O.; Trofimova, N.; Zlenko, L.; Zhuikov, A. Assessment of Central Siberia forest ecosystems sustainability to forest fires: Academic research outcomes. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 214, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharuk, V.I.; Ponomarev, E.I.; Ivanova, G.A.; Dvinskaya, M.L.; Coogan, S.C.P.; Flannigan, M.D. Wildfires in the Siberian taiga. Ambio 2021, 50, 1953–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Makhnykina, A.V.; Tychkov, I.I.; Prokushkin, A.S.; Pyzhev, A.I.; Vaganov, E.A. Factors of soil CO2 emission in boreal forests: Evidence from Central Siberia. iForest 2023, 16, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; 260p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseel, Y. lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pinés, E.; Schindlbacher, A.; Godino, M.; Kitzler, B.; Jandl, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Rubio, A. Effects of tree species composition on the CO2 and N2O efflux of a Mediterranean mountain forest soil. Plant Soil. 2014, 384, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koptsik, G.N.; Kupriianova, Y.V.; Kadulin, M.S. Spatial variability of carbon dioxide emission by soils in the main types of forest ecosystems at the Zvenigorod biological station of Moscow State University. Mosc. Univ. Soil. Sci. Bull. 2018, 73, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes De Gerenyu, V.O.; Kurganova, I.N.; Rozanova, L.N.; Kudeyarov, V.N. Effect of temperature and moisture on CO2 evolution rate of cultivated Phaeozem: Analyses of long-term field experiment. Plant Soil. Environ. 2005, 51, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J.; Shen, Q.; Hu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, G. Modeling interannual variability of global soil respiration from climate and soil properties. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyukarev, E.A.; Kurakov, S.A. Response of bare soil respiration to air and soil temperature variations according to different models: A case study of an urban grassland. Land. 2023, 12, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Tufekciogul, A. Vegetation and soil respiration: Correlations and controls. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhnykina, A.; Vaganov, E.; Panov, A.; Polosukhina, D.; Prokushkin, A. An Interseasonal comparison of soil respiration in xeric and mesic pine forest ecosystems in Central Siberia. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Belk, E.; Boone, R.D. Soil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest. Glob. Change Biol. 1998, 4, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Tatarinov, F.; Kurbatova, J. Soil respiration in paludified forests of European Russia. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; Merhautová, V.; Petránková, M.; Cajthaml, T.; Šnajdr, J. Distribution of microbial biomass and activity of extracellular enzymes in a hardwood forest soil reflect soil moisture content. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2010, 46, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, C.A.; Malghani, S.; Loescher, H.W. Interactions among temperature, moisture, and oxygen concentrations in controlling decomposition rates in a boreal forest soil. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucinskas, O.; Marozas, V. Diurnal and seasonal soil CO2 efflux variation in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) forests in the European hemi-boreal zone. Lith. J. Elem. 2021, 26, 731–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Edwards, N.T.; Garten, C.T.; Andrews, J.A. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, P.; Nordgren, A.; Buchmann, N.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Ekblad, A.; Högberg, M.N.; Nyberg, G.; Read, D.J. Large-scale forest girdling shows that current photosynthesis drives soil respiration. Nature 2001, 411, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wan, S. Impacts of fire on soil respiration and its components: A global meta-analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 336, 109496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Kumara, C.; Köster, E.; Aaltonen, H.; Köster, K. How do forest fires affect soil greenhouse gas emissions in upland boreal forests? A review. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glukhova, T.V.; Vompersky, S.E.; Kovalev, A.G. Emission of CO2 from the surface of oligotrophic bogs with due account for their microrelief in the southern taiga of European Russia. Eurasian Soil. Sc. 2013, 46, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumpanen, J.; Westman, C.J.; Ilvesniemi, H. Soil CO2 efflux from a podzolic forest soil before and after forest clear-cutting and site preparation. Boreal. Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, A.K.; Conard, S.L.; Blair, J.M. Determinants of soil CO2 flux from a sub-humid grassland: Effect of fire and fire history. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, K.M.; Malhi, Y.; Morecroft, M.D. Soil CO2 efflux in a temperate deciduous forest: Environmental drivers and component contributions. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, J.; Zona, D.; Arndt, K.; Kalhori, A.; Oechel, W. Seasonality buffers carbon budget variability across heterogeneous landscapes in Alaskan Arctic Tundra. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymov, A.A. The impact of clearcutting in boreal forests of Russia on soils: A review. Eurasian Soil. Sc. 2017, 50, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desyatkin, A.; Okoneshnikova, M.; Fedorov, P.; Ivanova, A.; Filippov, N.; Desyatkin, R. The Impact of catastrophic forest fires of 2021 on the light soils in Central Yakutia. Land 2024, 13, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, L.D.; Nichols, S.C.; Foyster, S.M.; Ondei, S.; Bowman, D.M.J.S. Soil not fire: Field, glasshouse and dendrochronology studies show how edaphic factors control post-fire woody plant growth across a sedgeland—forest boundary in Tasmania. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 553, 121639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayedi, S.S.; Abbott, B.W.; Vannière, B.; Leys, B.; Colombaroli, D.; Romera, G.G.; Slowinski, M.; Aleman, J.C.; Blarquez, O.; Feurdean, A.; et al. Assessing changes in global fire regimes. Fire Ecol. 2024, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, S.R.; Rogers, B.M.; Treseder, K.K.; Randerson, J.T. Fire severity influences the response of soil microbes to a boreal forest fire. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, K.; Kohli, J.; Lindberg, H.; Pumpanen, J. Post-fire soil greenhouse gas fluxes in boreal Scots pine forests—Are they affected by surface fires with different severities? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 349, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kukavskaya, E.A.; Panov, A.V.; Makhnykina, A.V.; Groisman, P.Y. Fire and Logging Decrease Soil CO2 Efflux in Siberian Central Taiga Forests. Forests 2025, 16, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071057
Kukavskaya EA, Panov AV, Makhnykina AV, Groisman PY. Fire and Logging Decrease Soil CO2 Efflux in Siberian Central Taiga Forests. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKukavskaya, Elena A., Alexey V. Panov, Anastasia V. Makhnykina, and Pavel Y. Groisman. 2025. "Fire and Logging Decrease Soil CO2 Efflux in Siberian Central Taiga Forests" Forests 16, no. 7: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071057
APA StyleKukavskaya, E. A., Panov, A. V., Makhnykina, A. V., & Groisman, P. Y. (2025). Fire and Logging Decrease Soil CO2 Efflux in Siberian Central Taiga Forests. Forests, 16(7), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071057








