Abstract
Bamboo, as a sustainable and renewable biomass resource, possesses significant application prospects along with underutilized potential. However, challenges such as mildew infestation, insect damage, and discoloration during processing and utilization negatively impact its service life and economic value. This study proposes a simplified hydrogen peroxide bleaching method for bamboo processing, resulting in bleached materials with uniform coloration and improved mildew resistance. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis of bleached bamboo showed significantly reduced starch and protein inclusions, expanded intercellular spacing, partial fiber detachment, and localized structural deformation in treated bamboo. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analyses revealed substantial lignin degradation in hydrogen peroxide-treated samples. The color difference (ΔE) was measured at 13.65 between treated and untreated samples, confirming effective bleaching efficacy. The mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) analysis revealed enhanced porosity accompanied by diameter enlargement in treated bamboo. Antifungal assessments indicated that hydrogen peroxide bleaching delayed the onset of mold colonization and significantly enhanced the mildew resistance of bamboo substrates.
1. Introduction
Bamboo (Bambusoideae, Poaceae family) is a natural biocomposite material characterized by the distinct biological attributes of renewability, rapid growth, and sustainability. With carbon sequestration and storage capacity, this eco-friendly material has been widely adopted in the construction, interior design, and food packaging industries. The major chemical components comprise cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and small amounts of starch and protein. Accounting for approximately 25% of bamboo’s composition, lignin contributes to its natural pigmentation [1]. Differences in growth conditions, particularly nutrient availability and light exposure, cause uneven distribution of chemical components, leading to inconsistent coloration. Moreover, bamboo contains substantially higher nutrient concentrations (including starch, proteins, and polysaccharides) compared to wood. Under favorable environmental conditions, this nutrient-rich composition makes bamboo prone to fungal colonization, structural degradation, and localized discoloration [2]. These inherent limitations restrict bamboo’s industrial applications. To achieve consistent coloration and mitigate mold-induced aesthetic deterioration, industrial processing commonly implements bleaching, mildew-resistant impregnation, and thermal modification for nutrient removal and lignin decolorization [3,4,5,6]. These treatments simultaneously improve color consistency and enhance mold resistance in bamboo [7].
Bleaching can be classified into reductive and oxidative types based on the type of bleaching agents employed [8]. Typical reductive bleaching agents encompass sulfur dioxide and sodium dithionite, whereas oxidative counterparts include chlorine, ozone, and hydrogen peroxide. As a widely acknowledged strong yet eco-friendly oxidizing agent [9], hydrogen peroxide demonstrates dual chemical functionality: it primarily acts as a potent oxidizer in acidic or alkaline solutions, but paradoxically exhibits reducing characteristics when encountering stronger oxidizing agents [10,11,12]. This versatile compound finds extensive applications across diverse industrial sectors, including paper manufacturing and bamboo processing. Notably, ethanol supplementation in hydrogen peroxide solutions enhances both bleaching efficiency and whiteness thresholds in bamboo chemomechanical pulp treatment, thereby facilitating its utilization in premium paper products [9]. In a complementary investigation [13], the synergistic application of hydrogen peroxide and the Co(salen) catalyst induced comprehensive lignin modification in sweet bamboo, including ring-opening reactions, side-chain oxidation, demethoxylation, and β-O-4 bond cleavage, while concurrently degrading lignin–carbohydrate complexes, resulting in breakthroughs with profound implications for pulp processing technologies. Furthermore, researchers have successfully isolated nanocellulose (NCC, nanocrystalline cellulose) through an integrated approach combining activated oxygen pretreatment, solid alkali digestion, hydrogen peroxide bleaching, and the controlled high-pressure homogenization of wood/bamboo residues [14].
Liquid permeability in bamboo, defined as its ability to allow fluids to enter, flow through, and exit the tissue under a pressure gradient, is recognized as a critical physical property. This property fundamentally determines the effectiveness of bamboo processing and functional modification techniques, including pulping, gluing, softening, polymer impregnation, dyeing, and treatments imparting flame retardancy, decay resistance, or hardness enhancement. Consequently, the comprehensive understanding and strategic enhancement of bamboo’s permeability are prerequisites for optimizing industrial processing and enabling high-value applications in advanced materials [15,16].
The aim of this study is to address multiple technical challenges in bamboo processing by developing a simplified hydrogen peroxide bleaching method. By systematically optimizing key treatment parameters, including hydrogen peroxide concentration and treatment duration, we aim to achieve efficient bleaching, maintain the structural integrity of the bamboo substrate, and enhance its liquid permeability. These improvements are intended to facilitate subsequent bamboo processing and functionalization, as well as enhance its resistance to fungal growth. Through comprehensive characterization, this study elucidates hydrogen peroxide-induced microstructural evolution and confirms the antifungal performance of the bleached bamboo.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All samples were obtained from the internodal sections of 3–5-year-old mature Moso bamboo culms grown in Anji, Zhejiang Province. This age range was selected based on existing studies confirming complete secondary cell wall formation and stabilized lignin–carbohydrate complex (LCC) structures [17,18]. Moso bamboo accounts for over 80% of industrial bamboo applications [19]. The outer bamboo green and inner bamboo yellow layers were excised, followed by the cutting of the strips into specimens measuring 30 mm (length) × 20 mm (width) × 5 mm (thickness). Prior to treatment, all bamboo strips were equilibrated for 72 h under controlled conditions (20 °C, 65% relative humidity) to ensure uniform material properties. The specimens were immersed in hydrogen peroxide solutions at concentrations ranging from 5% to 25% (w/w).
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Bleaching Treatment
The bamboo strips were subjected to bleaching in a hydrogen peroxide solution using a liquid ratio of 1:20–25 (w/v). The process was maintained at 70–75 °C for 4–24 h to control hydrogen peroxide decomposition (thermolysis initiates above 75 °C). Solutions with concentrations of 5%–25% (w/w). were employed. Subsequently, the specimens were thoroughly rinsed with deionized water until a neutral pH was achieved to eliminate residual oxidants. Finally, the bleached strips were conditioned in a convection oven at 60 ± 2 °C to achieve an equilibrium moisture content of 8%–12%, following the ASTM D4442-20 Standard Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measurement of Wood and Wood-Based Materials (American Society for Testing and Materials, 2020) [20].
