Promotion or Hindrance? Assessing Urbanization’s Impact on Forest Ecological Security Through the Lenses of Population, Economy, and Space: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Variable Selection and Measurement
2.1.1. Dependent Variable
- (1)
- Variable selection
- (2)
- Variable measurement
- Standardize the positive and negative indicator data:
- 2.
- Perform normalization processing on the standardized indicator data:
- 3.
- Calculate the information entropy of the jth indicator:
- 4.
- Calculate the entropy weight of the jth indicator:
- 5.
- Calculate the comprehensive index of forest ecological security:
2.1.2. Core Independent Variable
2.1.3. Control Variables
- (1)
- Regional Economic Development (PGDP), measured by per capita GDP (deflated to 2004 constant prices using the Consumer Price Index) to account for inflation.
- (2)
- Regional Innovation Level (INNO), proxied by the natural logarithm of the number of domestic invention patent applications accepted, reflecting the region’s capacity for technological innovation.
- (3)
- Environmental Regulation Intensity (ENVI), quantified as the ratio of investment in industrial pollution control to industrial value added, representing the intensity of local governmental efforts in environmental governance.
- (4)
- Government Intervention (GOVE), represented by per capita government fiscal expenditure, indicating the degree of government involvement in economic and social affairs.
2.2. Empirical Models and Methods
2.2.1. Baseline Regression Model
2.2.2. Robustness Test Methods
- (1)
- (2)
- Data winsorization at the 1% level. To mitigate the influence of extreme outliers on regression estimates, all continuous variables were subjected to 1% winsorization at both tails. This procedure replaces extreme values in the top and bottom 1% of each variable’s distribution with the nearest non-extreme values, thereby reducing distortion while preserving sample size.
- (3)
- Excluding samples from municipalities directly under the Central Government. Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing differ from other regions in administrative status and economic development, potentially introducing structural bias. The regression is re-estimated without these cities to ensure model robustness.
- (4)
- Alternative model specification. To evaluate the robustness of the estimation results to model specification, the two-way fixed effects model employed in the baseline regression is replaced with an ordinary least squares (OLS) regression model.
2.2.3. EKC Test Model
2.3. Data Sources and Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Baseline Regression Results
3.2. Robustness Test Results
3.3. Endogeneity Test Results
3.4. Heterogeneity Analysis Results
3.4.1. Regional Heterogeneity Analysis
3.4.2. Temporal Heterogeneity Analysis
3.5. EKC Test Results
3.6. Further Discussion on the Causes of the EKC Test Results
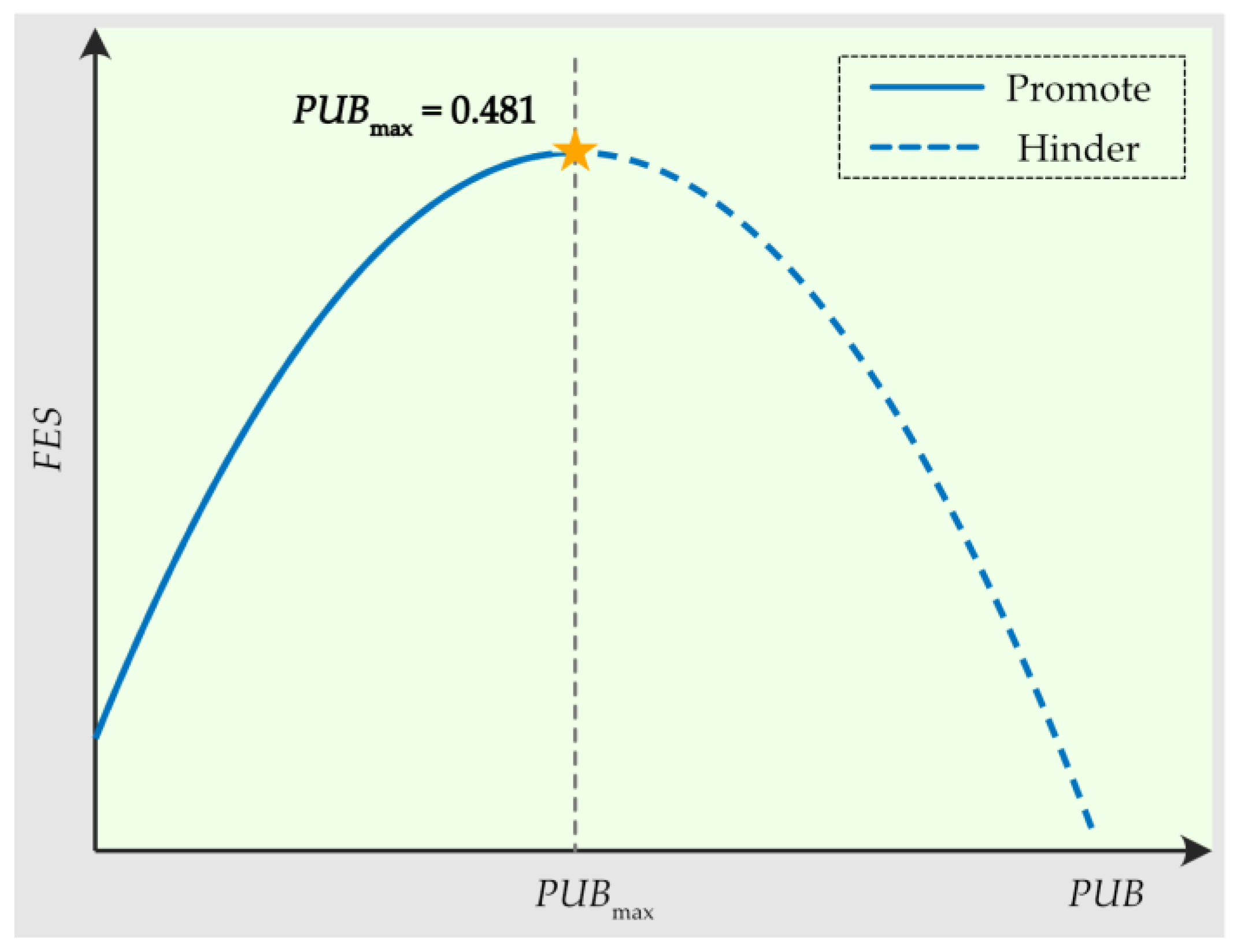
3.6.1. Discussion on the Causes of the EKC Test Results for the Impact of PUB on FES
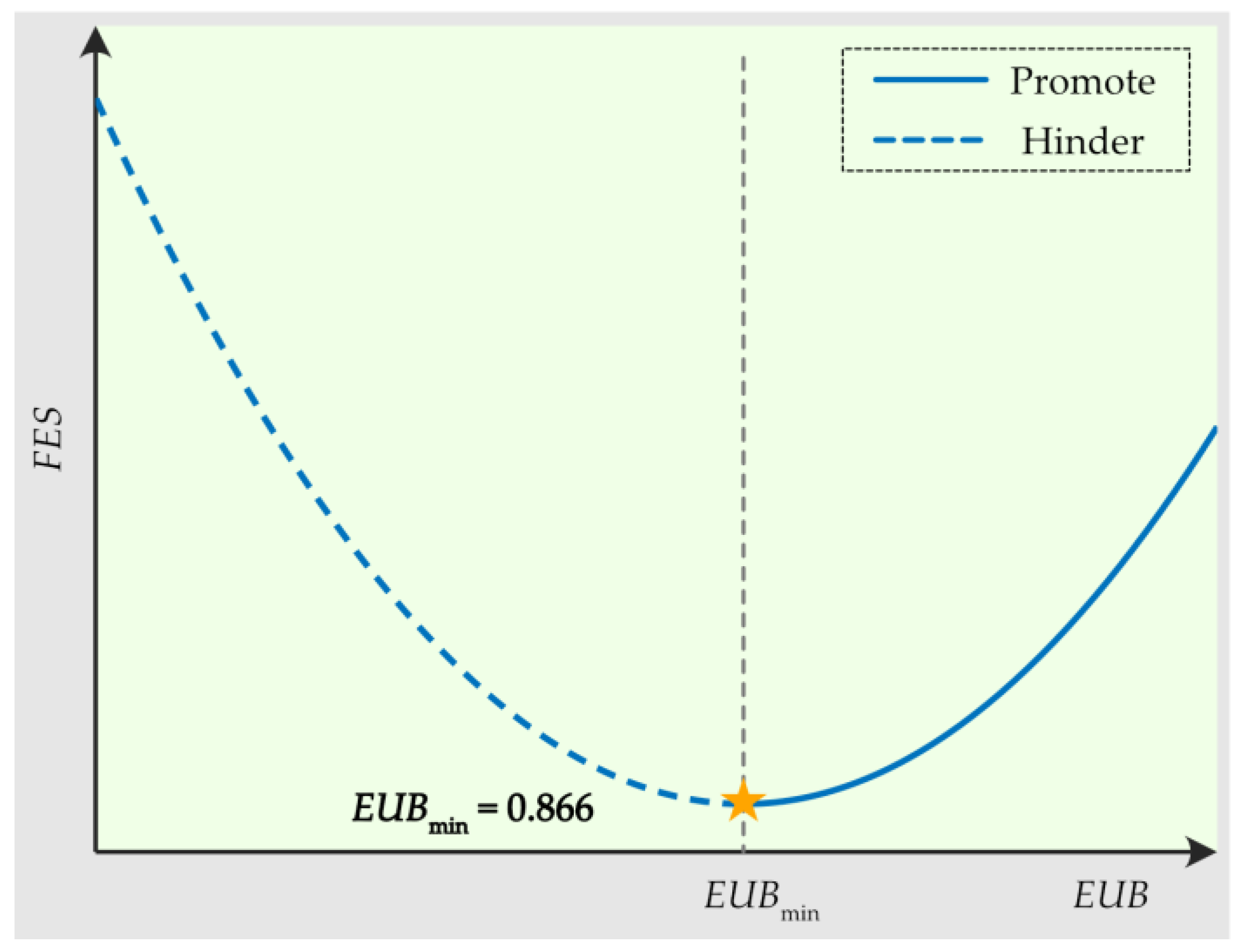
3.6.2. Discussion on the Causes of the EKC Test Results for the Impact of EUB on FES
