Nutrient Attraction and Secondary Metabolites Induce Eogystia hippophaecola (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) Larvae Transfer from Sea Buckthorn Trunks to Roots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Plants and Insects
2.2. Determination of Nutrients in Sea Buckthorn Roots and Trunks
2.2.1. Determination of Nutrients and Mineral Elements
2.2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Determination of Enzyme Activities in the Larval Midgut
2.3.1. Determination of Digestive Enzyme Activity in the Midgut of Larvae
2.3.2. Determination of Larval Intestinal Detoxification Enzyme Activity
2.3.3. Measurement of Intestinal Protective Enzyme Activity in Larvae
2.3.4. Data Analysis
2.4. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.4.1. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) Analysis
2.4.2. Analysis of Untargeted Metabolomics Raw Data
2.4.3. Metabolic Pathway Annotation and Enrichment Pathway Analysis
3. Results
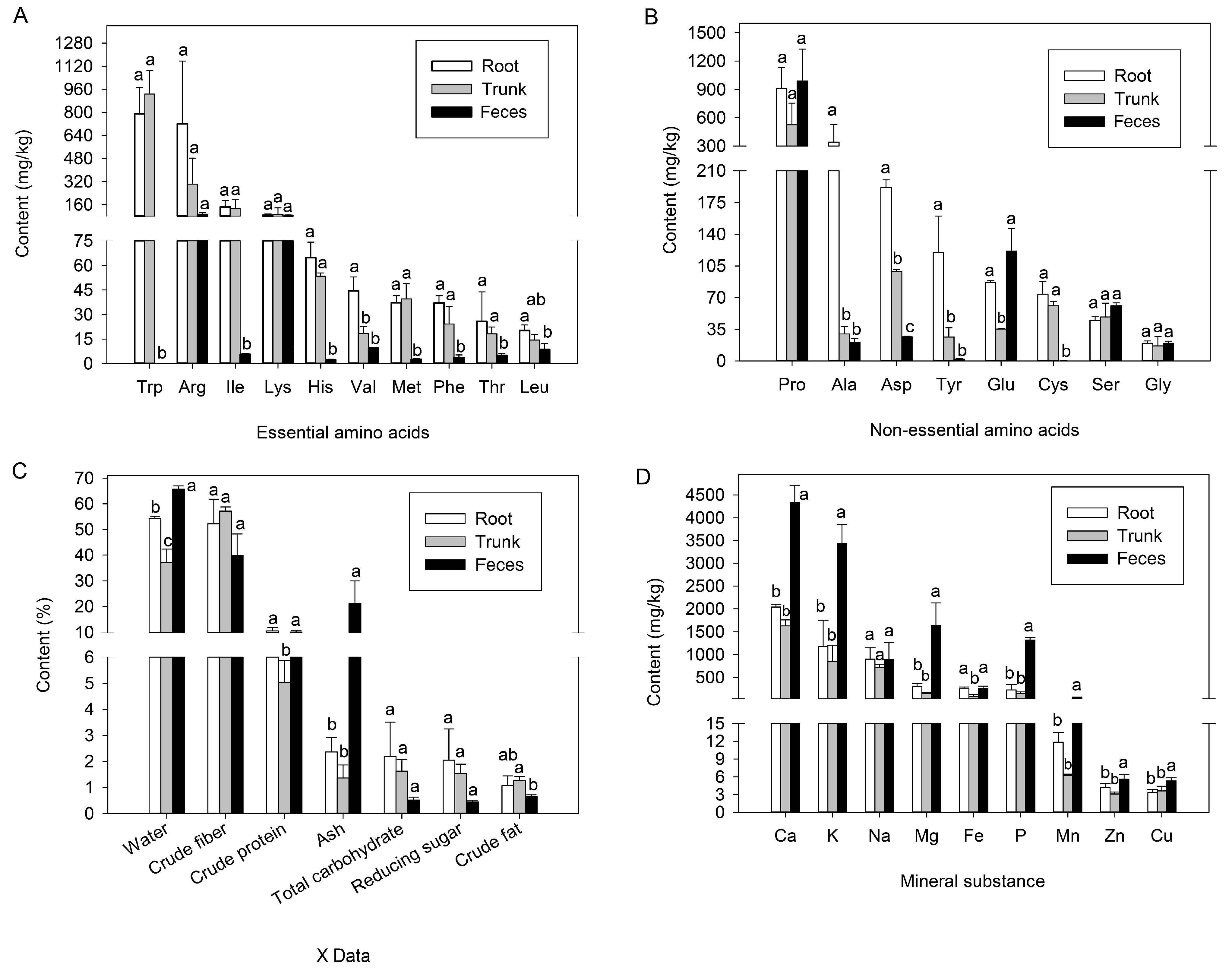
3.1. Nutrient Content of E. hippophaecola Larval Host Plants and Feces
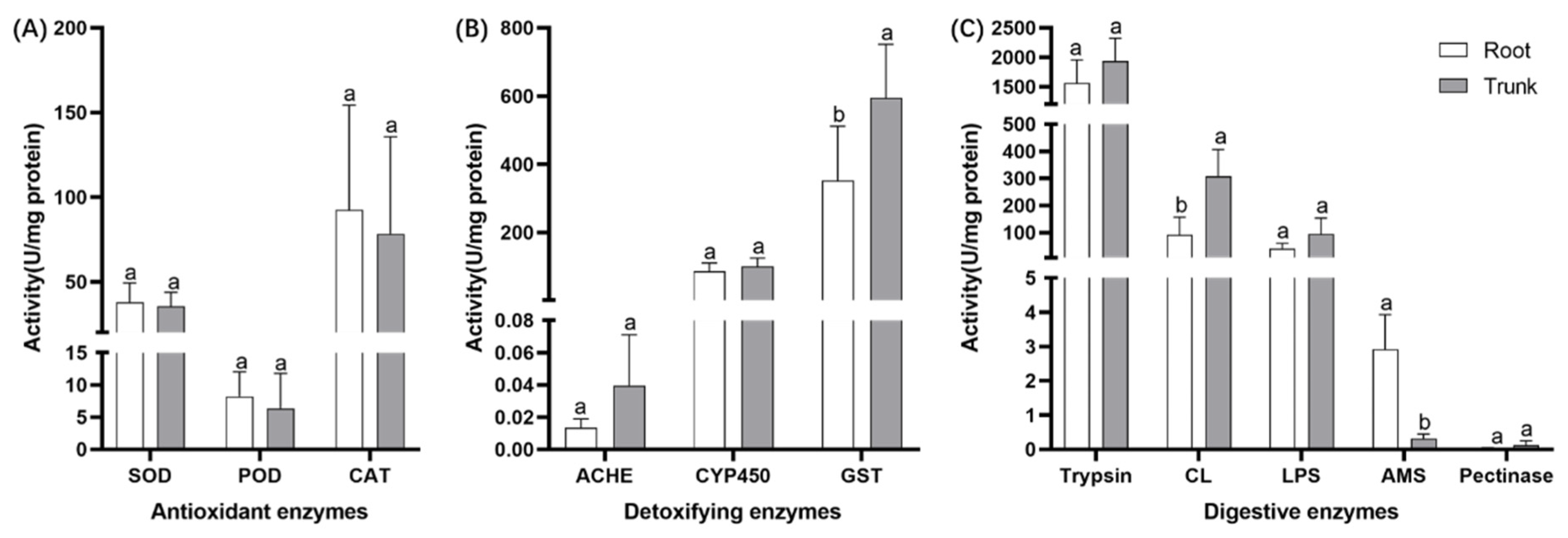
3.2. Effects of Different Feeding Sites on the Digestive and Metabolic Enzyme System of E. hippophaecola Larvae
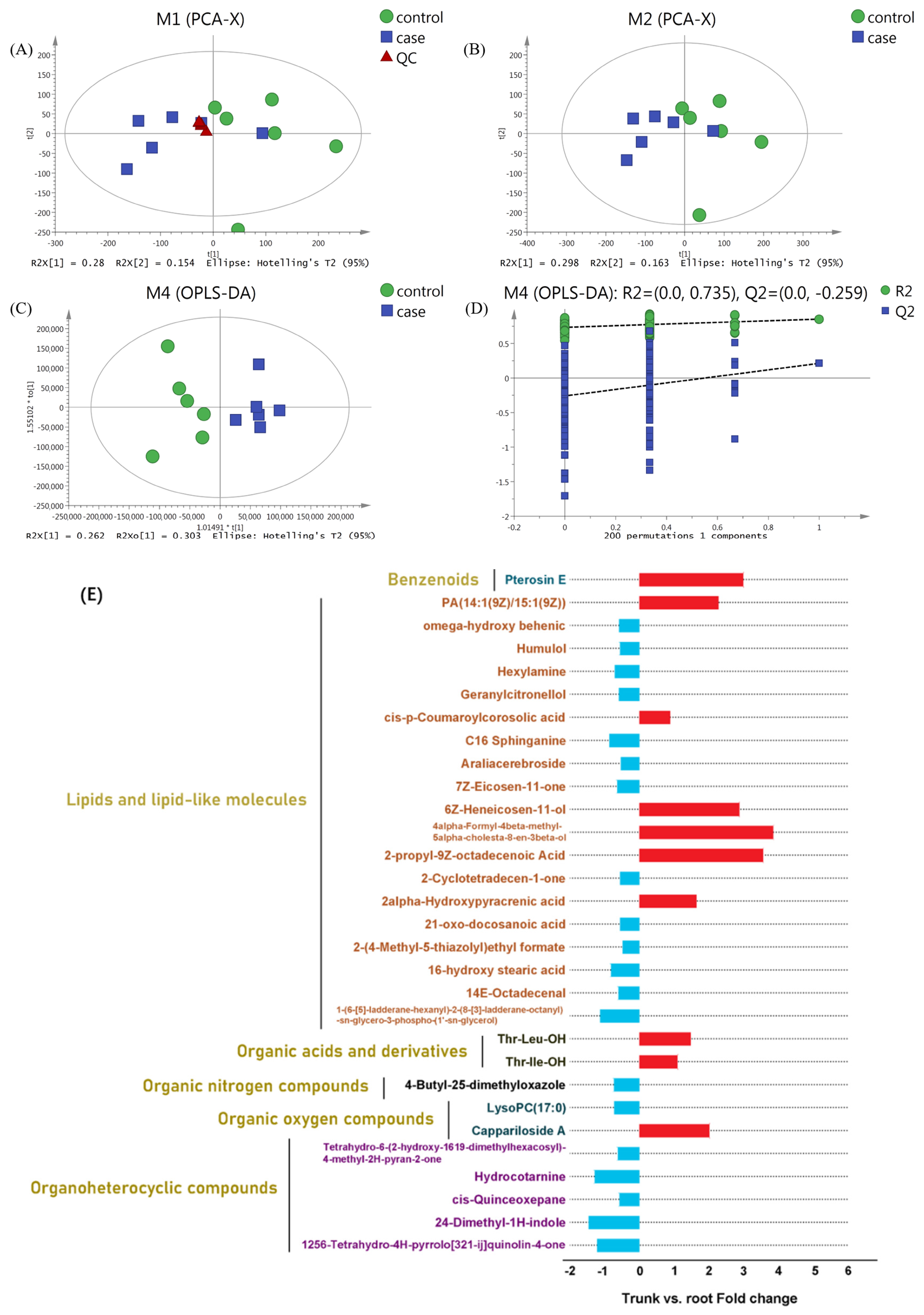
3.3. Metabolic Profile of Sea Buckthorn Roots and Trunks After Being Fed on
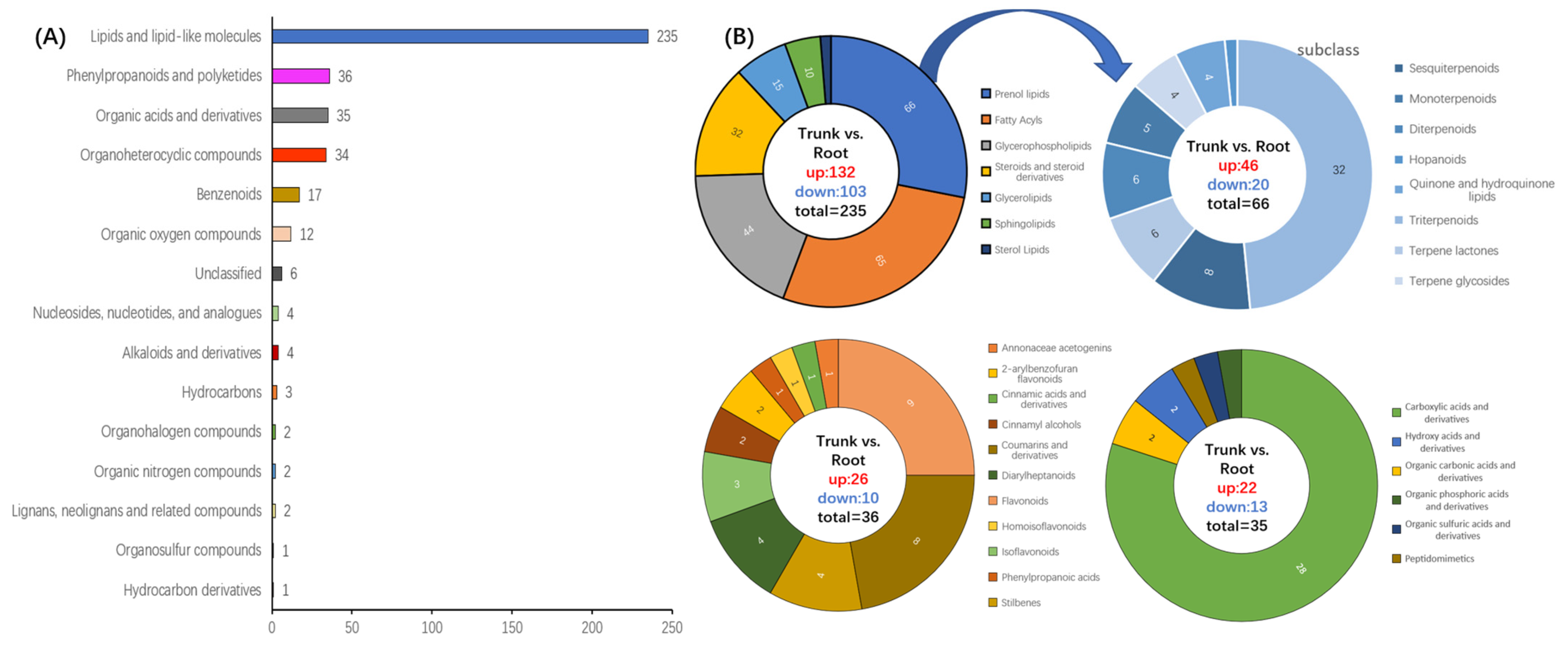
3.4. Analysis of the Expression Pattern of DEMs
3.5. Metabolic Pathway Analysis of DEMs
3.6. Metabolic Regulatory Network of Damaged Sea Buckthorn Roots and Trunks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calatayud, P.A.; Sauvion, N.; Thiery, D. Plant-Insect Interactions. Oxf. Bibliogr. 2018, 2, 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Schuler, M.A. P450s in Plant-Insect Interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, M.-W. Evaluation of Host Plant Quality and Host Selection Behavior of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius). Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, M.; Stireman, J. How Foraging Tactics Determine Host-Plant Use by a Polyphagous Caterpillar. Oecologia 2001, 129, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandra, F.; Unsicker, S.B.; Specht, J.; Köhler, G.; Weisser, W.W. Being a Generalist Herbivore in a Diverse World: How Do Diets from Different Grasslands Influence Food Plant Selection and Fitness of the Grasshopper Chorthippus parallelus? Ecol. Entomol. 2010, 35, 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jacek, O.; Reich, P.B.; Zytkowiak, R.; Karolewski, P.; Tjoelker, M.G. Needle Nutrients in Geographically Diverse Pinus sylvestris L. Populations. Ann. For. Sci. 2002, 59, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Forde, U.I.; Bose, E.A.; Hart, C.; Lahondère, C. Temperature and Sugar Feeding Effects on the Activity of a Laboratory Strain of Aedes aegypti. Insects 2019, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriane, A.; Terhzaz, S.; Terry, S.; McFarlane, M.; Gestuveo, R.J.; Szemiel, A.M.; Varjak, M.; McDonald, A.; Kohl, A.; Pondeville, E. Sugar Feeding Protects against Arboviral Infection by Enhancing Gut Immunity in the Mosquito Vector Aedes aegypti. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009870. [Google Scholar]