2.2.2. Color Analysis
The CIELAB color parameters (L*, a*, b*) of bamboo strips were measured using a calibrated colorimeter (Precision Colorimeter NR10QC, 3nh Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) at both pre- and post-bleaching stages. The total color difference () was calculated using the following equation:
where represents the total color difference, with L*1, a*1, b*1 denoting the pre-bleaching values of lightness, green-red coordinate, and blue-yellow coordinate, respectively, and L*0, a*0, b*0 representing the corresponding post-bleaching measurements [21].
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
Microstructural modifications in the cell walls, fibers, vessel structures, and inclusions of the Moso bamboo before and after bleaching were examined using cross-sectional slices from the central region of the bamboo strips using a scanning electron microscope (Hitachi SU8010, Hitachi High-Tech, Tokyo, Japan) at magnifications of 200×, 600×, and 1000×. All specimens underwent standardized thermal drying at 60 ± 2 °C until they reached an equilibrium moisture content (8%–12%), followed by direct sectioning without rinsing, in order to preserve native structural features. Before SEM imaging, samples were sputter-coated with a gold layer to ensure optimal surface conductivity. Biological triplicates (n = 9 specimens per group, 3 sections per specimen) were processed using identical pretreatment protocols (Section 2.2.1) to ensure analytical comparability. A comparative evaluation of the bleaching effects was conducted to assess microarchitectural changes in the bamboo strips.
2.2.4. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
Surface chemical composition changes of the bamboo strips pre- and post-bleaching were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (AXIS UltraDLD, Shimadzu, Japan).
2.2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Functional group characterization of the bamboo strips was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (VERTEX 80V spectrometer, Bruker, Germany) for the pre- and post-bleaching comparison.
2.2.6. Longitudinal Compressive Strength Testing
Bamboo specimens (10 mm radial × 10 mm tangential × 6 mm longitudinal) underwent axial loading along the longitudinal grain direction at a constant crosshead speed of 2 mm min−1 until failure. Longitudinal compressive strength was defined as the maximum stress recorded before specimen fracture. All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the PRC National Standard GB/T 15780-1995 (Test Methods for Physical and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo) [22].
2.2.7. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP) Analysis
Pore-structure characteristics of the bamboo strips pre- and post-bleaching were characterized by mercury intrusion porosimetry (AutoPore IV 9510, Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, GA, USA) to quantify pore-size distribution. The pore volume distribution was calculated based on the Washburn equation.
2.2.8. Water Absorption Analysis
The water absorption of bamboo strips was determined via a gravimetric method, comparing pre- and post-bleaching samples. Samples were dried to a constant mass in a convection oven at 70 °C for 6 h prior to initial weighing. Specimens were then immersed in deionized water with mass measurements recorded at 1, 2, 4, 8, 24, 48, and 96 h intervals. Water absorption parameters were calculated using the following relationships:
where m1 and m0 denote the wet mass and dry, respectively.
where T is the immersion time (h).
WPG (weight percent gain) = [(m1 − m0)/m0] × 100%
WAR (water absorption rate) = (m1 − m0)/(T) × 100%
2.2.9. Anti-Mold Test
Specimens were aseptically transferred to potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium pre-inoculated with Trichoderma viride Pers., Penicillium chrysogenum Thom, and Aspergillus niger Tiegh. spores, then maintained under controlled conditions (25 ± 1 °C, 85% RH) for 28 days. Anti-mold efficacy was assessed according to the Chinese National Standard GB/T 18261-2013 “Test method for anti-mildew agents in controlling wood mould and stain fungi” [23].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color Analysis
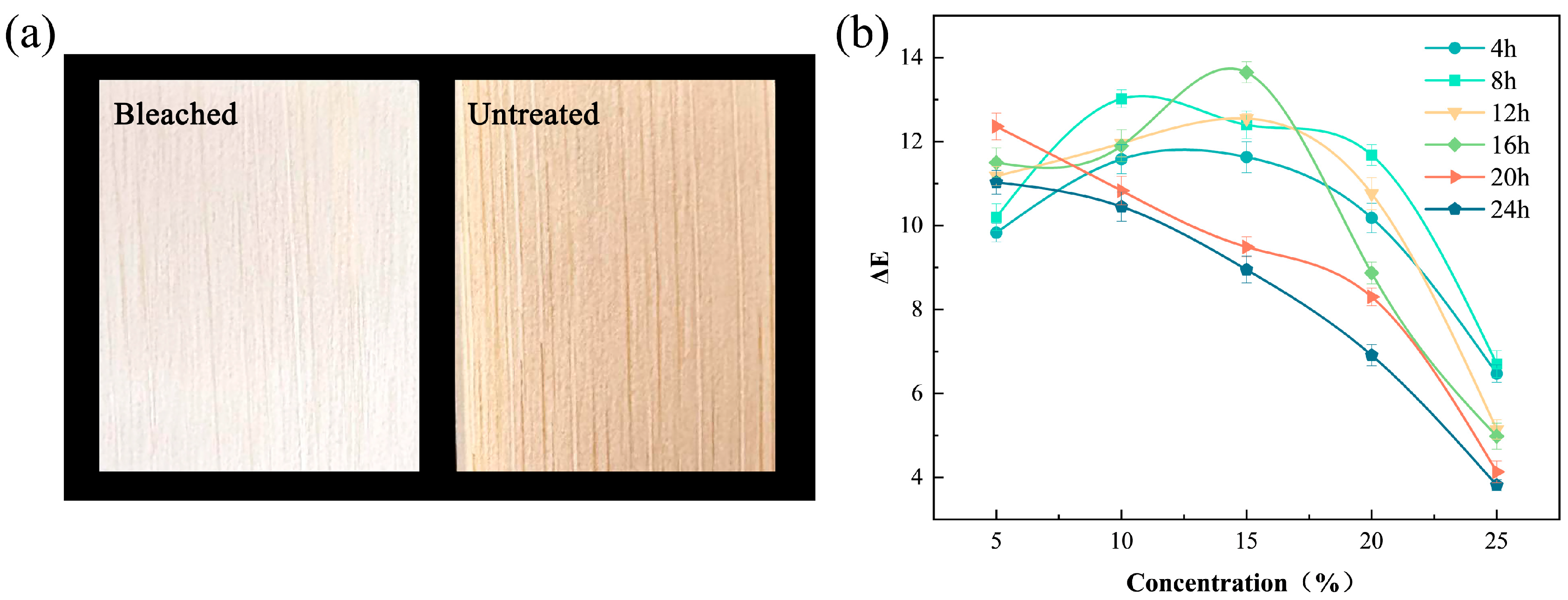
Lignin, the primary chromophoric component in bamboo, consists of cross-linked phenylpropane units. Conjugated systems comprising benzene rings, quinones, and α-carbonyl moieties generate chromophoric C=C/C=O conjugations, accounting for the inherent coloration. Auxochromic groups (-OH, -OCH3) further modulate color stability through photo-oxidative degradation [24,25]. Figure 1a demonstrates the bleaching efficacy, with treated specimens exhibiting pronounced whitening and improved chromatic homogeneity.
