Abstract
Paulownia trees are grown globally for their robust timber, agroforestry, and effective carbon dioxide drawdown. China possesses rich Paulownia germplasm resources, offering favorable material for the genetic improvement. Understanding the taxonomy and phylogenetic relationships of Paulownia species is essential for the advancement of germplasm innovation. In this study, we re-sequenced 67 typical accessions of 11 species within the Paulownia genus. A total of 16,163,790 high-quality single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified. Based on these markers, these accessions were classified into three groups: P. fortunei and P. lampropylla (Group I); P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, and P. kawakamii (Group II); and P. taiwaniana, P. jianshiensis, P. catalpifolia, P. elongata, P. ichangensis, and P. albiphloea (Group III). Using maximum likelihood estimation, population genetic structure analysis revealed that the 11 species originated from four different ancestral populations. The two predominant breeding species—P. fortunei and P. tomentosa—exhibit divergent origins: P. fortunei arose from hybridization between two ancestral species followed by complex admixture, whereas P. tomentosa retains a predominantly singular ancestral lineage, with traces of P. kawakamii. The genetic diversity (π) of P. tomentosa was 0.002588, which was considerably lower than that of P. fortunei (0.004181) suggesting that P. tomentosa is subjected to a stronger breeding selection during the evolution than P. fortunei. A total of 59 selected regions and 65 genes were identified by selective sweep analysis. These genes may be involved in biological processes such as morphological development and response to abiotic stress and hormonal activity regulation. These findings provide valuable references for further research on the genetic differentiation and adaptive evolutionary mechanisms of Paulownia species, laying a foundation for future germplasm innovation and variety improvement.
1. Introduction
The Paulownia genus, thought to be native to China, encompasses significant fast-growing, multi-purpose tree species with a rich history of cultivation and utilization spanning over 3000 years [1]. The exceptional properties of Paulownia wood, including its low density, superior moisture resistance, excellent thermal insulation, remarkable dimensional stability, and outstanding acoustic characteristics, make it highly valuable for diverse applications, such as high-quality furniture manufacturing, architectural wall paneling, musical instrument crafting, and various artistic handicrafts [2,3]. Notably, Paulownia’s remarkable growth rate surpasses that of conventional hardwood and softwood species [4], positioning it as an ideal option for carbon sequestration initiatives and ecosystem restoration projects [5]. Due to these advantageous characteristics, a lot of Paulownia species and hybrids have been successfully introduced to more than 20 countries worldwide, including the United States, Poland, and Australia [6,7,8]. In addition to these introductions, some countries have also bred proprietary newly cultivated hybrids of their own, such as Paulownia clone in Vitro 112 (P. elongata × P. fortunei), SUN TZU 104 (P. fortunei × P. tormentosa × P. elongate), and P. paulemia (P. elongata × P. fortunei × P. kawakamii) [9,10,11].
Continual genetic improvement of Paulownia, especially the ongoing development of new, fast-growing and high-quality cultivars, is one of the most effective ways to enhance the overall performance of Paulownia plantations. Within the Paulownia genus, there is no reproductive isolation in interspecific hybridization, and the hybrid progeny demonstrates significant heterosis [1]. Therefore, the breeding strategy of ‘sexual hybridization followed by vegetative propagation’ has been formulated and practiced by breeders over a long period of time, based on the biological characteristics of Paulownia species [12]. According to breeding objectives, proper parental selection is crucial for hybrid breeding work. China possesses the most comprehensive germplasm collection of Paulownia, supported by abundant natural resources that offer exceptional opportunities for genetic improvement [13]. Understanding the taxonomic and phylogenetic relationships within the Paulownia genus is critical for optimizing germplasm utilization and advancing genetic innovation strategies [14,15].
However, the taxonomic classification within the Paulownia genus has undergone significant evolution, driven by continuous discoveries of novel species and variants. The foundational classification framework established by Chu et al. (1981) [16] recognized seven species and one variety: Paulownia tomentosa, P. fortunei, P. fargesii, P. catalpifolia, P. australis, P. taiwaniana, P. elongata, and P. tomentosa var. tsinlingensis. This classification was substantially expanded by Jiang et al. (1990) [1], which incorporated: two additional species (P. albiphloea and P. lamprophylla), three varieties (P. tomentosa var. lanata, P. albiphloea var. chengtuensis, and P. tomentosa var. lucida), and four variants (P. lamprophylla f. rotunda, P. fargesii f. calva, P. fortunei × tomentosa f. pallida, and P. elongata f. alba). The taxonomy was further enriched through subsequent discoveries: P. henanensis C.Y.Zhang & Y.H.Zhao hybr. nov. [17], P. serrata D.L.Fu & T.B.Zhao sp. nov. [18], P. seriati-superimposita Y.M.Fan, Z.X.Chen & T.B.Zhao sp. nov., P. penduli-fructi-inflorescentia J.T.Chen, Y.M.Fan, Z.X.Chen & T.B.Zhao sp. nov. [19]. A comprehensive taxonomic revision by Li et al. [20], integrating morphological characteristics, ecological parameters, geographical distribution, and trait stability analyses, established the currently accepted classification system comprising, which included 11 species: P. fortunei, P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, P. kawakamii, P. catalpifolia, P. elongata, P. taiwaniana, P. albiphloea, P. lamprophylla, P. ichangensis and P. jianshiensis; four varieties: P. tomentosa var. tsinlingensis, P. tomentosa var. lucida, P. tomentosa var. lanata, P. albiphloea var. chengtuensis; 4 four variants: P. elongata f. alba, P. fortunei × tomentosa f. pallida, P. lamprophylla f. rotunda, P. fargesii f. calva.