- Joel, F.-H.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant Defense against Insect Herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X. Adaptive Mechanisms of Oedaleus asiaticus Bey-Bienko(Orthoptera: Acrididae) to Food Plants. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mamunur, A.M.R.; Ruhul, A. Insect Plant Interaction with Reference to Secondary Metabolites: A Review. Agric. Rev. 2021, 42, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M. Plant Secondary Metabolites Modulate Insect Behavior-Steps toward Addiction? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, M.A.-K.; Rashmi, R.; Toppo, V.; Chole, P.B.; Banadka, A.; Sudheer, W.N.; Nagella, P.; Shehata, W.F.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q.; Alessa, F.M.; et al. Plant Secondary Metabolites: The Weapons for Biotic Stress Management. Metabolites 2023, 13, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Robert, C.A.M. Sequestration of Plant Secondary Metabolites by Insect Herbivores: Molecular Mechanisms and Ecological Consequences. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 14, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.R.; Carroll, A.R.; Kitching, R.L. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Galling Insects on Host Plant Secondary Metabolites. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2017, 11, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralf, N.; Bass, C.; Feyereisen, R.; Vontas, J. The Role of Cytochrome P450s in Insect Toxicology and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.M.; Shi, Z.Y.; Yang, C.Q.; Li, J.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhang, A.B. Gut Transcriptome Analysis of P450 Genes and Cytochrome P450 Reductase in Three Moth Species Feeding on Almaghasla, and Adel Abdel-Sabour Rezk. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 948043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chien, Y.; Chien, C. Induction of Glutathione S-Transferases Activities in Drosophila melanogaster Exposed to Phenol. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 53, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.-S. Study on Enzymatic Properties and Biochemical Toxicology of the Enzymes from Dendrolimus superans (Butler). Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, N.F.; Ji, X.Y.; Yin, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.X. The Impact of Co-Infection by a Nucleopolyhedrovirus and the Endoparasitoid Microplitis pallidipes Szepligeti on the Protective Enzymes in Hemolymph of Spodoptera exigua. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2017, 63, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-L. Effect of Several Pesticides on the Activities of Detoxifying Enzymes and Protective Enzymes in Clostera anastomosis. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Vera, G.; Tosevski, I.; Caldara, R.; Emerson, B.C. Evolution of Host Plant Use and Diversification in a Species Complex of Parasitic weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Peerj 2019, 7, e6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, R. Evolutionary Interactions Between Insects and Plants Mediated by Phytochemicals. Kaken. 