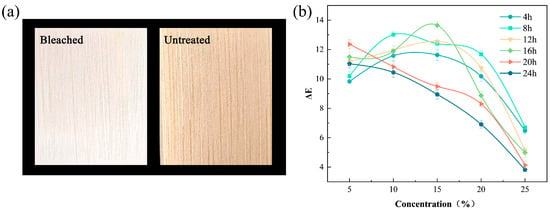
Figure 1.
(a) Comparative digital photographs of bamboo specimens before and after the bleaching treatment (15% H2O2, 16 h). (b) Dependence of color-difference values on the H2O2 concentration ( indicates the total color difference relative to untreated controls).
Table 1 shows the CIELAB parameters, revealing enhanced L* values with reduced a* and b* coordinates after treatment. Selective oxidation of lignin chromophores (quinonoid structures, conjugated olefins) mediates this decolorization [26,27]. Colorimetric evolution was assessed using the Lovric classification [28]. At H2O2 concentrations <25%, exceeded 6.0 (p < 0.05), indicating significant chromatic alterations. For 25% H2O2, prolonged treatment (>8 h) reduced below 6.0. This dual parameter dependency reflects competing kinetics between chromophore oxidation and peroxide decomposition.

Table 1.
Statistical analysis of chromatic parameters for bamboo specimens following the H2O2 bleaching treatment.
Figure 1b reveals diminished bleaching efficiency at concentrations >15%, with decreasing nonlinearly. Extended treatment (>16 h) induced secondary reactions that further reduced color differences. Autocatalytic H2O2 decomposition at high concentrations depleted active oxygen species through gas evolution, while prolonged bleaching promoted quinoid byproduct formation, causing yellowish hues. Surface oxidation gradients reduced visual uniformity. Optimal bleaching occurred at 15% H2O2 for 16 h ( = 13.65).
3.2. Microscopic Morphology Analysis
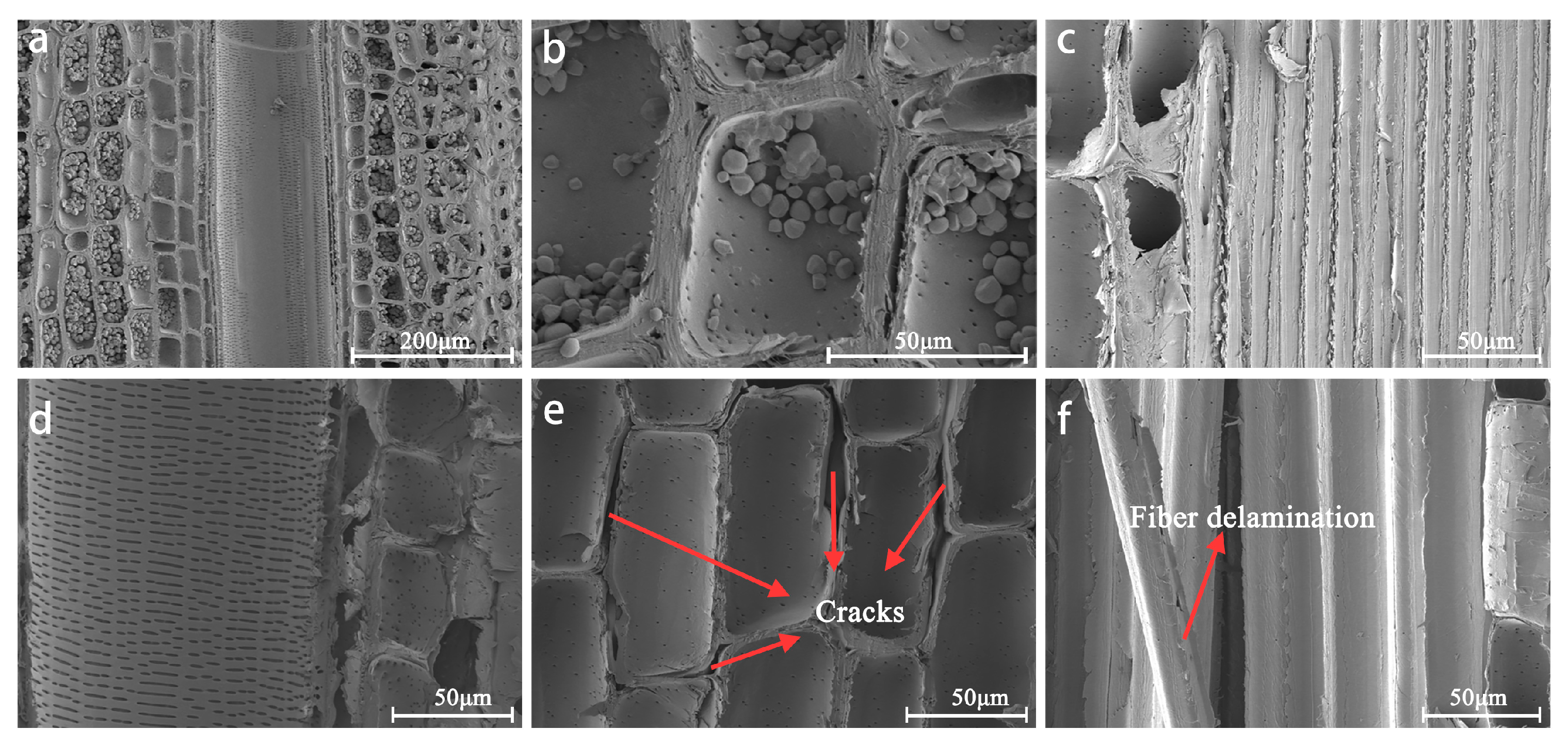
Figure 2 illustrates the comparative scanning SEM images of bamboo specimens before and after the bleaching treatment. In unbleached specimens (Figure 2a–c), parenchyma cell lumens were densely packed with cytoplasmic inclusions, exhibiting a compact cellular arrangement with minimal intercellular fissures, while bamboo fibers displayed well-aligned architectures. Post-bleaching observations (Figure 2d–f) revealed substantial dissolution of luminal deposits (e.g., protein bodies, starch granules), resulting in smoothened vessel surfaces and significantly depleted intracellular contents. Notably, distinct intercellular delamination was observed between parenchyma cells (Figure 2e). Fibrous cells demonstrated partial structural collapse, concomitant with increased porosity and expanded pore morphology, which may have facilitated enhanced liquid permeability. These ultrastructural modifications are principally attributable to the H2O2-induced degradation of lignin and hemicellulose—key structural components in bamboo cell walls.