Researchers have conducted numerous studies on the taxonomy within the Paulownia genus. Beyond traditional approaches like morphological taxonomy, numerical taxonomy, and palynological analysis, they have also developed various biotechnological methods [21,22,23]. However, due to the genus’ wide distribution, predominance of cross-pollination, historical migration, frequent interspecific hybridization, and prolonged artificial cultivation, phylogenetic relationships among Paulownia species remain highly complex, resulting in considerable inconsistencies across research findings. ISSR marker analysis [13] revealed three primary clades: the P. tomentosa group (P. tomentosa, P. lamprophylla, P. elongata f.alba, P. elongata, P. catalpifolia, P. henanensis C.Y.Zhang et Y.H.Zhao.hybr.nov., P. ichangensis, P. tomentosa var. lucida), the P. fortunei group (P. fortunei, P. australis, P. albiphloea, P. jianshiensis, P. albiphloea), and the P. fargesii group (P. taiwaniana, P. fargesii). In contrast, cpDNA-RFLP studies [24] established three sections: P. australis group (P. australis, P. albiphloea var. chengtuensis), P. tomentosa (P. tomentosa, P. elongata), and P. fortunei group (P. fortunei, P. lamprophylla, P. taiwaniana, P. kawakamii, P. jianshiensis, P. ichangensis, P. recurve, P. fargesii, P. catalpifolia, P. elongata f.alba). Subsequent investigations yielded alternative phylogenetic hypotheses: RAPD analysis [25] positioned P. fortunei and P. fargesii as sister taxa; plastome-based studies [26] suggested close evolutionary relationships between P. elongata/P. fortunei, P. taiwaniana/P. catalpifolia, and P. australis/P. tomentosa; while based on genome resequencing, 9 accessions were grouped into two major lineages-Lineage α (P. fortunei, P. australis, P. catalpifolia, P. albiphloea, P. elongata, P. lamprophylla) and Lineage β (P. fargesii, P. taiwaniana, P. tomentosa) [27]. To our knowledge, a truly comprehensive assessment of genetic diversity, population structure, and phylogenetic relationships by high quality SNP markers across all 11 species of Paulownia genus has not been published [28].
For the present study, 67 germplasm accessions covering all 11 Paulownia species were performed whole-genome resequencing, using the scaffold-level P. tomentosa genome as the reference. Our goals were analyzing the genetic diversity, population structure, and the genetic relationship within the Paulownia genus. The findings provide breeders critical information to establish core breeding populations, select elite parental lines, accelerate germplasm innovation, and advance research on adaptive evolution in Paulownia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and DNA Extraction
Samples were collected from the Paulownia germplasm repository located in Gongqing City, Jiangxi Province (N 115°48′33″; E 29°10′59″), covering typical germplasms of all Paulownia species. Young, disease-free leaves were collected, washed with distilled water, and quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen. Genomic DNA was extracted from the leaf samples using an improved CTAB method [29] and then stored at −80 °C for future use. Detailed information is available in Figure 1 and Supplement File S1.
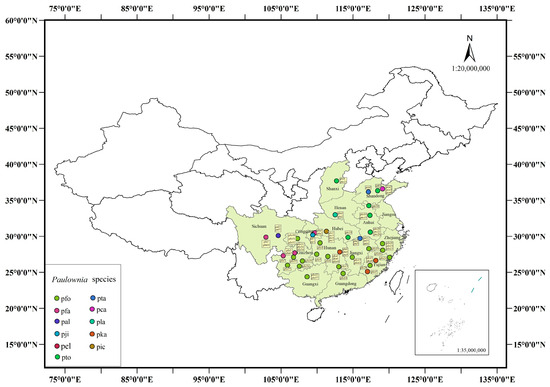
Figure 1.
Geographic distribution of Paulownia germplasm resources. pfo: P. fortunei; pta: P. taiwaniana; pfa: P. fargesii; pca: P. catalpifolia; pal: P. albiphloea; pla: P. lampropylla; pji: P. jianshiensis; pka: P. kawakamii; pel: P. elongata; pic: P. ichangensis; pto: P. tomentosa.
2.2. Library Construction and Sequencing
The concentration and quality of isolated DNA were checked and analyzed with the NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer and 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis, respectively [30]. Qualified DNA samples, selected after quality and concentration assessment via 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and UV spectrophotometry, were used for GBS library construction. The DNA was randomly fragmented into short segments using the Mse I restriction endonuclease. Following fragmentation, the DNA underwent end repair, followed by the addition of dA-overhangs to the fragment ends and ligation of sequencing adapters. Adapter-ligated DNA fragments were purified using AMPure XP beads, and fragments within the 300 bp to 400 bp size range were selected for PCR amplification and subsequent gel purification. Finally, paired-end PE150 sequencing was performed for 67 accessions on the Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform.
2.3. Read Mapping, SNP Calling, and SNP Annotation
Raw sequencing data was processed to yield high-quality clean reads by removing reads containing adapter sequences, reads where uncalled bases (N) exceeded 10% of the read length, and reads where bases with quality scores ≤5 exceeded 50% of the read length. These clean reads were then aligned to the P. tomentosa reference genome using BWA software (version 0.7.10) [31,32] with default parameters of the bwa mem algorithm. Duplicate reads in the alignment results were marked and removed using Picard. Variant calling across all samples was performed using GATK [33], and variant sites were flagged. Briefly, a joint genotyping step for comprehensive variations union was performed on the gVCF files. In the filtering step, the SNP filter expression was set as QD < 2.0 || MQ < 40.0 || FS > 60.0 || SOR > 3.0 || MQRankSum < −12.5 || ReadPosRankSum < −8.0 || QUAL < 30. SNPs with no bi-allelic, >40% missing calls and MAF < 0. 05 were removed, which yielded the basic set. To rule out plastid contamination, we aligned two P. tomentosa chloroplast genomes (GenBank accessions MK875778.1 and NC_031436.1) to the reference assembly. No regions with >50% sequence identity were detected, confirming that all loci analysed are nuclear. Annotation of SNP was performed using ANNOVAR program (https://annovar.openbioinformatics.org/en/latest/, accessed on 22 August 2025) [34] to determine their genomic location characteristics and functional attributes. SNPs were categorized into regions including intergenic regions, exons, and introns, with variants in exonic regions further classified as synonymous or nonsynonymous mutations [35].