1998. Available online: https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/grant/KAKENHI-PROJECT-10460049/ (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Agosta, S.J. On Ecological Fitting, Plant–Insect Associations, Herbivore Host Shifts, and Host Plant Selection. Oikos 2006, 114, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, L.A.; Philbin, C.S.; Ochsenrider, K.M.; Richards, L.A.; Massad, T.J.; Smilanich, A.M.; Forister, M.L.; Parchman, T.L.; Galland, L.M.; Hurtado, P.J.; et al. Modern Approaches to Study Plant–Insect Interactions in Chemical Ecology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebelo, S.A.; Maffei, M.E. Role of Early Signalling Events in Plant–Insect Interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 66, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Dong, Y.; Jun, Y.; Ming, Z.; Yong, Z.; Jianbin, D. The Wild Plant Resources and Utilization of Hippophae in China. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2004, 23, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Qiong, W.U.; Kun, S.; Hui, Z.; Wen, C.; Xue, S.U.; Xue-Lin, C. Study on Phenotypic Diversity of Natural Populations of Hippophae rhamnoides Subsp. Sinensis in Shanxi Province. J. Northwest Norm. Univ. 2007, 43, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yakovlev, R.V. A New Species and New Records of the Genus Meharia chretien 1915 (Lepidoptera, Cossidae) from the Middle East and Central Asia. Zool. Zhurnal 2018, 97, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S. Studies on the Bio-Ecological Characteristics of Seabuckthorn Carpenter Moth: Holcocerus hippophaecolus (Lcpidoptera: Cossidac). Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y. Integrated Management of Holcocerus hippophaecolus (Lepidoptera:Cossidae). Sci. Silvae Sin. 2007, 43, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zong, S.X.; Yu, L.F.; Lu, P.F.; Luo, Y.Q. Rhythms of Volatile Release from Female and Male Sea Buckthorn Plants and Electrophysiological Response of Sea Buckthorn Carpenter Moths. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.X.; Wang, R.; Cao, C.J.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y.Q. Impact of Chlorophorus caragana Damage on Nutrient Contents of Caragana korshinskii. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.S.C.; Beveridge, T.H.J. Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): Production and Utilization; NRC Research Press: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert, S.H. Pseudoreplication and the Design of Ecological Field Experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1984, 54, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.B.; Ellefson, W.C. Fat Analysis. In Food Analysis; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 117. [Google Scholar]
