Influence of Eucalyptus Plantation on Soil Microbial Characteristics in Severely Degraded Land of Leizhou Peninsula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
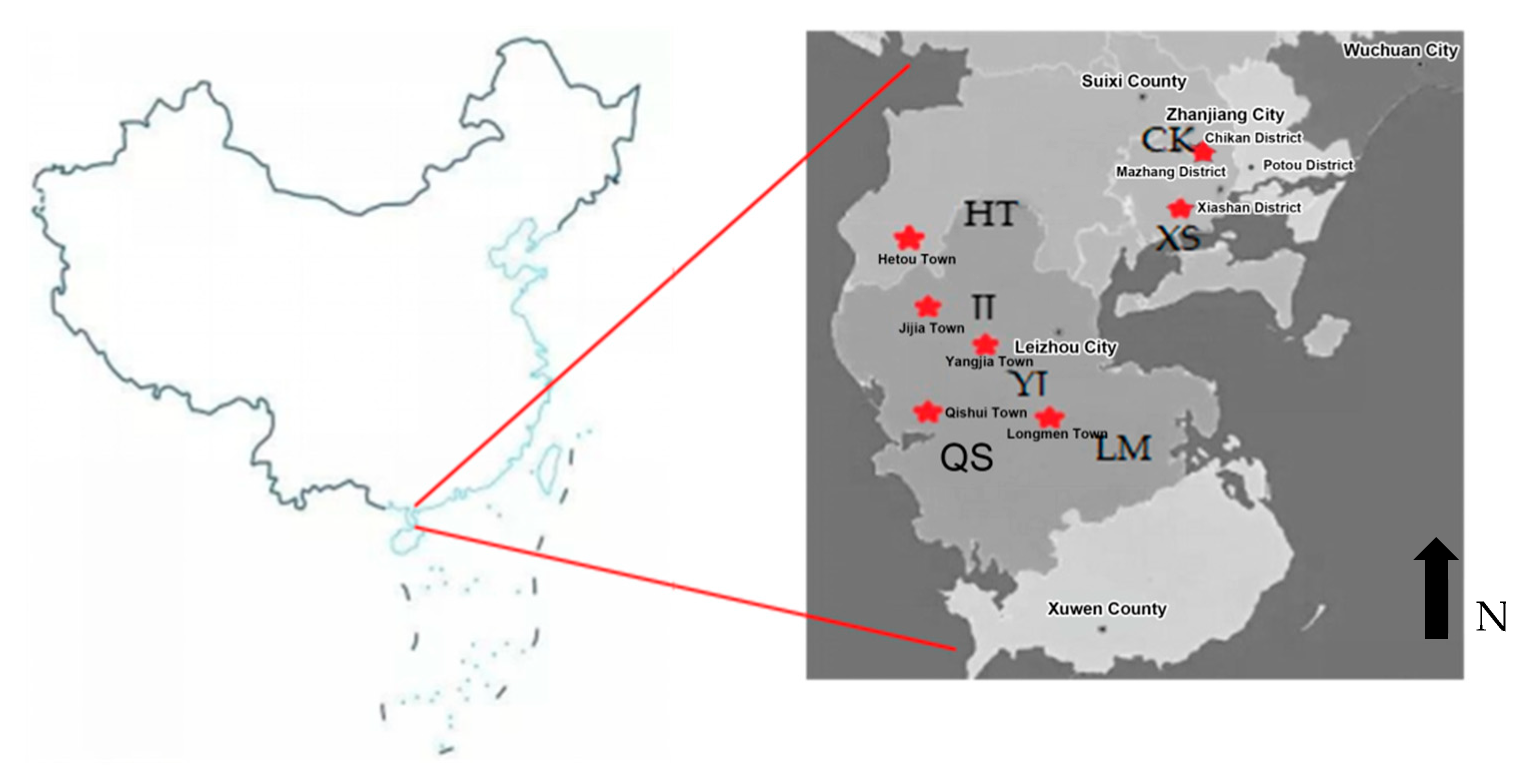
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Investigation and Sampling
2.4. Laboratory Analysis
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
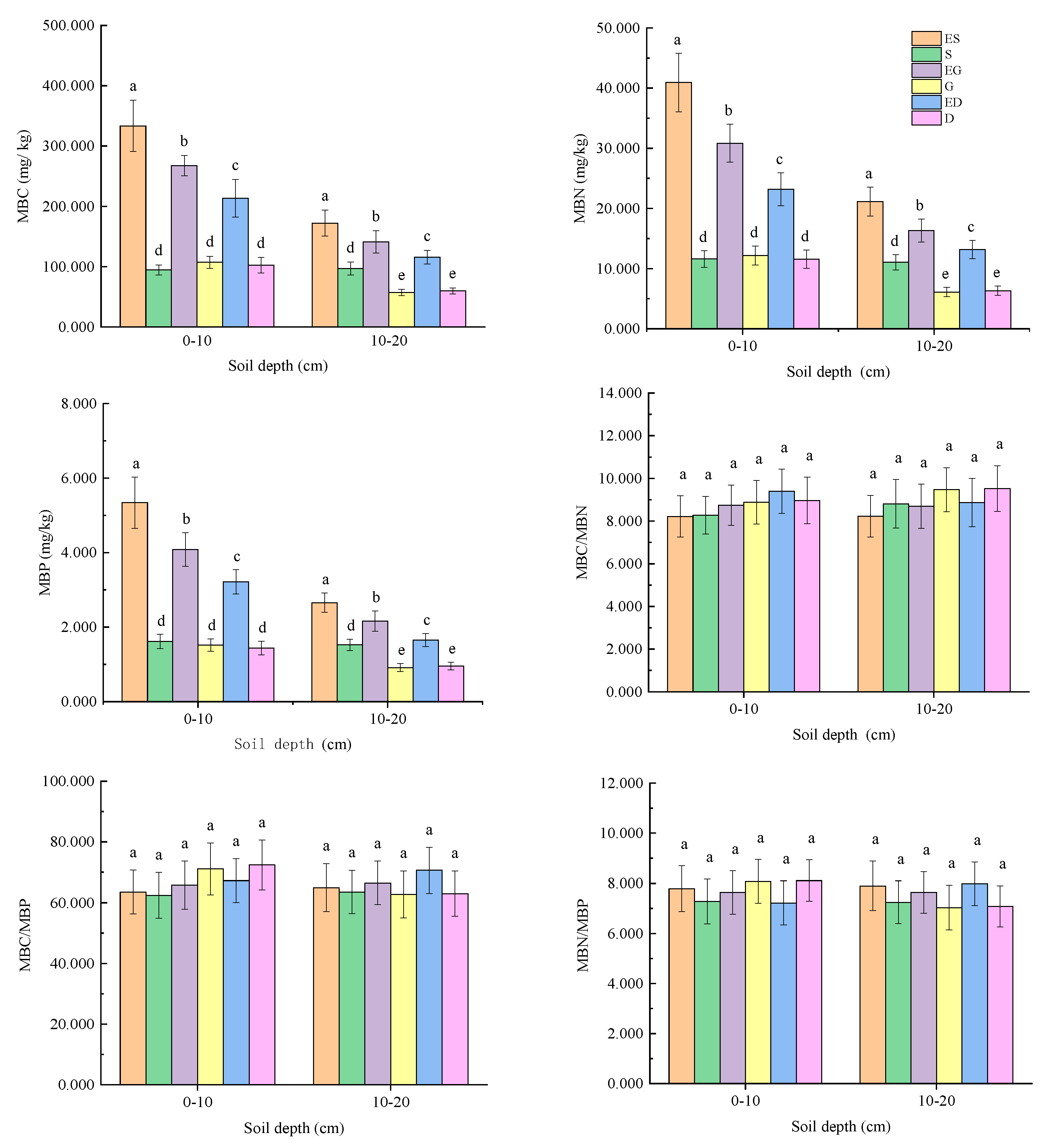
3.1. Soil MBC, MBN, and MBP and Their Stoichiometric Ratios in Different Vegetation Restoration Types
3.2. Microbial Diversity in Different Vegetation Restoration Types
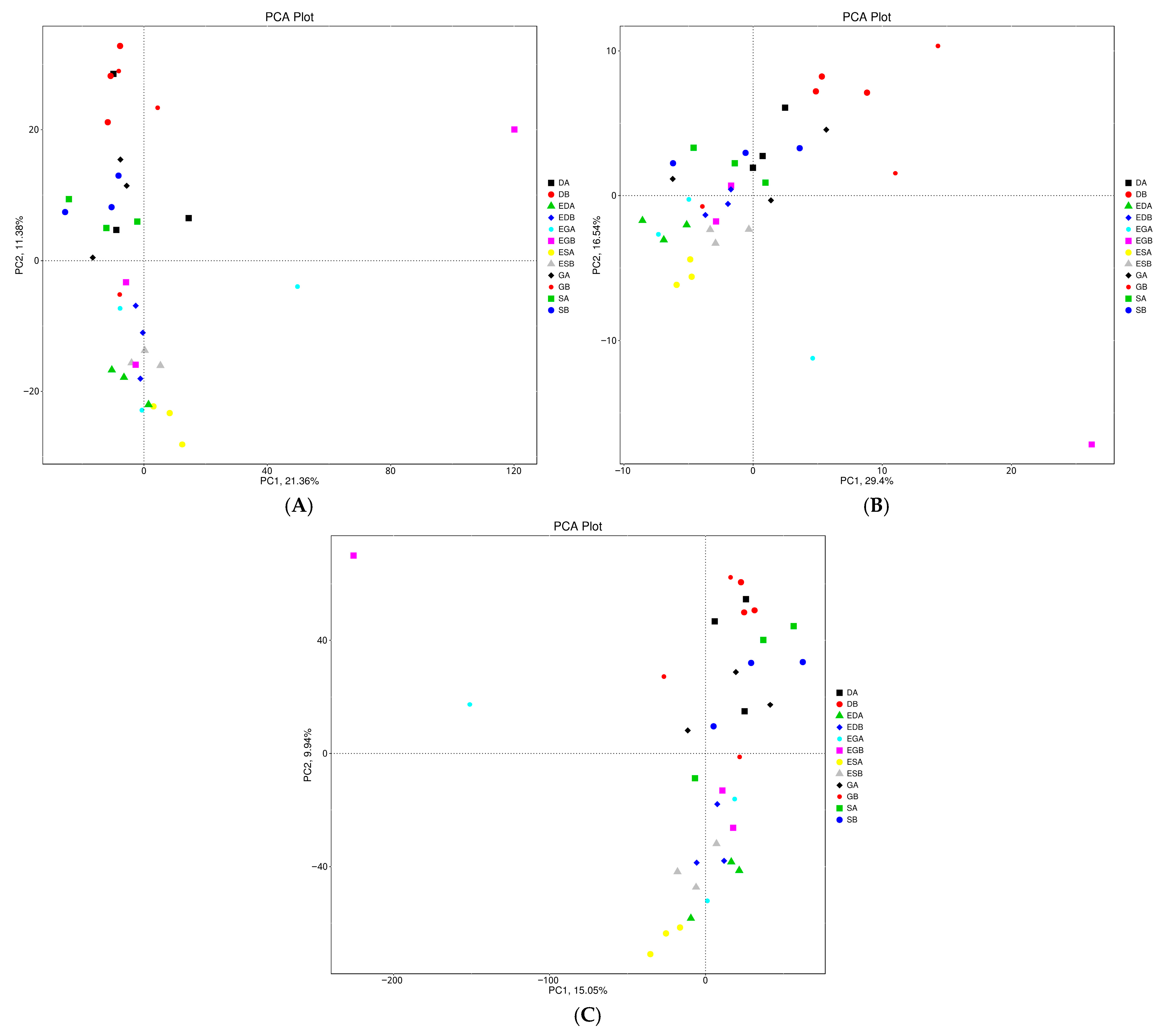
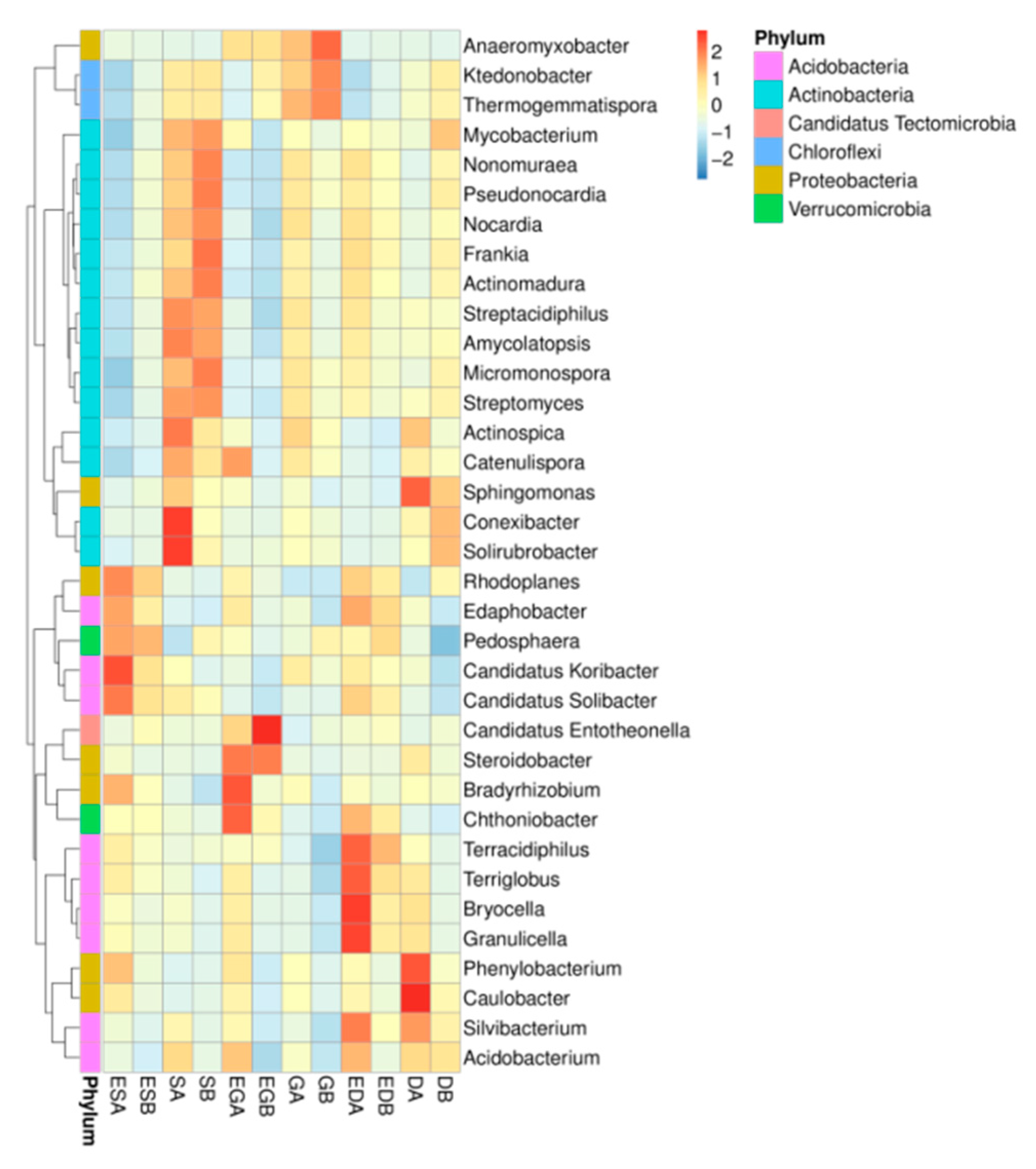
3.3. Microbial Community Structure and Composition in Different Vegetation Restoration Types
3.4. Microbial Functions in Different Vegetation Restoration Types
3.5. The Microbial Symbiosis Network in Different Vegetation Restoration Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Vegetation Restoration Types on Soil MBC, MBN, and MBP and Their Stoichiometric Ratios
4.2. Effects of Vegetation Restoration Types on Microbial Diversity
4.3. Effects of Vegetation Restoration Types on Microbial Species Structure and Composition
4.4. Effects of Vegetation Restoration Types on Microbial Functions
4.5. Effects of Vegetation Restoration Types on the Microbial Symbiosis Network
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breulmann, M.; Masyutenko, N.P.; Kogut, B.M.; Schroll, R.; Dörfler, U.; Buscot, F.; Schulz, E. Short-term bioavailability of carbon in soil organic matter fractions of different particle sizes and densities in grassland ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y. Updates on Plants, Soil, Microorganisms, and Their Interactions in Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2024, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, G.; Wu, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, C.; Bian, F.; Gai, X. Responses of soil nutrients and microbial communities to intercropping medicinal plants in moso bamboo plantations in subtropical China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 27, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J. Measurements of the soil microbial community for estimating the success of restoration. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Dejean, T. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yin, Y. Variations of soil microbial communities accompanied by different vegetation restoration in an open-cut iron mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135243–135254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Song, W. Phosphorus limitation of trees influences forest soil fungal diversity in China. Forests 2022, 13, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, D.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Niu, S. Controlling factors for soil bacterial and fungal diversity and composition vary with vegetation types in alpine grasslands. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2023, 184, 104777–104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, S.G.; Choudoir, M.; Fierer, N.; Strickland, M.S. Volatile organic compounds from leaf litter decomposition alter soil microbial communities and carbon dynamics. Ecology 2020, 101, e03130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Holloway, J.M.; Smith, D.B.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Drenovsky, R.E.; Scow, K.M.; Dick, R.; Howard, D.; Wylie, B.; Grace, J.B. The interacting roles of climate, soils, and plant production on soil microbial communities at a continental scale. Ecology 2017, 98, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Chen, B.Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.H.; Wang, C.S. Understory vegetation diversity, soil properties and microbial community response to different thinning intensities in Cryptomeria japonica var. sinensis plantations. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117384–1117397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Peng, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Lin, K.; Tu, X. The Spatial Patterns of Red Beds and Danxia Landforms: Implication for the formation factors-China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Lin, K.R.; Yu, C.X.; Tu, X.J. Spatial Variability of Soil Phosphorus and Potassium and Its Influencing Factors in the Fragile Red Beds Ecosystem in Southern China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 5307–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.G.; Wu, X.N.; Duan, C.Q.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Response of soil phosphorus fractions and fluxes to different vegetation restoration types in a subtropical mountain ecosystem. Catena 2020, 193, 104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; He, Y.; Cui, Y.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ye, S. Soil Microbial Communities Responses to Multiple Generations’ Successive Planting of Eucalyptus Trees. Forests 2024, 15, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.L.D.; Pimenta, A.S.; Miranda, N.D.O.; Melo, R.R.D.; Amorim, J.D.S.; Azevedo, T.K.B.D. The myth that Eucalyptus trees deplete soil water—A review. Forests 2025, 16, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulucio, V.D.O.; Silva, C.F.D.; Martins, M.A.; Pereira, M.G.; Schiavo, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.A. Reforestation of a degraded area with Eucalyptus and Sesbania: Microbial activity and chemical soil properties. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2017, 41, e0160239-52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulmane, M.; Oubrahim, H.; Halim, M.; Bakker, M.R.; Augusto, L. The potential of Eucalyptus plantations to restore degraded soils in semi-arid Morocco (NW Africa). Ann. For. Sci. 2017, 74, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Pan, P.; Xiao, S.; Ouyang, X. Influence of Eucalyptus plantation on soil organic carbon and its fractions in severely degraded soil in Leizhou Peninsula, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Yan, J. Labile and recalcitrant organic matter and microbial communities in soil after conversion of abandoned lands in the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, L.; Yang, R.