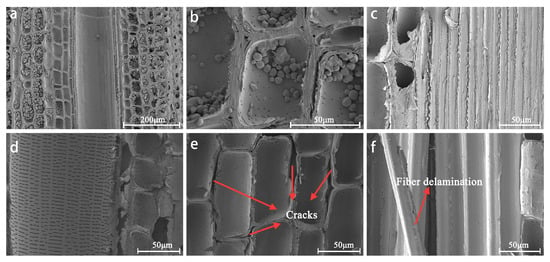
Figure 2.
SEM images of bamboo before and after bleaching (15% H2O2, 16 h). Before bleaching, the bamboo surface exhibits numerous particulate inclusions (a), adjacent cells maintain close intercellular connections (b), and lignocellulosic fibers demonstrate a tightly aligned orientation (c); after bleaching, the bamboo substrate appears free of visible inclusions, xylem vessels exhibit smooth surfaces (d), and cellular architecture displays structural collapse (e), with apparent fiber delamination (f).
3.3. XPS Analysis
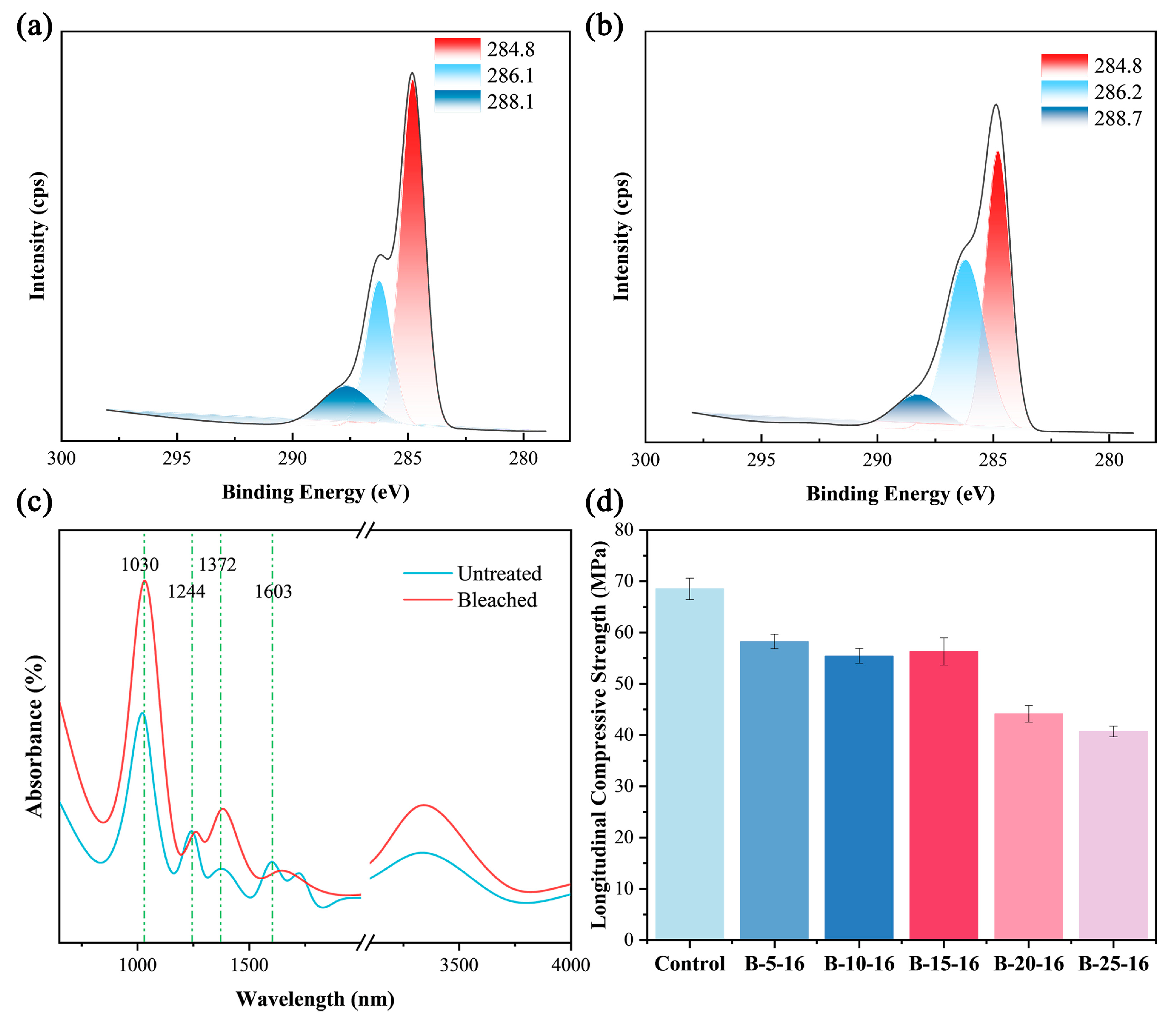
A narrow-scan XPS analysis was conducted on both untreated and bleached bamboo samples to examine alterations in chemical functional groups induced by the bleaching process. High-resolution XPS analysis of the C 1s region in untreated bamboo exhibited three deconvoluted peaks corresponding to distinct carbon states (Figure 3a): (i) C-H/C-C (284.8 eV, C1), (ii) C-O (286.1 eV, C2), and (iii) O-C-O/C=O (288.1 eV, C3) (Table 2). Untreated bamboo displayed characteristic peak area ratios of 58.3% (C1), 26.7% (C2), and 15% (C3). Bleaching treatment induced significant modifications in both elemental composition and carbon bonding configurations. Post-bleaching analysis revealed substantial alterations in peak distribution: 44.7% (C1), 43.7% (C2), and 11.6% (C3) (Figure 3b), corresponding to a 23.5% reduction in C1, 63.7% elevation in C2, and 22.7% decline in C3 relative to untreated samples. The observed C1 depletion correlates with the substantial removal of lignin and extractives during bleaching, as these components predominantly contribute to C-H/C-C bonding. The enhanced C2 signal reflects increased carbon oxidation states, while C3 reduction suggests the cleavage of conjugated C=O bonds in lignin’s chromophoric structures.