3.6.3. Discussion on the Causes of the EKC Test Results for the Impact of SUB on FES
4. Conclusions and Implications
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Implications
4.3. Research Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloom, D.E.; Canning, D.; Fink, G. Urbanization and the Wealth of Nations. Science 2008, 319, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Revitalize the World’s Countryside. Nature 2017, 548, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Xu, K. Road to Green Urbanization: How Does Urbanization Process Affect the Green Land Use Efficiency. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1581107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, Z. Connotation, Mechanism and Path of Chinese New Urbanization from the Perspective of Urban Agglomeration Spatial Structure. J. Xian Jiaotong Univ. Sci. 2023, 43, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Gao, L.; Shi, L. Analysis of the Coordinated Development and Influencing Factors between Urban Population and Environment: A Case Study of 35 Metropolises in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 121, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, T.; Fang, C.; Zeng, J. Global Urban Low-Carbon Transitions: Multiscale Relationship between Urban Land and Carbon Emissions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 100, 107076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X. Challenges Facing China’s Unbalanced Urbanization Strategy. Land Use Policy 2014, 39, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ge, J.; Huang, M.; Wu, X.; Fan, H. Uncovering the Triple Synergy of New-Type Urbanization, Greening and Digitalization in China. Land 2024, 13, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of Urbanization Level on Urban Air Quality: A Case of Fine Particles (PM2.5) in Chinese Cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bao, W. Exploring Symbiotic Pathways: Unveiling the Evolution and Key Drivers of China’s Human-Environment Relationship. Habitat Int. 2024, 154, 103195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, L. Ecological Degradation and Green Development at Crossroads: Incorporating the Sustainable Development Goals into the Regional Green Transformation and Reform. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, H.; He, H. Balancing Urban Expansion with a Focus on Ecological Security: A Case Study of Zhaotong City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bai, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Ecological Security in the Mountainous Areas: Implications for Supporting Sustainable Land Management and Ecological Planning. Sustain. Futures 2024, 8, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, H.; Wen, H. The Current Situation and Trend of Land Ecological Security Evaluation from the Perspective of Global Change. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, W.; Jiang, E.; Yuan, L.; Qu, B.; Degefu, D.M.; Ramsey, T.S. Evaluation and Prediction of Water Security Levels in Northwest China Based on the DPSIR Model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Hashimoto, S.; Cushman, S.A. Navigating Ecological Security Research over the Last 30 Years: A Scoping Review. Sustain. Sci. 2023, 18, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Mi, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X. Evaluation and Scenario Simulation for Forest Ecological Security in China. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 1651–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bao, Y.; Xu, J.; Han, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z. Ecological Security Evaluation and Ecological Regulation Approach of East-Liao River Basin Based on Ecological Function Area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, L.; Meng, J. Fuzzy Evaluation of the Ecological Security of Land Resources in Mainland China Based on the Pressure-State-Response Framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, Y. Ecological Security Assessment Based on Ecological Footprint Approach in Hulunbeir Grassland, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M. Assessing the Impact of China’s Forest Chief System on Forest Ecological Security: An Integrated ArcGIS and Econometric Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fu, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, X. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Forestry Ecological Security Level in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qin, F.; Zhai, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, R.; Cao, F. Evaluation of Coordinated Development of Forestry Management Efficiency and Forest Ecological Security: A Spatiotemporal Empirical Study Based on China’s Provinces. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, D. The Theoretical Logic, Practical Dilemma and Implementation Paths of New Quality Productive Forces Empowering the Construction of the Forest “Four Repositories”. Probl. For. Econ. 2025, 45, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepner, S.; Eckebil, P.P.T.; Mintah, F.; Azihou, A.F.; Sinsin, B.; Fischer, M.; Ifejika Speranza, C. Perceived and Measured Forest Degradation across Western Africa: Insights for Sustainable Forest Management. Trees For. People 2025, 22, 101061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.; Dinis, M.A.P.; Canova, M.A.; Cataldi, M.; da Costa, G.A.S.; Enrich-Prast, A.; Symeonakis, E.; Brearley, F.Q. Managing Ecosystem Services in the Brazilian Amazon: The Influence of Deforestation and Forest Degradation in the World’s Largest Rain Forest. Geosci. Lett. 2025, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, H.; Hu, M. Spatial Spillover Effects of Forest Ecological Security on Ecological Well-Being Performance in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, J.; Qiu, M.; Liu, Z. (John) Spatiotemporal Changes and Obstacle Factors of Forest Ecological Security in China: A Provincial-Level Analysis. Forests 2021, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Tang, X.; Guan, X.; Qin, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. The Assessment of Forest Ecological Security and Its Determining Indicators: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Evaluation Analysis of Forest Ecological Security in 11 Provinces (Cities) of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Raza, S.T. Evaluation of Forest Ecological Security and Its Influencing Factors in Multi-Climatic Zones: A Case Study of Yunnan Province. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. Research on Driving Factors of Forest Ecological Security: Evidence from 12 Provincial Administrative Regions in Western China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. Assessment of Forest Ecological Security in China Based on DPSIRM Model: Taking 11 Provincial Administrative Regions along the Yangtze River Basin as Examples. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2023, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, J.L.L.; Lopes, M.A.; Queiroz, H.L. de Development of a Flooded Forest Anthropization Index (FFAI) Applied to Amazonian Areas under Pressure from Different Human Activities. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral e Silva, A.; Braga, M.Q.; Ferreira, J.; Juste dos Santos, V.; do Carmo Alves, S.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Calijuri, M.L. Anthropic Activities and the Legal Amazon: Estimative of Impacts on Forest and Regional Climate for 2030. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, A.; Song, H.; Faheem, M.; Daud, A. Caring for the Environment. How Do Deforestation, Agricultural Land, and Urbanization Degrade the Environment? Fresh Insight through the ARDL Approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 11527–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; She, J.; Chen, C.; Lei, J. Urban Forest Health Under Rapid Urbanization: Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Mechanisms from the Chang–Zhu–Tan Green Heart Area. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qiu, R.; Yao, J.; Hu, X.; Lin, J. The Effects of Urbanization on China’s Forest Loss from 2000 to 2012: Evidence from a Panel Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, S.; Du, X.; Qin, Y.; Deng, L. Chinese Urbanization Promoted Terrestrial Ecosystem Health by Implementing High-Quality Development and Ecological Management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2000–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S. Identifying the Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and Forest Ecological Security and Its Impact Mechanism: Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Wei, X.; Duan, Z. Coupling and Coordination Analysis in Urban Agglomerations of China: Urbanization and Ecological Security Perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Duo, L.; Guo, X.; Zou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, D. Research on the Coupling Coordination and Driving Role of Urbanization and Ecological Resilience in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Analysis of the Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Water Ecological Security in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region: A Perspective of Industrial Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, B.