- Purificación, S.-P.; Micha, T.; Navas, M.J.; Asuero, A.G.; Wybraniec, A. An Overview of the Kjeldahl Method of Nitrogen Determination. Part I. Early History, Chemistry of the Procedure, and Titrimetric Finish. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 178–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ida, A.R.; Setyawan, A.R.; Suadi; Jayanti, A.D. Comparison of Nutritional Composition in Red and Green Strains of Kappaphycus alvarezii Cultivated in Gorontalo Province, Indonesia. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 147, 03029. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, P.S.; Landhäusser, S.M. A Method for Routine Measurements of Total Sugar and Starch Content in Woody Plant Tissues. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BeMiller, J.N. Carbohydrate Analysis. In Food Analysis; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 333–360. [Google Scholar]
- Yust, M.; Pedroche, J.; Girón-Calle, J.; Vioque, J.; Millán, F.; Alaiz, M. Determination of Tryptophan by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Alkaline Hydrolysates with Spectrophotometric Detection. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrikson, R.L.; Meredith, S.C. Amino Acid Analysis by Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Precolumn Derivatization with Phenylisothiocyanate. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 136, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Zhao, F.; Chen, M.; Ye, N.; Lin, Q.; Ouyang, L.; Cai, X.; Meng, P.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y. Determination of 21 Free Amino Acids in 5 Types of Tea by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (Uhplc–Ms/Ms) Using a Modified 6-Aminoquinolyl-N-Hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate (Aqc) Method. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 81, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, M.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Simultaneous Determination of Free Amino Acids in Pu-Erh Tea and Their Changes during Fermentation. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; Sharma, B.; Chawla, P.A.; Bhatia, R. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (Icp-Oes): A Powerful Analytical Technique for Elemental Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 666–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cara, J.B.; Moyano, F.J.; Cárdenas, S.; Fernández-Díaz, C.; Yúfera, M. Assessment of Digestive Enzyme Activities during Larval Development of White Bream. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmesha, K.K.; Lakshmidevi, N.; Mallikarjuna, S.A. Changes in Pectinase and Cellulase Activity of Colletotrichum capsici Mutants and Their Effect on Anthracnose Disease on Capsicum Fruit. Arch. Pflanzenschutz 2005, 38, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, H.; Blier, P.U. Trypsin Activity Measurement in Fish and Mammals: Comparison of Four Different Methods. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2007, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huo, X.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Gong, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genetic Variation in Gstm1 Is Associated with Susceptibility to Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in a Chinese Population. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 54, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Xu, B.J.; Dong, C. Recent Advances in Colorimetric Strategies for Acetylcholinesterase Assay and Their Applications. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpeinen, M.; Jouko, U.; Jorma, J.; Olavi, P. Multiple P450 Substrates in a Single Run: Rapid and Comprehensive in Vitro Interaction Assay. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Shen, M.; Zhu, C.C.; Yu, F.X.; Liu, Z.Q.; Ally, N.; Sun, S.C.; Li, K.; Liu, H.L. 3-Nitropropionic Acid Induces Ovarian Oxidative Stress and Impairs Follicle in Mouse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, P.F.; Xi, Z.J.; Xu, L.J.; Li, X.L.; He, N.Y. Comparison of Taurine, Gaba, Glu, and Asp as Scavengers of Malondialdehyde in Vitro and in Vivo. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, L.L.; Yan, X.; Li, C.; Shi, H.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Ye, Y.H. Cerebroside C Increases Tolerance to Chilling Injury and Alters Lipid Composition in Wheat Roots. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, J.L.; Ji, X.H.; Luo, X.G. Unraveling Response Mechanism of Photosynthetic Metabolism and Respiratory Metabolism to Uranium-Exposure in Vicia faba. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.L.; Deng, Z.X.; Ji, X.H.; Luo, X.G. Absorption and Interaction Mechanisms of Uranium & Cadmium in Purple Sweet Potato(Ipomoea batatas L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123264. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.N.; Qu, C.S.; Bian, Y.R.; Gu, C.G.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y. New Insights into the Responses of Soil Microorganisms to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Stress by Combining Enzyme Activity and Sequencing Analysis with Metabolomics. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, B.; Poisson, A.; Darwish, S.; Lacasse, J.; Merkx-Jacques, M.; Despland, E.; Bede, J.C. Influence of Dietary Nutritional Composition on Caterpillar Salivary Enzyme Activity. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Peng, Z. Effect of Palm Tree Leaves with Different Growth Phases on Midgut Digestive Enzyme Activity of Brontispa longissima. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, W.L.; Li, Z.; Niklas, K.J.; Sun, S.C. Plant Volatiles Mediate Evolutionary Interactions between Plants and Tephritid Flies and Are Evolutionarily More Labile Than Non-Volatile Defenses. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, C.-Q.; Sun, P.; Liu, D.-C.; Dilinuer, A.; Feng, H.-Z. Effects of Lygus pratensis (Hemiptera: Miridae) Infestation on the Nutrient Contents and Protective Enzyme Activities in Host Plants. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2018, 61, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.X.; Lei, X.H.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.W.; Shen, Z.R. Effects of Different Host Plants on the Development and Reproduction of the Peach Fruit Borer, Carposina sasakii Matsumura (Lepidoptera: Carposinidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 554–560. [Google Scholar]