2.4. Population Genetics Analysis
Genetic distance matrices were calculated with VCF2Dis, and a phylogenetic tree was constructed with the Neighbor-Joining method in MEGA 11, then the tree was plotted in FigTree [36]. Population structure was analyzed with ADMIXTURE v1.3.0 [37]. A series of hypothetical ancestral clusters was tested (K = 1–9). For each K, the proportion of every inferred ancestral component in each accession was estimated, and cross-validation errors were compared. The K value with the lowest error was taken as the optimal number of clusters. The results were visualized with the R package pophelper v2.3.0 [38]. Principal component analysis (PCA) of the accessions was performed with the R package GAPIT3 [39].
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) was calculated using PopLDdecay v3.30 [40] with the following parameters: PopLDdecay-MaxDist 300-MAF 0.005-Het 0.88-Miss 0.25-OutType1. Genetic diversity and population differentiation were assessed by nucleotide diversity, Tajima’s D, and genetic differentiation (FST), which were calculated with a 100 kb window size and 50 kb step, based on the VCFtools and SnpEff packages. The genomic regions with significantly high FST values (top 5% FST) were used as differentiation bins [41,42].
3. Results
3.1. Whole Genome Resequencing and SNP Calling
Whole-genome resequencing of all samples was carried out on the Illumina platform. After removing reads containing adaptors and low-quality bases, we obtained 7,112,024,671 pairs of clean reads in total, averaging 98,778,120 pairs per sample. Bases with an error rate below 1% (Q20) represented more than 96% of the data, and those with an error rate below 0.1% (Q30) accounted for over 90%. Reads were mapped to the reference genome at a rate ranging from 77.35% to 98.26%. The average sequencing depth was 28.37×, and bases covered at >1× depth averaged 91.48% (Supplementary File S2).
After quality control, alignment, SNP detection, filtering and merging, we obtained 16,163,790 population-level SNP loci. Among these SNPs, 11,801,358 SNPs (73.01%) were located in intergenic regions, 2,313,583 (14.31%) in introns, 576,255 (3.57%) in exons, and 991,270 (6.13%) and 794,119 (4.91%) in the upstream and downstream regions of genes, respectively. This indicated that most genomic variations occurred in non-coding regions. Further categorization of SNP mutation types showed that, among the six variation types, 11,125,502 SNPs were transitions (Ts) and 5,346,626 were transversions (Tv), yielding an overall Ts/Tv ratio of 2.08 (Supplement File S3). P. fortunei exhibited the highest Ts/Tv ratio (2.15), whereas P. tomentosa displayed the lowest (2.09) (Supplement File S4).
3.2. Phylogenetic Construction
Based on the genome-wide distributed SNPs, genetic distances were calculated, and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method. Results indicates that 67 germplasms from 11 Paulownia species can be divided into three major clades (Figure 2). P. fortunei and P. lamprophylla form one clade (Group I); P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, and P. kawakamii comprise another (Group II); while P. taiwaniana, P. catalpifolia, P. albiphloea, P. elongata, P. jianshiensis, and P. ichangensis cluster into the third clade (Group III). Moreover, it was observed that geographically proximate species did not cluster into the same group, and different provenances of the same species did not diverge into distinct clades despite geographical separation. This suggests no clear correlation between the phylogenetic relationships of these germplasms and their geographical origins.
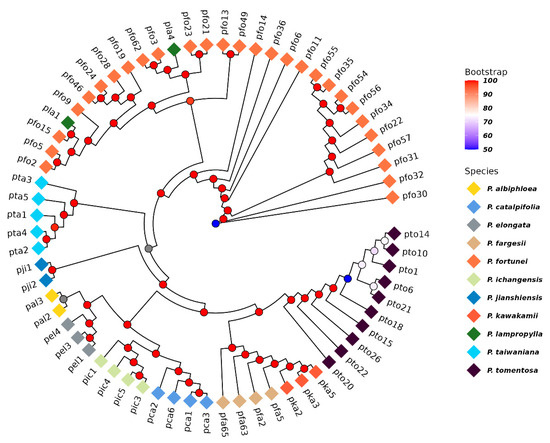
Figure 2.
Neighbor-Joining phylogenetic tree of 67 Paulownia germplasms.
The grouping results by principal component analysis (PCA) (Figure 3) were consistent with the NJ results. The first two principal components accounted for 69.76% of the total variation. The first principal component (PC1) explained 49.26% of the overall variation and separated the whole accessions into three major groups: Group I (P. fortunei and P. lamprophylla), Group II (P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, and P. kawakamii), and Group III (P. taiwaniana, P. catalpifolia, P. elongata, P. jianshiensis, P. ichangensis, and P. albiphloea). Within Group II, two subgroups named the P. fargesii and P. kawakamii subgroup, and the P. tomentosa subgroup were clearly displayed based on PC2; simultaneously, Group III was separated into the P. taiwaniana subgroup, and the P. catalpifolia, P. elongata, P. jianshiensis, P. ichangensis, P. albiphloea subgroup.
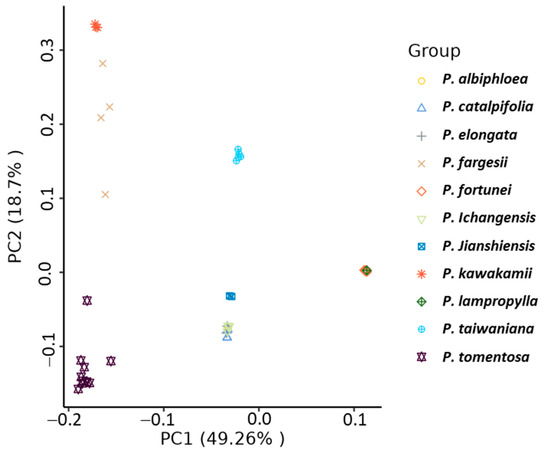
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis of 11 Paulownia species.