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Cui, B. Ecological Security Assessment, Prediction, and Zoning Management: An Integrated Analytical Framework. Engineering 2025, 49, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, B.; Lyu, J. Endogenous Transmission Mechanism and Spatial Effect of Forest Ecological Security in China. Forests 2021, 12, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Cai, X. Identifying the Internal Coupling Coordination Relationship of Forest Ecological Security and Its Spatial Influencing Factors. Forests 2023, 14, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Meng, J.; Cheng, B. Research on Impact Mechanisms of Digital Economy on High-Quality Development of Forestry. Forests 2025, 16, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Wang, T.; Cheng, L. A Study on the Quality and the Efficiency of Human-oriented New-type Urbanization: Based on the Evaluation and the Comparison of China’s Provincial Data. J. Yunnan Univ. Financ. Econ. 2015, 31, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, M. Land urbanization, population urbanization and urban eco-efficiency improvement in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: An empirical analysis based on panel data of 108 prefecture-level and above cities. Urban Probl. 2020, 12, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yu, K.; Chen, Z. How Does Urbanization Affect Carbon Dioxide Emissions? A Cross-Country Panel Data Analysis. Energy Policy 2017, 107, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Deng, Y. Impact of National Key Ecological Function Areas (NKEFAs) Construction on China’s Economic Resilience under the Background of Sustainable Development. Forests 2024, 15, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L. A System Dynamics Approach to Resilience Analysis in the Sino-Russian Timber Supply Chain. Forests 2025, 16, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic Growth and the Environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C. Understanding the Relation between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment in China’s Yangtze River Delta Using an Improved EKC Model and Coupling Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasman, A.; Duman, Y.S. CO2 Emissions, Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, Trade and Urbanization in New EU Member and Candidate Countries: A Panel Data Analysis. Econ. Model. 2015, 44, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liobikienė, G.; Butkus, M. Scale, Composition, and Technique Effects through Which the Economic Growth, Foreign Direct Investment, Urbanization, and Trade Affect Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, M.; Nishide, K.; Ohyama, A. Economic Models for the Environmental Kuznets Curve: A Survey. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2010, 34, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Ma, Z.; Feng, X. The Influence of Rural Land Transfer on Urban-Rural Integration Development in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China. Econ. Geogr. 