- Nutchaya, K.; Wiwattanawanichakun, P.; Phankaen, P.; Saiyaitong, C.; Koul, O.; Nobsathian, S.; Bullangpoti, V.; Dunkhunthod, B. Phenolic Secondary Metabolites from Acorus Calamus (Acorales: Acoraceae) Rhizomes: The Feeding Deterrents for Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.-M.; Di, X.-Y.; Yan, B.; Liu, J.-F.; Wang, X.-Q.; Yang, M.-F. Population Parameters and Feeding Preference of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on Different Asparagus Officinalis Tissues. Insects 2022, 13, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, B.; Reza, M.; Van den Ende, W. Sugars and Plant Innate Immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3989–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarai, N.; Doumandji, S. Feeding Preferences of Gregarious Nymphs and Adults of the Desert Locust, Schistocerca gregaria Forskal (Orthoptera, Cyrtacanthacridinae) in Different Habitats at Biskra Oasis, Algeria. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2009, 3, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, W.G.; Schoereder, J.H.; Sperber, C.F. Does the Age of the Host Plant Modulate Migratory Activity of Plutella xylostella? Entomol. Sci. 2004, 7, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, J.C.T.; Christopher, D. Ecological Aspects of Nitrogen Metabolism in Plants; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Shangguan, Z.; Shi, H.; Xu, W.; Ren, F.; Zhu, J.; He, J.-S. Leaf N:P Stoichiometry Overrides the Effect of Individual Nutrient Content on Insect Herbivore Population Dynamics in a Tibetan Alpine Grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 336, 108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ferry, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Edwards, M.G.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; He, K. A Proteomic Approach to Study the Mechanism of Tolerance to Bt Toxins in Ostrinia furnacalis Larvae Selected for Resistance to Cry1ab. Transgenic Res. 2013, 22, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashant, P.; Bandani, A.R.; Fitches, E.; Gatehouse, J.A. Protein Digestion in Cereal Aphids (Sitobion avenae) as a Target for Plant Defence by Endogenous Proteinase Inhibitors. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 881–891. [Google Scholar]
- Shimul, D.; Porter, L.D.; Ma, Y.; Coyne, C.J.; Chaves-Cordoba, B.; Naidu, R.A. Resistance in Lentil (Lens Culinaris) Genetic Resources to the Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2022, 170, 755–769. [Google Scholar]
- David, R.; Dorrah, M.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Abdelfattah, E.A.; Bassal, T.T.M. Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes Depicts the Negative Systemic Effect of Iron-Containing Fertilizers and Plant Phenolic Compounds in the Desert Locust. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21989–22000. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, T.N.; Welti, E.A.R.; Kaspari, M. Dietary Sodium Levels Affect Grasshopper Growth and Performance. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.M.; Afzal, M.; Ward, D.A.; Prescott, M.C.; Sait, S.M.; Rees, H.H.; Tomsett, A.B. Differential Proteomic Analysis of Arabidopsis Thaliana Genotypes Exhibiting Resistance or Susceptibility to the Insect Herbivore, Plutella xylostella. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, S. Chemical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Showler, A.T. Spodoptera exigua Oviposition and Larval Feeding Preferences for Pigweed, Amaranthus Hybridus, over Squaring Cotton, Gossypium hirsutum, and a Comparison of Free Amino Acids in Each Host Plant. J. Chem. Ecol. 2001, 27, 2013–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Duan, F.; Song, W. Transcriptomics Integrated with Metabolomics Reveals the Defense Response of Insect-Resistant Zea Mays Infested with Spodoptera exigua. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, P.D.; Sabri, W.; Verheggen, F.; Thonart, C.; Haubruge, E. Aphid-Host Plant Interactions:Does Aphid Honeydew Exactly Reflect the Host Plant Amino Acid Composition? Arthropod-Plant Inte 2011, 5, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Fang, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Pan, C.; Wu, H. Identification of Key Metabolites Based on Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Chemometrics Analyses Provides Insights into Bitterness in Kucha [Camellia kucha (Chang Et Wang) Chang]. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, C.; Kang, L. Tryptamine Accumulation Caused by Deletion of Mrmao-1 in Metarhizium Genome Significantly Enhances Insecticidal Virulence. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, K.; Fischer, K. Larval Starvation Reduces Responsiveness to Feeding Stimuli and Does Not Affect Feeding Preferences in a Butterfly. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Ascher, K.R.S.; Meisner, J.; Flowers, H.M. Effects of Amino Acids on the Feeding Behavior of the Larva of the Egyptian Cotton Leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis Boisd. Phytoparasitica 1976, 4, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogesh, Y.; Dhillon, M.K.; Tanwar, A.K.; Kumar, S. Amino and Fatty Acids Contributing to Antibiosis against Chilo partellus (Swinhoe) in Maize. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2021, 15, 721–736. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.J.; Zhu, W.C. Feeding Selectivity of Helicoverpa armigera Larvae on Amino Acids, Sugars, and Secondary Substances of Cotton. Plant Prot. 2001, 27, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, D.P.; Cameron, D.D.; Butlin, R.K. The Chemical Signatures Underlying Host Plant Discrimination by Aphids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, A.H.K.; Hossain, M.R.; Park, J.-I.; Kim, H.R.; Nou, I.-S. Glucosinolate Profiles in Cabbage Genotypes Influence the Preferential Feeding of Diamondback Moth (Plutella xylostella). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, P.D.; Lokvam, J.; Rudolph, K.; Bromberg, K.; Sackett, T.E.; Wright, L.; Brenes-Arguedas, T.; Dvorett, D.; Ring, S.; Clark, A.; et al. Divergent Defensive Strategies of Young Leaves in Two Species of Inga. Ecology 2005, 86, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kester, K.M.; Peterson, S.C.; Hanson, F.; Jackson, D.M.; Severson, R.F. The Roles of Nicotine and Natural Enemies in Determining Larval Feeding Site Distributions of Manduca sexta L. And Manduca quinquemaculata (Haworth) on Tobacco. Chemoecology 2002, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, W. Survival in a Hostile Environment. Evaluation of the Developmental Success of the Oligophagous Leaf Beetle Chrysomela vigintipunctata (Scop). In Vertical Food Web Interactions: Evolutionary Patterns and Driving Forces; Dettner, K., Bauer, G., Völkl, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Coley, P.D.E.; Ghabash, M.