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, K. Response of soil microbial communities to natural and managed vegetation restoration in a subtropical karst region. Catena 2020, 195, 104849–104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.D.; Cheng, X.L.; Zhou, X.X.; Liu, K.D.; Yuan, C.C.; Chen, Y. The analysis of Ceriops tagal development trend in different tide level. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2015, 35, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.D.; Huang, J.J. Study on tree species characteristics of natural forest community in Leizhou peninsula based on flora. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 8537–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Manral, V.; Bargali, K.; Bargali, S.S.; Jhariya, M.K.; Padalia, K. Relationships between soil and microbial biomass properties and annual flux of nutrients in Central Himalaya forests, India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J.; Amato, M. Relationship between microbial biomass carbon in soils and absorbance (260 nm) of extracts of fumigated soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1989, 21, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.; Powlson, D.; Jenkinson, D. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. Complex Syst. 2005, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Reich, P.B.; Banerjee, S.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Ishii, S.; Jia, X.X.; Shao, M.A.; et al. Erosion reduces soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2474–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Negative Linear or Unimodal: Why Forest Soil Fungal Latitudinal Diversity Differs across China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02515-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.R.; Zhao, W.Z.; Liu, J.L.; Huang, Z.G. Degraded vegetation and wind erosion influence soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation in sandy grasslands. Plant Soil. 2008, 317, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Yu, Y.H.; Song, Y.P. Stoichiometry of Soil, microorganisms, and extracellular enzymes of Zanthoxylum planispinum var. dintanensis plantations for different allocations. Agronomy 2022, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.S.; Joergensen, R.G. Stoichiometry of the soil microbial biomass in response to amendments with varying C/N/P/S ratios. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2019, 55, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Li, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.M.; Lou, Y. Community size, activity and C:N stoichiometry of soil microorganisms following reforestation in a Karst region. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2016, 73, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebler, C.; Lueders, T. Microbial biodiversity in groundwater ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 649–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Herath, L.; Moldrup, P.; Arthur, E.; Nicolaisen, M.; Norgaard, T.; Ferré, T.P.A.; de Jonge, L.W. Spatial variability of microbial richness and diversity and relationships with soil organic carbon, texture and structure across an agricultural field. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2016, 103, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyang, X.Z.; Ding, S. Species diversity and distribution pattern of main evergreen broad-leaved forests in Jinggangshan National Nature Reserve. Pract. forest Tech. 2014, 9, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Wu, Q.; Rao, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, E.; Liang, X.; Yan, W. Characteristics and interactions of soil bacteria, phytocommunity and soil properties in rocky desertification ecosystems of Southwest China. Catena 2023, 220, 106731–106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhou, Y. Linking leaf δ15N and δ13C with soil fungal biodiversity, ectomycorrhizal and plant pathogenic abundance in forest ecosystems of China. Catena 2021, 200, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, J.; Sun, Y. Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2019, 170, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cui, Z.; Guo, M.; Xi, R. Characteristics of the soil microbial community in the forestland of Camellia oleifera. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jia, S.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, A. Linking soil microbial community dynamics to straw-carbon distribution in soil organic carbon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5526–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, A.; Campbell, C.D.; Fitter, A.H. An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus accelerates decomposition and acquires nitrogen directly from organic material. Nature 2001, 413, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rineau, F.; Roth, D.; Shah, F.; Smits, M.; Johansson, T.; Canbäck, B.; Olsen, P.B.; Persson, P.; Grell, M.N.; Lindquist, E.; et al. The ectomycorrhizal fungus Paxillus involutus converts organic matter in plant litter using a trimmed brown-rot mechanism involving Fenton chemistry. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Crawford, D.L. Carbon nutrition and hydrolytic and cellulolytic activities in the ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus tinctorius. Can. J. Microbiol. 1993, 39, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletti, L.; Monciardini, P.; Bamonte, R.; Schumann, P.; Rohde, M.; Sosio, M.; Donadio, S. New lineage of filamentous, spore-forming, gram-positive bacteria from soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4360–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.K.; King, G.M. Short-term exposure to thermophilic temperatures facilitates co uptake by thermophiles maintained under predominantly mesophilic conditions. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xin, J.