2024, 44, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. How Digital Economy Promotes Entrepreneurship Development: Based on Macro and Micro Perspectives. Bus. Manag. J. 2024, 46, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Lu, D. Challenges and the Way Forward in China’s New-Type Urbanization. Land Use Policy 2016, 55, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Dong, C.; Bao, Q. Impact of urbanization on forest ecological security in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2984–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Deng, Y.; Yao, S.; Liu, G. EKC Test of the Relationship between Forest Quality and Economic Growth Considering Spatial Spillover Effects. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Hua, D.; Cui, Y.; Wu, Y. Global Hillside Urban Expansion Reduces Natural Habitat Quality. Land Use Policy 2026, 161, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wu, Y.; Sun, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, Z.; Song, L.; Fang, F.; Cao, W.; Ma, J.; Huang, C.; et al. Extensive Terrestrial Biodiversity Threats from Global Hillside Urban Expansion. Nat. Cities 2025, 2, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagulakshmi, K.; Arulraj, G.P.; Gautam, S.; Joshi, S.K. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Land Use and Land Cover, and Their Impact on Groundwater Quality in the Industrialized Muvattupuzha Basin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 39189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
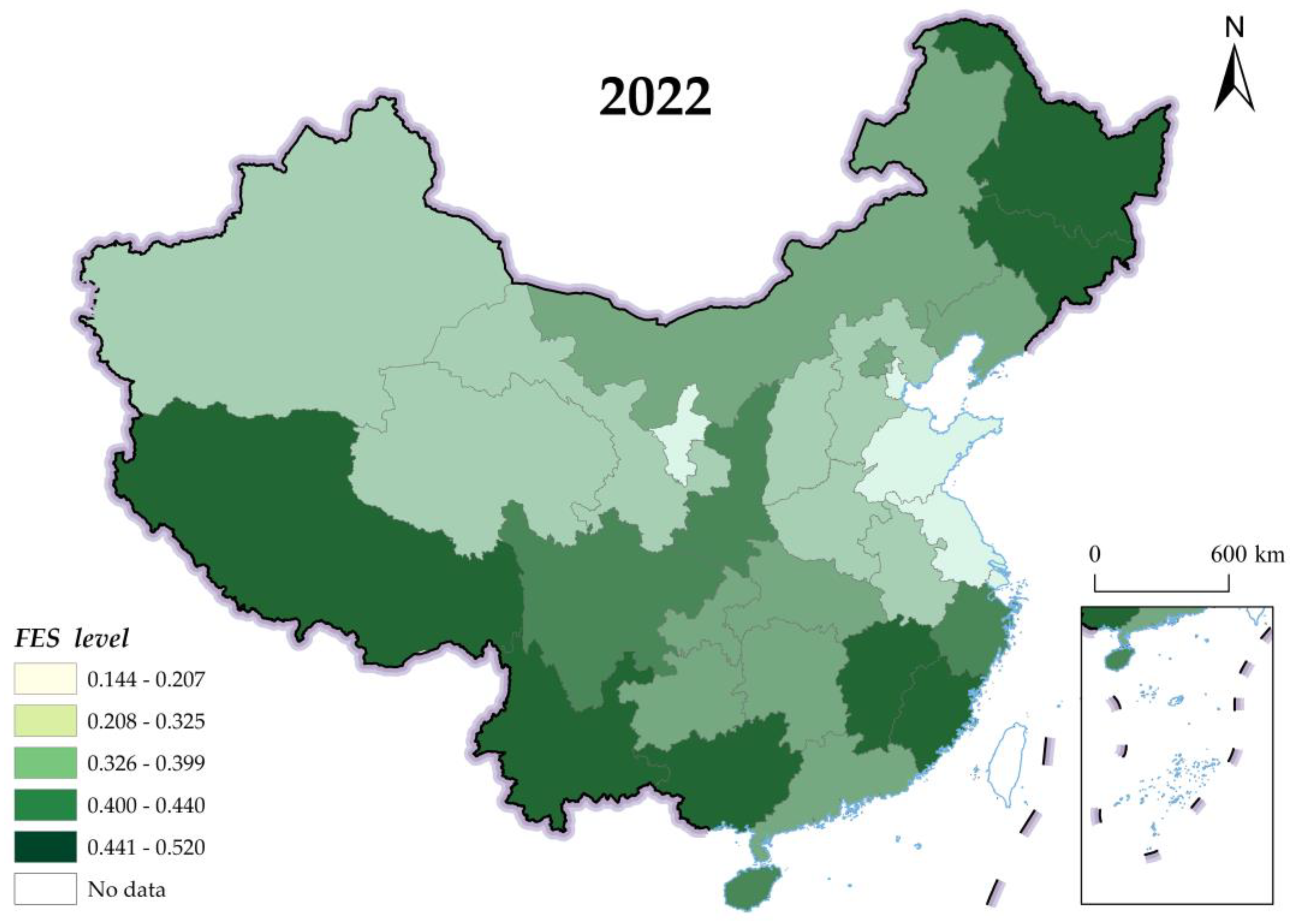
| Primary Index | Secondary Index (Unit) | Index Calculation Method | Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure (P) | Per capita wastewater discharge (tons/person) | Total regional wastewater discharge/total regional population at the end of the year | − |
| Per capita sulfur dioxide emissions (tons/person) | Regional sulfur dioxide emissions/regional total population at the end of the year | − | |
| Human Disturbance Index (%) | (Construction land area + cultivated land area)/jurisdiction area × 100% | − | |
| State (S) | Forest coverage rate (%) | Obtain it directly | + |
| Forest volume per unit area (cubic meters/hectare) | Regional forest stock volume/regional forest area | + | |
| Proportion of regional forest land area (%) | Forest land area/jurisdiction area × 100% | + | |
| Proportion of natural forests (%) | Regional natural forest area/regional forest area × 100% | + | |
| Response (R) | Proportion of newly added soil erosion control (%) | Newly added soil erosion control area/jurisdiction area × 100% | + |
| Intensity of government investment in forestry | Regional government forestry investment completion amount/GDP | + | |
| Green coverage rate of built-up area (%) | Obtain it directly | + |
| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators (Unit) | Calculation Method of Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Population urbanization (PUB) | The regional proportion of the urban population (%) | (Number of urban population in the region/total permanent population in the region) × 100% |
| Economic urbanization (EUB) | The share of regional output from the secondary and tertiary industries (%) | (Regional secondary and tertiary industry added value/regional gross domestic product) × 100% |
