A Comprehensive Evaluation of Simulating Thermal Conductivity in Oak Wood Using XCT Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.2.1. Computed Tomography
2.2.2. TPS Thermal Constant Analyzer
2.3. Methodology
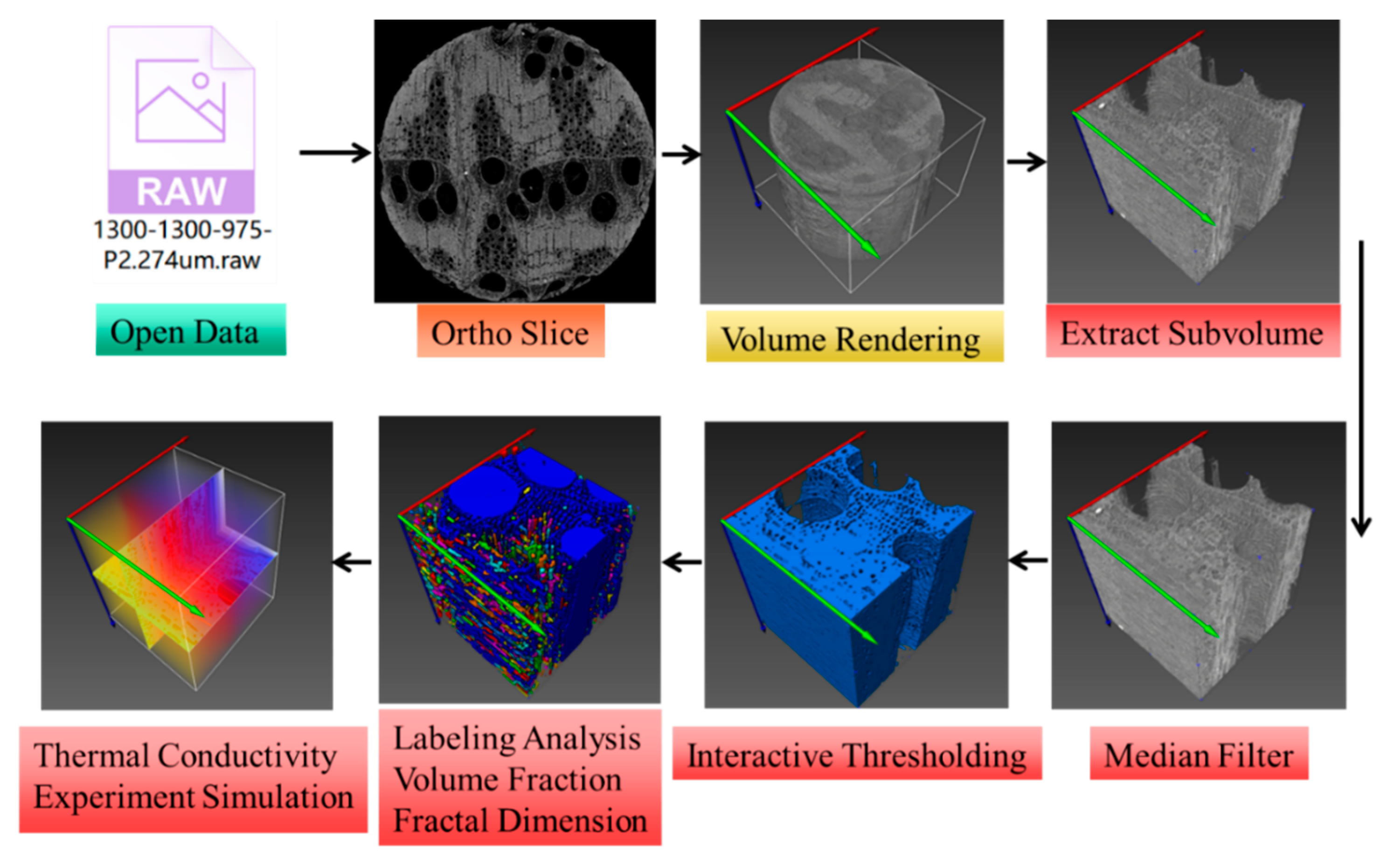
2.3.1. Digital Image Processing Method
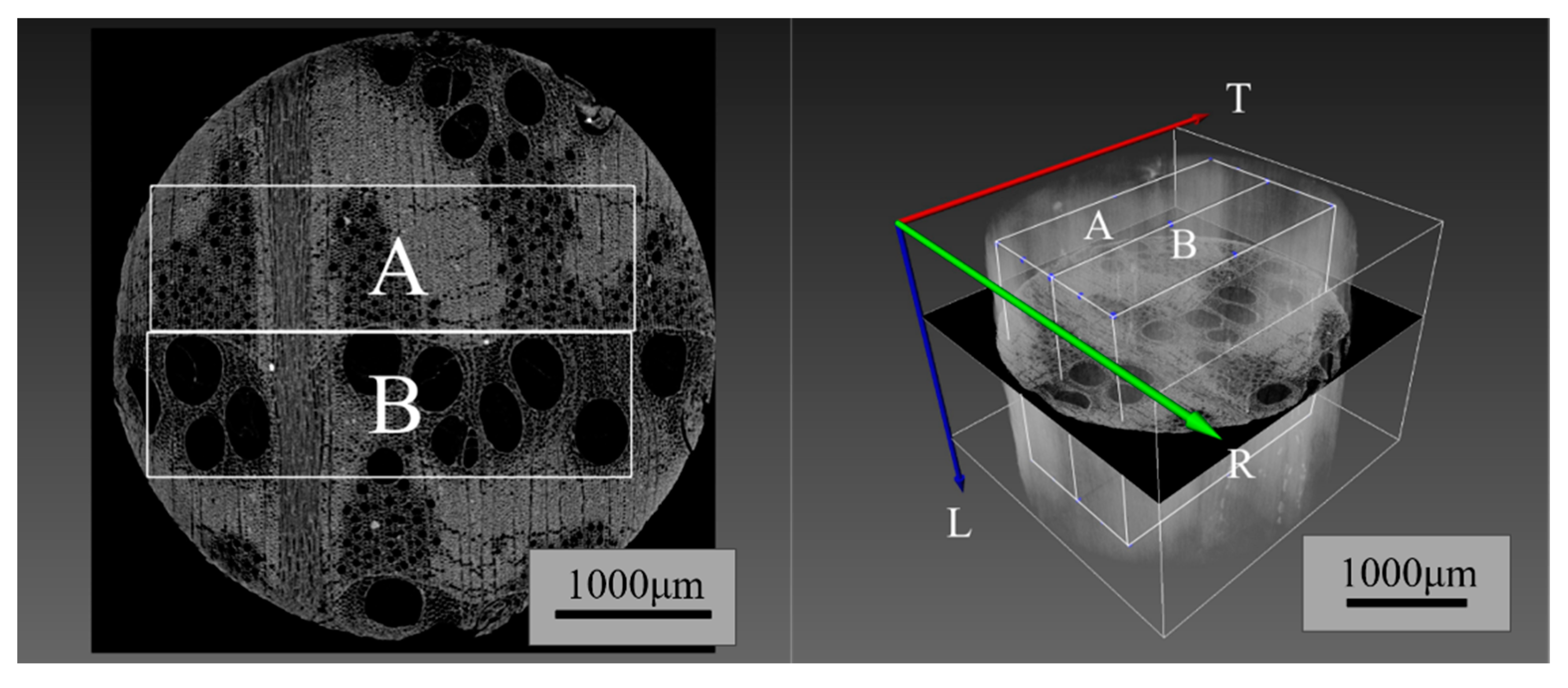
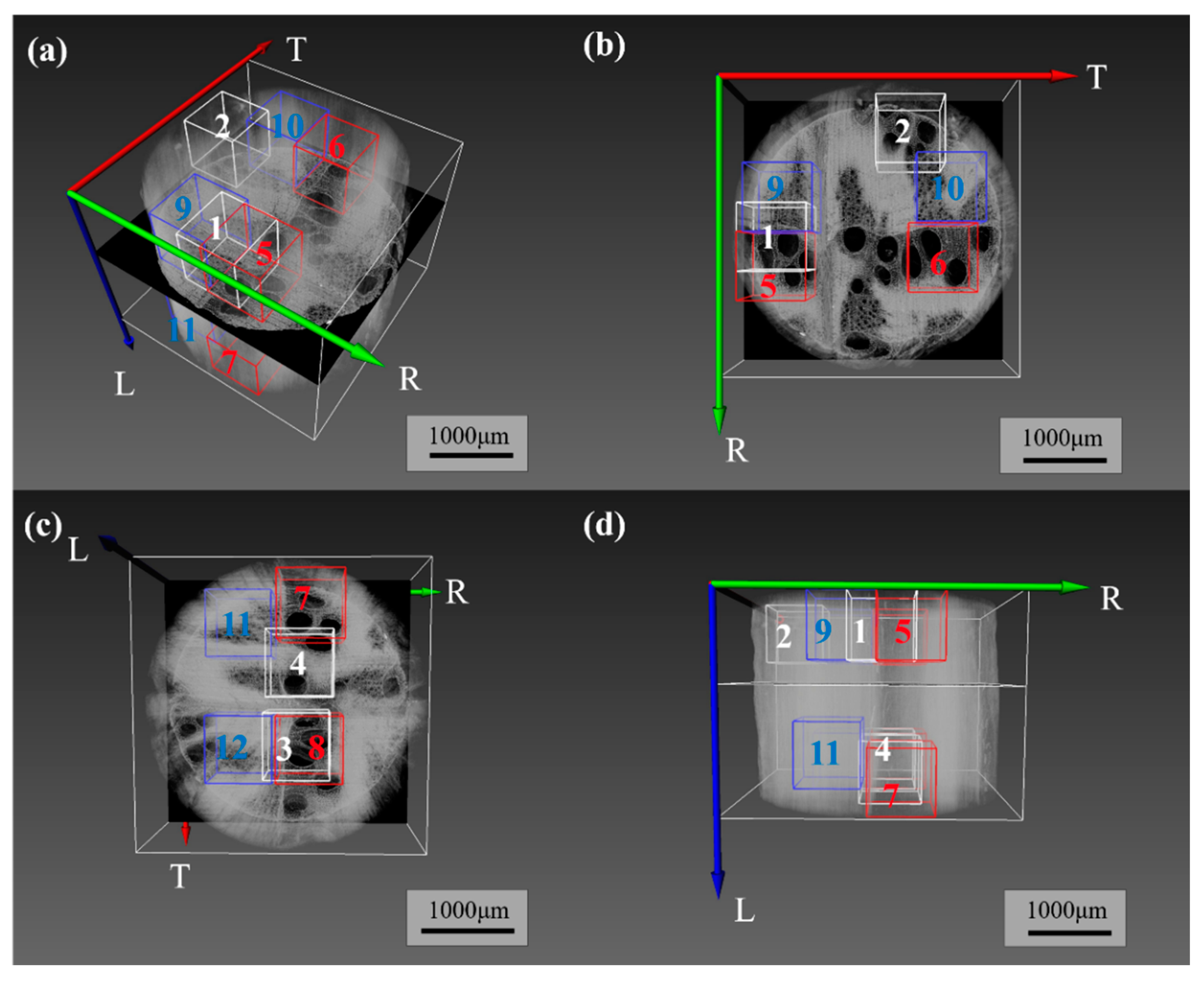
2.3.2. Selection of Characteristic Pore Areas in Wood
2.3.3. Effective Thermal Conductivity Simulation
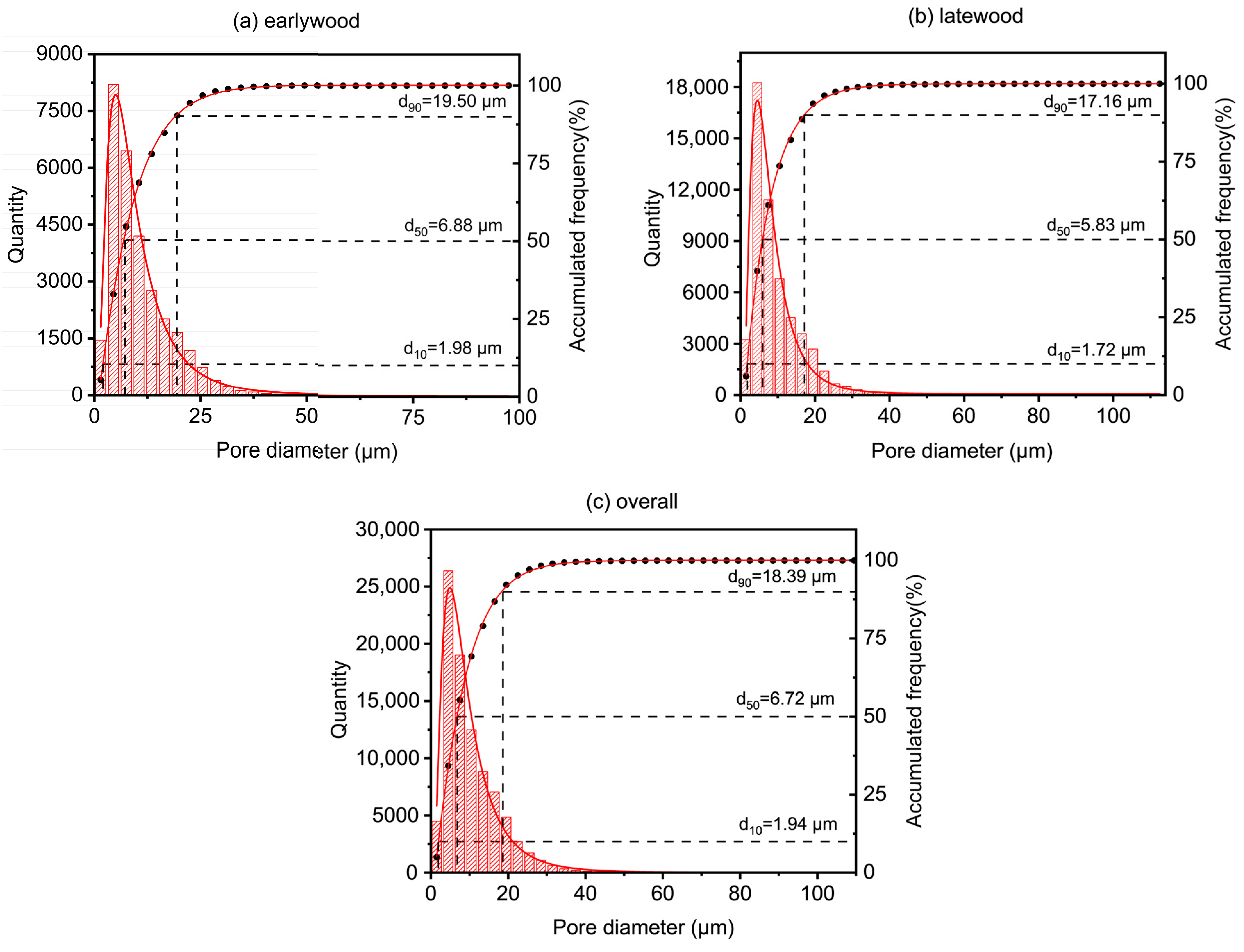
2.3.4. Pore Size Determination
3. Results and Discussion
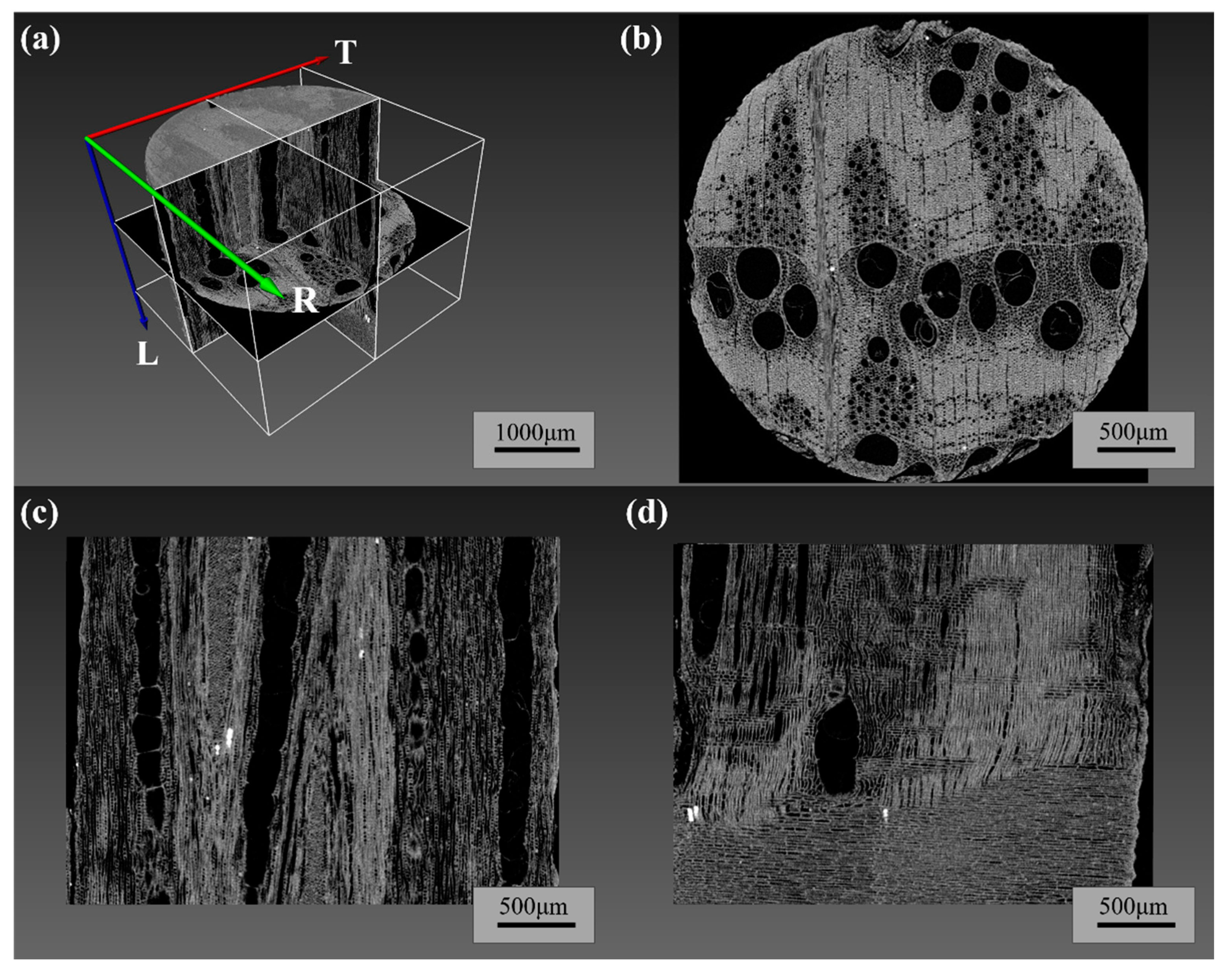
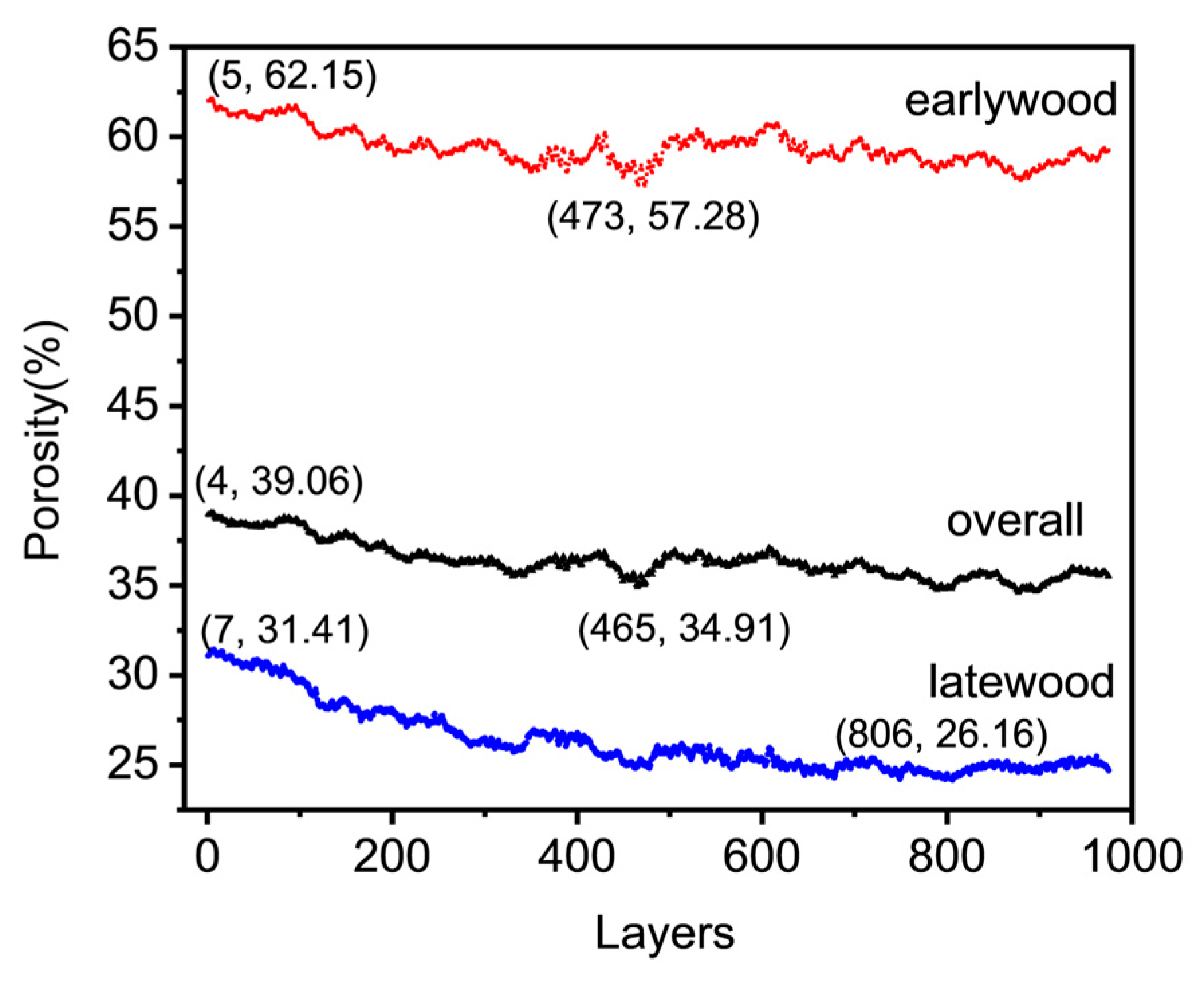
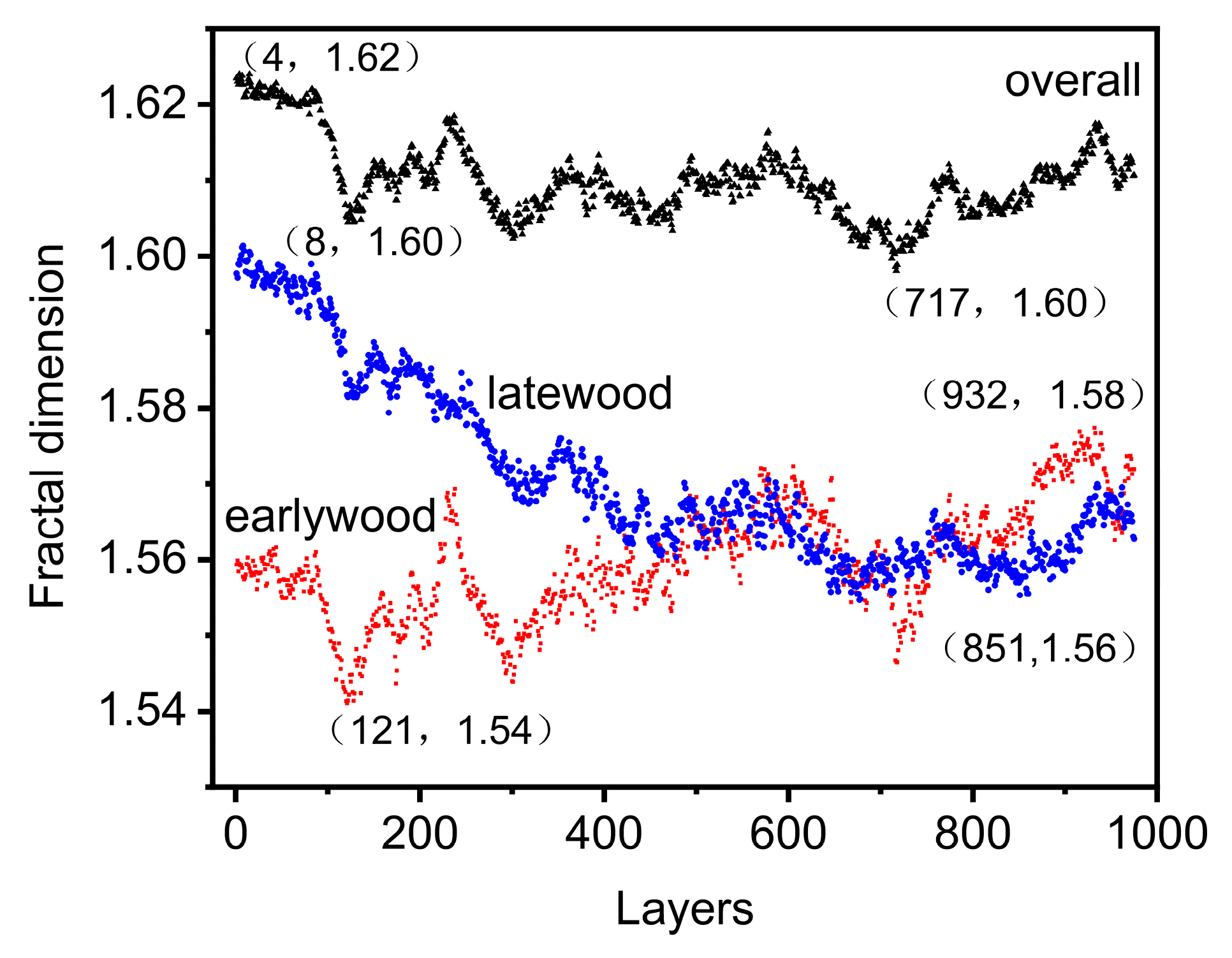
3.1. Pore Structure and Parameters
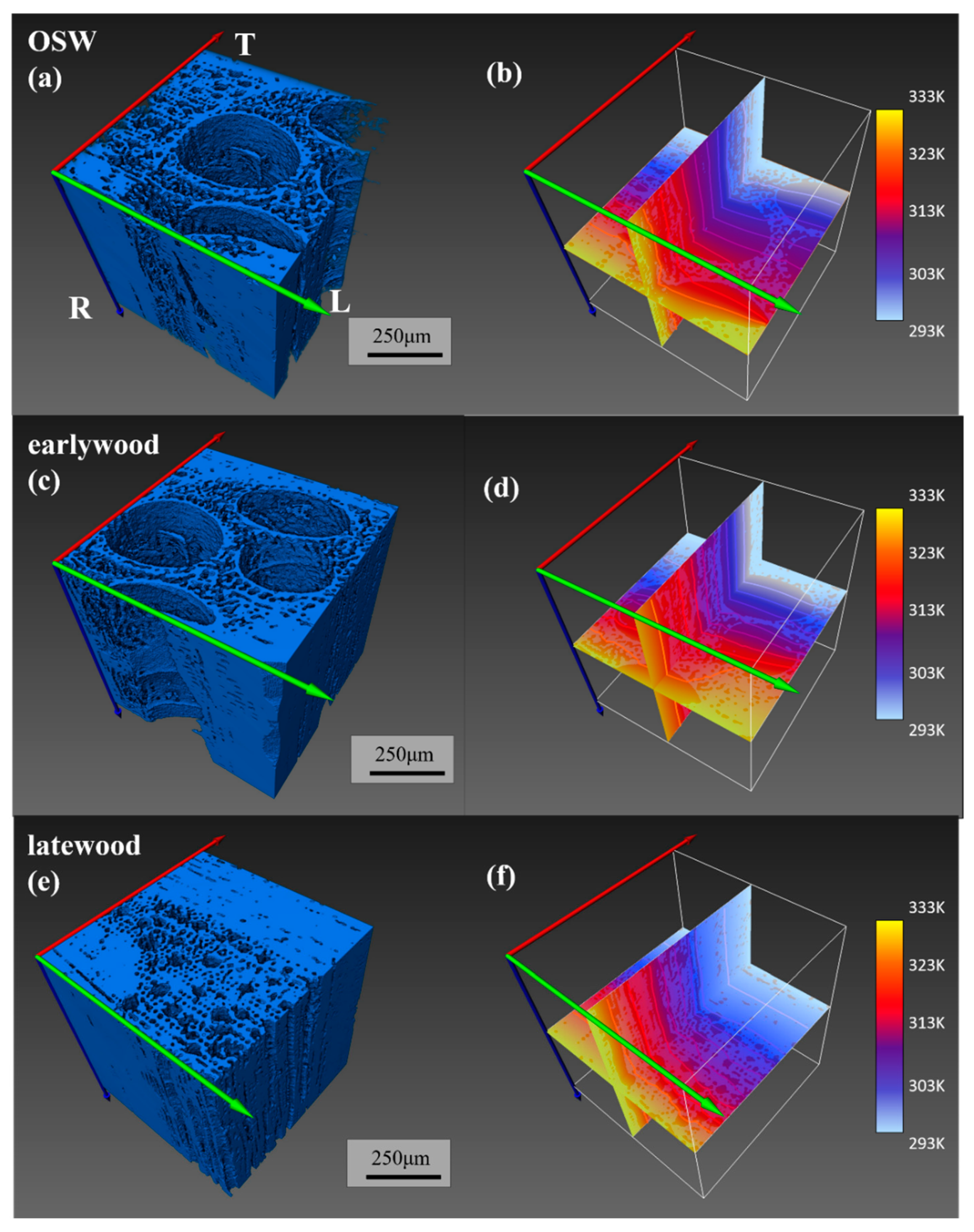
3.2. Heat Transfer Simulation and Validation
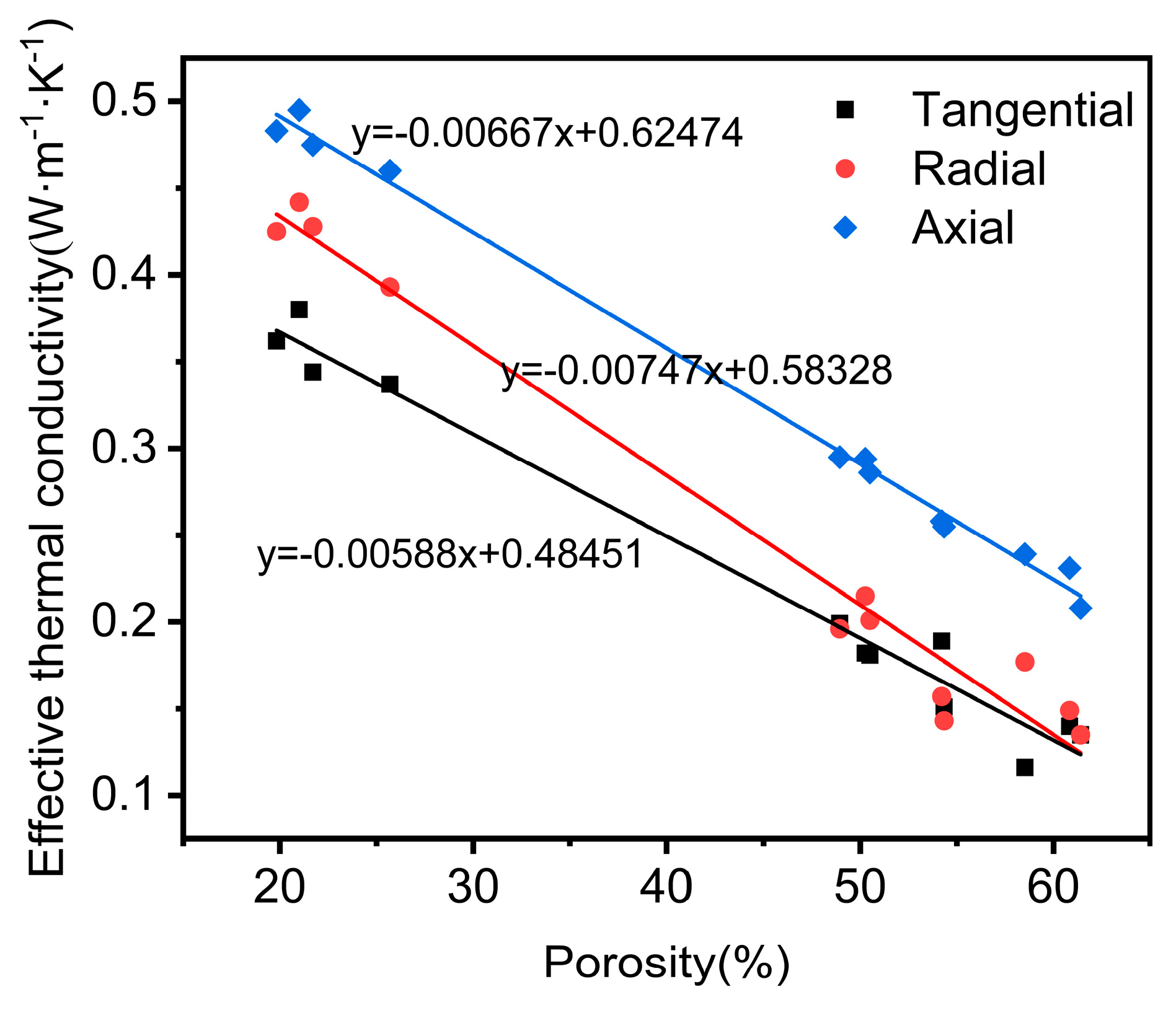
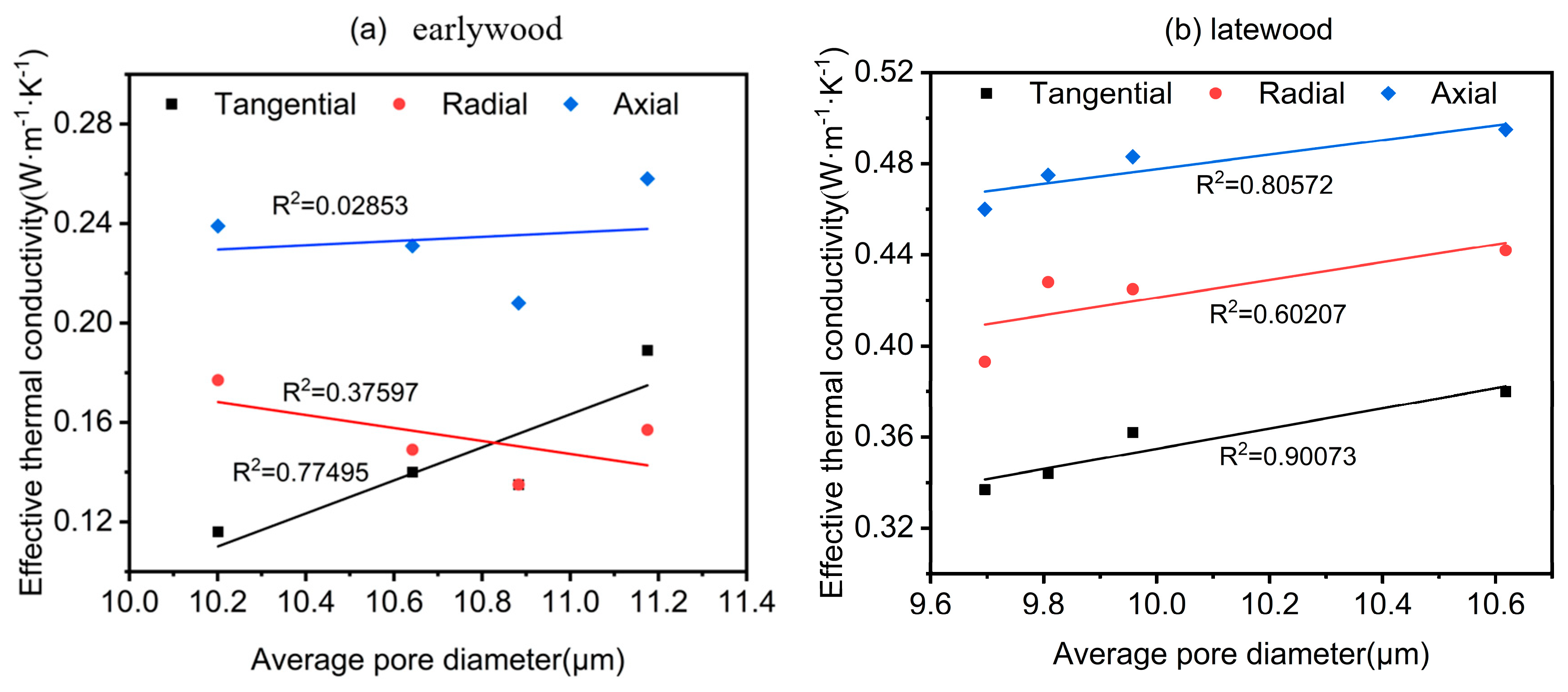
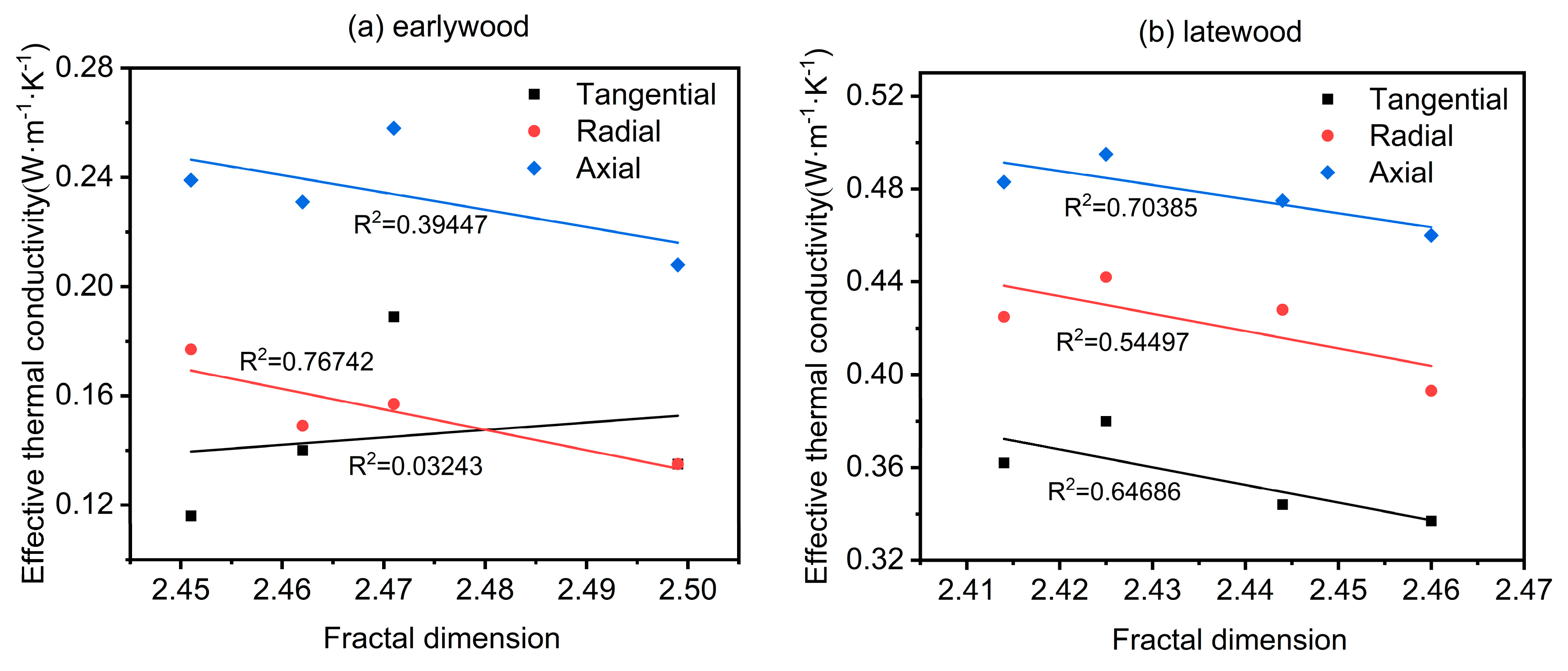
3.3. Relationship Between Pore Structure and Thermal Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, J.; Guo, L.; Cai, Y. A novel fractal model for the prediction and analysis of the equivalent thermal conductivity in wood. Holzforschung 2021, 75, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, C.; Ozdemir, E.; Baysal, E.; Ergun, M.E.; Toker, H. Physical, mechanical, and thermal characteristics of alkaline copper quaternary impregnated oriental beech wood. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2024, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinci, A.U.; Demir, A.; Ozturk, H. Comparison of thermal performances of plywood shear walls produced with different thermal insulation materials. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2022, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhao, L.; Yan, J.; Feng, H.-Y. Implementation of digital twin in actual production: Intelligent assembly paradigm for large-scale industrial equipment. Machines 2023, 11, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, M. Effect of extractive content on the thermal stability of two wood species from brazil. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2016, 18, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.L.; Qin, B.; Ma, Z.Y.; Gao, Y.C.; Guan, Q.F.; Yang, H.B.; Yu, S.H. Emerging bioinspired artificial woods. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2001086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, B.; Larfeldt, J.; Leckner, B.; Gustavsson, M. Thermal conductivity and diffusivity of wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prałat, K. Research on thermal conductivity of the wood and analysis of results obtained by the hot wire method. Exp. Tech. 2016, 40, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-S.; Tao, X.; Xu, W. Thermal conductivity of Poplar wood veneer impregnated with graphene/polyvinyl alcohol. Forests 2021, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flity, H.; Jannot, Y.; Terrei, L.; Lardet, P.; Schick, V.; Acem, Z.; Parent, G. Thermal conductivity parallel and perpendicular to fibers direction and heat capacity measurements of eight wood species up to 160 °C. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 195, 108661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sova, D.; Porojan, M.; Bedelean, B.; Huminic, G. Effective thermal conductivity models applied to wood briquettes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 124, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagüela, S.; Bison, P.; Peron, F.; Romagnoni, P. Thermal conductivity measurements on wood materials with transient plane source technique. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 600, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.F.; Gu, H. Two-dimensional finite element heat transfer model of softwood. Part I. Effective thermal conductivity. Wood Fiber Sci. 2006, 38, 592–598. [Google Scholar]
- Varnier, M.; Sauvat, N.; Ulmet, L.; Montero, C.; Dubois, F.; Gril, J. Influence of temperature in a mass transfer simulation: Application to wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 943–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.R.; Flores, E.I.S.; Yanez, S.J.; Vasco, D.A.; Pina, J.C.; Guzmán, C.F. Multiscale modeling of the thermal conductivity of wood and its application to cross-laminated timber. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 144, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochukhan, N.; Rafferty, A.; Canavan, M.; Daly, D.; Selkirk, A.; Rameshkumar, S.; Morris, M.A. Development and application of a 3D image analysis strategy for focused ion beam–Scanning electron microscopy tomography of porous soft materials. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Fu, F. High-permeability wood with microwave remodeling structure. Forests 2021, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plötze, M.; Niemz, P. Porosity and pore size distribution of different wood types as determined by mercury intrusion porosimetry. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2011, 69, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Cai, Y. Combining mercury intrusion porosimetry and fractal theory to determine the porous characteristics of wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhou, F.; Cai, J. Bound water content and pore size distribution of thermally modified wood studied by NMR. Forests 2020, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, X.; Jiang, J. Moisture transfer and stress development during high-temperature drying of Chinese fir. Drying Technol. 2020, 38, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombini, F.L.; Lautert, E.L.; Mariath, J.E.d.A.; de Oliveira, B.F. Combining numerical models and discretizing methods in the analysis of bamboo parenchyma using finite element analysis based on X-ray microtomography. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Zhao, J. Pore Structure Characterization of Oak via X-ray Computed Tomography. Bioresour. 2020, 15, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Lv, P.; Sun, Z.; Cai, Y. A comprehensive evaluation of axial gas permeability in wood using XCT imaging. Wood Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrä, H.; Dobrovolskij, D.; Engelhardt, M.; Godehardt, M.; Makas, M.; Mercier, C.; Rief, S.; Schladitz, K.; Staub, S.; Trawka, K. Image-based microstructural simulation of thermal conductivity for highly porous wood fiber insulation boards: 3D imaging, microstructure modeling, and numerical simulations for insight into structure–property relation. Wood Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 22007-2; Plastics-Determination of Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusivity-Part 2: Transient Plane Heat Source (Hot Disc) Method. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Wu, K.F.; Cao, T.F.; Li, W.B.; Zhang, H.; Tang, G.H. Quantitative evaluation of the natural convection effect on thermal conductivity measurement with transient plane source method. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 45, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X. Fractal Geometry–Fundamentals and Applications of Mathematics; Chongqing Publishing House: Chongqing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Asako, Y.; Kamikoga, H.; Nishimura, H.; Yamaguchi, Y. Effective thermal conductivity of compressed woods. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maku, T. Studies on the Heat Conductin in Wood: The present study is a discussion on the results of investigations made hitherto by author on heat conduction in wood. Wood Res. Rep. Inst. Wood Res. Kyoto Univ. Jpn. 1954, 13, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, M.; Cheng, M.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, P.; Cen, K. High resolution X-ray microtomography for the characterization of pore structure and effective thermal conductivity of iron ore sinter. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 127, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, D.H. Manual of symbols and terminology for physicochemical quantities and units, appendix II: Definitions, terminology and symbols in colloid and surface chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1972, 31, 577–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhoury, J.E.; Shankar, R.; Ramakrishnan, T. Resolution and limitations of X-ray micro-CT with applications to sandstones and limestones. Transp. Porous Media 2019, 129, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, J. The aspiration of bordered pits in conifer wood. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1972, 181, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibebu, D.T.; Avramidis, S. Fractal dimension of wood pores from pore size distribution. Holzforschung 2022, 76, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, G. Wood Science, 2nd ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, X. Thermal conductivity analysis of high porosity structures with open and closed pores. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 183, 122089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.A.; Mahmoudi, A.; Khan, A.M.; Javed, S.; Liu, S. A critical review: Shape optimization of welded plate heat exchangers based on grey correlation theory. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 144, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzikiriakos, S.; Avramidis, S. Fractal dimension of wood surfaces from sorption isotherms. Wood Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

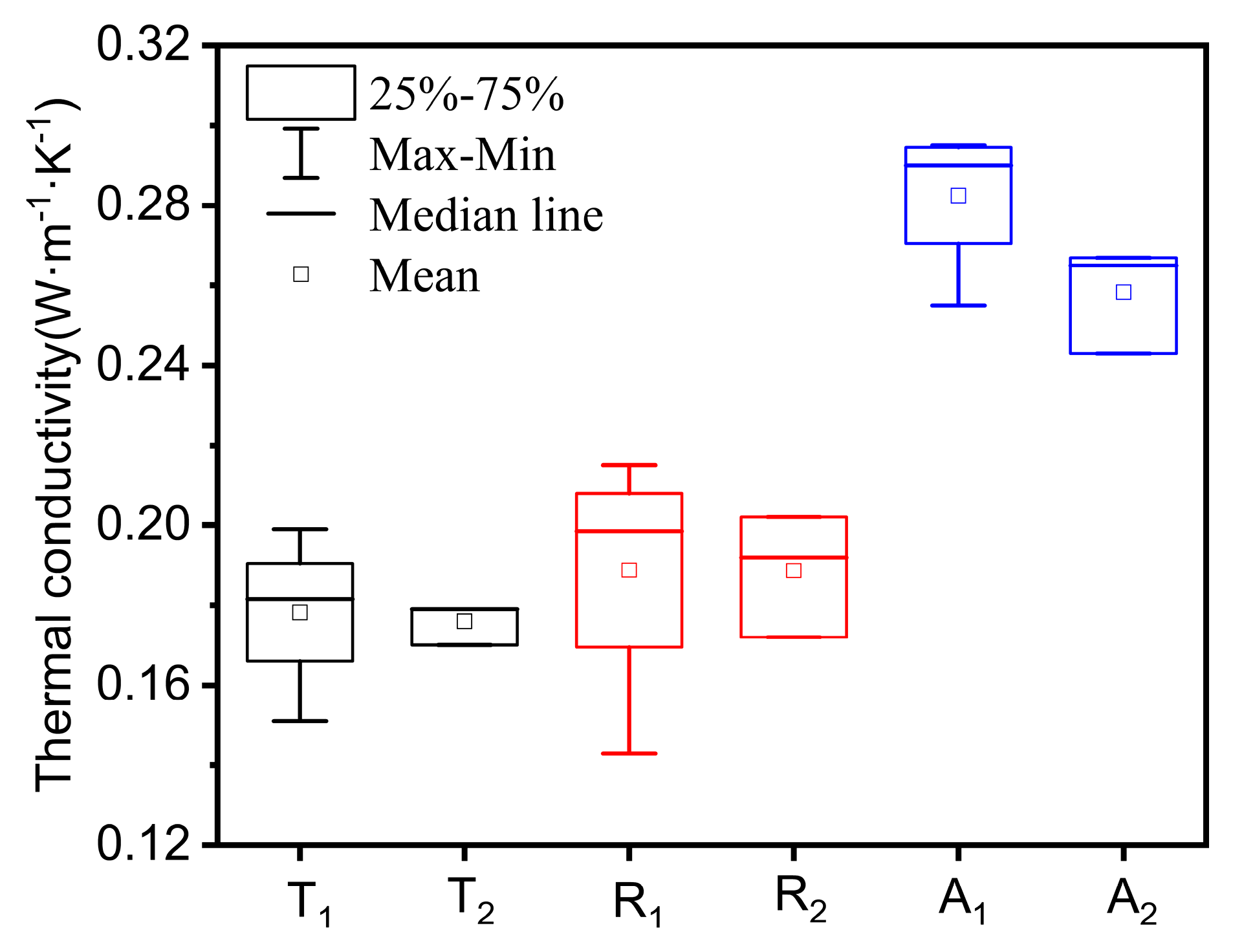
| Number | Tangential Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Radial Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Axial Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.151 | 0.143 | 0.255 |
| 2 | 0.181 | 0.201 | 0.286 |