To further elucidate the genetic relationships and evolutionary history among the 11 Paulownia germplasms, we conducted population genetic structure analysis using the Admixture software. The cross-validation (CV) error rates for all accessions across different k values indicated that the CV error rate was relatively low when k = 4 (Figure 4). Therefore, we concluded that the Paulownia genus likely comprises four distinct ancestral genetic components, which best characterizes the population genetic structure of these 67 germplasm accessions.
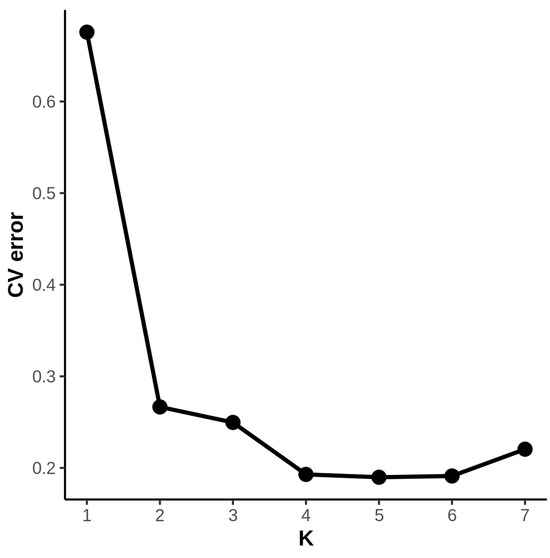
Figure 4.
CV error among different K values.
When the number of ancestral clusters (k) was set to 4, nearly all P. fortunei accessions originated from hybridization between the red and blue ancestral populations with repeated crosses; P. tomentosa exhibited a relatively homogeneous ancestral background (purple); P. tomentosa primarily derived from the green ancestral population, though a minority of individuals showed minor introgression from the purple ancestry; P. elongata originated from hybridization between green and blue ancestral populations; P. fargesii mainly originated from the purple ancestral population with most individuals admixed with green ancestry; P. catalpifolia and nearly all P. elongata germplasm derived from hybridization between green and red ancestral populations; while P. jianshiensis, P. albiphloea, and P. taiwaniana displayed complex ancestral backgrounds involving hybridization among three or more ancestral populations.
Specifically, Population I comprised 18 accessions (16 P. fortunei and 2 P. lamprophylla), among which 7 P. fortunei and both P. lamprophylla accessions showed Q = 1, indicating exclusive origin from the blue ancestral population. Population II included 12 P. fortunei accessions, 5 of which had Q = 1 signifying exclusive origin from the red ancestral population. Population III contained 12 accessions (4 P. fargesii, 5 P. taiwaniana, 3 P. kawakamii), with 1 P. fargesii and all 3 P. kawakamii showing Q = 1 confirming exclusive purple ancestry. Population IV consisted of 25 accessions (10 P. tomentosa, 4 P. catalpifolia, 4 P. ichangensis, 2 P. jianshiensis, 2 P. albiphloea, 3 P. elongata), including 6 P. tomentosa accessions with Q = 1 indicating exclusive origin from the green ancestral population (Figure 5).
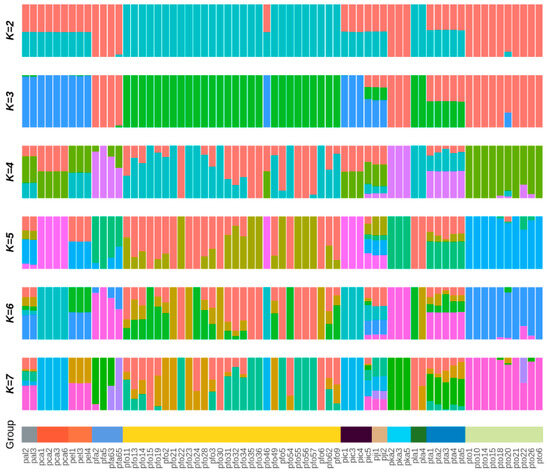
Figure 5.
The genetic structure of 67 Paulownia germplasms.
3.3. Genetic Differentiation
We compared genetic diversity metrics among the three predefined groups (Figure 6A). Group III, which contained the largest number of species, exhibited the highest level of internal diversity (π = 3.20 × 10−3). In contrast, Group I comprised only two species (P. fortunei and P. lamprophylla) and showed the lowest diversity (π = 1.04 × 10−3). Group II included three species (P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, and P. kawakamii) and displayed an intermediate level of diversity (π = 2.60 × 10−3), which was over two times greater than that of Group I. The pairwise FST between Group I and Group II was 0.27, and between Group I and Group III was 0.49, both exceeding 0.25 and thus indicating pronounced genetic differentiation. In contrast, Group II and Group III were the least differentiated, with an FST of 0.14.
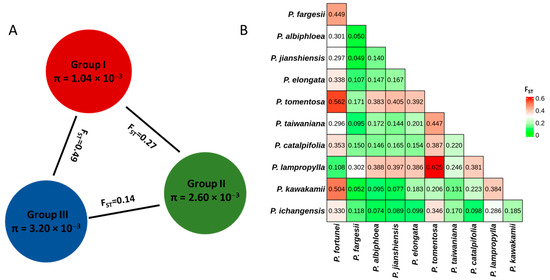
Figure 6.
Genetic differentiation. (A): Nucleotide diversity (π) and population divergence (FST) across the three groups. (B): Heat map of FST values for each two species.
Based on the calculated pairwise FST values among different Paulownia species, we assessed the degree of genetic differentiation and quantified the genetic relationship between them (Figure 6B). Paired FST values of the 11 Paulownia species ranged from 0.049 to 0.625. Among which, the FST values were relatively high between P. lamprophylla and P. tomentosa, between P. tomentosa and P. fortunei, and between P. kawakamii and P. fortunei, reaching 0.625, 0.562, and 0.504, respectively. Conversely, the FST values were relatively low between P. jianshiensis and P. fargesii, between P. albiphloea and P. fargesii, and between P. kawakamii and P. fargesii, being 0.049, 0.050, and 0.052, respectively.