-J.; Kidner, G.; Nicholls, C.A.; Pennington, J.A.; Mills, R.T.; Soule, A.G.; Lemes, A.J.; Stone, M.R.; Kursar, G.N.; et al. Macroevolutionary Patterns in Overexpression of Tyrosine: An Anti-Herbivore Defence in a Speciose Tropical Tree Genus, Inga (Fabaceae). J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 1620–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, P.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Zheng, R.; Lu, S.; Seyab, M.; Yang, F.; Li, Q.; Tang, Q. Insecticidal Potential of a Consolida ajacis Extract and Its Major Compound (Ethyl Linoleate) against the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 195, 105557. [Google Scholar]
- Eya, K.; Mustapha, M.B.; Chaieb, I.; Ascrizzi, R.; Flamini, G.; Harrath, A.H.; Jannet, H.B.; Zardi-Bergaoui, A. Chemical Composition and Insecticidal Activity against Tribolium castaneum of Thapsia garganica L. Seed Essential Oil. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202200646. [Google Scholar]
- Rubén, M.F.; Petek, M.; Gerasymenko, I.; Juteršek, M.; Baebler, Š.; Kallam, K.; Giménez, E.M.; Gondolf, J.; Nordmann, A.; Gruden, K.; et al. Insect Pest Management in the Age of Synthetic Biology. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanni, B.; Canale, A.; Toniolo, C.; Higuchi, A.; Murugan, K.; Pavela, R.; Nicoletti, M. Neem (Azadirachta indica): Towards the Ideal Insecticide? Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 31, 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Bian, S.; Liu, X.; Fang, N.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Timko, M.P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of Cembratriene-Ol and Cembratriene-Diol in Yeast via the Mva Pathway. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Tao, J.; Liu, S.; Lin, X.; Zong, S. Nutrient Attraction and Secondary Metabolites Induce Eogystia hippophaecola (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) Larvae Transfer from Sea Buckthorn Trunks to Roots. Forests 2025, 16, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050829
Li Y, Shao Y, Tao J, Liu S, Lin X, Zong S. Nutrient Attraction and Secondary Metabolites Induce Eogystia hippophaecola (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) Larvae Transfer from Sea Buckthorn Trunks to Roots. Forests. 2025; 16(5):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050829
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yurong, Yuying Shao, Jing Tao, Sanhe Liu, Xiangbo Lin, and Shixiang Zong. 2025. "Nutrient Attraction and Secondary Metabolites Induce Eogystia hippophaecola (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) Larvae Transfer from Sea Buckthorn Trunks to Roots" Forests 16, no. 5: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050829
APA StyleLi, Y., Shao, Y., Tao, J., Liu, S., Lin, X., & Zong, S. (2025). Nutrient Attraction and Secondary Metabolites Induce Eogystia hippophaecola (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) Larvae Transfer from Sea Buckthorn Trunks to Roots. Forests, 16(5), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050829