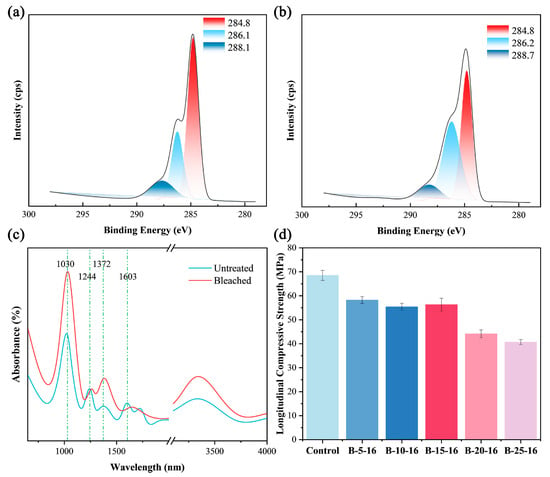
Figure 3.
Narrow spectrum of C1s in bamboo: (a) untreated; (b) bleach treatment (15% H2O2, 16 h). (c) FTIR spectra of untreated bamboo and bleached bamboo (15% H2O2, 16 h). (d) Longitudinal compressive strength of bamboo (B-5-16 denotes a 5% bleaching concentration with a 16-h duration).

Table 2.
The main chemical states and binding energy forms of the C element in bamboo.
3.4. FTIR Analysis
FTIR analysis (Figure 3c) identified a characteristic absorption band at 1603 cm−1 in untreated bamboo that was assigned to the C=C aromatic stretching in lignin structures, which was completely eliminated following bleaching. A distinct band at 1244 cm−1, characteristic of guaiacyl unit C-O stretching in lignin’s aromatic ether linkages, showed marked attenuation after treatment. Concomitantly, the C-O stretching vibration at 1030 cm−1 associated with carbohydrate polymers exhibited marked enhancement, correlating with lignin removal. The cellulose-specific CH2 bending mode at 1372 cm−1 displayed enhanced conspicuity in bleached specimens.
3.5. Mechanical Property Analysis
Longitudinal compressive strength tests demonstrated concentration-dependent deterioration in the mechanical properties of bamboo following H2O2 bleaching. Untreated bamboo specimens showed a baseline compressive strength of 68.52 MPa. Following 16 h of bleaching with 5%, 10%, or 15% H2O2 solutions, the compressive strength decreased to 58.23 MPa (14.9% reduction), 55.43 MPa (19.0% reduction), and 56.23 MPa (17.9% reduction), respectively. This initial strength attenuation phase primarily resulted from partial degradation of the hemicellulose–lignin matrix, whereas cellulose crystallinity remained largely preserved without inducing macroscopic structural collapse. A critical threshold was observed at the 20% H2O2 concentration, with compressive strength sharply decreasing to 44.13 MPa (35.6% reduction), followed by further deterioration to 40.7 MPa (40.6% reduction) at a 25% concentration. This abrupt decline indicates oxidative cleavage of cellulose chains under high-concentration conditions, leading to interfacial debonding and compromised stress transfer mechanisms. These findings highlight the necessity for strict control of the H2O2 concentration (<20%) and bleaching duration to maintain bamboo’s structural integrity during bleaching treatments.
3.6. MIP Test and Liquid Permeability Analysis of Bamboo
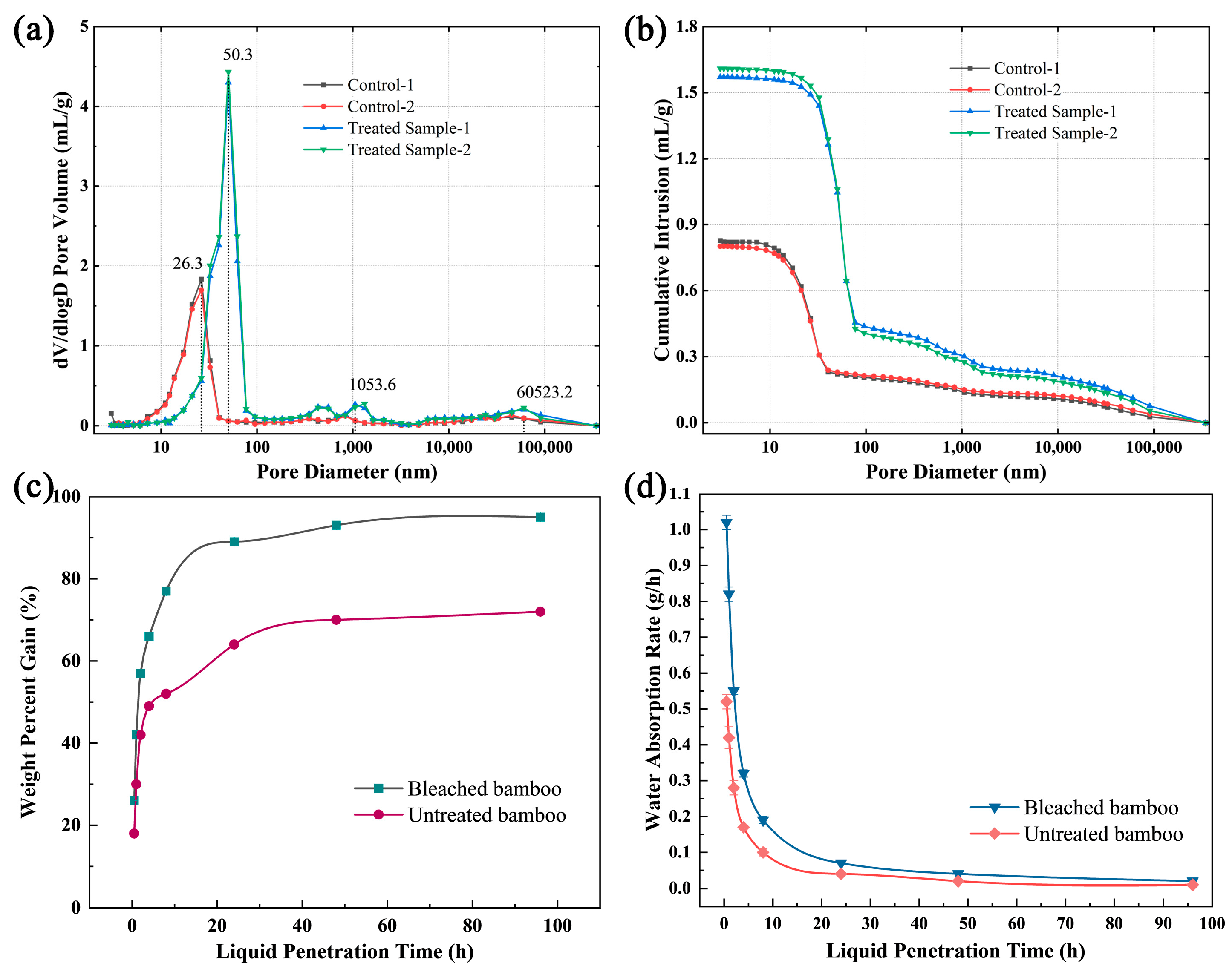
Enhancing the liquid permeability of bamboo promotes uniform agent penetration depth, resulting in optimized material performance and expanded applicability within engineered systems. Microstructural alterations in bamboo were confirmed by SEM after bleaching. These modifications influence the porosity and pore-size distribution, which are critical factors governing bamboo’s liquid permeability. MIP provides quantitative characterization of bamboo pore architecture parameters, including pore-size distribution and connectivity, while revealing critical pore-scale features governing liquid transport