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Li, F.; Song, W. Linking Leaf Functional Traits with Soil and Climate Factors in Forest Ecosystems in China. Plants 2022, 11, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omari, R.A.; Yuan, K.; Anh, K.T.; Reckling, M.; Halwani, M.; Egamberdieva, D.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Enhanced soybean productivity by inoculation with indigenous Bradyrhizobium strains in agroecological conditions of northeast Germany. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 707080–707094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pei, Z.Q.; Su, J.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Zheng, Y.R.; Ni, J.; Xiao, C.W.; Wang, R.Z. Comparing soil organic carbon dynamics in perennial grasses and shrubs in a saline-alkaline arid region, northwestern China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, D.N.; Bertiller, M.B.; Ares, J.O.; Carrera, A.L.; Sain, C.L. Soil C and N dynamics induced by leaf-litter decomposition of shrubs and perennial grasses of the Patagonian Monte. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, T.A.; Dedysh, S.N. Granulicella paludicola gen. nov., sp. nov., Granulicella pectinivorans sp. nov., Granulicella aggregans sp. nov. and Granulicella rosea sp. nov., acidophilic, polymer-degrading Acidobacteria from Sphagnum peat bogs. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2010, 60, 2951–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fraile, P.; Benada, O.; Cajthaml, T.; Baldrian, P.; Lladó, S. Terracidiphilus gabretensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an abundant and active forest soil acidobacterium important in organic matter transformation. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2016, 82, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Kulichevskaya, I.S.; Serkebaeva, Y.M.; Mityaeva, M.A.; Sorokin, V.V.; Suzina, N.E.; Rijpstra, I.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Bryocella elongata gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of subdivision 1 of the Acidobacteria isolated from a methanotrophic enrichment culture, and emended description of Edaphobacter aggregans Koch et al. 2008. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2012, 62 Pt 3, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, S.R.; Männistö, M.K.; Starovoytov, V.; Goodwin, L.; Nolan, M.; Hauser, L.; Land, M.; Davenport, K.W.; Woyke, T.; Häggblom, M.M. Complete genome sequence of Terriglobus saanensis type strain SP1PR4 T, an Acidobacteria from tundra soil. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2012, 7, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Wichern, F. Quantitative assessment of the fungal contribution to microbial tissue in soil. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2977–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G. Amino sugars as specific indices for fungal and bacterial residues in soil. Biol Fert Soils 2018, 54, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zuo, X.; Awada, T.; Medima-Roldán, E.; Feng, K.; Yue, P.; Lian, J.