3.4. Genetic Diversity and Evolutionary Patterns
P. fortunei and P. tomentosa are the most widely utilized genetic materials in Paulownia breeding program. Among 147 well-documented superior Paulownia germplasms (including improved varieties, new cultivars, elite clonal lines, and selected superior clones), either one or both parents of 107 germplasms (accounting for 72.94%) trace back to these two species. Conducting analyses of their genetic diversity and evolutionary patterns is highly significant for the genetic improvement of Paulownia cultivars.
Compared to P. tomentosa (mean π = 0.002588, median π = 0.002341), P. fortunei exhibited higher nucleotide diversity (mean π = 0.004181, median π = 0.004100), indicating a lower strength of selection in P. fortunei than in P. tomentosa. In contrast, Tajima’s D values were lower in P. fortunei (mean = −1.1226, median = −1.0905) than in P. tomentosa (mean = 0.2984, median = 0.2462). A Tajima’s D > 0 for P. tomentosa suggests an excess of intermediate frequency alleles, possibly caused by balancing selection and/or a population bottleneck. Conversely, a Tajima’s D < 0 for P. fortunei indicates an excess of low frequency alleles (Figure 7).
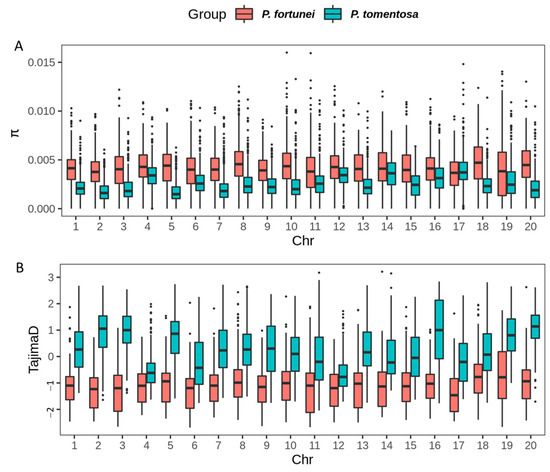
Figure 7.
The nucleic acid diversity, Tajima’s D value of P. fortunei and P. tomentosa. (A): Nucleotide diversity; (B): Tajima’s D value.
Further analysis of FST between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa across all 20 chromosomes is presented in Figure 8. The results reveal extensive regions of genetic differentiation between the two species, with varying FST values observed across different chromosomes. Using thresholds corresponding to the top 5% of values (FST > 0.725), 263 candidate genes within 136 genomic windows were identified. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of these genes (Figure 9) showed significant enrichment in biological processes including: regulation of response to salt stress (GO:1901000), regulation of response to osmotic stress (GO:0047484), and pH regulation (GO:0006885).
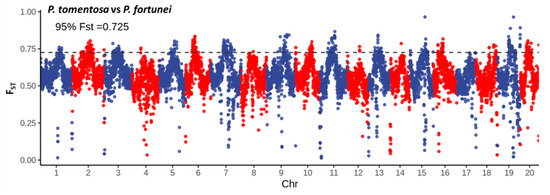
Figure 8.
Candidate differentiation regions identified in P. fortunei and P. tomentosa on the genome. Alternating point colors (red and blue) distinguish adjacent chromosomes for clarity.
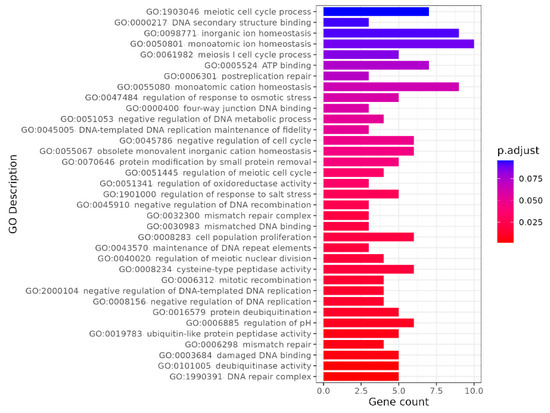
Figure 9.
Go enrichment analysis of the genes contained in differentiation region.
3.5. Linkage Disequilibrium Decay
LD analysis of P. tomentosa and P. fortunei (Figure 10) shows that P. tomentosa requires 251.43 bp for LD to decay to the baseline level (r2 = 0.3707), whereas P. fortunei reaches its baseline (r2 = 0.3068) at 225.70 bp, indicating a faster decay rate. This pattern suggests that P. tomentosa has experienced stronger positive selection, leading to reduced population genetic diversity and, consequently, a slower rate of LD decay.
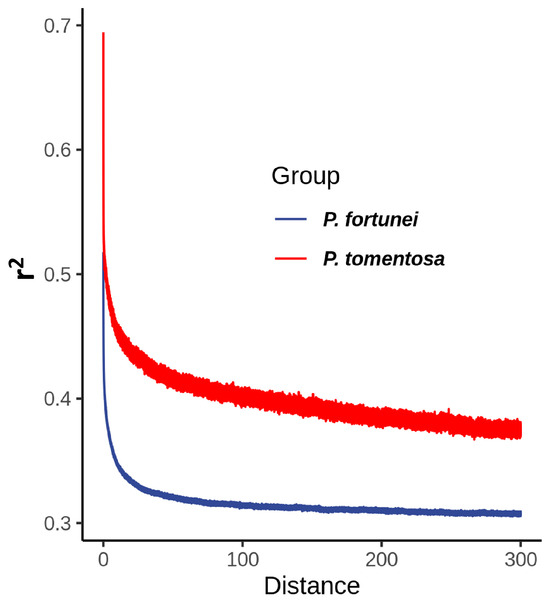
Figure 10.
Analysis of linkage disequilibrium decay.