dynamics. This analytical approach establishes a mechanistic foundation for process optimization in impregnation treatments and the development of engineered bamboo composites with enhanced permeability, ultimately improving treatment effectiveness and enabling advanced engineering applications [29]. Table 3 presents the MIP results for bamboo samples before and after bleaching. The total intrusion volume, porosity, and median pore diameter increased, whereas bulk density decreased, following bleaching. As shown in Figure 4a,b, notable differences were observed in pore-size distribution and pore volume between the control and bleached bamboo strips. The pore volume of bleached bamboo strips peaked at 4.4 mL/g at a pore diameter of 50.3 nm, suggesting a maximum micropore concentration at this size. In contrast, the pore volume of untreated bamboo peaked at 1.8 mL/g at a pore diameter of 26.3 nm (Figure 4a). This indicates that both the number and size of micropores increased after bleaching, contributing significantly to the rise in pore volume (Figure 4b). At pore diameters of 1053.6 nm and 60,523.2 nm, which correspond to microstructural features such as pits, parenchyma cell lumens, and vessels, bleached samples showed greater contributions to total pore volume. This occurs because bleaching dissolves extractives and degrades lignin, thereby increasing both pore number and size, which in turn enhances liquid transport by expanding permeation channels, lowering resistance, and shortening flow paths [30,31]. Bleaching-induced cracks may also contribute to the increase in cumulative pore volume.

Table 3.
The MIP test result of bamboo before and after the bleaching treatment (15% H2O2, 16 h).
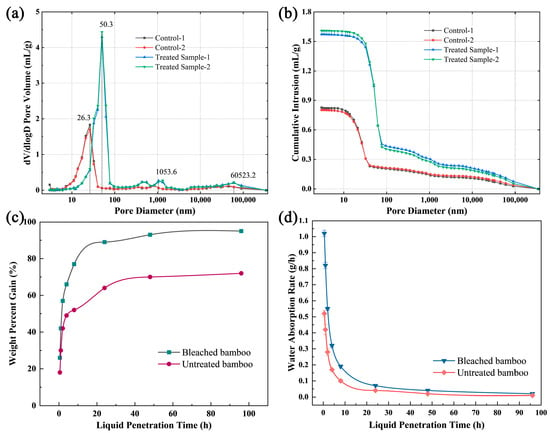
Figure 4.
(a) Log differential intrusion and (b) cumulative intrusion versus pore diameter of bamboo; (c) weight percent gain and (d) water absorption rate of bamboo versus infiltration time.
The water absorption behavior of bamboo significantly influences its processing performance [32,33]. As shown in Figure 4c,d, the weight percent gain and water absorption rate of bleached bamboo strips markedly exceeded those of untreated specimens at equivalent time points. This enhancement is attributed to the leaching of intracellular inclusions during bleaching, which increases cellular porosity. In parallel, lignin and hemicellulose degradation disrupt cell wall integrity, resulting in intercellular fissures and partial cellular collapse. These structural modifications, as illustrated by the pre- and post-bleaching microstructures in Figure 2, collectively enhance pore volume and facilitate fluid infiltration. Mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) data further confirm significant increases in both pore connectivity and diameter after bleaching, which directly correlates with enhanced water absorption capacity. A pronounced increase in bamboo strip mass was observed during the initial 24-h immersion, followed by stabilization with minimal additional weight gain, indicating progressive saturation.