| Spatial urbanization (SUB) | The proportion of built-up area of the total regional area (%) | (Area of built-up area in the region/total area of the jurisdiction) × 100% |
| Variable | Observations | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FES | 589 | 0.343 | 0.119 | 0.365 | 0.057 | 0.744 |
| PUB | 589 | 0.560 | 0.147 | 0.555 | 0.209 | 0.896 |
| EUB | 589 | 0.891 | 0.058 | 0.895 | 0.661 | 0.998 |
| SUB | 589 | 0.019 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.197 |
| PGDP | 589 | 9.240 | 0.493 | 9.131 | 8.012 | 10.806 |
| INNO | 589 | 8.776 | 1.849 | 8.906 | 2.485 | 12.399 |
| ENVI | 589 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.031 |
| GOVE | 589 | 1.088 | 0.883 | 0.963 | 0.091 | 7.124 |
| Variable | FES | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| PUB | −0.121 *** | −0.151 *** | ||||
| (−2.59) | (−2.61) | |||||
| EUB | 0.466 *** | 0.222 *** | ||||
| (9.30) | (3.49) | |||||
| SUB | −1.833 *** | −1.795 *** | ||||
| (−14.06) | (−12.60) | |||||
| Constant | 0.411 *** | 0.247 ** | −0.072 | −0.761 *** | 0.378 *** | 0.473 *** |
| (15.73) | (2.14) | (−1.62) | (−7.29) | (76.73) | (37.52) | |
| Controls | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R-squared | 0.952 | 0.954 | 0.941 | 0.949 | 0.848 | 0.980 |
| Observations | 589 | 589 | 589 | 589 | 589 | 589 |
| Variable | FES | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| PUB | −0.644 *** | −0.189 *** | −0.188 * | −0.386 * |
| (−3.63) | (−4.26) | (−1.94) | (−2.04) | |
| Constant | 0.490 | 0.161 * | 0.092 | 0.503 *** |
| (1.31) | (1.66) | (0.45) | (6.78) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| R-squared | 0.940 | 0.968 | 0.821 | 0.363 |
| Observations | 589 | 589 | 513 | 589 |
| Variable | FES | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| EUB | 0.227 *** | 0.223 *** | 0.243 *** | 0.186 *** |
| (3.54) | (4.11) | (3.50) | (2.87) | |
| Constant | −0.758 *** | −0.712 *** | −0.623 *** | −0.774 *** |
| (−7.26) | (−8.04) | (−4.84) | (−6.69) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| R-squared | 0.949 | 0.964 | 0.935 | 0.349 |
| Observations | 589 | 589 | 513 | 589 |
| Variable | FES | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| SUB | −1.270 *** | −1.899 *** | −3.459 *** | −1.825 *** |
| (−10.50) | (−12.60) | (−4.11) | (−8.18) | |
| Constant | 0.435 *** | 0.478 *** | 0.475 *** | 0.461 *** |
| (40.62) | (36.68) | (35.51) | (11.65) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| R-squared | 0.966 | 0.891 | 0.875 | 0.387 |
| Observations | 589 | 589 | 513 | 589 |
| Variable | FES | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| PUB | −0.193 *** | ||
| (−3.45) | |||
| EUB | 0.936 *** | ||
| (4.52) | |||
| SUB | −1.501 *** | ||
| (−7.54) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Anderson-LM statistic | 529.408 *** | 72.339 *** | 282.149 *** |
| [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | |
| Cragg-Donald Wald F statistic | 936.928 *** | 77.752 *** | 547.216 *** |
| Stock–Yogo 10% critical value | 16.380 | 16.380 | 16.380 |
| R-squared | 0.957 | 0.943 | 0.936 |