3.6. Selective Sweep Between P. Fortunei and P. Tomentosa
Using FST and θπ, we identified 11 selective-sweep regions in P. fortunei and 8 in P. tomentosa, encompassing a total of 22 genes (Figure 11A; Supplementary File S5). These genes are predicted to participate in biological processes such as signal transduction, regulation of hormone activity, and modulation of stress responses. Using Tajima’s D and θπ, 40 selective-sweep regions were detected across the two genomes (Figure 11B; Supplementary File S6), containing 43 genes. These genes are mainly associated with responses to abiotic stresses (e.g., salt and osmotic stress), signal transduction, and development of plant organs.
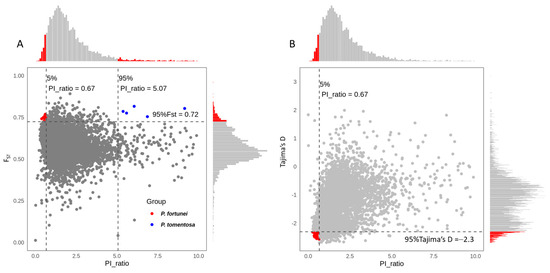
Figure 11.
Selective sweep identification between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa using FST & PI ratio (A) and Tajima’s D & PI ratio (B).
4. Discussion
China possesses abundant Paulownia germplasm resources, yet many accessions lack traceable pedigrees and have unclear genetic backgrounds. This poses significant challenges for establishing core breeding populations, selecting parental lines, and germplasm innovation in Paulownia. In this study, whole-genome resequencing of 67 germplasm accessions identified a total of 16,163,790 high-quality SNPs. The transition/transversion ratio (Ts/Tv) was 2.08, indicating that transitions constitute the predominant type of SNP variation in Paulownia genus. This finding aligns with SNP identification results in tea plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze] [43], Vitis [44], and Phyllostachys edulis [45], where a large proportion of SNPs exhibit minimal impact on protein amino acid sequences [46]. Moreover, most of the SNPs uncovered in this study fall within intergenic or other non-coding regions, mirroring the genomic distribution previously reported for SNPs in Coffea species [47] and tea plant [48]. Although these SNPs may not directly affect gene function [30], they effectively reflect genetic and evolutionary relationships among plant populations [49] and serve as valuable genetic markers for analyzing genetic relatedness.
Phylogenetic tree and principal component analysis (PCA) results were fully congruent, which consistently group the 11 Paulownia species into Group I (P. fortunei and P. lamprophylla), Group II (P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, and P. kawakamii), and Group III (remaining species). Our results were partly inconsistent with a previous study [23]. While we also grouped P. tomentosa and P. kawakamii into one clade, our findings differed by not supporting a separate clade that contained P. fargesii, P. catalpifolia, P. elongata, and P. fortunei (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Several factors could underlie these discrepancies, including the reliance on limited or uneven sampling, incomplete taxon coverage, and the differing evolutionary rates of the markers themselves [50,51,52].
In contrast, population genetic structure analysis revealed these species originated from four distinct ancestral populations: P. fortunei derived from recurrent hybridization between two ancestral populations; P. tomentosa and P. kawakamii exhibited relatively homogeneous ancestral backgrounds; while P. fargesii showed significant admixture primarily from the P. kawakamii ancestral population with minor contributions from P. tomentosa. One potential cause of the apparent incongruence is sampling bias. Although the 67 germplasm accessions analyzed here encompasses 11 Paulownia species and virtually the entire geographic range of the genus, earlier collection and conservation efforts focused mainly on P. fortunei and P. tomentosa. As a result, the other species are under-represented, and sample sizes across species are unbalanced. Once a more comprehensive germplasm repository is established, large-scale population re-sequencing should allow a more profound exploration of population evolution within Paulownia. Despite the sampling bias, results still yield meaningful insights into Paulownia evolution. Our results suggest P. tomentosa and P. kawakamii represent earlier diverged lineages and partially supports the hypothesis that P. fargesii constitutes a geographic race formed during P. kawakamii migration [53]. Furthermore, varying degrees of P. fortunei ancestral admixture were detected in P. albiphloea, P. jianshiensis, P. catalpifolia, P. ichangensis, and P. taiwaniana, providing novel evidence that P. fortunei rapidly became a direct/indirect parental source post-differentiation, driving increased genus richness and complexity.
Group I contained the largest number of accessions yet showed the lowest within-group nucleotide diversity (π = 1.04 × 10−3). Its accessions were strikingly uniform, forming a tight cluster in both the PCA and the phylogenetic tree, suggesting that this Group may have experienced a historical founder effect or population bottleneck [41]. The FST value between Group I and Group II (0.27), Group I and Group III (0.49) were more than 0.25, suggesting a high degree of genetic differentiation. Whereas Group II and Group III were the least differentiated (FST = 0.14), implying gene flow has occurred among these two groups [41]. Interestingly, the pairwise FST between Group II accessions of P. tomentosa and the two Group I species P. fortunei and P. lamprophylla, are 0.562 and 0.625, respectively, ranking second- and first-highest among all 11 interspecific comparisons, indicating pronounced genetic divergence between P. tomentosa and each of these two species. Among which, P. fortunei and P. tomentosa are two of the most important members of the eleven recognized species in the Paulownia genus. This divergence between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa is mirrored in their contrasting geographic ranges, morphological traits, growth rates, and wood properties. P. fortunei is highly sensitive to climate, when transplanted northward it often fails to survive the winter, with low temperature acting as a primary constraint on its range expansion [21]. Consequently, the species occurs mainly south of, and within, the Yangtze River basin, where it is largely found in natural stands and only rarely in plantations. By contrast, P. tomentosa is a broadly distributed species spanning the widest latitudinal range in the genus. It is cultivated extensively from the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River northward, while truly wild populations are limited to small areas in the Dabie Mountains, the Shennongjia region, and adjoining areas [1,20]. Prolonged artificial cultivation and intensive selection typically erode genetic diversity [53]. Following this principle, one would expect P. fortunei to retain greater diversity than P. tomentosa. Our data confirm this expectation. Indeed, nucleotide diversity is slightly higher in P. fortunei (π = 0.004181) than in P. tomentosa (π = 0.002588). Consistent with stronger selection, P. tomentosa also shows tighter linkage, evidenced by its slower LD decay and longer decay distance. Taken together, these patterns indicate that P. tomentosa accessions have been subjected to more intense selection pressure than those of P. fortunei.