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, H. Changes of soil bacterial and fungal community structure along a natural aridity gradient in desert grassland ecosystems, Inner Mongolia. Catena 2021, 205, 105470–105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, B.; Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Xiao, C. Structure and function of microbiomes in the rhizosphere and endosphere response to temperature and precipitation variation in Inner Mongolia steppes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1297399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Reeder, R.C. Soil thermal conductivity: Effects of density, moisture, salt concentration, and organic matter. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xiao, B.; Kidron, G.J.; Tuller, M. Towards the effects of moss-dominated biocrusts on surface soil aeration in drylands: Air permeability analysis and modeling. Catena 2023, 223, 106942–106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.H.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.Z.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L.P. Soil pH is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
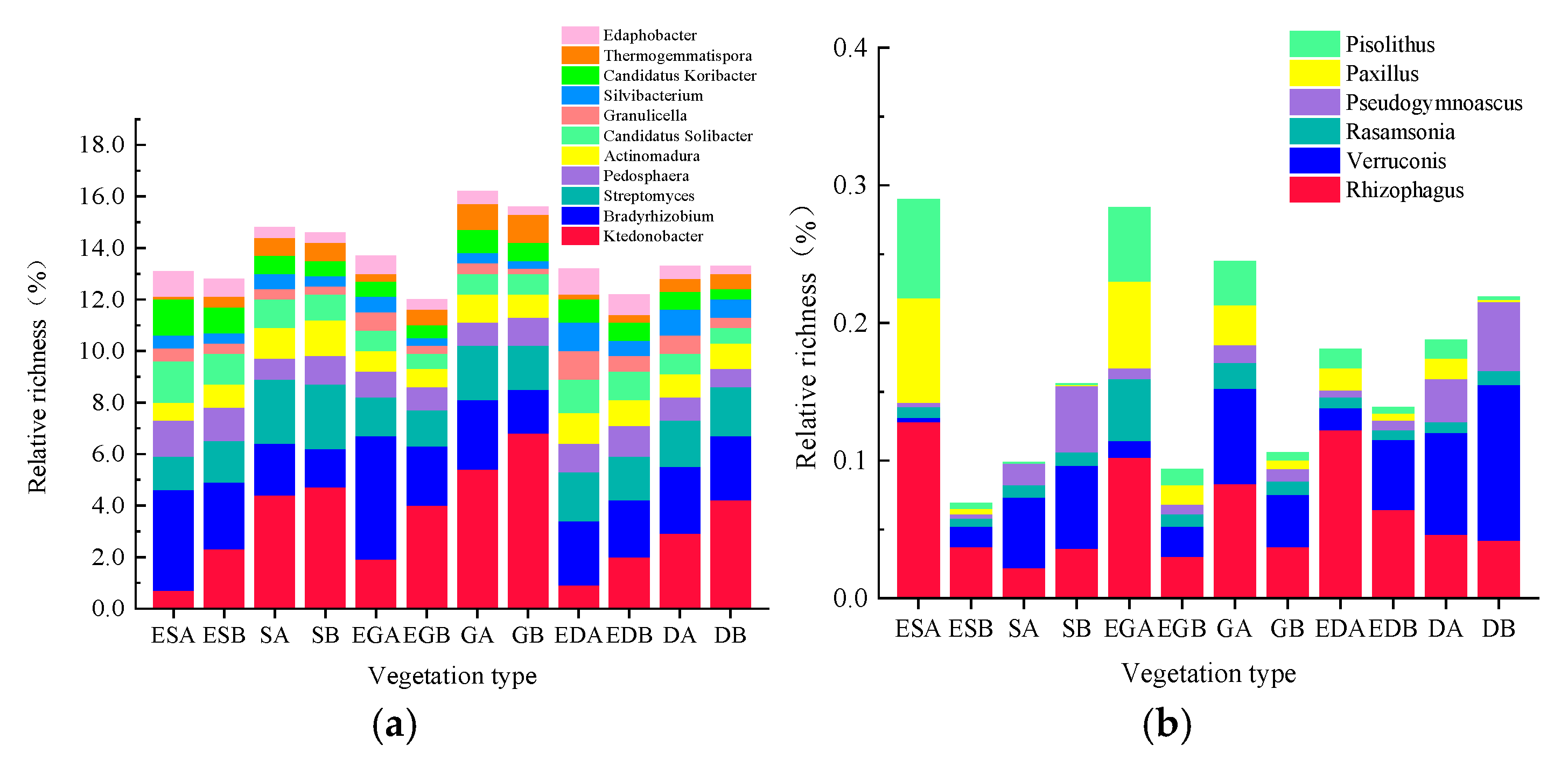
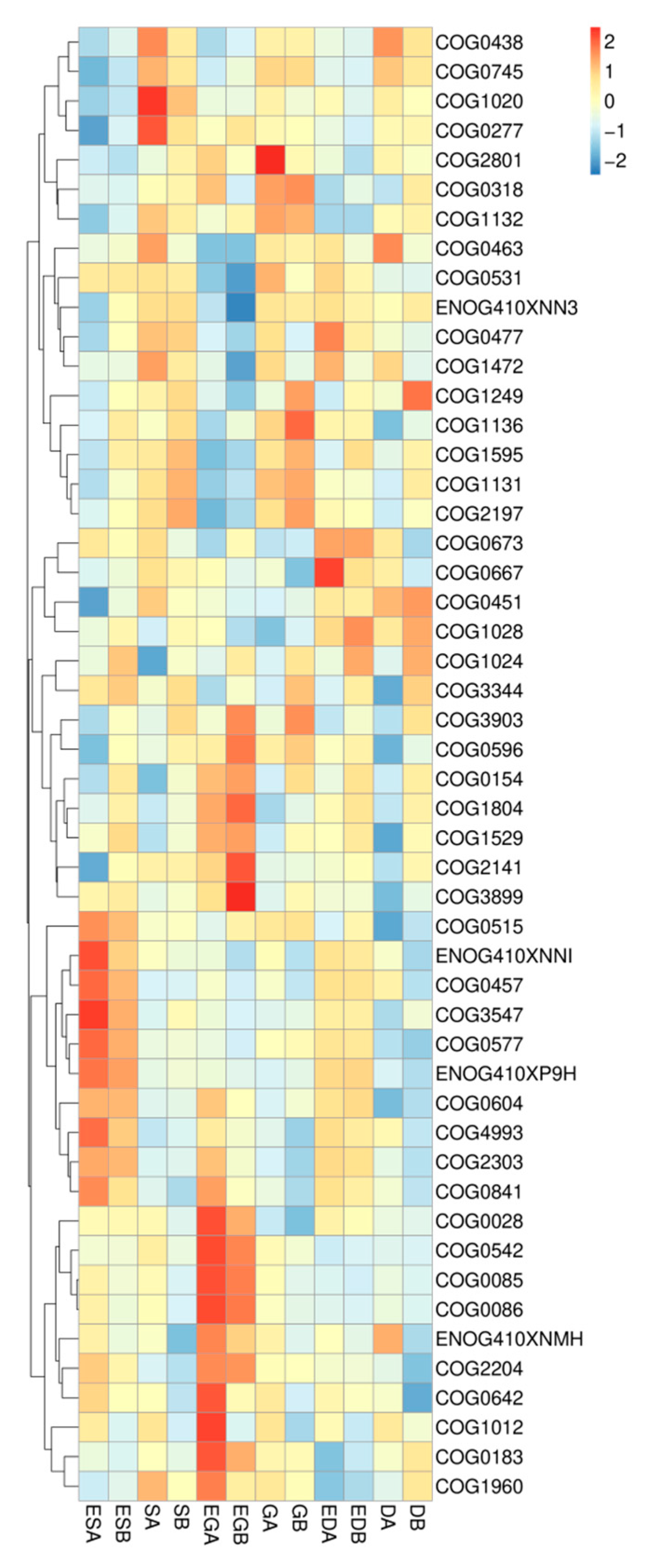
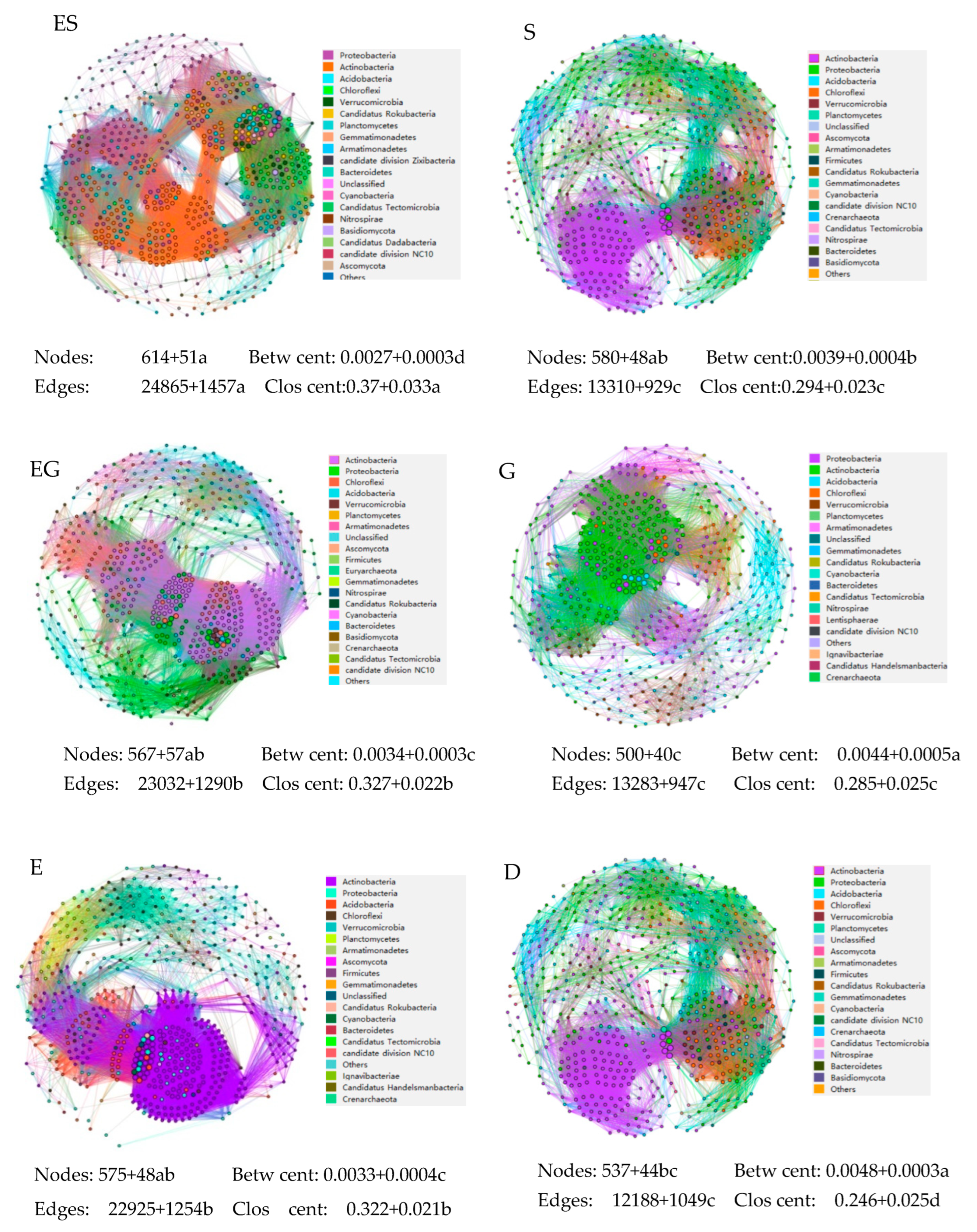
| Indicator | Vegetation Type | ES | S | EG | G | ED | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Surface Soil Depth (cm) | 30–40 | 10–15 | 30–40 | 5–10 | 30–40 | 5–10 |
| Vegetation | Total cover (%) | 75–85 | 15–20 | 75–85 | 15–25 | 80–90 | 25–35 |
| Eucalyptus | |||||||
| DBH (cm) | 12.6 ± 2.1 | - | 10.9 ± 2.7 | - | 9.4 ± 2.6 | - | |
| Height (m) | 11.9 ± 1.8 | - | 10.3 ± 1.7 | - | 9.4 ± 1.5 | - | |
| Canopy Cover (%) | 40–50 | - | 40–50 | - | 40–50 | - | |
| Understory | |||||||
| Cover (%) | 70–80 | 15–20 | 70–80 | 15–25 | 75–85 | 25–35 | |
| Height (m) | 1.4 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 | |
| Dominant Species | Aporosa dioica (Roxb.) Müll. Arg., Litsea glutinosa (Lour.) C. B. Rob., Micromelum falcatum (Lour.) Tan. | Aporosa dioica (Roxb.) Müll. Arg., Litsea glutinosa (Lour.) C. B. Rob., Antidesma ghaesembilla Gaertn. | Miscanthus sinensis Anderss., Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv. | Miscanthus sinensis Anderss., Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv. | Dicranopteris pedata (Houtt.) Nakaike | Dicranopteris pedata | |
| Leaf Litter | Cover (%) | 69 ± 5 | 9 ± 1 | 79 ± 7 | 2 ± 0 | 92 ± 1 | 38 ± 5 |
| Thickness (cm) | 3.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 6.7 ± 1.6 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 16.5 ± 1.7 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | |
| Biomass (g m−2) | 303.9 ± 5.9 | 16.1 ± 2.7 | 398.9 ± 4.7 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | 921.0 ± 17.1 | 58.8 ± 2.8 |
| Soil Layer | Vegetation Type | SW (%) | BD (g m−3) | pH | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | SOM (g kg−1) | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | ES | 10.21 ± 2.01 | 1.39 ± 0.08 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 1.49 ± 0.22 | 0.85 ± 0.10 | 238.2 ± 0.39 | 3.70 ± 0.58 | 32.49 ± 2.84 | 12.64 ± 0.15 |