| Observations | 558 | 558 | 558 |
| Variable | FES | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Eastern | Central-Western | Eastern | Central-Western | Eastern | Central-Western | |
| PUB | −0.185 *** | 0.189 *** | ||||
| (−2.85) | (2.13) | |||||
| EUB | 0.330 *** | 0.206 *** | ||||
| (2.43) | (2.77) | |||||
| SUB | −0.530 *** | 2.483 *** | ||||
| (−2.03) | (2.06) | |||||
| Constant | 0.414 *** | 0.279 *** | −1.092 *** | −0.660 *** | 0.299 *** | 0.319 *** |
| (9.46) | (6.33) | (−6.82) | (−4.23) | (10.85) | (23.61) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R-squared | 0.968 | 0.933 | 0.969 | 0.925 | 0.974 | 0.942 |
| Observations | 209 | 380 | 209 | 380 | 209 | 380 |
| Intergroup difference test | −0.374 *** | 0.125 | −3.013 *** | |||
| Variable | FES | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Traditional | New-Type | Traditional | New-Type | Traditional | New-Type | |
| PUB | 0.276 *** | −0.287 *** | ||||
| (2.28) | (−2.75) | |||||
| EUB | 0.245 *** | 0.571 *** | ||||
| (2.84) | (3.13) | |||||
| SUB | −1.783 *** | −1.719 *** | ||||
| (−6.57) | (−10.38) | |||||
| Constant | 2.096 *** | 0.894 *** | 0.114 *** | −0.161 *** | 0.489 *** | 0.478 *** |
| (7.78) | (4.95) | (1.51) | (−0.98) | (23.50) | (28.19) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R-squared | 0.943 | 0.912 | 0.959 | 0.955 | 0.938 | 0.944 |
| Observations | 279 | 310 | 279 | 310 | 279 | 310 |
| Intergroup difference test | 0.563 *** | −0.326 *** | −0.064 | |||
| Variable | FES | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
| PUB | 0.434 * | ||
| (1.93) | |||
| PUB 2 | −0.451 ** | ||
| (−2.39) | |||
| EUB | −2.804 *** | ||
| (−3.20) | |||
| EUB 2 | 1.618 *** | ||
| (3.04) | |||
| SUB | −0.163 | ||
| (−0.35) | |||
| SUB 2 | 2.029 | ||
| (1.16) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Curve type | Inverted U-shaped | U-shaped | Non-significant |
| R-squared | 0.953 | 0.949 | 0.957 |
| Observations | 589 | 589 | 589 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, X. Promotion or Hindrance? Assessing Urbanization’s Impact on Forest Ecological Security Through the Lenses of Population, Economy, and Space: Evidence from China. Forests 2025, 16, 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111746
Lyu J, Sun Z, Liu Y, Cai X. Promotion or Hindrance? Assessing Urbanization’s Impact on Forest Ecological Security Through the Lenses of Population, Economy, and Space: Evidence from China. Forests. 2025; 16(11):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111746
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Jiehua, Zhe Sun, Yandi Liu, and Xiuting Cai. 2025. "Promotion or Hindrance? Assessing Urbanization’s Impact on Forest Ecological Security Through the Lenses of Population, Economy, and Space: Evidence from China" Forests 16, no. 11: 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111746
APA StyleLyu, J., Sun, Z., Liu, Y., & Cai, X. (2025). Promotion or Hindrance? Assessing Urbanization’s Impact on Forest Ecological Security Through the Lenses of Population, Economy, and Space: Evidence from China. Forests, 16(11), 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16111746