3.7. Anti-Mold Results Analysis
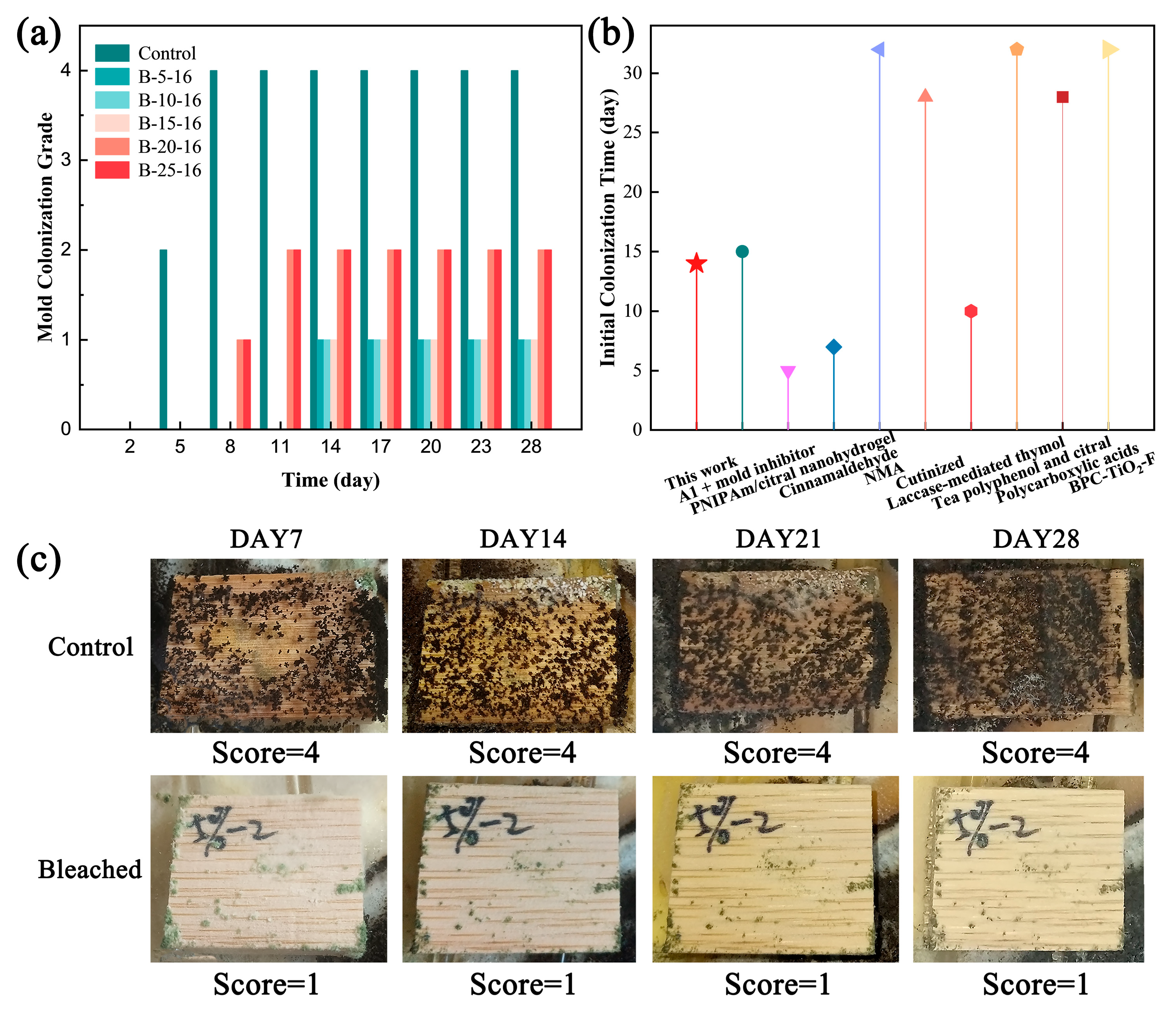
Enhancing the fungal resistance of bamboo materials extends service durability and expands their utility in humid environments and high-performance applications, while simultaneously enhancing product value and commercial competitiveness through the reduction of biodeterioration-induced losses throughout the storage and transport phases [34]. The mold resistance of bamboo specimens was evaluated before and after the bleaching treatment (Figure 5a,c). The specimens were placed in culture media inoculated with Trichoderma, Penicillium, and Aspergillus niger, and incubated in a climate-controlled chamber (28 °C, 85% RH) for 28 days. The results showed that untreated bamboo strips developed visible mold colonization that commenced on day 5. In bleached specimens, 60% exhibited initial fungal growth by day 14 post-inoculation, whereas 40% showed delayed colonization until day 21. Untreated specimens reached a grade IV mold infestation within 7 days, while 40% of bleached specimens developed grade II contamination by day 28, with 60% maintaining grade I. Comparative analysis with previous bamboo preservation studies (Figure 5b) demonstrated that bleached specimens in this study exhibited delayed initial colonization compared to some chemically treated materials, despite the lack of intentional fungicide additives in the experimental protocol.
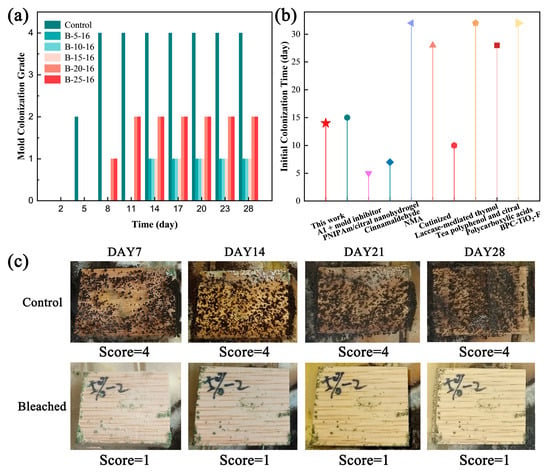
Figure 5.
(a) Mold colonization grades of the bamboo specimens before and after the bleaching treatment. (b) Time to initial colonization of bleached bamboo compared with chemical preservation methods from previous studies [3,4,6,35,36,37,38,39,40]. (c) Mold resistance performance of the bleached bamboo specimens.
4. Conclusions
The experimental results demonstrate that hydrogen peroxide bleaching significantly enhances bamboo’s material characteristics, yielding durable engineered bamboo materials. The treatment facilitates lignin degradation and eliminates cellular inclusions, resulting in surfaces with enhanced whiteness (L* = 12.3) and chromatic uniformity. Bleaching elevates porosity (from 53.37% to 69.13%) and expands the median pore diameter (from 28.4 to 57.4 nm), achieving a 93% increase in total intrusion volume relative to controls. This breakthrough in permeability resolves the persistent challenge of insufficient agent penetration, which has been a key industrial bottleneck in bamboo modification. Bleach-induced depletion of nutrient substrates confers superior mold resistance compared to conventional treatments, with 60% of specimens retaining grade I colonization status throughout the 28 days. This single-step process utilizes solely hydrogen peroxide, obviating complex chemical additives that are common in traditional preservation methods. Building on the demonstrated bleaching–permeability relationship, future studies should prioritize post-bleaching functionalization (e.g., in situ polymerization or nanocoatings) that addresses structural vulnerabilities while preserving permeability. The hydrogen peroxide bleaching process thus constitutes an eco-friendly and cost-effective modification strategy. This approach demonstrates significant potential for manufacturing value-added bamboo products, particularly sustainable construction materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.X. and S.H.; formal analysis, D.X. and H.Q.; data curation, D.X.; writing—original draft, D.X.; methodology, D.X. and S.H.; investigation, D.X., W.L. and S.H.; writing—review and editing, S.H. and W.L.; resources, Y.C.; funding acquisition, S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Forestry Science and Technology programs of Zhejiang (No: 2022SY12), the Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation Project (No: LY24C160005), and the Nanping Science and Technology program (No: N2023T023).