| S | 8.19 ± 0.12 | 1.35 ± 0.07 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 0.40 ± 0.10 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 44.25 ± 3.88 | 0.92 ± 0.12 | 7.9 ± 0.89 | 10.57 ± 0.38 | |
| EG | 13.51 ± 0.56 | 1.37 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 1.00 ± 0.11 | 0.61 ± 0.05 | 131.4 ± 4.28 | 2.14 ± 0.31 | 23.16 ± 2.91 | 13.39 ± 0.19 | |
| G | 7.97 ± 0.58 | 1.35 ± 0.13 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 47.81 ± 6.44 | 1.02 ± 0.14 | 7.09 ± 1.16 | 8.91 ± 0.99 | |
| ED | 14.90 ± 0.78 | 1.37 ± 0.02 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 0.76 ± 0.06 | 0.49 ± 0.03 | 94.8 ± 9.85 | 1.47 ± 0.29 | 19.39 ± 1.67 | 14.9 ± 0.62 | |
| D | 8.26 ± 0.15 | 1.38 ± 0.18 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 0.37 ± 0.05 | 0.34 ± 0.05 | 51.82 ± 6.03 | 1.12 ± 0.13 | 8.27 ± 0.93 | 10.77 ± 1.8 | |
| 10–20 cm | ES | 10.98 ± 1.55 | 1.42 ± 0.05 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 0.84 ± 0.08 | 0.51 ± 0.07 | 125.2 ± 8.12 | 1.87 ± 0.38 | 15.09 ± 1.86 | 10.01 ± 1.82 |
| S | 10.40 ± 0.25 | 1.44 ± 0.05 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.07 | 0.34 ± 0.08 | 54.07 ± 2.80 | 1.16 ± 0.1 | 6.55 ± 0.33 | 9.88 ± 1.92 | |
| EG | 13.53 ± 0.71 | 1.4 ± 0.09 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 0.69 ± 0.13 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 76.19 ± 5.13 | 1.13 ± 0.16 | 12.42 ± 0.91 | 10.22 ± 1.9 | |
| G | 10.11 ± 0.44 | 1.42 ± 0.04 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 46.50 ± 5.48 | 1.30 ± 0.05 | 4.26 ± 0.54 | 5.94 ± 1.99 | |
| ED | 15.22 ± 0.85 | 1.42 ± 0.08 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 0.48 ± 0.07 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 63.48 ± 3.14 | 1.21 ± 0.14 | 9.85 ± 0.84 | 11.86 ± 0.87 | |
| D | 10.96 ± 0.83 | 1.37 ± 0.13 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 0.31 ± 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.07 | 36.91 ± 6.61 | 1.4 ± 0.19 | 4.35 ± 0.34 | 8.44 ± 1.37 |
| Soil Layer S Soil Layer Cheme. | Vegetation Type | Family | Genus | Species | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChaoI | Shannon | Pielou | ChaoI | Shannon | Pielou | ChaoI | Shannon | Pielou | ||||
| 0–10 cm | ES | 613 + 42a | 4.26 + 0.21b | 0.80 + 0.05b | 2265 + 165a | 5.41 + 0.34c | 0.82 + 0.05b | 12,860 + 528a | 8.37 + 0.24c | 0.76 + 0.04c | ||
| S | 626 + 56a | 5.27 + 0.32a | 0.92 + 0.04a | 2303 + 205a | 7.24 + 0.47a | 0.93 + 0.05a | 12,957 + 237a | 9.13 + 0.14a | 0.92 + 0.03a | |||
| EG | 607 + 59a | 4.49 + 0.32b | 0.82 + 0.06b | 2294 + 151a | 5.74 + 0.41bc | 0.83 + 0.06b | 12,861 + 610a | 8.5 + 0.21bc | 0.80 + 0.05bc | |||
| G | 604 + 44a | 5.37 + 0.36a | 0.92 + 0.06a | 2324 + 214a | 7.15 + 0.34a | 0.92 + 0.06a | 12,429 + 640a | 9.08 + 0.42a | 0.93 + 0.05a | |||
| ED | 612 + 30a | 4.48 + 0.22b | 0.83 + 0.04b | 2370 + 203a | 6.14 + 0.51b | 0.81 + 0.05b | 12,912 + 490a | 8.73 + 0.26b | 0.83 + 0.03b | |||
| D | 626 + 42a | 5.48 + 0.34a | 0.94 + 0.05a | 2334 + 210a | 7.31 + 0.46a | 0.92 + 0.06a | 13,171 + 263a | 9.18 + 0.25a | 0.93 + 0.04a | |||