| 3 | 0.199 | 0.196 | 0.295 |
| 4 | 0.182 | 0.215 | 0.294 |
| Average/standard deviation | 0.178 (0.0199) | 0.189 (0.0314) | 0.282 (0.0185) |
| TPS experimental measurements | 0.176 | 0.188 | 0.258 |
| Reference values | 0.171 | 0.190 | 0.200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Chen, B.; Lv, J.; Yi, J.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chi, X. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Simulating Thermal Conductivity in Oak Wood Using XCT Imaging. Forests 2025, 16, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050834
Zhao J, Chen B, Lv J, Yi J, Yuan L, Liu Y, Cai Y, Chi X. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Simulating Thermal Conductivity in Oak Wood Using XCT Imaging. Forests. 2025; 16(5):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050834
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingyao, Bonan Chen, Jiajun Lv, Jiancong Yi, Liying Yuan, Yuanchu Liu, Yingchun Cai, and Xiang Chi. 2025. "A Comprehensive Evaluation of Simulating Thermal Conductivity in Oak Wood Using XCT Imaging" Forests 16, no. 5: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050834
APA StyleZhao, J., Chen, B., Lv, J., Yi, J., Yuan, L., Liu, Y., Cai, Y., & Chi, X. (2025). A Comprehensive Evaluation of Simulating Thermal Conductivity in Oak Wood Using XCT Imaging. Forests, 16(5), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050834