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dixon, P.G.; Gibson, L.J. The structure and mechanics of Moso bamboo material. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.X.; Ji, Y.H.; Yu, W.J. Development of bamboo scrimber: A literature review. J. Wood Sci. 2019, 65, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Fu, R. Anti-mold and hydrophobicity of cutinized bamboo prepared via different annealing processes. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2022, 187, 115399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Du, C.; Hu, A.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, F. Fabrication of core–shell type poly(NIPAm)-encapsulated citral and its application on bamboo as an anti-molding coating. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36884–36894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Han, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.-L. Improving the anti-mould capacity of bamboo through sequential alkaline extraction and laccase-mediated thymol modification. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 354, 129104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, L.; Xiang, L.; Liu, H.; Shao, H.; Qi, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, J. Improving the anti-mould property of Moso bamboo surface by using a bamboo green colour preservation approach. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 18, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicka, N.; Tavcer, P.F. Low-temperature bleaching of knit fabric from regenerated bamboo fibers with different peracetic acid bleaching processes. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiserova, M.; Opalena, E.; Gigac, J.; Stankovska, M. Oxidative and Reductive Bleaching of Deinked Pulp. Wood Res. 2018, 63, 639–653. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, F.; Fang, G.; Jiao, J.; Deng, Y.; Han, S.; Li, H.; Tian, Q.; Pan, A.; Zhu, B. Modified Hydrogen Peroxide Bleaching of Bamboo Chemo-mechanical Pulp Using Aqueous Alcohol Media. BioResources 2019, 14, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shamey, R.; Hinks, D. Activated peroxide bleaching of regenerated bamboo fiber using a butyrolactam-based cationic bleach activator. Cellulose 2010, 17, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tang, P.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G. An environmentally friendly bleaching process for cotton fabrics: Mechanism and application of UV/H2O2 system. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dou, H.; Fu, Y.; Qin, M. Improving the hydrogen peroxide bleaching efficiency of aspen chemithermomechanical pulp by using chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.F. Oxidation of lignin-carbohydrate complex from bamboo with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by Co(salen). Hem. Ind. 2014, 68, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zuo, M.; Ding, N.; Yan, G.; Zeng, X.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Lei, T.; Lin, L. Preparation of Nanocellulose with High-Pressure Homogenization from Pretreated Biomass with Cooking with Active Oxygen and Solid Alkali. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9378–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Ji, H.; Zhong, T.; Wang, G. A comparative study of the microstructure and water permeability between flattened bamboo and bamboo culm. J. Wood Sci. 2019, 65, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Kang, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Yi, S. A facile method for constructing non-carbonised puffed bamboo with hierarchical pore structure based on self-exploding mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 425, 136049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, B.; Sun, S.; Lin, X.; Song, L.; Wu, A.; Li, H. Characterization of Lignin Structures in Phyllostachys edulis (Moso Bamboo) at Different Ages. Polymers 2020, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Qu, M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B.; Lv, H.; Fei, B. Comprehensive spectroscopic analysis of the chemical properties of moso bamboo at different ages. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, L.C.; Fakudze, S.; Makombe, G.G.; Muse, S.; Zhu, J. Bamboo as a Valuable Resource and its Utilization in Historical and Modern-day China. BioResources 2022, 17, 1926–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D4442-20; Standard Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measurement of Wood and Wood-Based Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Akkus, M.; Budakçi, M. Determination of color-changing effects of bleaching chemicals on some heat-treated woods. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15780-1995; Testing Methods for Physical and Mechanical Properties of Bamboos. State Bureau of Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1995.
- GB/T 18261-2013; Test Method for Anti-Mildew Agents in Controlling Wood Mould and Stain Fungi. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ), Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2013.
- Horikawa, Y.; Tsushima, R.; Noguchi, K.; Nakaba, S.; Funada, R. Development of colorless wood via two-step delignification involving alcoholysis and bleaching with maintaining natural hierarchical structure. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Tang, C.; Huang, Q. Effect of H2O2 Bleaching Treatment on the Properties of Finished Transparent Wood. Polymers 2019, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakicier, N.; Ulay, G. Determination of Color Characteristics of Some Wood Species Treated with Bleaching Chemicals. BioResources 2023, 18, 7796–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xiong, X.; Lu, G.; Gui, C.; Pang, X. Effects of NaOH/H2O2<Na2SiO3 Bleaching Pretreatment Method on Wood Dyeing Properties. Coatings 2023, 13, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Lovric, A.; Zdravkovic, V.; Furtula, M. Influence of Thermal Modification on Colour of Poplar (Populus × euramericana) Rotary Cut Veneer. Wood Res. 2014, 59, 661–670. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, L.M.D.; Innocentini, M.D.d.M.; Kadivar, M.; Savastano, H. An exploratory study on bamboo permeability for evaluation of treatability with chemical solutions. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pang, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Li, X. Determining the pore structure and radial variability of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Wood Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Cao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y. Pore structure evolution of bamboo fiber and parenchyma cell wall during sequential chemical removal. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 193, 116165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; He, S.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L. Effect of Vacuum Freeze-drying on Enhancing Liquid Permeability of Moso Bamboo. BioResources 2018, 13, 4159–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. Improvement of Eucalyptus urophylla Wood Permeability via Urea Treatment. BioResources 2023, 18, 4790–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. A simple and sustainable method for preparing high-strength, lightweight, dimensional stable, and mildew resistant multifunctional bamboo. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 135027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Du, C.; Shan, Y.; Yin, W.; Yang, F.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Y. Process and Anti-Mildew Properties of Tea Polyphenol-Modified Citral-Treated Bamboo. Molecules 2022, 27, 7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Li, J. Evaluation of anti-mold, termite resistance and physical-mechanical properties of bamboo cross-linking modified by polycarboxylic acids. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Xu, S.; Huang, C.; Cao, Y.; Wu, X. Dual preservative strategy for facilitating bamboo durability using cinnamaldehyde and diethylenetriamine and its reaction characteristics on bamboo cell wall. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lin, X.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, W. In situ polymerization of N-methylol acrylamide (NMA) for bamboo anti-mold modification. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 363, 129887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Han, S.; Sun, F. Anti-mold activity and reaction mechanism of bamboo modified with laccase-mediated thymol. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, X.; Lu, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Tong, W.; Yuan, H.; et al. Anti-mold, self-cleaning superhydrophobic bamboo fiber/polypropylene composites with mechanical durability. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1150635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).