| 10–20 cm | ES | 621 + 58a | 4.27 + 0.33b | 0.82 + 0.07b | 2316 + 184a | 6.23 + 0.56b | 0.82 + 0.06b | 12,137 + 681a | 8.72 + 0.11c | 0.80 + 0.04b | ||
| S | 618 + 52a | 5.38 + 0.27a | 0.93 + 0.05a | 2313 + 195a | 7.26 + 0.41a | 0.93 + 0.06a | 12,590 + 333a | 9.15 + 0.18b | 0.92 + 0.05a | |||
| EG | 623 + 40a | 4.33 + 0.31b | 0.83 + 0.06b | 2380 + 203a | 6.27 + 0.56b | 0.82 + 0.06b | 12,431 + 317a | 8.7 + 0.14c | 0.82 + 0.04b | |||
| G | 615 + 39a | 5.24 + 0.32a | 0.92 + 0.05a | 2345 + 214a | 7.24 + 0.49a | 0.92 + 0.07a | 12,450 + 533a | 9.08 + 0.3b | 0.93 + 0.04a | |||
| ED | 630 + 46a | 4.44 + 0.23b | 0.84 + 0.06b | 2303 + 195a | 6.41 + 0.53b | 0.83 + 0.05b | 12,565 + 413a | 8.71 + 0.15c | 0.83 + 0.03b | |||
| D | 619 + 51a | 5.42 + 0.36a | 0.93 + 0.06a | 2374 + 199a | 7.21 + 0.51a | 0.93 + 0.05a | 12,823 + 412a | 9.44 + 0.19a | 0.93 + 0.05a | |||
| Phylum of Soil Microorganism | Vegetation Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES | S | EG | G | ED | D | |
| Actinobacteria | 36 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 53 | 0 |
| Proteobacteria | 18 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
| Acidobacteria | 17 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Chloroflexi | 8 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Candidatus_Rokubacteria | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gemmatimonadetes | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Candidatus_Tectomicrobia | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bacteroidetes | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nitrospirae | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cyanobacteria | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Candidatus_Handelsmanbacteria | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Armatimonadetes | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ignavibacteriae | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| total | 109 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 64 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, K.; Xiao, S.; Ouyang, X. Influence of Eucalyptus Plantation on Soil Microbial Characteristics in Severely Degraded Land of Leizhou Peninsula. Forests 2025, 16, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101602
Zhong J, Xu H, Chen Z, Yang K, Xiao S, Ouyang X. Influence of Eucalyptus Plantation on Soil Microbial Characteristics in Severely Degraded Land of Leizhou Peninsula. Forests. 2025; 16(10):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101602
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Jundi, Hanyuan Xu, Zina Chen, Kaiyan Yang, Shenghong Xiao, and Xunzhi Ouyang. 2025. "Influence of Eucalyptus Plantation on Soil Microbial Characteristics in Severely Degraded Land of Leizhou Peninsula" Forests 16, no. 10: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101602
APA StyleZhong, J., Xu, H., Chen, Z., Yang, K., Xiao, S., & Ouyang, X. (2025). Influence of Eucalyptus Plantation on Soil Microbial Characteristics in Severely Degraded Land of Leizhou Peninsula. Forests, 16(10), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16101602