The 136 divergent regions identified through FST analysis, combined with the 59 selected regions detected via selective sweep analysis, provide valuable resources for further investigation into the genetic differentiation and environmental adaptive evolution between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa. Enrichment analysis indicated that genes within some divergent regions were significantly associated with biological processes related to abiotic stress responses, such as regulation of response to salt stress, regulation of response to osmotic stress, and pH regulation. Other genes were potentially involved in morphogenesis, including regulation of shoot development, xylem and phloem pattern formation, and regulation of meristem growth. These genetic differences likely contribute to the phenotypic divergence between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa in growth and development, wood quality, and adaptability.
Elucidating the origin and evolutionary history of the various Paulownia species is crucial for understanding the genus’s overall evolution and the genetic attributes of each species. However, population evolution in Paulownia genus is both prolonged and intricate. Extensive interspecific hybridization, recurrent selfing, backcrossing, recombination, and natural selection have generated numerous transitional hybrid forms, while artificial selection has further shaped genetic patterns [54]. Consequently, a more systematic and comprehensive investigation is still required to fully elucidate the origin and phylogenetic relationships among all Paulownia species.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we performed the resequencing of 67 germplasms covering 11 Paulownia species, identifying and annotating 16,163,790 high-quality and genome-wide SNPs, and reported the characterization of these SNPs. The genetic diversity, population structure, and relationship among Paulownia species were clarified. Specially, 11 species can be divided to three groups: Group I (P. tomentosa, P. fargesii, and P. kawakamii), Group II (P. taiwaniana, P. catalpifolia, P. elongata, P. jianshiensis, P. ichangensis, and P. albiphloea), and Group III (P. fortunei and P. lamprophylla). Eleven species can be traced back to four ancestral populations. P. tomentosa and P. fortunei, the most widely used genetic materials in the Paulownia breeding program, are highly differentiated and represent two distantly related species within the genus. Nucleotide diversity (π) is lower in P. tomentosa than in P. fortunei, indicating stronger historical selection in the former. Genome-wide FST detected 136 highly divergent regions, and sweep analyses identified 59 candidate selective sweeps. GO enrichment and functional annotations highlighted several genes implicated in responses to abiotic stress, morphogenesis, and related biological processes, providing a foundation for further dissection of the genetic mechanisms underlying interspecific differentiation and adaptive evolution in Paulownia.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f16101533/s1, Supplement File S1: Geographic distribution of Paulownia germplasm resources; Supplement File S2: Sequencing depth and coverage statistics; Supplement File S3: Distribution of SNP variation type; Supplement File S4: SNP variation in different Paulownia species; Supplement File S5: Selection sweep regions identified by FST and θπ between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa; Supplement File S6: Selection sweep regions identified by Tajima’s D and θπ between P. fortunei and P. tomentosa.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. and Y.F. conceived and designed the project. Y.Z. and C.Y. collected the samples. Y.Z. and J.Q. analyzed the data. Y.Z., B.W. and Y.F. conceived the paper, wrote the first draft, and edited the manuscript. Y.S., S.L. and X.Z., participated in part of analysis of the trial. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Non-profit Research Institution of the Chinese Academy of Forestry [CAFYBB2022MA004] and a National Promotion Project for Forestry and Grassland Scientific and Technological Achievements [2023133108].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Taishan Li for insightful discussion of data analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jiang, J. Cultivation of Paulownia; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Seoane, P.; del Pozo, C.; Puy, N.; Bartroli, J.; Dominguez, H. Hydrothermal extraction of valuable components from leaves and petioles from Paulownia elongata x fortunei. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4525–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Latib, H.; Liat, L.C.; Ratnasingam, J.; Law, E.L.; Azim, A.A.; Mariapan, M.; Natkuncaran, J. Suitability of Paulownia wood from malaysia for furniture application. BioResources 2020, 15, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrilmis, N.; Kaymakci, A. Fast growing biomass as reinforcing filler in thermoplastic composites: Paulownia elongata wood. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazzawy, H.S.; Bakr, A.; Mansour, A.T.; Ashour, M. Paulownia trees as a sustainable solution for CO2 mitigation: Assessing progress toward 2050 climate goals. Front. Environ. Sci 2024, 12, 1307840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Miłek, M.; Grabek-Lejko, D.; Hęclik, J.; Jacek, B.; Litwińczuk, W. Antioxidant activity, polyphenolic profiles and antibacterial properties of leaf extract of various Paulownia spp. clones. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, M. Cultivation potential and uses of Paulownia wood: A review. Forests 2022, 13, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, M.E.L.; García, E.M.; Morote, F.A.G.; Serrano, F.R.L.; Abellán, M.A.; Pérez, D.C.; del Cerro Barja, A. Ei cultivo de Paulonia (“Paulownia elongata x fortunei”) para la obtención de maderay biomasa en castilla-la mancha: Primeros resultados. Foresta 2010, 47–48, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec, J.; Novosadová, K.; Kománek, M.; Pokornỳ, R. Testing the production potential of Paulownia clon in vitro 112® in the Czech Republic. Forests 2023, 14, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adach, W.; Żuchowski, J.; Moniuszko-Szajwaj, B.; Szumacher-Strabel, M.; Stochmal, A.; Olas, B.; Cieslak, A. In vitro antiplatelet activity of extract and its fractions of Paulownia clone in vitro 112 leaves. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 137, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feria, M.J.; García, J.C.; Zamudio, M.A.M.; Gomide, J.L.; Colodette, J.L.; López, F. Kraft pulping and bleaching of Paulownia SUN TZU 104® wood. Cellulose Chem. Technol. 2013, 47, 595–601. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, C.; Qiao, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, F.; Wang, B. Genetic parameters and genotype-environment interactions in Paulownia clonal tests intemperate and subtropical regions of China. Forests 2022, 13, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Fu, J.; Qiao, J.; Lei, L.; Li, F.; Yuan, D.; Qiu, Q. ISSR study on genetic relationship of genus Paulownia. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2013, 49, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X. Thoughts on tree breeding strategies. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2019, 41, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X. Research progress of forest genetics and tree breeding. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2020, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z. A discussion on the distribution centre and flora of Paulownia genus. Sci. Silvae Sin. 1981, 17, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y. A new natural hybrid of Paulownia (Scrophulariaceae). Acta Phytotaxxonomica Sinica 1995, 33, 503–505. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D. Paulownia serrata- a new species from China. Nat. Sci. 2003, 1, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y. Morphological Variation and New Classification System of Paulowniaceae Plants. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Qiao, J.; Wang, B.; Li, R. Atlas of Paulownia Germplasm Resources in China; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yao, C.; Hu, H.; Liang, Z. The origin phylogeny and distribution of Paulownia. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 2000, 18, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, B.; Guo, Y.; Yao, C. Analysis on patterns of SOD Isozyme and soluble proteins of Paulownia plants. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 1994, 13, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.P.; Lou, G.L.; Cai, X.R.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Wang, H.W. Comparison of the complete plastomes and the phylogenetic analysis of Paulownia species. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Deng, H. RFLP analysis of Paulownia plants. Bull. Bot. Res. 2001, 21, 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Xie, L.; Du, Q.; Chang, Z. RAPD analysis of seven species in Paulownia. Guihaia 2001, 21, 335–338. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences and Evolution Analysis of Eight Paulownia Species. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Analysis of Genome Sequencing and Variation Loci in Nine Paulownia Species. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, G.-L.; Fu, C.-M.; Tang, F.; Yin, J.; Guan, D.-L.; Shi, C.-Y. Population genomics analysis reveals footprints of selective breeding in a rapid-growth variety of Paulownia fortunei with apical dominance. Genomics 2024, 116, 110849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, F.; Fu, J.; Wuyun, T.; Wu, S. Comparison of two methods to extract DNA from trees of Diospyros L. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2012, 32, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Mekbib, Y.; Tesfaye, K.; Dong, X.; Saina, J.K.; Hu, G.-W.; Wang, Q.-F. Whole-genome resequencing of Coffea arabica L. (Rubiaceae) genotypes identify SNP and unravels distinct groups showing a strong geographical pattern. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows–wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Deng, Q.; Damaris, R.; Yang, M.; Xu, L.; Yang, P. LOTUS-DB: An integrative and interactive database for nelumbo nucifera study. Database 2015, 2015, bav023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The genome analysis toolkit: A map reduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whankaew, S.; Suksri, P.; Sinprasertporn, A.; Thawonsuwan, J.; Sathapondecha, P. Development of DNA markers for acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease tolerance in litopenaeus vannamei through a genome-wide association study. Biology 2024, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udriște, A.-A.; Iordachescu, M.; Ciceoi, R.; Bădulescu, L. Next-generation sequencing of local romanian tomato varieties and bioinformatics analysis of the velocus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiao, C.; Schwaninger, H.; Chao, C.T.; Ma, Y.; Duan, N.; Khan, A.; Ban, S.; Xu, K.; Cheng, L. Phased diploid genome assemblies and pan-genomes provide insights into the genetic history of apple domestication. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. GAPIT version 3: Boosting power and accuracy for genomic association and prediction. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W. Expression analysis of NAC genes during the growth and ripening of apples. Hortic. Sci. 2018, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Feng, L.; Deng, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Lin, P.; Qiao, Y.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Genomic resequencing reveals genetic diversity, population structure, and core collection of durian germplasm. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, F.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tu, X.; Xie, X.; Huang, P.; Tong, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zang, D. Resequencing of Rosa rugosa accessions revealed the history of population dynamics, breed origin, and domestication pathways. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qiao, D.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J. Genetic diversity of old tea plant resources in Jiuan City of Guizhou Province, using genome-wide SNP. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2019, 20, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Duan, S.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, S.; Ni, X.; Shao, J.; Liu, C.; Nick, P.; Du, F.; Fan, P. Whole-genome resequencing of 472 vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses. Na. Commun. 2019, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, S.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Gao, J. Analysis on the culm shape and color variation of 4 moso bamboo variants by whole genome re-sequencing. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2020, 35, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Colleoni, C.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Ruess, H.; Simon, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, G. Genomic analyses yield markers for identifying agronomically important genes in potato. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.; Long, Y.; Hao, C.; Yan, L.; Shi, T. Resequencing 93 accessions of coffee unveils independent and parallel selection during coffea species divergence. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 103, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.; Tong, W.; Hou, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Li, R. The reference genome of tea plant and resequencing of 81 diverse accessions provide insights into its genome evolution and adaptation. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Cong, P.; Li, L.; Piao, J. Genetic relationship and structure analysis of 15 species of malus mill. based on SNP markers. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zheng, T.; Gao, T.; Song, N. Whole-genome resequencing reveals genetic diversity and selection signals in Warm Temperate and Subtropical Sillago Sinica populations. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Yuan, L.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jie, W.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Qiang, L.; Han, C.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of Chinese Gizzard Shad Clupanodon Thrissa in South China based on morphological and molecular markers. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 41, e02367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, B.; Deng, M.; Zhao, T.; Liao, Y.; Ren, R.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y. Whole-genome resequencing reveals genetic diversity and adaptive evolution in Chinese Honeybee (Apis cerana cerana) in Guizhou, China. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1352455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Mi, X.; Zhao, S.; Guo, R.; Xia, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, C. Revealing distinctions in genetic diversity and adaptive evolution between two varieties of Camellia sinensis by whole-genome resequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 603819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T. Study on the Development of the System of Paulownia. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).